













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 429-439.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.015
相磊1( )(
)( ), 景金珠1, 梁震1, 阎国强1, 郭文峰1, 张萌1, 张威1, 刘亚军2(
), 景金珠1, 梁震1, 阎国强1, 郭文峰1, 张萌1, 张威1, 刘亚军2( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2023-02-13
修回日期:2023-04-21
出版日期:2023-08-25
发布日期:2023-08-25
通讯作者:
刘亚军(1975—),男,博士,主任医师,教授,主要从事脊柱外科研究。E-mail: drliuyajun@163.com。ORCID:0000-0002-0514-6055作者简介:相 磊(1982—),男,博士,高级兽医师,主要从事实验动物研究。E-mail: xianglei-322@163.com。ORCID:0000-0002-8652-5099
Lei XIANG1( )(
)( ), Jinzhu JING1, Zhen LIANG1, Guoqiang YAN1, Wenfeng GUO1, Meng ZHANG1, Wei ZHANG1, Yajun LIU2(
), Jinzhu JING1, Zhen LIANG1, Guoqiang YAN1, Wenfeng GUO1, Meng ZHANG1, Wei ZHANG1, Yajun LIU2( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-02-13
Revised:2023-04-21
Published:2023-08-25
Online:2023-08-25
Contact:
LIU Yajun (ORCID:0000-0002-0514-6055), E-mail: drliuyajun@163.com摘要:
目的 分析肌少症动物模型研究的现状、热点及发展趋势,为肌少症动物模型研究提供方向与基础资料。 方法 检索 Web of Science(WOS)核心合集数据库中1900-01-01至2022-12-31的肌少症动物模型研究英文文献,以及中国知网(CNKI)数据库中1915—2022年的肌少症动物模型研究中文文献。应用文献计量分析软件VOSviewer分析发文量、发文国家/地区、机构、作者、期刊及关键词,以揭示该领域研究的主要国家和机构以及热点和前沿方向。 结果 从WOS核心合集数据库共检索到肌少症动物模型相关文献2 819篇,第1篇文献发表于1995年;美国是肌少症动物模型研究最多的国家,发文量为1 105篇;发文机构最多的是美国佛罗里达大学,发文量为69篇;香港大学是我国发文量最多的机构,共发文20篇;美国学者Holly V R的发文量最多,发表50篇;肌少症动物模型研究刊文量最多的学术期刊是美国的FASEB Journal,刊文量为196篇。CNKI数据库共检索到文献423篇,中文发文量最多的作者是李柱一,共发文19篇。WOS检索文献的关键词共现聚类分析发现,肌少症动物模型研究的热点可概括为肌少症与代谢相关性研究,肌少症动物模型细胞学及再生医学研究,肌少症动物模型与骨、肌肉和神经研究,以及肌少症与运动治疗研究。CNKI数据库检索发现失神经性肌少症模型研究最为广泛,中药对肌少症的作用研究也多有报告。文献阅读发现肌少症动物模型主要包括自然衰老模型、遗传修饰模型、高脂饮食诱导模型、失用性肌少症模型、激素诱导模型及其他疾病复合性的肌少症模型。 结论 肌少症动物模型是近年来国内外研究的一个热点,文献计量分析在研究方向及热点、模式动物选择、动物模型制作、国内外交流与合作等方面可为肌少症动物模型研究提供基础。
中图分类号:
相磊,景金珠,梁震,等. 基于VOSviewer的肌少症动物模型研究可视化分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(4): 429-439. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.015.
Lei XIANG,Jinzhu JING,Zhen LIANG,et al. A Visual Analysis on Animal Model of Sarcopenia Based on VOSviewer[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 429-439. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.015.
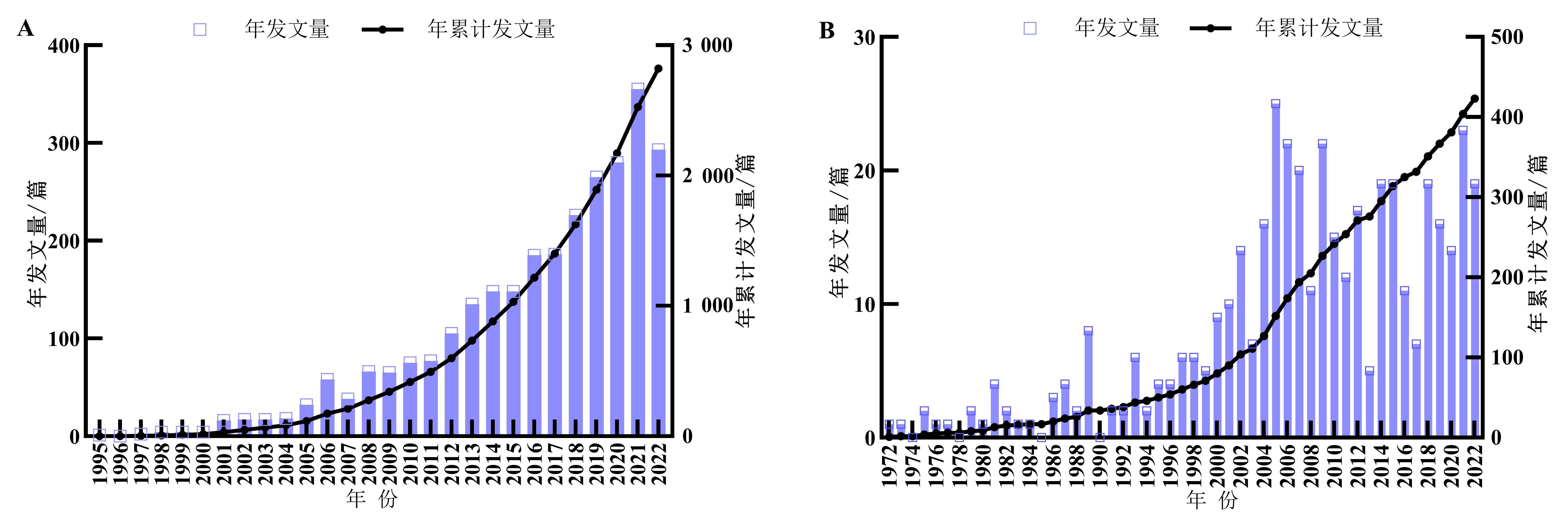
图1 肌少症动物模型研究的发文量统计注:A,英文发文量统计(WOS核心合集数据库);B,中文发文量统计(CNKI数据库)。
Figure 1 Statistics of the quantities of research articles on animal models of sarcopeniaNote:A, Statistics on the number of articles published in English(Web of Science core data); B, Statistics on the number of articles published in Chinese(CNKI database).
