













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 130-146.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.132
连辉1, 姜艳玲1, 刘佳1, 张玉立2, 谢伟2, 薛晓鸥2, 李健1( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-05
修回日期:2025-01-07
出版日期:2025-04-25
发布日期:2025-04-25
通讯作者:
李健(1970—),男,博士,教授,博士生导师,主要从事中西医结合防治炎症相关疾病的机制研究。E-mail:lijian@bucm.edu.cn。ORCID: 0000-0002-8864-0621作者简介:连 辉(1996—),男,硕士研究生,研究方向:中医药防治慢性非可控炎症。E-mail:20210931078@bucm.edu.cn
基金资助:
LIAN Hui1, JIANG Yanling1, LIU Jia1, ZHANG Yuli2, XIE Wei2, XUE Xiaoou2, LI Jian1( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-09-05
Revised:2025-01-07
Published:2025-04-25
Online:2025-04-25
Contact:
LI Jian (ORCID: 0000-0002-8864-0621), E-mail: lijian@bucm.edu.cn摘要:
目的 通过模拟排卵功能障碍型异常子宫出血(abnormal uterine bleeding-ovulatory dysfunction,AUB-O)病因,建立异常子宫出血大鼠模型,为异常子宫出血病理机制研究及治疗药物开发提供可靠的模型支持。 方法 将24只成年(10周龄)雌性SD大鼠适应性饲养后,随机分为正常对照组(6只)和模型组(18只)。正常对照组大鼠在屏障环境中正常饲养;模型组大鼠在屏障环境中经背侧入路行双侧卵巢切除术,休养1周后开始造模用药。模型组造模第1 ~ 3天每日每只大鼠背部皮下注射雌二醇0.5 mg,第4 ~ 7天每日皮下注射孕酮5.0 mg;同时于第6天经背侧相同手术切口向双侧子宫腔各注射0.5 mL大豆油,于第8天行米非司酮(10 mg/kg)灌胃,造模期间持续观察大鼠所处动情周期的阶段及其变化趋势。造模后48 h内观察并记录大鼠子宫出血情况,米非司酮灌胃后0、12、24、36、48 h模型组动态收集血清和子宫组织样本,正常对照组在36 h同时取材。取材后分别进行HE染色、血清性激素ELISA测定、免疫组织化学检测、TUNEL凋亡染色、蛋白质印迹检测、转录组学测序和生物信息学分析,对异常子宫出血大鼠模型进行综合评价。 结果 异常子宫出血大鼠表现为子宫出血,内膜剥脱损伤、复旧不全,内膜炎性细胞浸润、凋亡增强,间质、腺体和血管结构破坏。与正常对照组相比,异常子宫出血大鼠的血清卵泡刺激素、雌二醇和促黄体生成素水平明显升高(P<0.05);子宫内膜血管密度明显降低(P<0.05);血管内皮生长因子在子宫内膜剥脱处表达定性观察到明显增强,而在间质血管周围表达显著下降(P<0.01);基质金属蛋白酶-9在内膜损伤部位表达定性观察到明显增强,而在未剥脱间质和腺体处表达显著降低(P<0.01);子宫内膜间质细胞凋亡显著增强(P<0.01);成纤维细胞生长因子2和内皮素-1在子宫组织中的表达水平均明显下降(P<0.05)。比较异常子宫出血大鼠与正常大鼠子宫组织的转录组测序结果,共筛选到4 723个差异表达基因,其中表达上调基因为2 191个,表达下调基因为2 532个;KEGG富集分析显示,差异基因显著富集在炎症、免疫凋亡、细胞信号转导、增殖分化和肌肉收缩等相关通路。 结论 采用雌激素、孕激素和米非司酮序贯给药模拟AUB-O病因的方法,可成功建立异常子宫出血大鼠模型。该模型的子宫内膜损伤与炎症和凋亡相关,病理表现受血管收缩和内膜再生能力异常影响。该大鼠模型具有与临床非结构性病因异常子宫出血相近的病理特征,可以作为研究病理机制和治疗方法的有效模型。
中图分类号:
连辉,姜艳玲,刘佳,等. 异常子宫出血大鼠模型的构建与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 130-146. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.132.
LIAN Hui,JIANG Yanling,LIU Jia,et al. Construction and Evaluation of a Rat Model of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 130-146. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.132.
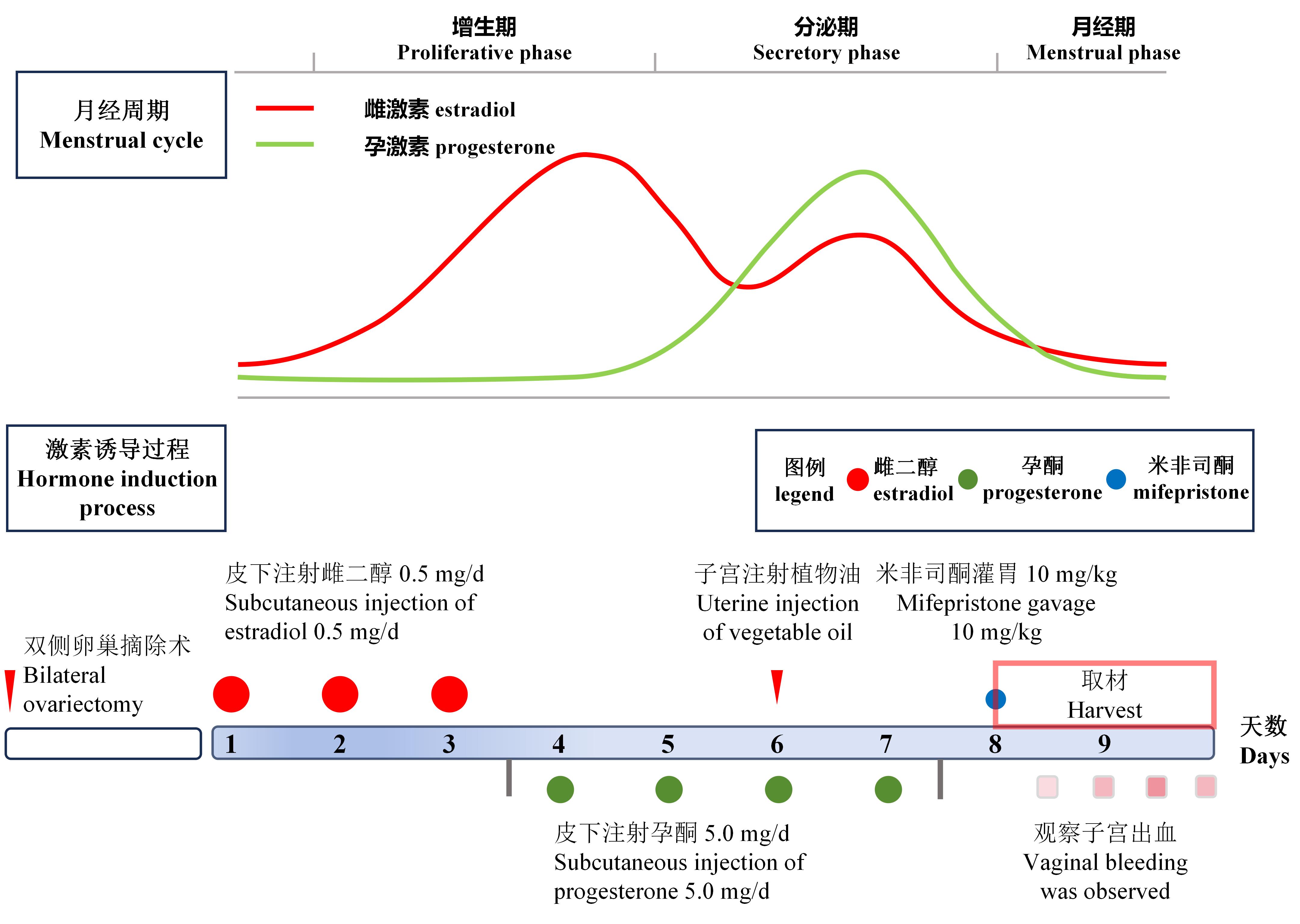
图 1 月经周期内雌孕激素水平变化示意图和异常子宫出血大鼠模型制备流程图注:图中曲线为正常人体月经周期中雌激素和孕激素水平的变化。图中流程为制备异常子宫出血大鼠模型的方案。
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of estrogen and progesterone level fluctuations during the menstrual cycle and flowchart of the preparation process for a rat model of abnormal uterine bleedingNote: Curves in the figure represent the changes in estrogen and progesterone levels during the normal human menstrual cycle. The process in the figure illustrates the protocol for preparing a rat model of abnormal uterine bleeding.
