













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 149-161.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.127
收稿日期:2023-09-14
修回日期:2024-02-07
出版日期:2024-04-25
发布日期:2024-04-25
通讯作者:
娄月芬(1974—),女,硕士,主任药师,从事药事管理研究。E-mail:louyuefen@tongji.edu.cn。ORCID:0009-0005-9622-6059作者简介:胡锦华(1989—),女,硕士,主管药师,从事临床药学研究。E-mail:hjhhujinhua@163.com。
基金资助:
Jinhua HU( ), Jingjie HAN, Min JIN, Bin HU, Yuefen LOU(
), Jingjie HAN, Min JIN, Bin HU, Yuefen LOU( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-09-14
Revised:2024-02-07
Published:2024-04-25
Online:2024-04-25
Contact:
LOU Yuefen (ORCID: 0009-0005-9622-6059), E-mail: louyuefen@tongji.edu.cn摘要:
目的 通过Meta分析评价葛根素对大鼠和小鼠骨密度的影响。 方法 通过中国知网、中国生物医学文献、万方、维普、PubMed、EMBase、Web of Science、Cochrane图书馆、Scopus数据库中自建库至2023年11月6日收录的有关葛根素治疗对大鼠和小鼠骨密度影响的文献。文献纳入标准包括研究类型为随机对照试验(对照为安慰剂或空白组),研究对象为大鼠或小鼠,干预措施为葛根素,结果包含骨密度检测。文献排除标准包括葛根素联合其他药物治疗,没有原始研究数据,未公开发表,骨密度检测部位为下颌骨。采用SYRCLE's RoB工具对纳入文献中的研究进行风险偏倚评估,采用Stata 16.0和Rev Man 5.3软件进行Meta分析。 结果 经数据库检索共获得429篇文献,根据纳入及排除标准最终纳入42篇文献。纳入文献中涉及41项研究,共925只动物纳入数据分析。与对照组相比,葛根素可改善大鼠和小鼠的骨密度:股骨37项研究,n=824,标准化均数差(standardized mean difference,SMD)=2.12,95%置信区间(confidence interval,CI)=1.69~2.54,P < 0.000 1]、腰椎(13项研究,n=271,SMD=2.25,95%CI=1.49~3.01,P < 0.000 1)、胫骨(4项研究,n=95,SMD=0.94,95%CI=0.05~1.83,P=0.04)和全身(4项研究,n=94,SMD=1.89,95%CI=0.50~3.29,P=0.008)的组间骨密度差异均具有统计学意义。 结论 葛根素能够改善大鼠和小鼠的骨密度,本研究可以为葛根素防治骨质疏松症的临床研究提供良好的参考。
中图分类号:
胡锦华,韩菁婕,金旻,等. 葛根素对大鼠和小鼠骨密度影响的Meta分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(2): 149-161. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.127.
Jinhua HU,Jingjie HAN,Min JIN,et al. Effects of Puerarin on Bone Density in Rats and Mice: A Meta-analysis[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 149-161. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.127.
纳入研究 Included studies | 动物 Animal | 动物数量/只 Animal quantity n | 周期/周 Period/week | 动物模型 Animal model | 葛根素剂量/ (mg·kg-1) Puerarin dosage | 检测部位 Detection site |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li B (2020)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 30 | 14 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50~100 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Li B (2022)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 20 | 14 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 100 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Li BB (2014)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 6 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50 (ip qod) | 胫骨 |
| Guo CJ (2019)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 12 | 14 | 链脲佐菌素诱导糖尿病模型 | 50 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| QIN CY (2023)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 6 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 8 (ip qd) | 股骨/腰椎 |
| Yang D (2023)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 29 | 6 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 15~30 (ip qd) | 股骨/腰椎 |
| Wang GB (2020)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 40 | 6 | 去卵巢大鼠骨折模型 | 35 (ih qd) | 股骨 |
| Li H (2012)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 48 | 4~20 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50 (ih qd) | 股骨 |
| Liang H (2012)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 18 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 20 (ig qd) | 股骨/腰椎 |
| Liu H (2012)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 20 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 5 (ip qd) | 股骨 |
| Huang HL (2011)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 20 | 10~20 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50 (ih qd) | 股骨 |
| Xi HR(1) (2018)[ | Wistar大鼠,雌 | 24 | 8 | / | 15.4 (ig qd) | 股骨/椎骨/全身 |
| Xi HR(2) (2018)[ | Wistar大鼠,雌 | 20 | 12 | / | 15.4 (ig qd) | 股骨/椎骨/全身 |
| Yue HZ (2021)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 24 | 6 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 35 (ih qd) | 股骨/腰椎 |
| Li K (2019)[ | Wistar大鼠,雌 | 20 | 4 | 废用性骨质疏松模型 | 15.4 (ig qd) | 胫骨/腰椎 |
| Xiao L (2009)[ | 大鼠,雌 | 24 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50 (ih qd) | 股骨/胫骨/腰椎 |
| Xiao L (2020)[ | C57BL/6J小鼠,雌 | 10 | 6 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 100 (ip qod) | 股骨 |
| Lyu LT (2022)[ | KKAY45+C57BL/6J15小鼠 | 30 | 8 | 链脲佐菌素诱导糖尿病模型 | 1.3 (ig qd) | 全身 |
| Lyu LT (2023)[ | Wistar大鼠,雌 | 30 | 4 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 80 (ih qd) | 股骨 |
| Wang PP (2012)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 8 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 20 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Tian Q (2006)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 26 | 7 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 20~100 (ih qd) | 股骨/腰椎 |
| Zhou Q (2006)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 40 | 8 | 去卵巢大鼠闭合性骨折模型 | 5~20 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Yu S (2019)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 16 | 8~16 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 40 (ih qd) | 股骨 |
| Zhou SH (2010)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 20 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 500 (ig qd) | 腰椎 |
| Zeng SL (2018)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 30 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50~100 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Zeng SL (2019)[ | SD大鼠 | 20 | 8 | 激素性股骨头坏死模型 | 200 (ip qd) | 股骨 |
| Yuan SY (2016)[ | 昆明小鼠,雌 | 32 | 4 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 2~8 (qd) | 股骨 |
| Niu SZ (2019)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 28 | 8 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50 (ih qd) | 股骨 |
| Huang T (2010)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 40 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 5~20 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Tang WK (2020)[ | SD大鼠,雄 | 15 | 4 | 股骨溶解模型 | 15.4~30. 8 (ip qd) | 股骨 |
| Chen WM (2021)[ | Wistar大鼠,雌 | 18 | 6 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 35 (ih qd) | 股骨/腰椎 |
| Yang X (2017)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 12 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 4 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Li XJ (2009)[ | Wistar大鼠,雌 | 15 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 20 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Xu XS (2021)[ | C57BL/6小鼠,雌 | 20 | 8 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 100 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Fang XY (2021)[ | 大鼠,雌 | 16 | 4~12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Huang YL (2004)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 16 | 10 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50 (ih qd) | 股骨 |
