













• •
出版日期:2025-11-20
通讯作者:
罗云霞(1991—),女,博士,讲师,研究生导师,研究方向:中医药防治脑病的临床与基础研究,E-mail:1249728545@qq.com,ORCID:0000-0002-2389-4049;作者简介:潘林琴(2000—),女,硕士研究生,研究方向:中药药效评价与应用研究,E-mail:19872719256@163.com基金资助:
PAN Linqin( ), DENG Xiangliang(
), DENG Xiangliang( )(
)( ), LUO Yunxia(
), LUO Yunxia( )(
)( )
)
Published:2025-11-20
Contact:
LUO Yunxia(ORCID:0000-0002-2389-4049),E-mail:1249728545@qq.com摘要:
缺血性中风(ischemic stroke,IS)是全球范围内造成死亡与长期致残的主要公共卫生问题之一,复杂的病理机制与有限的临床治疗窗口使得基础研究与临床转化亟待突破。本文系统综述了IS的关键病理环节,包括兴奋性毒性、氧化应激、代谢紊乱、神经炎症、神经血管单元与血-脑屏障损伤,以及多种程序性细胞死亡形式(如细胞凋亡、焦亡、铁死亡与近年提出的泛凋亡)在脑损伤不同阶段的相互作用与分子机制;归纳比较了常用动物模型的构建方法、适用场景与局限性(以局灶性模型如大脑中动脉闭塞、血栓/光化学栓塞、微球与内皮素-1模型,以及全脑缺血模型为代表),并评述了近年来将中医“病-证结合”理念纳入造模设计、以中药复方或证型模拟开展干预研究的进展与挑战。文章重点讨论了中西医结合研究的互补优势:通过在动物模型中明确证型分组并结合多组学与网络药理学分析,可揭示中药多靶点、多通路的神经保护与修复机制。最后,综述展望了模型标准化、基因编辑与人源化大动物模型、高分辨率影像、单细胞/多组学分析、人工智能辅助数据挖掘及类器官/多器官芯片等技术在优化模型与促进临床转化中的应用,并强调伦理规范与替代方法的重要性。本文旨在为IS机制研究、动物模型选择与改良、中西医结合的转化研究及个体化精准康复策略的开发提供系统参考与理论依据。
中图分类号:
潘林琴,邓向亮,罗云霞.缺血性中风动物模型的中西医机制与整合转化研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学.. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.107.
PAN Linqin,DENG Xiangliang,LUO Yunxia. Advances in Mechanistic and Integrative Translational Research on Ischemic Stroke Animal Models: Bridging Western Medicine and Traditional Chinese Medicine[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.107.
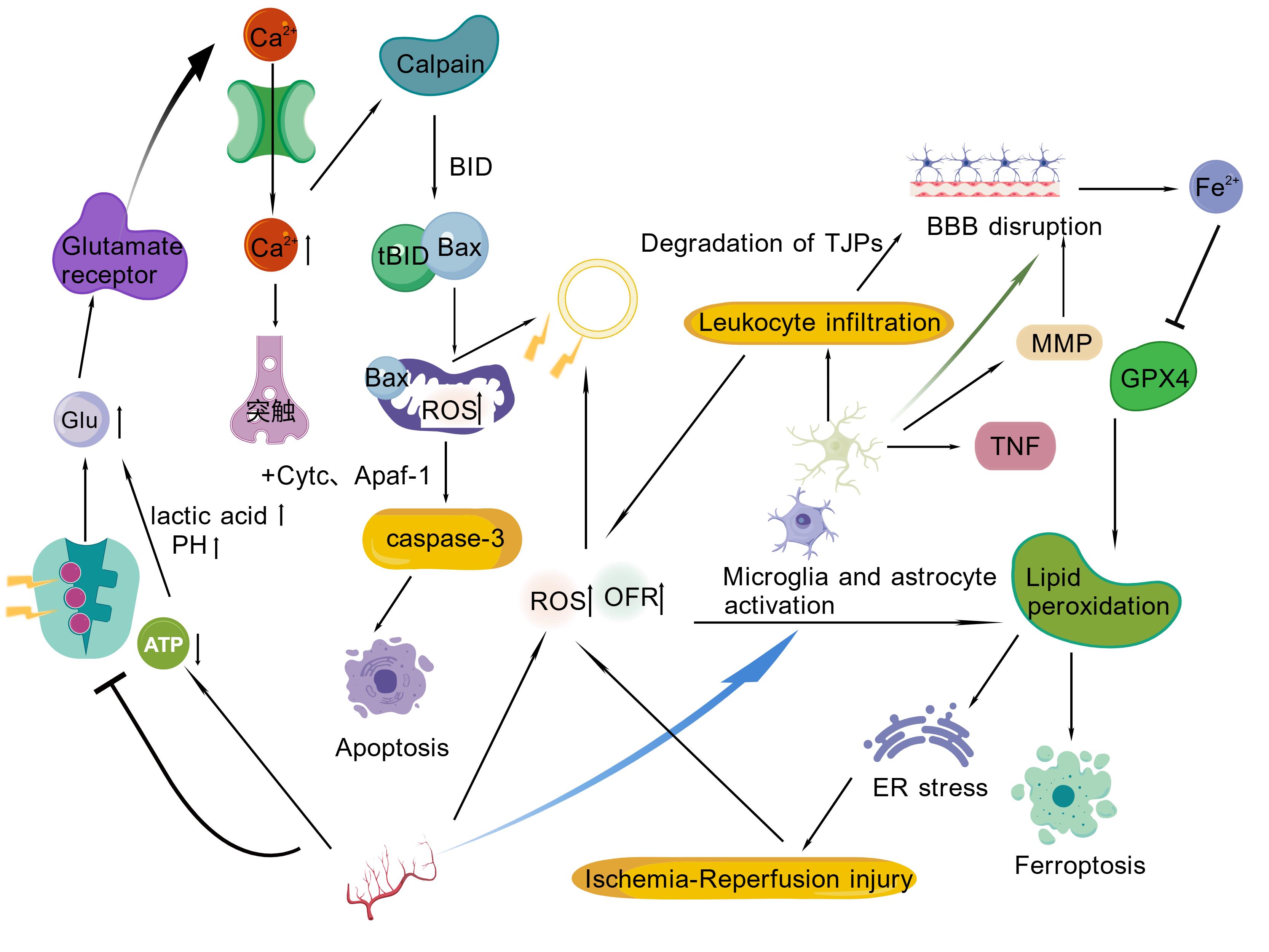
图1 缺血性中风的病理机制注:缺血性中风的多种病理机制及其相互作用,包括兴奋性毒性、氧化应激、代谢紊乱、炎症反应、神经血管单元以及血脑屏障损坏、细胞凋亡、铁死亡等。ATP:三磷酸腺苷;Bax:Bcl-2相关X蛋白;BBB:血脑屏障;BID:Bcl-2相互作用结构域;Cytc:细胞色素C;ER:内质网;Glu:谷氨酸;GPX4:谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4;MMP:基质金属蛋白酶;OFR:氧自由基;ROS:活性氧;TJPs:紧密连接蛋白;TNF:肿瘤坏子因子。
Figure 1 .Pathological mechanisms of Ischemic strokeNote: the various pathological mechanisms of ischemic stroke and their interactions, including excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, metabolic disturbances, neuroinflammation, disruption of the neurovascular unit and blood-brain barrier, apoptosis, ferroptosis, etc. ATP: adenosine triphosphate; Bax: Bcl-2-associated X protein; BBB: blood-brain barrier; BID: Bcl-2-interacting domain; Cytc: cytochrome c; ER: endoplasmic reticulum; Glu: glutamate; GPX4: glutathione peroxidase 4; MMP: matrix metalloproteinase; OFR: oxygen free radical; ROS: reactive oxygen species; TJPs: tight junction proteins; TNF: tumor necrosis factor.