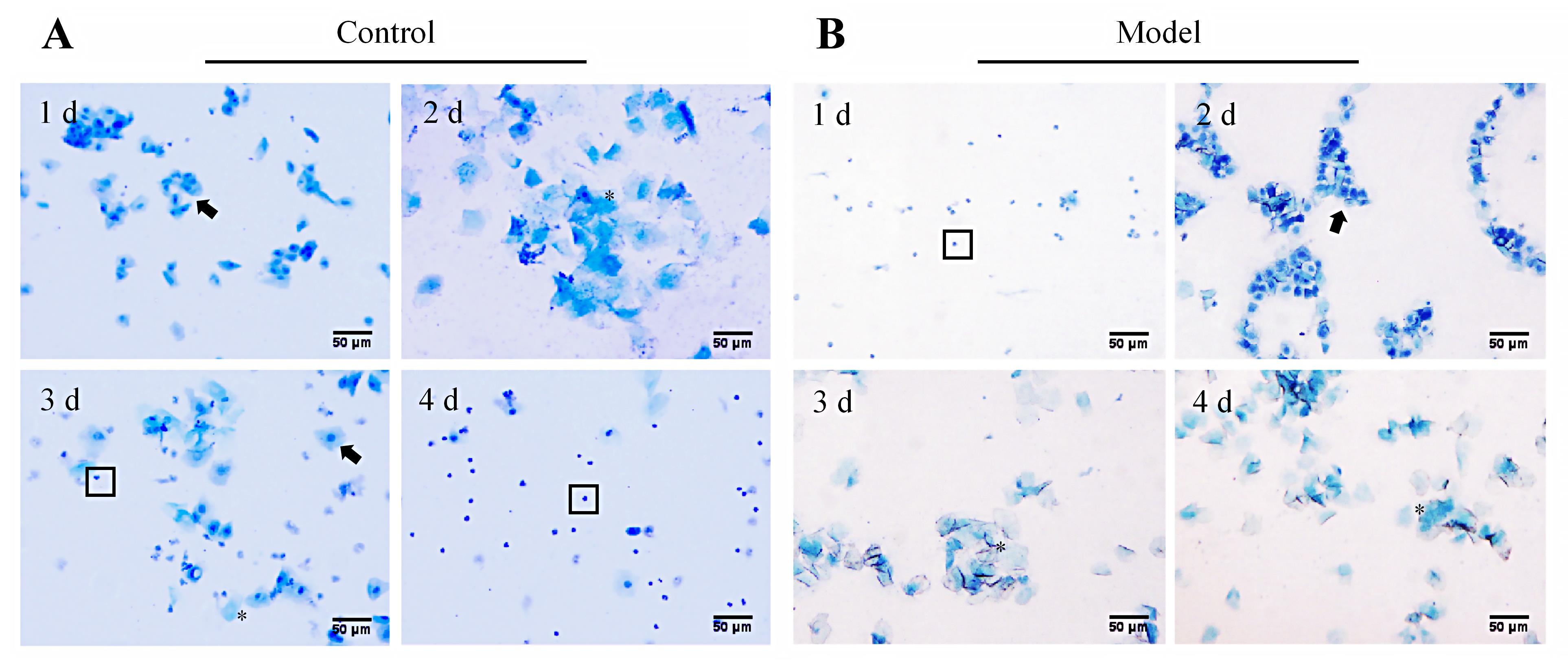
图 2 异常子宫出血模型大鼠动情周期改变的阴道脱落细胞涂片检测(亚甲蓝染色,×200)注:A,正常对照组一只代表性大鼠在一个动情周期内阴道脱落细胞的形态变化(1、2、3、4 d分别为动情前期、动情期、动情后期和动情间期,呈周期性改变);B,模型组一只代表性大鼠从卵巢切除、激素诱导到孕激素撤退的阴道脱落细胞形态变化(1、2、3、4 d分别为动情间期、动情前期、动情期和动情期,呈非周期性改变)。图片中黑色箭头(?)指向有核上皮细胞,星号(*)标记为角化上皮细胞,方框(□)内为白细胞。图中比例尺为50 μm。
Figure 2 Detection of changes in the estrous cycle in abnormal uterine bleeding model rats using vaginal exfoliated cell smear (methylene blue staining, ×200)Note: A, Morphological changes of vaginal exfoliated cells of a representative rat in the normal control group during one estrous cycle (Days 1, 2, 3, and 4 correspond to proestrus, estrus, metestrus, and diestrus, respectively, showing cyclical changes); B, Morphological changes of vaginal exfoliated cells of a representative rat in the model group from ovariectomy, hormone induction to progesterone withdrawal (Days 1, 2, 3, and 4 correspond to diestrus, proestrus, estrus, and estrus, respectively, showing a non-cyclic pattern). In figures, black arrows (?) indicate nucleated epithelial cells, asterisks (*) mark keratinized epithelial cells, and boxes (□) denote white blood cells. In figures, the scale bar is 50 μm.