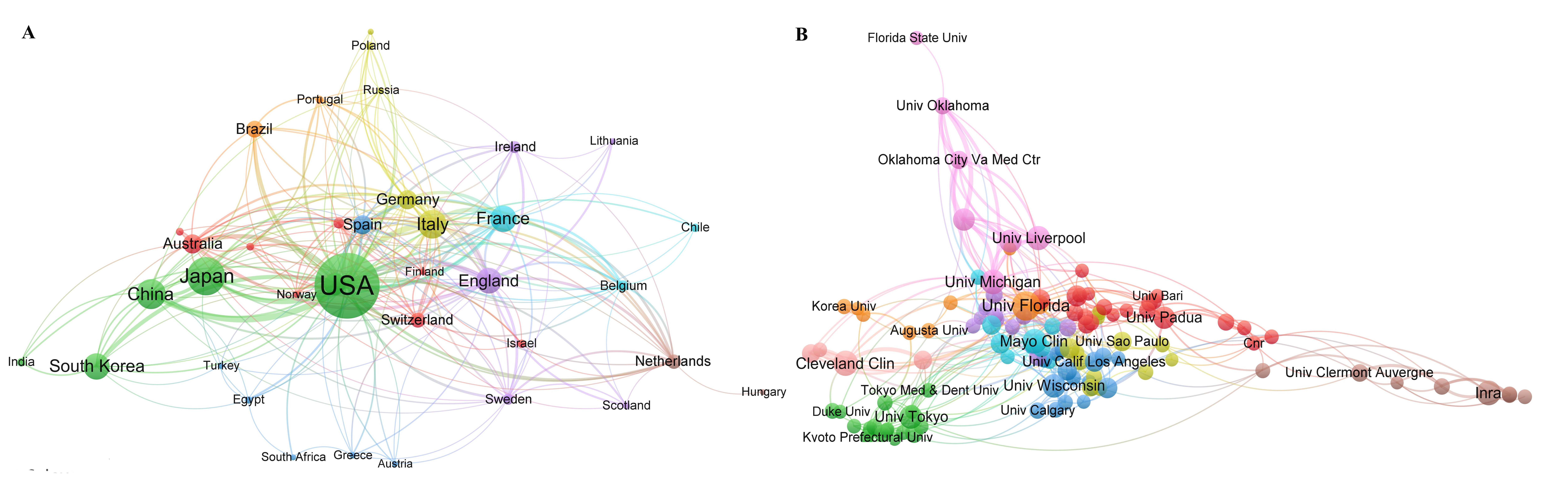
图2 肌少症动物模型研究的国家(或地区)和机构共现可视化图谱注:圆圈与标签组成一个单元,不同颜色的单元组成不同的簇。不同国家(或地区)和机构之间按不同颜色分类,节点的大小表示发文频次的多少,机构之间距离越近反映合作越密切。
Figure 2 Co-occurrence visualization map of institutions and countries/ regions for sarcopenia animal model researchNote: Circles and labels form a unit, and units of different colors form different clusters. The countries (or regions) and institutions are classified according to different colors, and the size of the nodes indicates the frequency of publishing articles. The closer the distance between the institutions, the closer the cooperation.