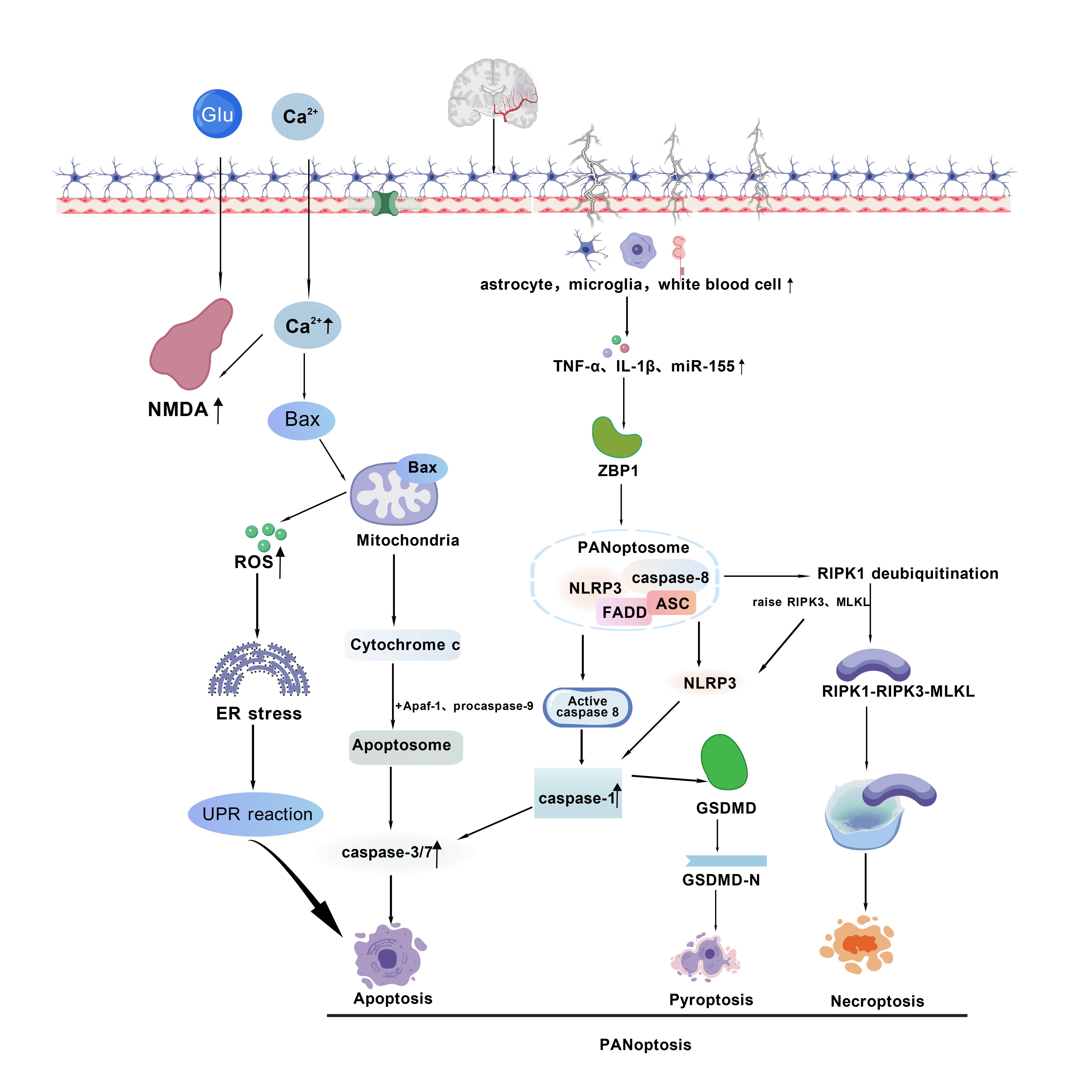
图2 缺血性中风的泛凋亡机制注: PANoptosome—死亡复合体,可同时激活焦亡(由GSDMD执行)、凋亡(依赖caspase-3/7)和坏死性凋亡(由RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL介导)的协同性细胞死亡通路。Bax:Bcl-2相关X蛋白;ER:内质网 ;FADD:Fas死亡结构域相关蛋白;Glu:谷氨酸;GSDMD:Gasdermin D;IL-1β:白介素-1β;MLKL:混合系列激酶结构域样蛋白;NLRP3:寡聚结构域样受体蛋白3;NMDA:N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体;RIPK1:受体相互作用丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶1;ROS:活性氧;TNF-α:肿瘤坏子因子α;UPR:未折叠蛋白反应。
Figure 2 PANoptosis mechanisms in Ischemic StrokeNote: PANoptosome — a death complex that activates a synergistic cell death pathway, triggering pyroptosis (executed by GSDMD), apoptosis (caspase-3/7- dependent), and necroptosis (mediated by RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL); Bax: Bcl-2-associated X protein; ER: endoplasmic reticulum; FADD: Fas-associated death domain; Glu: glutamate; GSDMD: Gasdermin D; IL-1β: interleukin-1β; MLKL: mixed-lineage kinase domain-like; NLRP3: NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing 3; NMDA: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; RIPK1: receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1; ROS: reactive oxygen species; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; UPR: unfolded protein response.
模型 Models | 造模方法 Modeling methods | 评价指标 Evaluation metrics | 优缺点 Advantages and limitations | 主要应用 Major applications | 实验动物 Laboratory animals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
开颅闭塞模型 Craniotomy-based occlusion models | 打开颅骨和切开硬脑膜以直接阻塞近端大脑动脉 | 1.神经功能评分:使用Bederson评分、Garcia评分等评估运动、感觉、反射功能 2.TTC染色测梗死面积 3.激光多普勒血流仪监测血流变化 | 优点:较小的梗塞;较低的死亡率;高重复性 缺点:破坏硬脑膜;颅内感染;片面盲目 | 评估急性缺血后的神经修复和神经可塑性 | 大鼠、小鼠、猫、羊、猪、猴 |
大脑中动脉闭塞模型 Middle cerebral artery occlusion model | 将4-0尼龙线插入颈内动脉。通过阻断颈外动脉分支以及颈内动脉的颅外分支,减少侧支血流量,阻断MCA血流 | 1.神经功能评分:使用Zea-longa评分、mNSS评分等评估运动、感觉、反射功能 2. TTC染色测梗死面积 3.激光多普勒血流仪监测血流变化 | 优点:操控方便;可控再灌注;缺血半暗带 缺点:巨大的变化;自发性高热;不适合溶栓 | 再灌注损伤的病理生理机制研究 | 大鼠、小鼠、兔 |
大脑中动脉电凝阻断模型 Middle cerebral artery electrocoagulation occlusion model | 暴露雄性SD大鼠的MCA起始部,在MCA靠近颈内动脉处将其用电凝阻断,造成供应区缺血 | 1.TTC染色测梗死面积 2.Bederson评分测神经功能 | 优点:缺血成功率高,重复性好 缺点:手术较复杂,且须开颅,破坏了颅腔完整性 | 永久性脑缺血损伤研究 | 大鼠 |
微球栓塞模型 Microsphere embolism model | 人造微球直径20~50μm,在注射后最多24h可引起血管微栓塞造成梗死 | 1.评估神经功能评分 2.TTC染色测梗死面积 3.观察微球栓塞后脑血流的变化 | 优点:微球诱发分级梗塞;大球栓塞的再现性 缺点:微球模型重现性差;不适合短暂性闭塞和溶栓 | 诱导分级梗死 | 大鼠、兔、灵长类动物 |
内皮素-1闭塞模型 Endothelin-1-induced occlusion model | 通过MCA附近的立体定位引导管将内皮素-1注入清醒大鼠的浅层皮质 | 1.激光多普勒血流仪观察脑血流 2.TTC染色或磁共振成像检测梗死面积 3.检测血管收缩相关分子标志物 | 优点:操控方便;灵活选择梗塞区域 缺点:受麻醉药影响;神经传递/调制 | IS恢复机制及药物治疗作用研究 | 大鼠 |
光化学栓塞模型 Photothrombosis occlusion model | 将光敏染料孟加拉红经尾静脉注入后,采用特定光波在颅骨表面做定向照射,形成大脑皮质区梗死 | 1.通过TTC染色或磁共振成像检测梗死面积 2.评估神经功能 3.观察光化学损伤后的病理变化 4.检测氧化应激相关标志物 | 优点:再现性;易于操控;创伤较小;长期生存 缺点:缺乏半影;对重组组织型纤溶酶原激活剂反应不佳 | 研究中风后癫痫发生的机制 | 大鼠、小鼠 |
表1 局灶性缺血动物模型
Table 1 Animal models of Focal Cerebral Ischemia
模型 Models | 造模方法 Modeling methods | 评价指标 Evaluation metrics | 优缺点 Advantages and limitations | 主要应用 Major applications | 实验动物 Laboratory animals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
开颅闭塞模型 Craniotomy-based occlusion models | 打开颅骨和切开硬脑膜以直接阻塞近端大脑动脉 | 1.神经功能评分:使用Bederson评分、Garcia评分等评估运动、感觉、反射功能 2.TTC染色测梗死面积 3.激光多普勒血流仪监测血流变化 | 优点:较小的梗塞;较低的死亡率;高重复性 缺点:破坏硬脑膜;颅内感染;片面盲目 | 评估急性缺血后的神经修复和神经可塑性 | 大鼠、小鼠、猫、羊、猪、猴 |
大脑中动脉闭塞模型 Middle cerebral artery occlusion model | 将4-0尼龙线插入颈内动脉。通过阻断颈外动脉分支以及颈内动脉的颅外分支,减少侧支血流量,阻断MCA血流 | 1.神经功能评分:使用Zea-longa评分、mNSS评分等评估运动、感觉、反射功能 2. TTC染色测梗死面积 3.激光多普勒血流仪监测血流变化 | 优点:操控方便;可控再灌注;缺血半暗带 缺点:巨大的变化;自发性高热;不适合溶栓 | 再灌注损伤的病理生理机制研究 | 大鼠、小鼠、兔 |
大脑中动脉电凝阻断模型 Middle cerebral artery electrocoagulation occlusion model | 暴露雄性SD大鼠的MCA起始部,在MCA靠近颈内动脉处将其用电凝阻断,造成供应区缺血 | 1.TTC染色测梗死面积 2.Bederson评分测神经功能 | 优点:缺血成功率高,重复性好 缺点:手术较复杂,且须开颅,破坏了颅腔完整性 | 永久性脑缺血损伤研究 | 大鼠 |
微球栓塞模型 Microsphere embolism model | 人造微球直径20~50μm,在注射后最多24h可引起血管微栓塞造成梗死 | 1.评估神经功能评分 2.TTC染色测梗死面积 3.观察微球栓塞后脑血流的变化 | 优点:微球诱发分级梗塞;大球栓塞的再现性 缺点:微球模型重现性差;不适合短暂性闭塞和溶栓 | 诱导分级梗死 | 大鼠、兔、灵长类动物 |
内皮素-1闭塞模型 Endothelin-1-induced occlusion model | 通过MCA附近的立体定位引导管将内皮素-1注入清醒大鼠的浅层皮质 | 1.激光多普勒血流仪观察脑血流 2.TTC染色或磁共振成像检测梗死面积 3.检测血管收缩相关分子标志物 | 优点:操控方便;灵活选择梗塞区域 缺点:受麻醉药影响;神经传递/调制 | IS恢复机制及药物治疗作用研究 | 大鼠 |
光化学栓塞模型 Photothrombosis occlusion model | 将光敏染料孟加拉红经尾静脉注入后,采用特定光波在颅骨表面做定向照射,形成大脑皮质区梗死 | 1.通过TTC染色或磁共振成像检测梗死面积 2.评估神经功能 3.观察光化学损伤后的病理变化 4.检测氧化应激相关标志物 | 优点:再现性;易于操控;创伤较小;长期生存 缺点:缺乏半影;对重组组织型纤溶酶原激活剂反应不佳 | 研究中风后癫痫发生的机制 | 大鼠、小鼠 |
模型 Models | 造模方法 Modeling methods | 评价指标 Evaluation metrics | 优缺点 Advantages and limitations | 主要应用 Major applications | 实验动物 Laboratory animals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
四支血管闭塞模型 4-VO | 第1天通过电凝永久闭塞椎动脉,第2天闭塞颈总动脉 | 1.神经功能评分 2.脑电图监测 3.组织学染色,评估缺血后脑组织的病理变化 4.注射蓝色染料到主动脉,观察脑组织的灌注情况 | 优点:简便性、可重复性、癫痫发作率低 缺点:两阶段外科手术;椎动脉永久性闭塞;高死亡率 | 研究溶栓药物疗效 | 大鼠、小鼠、兔、犬、猪 |
双血管闭塞模型 2-VO | 双侧颈动脉结扎 | 1.通过动脉-静脉O2和CO2的差异变化,估算脑血流减少程度 2.测量脑组织中的三磷酸腺苷、二磷酸腺苷、腺苷一磷酸、血流再灌注指数的浓度 3.测量脑组织中乳酸、丙酮酸等代谢产物含量 | 优点:一阶段外科手术;可控再循环;死亡率较低 缺点:重现性差;菌株依赖性 | 研究细胞损伤机制,评价药物对缺血损伤的保护机制 | 大鼠、小鼠、兔、猫、狗、羊、猪 |
心室颤动+心脏骤停模型 Ventricular fibrillation-induced cardiac arrest model | 通过电击心脏,引起心室颤动,进行紧急心肺复苏建立模型 | 1.HE染色观察正常神经元数量 2.用NDS进行神经功能评分 | 优点:导致心脏骤停和血栓栓塞的重要病因,模型能模拟临床病理过程 缺点:需通过电刺激、乙酰胆碱灌注或基因改造诱导房颤,手术难度高;动物存活率低 | 研究神经保护药物 | 鼠、兔、猫、狗、猪、羊 |