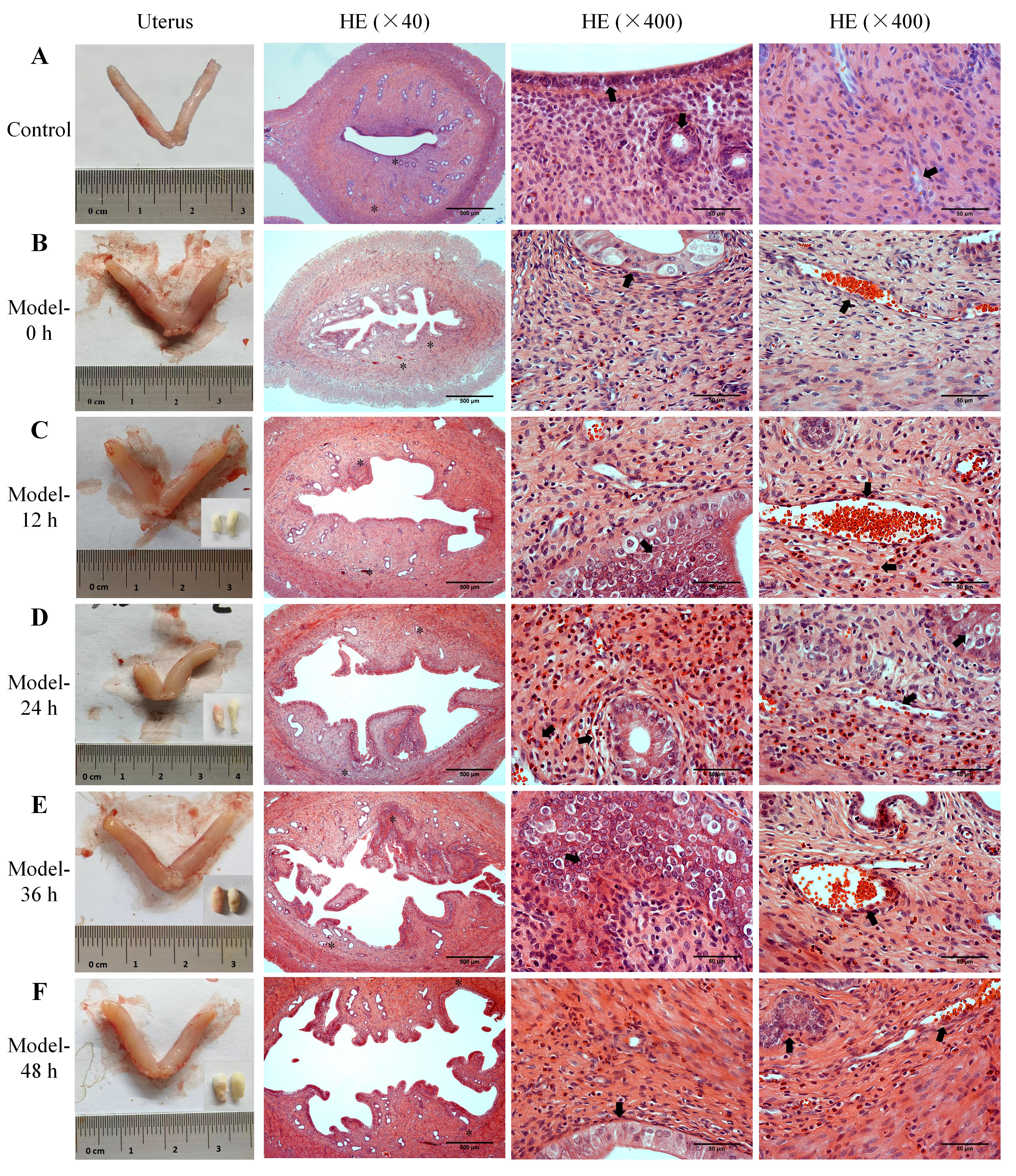
图3 异常子宫出血模型大鼠的子宫外观、出血情况和内膜组织病理变化注:A,正常对照大鼠的子宫外观和子宫内膜组织HE染色图片;B~F,异常子宫出血模型大鼠孕激素撤退0、12、24、36、48 h的子宫外观和收集每12 h子宫出血的阴道棉球(右下角)、子宫内膜组织HE染色图片。HE染色的低倍镜图片中两个星号(*)分别标记为两个高倍镜观察处,黑色箭头(?)指向内膜上皮、腺体、坏死的间质、血管和出血等结构和病理现象。HE染色图中比例尺从左到右分别为500 μm、50 μm和50 μm。
Figure 3 Uterine morphology, bleeding patterns, and histopathological changes of endometrial tissues in abnormal uterine bleeding model ratsNote: A, Uterine morphology and the HE-stained images of endometrial tissue in normal control rats; B-F, The uterine morphology in AUB model rats at 0 h, 12 h, 24 h, 36 h, and 48 h after progesterone withdrawal, along with vaginal cotton balls collected for uterine bleeding assessment every 12 hours (lower right corner), and the HE-stained images of endometrial tissue at the corresponding time points. The two asterisks (*) in each low-magnification HE-stained image indicate the two areas observed under high magnification, and the black arrows (?) point to the structures and pathological phenomena such as the endometrial epithelium, glands, necrotic stroma, blood vessels, and bleeding. In the HE-stained images, the scale bars from left to right column are 500 μm, 50 μm and 50 μm, respectively.
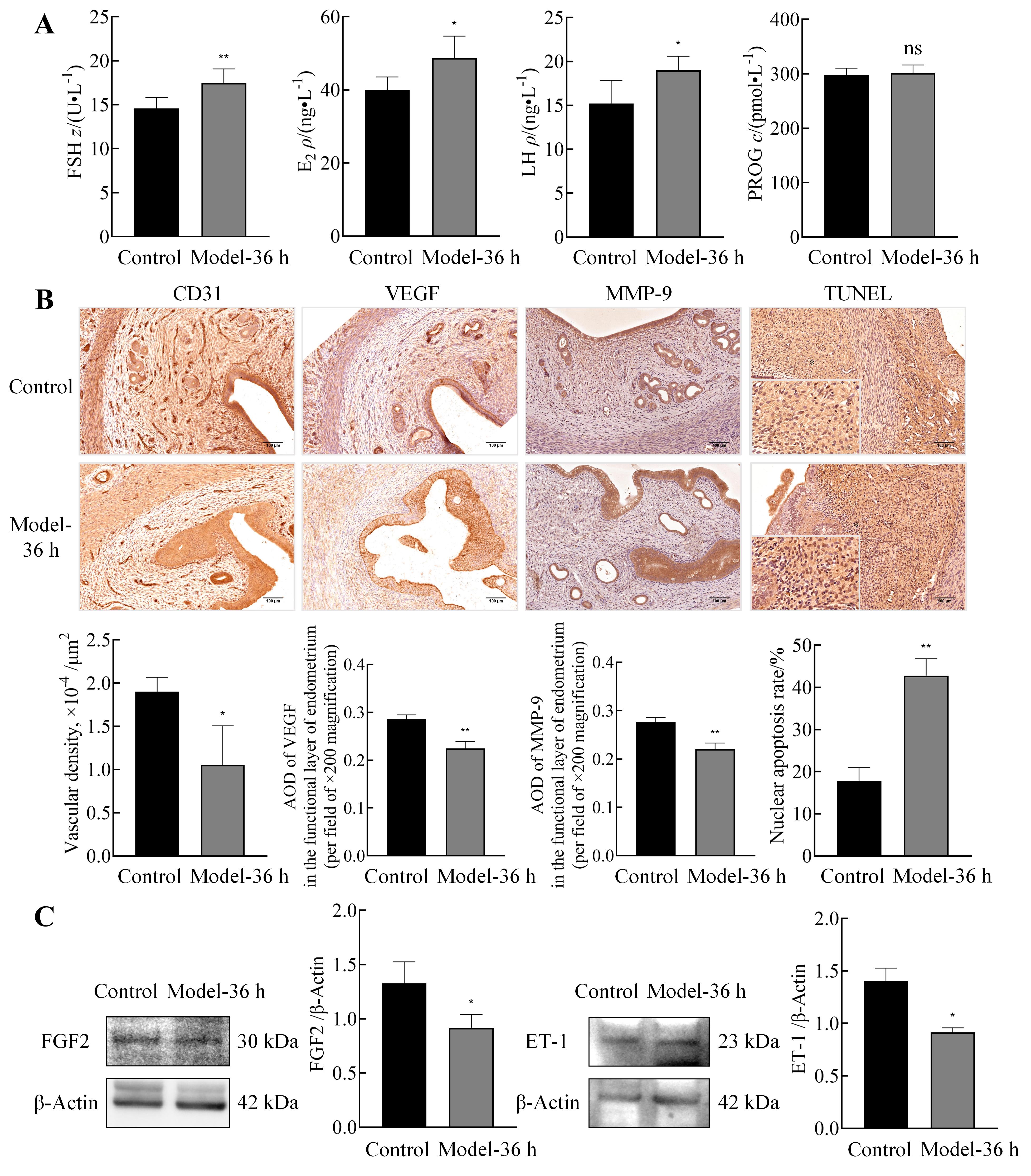
图 4 异常子宫出血模型大鼠的血清性激素水平、子宫血管和间质的损伤修复情况和血管收缩功能的变化注:A,ELISA检测正常对照大鼠和异常子宫出血模型大鼠孕激素撤退36 h血清中性激素包括FSH、E2、LH和PROG的水平(n=6);B,免疫组织化学染色检测两组大鼠子宫组织中血管内皮表达蛋白即血小板-内皮细胞黏附分子-1(CD31)、血管生成蛋白即血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)、间质损伤和修复蛋白即基质金属蛋白酶-9(MMP-9)的表达及其结果分析(n=3,照片图比例尺为100 μm),以及大鼠子宫内膜TUNEL染色结果及其阳性细胞占比统计[n=3,低倍镜图片(比例尺为100 μm)中星号(*)标记为高倍镜(比例尺为25 μm)观察处];C,蛋白质印迹法检测两组大鼠子宫组织中成纤维细胞生长因子2(FGF2)和内皮素-1(ET-1)的表达及其相对量分析(n=3,数据表示为平均值±标准误;与正常对照组比较,nsP>0.05,*P<0.05,**P<0.01)。
Figure 4 Changes in serum sex hormone levels, injury and repair of uterus blood vessels and stroma, and vascular contractile function of uterus in abnormal uterine bleeding model ratsNote: A, ELISA was used to measure serum levels of sex hormones, including FSH, E2, LH, and PROG, in normal control rats and the AUB model rats at 36 h after progesterone withdrawal (n=6). B, Immunohistochemistry was performed to assess the expression of vascular endothelial marker platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31), angiogenesis-related protein vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and stromal injury/repair protein matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in uterine tissues of both groups,along with statistical analysis of the results (n=3; scale bars: 100 