













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 475-486.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.038
涂颖欣1( ), 纪依澜1(
), 纪依澜1( ), 王菲2(
), 王菲2( ), 杨东明1, 王冬冬1, 孙芷馨1, 戴悦欣1, 王言吉2, 阚广捍2, 吴斌2, 赵德明1, 杨利峰1(
), 杨东明1, 王冬冬1, 孙芷馨1, 戴悦欣1, 王言吉2, 阚广捍2, 吴斌2, 赵德明1, 杨利峰1( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-05
修回日期:2024-07-02
出版日期:2024-10-25
发布日期:2024-10-25
通讯作者:
杨利峰(1980—),女,博士,教授,博士生导师,主要从事基础兽医学研究。E-mail: yanglf@cau.edu.cn。ORCID: 0000-0001-5175-7589作者简介:涂颖欣(1999—),女,硕士,研究实习员,研究方向:兽医病理学。E-mail: novatu@163.com;
纪依澜(1997—),女,硕士,研究方向:兽医病理学。E-mail: jyl599@sina.com;
王 菲(1988—),女,硕士,助理研究员,研究方向:航空航天实施医学。E-mail:182211493@qq.com
基金资助:
TU Yingxin1( ), JI Yilan1(
), JI Yilan1( ), WANG Fei2(
), WANG Fei2( ), YANG Dongming1, WANG Dongdong1, SUN Zhixin1, DAI Yuexin1, WANG Yanji2, KAN Guanghan2, WU Bin2, ZHAO Deming1, YANG Lifeng1(
), YANG Dongming1, WANG Dongdong1, SUN Zhixin1, DAI Yuexin1, WANG Yanji2, KAN Guanghan2, WU Bin2, ZHAO Deming1, YANG Lifeng1( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-03-05
Revised:2024-07-02
Published:2024-10-25
Online:2024-10-25
Contact:
YANG Lifeng (ORCID: 0000-0001-5175-7589), E-mail: yanglf@cau.edu.cn摘要:
目的 利用小型猪多个系统组织结构和功能接近于人类的特性,建立模拟失重动物模型,观察其病理生理学变化,为航空航天失重环境研究提供新方法。 方法 选取9头普通级小型猪,随机分为实验组(n=7)和对照组(n=2)。实验组小型猪使用定制金属笼固定,帆布吊带悬挂使其后肢离地去负荷,身体与地面呈-20°角,模拟失重30 d(每天24 h)。通过采集不同时间点各组小型猪的体重、血容量、血生化指标等数据,对其基础体征的变化进行统计分析。实验结束后,对小型猪实施安乐死并解剖取材,对心血管、骨骼、骨骼肌等各系统组织脏器进行HE、Masson染色后的组织病理学观察,并对各动脉血管厚度、骨骼肌肌纤维直径进行统计分析。同时,采用蛋白质免疫印迹法检测骨骼肌肌肉萎缩蛋白包括肌环指蛋白1(muscle-specific RING finger protein 1,MuRf-1)和肌萎缩素1(muscle atrophy F-box,MAFbx,又称Atrogin-1)的表达量,并采用免疫组织化学染色法检测脑内星形胶质细胞激活相关蛋白即胶质纤维酸性蛋白(glial fibrillary acidic protein,GFAP)的表达量,以反映各系统的病理生理学功能变化。 结果 后肢去负荷造模后,实验组小型猪体重显著下降(P<0.001),血容量也显著下降(P<0.01)。实验期间,实验组小型猪的血红蛋白、红细胞比容和红细胞计数水平显著降低(P<0.05),随后逐渐恢复;丙氨酸氨基转移酶和γ-谷氨酰转移酶表达水平呈现先下降(P<0.05)后回升的趋势,白蛋白水平显著下降(P<0.001),球蛋白水平显著上升(P<0.01),肌酐水平显著下降(P<0.05)。实验组小型猪腓肠肌的平均肌纤维直径显著缩短(P<0.05),肌纤维直径分布左移,小直径肌纤维增多;同时腓肠肌、椎旁肌肉Atrogin-1的表达水平显著增加(P<0.05)。这些变化与航天失重对人和动物的影响基本一致。此外,实验组小型猪的脑皮质顶叶、额叶和海马区域部分神经元变性,小脑区域浦肯野细胞数量轻度减少,而海马区的GFAP阳性信号显著增强(P<0.05)。 结论 -20°角后肢去负荷30 d的小型猪可作为一种新的模拟失重动物模型,用于航空航天领域相关研究。
中图分类号:
涂颖欣,纪依澜,王菲,等. 小型猪后肢去负荷模拟失重模型的建立与组织损伤研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 475-486. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.038.
TU Yingxin,JI Yilan,WANG Fei,et al. Evaluation of Simulated Weightlessness Model of Hindlimb Unloading Miniature Pigs and Their Tissue Damage[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 475-486. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.038.