| Gao YM (2019)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 20 | 8 | / | 30.82 (ig qd) | 股骨/全身 |
| Qiu ZC (2022)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 45 | 5~12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50~150 (ig qd) | 胫骨 |
| Fang ZH (2020)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 15 | 3 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50~75 (ih qd) | 股骨 |
| Wang ZH (2019)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 20 | 10 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50 (ig qd) | 股骨/腰椎 |
| Yang ZH (2021)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 22 | 6 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 35 (ih qd) | 股骨/腰椎 |
表1 有关葛根素对大鼠和小鼠骨密度影响的纳入研究的基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of the included studies on the effects of puerarin on bone density in rats and mice
纳入研究 Included studies | 动物 Animal | 动物数量/只 Animal quantity n | 周期/周 Period/week | 动物模型 Animal model | 葛根素剂量/ (mg·kg-1) Puerarin dosage | 检测部位 Detection site |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li B (2020)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 30 | 14 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50~100 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Li B (2022)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 20 | 14 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 100 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Li BB (2014)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 6 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50 (ip qod) | 胫骨 |
| Guo CJ (2019)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 12 | 14 | 链脲佐菌素诱导糖尿病模型 | 50 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| QIN CY (2023)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 6 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 8 (ip qd) | 股骨/腰椎 |
| Yang D (2023)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 29 | 6 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 15~30 (ip qd) | 股骨/腰椎 |
| Wang GB (2020)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 40 | 6 | 去卵巢大鼠骨折模型 | 35 (ih qd) | 股骨 |
| Li H (2012)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 48 | 4~20 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50 (ih qd) | 股骨 |
| Liang H (2012)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 18 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 20 (ig qd) | 股骨/腰椎 |
| Liu H (2012)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 20 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 5 (ip qd) | 股骨 |
| Huang HL (2011)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 20 | 10~20 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50 (ih qd) | 股骨 |
| Xi HR(1) (2018)[ | Wistar大鼠,雌 | 24 | 8 | / | 15.4 (ig qd) | 股骨/椎骨/全身 |
| Xi HR(2) (2018)[ | Wistar大鼠,雌 | 20 | 12 | / | 15.4 (ig qd) | 股骨/椎骨/全身 |
| Yue HZ (2021)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 24 | 6 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 35 (ih qd) | 股骨/腰椎 |
| Li K (2019)[ | Wistar大鼠,雌 | 20 | 4 | 废用性骨质疏松模型 | 15.4 (ig qd) | 胫骨/腰椎 |
| Xiao L (2009)[ | 大鼠,雌 | 24 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50 (ih qd) | 股骨/胫骨/腰椎 |
| Xiao L (2020)[ | C57BL/6J小鼠,雌 | 10 | 6 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 100 (ip qod) | 股骨 |
| Lyu LT (2022)[ | KKAY45+C57BL/6J15小鼠 | 30 | 8 | 链脲佐菌素诱导糖尿病模型 | 1.3 (ig qd) | 全身 |
| Lyu LT (2023)[ | Wistar大鼠,雌 | 30 | 4 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 80 (ih qd) | 股骨 |
| Wang PP (2012)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 8 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 20 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Tian Q (2006)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 26 | 7 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 20~100 (ih qd) | 股骨/腰椎 |
| Zhou Q (2006)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 40 | 8 | 去卵巢大鼠闭合性骨折模型 | 5~20 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Yu S (2019)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 16 | 8~16 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 40 (ih qd) | 股骨 |
| Zhou SH (2010)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 20 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 500 (ig qd) | 腰椎 |
| Zeng SL (2018)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 30 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50~100 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Zeng SL (2019)[ | SD大鼠 | 20 | 8 | 激素性股骨头坏死模型 | 200 (ip qd) | 股骨 |
| Yuan SY (2016)[ | 昆明小鼠,雌 | 32 | 4 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 2~8 (qd) | 股骨 |
| Niu SZ (2019)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 28 | 8 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50 (ih qd) | 股骨 |
| Huang T (2010)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 40 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 5~20 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Tang WK (2020)[ | SD大鼠,雄 | 15 | 4 | 股骨溶解模型 | 15.4~30. 8 (ip qd) | 股骨 |
| Chen WM (2021)[ | Wistar大鼠,雌 | 18 | 6 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 35 (ih qd) | 股骨/腰椎 |
| Yang X (2017)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 12 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 4 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Li XJ (2009)[ | Wistar大鼠,雌 | 15 | 12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 20 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Xu XS (2021)[ | C57BL/6小鼠,雌 | 20 | 8 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 100 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Fang XY (2021)[ | 大鼠,雌 | 16 | 4~12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50 (ig qd) | 股骨 |
| Huang YL (2004)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 16 | 10 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50 (ih qd) | 股骨 |
| Gao YM (2019)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 20 | 8 | / | 30.82 (ig qd) | 股骨/全身 |
| Qiu ZC (2022)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 45 | 5~12 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50~150 (ig qd) | 胫骨 |
| Fang ZH (2020)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 15 | 3 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50~75 (ih qd) | 股骨 |