μm). Additionally, TUNEL staining of rat endometrium was conducted, and the percentage of positive cells was quantified [n=3; asterisks (*) in low-magnification images (scale bars: 100 μm) indicate regions selected for high-magnification observation (scale bars: 25 μm)]. C, Western blotting was employed to detect the expression of fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) and endothelin-1 (ET-1) in uterine tissues of both groups, along with relative quantification (n=3; data presented as mean ± standard error (SE); Compared with normal control group, nsP>0.05, *P<0.05, **P<0.01).
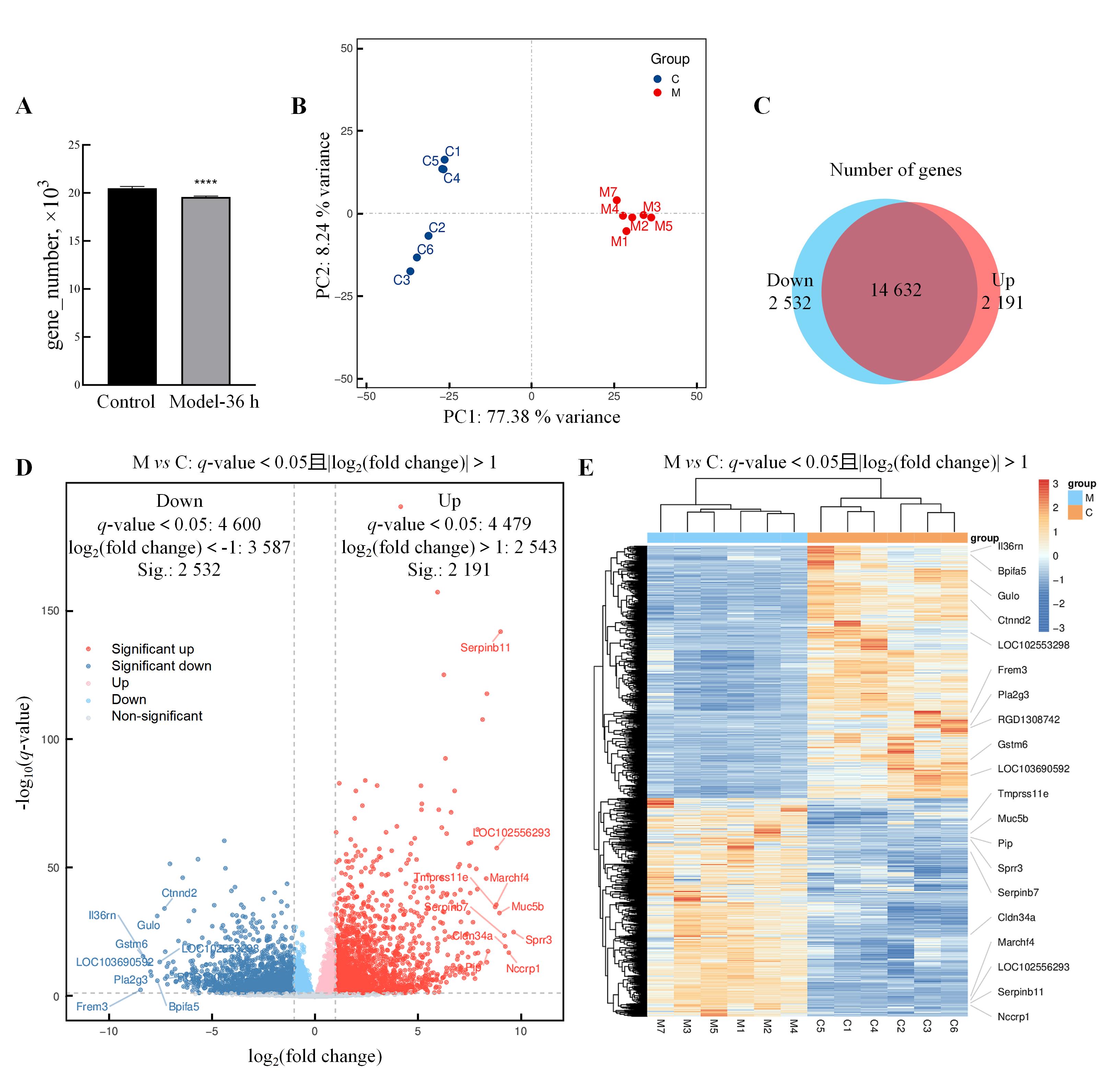
图 5 异常子宫出血模型大鼠子宫组织中差异表达基因的转录组学分析注:A,转录组学测序正常对照大鼠和异常子宫出血模型大鼠孕激素撤退36 h(Model-36 h)样本的基因数目(与正常对照组比较,****P<0.000 1);B,主成分分析结果;C,两组间表达基因差异的Venn图[图中蓝色区域表示Model-36 h相比正常对照组表达显著降低(Down)的基因集合,红色区域表示Model-36 h相比正常对照组表达显著升高(Up)的基因集合];D,差异表达基因分布火山图(下调差异表达基因中符合差异倍数筛选条件的用蓝色表示,不符合差异倍数筛选条件的用浅蓝色表示;上调差异表达基因中符合差异倍数筛选条件的用红色表示,不符合差异倍数筛选条件的用浅红色表示;差异不显著的表达基因用灰色表示。图中标注了部分差异倍数较高的下调和上调差异表达基因);E,差异表达基因分组聚类热图,图中颜色深浅代表数据点的数值高低(根据相似性进行分组聚类,图中标注了差异倍数较高的上调和下调基因)。
Figure 5 Transcriptomic analysis of differentially expressed genes in uterine tissue of abnormal uterine bleedingmodel ratsNote: A, The number of genes in rat samples from the normal control rats and the AUB model rats at 36 h after progesterone withdrawal (Model-36 h)(compared with normal control group, ****P<0.000 1); B, Results of principal component analysis; C, Venn diagram showing the differences in expressed genes between the two groups [The blue area represents the gene set with significantly decreased expression (Down) in the Model-36 h compared to normal control group, while the red area represents the gene set with significantly increased expression (Up) in the Model-36 h compared to normal control group]; D, Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes (down-regulated differentially expressed genes meeting fold change criteria in blue, non-meeting fold change criteria in light blue; up-regulated differentially expressed genes meeting criteria in red, non-meeting criteria in light red; non-significantly expressed genes in gray. The plot labels some of the differentially expressed genes with higher fold changes, including both down-regulated and up-regulated ones); E, Differentially expressed gene clustering heatmap by group, where the intensity of color represents the value of data points (grouping and clustering are based on similarity, and genes with higher fold changes in up-regulation and down-regulation are labeled in the heatmap).