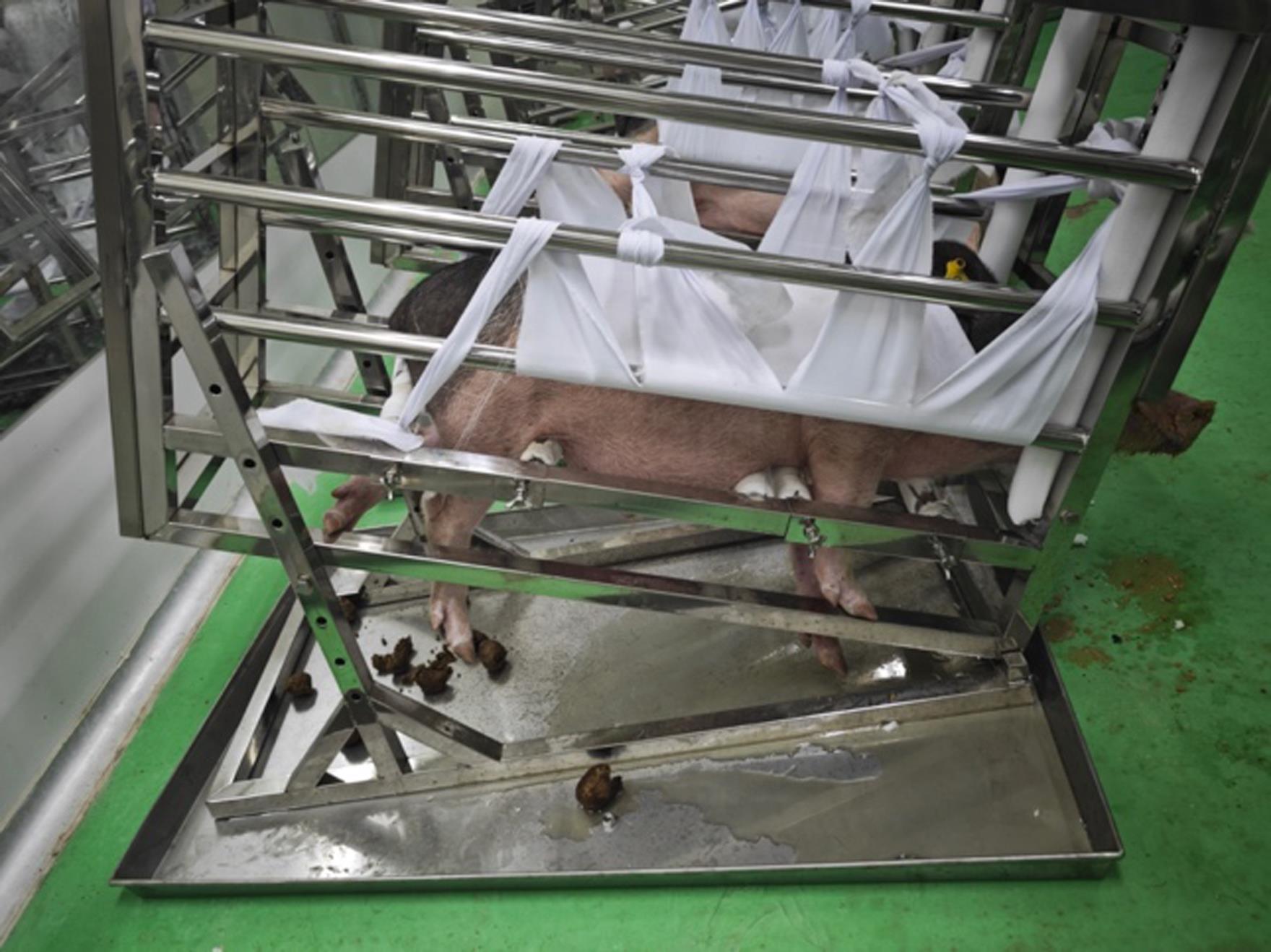

图1 后肢去负荷模拟失重实验中用定制金属笼固定实验组小型猪
Figure 1 Experimental group miniature pigs fixed in a customized metal cage for hindlimb unloading simulated weightlessness experiment
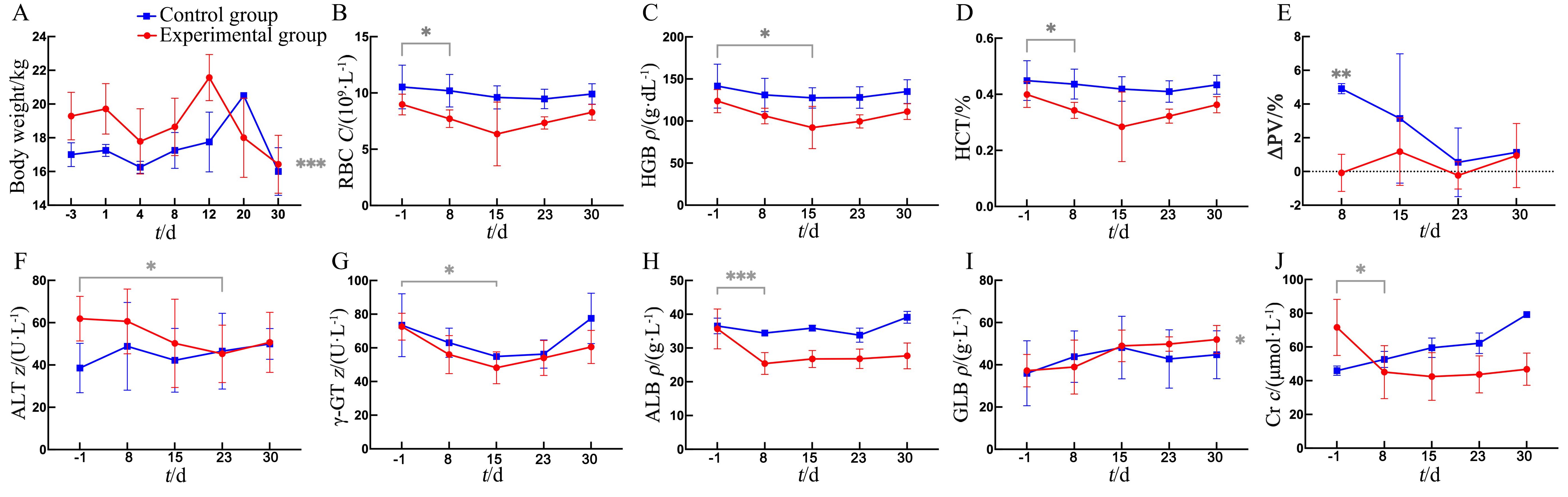
图 2 后肢去负荷模拟失重实验期间实验组和对照组小型猪的部分基础体征指标变化注:实验组小型猪(n=7)使用定制金属笼固定,并用帆布吊带悬挂,使其后肢离地去负荷,身体与地面呈-20°角。对照组小型猪(n=2)使用金属笼中饲养而不悬挂固定。A,体重变化(***实验期间实验组体重变化与对照组相比具有显著差异);B,血液红细胞(RBC)计数变化;C,血液血红蛋白(HGB)变化;D,血液红细胞比容(HCT)变化;E,血容量的变化(△PV为血浆容量变化量,**实验第8天的实验组△PV与对照组相比具有显著差异);F,血清丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)变化;G,血清γ-谷氨酰转移酶(γ-GT)变化;H,血清白蛋白(ALB)变化;I,血清球蛋白(GLB)变化;J,肌酐(Cr)变化。*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001。
Figure 2 Changes in selected basic physical indicators of miniature pigs in the experimental and control groups during hindlimb unloading simulated weightlessness experimentNote:Miniature pigs in the experimental group (n=7) were immobilized using customized metal cages and suspended from canvas slings so that their hind limbs were off the ground to unload and their bodies were at a -20° angle to the ground. Control group miniature pigs (n=2) were housed in metal cages without suspension immobilization. A, Changes in body weight during the experiment (*** the body weight change of the experimental group is significantly different from the control group); B, Changes