| Wang ZH (2019)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 20 | 10 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 50 (ig qd) | 股骨/腰椎 |
| Yang ZH (2021)[ | SD大鼠,雌 | 22 | 6 | 去卵巢骨质疏松模型 | 35 (ih qd) | 股骨/腰椎 |
纳入研究 Included studies | 评估内容 Evaluation contents | 评分 Score | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||
| Li B (2020)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Li B (2022)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Li BB (2014)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Guo CJ (2019)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| QIN CY (2023)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Yang D (2023)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Wang GB (2020)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Li H (2012)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Liang H (2012)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Liu H (2012)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Huang HL (2011)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Xi HR(1) (2018)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 6 | ||||
| Xi HR(2) (2018)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Yue HZ (2021)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Li K (2019)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Xiao L (2009)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Xiao L (2020)[ | √ | √ | √ | 3 | |||||||
| Lyu LT (2022)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Lyu LT (2023)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Wang PP (2012)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Tian Q (2006)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Zhou Q (2006)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Yu S (2019)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Zhou SH (2010)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Zeng SL (2018)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Zeng SL (2019)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Yuan SY (2016)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Niu SZ (2019)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Huang T (2010)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Tang WK (2020)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Chen WM (2021)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Yang X (2017)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Li XJ (2009)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Xu XS (2021)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Fang XY (2021)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Huang YL (2004)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Gao YM (2019)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Qiu ZC (2022)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 6 | ||||
| Fang ZH (2020)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Wang ZH (2019)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Yang ZH (2021)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
表2 有关葛根素对大鼠和小鼠骨密度影响的SYRCLE研究质量偏倚风险评估表
Table 2 SYRCLE's risks of bias assessment for studies on the effects of puerarin on bone density in rats and mice
纳入研究 Included studies | 评估内容 Evaluation contents | 评分 Score | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||
| Li B (2020)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Li B (2022)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Li BB (2014)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Guo CJ (2019)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| QIN CY (2023)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Yang D (2023)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Wang GB (2020)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Li H (2012)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Liang H (2012)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Liu H (2012)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Huang HL (2011)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Xi HR(1) (2018)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 6 | ||||
| Xi HR(2) (2018)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Yue HZ (2021)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Li K (2019)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Xiao L (2009)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Xiao L (2020)[ | √ | √ | √ | 3 | |||||||
| Lyu LT (2022)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Lyu LT (2023)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Wang PP (2012)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Tian Q (2006)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Zhou Q (2006)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Yu S (2019)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Zhou SH (2010)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Zeng SL (2018)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Zeng SL (2019)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Yuan SY (2016)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Niu SZ (2019)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Huang T (2010)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Tang WK (2020)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Chen WM (2021)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Yang X (2017)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Li XJ (2009)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Xu XS (2021)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Fang XY (2021)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Huang YL (2004)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Gao YM (2019)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Qiu ZC (2022)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 6 | ||||
| Fang ZH (2020)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
| Wang ZH (2019)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | ||||||
| Yang ZH (2021)[ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | |||||
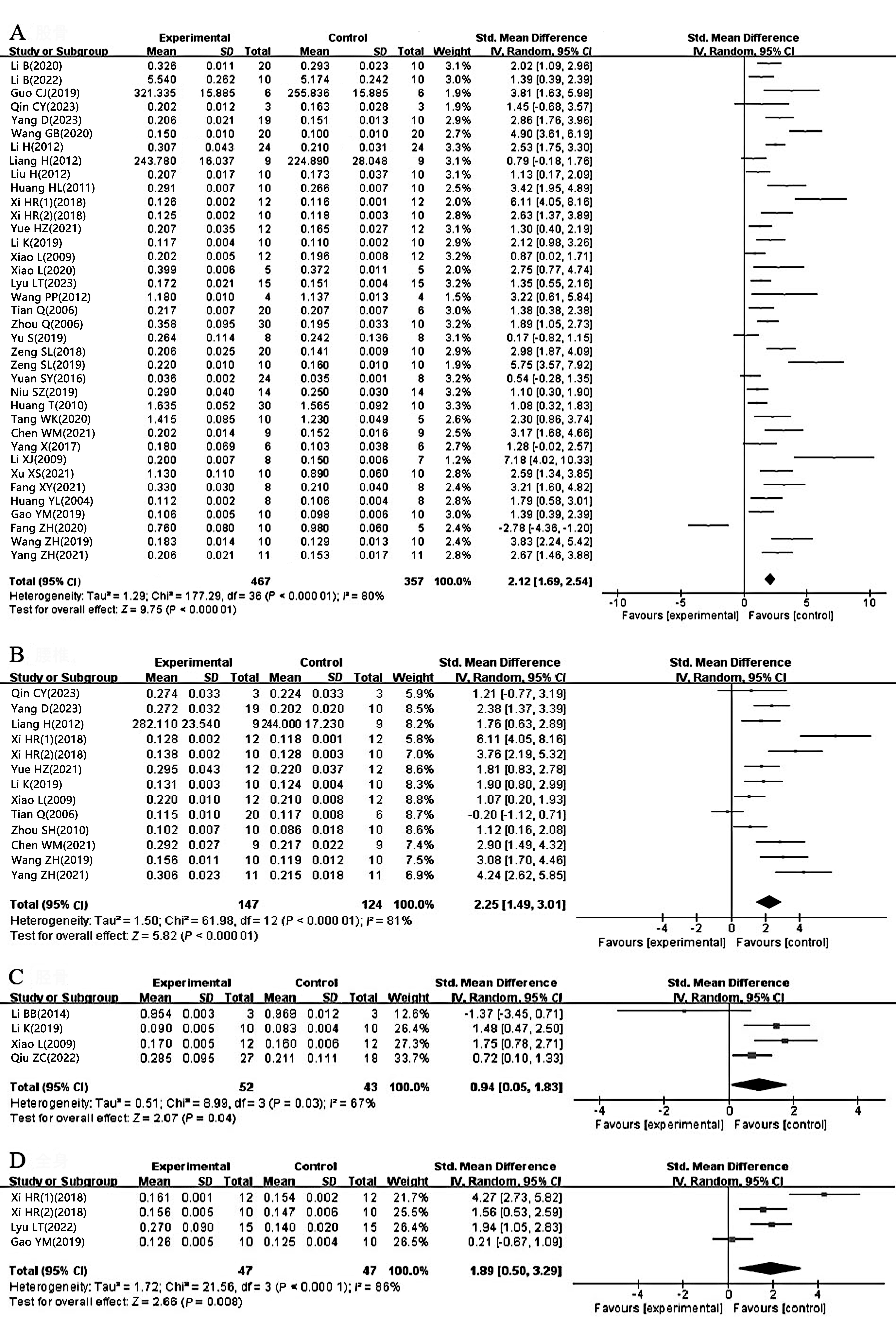
图2 葛根素对大鼠和小鼠各部位骨密度作用的森林图注:A,股骨;B,腰椎骨;C,胫骨;D,全身。
Figure 2 Forest plot of the effects of puerarin on bone mineral density at various parts in rats and miceNote:A, Femur; B, Lumbar spine; C, Tibia; D, Whole body.
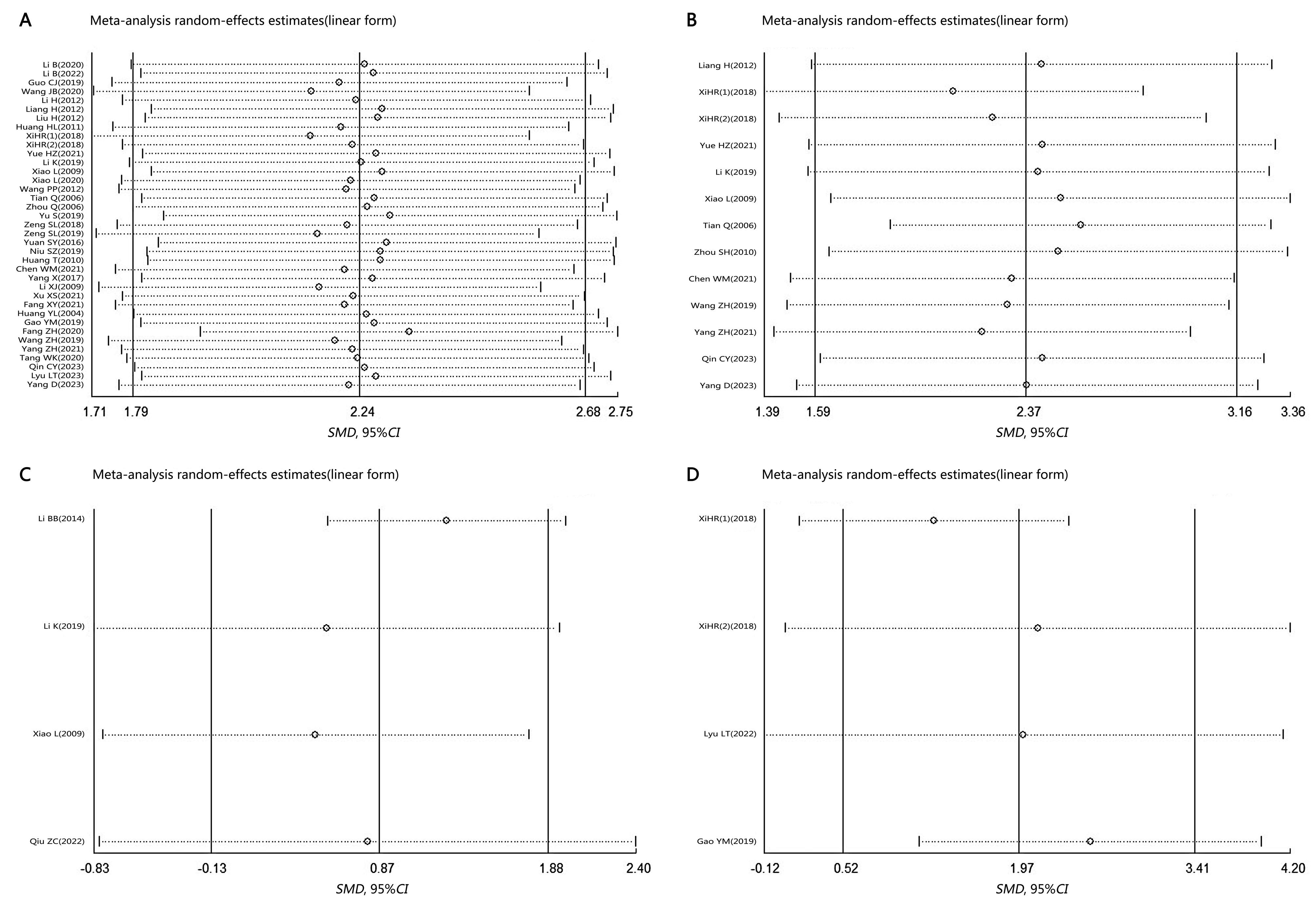
图3 葛根素对大鼠和小鼠骨密度作用的敏感性分析注:A,股骨;B,腰椎骨;C,胫骨;D,全身。SMD,标准化均数差;95%CI,95%置信区间。
Figure 3 Sensitivity analysis of the effects of puerarin on bone mineral density in rats and miceNote: A, Femur; B, Lumbar spine; C, Tibia; D, Whole body. SMD, Standardized mean difference; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval.