编号 No. | 基因符号 Gene symbol | log2差异倍数 log2(fold change) | q值 q-value | 功能概述 Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up-regulated genes | ||||
| 1 | Scin | 4.173 | 4.546×10-191 | Predicted to enable actin filament binding activity and phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding activity. etc. |
| 2 | Btc | 5.961 | 7.347×10-158 | Enables epidermal growth factor receptor binding activity and growth factor activity. etc. |
| 3 | Serpinb11 | 9.021 | 1.630×10-142 | Predicted to enable serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity. etc. |
| 4 | Slc16a12 | 6.266 | 9.424×10-126 | Enables creatine transmembrane transporter activity. etc. |
| 5 | Tprg1 | 8.356 | 2.229×10-118 | Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. etc. |
| 6 | Olfm4 | 8.147 | 2.346×10-108 | Predicted to enable cadherin binding activity and structural molecule activity. etc. |
| 7 | Tnfaip6 | 6.344 | 3.099×10-93 | Predicted to enable several functions, including carboxylesterase activity. etc. |
| 8 | Nck1 | 2.451 | 1.127×10-84 | Predicted to enable several functions, including eukaryotic initiation factor eIF2 binding activity. etc. |
| 9 | Actn4 | 1.188 | 1.391×10-83 | Enables ubiquitin protein ligase binding activity. etc. |
| 10 | Tmbim1 | 3.027 | 1.062×10-82 | Predicted to enable calcium channel activity and death receptor binding activity. etc. |
| Down-regulated genes | ||||
| 1 | Gstm5 | -4.393 | 3.077×10-61 | Enables glutathione transferase activity and identical protein binding activity. etc. |
| 2 | Armh4 | -5.671 | 4.422×10-54 | Predicted to enable TORC2 complex binding activity. etc. |
| 3 | LOC102548820 | -7.032 | 2.774×10-52 | - |
| 4 | Arg2 | -4.338 | 1.561×10-50 | Enables arginase activity and nitric-oxide synthase binding activity. etc. |
| 5 | Frem2 | -6.413 | 6.963×10-47 | Predicted to be involved in anatomical structure morphogenesis and cell adhesion. etc. |
| 6 | Mppe1 | -1.346 | 1.575×10-44 | Predicted to enable GPI anchor binding activity. etc. |
| 7 | Lef1 | -3.875 | 3.022×10-43 | Predicted to enable several functions, including DNA binding activity. etc. |
| 8 | Smad9 | -4.048 | 8.538×10-42 | Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase Ⅱ-specific. etc. |
| 9 | Miga1 | -1.944 | 4.052×10-41 | Predicted to enable protein heterodimerization activity and protein homodimerization activity. etc. |
| 10 | Bmpr1b | -2.515 | 1.387×10-38 | Predicted to enable several functions, including ATP binding activity. etc. |
表1 异常子宫出血模型大鼠与正常对照大鼠子宫组织的差异表达基因中前10个上调和前10个下调基因的基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of the top 10 up-regulated and the top 10 down-regulated differentially expressed genes in uterine tissues between abnormal uterine bleeding model rats and normal control rats
编号 No. | 基因符号 Gene symbol | log2差异倍数 log2(fold change) | q值 q-value | 功能概述 Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up-regulated genes | ||||
| 1 | Scin | 4.173 | 4.546×10-191 | Predicted to enable actin filament binding activity and phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding activity. etc. |
| 2 | Btc | 5.961 | 7.347×10-158 | Enables epidermal growth factor receptor binding activity and growth factor activity. etc. |
| 3 | Serpinb11 | 9.021 | 1.630×10-142 | Predicted to enable serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity. etc. |
| 4 | Slc16a12 | 6.266 | 9.424×10-126 | Enables creatine transmembrane transporter activity. etc. |
| 5 | Tprg1 | 8.356 | 2.229×10-118 | Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. etc. |
| 6 | Olfm4 | 8.147 | 2.346×10-108 | Predicted to enable cadherin binding activity and structural molecule activity. etc. |
| 7 | Tnfaip6 | 6.344 | 3.099×10-93 | Predicted to enable several functions, including carboxylesterase activity. etc. |
| 8 | Nck1 | 2.451 | 1.127×10-84 | Predicted to enable several functions, including eukaryotic initiation factor eIF2 binding activity. etc. |
| 9 | Actn4 | 1.188 | 1.391×10-83 | Enables ubiquitin protein ligase binding activity. etc. |
| 10 | Tmbim1 | 3.027 | 1.062×10-82 | Predicted to enable calcium channel activity and death receptor binding activity. etc. |
| Down-regulated genes | ||||
| 1 | Gstm5 | -4.393 | 3.077×10-61 | Enables glutathione transferase activity and identical protein binding activity. etc. |
| 2 | Armh4 | -5.671 | 4.422×10-54 | Predicted to enable TORC2 complex binding activity. etc. |
| 3 | LOC102548820 | -7.032 | 2.774×10-52 | - |
| 4 | Arg2 | -4.338 | 1.561×10-50 | Enables arginase activity and nitric-oxide synthase binding activity. etc. |
| 5 | Frem2 | -6.413 | 6.963×10-47 | Predicted to be involved in anatomical structure morphogenesis and cell adhesion. etc. |
| 6 | Mppe1 | -1.346 | 1.575×10-44 | Predicted to enable GPI anchor binding activity. etc. |
| 7 | Lef1 | -3.875 | 3.022×10-43 | Predicted to enable several functions, including DNA binding activity. etc. |
