













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 279-289.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.128
收稿日期:2024-08-28
修回日期:2024-12-18
出版日期:2025-07-07
发布日期:2025-06-25
通讯作者:
蒋汶洪(1989—),男,博士研究生,主治医师,课题负责人,研究方向:外周血管疾病。E-mail: jwhongxszy@163.com。ORCID: 0000-0001-6677-4533作者简介:潘颐聪(1988—),男,博士研究生,研究方向:血管钙化。 E-mail: 375752640@qq.com。ORCID: 0009-0004-6758-9507
基金资助:
PAN Yicong( ), JIANG Wenhong(
), JIANG Wenhong( )(
)( ), HU Ming, QIN Xiao
), HU Ming, QIN Xiao
Received:2024-08-28
Revised:2024-12-18
Published:2025-06-25
Online:2025-07-07
Contact:
JIANG Wenhong (ORCID: 0000-0001-6677-4533), E-mail: jwhongxszy@163.com摘要:
目的 通过不同的肾脏切除手术方法建立SD大鼠慢性肾脏病主动脉钙化模型,并进行手术时间及存活时间比较和效果评价,以探索更优化的建模方法。 方法 根据不同手术方式分为腹腔入路先切2/3左肾后二期右全肾切除组(A组)、腹腔入路2/3左肾及右全肾同时切除组(B组)、背入路先切右全肾后二期2/3左肾切除组(C组)、背入路先切2/3左肾后二期切除右全肾组(D组)共4组,比较腹腔入路及背入路、分期及一次性肾脏切除术的SD大鼠生存曲线确定最优的肾脏切除手术方式后,选取24只8周龄雄性SPF级SD大鼠进行肾脏切除联合骨化三醇钙化诱导:其中实验组12只大鼠行背入路的左侧2/3肾切除后右侧全肾切除术,1周后腹腔注射骨化三醇溶液1 μg/kg,以进行主动脉钙化诱导;对照组12只大鼠行假手术后1周,腹腔注射含1%DMSO的生理盐水250 μL/kg。腹腔注射药物3个月后,观察各组大鼠的存活情况。麻醉状态下,采集各组大鼠的血液样本,测定血清磷和钙离子浓度、血清尿素氮和肌酐含量。安乐死大鼠后进行剖检,肉眼观察残余肾脏形态,HE染色观察肾冠状切面的病理学变化。另外取各组大鼠的全主动脉,茜素红S及von Kossa染色观察主动脉钙化程度,实时荧光定量PCR法检测大鼠主动脉组织中平滑肌肌动蛋白相关蛋白α (smooth muscle actin-associated protein α ,Sm22)、Runt相关转录因子2(Runt-related transcription factor 2,Runx2)、骨桥蛋白(osteopontin,OPN)基因表达情况,以评价建模效果。 结果 不同术式优化探索实验发现,背入路先切除2/3左肾再切除右侧全肾的D组大鼠的存活率最高,提示该术式是建立肾功能不全的慢性肾脏病模型的最佳手术方式。运用该术式联合高剂量骨化三醇注射的实验组大鼠血清钙离子浓度显著低于假手术对照组(P<0.05),而血清磷离子浓度、血清肌酐及血清尿素氮含量则显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。肾脏HE染色可见实验组大鼠肾脏发生明显器质性改变,其中实验组大鼠的肾小球计数比对照组明显减少(P<0.05),提示肾衰竭模型成功建立。茜素红S染色可见实验组大鼠的主动脉中膜中有明显的色素沉着,von Kossa染色可见实验组大鼠的主动脉中膜层明显有硝酸银沉积,符合肾衰竭主动脉钙化的表现。实时荧光定量PCR表明,实验组大鼠的主动脉组织中Sm22表达水平下降(P<0.05),OPN和Runx2表达水平上升(P<0.05),提示主动脉平滑肌细胞由平滑肌表型向骨样表型转变,主动脉钙化模型诱导成功。 结论 采用背入路先切除2/3左肾,再进行右侧全肾切除,联合高剂量骨化三醇溶液摄入的方法,可成功建立SD大鼠慢性肾脏病主动脉钙化模型。该方案能缩短手术时间,提高建模成功率和动物存活率。
中图分类号:
潘颐聪,蒋汶洪,胡明,等. 慢性肾脏病大鼠主动脉钙化模型的术式优化及效果评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 279-289. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.128.
PAN Yicong,JIANG Wenhong,HU Ming,et al. Optimization of Surgical Procedure and Efficacy Evaluation of Aortic Calcification Model in Rats with Chronic Kidney Disease[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 279-289. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.128.
