













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 566-573.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.022
收稿日期:2023-02-20
修回日期:2023-05-30
出版日期:2023-10-25
发布日期:2023-10-25
通讯作者:
魏晓锋(1980—),男,硕士,副研究员,主要从事实验动物质量控制研究。E-mail: wei.xf@outlook.com。ORCID:0009-0009-5089-8342作者简介:于灵芝(1980—),女,博士,助理研究员,主要从事病原体核酸检测方法研究。E-mail: yulingzhi@slarc.org.cn
基金资助:
Lingzhi YU, Jianyun XIE, Liping FENG, Xiaofeng WEI( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-02-20
Revised:2023-05-30
Published:2023-10-25
Online:2023-10-25
Contact:
WEI Xiaofeng (0009-0009-5089-8342), E-mail: wei.xf@outlook.com摘要:
目的 建立一种快速灵敏的金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus)检测方法。 方法 选择金黄色葡萄球菌特异性基因nuc作为靶基因,设计并合成一对特异性引物和一条TaqMan探针,利用荧光定量PCR技术建立nuc基因的核酸检测方法,并在大鼠、小鼠粪便样本检测中进行应用。 结果 对金黄色葡萄球菌和其他非金黄色葡萄球菌菌株中提取的DNA进行荧光定量PCR检测,结果显示金黄色葡萄球菌出现特异性扩增曲线,而其他非金黄色葡萄球菌未出现,表明设计的引物和探针对金黄色葡萄球菌检测具有特异性。将提取的金黄色葡萄球菌DNA进行10倍梯度稀释后测定其灵敏度,结果显示最低检出限是10 fg的DNA量,比普通PCR方法高2个数量级。本研究共检测91份样品,有4份来自同一设施的大鼠样品,扩增曲线为典型的S曲线;将该PCR产物测序并进行BLAST比对,该样本的基因序列与金黄色葡萄球菌的基因序列相似度为100%,表明该样本为金黄色葡萄球菌nuc基因核酸阳性,阳性率为4.40%,与细菌培养法的检测结果一致。核酸提取采用全自动核酸纯化仪,从核酸提取到检测结果判定快速,所需时间小于1.5 h。 结论 建立的以nuc为靶基因鉴定金黄色葡萄球菌的qPCR方法,具有快速、灵敏度高和特异性强的优点,可用于实验动物大鼠、小鼠粪便中金黄色葡萄球菌的检测。
中图分类号:
于灵芝,谢建芸,冯丽萍,等. 金黄色葡萄球菌荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立及其在大鼠、小鼠粪便检测中的应用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(5): 566-573. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.022.
Lingzhi YU,Jianyun XIE,Liping FENG,et al. Establishment of Fluorescence qPCR Method for Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus and Its Application in Feces Detection of Rats and Mice[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 566-573. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.022.
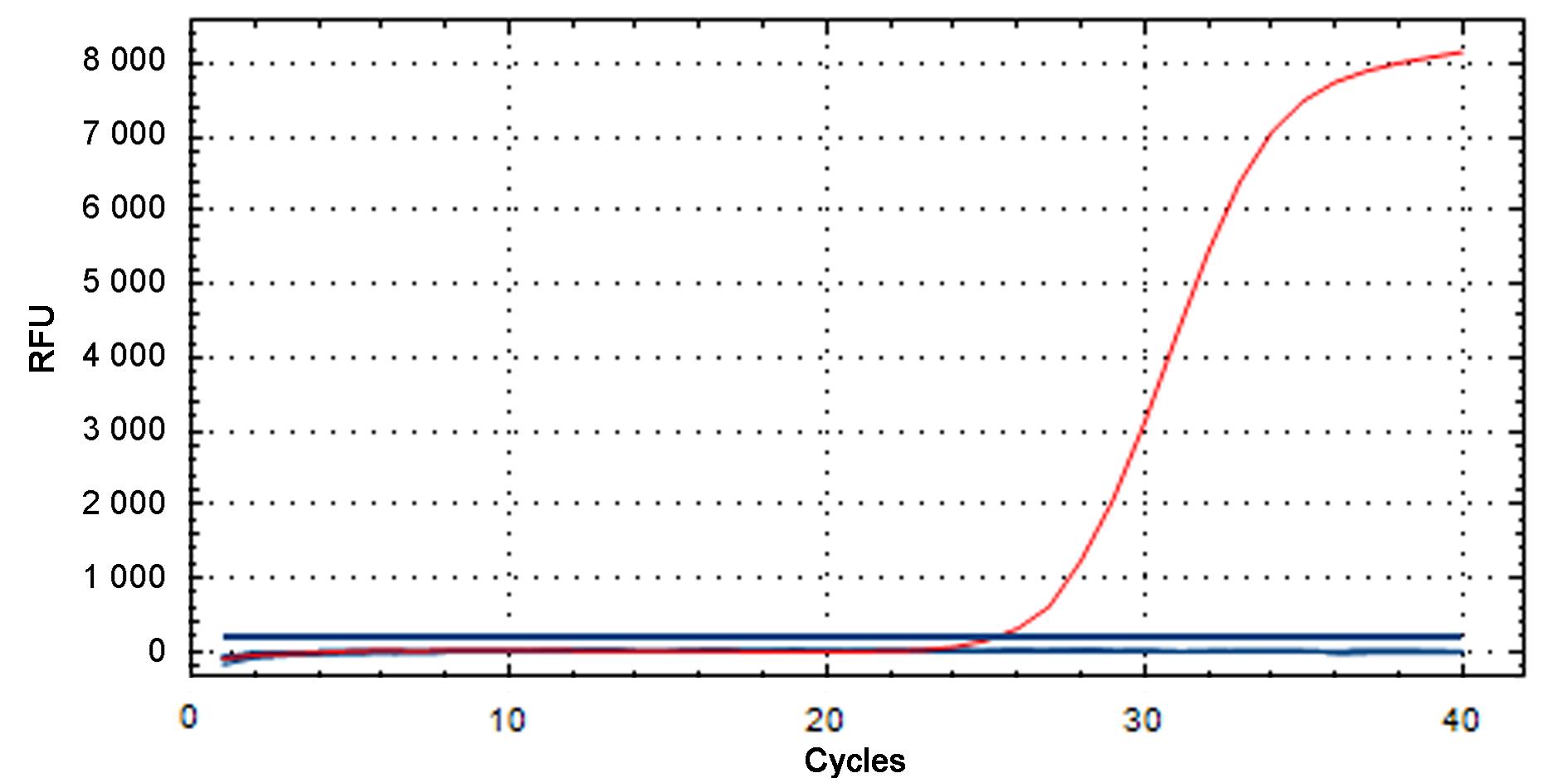
图1 金黄色葡萄球菌实时荧光定量PCR特异性检测结果注:红色S型曲线代表阳性对照。RFU是相对荧光单位。
Figure 1 Specificity for Staphylococcus aureus detected by real-time fluorescent quantitative PCRNote:Red S-type curve represents the positive control.RFU, Relative fluorescence unit.
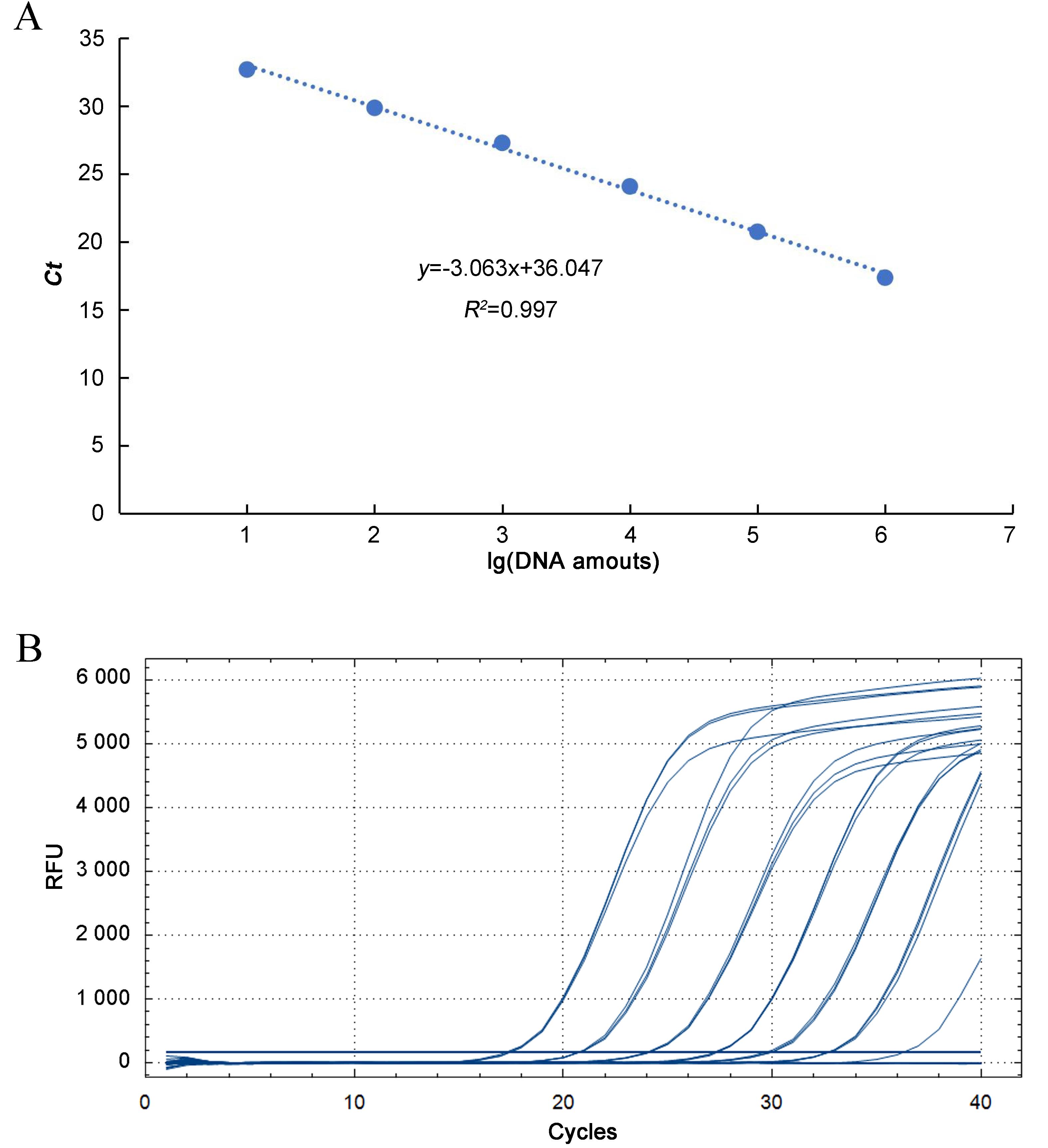
图2 金黄色葡萄球菌进行实时荧光定量PCR的标准曲线(A)和灵敏度检测结果(B)注:从左向右的曲线依次代表的核酸量为1 ng、100 pg、10 pg、1 pg、100 fg、10 fg和1 fg。
Figure 2 Standard curve (A) and sensitivity (B) for Staphylococcus aureus detected by real-time fluorescent quantitative PCRNote:The amounts of nucleic acid represented by the curves from left to right is 1 ng, 100 pg, 10 pg, 1 pg, 100 fg, 10 fg and 1 fg, respectively.