in red blood cell count (RBC) during the experiment; C, Changes in hemoglobin(HGB) during the experiment; D, Changes in hematocrit (HCT) during the experiment; E, Changes in plasma volume change (△PV) during the experiment (** the ΔPV of experimental group is significantly higher than the control group at the 8th day); F, Changes in serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) during the experiment; G, Changes in serum γ-glutamyl transferase (γ-GT) during the experiment; H, Changes in serum albumin (ALB) during the experiment; I, Changes in serum globulin (GLB) during the experiment; J, Changes in creatinine (Cr) during the experiment. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
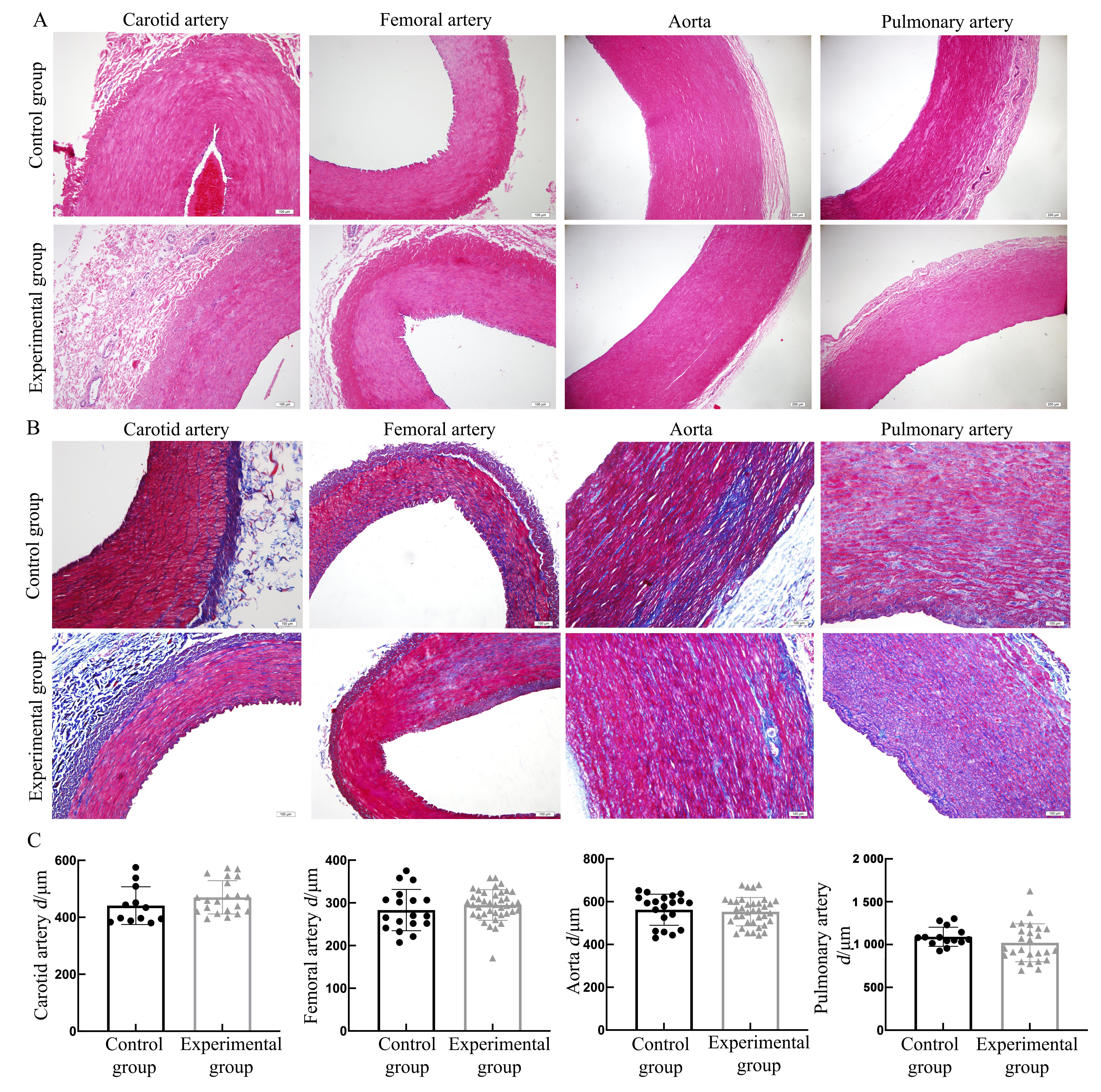
图3 后肢去负荷模拟失重实验结束后小型猪动脉血管组织病理学及厚度变化注:实验组小型猪(n=7)使用定制金属笼固定,并用帆布吊带悬挂,使其后肢离地去负荷,身体与地面呈-20°角。对照组小型猪(n=2)使用金属笼中饲养而不悬挂固定。A,各动脉血管的HE染色图(比例尺大小为100 μm);B,各动脉血管的Masson染色图(比例尺大小为100 μm);C,各动脉血管内-中膜厚度的统计分析结果。
Figure 3 Histopathology and thickness changes of arterial blood vessels in miniature pigs after the hindlimb unloading simulated weightlessness experimentNote:Miniature pigs in the experimental group (n=7) were immobilized using customized metal cages and suspended from canvas slings so that their hind limbs were off the ground to unload and their bodies were at a -20° angle to the ground. Control