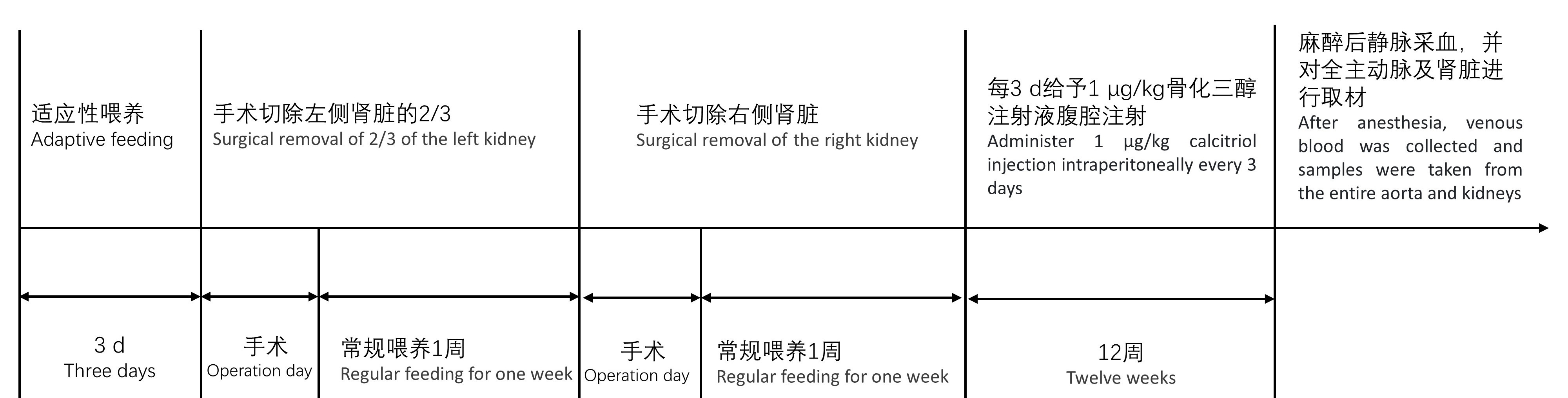
图1 SD大鼠慢性肾脏病主动脉钙化建模及评价实验流程图注:8周龄SD大鼠饲养于SPF级动物屏障设施,常规饮食适应3 d后进行左肾2/3切除术,术后常规饲养,1周后进行右肾切除术。1周后每3 d给予1 μg/kg骨化三醇注射液。注射12周后进行静脉采血,并对全主动脉及肾脏进行取材,血清用于血生化检测,肾脏行冠状面石蜡切片后进行HE染色,主动脉一部分制成石蜡切片进行茜素红S染色、von Kossa染色,一部分进行冻存用于实时荧光定量PCR检测。
Figure1 Flowchart of the experimental process for modeling and evaluating aortic calcification in SD rats with chronic kidney diseaseNote:Eight-week-old SD rats were housed in SPF-grade animal barrier facilities and underwent left kidney two-thirds nephrectomy after three days of regular dietary adaptation. After surgery, they were routinely housed and underwent right kidney nephrectomy one week later. After one week, administer 1 μg/kg calcitriol injection every three days. After 12 weeks of injection, venous blood collection was performed, and samples were taken from the entire aorta and kidneys. Serum was used for blood biochemistry testing, and paraffin-embedded kidneys were sectioned in coronal side for HE staining. A portion of the aorta was sectioned in paraffin for Alizarin Red S staining and von Kossa staining, and a portion was frozen for real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection.
目标基因名称 Target gene name | NCBI基因序列号 NCBI reference sequence | 引物序列信息 Primer sequence information | 扩增片段大小/bp Amplification fragment size/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sm22 (Tagln) | NC-086026.1 | F:5’-CAGATGGAACAGGTGGCTCAA-3’ | 161 |
| R:5’-GCCCAAAGCCATTACAGTCCTC-3’ | |||
| OPN (Spp1) | NC-086032.1 | F:5’-GCCGAGGTGATAGCTTGGCTTA-3’ | 145 |
| R:5’-TTGATAGCCTCATCGGACTCCTG-3’ | |||
| Runx2 | NC-086027.1 | F:5’-GGATGCCTTAGTGCCCAAATG-3’ | 120 |
| R:5’-CACCCTGTGAGGTGGCTGAA-3’ | |||
| β-actin | NC-086030.1 | F:5’-CACCCGCGAGTACAACCTTC-3’ | 207 |