排名 Sort | 国家 Countries | 发文量 Documents | 引用频次 Citations | 排名 Sort | 机构 Organizations | 发文量 Documents | 引用频次 Citations | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 美国 | 1 105 | 45 206 | 1 | 美国佛罗里达大学 | 69 | 4 549 | |
| 2 | 日本 | 369 | 6 570 | 2 | 美国克利夫兰诊所 | 49 | 931 | |
| 3 | 中国(含港澳台) | 278 | 3 677 | 3 | 美国妙佑医疗国际 | 46 | 958 | |
| 4 | 意大利 | 211 | 9 291 | 4 | 法国农业科学研究院 | 45 | 1 889 | |
| 5 | 法国 | 179 | 5 879 | 5 | 美国密歇根大学 | 45 | 2 280 | |
| 6 | 韩国 | 177 | 2 107 | 6 | 英国利物浦大学 | 42 | 1 117 | |
| 7 | 英国 | 170 | 5 506 | 7 | 日本东京大学 | 40 | 1 232 | |
| 8 | 加拿大 | 127 | 4 111 | 8 | 美国威斯康星大学 | 40 | 2 582 | |
| 9 | 德国 | 96 | 2 267 | 9 | 美国得克萨斯大学 | 37 | 2 067 | |
| 10 | 西班牙 | 95 | 3 917 | 10 | 美国俄克拉何马医学院 | 36 | 688 |
表1 不同国家和机构的肌少症动物模型研究发文量与引用统计(前10位)
Table 1 The number of articles and citations statistics of sarcopenia animal models in different countries and institutions (top 10)
排名 Sort | 国家 Countries | 发文量 Documents | 引用频次 Citations | 排名 Sort | 机构 Organizations | 发文量 Documents | 引用频次 Citations | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 美国 | 1 105 | 45 206 | 1 | 美国佛罗里达大学 | 69 | 4 549 | |
| 2 | 日本 | 369 | 6 570 | 2 | 美国克利夫兰诊所 | 49 | 931 | |
| 3 | 中国(含港澳台) | 278 | 3 677 | 3 | 美国妙佑医疗国际 | 46 | 958 | |
| 4 | 意大利 | 211 | 9 291 | 4 | 法国农业科学研究院 | 45 | 1 889 | |
| 5 | 法国 | 179 | 5 879 | 5 | 美国密歇根大学 | 45 | 2 280 | |
| 6 | 韩国 | 177 | 2 107 | 6 | 英国利物浦大学 | 42 | 1 117 | |
| 7 | 英国 | 170 | 5 506 | 7 | 日本东京大学 | 40 | 1 232 | |
| 8 | 加拿大 | 127 | 4 111 | 8 | 美国威斯康星大学 | 40 | 2 582 | |
| 9 | 德国 | 96 | 2 267 | 9 | 美国得克萨斯大学 | 37 | 2 067 | |
| 10 | 西班牙 | 95 | 3 917 | 10 | 美国俄克拉何马医学院 | 36 | 688 |
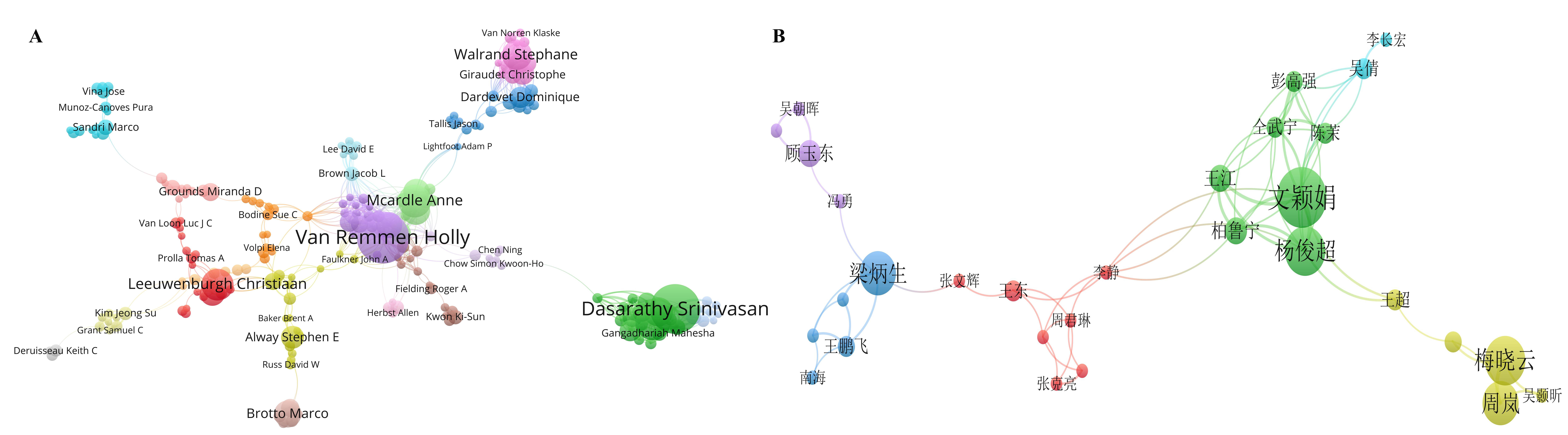
图3 肌少症动物模型研究的作者共现可视化图谱注:A,英文文献发文作者共现;B,中文文献发文作者共现。圆圈和标签组成一个单元,不同颜色的单元组成不同的簇。作者之间按不同颜色分类,分别代表不同的研究团队,节点的大小表示作者出现的频率高低。作者间无相互关联性,图中均不呈现。
Figure 3 Co-occurrence map of the authors in the study of animal model of sarcopeniaNote: A, The co-occurrence of the authors in the English literature; B, The co-occurrence of the authors in Chinese literature. Circles and labels form a unit, and units of different colors form different clusters. The authors are classified according to different colors that represent different research teams. The size of the node indicates the frequency of the occurrence of the authors. There is no correlation between the authors, and these authors are not shown in the figure.