DNA量 DNA quantities | 10次检测结果(Ct值) 10 test results (Ct value) | CV值/% CV value/% | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |||
| 10 pg | 25.23 | 25.17 | 24.99 | 25.23 | 25.16 | 25.04 | 25.2 | 25.15 | 25.16 | 25.21 | 0.33 | |
| 10 fg | 33.32 | 33.93 | 34.33 | 34.72 | 33.77 | 33.68 | 33.56 | 33.93 | 33.84 | 34.18 | 1.18 | |
表1 组内重复性实验数据(Ct值)及变异系数(CV)
Table 1 Intragroup repeatability data (Ct) and coefficient of variation (CV)
DNA量 DNA quantities | 10次检测结果(Ct值) 10 test results (Ct value) | CV值/% CV value/% | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |||
| 10 pg | 25.23 | 25.17 | 24.99 | 25.23 | 25.16 | 25.04 | 25.2 | 25.15 | 25.16 | 25.21 | 0.33 | |
| 10 fg | 33.32 | 33.93 | 34.33 | 34.72 | 33.77 | 33.68 | 33.56 | 33.93 | 33.84 | 34.18 | 1.18 | |
DNA量 DNA quantities | 5次检测结果(Ct值) 5 test results(Ct value) | DNA量 DNA quantities | 5次检测结果(Ct值) 5 test results(Ct value) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 10 pg | 33.13 | 34.08 | 36.00 | 34.19 | 33.02 | 10 fg | 26.04 | 26.10 | 26.20 | 26.12 | 26.08 |
| 34.44 | 32.27 | 33.47 | 34.04 | 34.56 | 25.80 | 25.89 | 25.83 | 26.15 | 26.10 | ||
| 32.72 | 32.60 | 32.35 | 31.90 | 32.56 | 26.17 | 25.39 | 25.86 | 25.76 | 25.91 | ||
| 32.13 | 32.88 | 34.21 | 33.14 | 32.90 | 25.87 | 25.96 | 25.86 | 25.90 | 25.66 | ||
| 33.83 | 35.05 | 32.60 | 33.99 | 33.41 | 25.86 | 25.78 | 26.10 | 26.12 | 25.69 | ||
平均数1 Mean 1 | 33.25 | 33.38 | 33.73 | 33.45 | 33.29 | 25.95 | 25.82 | 25.97 | 26.01 | 25.89 | |