| R:5’-CCCATACCCACCATCACACC-3’ |
表1 PCR引物序列信息
Table 1 Primers for real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR
目标基因名称 Target gene name | NCBI基因序列号 NCBI reference sequence | 引物序列信息 Primer sequence information | 扩增片段大小/bp Amplification fragment size/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sm22 (Tagln) | NC-086026.1 | F:5’-CAGATGGAACAGGTGGCTCAA-3’ | 161 |
| R:5’-GCCCAAAGCCATTACAGTCCTC-3’ | |||
| OPN (Spp1) | NC-086032.1 | F:5’-GCCGAGGTGATAGCTTGGCTTA-3’ | 145 |
| R:5’-TTGATAGCCTCATCGGACTCCTG-3’ | |||
| Runx2 | NC-086027.1 | F:5’-GGATGCCTTAGTGCCCAAATG-3’ | 120 |
| R:5’-CACCCTGTGAGGTGGCTGAA-3’ | |||
| β-actin | NC-086030.1 | F:5’-CACCCGCGAGTACAACCTTC-3’ | 207 |
| R:5’-CCCATACCCACCATCACACC-3’ |
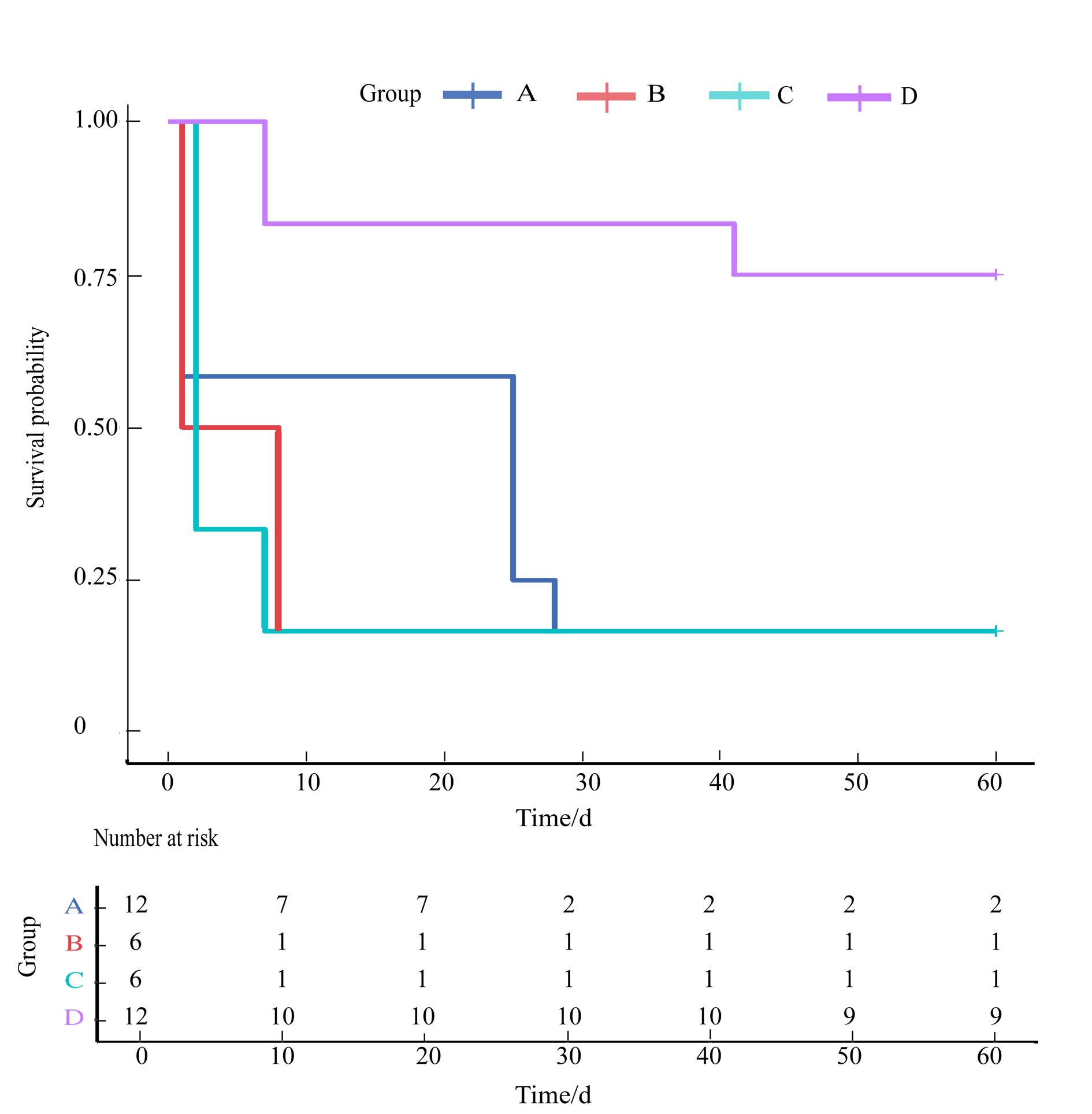
图2 不同手术方式构建的慢性肾功能不全模型组大鼠的Kaplan-Meier生存曲线分析注:横坐标表示切除两侧肾脏后第2天开始记录的时间(单位为天)。上图展示了接受不同方式手术的大鼠术后60 d累积生存率(Log-Rank检验,P=0.007 7),其中D组大鼠的存活率最高,与A、B、C组相比差异有统计学意义(P值分别为0.003 0、0.007 4、0.003 0),而且A、B、C组的大鼠均在术后10 d内大量死亡。
Figure 2 Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis of rats in chronic renal insufficiency model groups constructed using different surgical methodsNote: The horizontal axis represents the time (in days) recorded from the second day after the removal of both kidneys. Upper of the figure shows that there is a significant difference in the cumulative survival rate of rats after 60 days of surgery using different surgical methods (log-rank test, P=0.007 7), The survival rate of rats in group D was the highest, with statistically significant differences compared to groups A, B, and C (P=0.003 0, P=0.007 4, P=0.003 0, respectively). Moreover, rats in groups A, B, and C experienced high mortality within 10 days after surgery.