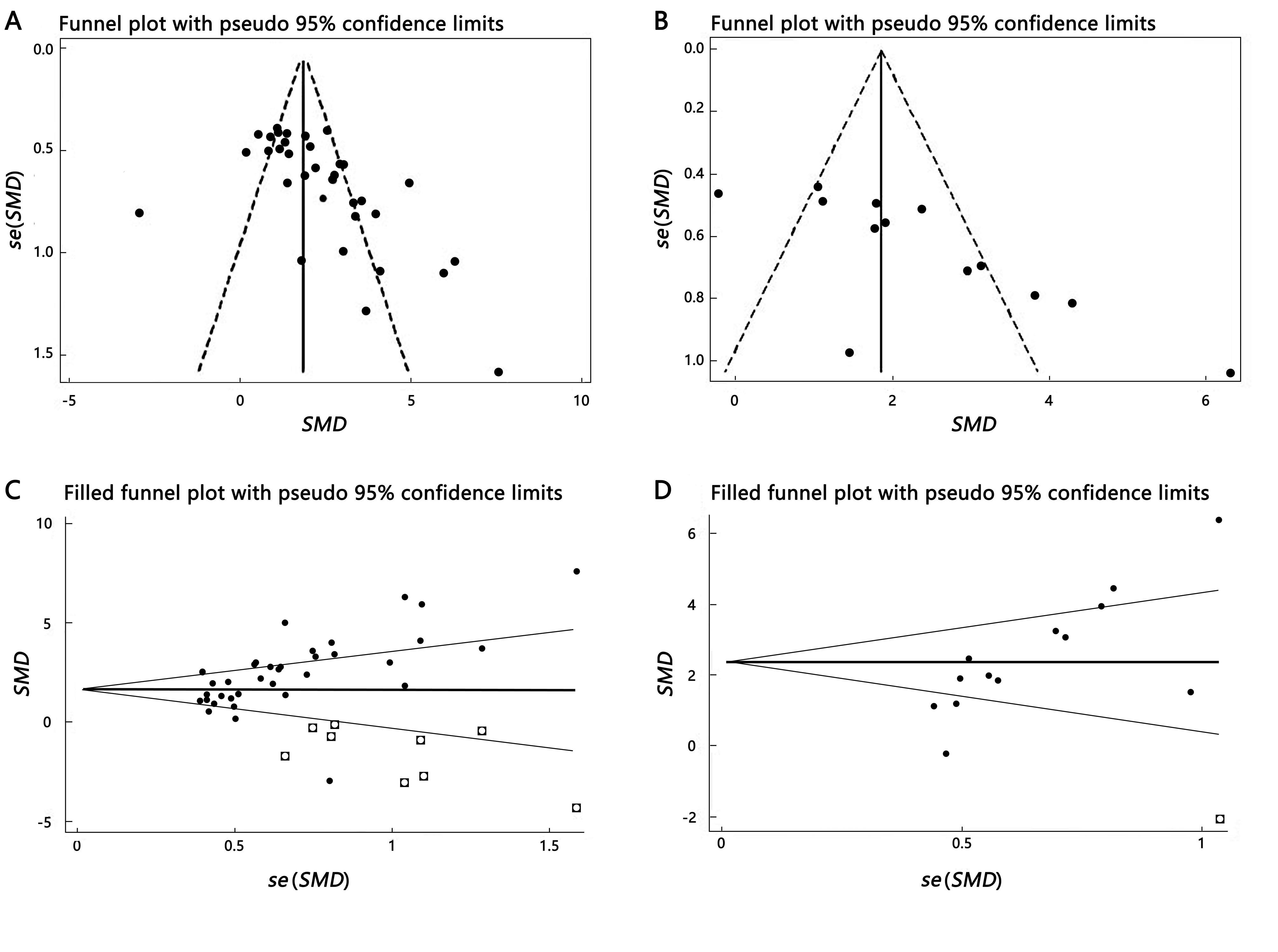
图4 葛根素对大鼠和小鼠骨密度作用的相关研究文献发表偏倚检验注:A股骨密度漏斗图,B腰椎骨密度漏斗图,C股骨减补漏斗图,D腰椎减补漏斗图。SMD,标准化均数差;se,标准误。
Figure 4 Publication bias test of related research studies on the effects of puerarin on bone density in rats and miceNote:A, Funnel plot of bone mineral density at femur; B, Funnel plot of bone mineral density at lumbar spine; C, Filled funnel plot at femur; D, Filled funnel plot at lumbar spine. SMD, Standardized mean difference; se, Standard error.
分组 Group | 纳入研究/篇 Included studies/piece | 动物数量/只 Animal quantity (n) | I2值 I square | 效应模型 Effect model | 效应量 Effect size | 效应量(95%CI) Effect size (95% confidence interval) | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 给药方式Tyeps of administration | |||||||
| 口服Oral | 397 | 75 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.30 (1.73, 2.88) | <0.001 | |
| 皮下注射Hypodermic injection | 327 | 86 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.68 (0.90, 2,45) | <0.001 | |
| 腹腔注射Intraperitoneal injection | 100 | 71 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.57 (1.43, 3.70) | 0.004 | |
| 给药剂量Dosage | |||||||
| ≤20 mg/kg | 296 | 75 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.00 (1.35, 2.64) | <0.001 | |
| 20~50 mg/kg | 476 | 80 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.23 (1.65, 2.80) | <0.001 | |
| >50 mg/kg | 104 | 89 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.29 (0.29, 4.28) | 0.020 | |
| 治疗周期Therapy period | |||||||
| ≤8 weeks | 487 | 83 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.11 (1.50, 2.72) | <0.001 | |
| >8 weeks | 353 | 70 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.06 (1.53, 2.58) | <0.001 | |
| 动物模型Animal model | |||||||
| 未造模Blank model | 64 | 88 | 随机效应 | SMD | 3.21 (0.93, 5.49) | 0.006 | |
| 去卵巢Ovariectomized | 693 | 79 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.90 (1.45, 2.35) | <0.001 | |
| 其他模型Other models | 67 | 69 | 随机效应 | SMD | 3.28 (1.79, 4.77) | <0.001 | |
| 葛根素来源Source of puerarin | |||||||
| 单体成分Monomer component | 396 | 77 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.36 (1.76, 2.96) | <0.001 | |
| 药品注射剂Drug injection | 344 | 85 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.86 (1.11, 2.61) | <0.001 | |
| 其他Others | 84 | 64 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.93 (0.87, 2.99) | <0.001 |
表3 葛根素对股骨密度作用的亚组分析
Table 3 Subgroup analysis of the effects of puerarin on bone mineral density at femur
分组 Group | 纳入研究/篇 Included studies/piece | 动物数量/只 Animal quantity (n) | I2值 I square | 效应模型 Effect model | 效应量 Effect size | 效应量(95%CI) Effect size (95% confidence interval) | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 给药方式Tyeps of administration | |||||||
| 口服Oral | 397 | 75 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.30 (1.73, 2.88) | <0.001 | |
| 皮下注射Hypodermic injection | 327 | 86 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.68 (0.90, 2,45) | <0.001 | |
| 腹腔注射Intraperitoneal injection | 100 | 71 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.57 (1.43, 3.70) | 0.004 | |
| 给药剂量Dosage | |||||||
| ≤20 mg/kg | 296 | 75 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.00 (1.35, 2.64) | <0.001 | |
| 20~50 mg/kg | 476 | 80 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.23 (1.65, 2.80) | <0.001 | |
| >50 mg/kg | 104 | 89 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.29 (0.29, 4.28) | 0.020 | |
| 治疗周期Therapy period | |||||||
| ≤8 weeks | 487 | 83 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.11 (1.50, 2.72) | <0.001 | |
| >8 weeks | 353 | 70 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.06 (1.53, 2.58) | <0.001 | |
| 动物模型Animal model | |||||||
| 未造模Blank model | 64 | 88 | 随机效应 | SMD | 3.21 (0.93, 5.49) | 0.006 | |
| 去卵巢Ovariectomized | 693 | 79 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.90 (1.45, 2.35) | <0.001 | |
| 其他模型Other models | 67 | 69 | 随机效应 | SMD | 3.28 (1.79, 4.77) | <0.001 | |
| 葛根素来源Source of puerarin | |||||||
| 单体成分Monomer component | 396 | 77 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.36 (1.76, 2.96) | <0.001 | |
| 药品注射剂Drug injection | 344 | 85 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.86 (1.11, 2.61) | <0.001 | |
| 其他Others | 84 | 64 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.93 (0.87, 2.99) | <0.001 |
分组 Group | 纳入研究/篇 Included studies/piece | 动物数量/只 Animal quantity(n) | I2值 I square | 效应模型 Effect model | 效应量 Effect size | 效应量(95%CI) Effect size (95% confidence interval) | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 给药方式Tyeps of administration | |||||||
| 口服Oral | 122 | 80 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.76 (1.58, 3.93) | <0.001 | |
| 皮下注射Hypodermic injection | 114 | 86 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.85 (0.53, 3.17) | 0.006 | |
| 腹腔注射Intraperitoneal injection | 35 | 6 | 固定效应 | SMD | 2.14 (1.24, 3.04) | <0.001 | |
| 给药剂量Dosage | |||||||
| ≤20 mg/kg | 119 | 84 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.87 (1.37, 2.37) | <0.001 | |
| 20~50 mg/kg | 140 | 87 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.85 (1.39, 2.31) | <0.001 | |
| >50 mg/kg | 34 | 40 | 固定效应 | SMD | 0.68 (-0.24, 1.60) | 0.150 | |
| 治疗周期Therapy period | |||||||
| ≤8 weeks | 169 | 85 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.91 (1.48, 2.34) | <0.001 | |
| >8 weeks | 102 | 71 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.73 (1.24, 2.22) | <0.001 | |
| 动物模型Animal model | |||||||
| 未造模Blank model | 44 | 69 | 随机效应 | SMD | 4.83 (2.54, 7.13) | <0.001 | |
| 去卵巢Ovariectomized | 207 | 76 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.85 (1.11, 2.60) | <0.001 | |
| 其他模型Other models | 20 | / | / | / | 1.90 (0.80, 2.99) | <0.001 | |
| 葛根素来源Source of puerarin | |||||||
| 单体成分Monomer component | 128 | 89 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.60 (1.05, 4.14) | 0.001 | |
| 药品注射剂Drug injection | 123 | 66 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.20 (1.34, 3.05) | <0.001 | |
| 其他Others | 20 | / | / | / | 1.12 (0.16, 2.08) | 0.020 |
表4 葛根素对腰椎骨密度作用的亚组分析
Table 4 Subgroup analysis of the effects of puerarin on bone mineral density at lumbar spine