化学性/气体性缺氧模型 Chemical/gas-induced hypoxic models | 气体缺氧10分钟,看到视顶核梗死,随着缺氧时间延长,损伤会扩大到视叶深部 | TTC染色测梗死面积 | 优点:操作简便;适用于离体细胞培养或整体动物实验 缺点:非特异性效应;缺氧程度不均 | IS药物的高通量筛选 | 斑马鱼 |
表2 全脑缺血动物模型
Table 2 Animal models of Global Cerebral Ischemia
模型 Models | 造模方法 Modeling methods | 评价指标 Evaluation metrics | 优缺点 Advantages and limitations | 主要应用 Major applications | 实验动物 Laboratory animals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
四支血管闭塞模型 4-VO | 第1天通过电凝永久闭塞椎动脉,第2天闭塞颈总动脉 | 1.神经功能评分 2.脑电图监测 3.组织学染色,评估缺血后脑组织的病理变化 4.注射蓝色染料到主动脉,观察脑组织的灌注情况 | 优点:简便性、可重复性、癫痫发作率低 缺点:两阶段外科手术;椎动脉永久性闭塞;高死亡率 | 研究溶栓药物疗效 | 大鼠、小鼠、兔、犬、猪 |
双血管闭塞模型 2-VO | 双侧颈动脉结扎 | 1.通过动脉-静脉O2和CO2的差异变化,估算脑血流减少程度 2.测量脑组织中的三磷酸腺苷、二磷酸腺苷、腺苷一磷酸、血流再灌注指数的浓度 3.测量脑组织中乳酸、丙酮酸等代谢产物含量 | 优点:一阶段外科手术;可控再循环;死亡率较低 缺点:重现性差;菌株依赖性 | 研究细胞损伤机制,评价药物对缺血损伤的保护机制 | 大鼠、小鼠、兔、猫、狗、羊、猪 |
心室颤动+心脏骤停模型 Ventricular fibrillation-induced cardiac arrest model | 通过电击心脏,引起心室颤动,进行紧急心肺复苏建立模型 | 1.HE染色观察正常神经元数量 2.用NDS进行神经功能评分 | 优点:导致心脏骤停和血栓栓塞的重要病因,模型能模拟临床病理过程 缺点:需通过电刺激、乙酰胆碱灌注或基因改造诱导房颤,手术难度高;动物存活率低 | 研究神经保护药物 | 鼠、兔、猫、狗、猪、羊 |
化学性/气体性缺氧模型 Chemical/gas-induced hypoxic models | 气体缺氧10分钟,看到视顶核梗死,随着缺氧时间延长,损伤会扩大到视叶深部 | TTC染色测梗死面积 | 优点:操作简便;适用于离体细胞培养或整体动物实验 缺点:非特异性效应;缺氧程度不均 | IS药物的高通量筛选 | 斑马鱼 |
模型 Models | 造模方法 Modeling methods | 病理特点 Pathological features | 优缺点 Advantages and limitations | 应用药物与机制 Therapeutic agents and mechanisms of action | 实验动物 Laboratory animals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 气虚血瘀证模型Qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome model | 睡眠剥夺+多发性脑梗死手术/大鼠负重游泳,每天力竭性游泳1次,持续21天, MCAO模型 | ATP生成减少;炎症因子激活;微循环障碍 | 优点:应用最多,认为是经典的中风模型 缺点:造模时间长,成功率低,模型不统一 | 益气通窍活血汤:增加超氧化物歧化酶水平,降低丙醛,改善神经功能[ | 大鼠 |
肝阳上亢证模型 Liver Yang hyperactivity syndrome model | 用附子汤对大鼠灌胃,高浓度盐水饮水4周,使用MCAO造模方法 | 氧化应激水平升高;脑组织炎症反应;细胞凋亡 | 优点:该模型制作简单,表现为心率增快,性情急躁易怒,具有人类肝阳上亢证的某些特征 缺点:该模型手术损伤较大容易造成动物死亡 | 附子汤:调控神经递质平衡,改善行为症状;平肝潜阳 | 大鼠 |
肝阳化风证模型 Liver yang transforming into wind pattern model | 灌附子汤4周,MCAO模型 | 氧化应激加剧; 阳热状态诱导脑炎症 | 优点:与人类肝阳上亢证的某些临床特征相似,中风肝阳化风证型在临床上出现较多 缺点:没有体现模型的成功率、死亡率及重现率,对肝阳化风中风动物模型研究不多 | 中药活性成分:调节神经递质平衡,改善神经功能 | 大鼠 |
风痰入络证模型 Wind-phlegm invading collaterals syndrome model | 喂食高脂饲料,灌服附子汤剂,MCAO模型 | 血脂异常;白介素和TNF-α升高;神经功能障碍 | 优点:肝阳化风证与痰证模型相结合制备风痰入络证 缺点:经高脂饮食喂养后,大鼠体重飙升,MCA直径变宽,线栓阻塞的效果有一定负面影响 | 川芎嗪:抗炎、调脂作用;改善痰湿与神经功能[ | 大鼠 |
痰热腑实证模型 Phlegm-heat bowel excess syndrome model | MCAO模型,高脂低纤维饮食4周 | 血小板聚集,氧自由基大量产生 | 缺点:未能全面反映出“痰热腑实”的实质,关于痰热腑实的研究较少 | 星蒌承气汤,调节血清白介素水平,调脂 | 大、小鼠 |
痰瘀互结证模型 Phlegm-stasis intermingling syndrome model | 高脂饲料喂养,同时用脂肪乳剂灌胃1个月,次日结扎左侧颈总动脉 | 血液高黏状态; 神经炎症反应 | 优点:症状符合动脉粥样硬化及中医中“痰瘀”特点 缺点:复合影响因素较多 | 丹参、红花提取物:抑制细胞间黏附因子-1和血管细胞黏附因子表达,减轻血管内皮损伤,改善脑水肿[ | 大鼠 |
阴虚风动证模型 Yin deficiency with Wind stirring syndrome model | 第一天对SHR大鼠颈内动脉注射100μg月桂酸钠溶液后48h再接受100μg月桂酸钠溶液注射结扎颈总动脉+激怒实验 | 神经功能障碍; 内分泌紊乱 | 优点:长期激怒模拟“暴怒伤肝”后,大鼠出现嗜睡,弓背,大便干燥的特点,符合阴虚风动证 缺点:MCA无明显受损,缺血症状不明显。成模率不稳定,受多种因素干扰 | 滋阴类中药(如天麻):调节PI3K/Akt通路,促进神经元存活,抑制凋亡[ | 大鼠 |
肾阳虚证模型 Kidney Yang deficiency syndrome model | 对大鼠腿部连续21天注射氢化可的松琥珀酸钠,MCAO模型 | 大便稀溏、精神萎靡、喜卧嗜睡、消瘦等症状,血浆中cAMP降低;神经功能缺损;细胞凋亡 | 优点:该方法简单且稳定,相比手术造模法风险性较低 缺点:肾阳虚证脑缺血的发生发展过程十分复杂,体外或体内试验得出的研究结果是否适用于人体复杂的内环境未知 | 温阳逐瘀汤,上调miR-210,缓解缺血缺氧,保护脑组织[ | 大鼠 |
瘀毒互结证模型 Stasis-toxicity intermingling syndrome model | 通过肾上腺素/内毒素、角叉菜胶和角叉菜胶/干酵母菌3组药物干预,MCAO模型 | 血液黏滞,流动缓慢;免疫细胞浸润;红细胞聚集 | 优点:血液因注射角叉菜胶+干酵母混悬液而呈现高粘状态,符合瘀毒互结证指标 缺点:神经功能受损程度会随瘀血、毒邪作用的强弱,时间的长短而出现差异 | 化瘀解毒方(益气活血化瘀药—脑泰方和清热解毒药—黄连解毒汤联合)改善内皮细胞、血小板功能,抑制细胞自噬,保护血脑屏障[ | 大鼠 |
表3 缺血性中风中医病证结合动物模型
Table 3 Syndrome- and Disease-Integrated animal models of Ischemic Stroke
模型 Models | 造模方法 Modeling methods | 病理特点 Pathological features | 优缺点 Advantages and limitations | 应用药物与机制 Therapeutic agents and mechanisms of action | 实验动物 Laboratory animals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 气虚血瘀证模型Qi deficiency and blood stasis syndrome model | 睡眠剥夺+多发性脑梗死手术/大鼠负重游泳,每天力竭性游泳1次,持续21天, MCAO模型 | ATP生成减少;炎症因子激活;微循环障碍 | 优点:应用最多,认为是经典的中风模型 缺点:造模时间长,成功率低,模型不统一 | 益气通窍活血汤:增加超氧化物歧化酶水平,降低丙醛,改善神经功能[ | 大鼠 |
肝阳上亢证模型 Liver Yang hyperactivity syndrome model | 用附子汤对大鼠灌胃,高浓度盐水饮水4周,使用MCAO造模方法 | 氧化应激水平升高;脑组织炎症反应;细胞凋亡 | 优点:该模型制作简单,表现为心率增快,性情急躁易怒,具有人类肝阳上亢证的某些特征 缺点:该模型手术损伤较大容易造成动物死亡 | 附子汤:调控神经递质平衡,改善行为症状;平肝潜阳 | 大鼠 |
肝阳化风证模型 Liver yang transforming into wind pattern model | 灌附子汤4周,MCAO模型 | 氧化应激加剧; 阳热状态诱导脑炎症 | 优点:与人类肝阳上亢证的某些临床特征相似,中风肝阳化风证型在临床上出现较多 缺点:没有体现模型的成功率、死亡率及重现率,对肝阳化风中风动物模型研究不多 | 中药活性成分:调节神经递质平衡,改善神经功能 | 大鼠 |
风痰入络证模型 Wind-phlegm invading collaterals syndrome model | 喂食高脂饲料,灌服附子汤剂,MCAO模型 | 血脂异常;白介素和TNF-α升高;神经功能障碍 | 优点:肝阳化风证与痰证模型相结合制备风痰入络证 缺点:经高脂饮食喂养后,大鼠体重飙升,MCA直径变宽,线栓阻塞的效果有一定负面影响 | 川芎嗪:抗炎、调脂作用;改善痰湿与神经功能[ | 大鼠 |
痰热腑实证模型 Phlegm-heat bowel excess syndrome model | MCAO模型,高脂低纤维饮食4周 | 血小板聚集,氧自由基大量产生 | 缺点:未能全面反映出“痰热腑实”的实质,关于痰热腑实的研究较少 | 星蒌承气汤,调节血清白介素水平,调脂 | 大、小鼠 |
痰瘀互结证模型 Phlegm-stasis intermingling syndrome model | 高脂饲料喂养,同时用脂肪乳剂灌胃1个月,次日结扎左侧颈总动脉 | 血液高黏状态; 神经炎症反应 | 优点:症状符合动脉粥样硬化及中医中“痰瘀”特点 缺点:复合影响因素较多 | 丹参、红花提取物:抑制细胞间黏附因子-1和血管细胞黏附因子表达,减轻血管内皮损伤,改善脑水肿[ | 大鼠 |