平均数2 Mean 2 | 33.42 | 25.93 | |||||||||
| 标准差SD | 0.19 | 0.19 | |||||||||
| CV/% | 0.56 | 0.75 | |||||||||
表2 组间重复性实验数据(Ct值)及变异系数(CV)
Table 2 Intergroup repeatability data (Ct) and coefficient of variation(CV)
DNA量 DNA quantities | 5次检测结果(Ct值) 5 test results(Ct value) | DNA量 DNA quantities | 5次检测结果(Ct值) 5 test results(Ct value) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 10 pg | 33.13 | 34.08 | 36.00 | 34.19 | 33.02 | 10 fg | 26.04 | 26.10 | 26.20 | 26.12 | 26.08 |
| 34.44 | 32.27 | 33.47 | 34.04 | 34.56 | 25.80 | 25.89 | 25.83 | 26.15 | 26.10 | ||
| 32.72 | 32.60 | 32.35 | 31.90 | 32.56 | 26.17 | 25.39 | 25.86 | 25.76 | 25.91 | ||
| 32.13 | 32.88 | 34.21 | 33.14 | 32.90 | 25.87 | 25.96 | 25.86 | 25.90 | 25.66 | ||
| 33.83 | 35.05 | 32.60 | 33.99 | 33.41 | 25.86 | 25.78 | 26.10 | 26.12 | 25.69 | ||
平均数1 Mean 1 | 33.25 | 33.38 | 33.73 | 33.45 | 33.29 | 25.95 | 25.82 | 25.97 | 26.01 | 25.89 | |
平均数2 Mean 2 | 33.42 | 25.93 | |||||||||
| 标准差SD | 0.19 | 0.19 | |||||||||
| CV/% | 0.56 | 0.75 | |||||||||
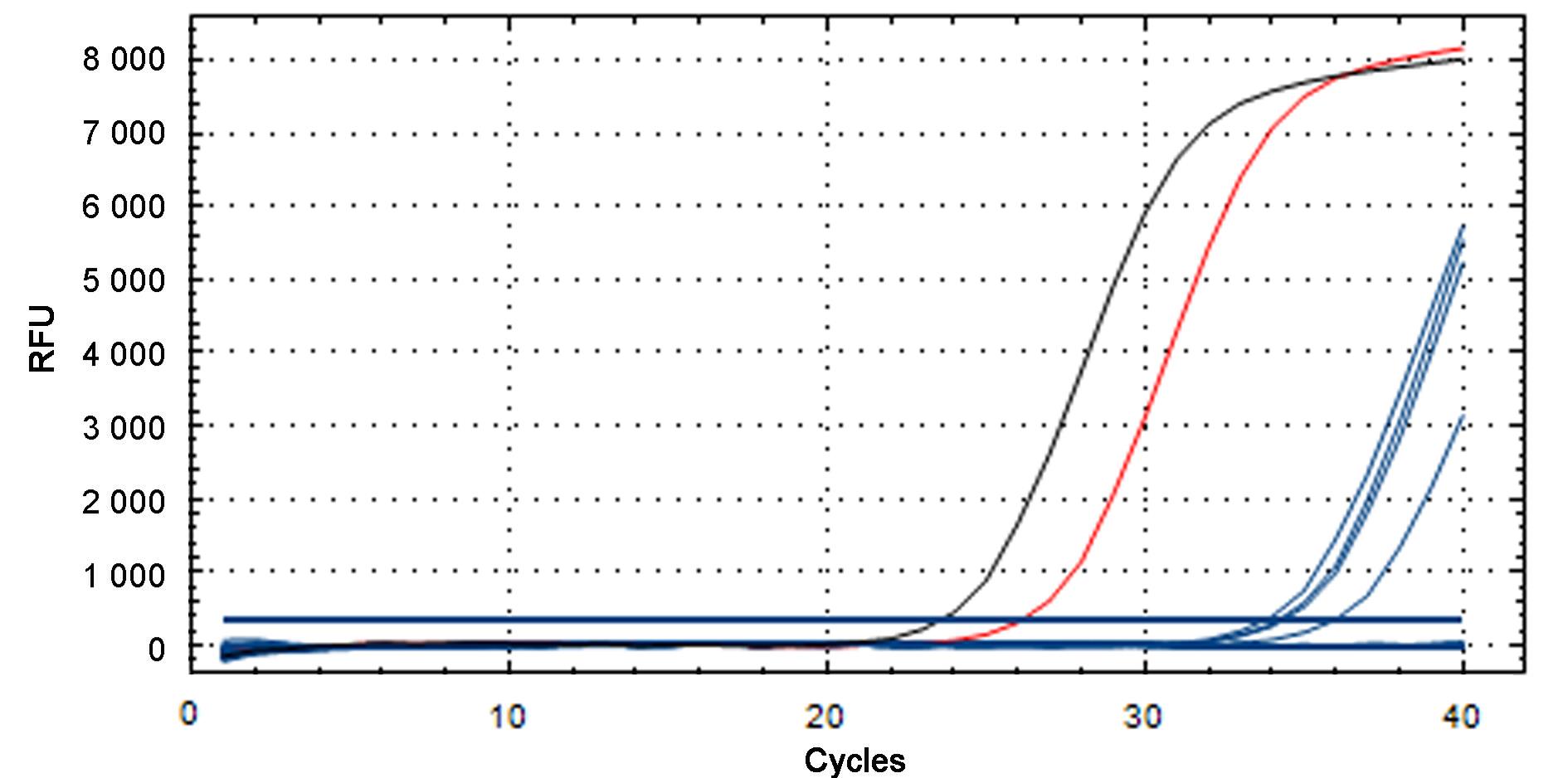
图3 金黄色葡萄球菌实时荧光定量PCR的临床检测结果注:红色S型曲线代表扩增阳性对照,黑色S型曲线代表核酸提取阳性对照,蓝色S型曲线代表阳性样本。
Figure 3 Clinical detection results for Staphylococcus aureus by real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detectionNote:The red S curve represents the positive control for amplification, the black S curve represents the positive control for nucleic acid extraction, and the four blue S curves represent the positive samples.