| 8 | Smad9 | -4.048 | 8.538×10-42 | Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase Ⅱ-specific. etc. |
| 9 | Miga1 | -1.944 | 4.052×10-41 | Predicted to enable protein heterodimerization activity and protein homodimerization activity. etc. |
| 10 | Bmpr1b | -2.515 | 1.387×10-38 | Predicted to enable several functions, including ATP binding activity. etc. |
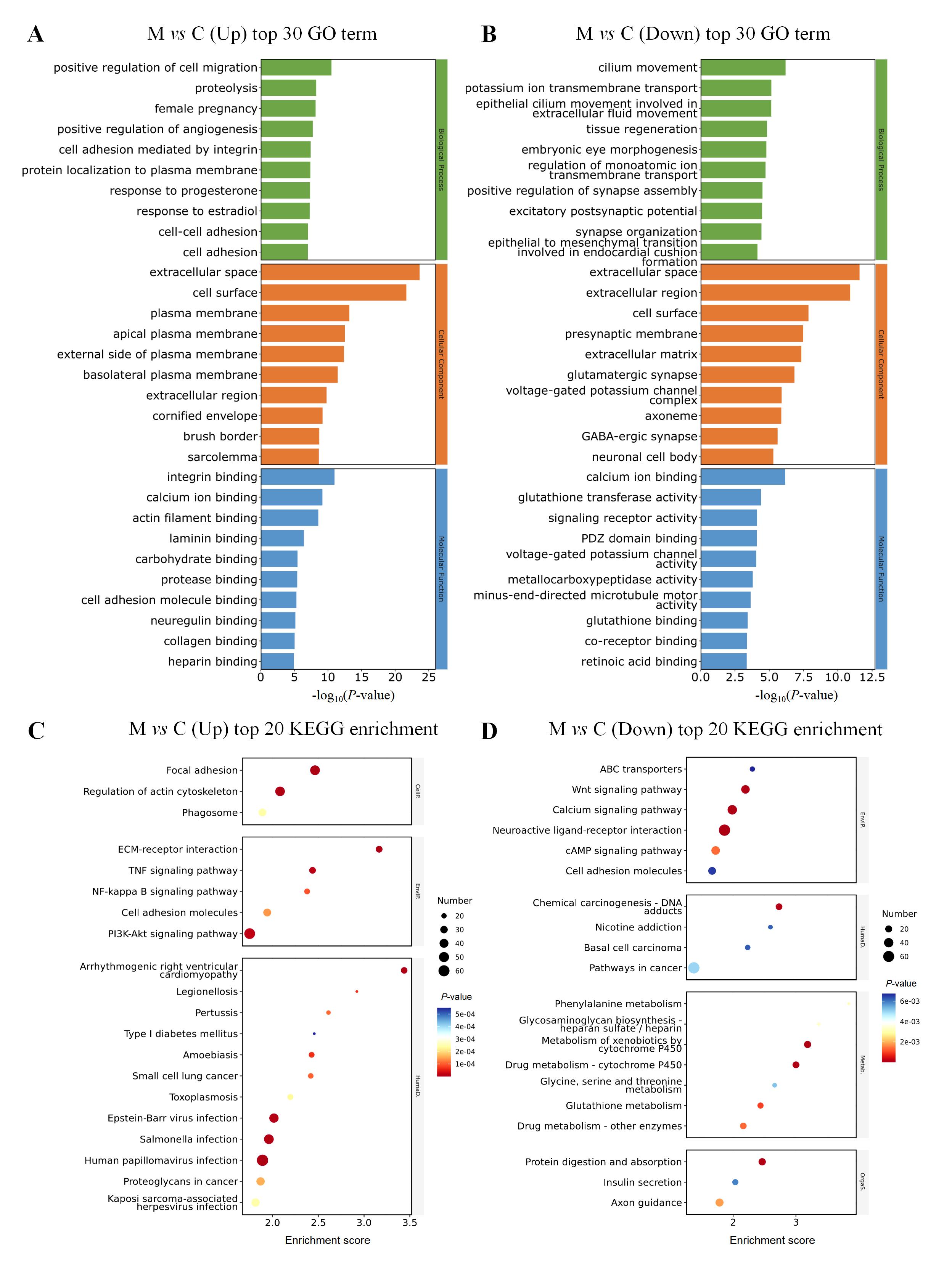
图6 异常子宫出血模型大鼠子宫组织中差异表达基因的转录组学分析注:A,上调差异表达基因的GO功能分析;B,下调差异表达基因的GO功能分析;C,上调差异表达基因的KEGG富集分析;D,下调差异表达基因的KEGG富集分析。
Figure 6 Transcriptomic analysis of differentially expressed genes in uterine tissue of model rats with abnormal uterine bleedingNote: A, GO functional analysis of up-regulated differentially expressed genes; B, GO functional analysis of down-regulated differentially expressed genes; C, KEGG enrichment analysis of up-regulated differentially expressed genes; D, KEGG enrichment analysis of down-regulated differentially expressed genes.
| 1 | 中华医学会妇产科学分会妇科内分泌学组. 异常子宫出血诊断与治疗指南(2022更新版)[J]. 中华妇产科杂志, 2022, 57(7):481-490. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112141-20220421-00258 . |
| Gynecologic Endocrinology Subgroup, Chinese Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline on diagnosis and treatment of abnormal uterine bleeding: 2022 revisions[J]. Chin J Obstet Gynecol, 2022, 57(7):481-490. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112141-20220421-00258 . | |
| 2 | JAIN V, CHODANKAR R R, MAYBIN J A, et al. Uterine bleeding: how understanding endometrial physiology underpins menstrual health[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2022, 18(5):290-308. DOI:10.1038/s41574-021-00629-4 . |
| 3 | MUNRO M G, CRITCHLEY H O D, FRASER I S, et al. The two FIGO systems for normal and abnormal uterine bleeding symptoms and classification of causes of abnormal uterine bleeding in the reproductive years: 2018 revisions[J]. Int J Gynaecol Obstet, 2018, 143(3):393-408. DOI:10.1002/ijgo.12666 . |
| 4 | KITAHARA Y, HIRAIKE O, ISHIKAWA H, et al. National survey of abnormal uterine bleeding according to the FIGO classification in Japan[J]. J Obstet Gynaecol Res, 2023, 49(1):321-330. DOI:10.1111/jog.15464 . |
| 5 | LI Q H, REN J L, YANG L, et al. Parsing the Q-markers of Baoyin Jian to treat abnormal uterine bleeding by high-throughput chinmedomics strategy[J]. Pharmaceuticals, 2023, 16(5):719. DOI:10.3390/ph16050719 . |
| 6 | 高兰, 王侃, 贾媛, 等. 茜草不同炮制品对子宫内膜出血模型大鼠的影响[J]. 中医学报, 2020, 35(1):144-148. DOI: 10.16368/j.issn.1674-8999.2020.01.033 . |
| GAO L, WANG K, JIA Y, et al. Effects of different processed medicine of Rubia cordifolia L on endometrial hemorrhage model rats[J]. Acta Chin Med, 2020, 35(1):144-148. DOI: 10.16368/j.issn.1674-8999.2020.01.033 . | |
| 7 | KRIKUN G, BOOTH C J, BUCHWALDER L, et al. Long-term progestin-only contraception in humans versus animal models[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2011, 1221:119-123. DOI:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05930.x . |
| 8 | 陈钢, 薛红, 孟宪丽, 等. 柴胡止血液对家兔置Cu-IUD的实验研究[J]. 辽宁中医学院学报, 1999, 1(3):200-201. DOI: 10.13194/j.jlunivtcm.1999.03.56.cheng.035 . |
| CHEN G, XUE H, MENG X L, et al. Experimental study on the effect of Chaihu Hemostatic solution on the placement of Cu-IUD in rabbits [J]. J Liaoning Coll Tradit Chin Med, 1999, 1(3):200-201. DOI: 10.13194/j.jlunivtcm.1999.03.56.cheng.035 . | |
| 9 | 尤昭玲, 马红霞, 陈俊明, 等. 恒河猴子宫内膜炎性出血模型的建立[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2003, 13(5): 310-312. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2003.05.015 . |
| YOU Z L, MA H X, CHEN J M, et al. Establishment of animal model with metrorrhagia induced by endometritis in experimental Rhesus monkey[J]. Chin J Comp Med, 2003, 13(5): 310-312. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2003.05.015 . | |
| 10 | FINN C A, POPE M. Vascular and cellular changes in the decidualized endometrium of the ovariectomized mouse following cessation of hormone treatment: a possible model for menstruation[J]. J Endocrinol, 1984, 100(3):295-300. DOI:10.1677/joe.0.1000295 . |
| 11 | CATALINI L, FEDDER J. Characteristics of the endometrium in menstruating species: lessons learned from the animal Kingdom[J]. Biol Reprod, 2020, 102(6):1160-1169. DOI:10.1093/biolre/ioaa029 . |
| 12 | BELLOFIORE N, RANA S, DICKINSON H, et al. Characterization of human-like menstruation in the spiny mouse: comparative studies with the human and induced mouse model[J]. Hum Reprod, 2018, 33(9):1715-1726. DOI:10.1093/humrep/dey247 . |
| 13 | J J 4th RASWEILER. Spontaneous decidual reactions and menstruation in the black mastiff bat, Molossus ater[J]. Am J Anat, 1991, 191(1):1-22. DOI:10.1002/aja.1001910102 . |
| 14 | CARTER A M. Classics revisited: C. J. van der Horst on pregnancy and menstruation in elephant shrews[J]. Placenta, 2018, 67:24-30. DOI:10.1016/j.placenta.2018.05.010 . |