group miniature pigs (n=2) were housed in metal cages without suspension immobilization. A, HE staining of each artery (the scale size is 100 μm); B, Masson staining of each artery (the scale size is 100 μm); C, Statistical analysis of intima-media thickness in each artery.

图4 后肢去负荷模拟失重实验结束后小型猪骨骼肌结构和肌纤维直径变化注:实验组小型猪(n=7)使用定制金属笼固定,并用帆布吊带悬挂,使其后肢离地去负荷,身体与地面呈-20°角。对照组小型猪(n=2)使用金属笼中饲养而不悬挂固定。A、B、C,分别是各骨骼肌组织(腓肠肌、比目鱼肌、椎旁肌肉和前肢肌肉)的HE染色图(低倍镜及高倍镜视野下比例尺大小分别为100 μm和20 μm)、肌纤维直径统计图和肌纤维直径分布图。*P<0.05。
Figure 4 Changes in skeletal muscle structure and muscle fiber diameter of miniature pigs after the hindlimb unloading simulated weightlessness experimentNote:Miniature pigs in the experimental group (n=7) were immobilized using customized metal cages and suspended from canvas slings so that their hind limbs were off the ground to unload and their bodies were at a -20° angle to the ground. Control group miniature pigs (n=2) were housed in metal cages without suspension immobilization. Figures A, B, and C represent the HE staining images (the scale size is 100 μm or 20 μm by low and high magnification) , the statistical chart of muscle fiber diameters, and the distribution chart of muscle fiber diameters for various skeletal muscle tissues (gastrocnemius muscle, soleus muscle, paravertebral muscle, and forelimb muscle),respectively. *P<0.05.