阴虚风动证模型 Yin deficiency with Wind stirring syndrome model | 第一天对SHR大鼠颈内动脉注射100μg月桂酸钠溶液后48h再接受100μg月桂酸钠溶液注射结扎颈总动脉+激怒实验 | 神经功能障碍; 内分泌紊乱 | 优点:长期激怒模拟“暴怒伤肝”后,大鼠出现嗜睡,弓背,大便干燥的特点,符合阴虚风动证 缺点:MCA无明显受损,缺血症状不明显。成模率不稳定,受多种因素干扰 | 滋阴类中药(如天麻):调节PI3K/Akt通路,促进神经元存活,抑制凋亡[ | 大鼠 |
肾阳虚证模型 Kidney Yang deficiency syndrome model | 对大鼠腿部连续21天注射氢化可的松琥珀酸钠,MCAO模型 | 大便稀溏、精神萎靡、喜卧嗜睡、消瘦等症状,血浆中cAMP降低;神经功能缺损;细胞凋亡 | 优点:该方法简单且稳定,相比手术造模法风险性较低 缺点:肾阳虚证脑缺血的发生发展过程十分复杂,体外或体内试验得出的研究结果是否适用于人体复杂的内环境未知 | 温阳逐瘀汤,上调miR-210,缓解缺血缺氧,保护脑组织[ | 大鼠 |
瘀毒互结证模型 Stasis-toxicity intermingling syndrome model | 通过肾上腺素/内毒素、角叉菜胶和角叉菜胶/干酵母菌3组药物干预,MCAO模型 | 血液黏滞,流动缓慢;免疫细胞浸润;红细胞聚集 | 优点:血液因注射角叉菜胶+干酵母混悬液而呈现高粘状态,符合瘀毒互结证指标 缺点:神经功能受损程度会随瘀血、毒邪作用的强弱,时间的长短而出现差异 | 化瘀解毒方(益气活血化瘀药—脑泰方和清热解毒药—黄连解毒汤联合)改善内皮细胞、血小板功能,抑制细胞自噬,保护血脑屏障[ | 大鼠 |
| [1] | MENDELSON S J, PRABHAKARAN S. Diagnosis and management of transient ischemic attack and acute ischemic stroke: a review[J]. JAMA, 2021, 325(11):1088-1098. DOI:10.1001/jama.2020.26867 . |
| [2] | BATHLA G, AJMERA P, MEHTA P M, et al. Advances in acute ischemic stroke treatment: current status and future directions[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2023, 44(7):750-758. DOI:10.3174/ajnr.A7872 . |
| [3] | POWERS W J, RABINSTEIN A A, ACKERSON T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American heart association/American stroke association[J]. Stroke, 2019, 50(12): e344-e418. DOI:10.1161/STR.0000000000000211 . |
| [4] | CHEN L Y, WANG X, WANG S Q, et al. The impact of gut microbiota on the occurrence, treatment, and prognosis of ischemic stroke[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2025, 207:106836. DOI:10.1016/j.nbd.2025.106836 . |
| [5] | SHANG X Y, WEI R, YANG D, et al. Bioinformatics identification and validation of pyroptosis-related gene for ischemic stroke[J]. BMC Med Genomics, 2025, 18(1):1-15. DOI:10.1186/s12920-025-02119-2 . |
| [6] | WEN H Z, TU X X, LUO F L, et al. A novel PDE4 inhibitor ZX21011 alleviates neuronal apoptosis by decreasing GSK3β-mediated Drp1 Ser616 phosphorylation in cerebral ischemia reperfusion[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2025, 408:111405. DOI:10.1016/j.cbi.2025.111405 . |
| [7] | HAUPT M, GERNER S T, BÄHR M, et al. Neuroprotective strategies for ischemic stroke—future perspectives[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(5):1-17. DOI:10.3390/ijms24054334 . |
| [8] | WANG F, XIE X H, XING X Y, et al. Excitatory synaptic transmission in ischemic stroke: a new outlet for classical neuroprotective strategies[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(16):1-29. DOI:10.3390/ijms23169381 . |
| [9] | SHEN Z H, XIANG M, CHEN C, et al. Glutamate excitotoxicity: Potential therapeutic target for ischemic stroke[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2022, 151:113125. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113125 . |
| [10] | MAO R, ZONG N N, HU Y J, et al. Neuronal death mechanisms and therapeutic strategy in ischemic stroke[J]. Neurosci Bull, 2022, 38(10):1229-1247. DOI:10.1007/s12264-022-00859-0 . |
| [11] | QIN C, YANG S, CHU Y H, et al. Signaling pathways involved in ischemic stroke: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7(1):1-29. DOI:10.1038/s41392-022-01064-1 . |
| [12] | BRIYAL S, RANJAN A K, GULATI A. Oxidative stress: a target to treat Alzheimer's disease and stroke[J]. Neurochem Int, 2023, 165:105509. DOI:10.1016/j.neuint.2023.105509 . |
| [13] | DAVID C, RUCK T, ROLFES L, et al. Impact of NKG2D signaling on natural killer and T-cell function in cerebral ischemia[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2023, 12(12): 1-15. DOI:10.1161/JAHA.122.029529 . |
| [14] | 杜青, 赵晓慧, 马先军, 等. 血清钙离子水平与轻型缺血性脑卒中早期预后的相关性分析[J]. 中国临床神经科学, 2023, 31(6):677-680. |
| DU Q, ZHAO X H, MA X J, et al. Correlation analysis between serum calcium level and early prognosis of mild ischemic stroke[J]. Chin J Clin Neurosci, 2023, 31(6):677-680. | |
| [15] | ZHANG Y M, GUO Y L, LI R Q, et al. Novel CH25H+ and OASL+ microglia subclusters play distinct roles in cerebral ischemic stroke[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2023, 20(1):1-16. DOI:10.1186/s12974-023-02799-6 . |
| [16] | PAN B, SUN J, LIU Z Y, et al. Longxuetongluo Capsule protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through endoplasmic reticulum stress and MAPK-mediated mechanisms[J]. J Adv Res, 2021, 33:215-225. DOI:10.1016/j.jare.2021.01.016 . |
| [17] | LI L, ZHI D Y, CHENG R B, et al. The neuroprotective role of SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling in limb postconditioning in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2021, 749:135736. DOI:10.1016/j.neulet.2021.135736 . |
| [18] | DELONG J H, OHASHI S N, O'CONNOR K C, et al. Inflammatory responses after ischemic stroke[J]. Semin Immunopathol, 2022, 44(5):625-648. DOI:10.1007/s00281-022-00943-7 . |
| [19] | QIU Y M, ZHANG C L, CHEN A Q, et al. Immune cells in the BBB disruption after acute ischemic stroke: targets for immune therapy?[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12:1-29. DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2021.678744 . |