分组 Group | 纳入研究/篇 Included studies/piece | 动物数量/只 Animal quantity(n) | I2值 I square | 效应模型 Effect model | 效应量 Effect size | 效应量(95%CI) Effect size (95% confidence interval) | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 给药方式Tyeps of administration | |||||||
| 口服Oral | 122 | 80 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.76 (1.58, 3.93) | <0.001 | |
| 皮下注射Hypodermic injection | 114 | 86 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.85 (0.53, 3.17) | 0.006 | |
| 腹腔注射Intraperitoneal injection | 35 | 6 | 固定效应 | SMD | 2.14 (1.24, 3.04) | <0.001 | |
| 给药剂量Dosage | |||||||
| ≤20 mg/kg | 119 | 84 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.87 (1.37, 2.37) | <0.001 | |
| 20~50 mg/kg | 140 | 87 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.85 (1.39, 2.31) | <0.001 | |
| >50 mg/kg | 34 | 40 | 固定效应 | SMD | 0.68 (-0.24, 1.60) | 0.150 | |
| 治疗周期Therapy period | |||||||
| ≤8 weeks | 169 | 85 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.91 (1.48, 2.34) | <0.001 | |
| >8 weeks | 102 | 71 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.73 (1.24, 2.22) | <0.001 | |
| 动物模型Animal model | |||||||
| 未造模Blank model | 44 | 69 | 随机效应 | SMD | 4.83 (2.54, 7.13) | <0.001 | |
| 去卵巢Ovariectomized | 207 | 76 | 随机效应 | SMD | 1.85 (1.11, 2.60) | <0.001 | |
| 其他模型Other models | 20 | / | / | / | 1.90 (0.80, 2.99) | <0.001 | |
| 葛根素来源Source of puerarin | |||||||
| 单体成分Monomer component | 128 | 89 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.60 (1.05, 4.14) | 0.001 | |
| 药品注射剂Drug injection | 123 | 66 | 随机效应 | SMD | 2.20 (1.34, 3.05) | <0.001 | |
| 其他Others | 20 | / | / | / | 1.12 (0.16, 2.08) | 0.020 |
| 1 | 李斌斌, 于世凤. 葛根素调控骨代谢的体外实验研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版), 2003, 35(1):74-77. DOI: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167x.2003.01.022 . |
| LI B B, YU S F. Effect of puerarin on the bone metabolism in vitro [J]. J Beijing Med Univ, 2003, 35(1):74-77. DOI: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167x.2003.01.022 . | |
| 2 | TIYASATKULKOVIT W, CHAROENPHANDHU N, WONGDEE K, et al. Upregulation of osteoblastic differentiation marker mRNA expression in osteoblast-like UMR106 cells by puerarin and phytoestrogens from Pueraria mirifica [J]. Phytomedicine, 2012, 19(13):1147-1155. DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2012.07.010 . |
| 3 | SHAN Z M, CHENG N, HUANG R, et al. Puerarin promotes the proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells via microRNA-106b by targeting receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2018, 15(1):55-60. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.5405 . |
| 4 | TIYASATKULKOVIT W, MALAIVIJITNOND S, CHAROENPHANDHU N, et al. Pueraria mirifica extract and puerarin enhance proliferation and expression of alkaline phosphatase and type I collagen in primary baboon osteoblasts[J]. Phytomedicine, 2014, 21(12):1498-1503. DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2014.06.019 . |
| 5 | WANG N, WANG X L, CHENG W X, et al. Puerarin promotes osteogenesis and inhibits adipogenesis in vitro [J]. Chin Med, 2013, 8(1):17. DOI: 10.1186/1749-8546-8-17 . |
| 6 | LI H, CHEN B P, PANG G F, et al. Anti-osteoporotic activity of puerarin 6"-O-xyloside on ovariectomized mice and its potential mechanism[J]. Pharm Biol, 2016, 54(1):111-117. DOI: 10.3109/13880209.2015.1017885 . |
| 7 | LEE M R, KIM B, LEE Y J, et al. Ameliorative effects of Pueraria lobata extract on postmenopausal symptoms through promoting estrogenic activity and bone markers in ovariectomized rats[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2021, 2021:7924400. DOI: 10.1155/2021/7924400 . |
| 8 | ZHOU G N, AN Z P, ZHAO W J, et al. Sex differences in outcomes after stroke among patients with low total cholesterol levels: a large hospital-based prospective study[J]. Biol Sex Differ, 2016, 7:62. DOI: 10.1186/s13293-016-0109-3 . |
| 9 | GUO C J, XIE J J, HONG R H, et al. Puerarin alleviates streptozotocin (STZ)-induced osteoporosis in rats through suppressing inflammation and apoptosis via HDAC1/HDAC3 signaling[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 115:108570. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.01.031 . |
| 10 | KULCZYŃSKI B, GRAMZA-MICHAŁOWSKA A, SULIBURSKA J, et al. Puerarin—an isoflavone with beneficial effects on bone health[J]. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 2021, 26(12):1653-1667. DOI: 10.52586/5058 . |
| 11 | HOOIJMANS C R, ROVERS M M, DE VRIES R B M, et al. SYRCLE's risk of bias tool for animal studies[J]. BMC Med Res Methodol, 2014, 14:43. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2288-14-43 . |
| 12 | LI B, LIU M Y, WANG Y, et al. Puerarin improves the bone micro-environment to inhibit OVX-induced osteoporosis via modulating SCFAs released by the gut microbiota and repairing intestinal mucosal integrity[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 132:110923. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha. 2020.110923 . |
| 13 | LI B, WANG Y, GONG S Q, et al. Puerarin improves OVX-induced osteoporosis by regulating phospholipid metabolism and biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids based on serum metabolomics[J]. Phytomedicine, 2022, 102:154198. DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154198 . |
| 14 | LI B B, LIU H, JIA S N. Puerarin enhances bone mass by promoting osteoblastogenesis and slightly lowering bone marrow adiposity in ovariectomized rats[J]. Biol Pharm Bull, 2014, 37(12):1919-1925. DOI: 10.1248/bpb.b14-00513 . |
| 15 | 覃成禹, 周昊楠, 陈远明. 葛根素对绝经后骨质疏松大鼠不同部位骨骼的抗骨质疏松作用差异的研究[J]. 中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志, 2023, 9(1):23-27. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2096-0263.2023.01.005 . |
| QIN C Y, ZHOU H N, CHEN Y M. The difference of anti-osteoporosis effect of Puerarin on different parts of bone in postmenopausal osteoporosis rats[J]. Chin J Geriatr Orthop Rehabil Electron Ed, 2023, 9(1):23-27. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2096-0263.2023.01.005 . | |
| 16 | 杨砥, 关智宇. 葛根素基于PPAR-γ/Axin2/Wnt信号通路对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠的干预作用[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2023, 43(13):3228-3232. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2023.13.041 . |