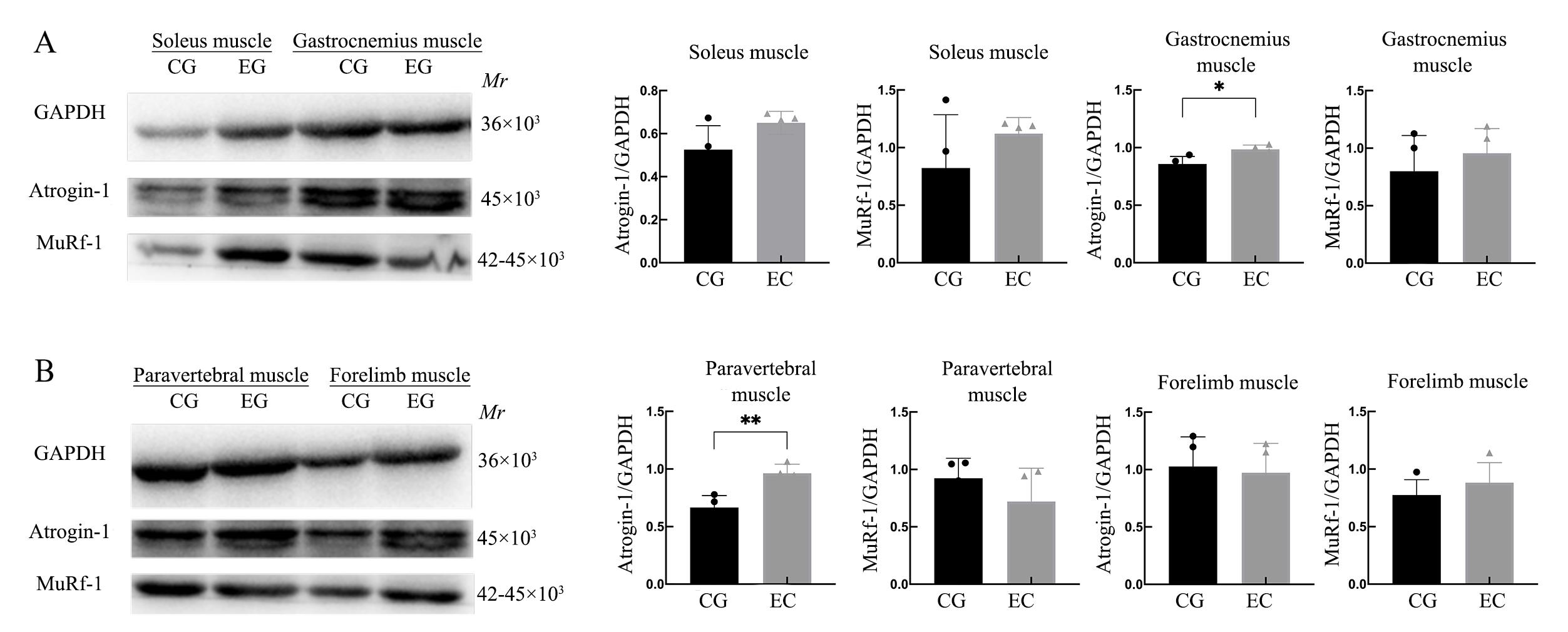
图5 后肢去负荷模拟失重实验结束后小型猪的肌肉萎缩相关蛋白表达量变化注:实验组小型猪(n=7)使用定制金属笼固定,并用帆布吊带悬挂,使其后肢离地去负荷,身体与地面呈-20°角。对照组小型猪(n=2)使用金属笼中饲养而不悬挂固定。A,蛋白质印迹法检测比目鱼肌和腓肠肌中MuRf-1和Atrogin-1的表达量;B, 蛋白质印迹法检测椎旁肌肉和前肢肌肉中MuRf-1和Atrogin-1的表达量。*P<0.05,**P<0.01。
Figure 5 Changes in expression levels of muscle atrophy proteins MuRf-1 and Atrogin-1 in miniature pigs after the hindlimb unloading simulated weightlessness experimentNote:Miniature pigs in the experimental group (n=7) were immobilized using customized metal cages and suspended from canvas slings so that their hind limbs were off the ground to unload and their bodies were at a -20° angle to the ground. Control group miniature pigs (n=2) were housed in metal cages without suspension immobilization. A, Expression levels of MuRf-1 and Atrogin-1 in soleus muscle and gastrocnemius muscle detected using western blotting; B, Expression levels of MuRf-1 and Atrogin-1 in paravertebral muscle and forelimb muscle detected using western blotting. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.