| 排名 | Web of Science核心合集数据库(WOS) | CNKI数据库(CNKI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sort | 作者 Authors | 发文量 No. of published articles | 作者 Authors | 发文量 No. of published articles | |
| 1 | Van remmen Holly | 50 | 李柱一 | 19 | |
| 2 | Dasarathy Srinivasan | 48 | 孙圣刚 | 15 | |
| 3 | Kumar Avinash | 31 | 王云甫 | 15 | |
| 4 | Mcardle Anne | 29 | 曹学兵 | 14 | |
| 5 | Leeuwenburgh Christiaan | 28 | 文颖娟 | 10 | |
| 6 | Walrand Stephane | 26 | 孟繁平 | 9 | |
| 7 | Davuluri Gangarao | 25 | 杨俊超 | 8 | |
| 8 | Sieck Gary C | 24 | 梅晓云 | 8 | |
| 9 | Vasilaki Aphrodite | 24 | 何国厚 | 7 | |
| 10 | Brotto Marco | 23 | 刘 睿 | 7 | |
表2 中外作者在肌少症动物模型研究中的发文量统计(前10位)
Table 2 Statistics of the number of articles published by Chinese and foreign authors in the study of animal models of sarcopenia (top 10)
| 排名 | Web of Science核心合集数据库(WOS) | CNKI数据库(CNKI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sort | 作者 Authors | 发文量 No. of published articles | 作者 Authors | 发文量 No. of published articles | |
| 1 | Van remmen Holly | 50 | 李柱一 | 19 | |
| 2 | Dasarathy Srinivasan | 48 | 孙圣刚 | 15 | |
| 3 | Kumar Avinash | 31 | 王云甫 | 15 | |
| 4 | Mcardle Anne | 29 | 曹学兵 | 14 | |
| 5 | Leeuwenburgh Christiaan | 28 | 文颖娟 | 10 | |
| 6 | Walrand Stephane | 26 | 孟繁平 | 9 | |
| 7 | Davuluri Gangarao | 25 | 杨俊超 | 8 | |
| 8 | Sieck Gary C | 24 | 梅晓云 | 8 | |
| 9 | Vasilaki Aphrodite | 24 | 何国厚 | 7 | |
| 10 | Brotto Marco | 23 | 刘 睿 | 7 | |

图4 肌少症动物模型相关研究发表期刊及中英文文献中关键词共现聚类图谱注:A,发表期刊的共现分析;B,英文文献关键词共现;C,中文文献关键共现。圆圈和标签组成一个单元,不同颜色的单元组成不同的簇,不同颜色分别代表不同的杂志或研究方向,节点的大小表示杂志刊文的频次高低或关键词出现的频率高低。
Figure 4 Published journals and keywords co-occurrence cluster map in animal model study of sarcopenia in Chinese and English literatureNote:A, co-occurrence analysis of published journals; B, Co-occurrence of key words in English literature; B, Co-occurrence of key words in Chinese literature. Circles and labels form a unit, units of different colors form different clusters, different colors represent different magazines or different research directions, and the size of nodes indicates the frequency of magazine articles or keyword occurrence.
排名 Sort | 杂志名称 Journal | 影响因子(2023) Impact factor | 发文量/篇 Documents | 共引用频次/次 Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FASEB Journal | 4.8 | 196 | 3 020 |
| 2 | Experimental Gerontology | 3.9 | 111 | 3 906 |
| 3 | Journal of Cachexia Sarcopenia and Muscle | 8.9 | 107 | 1 963 |
| 4 | Nutrients | 5.9 | 67 | 1 140 |
| 5 | Aging Cell | 7.8 | 58 | 2 770 |
| 6 | Aging-Us | 5.2 | 52 | 1 486 |
| 7 | International Journal of Molecular Sciences | 5.6 | 50 | 356 |
| 8 | Journals of Gerontology Series A-Biological Sciences and Medical | 5.1 | 48 | 2 295 |
| 9 | Journal of Applied Physiology | 3.3 | 45 | 1 803 |
| 10 | Frontiers in Physiology | 4.0 | 44 | 652 |
表3 肌少症动物模型研究期刊发表文献的共引用统计(前10位)
Table 3 Co-citation statistics of articles published in animal model research journals of sarcopenia(top 10)
排名 Sort | 杂志名称 Journal | 影响因子(2023) Impact factor | 发文量/篇 Documents | 共引用频次/次 Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FASEB Journal | 4.8 | 196 | 3 020 |
| 2 | Experimental Gerontology | 3.9 | 111 | 3 906 |
| 3 | Journal of Cachexia Sarcopenia and Muscle | 8.9 | 107 | 1 963 |
| 4 | Nutrients | 5.9 | 67 | 1 140 |
| 5 | Aging Cell | 7.8 | 58 | 2 770 |
| 6 | Aging-Us | 5.2 | 52 | 1 486 |
| 7 | International Journal of Molecular Sciences | 5.6 | 50 | 356 |
| 8 | Journals of Gerontology Series A-Biological Sciences and Medical | 5.1 | 48 | 2 295 |
| 9 | Journal of Applied Physiology | 3.3 | 45 | 1 803 |
| 10 | Frontiers in Physiology | 4.0 | 44 | 652 |
排名 Sort | 英文关键词 English keywords | 共现频率 Co-occurrence frequency | 排名 Sort | 中文关键词 Chinese keywords | 共现频率 Co-occurrence frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | sarcopenia | 961 | 1 | 重症肌无力 | 153 | |
| 2 | aging | 590 | 2 | 肌萎缩 | 124 | |
| 3 | skeletal muscle/muscle | 529 | 3 | 大鼠 | 41 | |
| 4 | muscle atrophy | 239 | 4 | 失神经 | 23 | |
| 5 | mitochondria | 142 | 5 | 乙酰胆碱受体 | 21 | |
| 6 | oxidative stress | 123 | 6 | 骨骼肌 | 17 | |
| 7 | exercise | 93 | 7 | 小鼠 | 16 | |
| 8 | inflammation | 75 | 8 | 失重模拟 | 14 | |
| 9 | autophagy | 70 | 9 | 肌少症 | 13 | |
| 10 | cachexia | 68 | 10 | 乙酰胆碱受体抗体 | 11 |
表4 肌少症动物模型研究中的中英文关键词分析(前10位)
Table 4 English and Chinese keywords analysis in the study of animal model of sarcopenia (top 10)