| YANG D, GUAN Z Y. Intervention of puerarin on ovariectomized osteoporosis rats based on PPAR-γ/Axin2/wnt signal pathway[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2023, 43(13):3228-3232. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2023.13.041 . | |
| 17 | 王国波, 罗波, 苟印尧, 等. 葛根素联合雌二醇对大鼠骨质疏松性骨折愈合的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2020, 36(14):2052-2055. DOI: 10.13699/j.cnki.1001-6821.2020.14.039 . |
| WANG G B, LUO B, GOU Y R, et al. Effect of puerarin combined with estradiol on the healing of osteoporotic fracture in rats[J]. Chin J Clin Pharmacol, 2020, 36(14):2052-2055. DOI: 10.13699/j.cnki.1001-6821.2020.14.039 . | |
| 18 | 李海, 王金花, 黄海玲, 等. 葛根素联合雌二醇对去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松的治疗作用[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2012, 32(18):3950-3952. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2012.18.039 . |
| LI H, WANG J H, HUANG H L, et al. Effect of Puerarin combined estradiol on ovariectomized osteoporosis[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2012, 32(18):3950-3952. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2012.18.039 . | |
| 19 | 梁恒, 邝志强, 王攀攀, 等. 葛根素通过BMP-2调节去卵巢大鼠骨代谢[J]. 广州医学院学报, 2012, 40(3):1-4. |
| LIANG H, KUANG Z Q, WANG P P, et al. Puerarin regulates bone metabolism via bone morphogenic protein-2 in ovariectomized rats[J]. Acad J Guangzhou Med Coll, 2012, 40(3):1-4. | |
| 20 | 刘浩, 李斌斌. 葛根素预防雌激素缺乏性骨质疏松的机制探讨[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2012, 22(6):16-20. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2012.06.005 . |
| LIU H, LI B B. Effect of puerarin on the osteoporosis resulted from ovariectomy in rats[J]. Chin J Comp Med, 2012, 22(6):16-20. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2012.06.005 . | |
| 21 | 黄海玲, 李海, 王金花, 等. 雌激素与不同剂量的葛根素联合对去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松的影响[J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2011, 26(33):5228-5231. |
| HUANG H L, LI H, WANG J H, et al. Effect of estradiol combined with different doses of puerarin on osteoporosis of ovariectomized rats[J]. Matern Child Health Care China, 2011, 26(33):5228-5231. | |
| 22 | 葸慧荣, 李文苑, 杨芳芳, 等. 中药葛根素对青年大鼠峰值骨量的影响研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2018, 24(4):514-519. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2018.04.019 . |
| XI H R, LI W Y, YANG F F, et al. Effect of Puerarin on peak bone mass in young rats[J]. Chin J Osteoporos, 2018, 24(4):514-519. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2018.04.019 . | |
| 23 | 葸慧荣, 杨芳芳, 高玉海, 等. 葛根素和白藜芦醇对青年大鼠峰值骨量的影响研究[J]. 中国骨伤, 2018, 31(7):635-641. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0034.2018.07.010 . |
| XI H R, YANG F F, GAO Y H, et al. Resveratrol and puerarin on peak bone mass in young rats[J]. China J Orthop Traumatol, 2018, 31(7):635-641. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0034.2018.07.010 . | |
| 24 | 岳海振, 蔡军, 马新强, 等. 葛根素对绝经后骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢、骨密度及骨生物力学的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2021, 27(1):77-81. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2021.01.017 . |
| YUE H Z, CAI J, MA X Q, et al. Effect of puerarin on bone metabolism, bone mineral density, and bone biomechanics in postmenopausal osteoporosis rats[J]. Chin J Osteoporos, 2021, 27(1):77-81. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2021.01.017 . | |
| 25 | 李凯, 秦荣, 邵佳乐, 等. 葛根素对废用性骨质疏松大鼠模型的防治作用及机制研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2019, 44(3):535-540. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20181012.003 . |
| LI K, QIN R, SHAO J L, et al. Preventive effect and mechanism of puerarin on rat models of disuse osteoporosis[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2019, 44(3):535-540. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20181012.003 . | |
| 26 | 李凯, 高玉海, 王玺, 等. 葛根素对尾吊大鼠发生废用性骨质疏松的防治作用[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2019, 12(1):50-57. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2591.2019.01.007 . |
| LI K, GAO Y H, WANG X, et al. Effects of puerarin on prevention of disuse osteoporosis in hindlimb suspension rats[J]. Chin J Osteoporos Bone Miner Res, 2019, 12(1):50-57. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2591.2019.01.007 . | |
| 27 | 肖兰, 李靖. 有氧运动配合葛根素对去卵巢大鼠骨密度、血清细胞因子和骨代谢相关生化指标的影响[J]. 西安体育学院学报, 2009, 26(5):575-579, 601. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-747X.2009.05.017 . |
| XIAO L, LI J. Effect of exercise training and puerarin on bone mineral density, cytokine, bone metabolism index in ovariectomized rats[J]. J Xi'an Phys Educ Univ, 2009, 26(5):575-579, 601. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-747X.2009.05.017 . | |
| 28 | XIAO L, ZHONG M D, HUANG Y, et al. Puerarin alleviates osteoporosis in the ovariectomy-induced mice by suppressing osteoclastogenesis via inhibition of TRAF6/ROS-dependent MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways[J]. Aging, 2020, 12(21):21706-21729. DOI: 10.18632/aging.103976 . |
| 29 | 吕立桃, 范卫闯, 白登彦, 等. 葛根素对糖尿病性骨质疏松小鼠骨密度及氧化应激的影响[J]. 新中医, 2022, 54(21):7-12. DOI: 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2022.21.002 . |
| LYU L T, FAN W C, BAI D Y, et al. Effect of puerarin on bone mineral density and oxidative stress in mice with diabetic osteoporosis[J]. N Chin Med, 2022, 54(21):7-12. DOI: 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2022.21.002 . | |
| 30 | 吕立桃, 范卫闯. 葛根素对去卵巢大鼠骨代谢平衡的影响[J]. 西部中医药, 2023, 36(7):27-30. DOI: 10.12174/j.issn.2096-9600.2023.07.06 . |
| LYU L T, FAN W C. Influence of puerarin on bone metabolic equilibrium in ovariectomized rats[J]. West J Tradit Chin Med, 2023, 36(7):27-30. DOI: 10.12174/j.issn.2096-9600.2023.07.06 . | |
| 31 | WANG P P, ZHU X F, YANG L, et al. Puerarin stimulates osteoblasts differentiation and bone formation through estrogen receptor, p38 MAPK, and Wnt/β-catenin pathways[J]. J Asian Nat Prod Res, 2012, 14(9):897-905. DOI: 10.1080/10286020.2012.702757 . |
| 32 | 田泉, 汤旭磊, 白孟海, 等. 葛根素对去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松和血脂的作用[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2006, 25(7):543-545. DOI: 10.3760/j: issn: 0254-9026.2006.07.023 . |