| [20] | QIN X Y, WANG J N, CHEN S J, et al. Astrocytic p75NTR expression provoked by ischemic stroke exacerbates the blood-brain barrier disruption[J]. Glia, 2022, 70(5):892-912. DOI:10.1002/glia.24146 . |
| [21] | DO P T, WU C C, CHIANG Y H, et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell therapy in blood-brain barrier preservation following ischemia: molecular mechanisms and prospects[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(18):1-22. DOI:10.3390/ijms221810045 . |
| [22] | FANG J, WANG Z, MIAO C Y. Angiogenesis after ischemic stroke[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2023, 44(7):1305-1321. DOI:10.1038/s41401-023-01061-2 . |
| [23] | CHEN X, KANG R, KROEMER G, et al. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2021, 18(5):280-296. DOI:10.1038/s41571-020-00462-0 . |
| [24] | ZHENG X Y, REN B D, GAO Y. Tight junction proteins related to blood-brain barrier and their regulatory signaling pathways in ischemic stroke[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2023, 165:115272. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115272 . |
| [25] | PAN J M, WANG Z H, HUANG X H, et al. Bacteria-derived outer-membrane vesicles hitchhike neutrophils to enhance ischemic stroke therapy[J]. Adv Mater, 2023, 35(38): e2301779. DOI:10.1002/adma.202301779 . |
| [26] | TANG H, WEN J, QIN T, et al. New insights into Sirt1: potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of cerebral ischemic stroke[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2023, 17:1-14. DOI:10.3389/fncel.2023.1228761 . |
| [27] | TUO Q Z, ZHANG S T, LEI P. Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke and their therapeutic implications[J]. Med Res Rev, 2022, 42(1):259-305. DOI:10.1002/med.21817 . |
| [28] | NAITO M G, XU D C, AMIN P, et al. Sequential activation of necroptosis and apoptosis cooperates to mediate vascular and neural pathology in stroke[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2020, 117(9):4959-4970. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1916427117 . |
| [29] | GONG Z Y, GUO J, LIU B, et al. Mechanisms of immune response and cell death in ischemic stroke and their regulation by natural compounds[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14:1-23. DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1287857 . |
| [30] | WANG Y Q, KANNEGANTI T D. From pyroptosis, apoptosis and necroptosis to PANoptosis: a mechanistic compendium of programmed cell death pathways[J]. Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 2021, 19:4641-4657. DOI:10.1016/j.csbj.2021.07.038 . |
| [31] | LIU J Y, ZHENG J, XU Y, et al. Enriched environment attenuates pyroptosis to improve functional recovery after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2021, 13:1-13. DOI:10.3389/fnagi.2021.717644 . |
| [32] | YANG L, TAO Y W, LUO L L, et al. Dengzhan Xixin injection derived from a traditional Chinese herb Erigeron breviscapus ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via modulation of mitophagy and mitochondrial apoptosis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 288:114988. DOI:10.1016/j.jep.2022.114988 . |
| [33] | WANG N, FEI C Y, CHU F R, et al. Taohong Siwu decoction regulates cell necrosis and neuroinflammation in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12:1-9. DOI:10.3389/fphar.2021.732358 . |
| [34] | 刘向哲, 宋艳芳, 王彦华, 等. 基于关键证候演变规律探讨急性缺血性中风的辨治[J]. 中医杂志, 2021, 62(23):2051-2054. DOI:10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2021.23.006 . |
| LIU X Z, SONG Y F, WANG Y H, et al. Discussion on the syndrome differentiation and treatment of acute ischemic stroke through the evolution of key syndromes[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2021, 62(23):2051-2054. DOI:10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2021.23.006 . | |
| [35] | 杨皓博, 周铭晗, 范文涛. 基于中西医临床病证特点的缺血性中风动物模型评价分析[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2025, 41(3):96-102. DOI:10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.20240423.002 . |
| YANG H B, ZHOU M H, FAN W T. Evaluation and analysis of ischemic stroke animal models based on clinical characteristics of traditional Chinese and western medicine[J]. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Med, 2025, 41(3):96-102. DOI:10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.20240423.002 . | |
| [36] | 赵欣, 周明. 中医药治疗缺血性中风的研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2021, 27(22):4548-4552. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2021.22.032 . |
| XIN Z, MING Z. Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of ischemic stroke[J]. Med Recapitul, 2021, 27(22):4548-4552. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2021.22.032 . | |
| [37] | TSENG C Y, HSU P S, LEE C T, et al. Acupuncture and traditional Chinese herbal medicine integrated with conventional rehabilitation for post-stroke functional recovery: a retrospective cohort study[J]. Front Neurosci, 2022, 16:1-10. DOI:10.3389/fnins.2022.851333 . |