图6 后肢去负荷模拟失重实验结束后小型猪各脑区的组织病理学及相关蛋白表达变化注:实验组小型猪(n=7)使用定制金属笼固定,并用帆布吊带悬挂,使其后肢离地去负荷,身体与地面呈-20°角。对照组小型猪(n=2)使用金属笼中饲养而不悬挂固定。A,各脑区的HE染色(比例尺大小为20 μm),箭头示变性的神经元;B,各脑区神经胶质原纤维酸性蛋白(GFAP)免疫组织化学染色结果(比例尺大小为50 μm);C,各脑区GFAP表达定量分析(IOD,累积光密度)。**P<0.01。
Figure 6 Changes in histopathology and related protein expression in each brain region of miniature pigs after the hindlimb unloading simulated weightlessness experimentNote:Miniature pigs in the experimental group (n=7) were immobilized using customized metal cages and suspended from canvas slings so that their hind limbs were off the ground to unload and their bodies were at a -20° angle to the ground. Control group miniature pigs (n=2) were housed in metal cages without suspension immobilization. A, HE staining of each brain region (the scale size is 20 μm), the arrow indicates the degenerating neuron; B, Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunohistochemistry staining of each brain region (the scale size is 50 μm); C, Quantitative analysis of GFAP expression in each brain region (IOD, integrated optical density).**P<0.01.
| 1 | ZÉRATH E, GRYNPAS M, HOLY X, et al. Spaceflight affects bone formation in rhesus monkeys: a histological and cell culture study[J]. J Appl Physiol, 2002, 93(3):1047-1056. DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00610.2001 . |
| 2 | VICO L, CHAPPARD D, ALEXANDRE C, et al. Effects of weightlessness on bone mass and osteoclast number in pregnant rats after a five-day spaceflight (COSMOS 1514)[J]. Bone, 1987, 8(2):95-103. DOI: 10.1016/8756-3282(87)90077-9 . |
| 3 | MIU B, MARTIN T P, ROY R R, et al. Metabolic and morphologic properties of single muscle fibers in the rat after spaceflight, Cosmos 1887[J]. FASEB J, 1990, 4(1):64-72. DOI: 10.1096/fasebj.4.1.2136839 . |
| 4 | GOLDSTEIN M A, EDWARDS R J, SCHROETER J P. Cardiac morphology after conditions of microgravity during COSMOS 2044[J]. J Appl Physiol, 1992, 73(2 ):94S-100S. DOI: 10.1152/jappl.1992.73.2.S94 . |
| 5 | TISCHLER M E, HENRIKSEN E J, MUNOZ K A, et al. Spaceflight on STS-48 and earth-based unweighting produce similar effects on skeletal muscle of young rats[J]. J Appl Physiol, 1993, 74(5):2161-2165. DOI: 10.1152/jappl. 1993. 74. 5.2161 . |
| 6 | 刘焕, 茹凝玉, 吕强, 等. 中期及长期模拟失重对大鼠颈总动脉钙化的影响[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2021, 46(1):1-6. DOI: 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2021.01.01 . |
| LIU H, RU N Y, LV Q, et al. Mid-term and long-term simulated microgravity causes calcification of common carotid artery in rats[J]. Med J Chin People's Liberation Army, 2021, 46(1):1-6. DOI: 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2021.01.01 . | |
| 7 | 陈励, 张斌, 杨璐, 等. 模拟失重对大鼠动脉血压、心率昼夜节律的影响及其机制[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2016, 41(4):289-294. DOI: 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2016.04.06 . |
| CHEN L, ZHANG B, YANG L, et al. Effects of simulated microgravity on circadian rhythm of caudal arterial pressure and heart rate in rats and their underlying mechanism[J]. Med J Chin People's Liberation Army, 2016, 41(4):289-294. DOI: 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2016.04.06 . | |
| 8 | 高放, 程九华, 薛军辉, 等. 模拟失重致大鼠弹力型大动脉血管区域特异性重塑及其重力性对抗措施[J]. 生理学报, 2012, 64(1):14-26. DOI: 10.13294/j.aps.2012.01.002 . |
| GAO F, CHENG J H, XUE J H, et al. In-vivo and ex-vivo studies on region-specific remodeling of large elastic arteries due to simulated weightlessness and its prevention by gravity-based countermeasure[J]. Acta Physiol Sin, 2012, 64(1):14-26. DOI: 10.13294/j.aps.2012.01.002 . | |
| 9 | 孙喜庆, 王冰, 孙会品, 等. 间断性头高位对模拟失重兔动脉内皮素表达和组织形态的影响[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 2006, 19(4):265-268. DOI: 10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.2006.04.007 . |
| SUN X Q, WANG B, SUN H P, et al. Effects of intermittent head-up tilt on the endothelin expression and morphological changes of artery during simulated weightlessness in rabbits[J]. Space Med Med Eng, 2006, 19(4):265-268. DOI: 10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.2006.04.007 . | |