| TIAN Q, TANG X L, BAI M H, et al. Effects of puerarin on osteoporosis and blood lipids in ovariectomized rats[J]. Chin J Geriatr, 2006, 25(7):543-545. DOI: 10.3760/j: issn: 0254-9026.2006.07.023 . | |
| 33 | 周强, 付庭斌. 葛根素对去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松性骨折愈合的促进作用[J]. 中国临床康复, 2006, 10(27):45-47. |
| ZHOU Q, FU T B. Effect of puerarin on the healing of osteoporotic fracture in ovariectomized rats[J]. Chin J Clin Rehabil, 2006, 10(27):45-47. | |
| 34 | 遇实, 季庆辉, 王婧, 等. 葛根素联合雌激素对PMOP大鼠治疗作用及机制实验研究[J]. 黑龙江医药科学, 2019, 42(4):213-215, 217. |
| YU S, JI Q H, WANG J, et al. Experimental study on therapeutic effect and mechanism of puerarin combined with estrogen on PMOP rats[J]. Heilongjiang Med Pharm, 2019, 42(4):213-215, 217. | |
| 35 | 周胜虎, 刘兴炎, 王湘辉, 等. 葛根素对卵巢切除大鼠血清E2、腰椎BMD及骨髓细胞IL-6 mRNA表达的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2010, 16(12):946-948. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2010.12.011 . |
| ZHOU S H, LIU X Y, WANG X H, et al. Effects of puerarin on the level of serum E2, bone mineral density of the lumbar vertebrae, and the mRNA expression of interleukin 6 in ovariectomized rats[J]. Chin J Osteoporos, 2010, 16(12):946-948. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2010.12.011 . | |
| 36 | 曾锁林, 施熊兵. 葛根素对去势雌性大鼠骨质疏松症及PI3 KAKT信号转导通路的影响[J]. 河北医药, 2018, 40(23):3566-3569. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2018.23.010 . |
| ZENG S L, SHI X B. Effects of puerarin on osteoporosis and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in ovariectomized female rats[J]. Hebei Med J, 2018, 40(23):3566-3569. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2018.23.010 . | |
| 37 | 曾锁林, 施能兵, 刘异. 葛根素对激素性股骨头坏死大鼠骨组织及PI3K/Akt信号转导通路的影响[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报, 2019, 44(11):1441-1444. DOI: 10.13898/j.cnki.issn.1000-2200.2019.11.002 . |
| ZENG S L, SHI N B, LIU Y. Effect of puerarin on the bone tissue and PI3K/Akt signal transduction pathway in rats with femoral head osteonecrosis induced by hormone[J]. J Bengbu Med Coll, 2019, 44(11):1441-1444. DOI: 10.13898/j.cnki.issn.1000-2200.2019.11.002 . | |
| 38 | YUAN S Y, SHENG T, LIU L Q, et al. Puerarin prevents bone loss in ovariectomized mice and inhibits osteoclast formation in vitro [J]. Chin J Nat Med, 2016, 14(4):265-269. DOI: 10.1016/S1875-5364(16)30026-7 . |
| 39 | 牛士贞, 牛通, 倪勇, 等. 葛根素注射液联合雌二醇注射液对大鼠骨质疏松性骨折愈合的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2019, 35(23):3077-3080. DOI: 10.13699/j.cnki.1001-6821.2019.23.034 . |
| NIU S Z, NIU T, NI Y, et al. Effect of puerarin injection combined with estradiol injection on healing of osteoporotic fracture in rats[J]. Chin J Clin Pharmacol, 2019, 35(23):3077-3080. DOI: 10.13699/j.cnki.1001-6821.2019.23.034 . | |
| 40 | 黄彤, 金邦荃, 孙桂菊, 等. 葛根素对去卵巢大鼠骨密度和骨强度的改善[J]. 现代预防医学, 2010, 37(20):3894-3896. |
| HUANG T, JIN B Q, SUN G J, et al. Effects of puerarin on osteoporosis of ovariectomized rats[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2010, 37(20):3894-3896. | |
| 41 | TANG W K, XIAO L, GE G R, et al. Puerarin inhibits titanium particle-induced osteolysis and RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via suppression of the NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2020, 24(20):11972-11983. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.15821 . |
| 42 | 陈文明, 胡芯源. 葛根素联合阿仑膦酸钠对绝经后骨质疏松大鼠氧化应激、炎症反应及骨代谢的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2021, 27(1):73-76, 100. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2021.01.016 . |
| CHEN W M, HU X Y. Effect of puerarin combined with alendronate on oxidative stress, inflammation reaction, and bone metabolism in postmenopausal osteoporotic rats[J]. Chin J Osteoporos, 2021, 27(1):73-76, 100. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2021.01.016 . | |
| 43 | YANG X, YANG Y, ZHOU S, et al. Puerarin stimulates osteogenic differentiation and bone formation through the ERK1/2 and p38-MAPK signaling pathways[J]. Curr Mol Med, 2018, 17(7):488-496. DOI: 10.2174/1566524018666171219101142 . |
| 44 | 李旭炯, 张翠英. 葛根素对去卵巢大鼠骨密度及血清IL-6的影响[J]. 长治医学院学报, 2009, 23(1):13-15. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0588.2009.01.005 . |
| LI X J, ZHANG C Y. Effects of puerarin on bone mineral density and IL-6 in ovariectomized rats[J]. J Changzhi Med Coll, 2009, 23(1):13-15. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0588.2009.01.005 . | |
| 45 | 许晓山, 庞正宝, 杨军, 等. 葛根素治疗去卵巢小鼠骨量丢失的疗效及对RANKL/RANK/OPG信号通路的影响[J]. 浙江医学, 2021, 43(5):471-474, 481. DOI: 10.12056/j.issn.1006-2785.2021.43.5.2020-2134 . |
| XU X S, PANG Z B, YANG J, et al. Effict of puerarin on bone loss in ovariectomized mice and its effect on RANKL/RANK/OPG signaling pathway[J]. Zhejiang Med J, 2021, 43(5):471-474, 481. DOI: 10.12056/j.issn.1006-2785.2021.43.5.2020-2134 . | |
| 46 | 方晓燕, 李海, 顾建忠, 等. 山茶籽与葛根素对去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松的防治作用比较[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2021, 41(2):343-345. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2021.02.034 . |
| FANG X Y, LI H, GU J Z, et al. Comparison of effects of camellia seed and puerarin on osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2021, 41(2):343-345. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2021.02.034 . | |
| 47 | 黄延玲, 石凤英. 葛根素对去卵巢大鼠骨密度和骨代谢生化指标的影响[J]. 中国临床康复, 2004, 8(12):2307-2309. |
| HUANG Y L, SHI F Y. Effects of puerarin on the bone mineral density and biochemical markers of bone metabolism in ovariectomized rats[J]. Chin J Clin Rehabil, 2004, 8(12):2307-2309. | |
| 48 | 高玉海, 杨芳芳, 游丽娟, 等. 淫羊藿苷与葛根素的复方药对生长期大鼠峰值骨量的影响[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2019, 35(2):148-152. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6699.2019.02.011 . |
| GAO Y H, YANG F F, YOU L J, et al. Effects of compound medicine of icariin and puerarin on peak bone mass in growing rats[J]. Chin J Endocrinol Metab, 2019, 35(2):148-152. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6699.2019.02.011 . | |
| 49 | QIU Z C, LI L, HUANG Y Y, et al. Puerarin specifically disrupts osteoclast activation via blocking integrin-β3 Pyk2/Src/Cbl signaling pathway[J]. J Orthop Translat, 2022, 33:55-69. DOI: 10.1016/j.jot.2022.01.003 . |