| [38] | CARMICHAEL S T. Rodent models of focal stroke: size, mechanism, and purpose[J]. NeuroRx, 2005, 2(3):396-409. DOI:10.1602/neurorx.2.3.396 . |
| [39] | YANG G, KITAGAWA K, MATSUSHITA K, et al. C57BL/6 strain is most susceptible to cerebral ischemia following bilateral common carotid occlusion among seven mouse strains: selective neuronal death in the murine transient forebrain ischemia[J]. Brain Res, 1997, 752(1-2):209-218. DOI:10.1016/s0006-8993(96)01453-9 . |
| [40] | MOISENOVICH M M, SILACHEV D N, MOYSENOVICH A M, et al. Effects of recombinant spidroin rS1/9 on brain neural progenitors after photothrombosis-induced ischemia[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8:1-17. DOI:10.3389/fcell.2020.00823 . |
| [41] | STEELE P R, CAVARSAN C F, DOWALIBY L, et al. Altered motoneuron properties contribute to motor deficits in a rabbit hypoxia-ischemia model of cerebral palsy[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2020, 14:1-12. DOI:10.3389/fncel.2020.00069 . |
| [42] | 董波, 刘嘉欣, 熊伟, 等. 缺血性脑卒中动物模型的研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2022, 42(1):54-61. DOI:10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2021.049 . |
| DONG B, LIU J X, XIONG W, et al. Progress in animal models of ischemic stroke[J]. Lab Anim Comp Med, 2022, 42(1):54-61. DOI:10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2021.049 . | |
| [43] | 胡志斌, 黄缨, 丁玉强. 脑缺血动物模型的制备及评估进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2021, 41(4):271-283. DOI:10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2021.085 . |
| HU Z B, HUANG Y, DING Y Q. Construction and evaluation of animal models for cerebral ischemia[J]. Lab Anim Comp Med, 2021, 41(4):271-283. DOI:10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2021.085 . | |
| [44] | LONGA E Z, WEINSTEIN P R, CARLSON S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats[J]. Stroke, 1989, 20(1):84-91. DOI:10.1161/01.str.20.1.84 . |
| [45] | SCHMID-ELSAESSER R, ZAUSINGER S, HUNGERHUBER E, et al. A critical reevaluation of the intraluminal thread model of focal cerebral ischemia: evidence of inadvertent premature reperfusion and subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats by laser-Doppler flowmetry[J]. Stroke, 1998, 29(10):2162-2170. DOI:10.1161/01.str.29.10.2162 . |
| [46] | 席娅琳, 王慧瑜, 鹿树军. 局灶性缺血性卒中动物模型制作研究进展[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2023, 33(2):140-148. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2023.02.019 . |
| XI Y L, WANG H Y, LU S J. Research progress of focal ischemic stroke in production of animal models[J]. Chin J Comp Med, 2023, 33(2):140-148. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2023.02.019 . | |
| [47] | DURUKAN A, TATLISUMAK T. Acute ischemic stroke: overview of major experimental rodent models, pathophysiology, and therapy of focal cerebral ischemia[J]. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 2007, 87(1):179-197. DOI:10.1016/j.pbb.2007.04.015 . |
| [48] | TRAYSTMAN R J, KIRSCH J R, KOEHLER R C. Oxygen radical mechanisms of brain injury following ischemia and reperfusion[J]. J Appl Physiol, 1991, 71(4):1185-1195. DOI:10.1152/jappl.1991.71.4.1185 . |
| [49] | SALAMEH A, DHEIN S, MEWES M, et al. Anti-oxidative or anti-inflammatory additives reduce ischemia/reperfusions injury in an animal model of cardiopulmonary bypass[J]. Saudi J Biol Sci, 2020, 27(1):18-29. DOI:10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.04.003 . |
| [50] | PENG S X, WEI C, LEI J Y, et al. Network Meta-analysis of Chinese medicine injections for activating blood and resolving stasis in adjuvant treatment of acute ischemic stroke[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi, 2023, 48(15):4215-4230. DOI:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230425.501 . |
| [51] | 谢映. 肝阳上亢证与肝阳化风证模型大鼠的UCH-L1、StAR mRNA表达的研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2007. DOI:10.7666/d.y1084510 . |
| XIE Y. Research on the expression of UCH-L1 and StAR mRNA in rats with liver-yang-hyperactivity syndrome and liver-yang-transforming-wind syndrome models[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2007. DOI:10.7666/d.y1084510 . | |
| [52] | 刘祎, 刘旺华, 李花, 等. 脑梗死风痰入络证病证结合动物模型的研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2022, 33(1):255-256, 封3-封4. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2022.01.69 . |
| LIU Y, LIU W H, LI H, et al. Study on combining animal models with cerebral infarction, wind and phlegm entering collateral syndrome[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2022, 33(1):255-256, 封3-封4. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2022.01.69 . | |
| [53] | 申晓琳, 方伟, 王艳. 星蒌化痰汤在急性缺血性中风痰热腑实证中的应用价值[J]. 医学理论与实践, 2024, 37(22):3826-3828. DOI:10.19381/j.issn.1001-7585.2024.22.013 . |
| SHEN X L, FANG W, WANG Y. Application value of xinglou Huatan decoction in acute ischemic stroke with phlegm-heat deficiency syndrome[J]. J Med Theory Pract, 2024, 37(22):3826-3828. DOI:10.19381/j.issn.1001-7585.2024.22.013 . | |
| [54] | 林晓伟, 王家艳, 王能, 等. 益气通窍活血汤对急性脑梗死(气虚血瘀型)患者HIF-1α、MMP-9、Cys-C及神经功能的影响[J]. 广州中医药大学学报, 2022, 39(6):1268-1274. DOI:10.13359/j.cnki.gzxbtcm.2022.06.008 . |