血生化指标 Biochemistry index | 实验组(n=9) Experimental group | 对照组(n=12) Control group | t值 t value | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
血清钙 c/(mmol·L-1) Serum calcium ions | 1.876±0.036 | 1.929±0.042 | 3.431 | 0.004 |
血清磷c/(mmol·L-1) Serum phosphate ions | 2.059±0.333 | 1.580±0.271 | 3.046 | 0.014 |
血清肌酐c/(μmol·L-1) Serum creatinine | 119.960±35.640 | 21.164±8.076 | 8.984 | <0.000 1 |
血清尿素氮c/(mmol·L-1) Serum urea nitrogen | 57.991±8.745 | 22.609±8.058 | 6.895 | <0.000 1 |
表2 实验组与对照组大鼠血清生化指标对比 (xˉ±s)
Table 2 Comparison of biochemical indicators between the experimental group and the control group
血生化指标 Biochemistry index | 实验组(n=9) Experimental group | 对照组(n=12) Control group | t值 t value | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
血清钙 c/(mmol·L-1) Serum calcium ions | 1.876±0.036 | 1.929±0.042 | 3.431 | 0.004 |
血清磷c/(mmol·L-1) Serum phosphate ions | 2.059±0.333 | 1.580±0.271 | 3.046 | 0.014 |
血清肌酐c/(μmol·L-1) Serum creatinine | 119.960±35.640 | 21.164±8.076 | 8.984 | <0.000 1 |
血清尿素氮c/(mmol·L-1) Serum urea nitrogen | 57.991±8.745 | 22.609±8.058 | 6.895 | <0.000 1 |
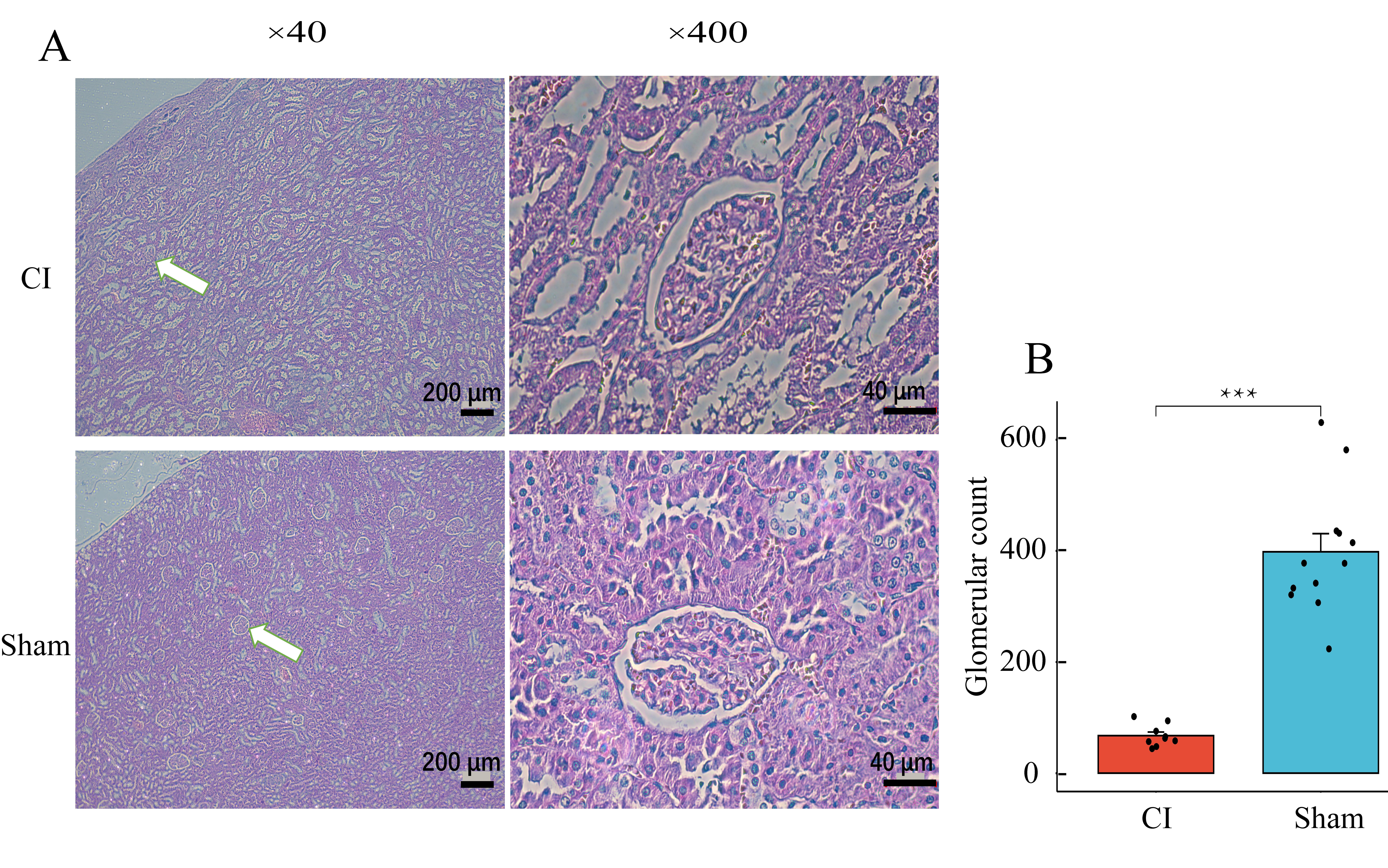
图3 实验组与对照组大鼠的肾脏HE染色观察注:实验组是肾脏切除术+骨化三醇钙化诱导3个月的大鼠肾脏,对照组为假手术+DMSO注射3个月的大鼠肾脏。图中白色箭头指示肾小球。实验组(CI组,n=9)的肾小球数量显著少于对照组(Sham组,n=12),***P<0.001。
Figure 3 HE staining observation of kidneys from rats in the experimental and control groupsNote: The experimental group consisted of rats undergoing nephrectomy and calcitriol calcification induction for 3 months, while the control group consisted of rats undergoing sham surgery and DMSO injection for 3 months. The white arrow in the picture represents the glomerulus. The number of glomeruli in the experimental group (CI group, n=9) was significantly less than that in the control group (sham group, n=12),***P<0.001.