排名 Sort | 英文关键词 English keywords | 共现频率 Co-occurrence frequency | 排名 Sort | 中文关键词 Chinese keywords | 共现频率 Co-occurrence frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | sarcopenia | 961 | 1 | 重症肌无力 | 153 | |
| 2 | aging | 590 | 2 | 肌萎缩 | 124 | |
| 3 | skeletal muscle/muscle | 529 | 3 | 大鼠 | 41 | |
| 4 | muscle atrophy | 239 | 4 | 失神经 | 23 | |
| 5 | mitochondria | 142 | 5 | 乙酰胆碱受体 | 21 | |
| 6 | oxidative stress | 123 | 6 | 骨骼肌 | 17 | |
| 7 | exercise | 93 | 7 | 小鼠 | 16 | |
| 8 | inflammation | 75 | 8 | 失重模拟 | 14 | |
| 9 | autophagy | 70 | 9 | 肌少症 | 13 | |
| 10 | cachexia | 68 | 10 | 乙酰胆碱受体抗体 | 11 |
聚类 Clusters | 英文文献关键词 Keywords in English literature | 中文文献关键词 Keywords in Chinese literature |
|---|---|---|
1 | body composition, cachexia, cancer cachexia, chronic kidney disease, inflammation, insulin resistance, metabolism, muscle atrophy, muscle regeneration, muscle wasting, myogenesis, myostatin, obesity, sarcopenia, sarcopenia obesity, skeletal muscle atrophy | 动物、失重模拟、小鼠、模拟失重、比目鱼肌、电针、肌、骨骼 |
| 2 | aging, atrophy, hypertrophy, motor, protein synthesis, regeneration, satellite cells, skeletal muscle | 乙酰胆碱受体、兔、动物模型、实验性自身免疫性重症肌无力、糖尿病、肌少症 |
| 3 | aging, apoptosis, autophagy, mice, mitochondria, mitophagy, oxidative stress, reactive oxygen species | 多发性硬化、帕金森病大鼠、肌阵挛、阿尔茨海默病 |
| 4 | bone, muscle, osteoporosis, senescence, vitamin D | 中枢神经系统、乙酰胆碱受体抗体、受体、抗体、胆碱能 |
| 5 | Exercise, frailty, nutrition | Bcl-2、大鼠、细胞凋亡、肌损伤、腓肠肌 |
| 6 | denervation, neuromuscular junction | MAFBX、去神经支配、肌纤维、肌萎缩、骨骼肌 |
| 7 | muscle mass | 咬肌、线粒体、葛根复方、超微结构 |
| 8 | 失神经、胫前肌、补阳还五汤、黄芪 | |
| 9 | 免疫性、细胞因子、重症肌无力 |
表5 英文和中文文献中肌少症动物模型研究关键词聚类分析
Table 5 Cluster analysis of key words in animal model of sarcopenia in English and Chinese literature
聚类 Clusters | 英文文献关键词 Keywords in English literature | 中文文献关键词 Keywords in Chinese literature |
|---|---|---|
1 | body composition, cachexia, cancer cachexia, chronic kidney disease, inflammation, insulin resistance, metabolism, muscle atrophy, muscle regeneration, muscle wasting, myogenesis, myostatin, obesity, sarcopenia, sarcopenia obesity, skeletal muscle atrophy | 动物、失重模拟、小鼠、模拟失重、比目鱼肌、电针、肌、骨骼 |
| 2 | aging, atrophy, hypertrophy, motor, protein synthesis, regeneration, satellite cells, skeletal muscle | 乙酰胆碱受体、兔、动物模型、实验性自身免疫性重症肌无力、糖尿病、肌少症 |
| 3 | aging, apoptosis, autophagy, mice, mitochondria, mitophagy, oxidative stress, reactive oxygen species | 多发性硬化、帕金森病大鼠、肌阵挛、阿尔茨海默病 |
| 4 | bone, muscle, osteoporosis, senescence, vitamin D | 中枢神经系统、乙酰胆碱受体抗体、受体、抗体、胆碱能 |
| 5 | Exercise, frailty, nutrition | Bcl-2、大鼠、细胞凋亡、肌损伤、腓肠肌 |
| 6 | denervation, neuromuscular junction | MAFBX、去神经支配、肌纤维、肌萎缩、骨骼肌 |
| 7 | muscle mass | 咬肌、线粒体、葛根复方、超微结构 |
| 8 | 失神经、胫前肌、补阳还五汤、黄芪 | |
| 9 | 免疫性、细胞因子、重症肌无力 |
| 1 | CRUZ-JENTOFT A J, BAEYENS J P, BAUER J M, et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People[J]. Age Ageing, 2010, 39(4):412-423. DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afq034 . |
| 2 | CRUZ-JENTOFT A J, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis[J]. Age Ageing, 2019, 48(4):601. DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afz046 . |
| 3 | CHEN L K, WOO J, ASSANTACHAI P, et al. Asian working group for sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment[J]. J Am Med Dir Assoc, 2020, 21(3):300-307. e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.12.012 . |
| 4 | VAN ECK N J, WALTMAN L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping[J]. Sciento-metrics, 2010, 84(2):523–538. DOI: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3 . |
| 5 | ARRUDA H, SILVA E R, LESSA M, et al. VOSviewer and bibliometrix[J]. J Med Libr Assoc, 2022, 110(3):392-395. DOI: 10.5195/jmla.2022.1434 . |
| 6 | XU D, WANG Y L, WANG K T, et al. A scientometrics analysis and visualization of depressive disorder[J]. Curr Neuro-pharmacol, 2021,19(6):766-786. DOI: 10.2174/1570159X18666200905151333 . |
| 7 | SHEN J M, SHEN H, KE L X, et al. Knowledge mapping of immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a bibliometric study[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 31(13):815575. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.815575 . |