| 1 | AHMAD-MANSOUR N, LOUBET P, POUGET C, et al. Staphylococcus aureus toxins: an update on their pathogenic properties and potential treatments[J]. Toxins, 2021, 13(10):677. DOI: 10.3390/toxins13100677 . |
| 2 | HOWDEN B P, GIULIERI S G, WONG FOK LUNG T, et al. Staphylococcus aureus host interactions and adaptation[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2023, 21(6):380-395. DOI: 10.1038/s41579-023-00852-y . |
| 3 | TUON F F, SUSS P H, TELLES J P, et al. Antimicrobial treatment of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms[J]. Antibiotics (Basel), 2023, 12(1):87. DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics12010087 . |
| 4 | 国家市场监督管理总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 实验动物 微生物、寄生虫学等级及监测: GB 14922—2022[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2022. |
| State Administration for Market Regulation; Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Laboratory animals—Microbiological and parasitical standards and monitoring: GB 14922-2022[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2022. | |
| 5 | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会.实验动物微生物学检测方法: GB/T 14926—2001[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2022. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine; Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Laboratory animals—Microbiological examination methods: GB/T 14926-2001[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2001. | |
| 6 | 翟俊辉, 宋亚军, 杜宗敏, 等. 通用基因芯片检测感染性细菌方法的研究[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2003, 19(4): 430-431. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn: 1001-0580.2003.04.021 . |
| ZHAI J H, SONG Y J, DU Z M, et al. Study on universal microarray system for detection of common clinical infectious bacteria[J]. China J Public Health, 2003, 19(4): 430-431.DOI: 10.3321/j.issn: 1001-0580.2003.04.021 . | |
| 7 | STRAUB J A, HERTEL C, HAMMES W P. A 23S rDNA-targeted polymerase chain reaction-based system for detection of Staphylococcus aureus in meat starter cultures and dairy products[J]. J Food Prot, 1999, 62(10):1150-1156. DOI: 10.4315/0362-028x-62.10.1150 . |
| 8 | ONO H K, HIROSE S, NAITO I, et al. The emetic activity of staphylococcal enterotoxins, SEK, SEL, SEM, SEN and SEO in a small emetic animal model, the house musk shrew[J]. Microbiol Immunol, 2017, 61(1):12-16. DOI: 10.1111/1348-0421.12460 . |
| 9 | KRONING I S, IGLESIAS M A, MENDONÇA K S, et al. Presence of classical enterotoxin genes, agr typing, antimicrobial resistance, and genetic diversity of Staphylococcus aureus from milk of cows with mastitis in southern Brazil[J]. J Food Prot, 2018, 81(5):738-742. DOI: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-17-436 . |
| 10 | MATSUDA K, TSUJI H, ASAHARA T, et al. Sensitive quantitative detection of commensal bacteria by rRNA-targeted reverse transcription-PCR[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2007, 73(1):32-39. DOI: 10.1128/aem.01224-06 . |
| 11 | 王敏, 范婧, 李先平. PCR扩增法检测耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌的mecA基因[J]. 广东医学, 2008, 29(4):566-568. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9448.2008.04.015 . |
| WANG M, FAN J, LI X P. Detection of mecA gene in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by PCR amplification[J]. Guangdong Medical Journal, 2008, 29(4):566-568. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9448.2008.04.015 . | |
| 12 | 杨波. MecA基因聚合酶链反应扩增法与细菌鉴定仪法对耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌的鉴定比较及药敏分析[J]. 实用医技杂志, 2017, 24(2):141-142. DOI: 10.19522/j.cnki.1671-5098.2017.02.007 . |
| YANG B. Comparison and drug sensitivity analysis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by MecA gene polymerase chain reaction amplification method and bacterial identification instrument method[J]. Journal of Practical Medical Techniques, 2017, 24(2):141-142. DOI: 10.19522/j.cnki.1671-5098.2017.02.007 . | |
| 13 | FAOUZI, BEKKAOUI, . Rapid detection of the mecA gene in methicillin resistant staphylococci using a colorimetric cycling probe technology[J]. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis, 1999, 34(2):83-90. DOI: 10.1016/S0732-8893(99)00012-7 . |