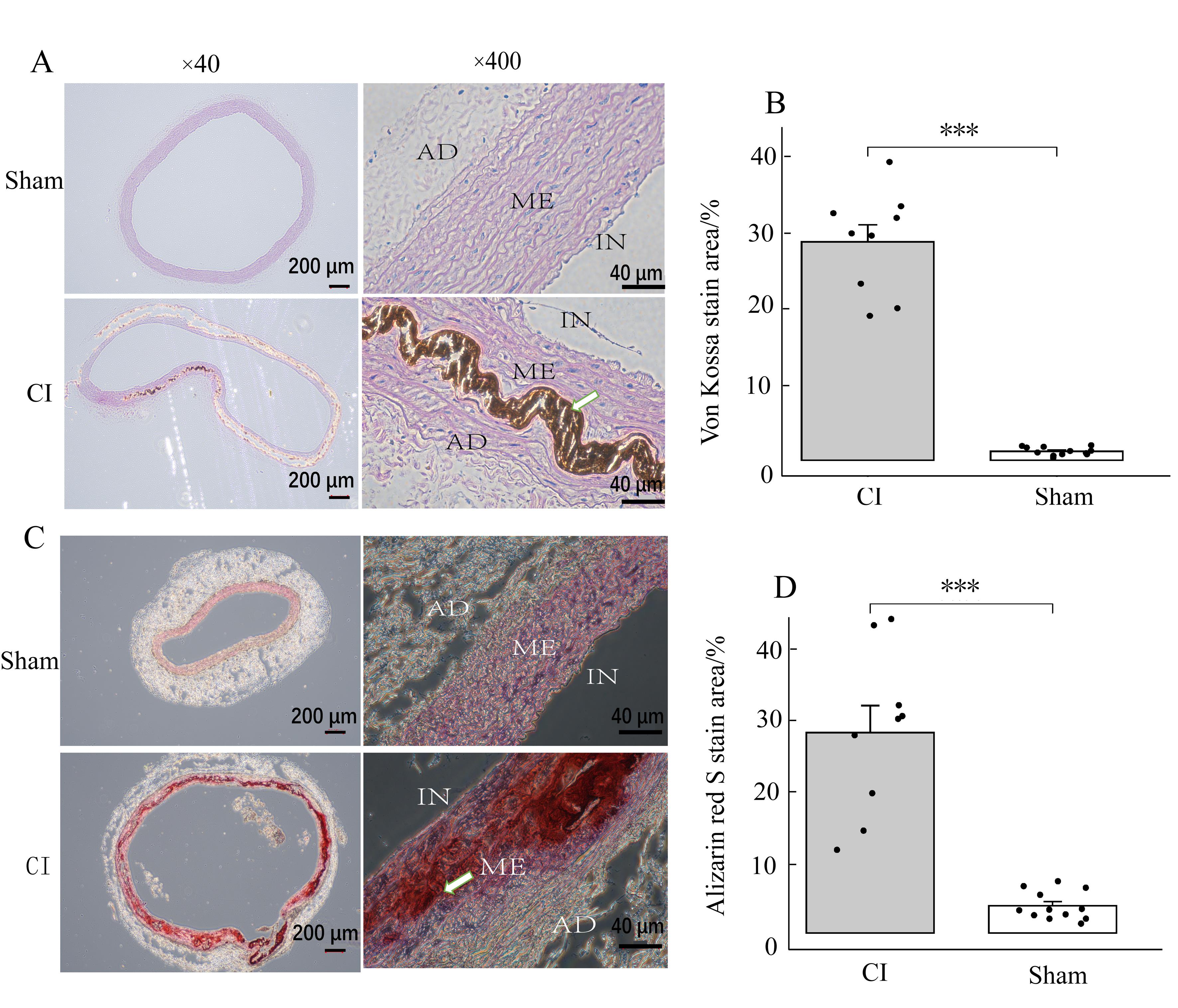
图4 实验组和对照组大鼠的主动脉von Kossa染色及茜素红S染色观察注:IN表示主动脉内膜;ME表示主动脉中膜;AD表示主动脉外膜。图A、B为von Kossa染色;图C、D为茜素红S染色。实验组(CI,n=9)的染色面积占比明显大于对照组(sham,n=12)(***P<0.001)。白色箭头处为高倍镜下动脉中膜钙化沉积。
Figure 4 Observation of von Kossa and Alizarin red S staining in the aorta of rats from the experimental and control groupsNote: IN represents the intima of the aorta; ME stands for the media of the aortic; AD represents the adventitia of the aorta. Figures A and B show von Kossa staining; Figures C and D show Alizarin red S staining. The proportion of stained area in the experimental group (CI, n=9) was significantly larger than that in the control group (sham, n=12)(***P<0.001). The white arrow indicates arterial media calcification deposition under high magnification view.