| LIN X W, WANG J Y, WANG N, et al. Effects of Yiqi Tongqiao Huoxue decoction on HIF-1α, MMP-9, cys-C and nerve function in patients with acute cerebral infarction of qi deficiency and blood stasis type[J]. J Guangzhou Univ Tradit Chin Med, 2022, 39(6):1268-1274. DOI:10.13359/j.cnki.gzxbtcm.2022.06.008 . | |
| [55] | 谢映, 梁清华, 熊新贵, 等. 泛素羧基末端水解酶在肝阳化风证中的表达[J]. 实用预防医学, 2007, 14(2):270-272. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2007.02.004 . |
| XIE Y, LIANG Q H, XIONG X G, et al. Expression of ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 in liver-Yang forming wind of rats[J]. Pract Prev Med, 2007, 14(2):270-272. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2007.02.004 . | |
| [56] | 白永军, 张令霖, 连新福. 脑缺血再灌注痰瘀互结证动物模型的研究进展[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2022, 20(3):459-462. DOI:10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2022.03.014 . |
| BAI Y J, ZHANG L L, LIAN X F. Research progress on animal models of phlegm and blood stasis syndrome after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion[J]. Chin J Integr Med Cardio/cerebrovascular Dis, 2022, 20(3):459-462. DOI:10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2022.03.014 . | |
| [57] | 鲍勇, 项尚, 朱莎, 等. 天麻钩藤饮联合抗血小板治疗对阴虚风动型缺血性中风患者疗效、血清HCY与CRP影响[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2021, 23(8):175-178. DOI:10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2021.08.037 . |
| BAO Y, XIANG S, ZHU S, et al. Effects of Tianma Gouteng decoction(天麻钩藤饮)combined with antiplatelet therapy on efficacy, serum HCY and CRP in patients with ischemic stroke of wind formation from Yin deficiency type[J]. J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med, 2021, 23(8):175-178. DOI:10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2021.08.037 . | |
| [58] | 孙诗杰. 温阳逐瘀汤对肾阳虚证大鼠局灶性脑缺血后微小RNA-210及其靶基因的影响[D]. 南宁: 广西中医药大学, 2021. DOI:10.27879/d.cnki.ggxzy.2021.000338 . |
| SUN S J. The effect of Wenyang Zhuyu Decoction on microRNA-210 and its target genes in rats with kidney-yang deficiency after focal cerebral ischemia[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, 2021. DOI:10.27879/d.cnki.ggxzy.2021.000338 . | |
| [59] | 彭珣, 李定祥, 马若梦, 等. 化瘀解毒方对缺血性中风瘀毒互结证模型大鼠脑细胞自噬及血脑屏障通透性的影响[J]. 中医杂志, 2022, 63(9):862-868. DOI:10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2022.09.013 . |
| PENG X, LI D X, MA R M, et al. Effects of Huayu Jiedu formula(化瘀解毒方) on brain cell autophagy and blood brain barrier permeability in ischemic stroke model rats with binding of stasis and toxin syndrome[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2022, 63(9):862-868. DOI:10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2022.09.013 . | |
| [60] | 李卫民, 池建淮. 缺血性中风痰瘀互结证动物模型的初步探讨[J]. 山西中医学院学报, 2012, 13(1):15-18. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-0258.2012.01.006 . |
| LI W M, CHI J H. Study on animal model with ischemic stroke disease and syndrome of phlegm and stagnated blood[J]. J Shanxi Coll Tradit Chin Med, 2012, 13(1):15-18. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-0258.2012.01.006 . | |
| [61] | ZUO H J, WANG P X, REN X Q, et al. Gastrodin regulates PI3K/AKT-Sirt3 signaling pathway and proinflammatory mediators in activated microglia[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2024, 61(5):2728-2744. DOI:10.1007/s12035-023-03743-8 . |
| [62] | 何宏盾, 韦亮, 孙诗杰, 等. 温阳逐瘀汤对肾阳虚证大鼠急性脑缺血损伤后Wnt3a、β-catenin表达的影响[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2024, 22(14):2568-2574. DOI:10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2024.14.012 . |
| HE H D, WEI L, SUN S J, et al. Effect of Wenyang Zhuyu decoction on expressions of Wnt3a and β-catenin after acute cerebral ischemic injury in rats with kidney-Yang deficiency syndrome[J]. Chin J Integr Med Cardio/cerebrovascular Dis, 2024, 22(14):2568-2574. DOI:10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2024.14.012 . | |
| [63] | ZHAO T K, HE F J, ZHAO K Q, et al. A triple-targeted rutin-based self-assembled delivery vector for treating ischemic stroke by vascular normalization and anti-inflammation via ACE2/Ang1-7 signaling[J]. ACS Cent Sci, 2023, 9(6):1180-1199. DOI:10.1021/acscentsci.3c00377 . |
| [64] | YAN R R, CIGLIOLA V, OONK K A, et al. An enhancer-based gene-therapy strategy for spatiotemporal control of cargoes during tissue repair[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30(1):96-111.e6. DOI:10.1016/j.stem.2022.11.012 . |
| [65] | LI Y, WANG T Y, ZHANG T X, et al. Fast high-resolution metabolic imaging of acute stroke with 3D magnetic resonance spectroscopy[J]. Brain, 2020, 143(11):3225-3233. DOI:10.1093/brain/awaa264 . |
| [66] | 曾琬婷, 周丽婷, 贾茹, 等. 关白附炮制前后对缺血性中风沙鼠药效学和代谢组学的影响[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2024, 26(4):55-63. DOI:10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2024.04.011 . |