| 8 | MA D, YANG B, GUAN B Y, et al. A bibliometric analysis of pyroptosis from 2001 to 2021[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12:731933. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.731933 . |
| 9 | AGEEL M. Pandemic critical care research during the COVID-19 (2020-2022): a bibliometric analysis using VOSviewer[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2022, 2022:8564649. DOI: 10.1155/2022/8564649 |
| 10 | 刘玉旋, 史大卓, 高铸烨, 等. 基于CiteSpace和VOSviewer可视化分析心房颤动与电重构研究的热点与趋势[J]. 中国医药导报,2023, 20(20):91-96. DOI:10.20047/j.issn1673-7210.2023.20.19 . |
| LIU Y X, SHI D Z, GAO Z Y, et al. Hotspots and trends in visual analysis of atrial fibrillation and electrical remodeling based on CiteSpace and VOSviewer[J]. China Med Her, 2023, 20(20): 91-96. DOI:10.20047/j.issn1673-7210.2023.20.19 . | |
| 11 | 王亚洁, 宋心宇, 徐霞. 基于VOSviewer软件的神经根型颈椎病护理研究热点分析[J].华南预防医学杂志, 2020, 34(2):78-81, 95. DOI: 10.13730/j.issn.1009-2595.2020.02.002 . |
| WANG Y J, SONG X Y, XU X. Hot spot analysis of nursing research on cervical spondylotic radiculopathy based on VOSviewer software[J]. Mil Med J South China, 2020, 34(2):78- 81, 95. DOI: 10.13730/j.issn.1009-2595.2020.02.002 . | |
| 12 | CHRISTIAN C J, BENIAN G M. Animal models of sarcopenia[J]. Aging Cell, 2020, 19(10):e13223. DOI: 10.1111/acel.13223 . |
| 13 | PARKS R J, FARES E, MACDONALD J K, et al. A procedure for creating a frailty index based on deficit accumulation in aging mice[J]. J Gerontol Ser A, 2012, 67A(3):217-227. DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glr193 . |
| 14 | SCHIAFFINO S, REGGIANI C. Fiber types in mammalian skeletal muscles[J]. Physiol Rev, 2011, 91(4):1447-1531. DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00031.2010 . |
| 15 | HERNDON L A, SCHMEISSNER P J, DUDARONEK J M,et al. Stochastic and genetic factors influence tissue-specific decline in ageing C. elegans [J]. Nature, 2002, 419:808-814. DOI: 10.1038/nature01135 . |
| 16 | GERHARD G S. Comparative aspects of zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a model for aging research[J]. Exp Gerontol, 2003, 38(11-12):1333-1341. DOI: 10.1016/j.exger.2003.10.022 . |
| 17 | GARCIA-CONTRERAS C, VAZQUEZ-GOMEZ M, TORRES-ROVIRA L, et al. Characterization of ageing- and diet-related swine models of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(3):823. DOI: 10.3390/ijms19030823 . |
| 18 | CHOW S K H, VAN MOURIK M, HUNG V W Y, et al. HR-pQCT for the evaluation of muscle quality and intramuscular fat infiltration in ageing skeletal muscle[J]. J Pers Med, 2022, 12(6):1016. DOI: 10.3390/jpm12061016 . |
| 19 | KOB R, FELLNER C, BERTSCH T, et al. Gender-specific differences in the development of sarcopenia in the rodent model of the ageing high-fat rat[J]. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2015, 6(2):181-191. DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.12019 . |
| 20 | FERNÁNDEZ A M, KIM J K, YAKAR S, et al. Functional inactivation of the IGF-I and insulin receptors in skeletal muscle causes type 2 diabetes[J]. Genes Dev, 2001, 15(15):1926-1934. DOI: 10.1101/gad.908001 . |
| 21 | MAVALLI M D, DIGIROLAMO D J, FAN Y, et al. Distinct growth hormone receptor signaling modes regulate skeletal muscle development and insulin sensitivity in mice[J]. J Clin Invest, 2010, 120(11):4007-4020. DOI: 10.1172/JCI42447 . |
| 22 | LIU J P, BAKER J, PERKINS A S, et al. Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r)[J]. Cell, 1993, 75(1):59-72. DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(05)80084-4 . |
| 23 | ROMANICK M, THOMPSON L V, BROWN-BORG H M. Murine models of atrophy, cachexia, and sarcopenia in skeletal muscle[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA Mol Basis Dis, 2013, 1832(9):1410-1420. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.03.011 . |
| 24 | HAMBRIGHT W S, NIEDERNHOFER L J, HUARD J, et al. Murine models of accelerated aging and musculoskeletal disease[J]. Bone, 2019, 125:122-127. DOI: 10.1016/j.bone. 2019. 03.002 . |
| 25 | COLMAN R J, MCKIERNAN S H, AIKEN J M, et al. Muscle mass loss in Rhesus monkeys: age of onset[J]. Exp Gerontol, 2005, 40(7):573-581. DOI: 10.1016/j.exger.2005.05.001 . |
| 26 | SHETH K A, IYER C C, WIER C G, et al. Muscle strength and size are associated with motor unit connectivity in aged mice[J]. Neurobiol Aging, 2018, 67:128-136. DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.03.016 . |