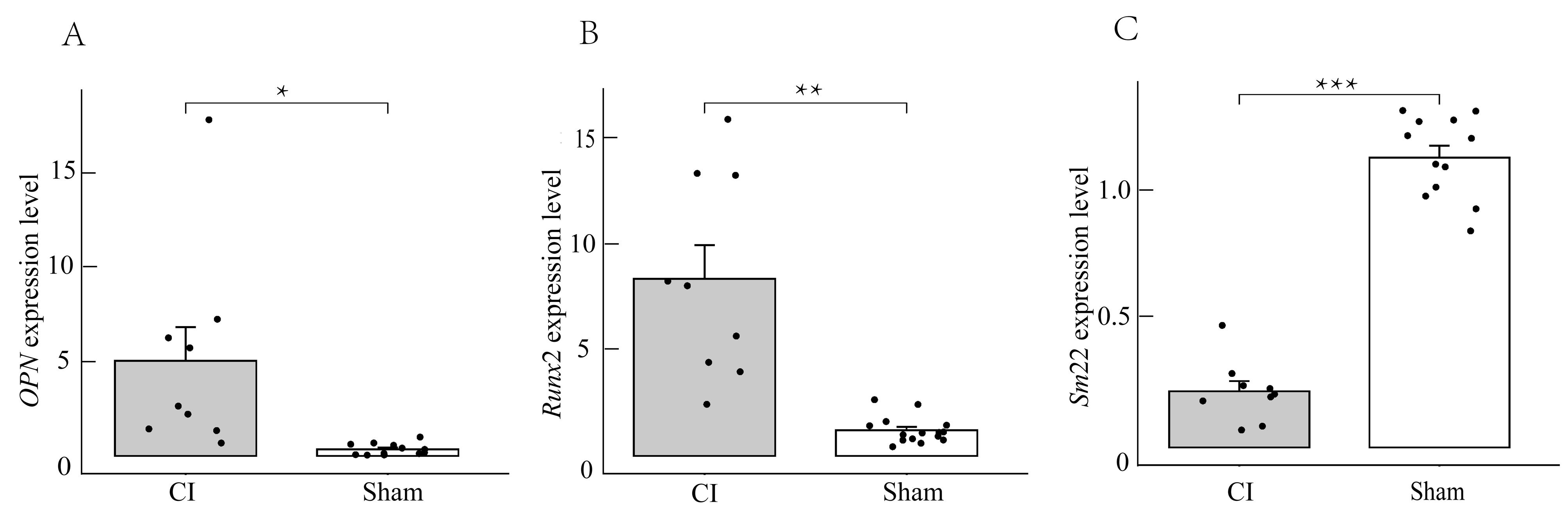
图5 实时荧光定量PCR检测实验组和对照组大鼠的主动脉组织细胞中OPN、Runx2及Sm22基因表达注:相较于对照组(sham),实验组(CI)中反映血管平滑肌成骨样分化表型的OPN及Runx2相对表达量明显增加(*P<0.05,**P<0.01),而反映血管平滑肌收缩表型的Sm22表达量减少(***P<0.001)。
Figure 5 Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection of OPN, Runx2, and Sm22 gene expression in aortic tissue of rats from the experimental and control groupsNote: Compared with the control group (sham), the expression level of Sm22, which reflects the vascular smooth muscle contraction phenotype, decreased in the experimental group (CI) (***P<0.001), while the expression levels of OPN and Runx2, which reflects the osteogenic differentiation phenotype of vascular smooth muscle, increased significantly ( * P<0.05, ** P<0.01).