| 15 | MORISON N B, ZHANG J, KAITU'U-LINO T J, et al. The long-term actions of etonogestrel and levonorgestrel on decidualized and non-decidualized endometrium in a mouse model mimic some effects of progestogen-only contraceptives in women[J]. Reproduction, 2007, 133(1):309-321. DOI:10.1530/rep.1.01171 . |
| 16 | 王晓东, 赵军宁, 张白嘉, 等. 药物致早孕大鼠子宫出血模型的建立[J]. 中国药理学通报, 1999, 15(2):182-184. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn: 1001-1978.1999.02.025 . |
| WANG X D, ZHAO J N, ZHANG B J, et al. Establishment of uterine bleeding model by mifepristoneand misoprostol in eraly-pregnancy rats[J]. Chin Pharmacol Bull, 1999, 15(2):182-184. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn: 1001-1978.1999.02.025 . | |
| 17 | TSOLOVA A O, AGUILAR R M, MAYBIN J A, et al. Pre-clinical models to study abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB)[J]. EBioMedicine, 2022, 84:104238. DOI:10.1016/j.ebiom. 2022. 104238 . |
| 18 | TERKEL J. Neuroendocrine processes in the establishment of pregnancy and pseudopregnancy in rats[J]. Psychoneuro-endocrinology, 1988, 13(1-2):5-28. DOI:10.1016/0306-4530(88)90004-2 . |
| 19 | 孔令伶俐, 许良智. 青春期排卵障碍性异常子宫出血的诊疗策略[J]. 实用妇产科杂志, 2022, 38(10):731-733. |
| KONG L L L, XU L Z. Diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for ovulatory dysfunctional uterine bleeding in adolescence [J]. J Pract Obstet Gynecol, 2022, 38(10):731-733. | |
| 20 | 朱小明, 徐君碧, 何人可, 等. 围绝经期妇女内分泌变化及相关疾病[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版), 2019, 57(2):6-10, 15. DOI: 10.6040/j.issn.1671-7554.0.2018.1459 . |
| ZHU X M, XU J B, HE R K, et al. Endocrine changes in perimenopausal women and the related diseases[J]. J Shandong Univ Health Sci, 2019, 57(2):6-10, 15. DOI: 10.6040/j.issn.1671-7554.0.2018.1459 . | |
| 21 | 李升华, 何涓, 唐健, 等. 自拟加味生化汤联合安宫黄体酮治疗围绝经期排卵障碍性异常子宫出血的临床研究[J/OL]. 中华中医药学刊, 2024:1-7. (2024-08-06)[2025-01-06]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/21.1546.r.20240805.1120.004. |
| LI S H, HE J, TANG J, et al. Clinical study of self-made modified shenghua decoctioncombined with medroxy-progesteronein treatment of patients with perimenopausal abnormal uterine bleeding-ovulatory dysfunction [J/OL]. China Arch Trad Chin Med, 2024:1-7. (2024-08-06)[2025-01-06]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/21.1546.r.20240805.1120.004. | |
| 22 | BRASTED M, WHITE CA, KENNEDY TG, et al. Mimicking the events of menstruation in the murine uterus[J]. Biol Reprod, 2003, 69(4):1273-1280. DOI: 10.1095/biolreprod.103.016550 . |
| 23 | MAYBIN J A, MURRAY A A, SAUNDERS P T K, et al. Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factor-1α are required for normal endometrial repair during menstruation[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1):295. DOI:10.1038/s41467-017-02375-6 . |
| 24 | 郎建霞, 毛晓红, 徐翠萍. 排卵障碍性异常子宫出血患者神经内分泌功能及变化研究[J]. 现代实用医学, 2018, 30(10):1327-1329. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0800.2018.10.036 . |
| LANG J X, MAO X H, XU C P. Research on neuroendocrine function and changes in patients with abnormal uterine bleeding-ovulatory dysfunction [J]. Mod Pract Med, 2018, 30(10):1327-1329. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0800.2018.10.036 . | |
| 25 | 杨尚芝, 金红, 李娟, 等. 坤泰胶囊联合米非司酮治疗围绝经期异常子宫出血的疗效及对bFGF、VEGF水平的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2023, 23(17):3320, 3340-3344. DOI: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2023.17.027 . |
| YANG S Z, JIN H, LI J, et al. Therapeutic effects of Kuntai capsule combined with mifepristone on perimenopausal abnormal uterine bleeding and its influence on bFGF and VEGF levels[J]. Prog Mod Biomed, 2023, 23(17):3320, 3340-3344. DOI: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2023.17.027 . | |
| 26 | MARSH M M, MALAKOOTI N, TAYLOR N H, et al. Endothelin and neutral endopeptidase in the endometrium of women with menorrhagia[J]. Hum Reprod, 1997, 12(9):2036-2040. DOI:10.1093/humrep/12.9.2036 . |
| 27 | CHODANKAR R, CRITCHLEY H O D. Biomarkers in abnormal uterine bleeding[J]. Biol Reprod, 2019, 101(6):1155-1166. DOI:10.1093/biolre/ioy231 . |
| 28 | SCHATZ F, GUZELOGLU-KAYISLI O, ARLIER S, et al. The role of decidual cells in uterine hemostasis, menstruation, inflammation, adverse pregnancy outcomes and abnormal uterine bleeding[J]. Hum Reprod Update, 2016, 22(4):497-515. DOI:10.1093/humupd/dmw004 . |
| 29 | MILLING SMITH O P, JABBOUR H N, CRITCHLEY H D. Cyclooxygenase enzyme expression and E series prostaglandin receptor signalling are enhanced in heavy menstruation[J]. Hum Reprod, 2007, 22(5):1450-1456. DOI:10.1093/humrep/del503 . |
| 30 | MALIK S, DAY K, PERRAULT I, et al. Reduced levels of VEGF-A and MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity and increased TNF-alpha in menstrual endometrium and effluent in women with menorrhagia[J]. Hum Reprod, 2006, 21(8):2158-2166. DOI:10.1093/humrep/del089 . |