| 14 | KOBAYASHI N, WU H, KOJIMA K, et al. Detection of mecA, femA, and femB genes in clinical strains of staphylococci using polymerase chain reaction[J]. Epidemiol Infect, 1994, 113(2):259-266. DOI: 10.1017/s0950268800051682 . |
| 15 | OU A F, WANG K, MAO Y X, et al. First report on the rapid detection and identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in viable but non-culturable (VBNC) under food storage conditions[J]. Front Microbiol, 2021, 11:615875. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.615875 . |
| 16 | SHOAIB M, AQIB A I, ALI M M, et al. Tracking infection and genetic divergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus at pets, pet owners, and environment interface[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2022, 9:900480. DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.900480 . |
| 17 | HENNEKINNE J A, DE BUYSER M L, DRAGACCI S. Staphylococcus aureus and its food poisoning toxins: characterization and outbreak investigation[J]. FEMS Microbiol Rev, 2012, 36(4):815-836. DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00311.x . |
| 18 | NADIYA S, KOLLA H B, REDDY P N. Optimization and evaluation of a multiplex PCR assay for detection of Staphylococcus aureus and its major virulence genes for assessing food safety[J]. Publ Braz Soc Microbiol, 2023, 54(1):311-321. DOI: 10.1007/s42770-023-00906-6 . |
| 19 | GONET M, KROWARSCH D, SCHUBERT J, et al. Stability and resistance to proteolysis of enterotoxins SEC and SEL produced by Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Foodborne Pathog Dis, 2023, 20(1):32-37. DOI: 10.1089/fpd.2022.0059 . |
| 20 | MORADIKIAN M, KOMIJANI M, SHAYESTEHFAR A. Detection of Staphylococcus aureus and their toxin genes inhabit on the scorpions surface[J]. Arch Microbiol, 2022, 204(9):576. DOI: 10.1007/s00203-022-03176-2 . |
| 21 | SU Y C, WONG A C. Identification and purification of a new staphylococcal enterotoxin, H[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1995, 61(4):1438-1443. DOI: 10.1128/aem.61.4.1438-1443.1995 . |
| 22 | MUNSON S H, TREMAINE M T, BETLEY M J, et al. Identification and characterization of staphylococcal enterotoxin types G and I from Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Infect Immun, 1998, 66(7):3337-3348. DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66. 7.3337-3348.1998 . |
| 23 | GERGOVA R, TSITOU V M, DIMOV S G, et al. Molecular epidemiology, virulence and antimicrobial resistance of Bulgarian methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates[J]. AMicr, 2022, 69(3):193-200. DOI: 10.1556/030.2022. 01766 . |
| 24 | TUCKER P W, HAZEN E E Jr, COTTON F A. Staphylococcal nuclease reviewed: a prototypic study in contemporary enzymology. I. Isolation; physical and enzymatic properties[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 1978, 22(2-3):67-77. DOI: 10.1007/BF00496235 . |
| 25 | BRAKSTAD O G, MÆLAND J A. Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Staphylococcus aureus thermonuclease[J]. APMIS, 1989, 97(1-6):166-174. DOI: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1989.tb00772.x . |
| 26 | KOVACEVIC S, VEAL L E, HSIUNG H M, et al. Secretion of staphylococcal nuclease by Bacillus subtilis [J]. J Bacteriol, 1985, 162(2):521-528. DOI: 10.1128/jb.162.2.521-528.1985 . |
| 27 | CHESNEAU O, ALLIGNET J, SOLH N EL. Thermonuclease gene as a target nucleotide sequence for specific recognition of Staphylococcus aureus [J]. Mol Cell Probes, 1993, 7(4):301-310. DOI: 10.1006/mcpr.1993.1044 . |
| 28 | MADISON B M, BASELSKI V S. Rapid identification of Staphylococcus aureus in blood cultures by thermonuclease testing[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 1983, 18(3):722-724. DOI: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.722-724.1983 . |
| 29 | CANNING B, MOHAMED I, WICKRAMASINGHE N, et al. Thermonuclease test accuracy is preserved in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates[J]. J Med Microbiol, 2020, 69(4):548-551. DOI: 10.1099/jmm.0.001166 . |