| [1] | HUANG A R, GUO G Y, YU Y Q, et al. The roles of collagen in chronic kidney disease and vascular calcification[J]. J Mol Med, 2021, 99(1):75-92. DOI:10.1007/s00109-020-02014-6 . |
| [2] | 李贵森. 2019年«中国慢性肾脏病矿物质和骨异常诊治指南»解读[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2020, 19(3):229-231. DOI: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2020.03.005 . |
| LI G S. Interpretation of Chinese Guideline for Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (2019 version)[J]. J Diagn Concepts Pract, 2020, 19(3):229-231. DOI: 10.16150/j.1671-2870.2020.03.005 . | |
| [3] | YE Y Z, CHEN A, LI L, et al. Repression of the antiporter SLC7A11/glutathione/glutathione peroxidase 4 axis drives ferroptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells to facilitate vascular calcification[J]. Kidney Int. 2022 102(6):1259-1275. DOI:10.1016/j.kint.2022.07.034 . |
| [4] | 柳潇雨. Shox2促进血管钙化的作用及机制研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2023. DOI:10.27003/d.cnki.gojyu.2023.000180 . |
| LIU X Y. The role and mechanism of Shox2 in promoting vascular calcification[D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2023. DOI:10.27003/d.cnki.gojyu.2023.000180 . | |
| [5] | 阙冬冬. 五羟色胺对慢性肾脏病大鼠血管钙化的作用及其机制研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2023. DOI:10.27003/d.cnki.gojyu.2023.000170 . |
| QUE D D. Study on the effect and mechanism of serotonin on vascular calcification in rats with chronic kidney disease [D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2023. DOI:10.27003/d.cnki.gojyu.2023.000170 . | |
| [6] | 冯丽芸. 二氢杨梅素抑制慢性肾脏病大鼠血管钙化及其机制研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2022. DOI:10.27003/d.cnki.gojyu.2022.000227 . |
| FENG L Y. Study on the inhibition of vascular calcification and its mechanism by dihydromyricetin in rats with chronic kidney disease [D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2022. DOI:10.27003/d.cnki.gojyu.2022.000227 . | |
| [7] | SHOBEIRI N, ADAMS M A, HOLDEN R M. Vascular calcification in animal models of CKD: a review[J]. Am J Nephrol, 2010, 31(6):471-481. DOI:10.1159/000299794 . |
| [8] | LIU Y J, GUO Y, BAO S M, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-381-3p alleviates vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease by targeting NFAT5[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(3):278. DOI:10.1038/s41419-022-04703-1 . |
| [9] | 苏培培. 不同剂量骨化三醇对慢性肾衰竭大鼠主动脉钙化的影响[D]. 唐山: 华北理工大学, 2021. DOI:10.27108/d.cnki.ghelu.2021.000272 . |
| SU P P. Effects of different doses of calcitriol on aortic calcification in rats with chronic renal failure [D]. Tangshan: North China University of Science and Technology, 2021. DOI:10.27108/d.cnki.ghelu.2021.000272 . | |
| [10] | WU X J, SHEN S J, WU J Y, et al. ENPP1 ameliorates vascular calcification via inhibiting the osteogenic transformation of VSMCs and generating PPi[J]. Open Med, 2023, 18(1):20230861. DOI:10.1515/med-2023-0861 . |
| [11] | CHEN C Z, LI Y D, LU H L, et al. Curcumin attenuates vascular calcification via the exosomal miR-92b-3p/KLF4 axis[J]. Exp Biol Med, 2022, 247(16):1420-1432. DOI:10.1177/1535370222 1095456 . |
| [12] | LIU X Y, CHEN A, LIANG Q C, et al. Spermidine inhibits vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease through modulation of SIRT1 signaling pathway[J]. Aging Cell, 2021, 20(6): e13377. DOI:10.1111/acel.13377 . |
| [13] | ZHANG X L, LI Y N, YANG P Z, et al. Trimethylamine-N-oxide promotes vascular calcification through activation of NLRP3 (nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich-containing family, pyrin domain-containing-3) inflammasome and NF-κB (nuclear factor κB) signals[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2020, 40(3):751-765. DOI:10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.313414 . |
| [14] | ROWE P S, MCCARTHY E M, YU A L, et al. Correction of vascular calcification and hyperphosphatemia in CKD rats treated with ASARM peptide[J]. Kidney360, 2022, 3(10):1683-1698. DOI:10.34067/KID.0002782022 . |
| [15] | MA W Q, SUN X J, ZHU Y, et al. PDK4 promotes vascular calcification by interfering with autophagic activity and metabolic reprogramming[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(11):991. DOI:10.1038/s41419-020-03162-w . |