| 31 | CRITCHLEY H O D, MAYBIN J A, ARMSTRONG G M, et al. Physiology of the endometrium and regulation of menstruation[J]. Physiol Rev, 2020, 100(3):1149-1179. DOI:10.1152/physrev.00031.2019 . |
| 32 | ARMSTRONG G M, MAYBIN J A, MURRAY A A, et al. Endometrial apoptosis and neutrophil infiltration during menstruation exhibits spatial and temporal dynamics that are recapitulated in a mouse model[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1):17416. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-17565-x . |
| 33 | 于明明, 谢卓, 金华, 等. 孕酮回植通过调节内质网应激诱导的细胞自噬与凋亡阻止小鼠月经发生[J]. 遵义医学院学报, 2019, 42(3):276-281. DOI: 10.14169/j.cnki.zunyixuebao.2019.0057 . |
| YU M M, XIE Z, JIN H, et al. Progesterone replantation to prevent menstruation in mice by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced autophagy and apoptosis[J]. J Zunyi Med Univ, 2019, 42(3):276-281. DOI: 10.14169/j.cnki.zunyixuebao.2019.0057 . | |
| 34 | LI J M, LIAO C C, HUANG HC, et al. Regulation effect and mechanism of Sheng-Hua-Tang on female reproductive system: From experimental transcriptomic analysis to clinical applications[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2020, 249:112431. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112431 . |
| 35 | LIU T, SHI F L, YING Y, et al. Mouse model of menstruation: an indispensable tool to investigate the mechanisms of menstruation and gynaecological diseases (Review)[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2020, 22(6):4463-4474. DOI:10.3892/mmr.2020.11567 . |
| 36 | MENNING A, WALTER A, RUDOLPH M, et al. Granulocytes and vascularization regulate uterine bleeding and tissue remodeling in a mouse menstruation model[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(8): e41800. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0041800 . |
| 37 | PETERSE D, CLERCQ K, GOOSSENS C, et al. Optimization of endometrial decidualization in the menstruating mouse model for preclinical endometriosis research[J]. Reprod Sci, 2018, 25(11):1577-1588. DOI:10.1177/1933719118756744 . |
| 38 | TONG M, KAYANI T, JONES D M, et al. Antiphospholipid antibodies increase endometrial stromal cell decidualization, senescence, and inflammation via toll-like receptor 4, reactive oxygen species, and p38 MAPK signaling[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2022, 74(6):1001-1012. DOI:10.1002/art.42068 . |
| 39 | XU X B, HE B, WANG J D. Menstrual-like changes in mice are provoked through the pharmacologic withdrawal of progesterone using mifepristone following induction of decidualization[J]. Hum Reprod, 2007, 22(12):3184-3191. DOI:10.1093/humrep/dem312 . |
| 40 | ZOOK B C, JÄNNE O A, ABRAHAM A A, et al. The development and regression of deciduosarcomas and other lesions caused by estrogens and progestins in rabbits[J]. Toxicol Pathol, 2001, 29(4):411-416. DOI:10.1080/0192623 0152499755 . |
| [1] | 陈钰涵, 陈瑾玲, 李欣, 区燕华, 王斯, 陈镜伊, 王兴易, 袁嘉丽, 段媛媛, 羊忠山, 牛海涛. 基于中西医临床病证特点的重症肌无力动物模型分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 176-186. |
| [2] | 罗世雄, 张赛, 陈慧. 常见哮喘动物模型的建立方法与评价研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 167-175. |
| [3] | 王碧莹, 鲁家铄, 昝桂影, 陈若松, 柴景蕊, 刘景根, 王瑜珺. 啮齿类动物药物成瘾模型的构建方法和应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 158-166. |
| [4] | 费彬, 郭文科, 郭建平. 疝疾病动物模型研究及新型疝修补材料应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(1): 55-66. |
| [5] | 杨家豪, 丁纯蕾, 钱风华, 孙旗, 姜旭升, 陈雯, 沈梦雯. 脓毒症相关脏器损伤动物模型研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 636-644. |
| [6] | 孙效容, 苏丹, 贵文娟, 陈玥. 手术诱导大鼠中重度膝骨关节炎模型的建立与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 597-604. |
| [7] | 田芳, 潘滨, 史佳怡, 徐燕意, 李卫华. 大气细颗粒物PM2.5暴露动物模型建立方法及在生殖毒性研究中的应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 626-635. |
| [8] | 赵小娜, 王鹏, 叶茂青, 曲新凯. 应用Triacsin C构建新型高血糖肥胖小鼠心功能减退模型[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 605-612. |
| [9] | 殷玉莲, 马丽娜, 屠思远, 陈玲, 叶媚娜, 陈红风. 非哺乳期乳腺炎大鼠模型的建立及评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 587-596. |
| [10] | 涂颖欣, 纪依澜, 王菲, 杨东明, 王冬冬, 孙芷馨, 戴悦欣, 王言吉, 阚广捍, 吴斌, 赵德明, 杨利峰. 小型猪后肢去负荷模拟失重模型的建立与组织损伤研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 475-486. |
| [11] | 杨劲, 俞诗雅, 林楠, 方永超, 赵虎, 邱锦维, 林鸿铭, 陈惠燕, 王瑜, 吴伟航. 改良型十二指肠旷置术对2型糖尿病大鼠糖代谢的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 523-530. |
| [12] | 戚龙菊, 陈世园, 廖泽华, 石袁虎, 孙郁雨, 王庆华. 经血干细胞移植联合运动训练促进大鼠脊髓损伤康复的转录组学分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 531-542. |
| [13] | 张乃群, 袁飘漂, 曹琳茸, 应娜, 杨涛涛. PNR检测在糖尿病肾脏疾病模型大鼠诊断及药效评价中的应用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 543-549. |
| [14] | 黄冬妍, 吴建辉. 生殖毒理学研究动物模型的建立方法及应用评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 550-559. |
| [15] | 郑艺清, 邓亚胜, 范燕萍, 梁天薇, 黄慧, 刘永辉, 倪召兵, 林江. 基于数据挖掘的盆腔炎性疾病动物模型应用分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(4): 405-418. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||