| 10 | 王晓平, 陆明, 马培, 等. 模拟失重对恒河猴腰椎运动单元生物力学的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(26):3843-3848. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.26.007 . |
| WANG X P, LU M, MA P, et al. Effects of simulated weightlessness on biomechanics of motion unit of rhesus monkey lumbar vertebra[J]. Chin J Tissue Eng Res, 2016, 20(26):3843-3848. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.26.007 . | |
| 11 | 曹新生, 付崇建, 杨连甲. 3周模拟失重对大鼠后肢骨生长代谢的影响[J]. 中华航空航天医学杂志, 2000, 11(4):221-224. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-6239.2000.04.007 . |
| CAO X S, FU C J, YANG L J. Effects of 3 week simulated weightlessness on the growth and metabolism of hindlimb bones in rats[J]. Chin J Aerosp Med, 2000, 11(4):221-224. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-6239.2000.04.007 . | |
| 12 | 付崇建, 郁冰冰, 杨连甲, 等. 尾悬吊大鼠骨和骨髓中骨钙素的变化[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 2003, 16(4):260-263. DOI: 10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.2003.04.007 . |
| FU C J, YU B B, YANG L J, et al. Changes of osteocalcin in bone and bone marrow in tail suspended rats[J]. Space Med Med Eng, 2003, 16(4):260-263. DOI: 10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.2003.04.007 . | |
| 13 | 赵赞延, 马宇, 张恒伟, 等. 模拟微重力效应下小鼠骨流失的性别差异[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2022, 15(2):182-188. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2591.2022.02.009 . |
| ZHAO Z Y, MA Y, ZHANG H W, et al. Gender differences in bone loss under microgravity effect in mice[J]. Chin J Osteoporos Bone Miner Res, 2022, 15(2):182-188. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2591.2022.02.009 . | |
| 14 | 刘书林, 姚永杰, 刘秋红, 等. 犬头低位后肢去负荷模拟失重模型的建立与验证[J]. 载人航天, 2021, 27(5):596-602. DOI: 10.16329/j.cnki.zrht.2021.05.009 . |
| LIU S L, YAO Y J, LIU Q H, et al. Establishment and validation of simulated weightlessness model of dog with head down hindlimb unloading[J]. Manned Spacefl, 2021, 27(5):596-602. DOI: 10.16329/j.cnki.zrht.2021.05.009 . | |
| 15 | 孙亚志, 黄丽昀, 张谦, 等. 尾吊大鼠骨骼肌线粒体钙、镁含量和体视学的变化[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 1998, 11(4): 298-300. DOI: 10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.1998.04.016 . |
| SUN Y Z, HUANG L Y, ZHANG Q, et al. Changes of calcium and magnesium contents and stereology in skeletal muscle mitochondria of tail-suspended rats[J]. Space Med Med Eng, 1998, 11(4): 298-300. DOI: 10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.1998.04.016 . | |
| 16 | 吴苏娣, 樊小力, 唐斌, 等. 模拟失重对大鼠比目鱼肌肌梭超微结构的影响[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 2002, 15(1):32-35. DOI: 10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.2002.01.007 . |
| WU S D, FAN X L, TANG B, et al. Effects of simulated weightlessness on ultrastructure of soleus muscle spindle in rats[J]. Space Med Med Eng, 2002, 15(1):32-35. DOI: 10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.2002.01.007 . | |
| 17 | 陈英, 杨春敏, 毛高平, 等. 模拟失重对大鼠小肠黏膜紧密连接蛋白表达的影响[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 2011, 24(5):327-331. DOI: 10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.2011.05.005 . |
| CHEN Y, YANG C M, MAO G P, et al. Impact of simulated weightlessness on expression of tight junction proteins of small intestine mucous membrane in rats[J]. Space Med Med Eng, 2011, 24(5):327-331. DOI: 10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.2011.05.005 . | |
| 18 | 武强强, 张学英, 王德华, 等. 模拟失重对啮齿动物情绪和认知的影响及缓解措施研究进展[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 2021, 34(2):183-188. DOI: 10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.2021.02.013 . |
| WU Q Q, ZHANG X Y, WANG D H, et al. Research progress in effects of simulated weightlessness on emotion and cognition of rodents and mitigating measures[J]. Space Med Med Eng, 2021, 34(2):183-188. DOI: 10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.2021.02.013 . | |
| 19 | BAQAI F P, GRIDLEY D S, SLATER J M, et al. Effects of spaceflight on innate immune function and antioxidant gene expression[J]. J Appl Physiol, 2009, 106(6):1935-1942. DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.91361.2008 . |