| 27 | 郭丹, 温旭, 吴丹妮, 等. 增龄性肌肉减少症小鼠肌肉组织抗氧化能力的特点[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2022, 48(5): 1209-1215. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220514 . |
| GUO D, WEN X, WU D N, et al. Characteristics of antioxidant capacity of muscle tissue in aging sarcopenia mice[J]. J Jilin Univ Med Ed, 2022, 48(5): 1209-1215. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220514 . | |
| 28 | 朱师宇, 吕安康, 赵宇星, 等. 基质金属蛋白酶-1、金属蛋白酶组织抑制因子-1在老年肌少症大鼠中的表达及意义[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(1): 104-109. DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.01.17 . |
| ZHU S Y, LÜ A K, ZHAO Y X, et al. Expressions of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 in skeletal muscles of aged rats with sarcopenia[J]. J South Med Univ, 2020, 40(1): 104-109. DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.01.17 . | |
| 29 | ZHANG N, CHOW S K, LEUNG K S, et al. An animal model of co-existing sarcopenia and osteoporotic fracture in senescence accelerated mouse prone 8 (SAMP8)[J]. Exp Gerontol, 2017, 97:1-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.exger.2017.07.008 . |
| 30 | HIROFUJI C, ISHIHARA A, ROY R R, et al. SDH activity and cell size of tibialis anterior motoneurons and muscle fibers in SAMP6[J]. Neuroreport, 2000, 11(4):823-828. DOI: 10.1097/00001756-200003200-00033 . |
| 31 | NISHIKAWA T, TAKAHASHI J A, MATSUSHITA T, et al. Tubular aggregates in the skeletal muscle of the senescence-accelerated mouse; SAM[J]. Mech Ageing Dev, 2000, 114(2):89-99. DOI: 10.1016/s0047-6374(00)00088-9 . |
| 32 | DERAVE W, EIJNDE B O, RAMAEKERS M, et al. Soleus muscles of SAMP8 mice provide an accelerated model of skeletal muscle senescence[J]. Exp Gerontol, 2005, 40(7):562-572. DOI: 10.1016/j.exger.2005.05.005 . |
| 33 | TRIFUNOVIC A, WREDENBERG A, FALKENBERG M, et al. Premature ageing in mice expressing defective mitochondrial DNA polymerase[J]. Nature, 2004, 429(6990):417-423. DOI: 10.1038/nature02517 . |
| 34 | ARU M R, ALEV K, PEHME A, et al. Changes in body composition of old rats at different time points after dexamethasone administration[J]. Curr Aging Sci, 2019, 11(4):255-260. DOI: 10.2174/1874609812666190114144238 . |
| 35 | CHIU C S, WEBER H, ADAMSKI S, et al. Non-invasive muscle contraction assay to study rodent models of sarcopenia[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2011, 12:246. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-12-246 . |
| 36 | CLEGG A, HASSAN-SMITH Z. Frailty and the endocrine system[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2018, 6(9):743-752. DOI: 10.1016/s2213-8587(18)30110-4 . |
| 37 | 王丛丛, 李军, 鲁飞翔, 等. 尿石素B对地塞米松诱导小鼠肌萎缩的改善作用及机制[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2018, 38(8): 1963-1966. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.08.070 . |
| WANG C C, LI J, LU F X, et al. Effect and mechanism of urushin B on dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy in mice[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2018, 38(8): 1963-1966. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.08.070 . | |
| 38 | DAMAS F, PHILLIPS S, VECHIN F C, et al. A review of resistance training-induced changes in skeletal muscle protein synthesis and their contribution to hypertrophy[J]. Sports Med, 2015, 45(6):801-807. DOI: 10.1007/s40279-015-0320-0 . |
| 39 | NAKAOKA K, YAMADA A, NODA S, et al. Influence of dietary vitamin D deficiency on bone strength, body composition, and muscle in ovariectomized rats fed a high-fat diet[J]. Nutrition, 2019, 60:87-93. DOI: 10.1016/j.nut.2018.09.001 . |
| 40 | 鲁飞翔, 李军, 周仙杰, 等. 地塞米松诱导少肌性肥胖小鼠模型的建立与评价[J]. 中华灾害救援医学, 2017, 5(3): 152-156. DOI: 10.13919/j.issn.2095-6274.2017.03.008 . |
| LU F X, LI J, ZHOU X J, et al. Evaluation and establishment of a sarcopenic obesity mouse model induced by dexa-methasone[J]. Chin J Disaster Med, 2017, 5(3): 152-156. DOI: 10.13919/j.issn.2095-6274.2017.03.008 . | |
| 41 | MOREY-HOLTON E R, GLOBUS R K. Hindlimb unloading rodent model: technical aspects[J]. J Appl Physiol, 2002, 92(4):1367-1377. DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00969.2001 . |