| ZENG W T, ZHOU L T, JIA R, et al. Effect of Guanbaifu (Radix aconiti Coreani)before and after processing on the metabolomics of gerbils with ischemic stroke[J]. J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med, 2024, 26(4):55-63. DOI:10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2024.04.011 . | |
| [67] | 朱冬宁, 吴纯伟, 陈驰, 等. 基于分子对接模拟预测复方脑脉通治疗缺血性脑卒中的物质基础[J]. 中药材, 2017, 40(3):673-679. DOI:10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2017.03.038 . |
| ZHU D N, WU C W, CHEN C, et al. Simulation and prediction of the material foundation of Naomaitong formula for ischemic stroke based on molecular docking technology[J]. J Chin Med Mater, 2017, 40(3):673-679. DOI:10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2017.03.038 . | |
| [68] | 邓秋媚, 黄泽, 黎军宏, 等. 基于蛋白组学的加味四逆汤治疗缺血性中风恢复期的作用机制[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2022, 33(6):1378-1381. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2022.06.29 . |
| DENG Q M, HUANG Z, LI J H, et al. Study on the mechanism of modified Sini decoction in treating ischemic stroke in recovery period based on proteomics[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2022, 33(6):1378-1381. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2022.06.29 . | |
| [69] | PAUL S, CANDELARIO-JALIL E. Emerging neuroprotective strategies for the treatment of ischemic stroke: an overview of clinical and preclinical studies[J]. Exp Neurol, 2021, 335:1-56. DOI:10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113518 . |
| [70] | WANG S N, WANG Z, WANG X Y, et al. Humanized cerebral organoids-based ischemic stroke model for discovering of potential anti-stroke agents[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2023, 44(3):513-523. DOI:10.1038/s41401-022-00986-4 . |
| [71] | ZHANG J, LI Y, CHANG M L, et al. Naoxintong capsule attenuates heart damage after ischemic stroke via Nuclear factor-κB/Pyrin domain-containing protein 3/Caspase-1 signaling[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2025, 341:119240. DOI:10.1016/j.jep.2024.119240 . |
| [72] | YE J, SHANG H L, DU H D, et al. An optimal animal model of ischemic stroke established by digital subtraction angiography-guided autologous thrombi in Cynomolgus Monkeys[J]. Front Neurol, 2022, 13:1-10. DOI:10.3389/fneur.2022.864954 . |
| [73] | 汪学军, 陈孝银. 缺血性脑血管病的中医研究基础: 病证结合的动物模型[J]. 辽宁中医杂志, 2005, 32(10): 1097-1099. DOI:10.13192/j.ljtcm.2005.10.116.wangxj.090 . |
| WANG X J, CHEN X Y. The animal model of combination of illness and syndrome is foundation to study the ischemia of cerebrovascular disease in TCM[J]. Liaoning J Tradit Chin Med, 2005, 32(10): 1097-1099. DOI:10.13192/j.ljtcm.2005.10.116.wangxj.090 . | |
| [74] | 吕文良, 王丽, 汪青楠. 新时代下对促进中西医结合发展的思考[J]. 中国科学基金, 2023, 37(1):67-71. DOI:10.16262/j.cnki.1000-8217.20230215.002 . |
| LYU W L, WANG L, WANG Q N. Thoughts on promoting the integration of traditional Chinese and western medicine in the new era[J]. Bull Natl Nat Sci Found China, 2023, 37(1):67-71. DOI:10.16262/j.cnki.1000-8217.20230215.002 . | |
| [75] | CHEN Y T, TOZER D J, LIU W R, et al. Prediction of response to thrombolysis in acute stroke using neural network analysis of CT perfusion imaging[J]. Eur Stroke J, 2023, 8(3):629-637. DOI:10.1177/23969873231183206 . |
| [1] | 王笑铭, 孟晨晨, 范鹿, 李艳阳, 张军平, 吕仕超. 中医证候类动物模型构建方法概述[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(5): 596-610. |
| [2] | 高超奇, 祝志波, 孙显东. 大鼠血管重构模型的应用进展与分类分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(5): 542-550. |
| [3] | 刘子琪, 李云英, 李钦, 李元涵, 何芳雁, 温伟波. 脾胃虚寒型胃溃疡动物模型研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(5): 574-585. |
| [4] | 刘洋, 程来洋, 郭中坤. 中医病症结合的围绝经期综合征动物模型研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(5): 586-595. |
| [5] | 中国研究型医院学会医学动物实验专家委员会, 中国研究型医院学会神经再生与 组织器官损伤修复专业委员会, 中国解剖学会工程解剖学分会, 李忠海, 李斌, 赵杰, 杨操, 李英俊. 椎间盘退行性病变的临床前研究动物模型选择指南(2025年版)[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(5): 524-541. |
| [6] | 刘亚益, 贾云凤, 左一鸣, 张军平, 吕仕超. 心气阴两虚证动物模型的构建方法与评价进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 411-421. |
| [7] | 赵鑫, 王晨曦, 石文清, 娄月芬. 斑马鱼在炎症性肠病机制及药物研究中的应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 422-431. |
| [8] | 李会萍, 高洪彬, 温金银, 杨锦淳. 疾病动物模型数字化图谱数据库平台的构建与初步应用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 300-308. |
| [9] | 潘颐聪, 蒋汶洪, 胡明, 覃晓. 慢性肾脏病大鼠主动脉钙化模型的术式优化及效果评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 279-289. |
| [10] | 陈钰涵, 陈瑾玲, 李欣, 区燕华, 王斯, 陈镜伊, 王兴易, 袁嘉丽, 段媛媛, 羊忠山, 牛海涛. 基于中西医临床病证特点的重症肌无力动物模型分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 176-186. |
| [11] | 连辉, 姜艳玲, 刘佳, 张玉立, 谢伟, 薛晓鸥, 李健. 异常子宫出血大鼠模型的构建与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 130-146. |
| [12] | 罗世雄, 张赛, 陈慧. 常见哮喘动物模型的建立方法与评价研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 167-175. |
| [13] | 王碧莹, 鲁家铄, 昝桂影, 陈若松, 柴景蕊, 刘景根, 王瑜珺. 啮齿类动物药物成瘾模型的构建方法和应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 158-166. |
| [14] | 费彬, 郭文科, 郭建平. 疝疾病动物模型研究及新型疝修补材料应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(1): 55-66. |
| [15] | 杨家豪, 丁纯蕾, 钱风华, 孙旗, 姜旭升, 陈雯, 沈梦雯. 脓毒症相关脏器损伤动物模型研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 636-644. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||