| 20 | 纪依澜, 赵德明, 王菲, 等. 模拟失重实验动物模型的建立与评价[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2023, 31(1):106-111. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2023.01.013 . |
| JI Y L, ZHAO D M, WANG F, et al. Establishment and evaluation of experimental animal models simulating weightlessness[J]. Acta Lab Animalis Sci Sin, 2023, 31(1):106-111. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2023.01.013 . | |
| 21 | 吴华莉, 涂尾龙, 曹建国, 等. 小型猪在人类疾病模型方面的研究进展[J]. 养猪, 2021(4):63-67. DOI: 10.13257/j.cnki.21-1104/s.2021.04.019 . |
| WU H L, TU W L, CAO J G, et al. Research progress of miniature pig in human disease models[J]. Swine Prod, 2021(4):63-67. DOI: 10.13257/j.cnki.21-1104/s.2021.04.019 . | |
| 22 | 谈诚, 李志利, 汪德生, 等. 四肢悬吊法对小型猪骨骼抗动态载荷功能的影响[C]//中国力学学会, 中国生物医学工程学会生物力学专业委员会. 第八届全国生物力学学术会议论文集. 上海: 医用生物力学, 2006: 160-161. |
| TAN C, LI Z L, WANG D S, et al. Effect of hindlimb suspension on the dynamic load-bearing capacity of miniature pig skeleton[C]//Chinese Society of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, Biomechanics Professional Committee of Chinese Society of Biomedical Engineering. Proceedings of the 8th National Conference on Biomechanics. Shanghai: Journal of Medical Biomechanics, 2006: 160-161. | |
| 23 | 杨超, 徐子涵, 李铠, 等. 头低位卧床对恒河猴骨代谢、糖脂代谢的抑制效应及其相关性分析[J]. 空间科学学报, 2020, 40(4):540-546. DOI: 10.11728/cjss2020.04.540 . |
| YANG C, XU Z H, LI K, et al. Inhibitory effects of head-down bed rest on bone, glycolipid metabolism of Rhesus and their correlation analysis[J]. Chin J Space Sci, 2020, 40(4):540-546. DOI: 10.11728/cjss2020.04.540 . | |
| 24 | MATOMÄKI P, KAINULAINEN H, KYRÖLÄINEN H. Corrected whole blood biomarkers - the equation of Dill and Costill revisited[J]. Physiol Rep, 2018, 6(12): e13749. DOI: 10.14814/phy2.13749 . |
| 25 | 李家卉, 李方方, 张敏, 等. 海马神经元退行性变参与模拟失重所致大鼠认知损伤[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 2021, 34(2):122-127. DOI: 10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.2021.02.005 . |
| LI J H, LI F F, ZHANG M, et al. Hippocampal neuronal degeneration involved in cognitive impairment induced by simulated weight-lessness in rats[J]. Space Med Med Eng, 2021, 34(2):122-127. DOI: 10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.2021.02.005 . |
| [1] | 刘亚益, 贾云凤, 左一鸣, 张军平, 吕仕超. 心气阴两虚证动物模型的构建方法与评价进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 411-421. |
| [2] | 赵鑫, 王晨曦, 石文清, 娄月芬. 斑马鱼在炎症性肠病机制及药物研究中的应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 422-431. |
| [3] | 李会萍, 高洪彬, 温金银, 杨锦淳. 疾病动物模型数字化图谱数据库平台的构建与初步应用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 300-308. |
| [4] | 潘颐聪, 蒋汶洪, 胡明, 覃晓. 慢性肾脏病大鼠主动脉钙化模型的术式优化及效果评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 279-289. |
| [5] | 王碧莹, 鲁家铄, 昝桂影, 陈若松, 柴景蕊, 刘景根, 王瑜珺. 啮齿类动物药物成瘾模型的构建方法和应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 158-166. |
| [6] | 陈钰涵, 陈瑾玲, 李欣, 区燕华, 王斯, 陈镜伊, 王兴易, 袁嘉丽, 段媛媛, 羊忠山, 牛海涛. 基于中西医临床病证特点的重症肌无力动物模型分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 176-186. |
| [7] | 连辉, 姜艳玲, 刘佳, 张玉立, 谢伟, 薛晓鸥, 李健. 异常子宫出血大鼠模型的构建与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 130-146. |
| [8] | 罗世雄, 张赛, 陈慧. 常见哮喘动物模型的建立方法与评价研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 167-175. |
| [9] | 费彬, 郭文科, 郭建平. 疝疾病动物模型研究及新型疝修补材料应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(1): 55-66. |
| [10] | 杨家豪, 丁纯蕾, 钱风华, 孙旗, 姜旭升, 陈雯, 沈梦雯. 脓毒症相关脏器损伤动物模型研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 636-644. |
| [11] | 孙效容, 苏丹, 贵文娟, 陈玥. 手术诱导大鼠中重度膝骨关节炎模型的建立与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 597-604. |
| [12] | 田芳, 潘滨, 史佳怡, 徐燕意, 李卫华. 大气细颗粒物PM2.5暴露动物模型建立方法及在生殖毒性研究中的应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 626-635. |
| [13] | 赵小娜, 王鹏, 叶茂青, 曲新凯. 应用Triacsin C构建新型高血糖肥胖小鼠心功能减退模型[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 605-612. |
| [14] | 黄冬妍, 吴建辉. 生殖毒理学研究动物模型的建立方法及应用评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 550-559. |
| [15] | 郑艺清, 邓亚胜, 范燕萍, 梁天薇, 黄慧, 刘永辉, 倪召兵, 林江. 基于数据挖掘的盆腔炎性疾病动物模型应用分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(4): 405-418. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||