| 50 | 方志辉, 张天锋. 葛根素对骨质疏松大鼠成骨细胞增殖和活性的影响及其作用机制[J]. 广西医学, 2020, 42(20):2680-2684. DOI: 10.11675/j.issn.0253-4304.2020.20.16 . |
| FANG Z H, ZHANG T F. Effect of puerarin on osteoblast proliferation and activity and its action mechanism in rats with osteoporosis[J]. Guangxi Med J, 2020, 42(20):2680-2684. DOI: 10.11675/j.issn.0253-4304.2020.20.16 . | |
| 51 | 王振昊, 林涨源. 葛根素联合锌治疗去势大鼠骨质疏松症的实验研究[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17(9):1450-1453. DOI: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000967 . |
| WANG Z H, LIN Z Y. Experimental study on treatment of osteoporosis with puerarin and zinc in ovariectomized rats[J]. Chin J Gen Pract, 2019, 17(9):1450-1453. DOI: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000967 . | |
| 52 | 杨占华, 郝连升, 张建新. 葛根素对骨质疏松大鼠氧化应激反应、骨代谢和骨密度的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2021, 27(3):413-417. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2021.03.020 . |
| YANG Z H, HAO L S, ZHANG J X. Effects of puerarin on oxidative stress response, bone metabolism, and bone mineral density in osteoporotic rats[J]. Chin J Osteoporos, 2021, 27(3):413-417. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2021.03.020 . | |
| 53 | YANG Y R, CHEN D Y, LI Y L, et al. Effect of Puerarin on Osteogenic Differentiation in vitro and on New Bone Formation in vivo [J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2022, 16:2885-2900. DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S379794 . |
| 54 | 周昊楠, 陈远明. 葛根素防治绝经后骨质疏松症的研究进展[J]. 广西医学, 2019, 41(7):878-883. DOI: 10.11675/j.issn.0253-4304.2019.07.20 . |
| ZHOU H N, CHEN Y M. Research progress of puerarin in prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis[J]. Guangxi Med J, 2019, 41(7):878-883. DOI: 10.11675/j.issn.0253-4304.2019.07.20 . | |
| 55 | LV H H, CHE T J, TANG X L, et al. Puerarin enhances proliferation and osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells via a nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine monophosphate signaling pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2015, 12(2):2283-2290. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3647 . |
| 56 | WANG Y, WANG W L, XIE W L, et al. Puerarin stimulates proliferation and differentiation and protects against cell death in human osteoblastic MG-63 cells via ER-dependent MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt activation[J]. Phytomedicine, 2013, 20(10):787-796. DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2013.03.005 . |
| 57 | ZHANG Y, YAN M, YU Q F, et al. Puerarin prevents LPS-induced osteoclast formation and bone loss via inhibition of Akt activation[J]. Biol Pharm Bull, 2016, 39(12):2028-2035. DOI: 10.1248/bpb.b16-00522 . |
| 58 | 罗琳. 葛根素联合阿仑膦酸钠治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的效果观察[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2018, 24(7):930-933, 943. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2018.07.019 . |
| LUO L. Observation on the effect of puerarin combined with alendronate in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis[J]. Chin J Osteoporos, 2018, 24(7):930-933, 943. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2018.07.019 . | |
| 59 | 彭诗洁. 葛根素配合阿仑膦酸钠治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的效果观察[J]. 西南国防医药, 2019, 29(5):543-546. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0188.2019.05.010 . |
| PENG S J. Observation on the effect of Puerarin combined with alendronate sodium in the treatment of post-menopausal osteoporosis[J]. Med J Natl Defending Forces Southwest China, 2019, 29(5):543-546. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0188.2019.05.010 . | |
| 60 | 申彦菊, 沈亚非. 葛根素联合阿仑膦酸钠对绝经后骨质疏松症患者骨密度的影响[J]. 北方药学, 2019, 16(7):93-94. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8351.2019.07.065 . |
| SHEN Y J, SHEN Y F. Effect of puerarin combined with alendronate on bone mineral density in postmenopausal osteoporosis patients[J]. J N Pharm, 2019, 16(7):93-94. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8351.2019.07.065 . |
| [1] | 贡磊磊, 王晓霞, 封学伟, 李心蕾, 赵涵, 张雪艳, 冯欣. 不同浓度环磷酰胺诱导早发性卵巢功能不全小鼠模型及作用机制研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 403-410. |
| [2] | 姜娟, 宋宁, 连文博, 邵丛丛, 顾文文, 石燕. 两种浓度乙醇溶液灌注建立小鼠宫腔粘连模型的组织病理和分子病理表型比较[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 393-402. |
| [3] | 刘月琴, 薛卫国, 王淑友, 申耀华, 贾术永, 王广军, 宋晓晶. 探头式激光共聚焦成像技术用于小鼠消化道组织形态特征分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 457-465. |
| [4] | 郑卿勇, 杨冬华, 马智超, 周姿余, 陆洋, 王晶宇, 邢丽娜, 康迎英, 杜莉, 赵春香, 狄宝山, 田金徽. 动物实验系统评价与Meta分析报告的规范撰写建议[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 496-507. |
| [5] | 秦超, 李双星, 赵婷婷, 蒋晨晨, 赵晶, 杨艳伟, 林志, 王三龙, 文海若. 药物安全评价用SD大鼠90 d喂养试验的背景数据研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 439-448. |
| [6] | 刘力瑜, 嵇波, 刘小玄, 方洋, 张玲, 郭亭廷, 全烨, 李鹤文, 刘翼天. 大鼠胎儿期肺组织固定方法的探索[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 432-438. |
| [7] | 肖林林, 杨逸萱, 黎珊杉, 罗兰诗雨, 尹思威, 孙俊铭, 施维, 欧阳轶强, 李习艺. 利用脑立体定位技术将人源三突变APP基因导入海马区构建阿尔茨海默病大鼠模型[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 269-278. |
| [8] | 刘智伟, 杨然, 连浩, 张玉, 金立伦. 秦皮素对碘乙酸钠诱导骨关节炎模型大鼠的软骨保护与抗炎作用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 259-268. |
| [9] | 罗莲莲, 袁艳春, 王俊岭, 时广森. 肌萎缩侧索硬化症小鼠模型研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 290-299. |
| [10] | 姜萌, 郝淑兰, 仝立国, 仲启明, 高振飞, 王永辉, 王晞星, 吉海杰. 长春瑞滨诱导大鼠足背静脉炎模型的动态评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 251-258. |
| [11] | 孔志豪, 魏晓锋, 于灵芝, 冯丽萍, 朱琦, 施国君, 王晨. 鳞状皮屑裸小鼠木糖葡萄球菌的分离鉴定[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 368-375. |
| [12] | 潘颐聪, 蒋汶洪, 胡明, 覃晓. 慢性肾脏病大鼠主动脉钙化模型的术式优化及效果评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 279-289. |
| [13] | 许秋雨, 严国锋, 付丽, 范文华, 周晶, 朱莲, 仇淑雯, 张洁, 吴铃. 来曲唑缓释片皮下给药构建小鼠多囊卵巢综合征模型及其肝脏转录组学分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 119-129. |
| [14] | 潘钱家, 葛峻沂, 胡楠, 华飞, 顾敏. 基于16S rRNA测序的2型糖尿病db/db小鼠模型口腔菌群差异分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 147-157. |
| [15] | 连辉, 姜艳玲, 刘佳, 张玉立, 谢伟, 薛晓鸥, 李健. 异常子宫出血大鼠模型的构建与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 130-146. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||