| 42 | GOLDSPINK D F, MORTON A J, LOUGHNA P, et al. The effect of hypokinesia and hypodynamia on protein turnover and the growth of four skeletal muscles of the rat[J]. Pflügers Arch, 1986, 407(3):333-340. DOI: 10.1007/BF00585311 . |
| 43 | OHIRA Y, YOSHINAGA T, OHARA M, et al. The role of neural and mechanical influences in maintaining normal fast and slow muscle properties[J]. Cells Tissues Organs, 2006, 182(3-4):129-142. DOI: 10.1159/000093963 . |
| 44 | SAUL D, KOSINSKY R L. Dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis as a model for sarcopenia in mice[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2020, 26(1):56-65. DOI: 10.1093/ibd/izz127 . |
| 45 | CAMPOS F, ABRIGO J, AGUIRRE F, et al. Sarcopenia in a mice model of chronic liver disease: role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system and oxidative stress[J]. Pflugers Arch, 2018, 470(10):1503-1519. DOI: 10.1007/s00424-018-2167-3 . |
| 46 | AGUIRRE F, ABRIGO J, GONZALEZ F, et al. Protective effect of angiotensin 1-7 on sarcopenia induced by chronic liver disease in mice[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(11):3891. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21113891 . |
| 47 | SATO E, MORI T, MISHIMA E, et al. Metabolic alterations by indoxyl sulfate in skeletal muscle induce uremic sarcopenia in chronic kidney disease[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6:36618. DOI: 10.1038/srep36618 . |
| 48 | 吴永耀, 余日臻, 孙京华, 等. 尿毒症大鼠肌少症模型的造模方法及评价[J]. 现代实用医学, 2022, 34(8)1006-1008. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0800.2022.08.010 . |
| WU Y Y, YU R Z, SUN J H, et al. Modeling method and evaluation of sarcopenia model in uremia rats[J]. Mod Pract Med, 2022, 34(8)1006-1008. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0800.2022.08.010 . | |
| 49 | 黄研, 邢三丽, 胡怡然, 等. 补肾还精方通过调节铁死亡干预小鼠肌少症的效应和机制研究[J]. 上海中医药杂志, 2022, 56(7): 74-82. DOI: 10.16305/j.1007-1334.2022.2107040 . |
| HUANG Y, XING S L, HU Y R, et al. Effect and mechanism of Bushen Huanjing recipe on sarcopenia in mice by regulating iron death[J]. Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med, 2022, 56(7): 74-82. DOI: 10.16305/j.1007-1334.2022.2107040 . | |
| 50 | 左祥宇, 姚荣飞, 赵麟毅, 等. 中药土党参激活PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路并减少2型糖尿病大鼠骨骼肌减少症[J]. 针灸和草药(英文), 2022(2):99-108. |
| ZUO X Y, YAO R F, ZHAO L Y, et al. Campanumoea javanica Bl. activates the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and reduces sarcopenia in a T2DM rat model[J]. Acupunct Herb Med, 2022(2):99-108. |
| [1] | 刘亚益, 贾云凤, 左一鸣, 张军平, 吕仕超. 心气阴两虚证动物模型的构建方法与评价进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 411-421. |
| [2] | 赵鑫, 王晨曦, 石文清, 娄月芬. 斑马鱼在炎症性肠病机制及药物研究中的应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 422-431. |
| [3] | 李会萍, 高洪彬, 温金银, 杨锦淳. 疾病动物模型数字化图谱数据库平台的构建与初步应用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 300-308. |
| [4] | 潘颐聪, 蒋汶洪, 胡明, 覃晓. 慢性肾脏病大鼠主动脉钙化模型的术式优化及效果评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 279-289. |
| [5] | 王碧莹, 鲁家铄, 昝桂影, 陈若松, 柴景蕊, 刘景根, 王瑜珺. 啮齿类动物药物成瘾模型的构建方法和应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 158-166. |
| [6] | 陈钰涵, 陈瑾玲, 李欣, 区燕华, 王斯, 陈镜伊, 王兴易, 袁嘉丽, 段媛媛, 羊忠山, 牛海涛. 基于中西医临床病证特点的重症肌无力动物模型分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 176-186. |
| [7] | 连辉, 姜艳玲, 刘佳, 张玉立, 谢伟, 薛晓鸥, 李健. 异常子宫出血大鼠模型的构建与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 130-146. |
| [8] | 罗世雄, 张赛, 陈慧. 常见哮喘动物模型的建立方法与评价研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 167-175. |
| [9] | 费彬, 郭文科, 郭建平. 疝疾病动物模型研究及新型疝修补材料应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(1): 55-66. |
| [10] | 杨家豪, 丁纯蕾, 钱风华, 孙旗, 姜旭升, 陈雯, 沈梦雯. 脓毒症相关脏器损伤动物模型研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 636-644. |
| [11] | 孙效容, 苏丹, 贵文娟, 陈玥. 手术诱导大鼠中重度膝骨关节炎模型的建立与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 597-604. |
| [12] | 田芳, 潘滨, 史佳怡, 徐燕意, 李卫华. 大气细颗粒物PM2.5暴露动物模型建立方法及在生殖毒性研究中的应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 626-635. |
| [13] | 赵小娜, 王鹏, 叶茂青, 曲新凯. 应用Triacsin C构建新型高血糖肥胖小鼠心功能减退模型[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 605-612. |
| [14] | 涂颖欣, 纪依澜, 王菲, 杨东明, 王冬冬, 孙芷馨, 戴悦欣, 王言吉, 阚广捍, 吴斌, 赵德明, 杨利峰. 小型猪后肢去负荷模拟失重模型的建立与组织损伤研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 475-486. |
| [15] | 黄冬妍, 吴建辉. 生殖毒理学研究动物模型的建立方法及应用评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 550-559. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||