| [16] | SATO H, GOTO M, NISHIMURA G, et al. Upacicalcet, a positive allosteric modulator of the calcium-sensing receptor, prevents vascular calcification and bone disorder in a rat adenine-induced secondary hyperparathyroidism model[J]. Bone, 2023, 167:116613. DOI:10.1016/j.bone.2022.116613 . |
| [17] | LI Z H, WU J, ZHANG X L, et al. CDC42 promotes vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease[J]. J Pathol, 2019, 249(4):461-471. DOI:10.1002/path.5334 . |
| [18] | CHANG J R, GUO J, WANG Y, et al. Intermedin1-53 attenuates vascular calcification in rats with chronic kidney disease by upregulation of α-Klotho[J]. Kidney Int, 2016, 89(3):586-600. DOI:10.1016/j.kint.2015.12.029 . |
| [19] | LEE S J, LEE I K, JEON J H. Vascular calcification-new insights into its mechanism[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(8):2685. DOI:10.3390/ijms21082685 . |
| [20] | 张佳莉, 张岩. 急性肾损伤动物模型构建方法与研究现状[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2022, 30(7):955-965. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2022.07.011 . |
| ZHANG J L, ZHANG Y. Research approaches and status of animal models for acute kidney injury[J]. Acta Lab Anim Sci Sin, 2022, 30(7):955-965. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2022.07.011 . | |
| [21] | 陈娟, 易香伶, 罗佳, 等. 急性肾损伤动物模型及体外模型研究进展[J]. 华西医学, 2023, 38(5):777-783. DOI:10.7507/1002-0179.202210185 . |
| CHEN J, YI X L, LUO J, et al. Advances in animal models and in vitro models of acute kidney injury[J]. West China Med J, 2023, 38(5):777-783. DOI:10.7507/1002-0179.202210185 . | |
| [22] | HERRMANN J, BABIC M, TÖLLE M, et al. Research models for studying vascular calcification[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(6):2204. DOI:10.3390/ijms21062204 . |
| [23] | BAO Y W, YUAN Y, CHEN J H, et al. Kidney disease models: tools to identify mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets[J]. Zool Res, 2018, 39(2):72-86. DOI:10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2017.055 . |
| [24] | FU Y, TANG C Y, CAI J, et al. Rodent models of AKI-CKD transition[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2018, 315(4):F1098-F1106. DOI:10.1152/ajprenal.00199.2018 . |
| [25] | HERRMANN J, GUMMI M R, XIA M D, et al. Vascular calcification in rodent models-keeping track with an extented method assortment[J]. Biology, 2021, 10(6):459. DOI:10.3390/biology10060459 . |
| [1] | 李会萍, 高洪彬, 温金银, 杨锦淳. 疾病动物模型数字化图谱数据库平台的构建与初步应用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 300-308. |
| [2] | 陈钰涵, 陈瑾玲, 李欣, 区燕华, 王斯, 陈镜伊, 王兴易, 袁嘉丽, 段媛媛, 羊忠山, 牛海涛. 基于中西医临床病证特点的重症肌无力动物模型分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 176-186. |
| [3] | 连辉, 姜艳玲, 刘佳, 张玉立, 谢伟, 薛晓鸥, 李健. 异常子宫出血大鼠模型的构建与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 130-146. |
| [4] | 罗世雄, 张赛, 陈慧. 常见哮喘动物模型的建立方法与评价研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 167-175. |
| [5] | 王碧莹, 鲁家铄, 昝桂影, 陈若松, 柴景蕊, 刘景根, 王瑜珺. 啮齿类动物药物成瘾模型的构建方法和应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 158-166. |
| [6] | 费彬, 郭文科, 郭建平. 疝疾病动物模型研究及新型疝修补材料应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(1): 55-66. |
| [7] | 杨家豪, 丁纯蕾, 钱风华, 孙旗, 姜旭升, 陈雯, 沈梦雯. 脓毒症相关脏器损伤动物模型研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 636-644. |
| [8] | 孙效容, 苏丹, 贵文娟, 陈玥. 手术诱导大鼠中重度膝骨关节炎模型的建立与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 597-604. |
| [9] | 田芳, 潘滨, 史佳怡, 徐燕意, 李卫华. 大气细颗粒物PM2.5暴露动物模型建立方法及在生殖毒性研究中的应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 626-635. |
| [10] | 赵小娜, 王鹏, 叶茂青, 曲新凯. 应用Triacsin C构建新型高血糖肥胖小鼠心功能减退模型[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 605-612. |
| [11] | 涂颖欣, 纪依澜, 王菲, 杨东明, 王冬冬, 孙芷馨, 戴悦欣, 王言吉, 阚广捍, 吴斌, 赵德明, 杨利峰. 小型猪后肢去负荷模拟失重模型的建立与组织损伤研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 475-486. |
| [12] | 黄冬妍, 吴建辉. 生殖毒理学研究动物模型的建立方法及应用评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 550-559. |
| [13] | 郑艺清, 邓亚胜, 范燕萍, 梁天薇, 黄慧, 刘永辉, 倪召兵, 林江. 基于数据挖掘的盆腔炎性疾病动物模型应用分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(4): 405-418. |
| [14] | 吴玥, 李璐, 张阳, 王珏, 冯婷婷, 李依桐, 王凯, 孔琪. 冠状病毒感染动物模型组学数据集成分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(4): 357-373. |
| [15] | 丁天送, 谢京红, 杨斌, 李河桥, 乔一倬, 陈心如, 田纹凡, 李佳佩, 张婉怡, 李帆旋. 复发性流产动物模型特点评价与应用分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(4): 393-404. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||