| 30 | 王纯, 张若鸿, 王晓芳, 等. 乳制品中金黄色葡萄球菌PCR快速检测方法的建立[J]. 核农学报, 2022, 36(6): 1193-1203. DOI: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2022.06.1193 . |
| WANG C, ZHANG R H, WANG X F, et al. Development of PCR rapid detection method for Staphylococcus aureus in dairy products[J]. J Nucl Agric Sci, 2022, 36(6): 1193-1203. DOI: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2022.06.1193 . | |
| 31 | DONG Q S, WANG Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, and staphylococcal toxin genes of blaTEM-1a-producing Staphylococcus aureus isolated from animals in Chongqing, China[J]. Vet Med Sci, 2023, 9(1):513-522. DOI: 10.1002/vms3.1028 . |
| 32 | BRAKSTAD O G, AASBAKK K, MAELAND J A. Detection of Staphylococcus aureus by polymerase chain reaction amplification of the nuc gene[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 1992, 30(7):1654-1660. DOI: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1654-1660.1992 . |
| 33 | 高正琴, 邢华, 李厚达. PCR技术在鼠金黄色葡萄球菌检测中的初步研究[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2002, 34(8):5-7. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-5130.2002.08.003 . |
| GAO Z Q, XING H, LI H D. The pilot study of polymerase chain reaction for detecting Staphylococcus aureus in rats and mice[J]. Animal Husb Vet Med, 2002, 34(8):5-7. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-5130.2002.08.003 . | |
| 34 | 王鹏飞. 实验动物金黄色葡萄球菌、绿脓杆菌和肺支原体多重PCR检测方法的建立与初步应用[D]. 石家庄:河北医科大学,2016. |
| WANG P F. The Establishment and preliminary applications of Multiple PCR for detecting Staphylococcus aureus,Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Mycoplasma pulmonis in Laboratory Animals[D]. SHIJIAZHUANG: Hebei Medical University, 2016. | |
| 35 | 陆文俊. 金黄色葡萄球菌特异性靶点的筛选与PCR快速检测方法的建立[D]. 南京:南京农业大学, 2017. |
| LU W J. The screening of specific target for Staphylococcus aureus and establishment of rapid PCR detection method[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agriculture University. 2017. |
| [1] | 贡磊磊, 王晓霞, 封学伟, 李心蕾, 赵涵, 张雪艳, 冯欣. 不同浓度环磷酰胺诱导早发性卵巢功能不全小鼠模型及作用机制研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 403-410. |
| [2] | 姜娟, 宋宁, 连文博, 邵丛丛, 顾文文, 石燕. 两种浓度乙醇溶液灌注建立小鼠宫腔粘连模型的组织病理和分子病理表型比较[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 393-402. |
| [3] | 刘月琴, 薛卫国, 王淑友, 申耀华, 贾术永, 王广军, 宋晓晶. 探头式激光共聚焦成像技术用于小鼠消化道组织形态特征分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 457-465. |
| [4] | 秦超, 李双星, 赵婷婷, 蒋晨晨, 赵晶, 杨艳伟, 林志, 王三龙, 文海若. 药物安全评价用SD大鼠90 d喂养试验的背景数据研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 439-448. |
| [5] | 刘力瑜, 嵇波, 刘小玄, 方洋, 张玲, 郭亭廷, 全烨, 李鹤文, 刘翼天. 大鼠胎儿期肺组织固定方法的探索[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 432-438. |
| [6] | 肖林林, 杨逸萱, 黎珊杉, 罗兰诗雨, 尹思威, 孙俊铭, 施维, 欧阳轶强, 李习艺. 利用脑立体定位技术将人源三突变APP基因导入海马区构建阿尔茨海默病大鼠模型[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 269-278. |
| [7] | 罗莲莲, 袁艳春, 王俊岭, 时广森. 肌萎缩侧索硬化症小鼠模型研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 290-299. |
| [8] | 姜萌, 郝淑兰, 仝立国, 仲启明, 高振飞, 王永辉, 王晞星, 吉海杰. 长春瑞滨诱导大鼠足背静脉炎模型的动态评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 251-258. |
| [9] | 孔志豪, 魏晓锋, 于灵芝, 冯丽萍, 朱琦, 施国君, 王晨. 鳞状皮屑裸小鼠木糖葡萄球菌的分离鉴定[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 368-375. |
| [10] | 潘颐聪, 蒋汶洪, 胡明, 覃晓. 慢性肾脏病大鼠主动脉钙化模型的术式优化及效果评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 279-289. |
| [11] | 刘智伟, 杨然, 连浩, 张玉, 金立伦. 秦皮素对碘乙酸钠诱导骨关节炎模型大鼠的软骨保护与抗炎作用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 259-268. |
| [12] | 许秋雨, 严国锋, 付丽, 范文华, 周晶, 朱莲, 仇淑雯, 张洁, 吴铃. 来曲唑缓释片皮下给药构建小鼠多囊卵巢综合征模型及其肝脏转录组学分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 119-129. |
| [13] | 潘钱家, 葛峻沂, 胡楠, 华飞, 顾敏. 基于16S rRNA测序的2型糖尿病db/db小鼠模型口腔菌群差异分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 147-157. |
| [14] | 连辉, 姜艳玲, 刘佳, 张玉立, 谢伟, 薛晓鸥, 李健. 异常子宫出血大鼠模型的构建与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 130-146. |
| [15] | 吴志浩, 曹舒扬, 周正宇. 肝螺杆菌感染引起VDR-/-小鼠炎性肠病相关肠纤维化模型的建立及机制探讨[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(1): 37-46. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||