













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 340-348.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.135
刘园园1,2, 辛文水2, 晁哲2, 曹宗喜1,2, 蔡艺菲3, 李强1,2, 李凌伟1,2, 刘光亮1,2,3( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-18
修回日期:2024-12-15
出版日期:2025-07-07
发布日期:2025-06-25
通讯作者:
刘光亮(1975—),男,博士,研究员,博士生导师,研究方向:猪消化道感染与黏膜免疫。E-mail:LiuGuangliang01@caas.cn。ORCID:0000-0001-8185-5749作者简介:刘园园(1996—),女,硕士研究生,研究方向:预防兽医学。E-mail:3125177841@qq.com
基金资助:
LIU Yuanyuan1,2, XIN Wenshui2, CHAO Zhe2, CAO Zongxi1,2, CAI Yifei3, LI Qiang1,2, LI Lingwei1,2, LIU Guangliang1,2,3( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-09-18
Revised:2024-12-15
Published:2025-06-25
Online:2025-07-07
Contact:
LIU Guangliang (ORCID: 0000-0001-8185-5749), E-mail: LiuGuangliang01@caas.cn摘要:
目的 获得五指山猪主要组织相容性复合体(major histocompatibility complex,MHC)Ⅱ类分子基因序列,并分析其遗传信息,探究五指山猪MHC的生物学功能。 方法 采集3头成年雄性五指山猪的脾脏样本,根据MHC Ⅱ类分子基因序列设计引物,采用RT-PCR法扩增五指山猪MHC Ⅱ类分子基因的编码序列,通过Sanger测序确定MHC Ⅱ类分子基因序列,利用生物信息学软件分析五指山猪MHC Ⅱ类分子基因的理化性质、系统进化关系、保守基序和结构域,以及染色体位置和共线性关系。 结果 共鉴定出8个五指山猪MHC Ⅱ类分子基因,分别为SLA-DRA、SLA-DQA、SLA-DQB、SLA-DRB、SLA-DOB、SLA-DMB、SLA-DMA和SLA-DOA。Sanger测序后确定MHC Ⅱ类分子基因序列,并将序列上传至GenBank获得登录号,分别为PQ182796、PQ182797、PQ182798、PQ182799、PQ182800、PQ182801、PQ182802和PQ164779。系统进化树分析表明,五指山猪6个MHCⅡ类分子基因与杜洛克猪、梅山猪、大白猪和巴马猪等不同品种猪的MHC Ⅱ类分子基因不在同一个分支上。生物信息学分析表明,MHC Ⅱ类分子大部分为疏水性蛋白,其相对分子质量为27 700 ~ 30 000,归于同一亚区的基因含有相似的保守基序,其中SLA-DQB、SLA-DRB、SLA-DOB和SLA-DMB基因编码的4个MHC Ⅱ类分子包含MHC Ⅱβ保守结构域,SLA-DRA、SLA-DQA、SLA-DMA和SLA-DOA基因编码的4个MHC Ⅱ类分子包含MHC Ⅱɑ保守结构域。8个MHC Ⅱ类分子基因散在分布于五指山猪的7号染色体长臂上,与人的3个基因之间具有共线性关系,而与杜洛克猪的5个基因之间呈现共线性关系。 结论 五指山猪的MHC Ⅱ类分子基因可能具有特殊的遗传学起源。
中图分类号:
刘园园,辛文水,晁哲,等. 五指山猪MHCⅡ类分子基因鉴定与分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 340-348. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.135.
LIU Yuanyuan,XIN Wenshui,CHAO Zhe,et al. Identification and Analysis of MHCⅡ Genes in Wuzhishan Pigs[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 340-348. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.135.
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5' to 3') Primer sequence(5' to 3') | 扩增片段长度/bp Amplicon size /bp | 退火温度/℃ Annealing temperature/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLA-DRA-F | GCTTGTATTGCTGTCCATCC | 851 | 55 |
| SLA-DRA-R | CAAAGTCCATTCCCTGCAAG | ||
| SLA-DQA-F | ATGGTCCCAGGCCGAGTT | 768 | 55 |
| SLA-DQA-R | TCACAAGGACCCTTGGTGTC | ||
| SLA-DQB-F | CCATTACTTCTTCGTTTGCCC | 995 | 55 |
| SLA-DQB-R | GAAGAAGCTTCACAGCCAGAG | ||
| SLA-DRB-F | CACACTGTCCTCTCCTGTTC | 886 | 58 |
| SLA-DRB-R | CTCATGCTGTGAAGACGCTG | ||
| SLA-DOB-F | CCTCATTTTCTTTTTCCCCCTCC | 926 | 55 |
| SLA-DOB-R | GGAATCATCCAGAACATCGACC | ||
| SLA-DMB-F | CCGCTCAGTGTTTGGAGAT | 967 | 55 |
| SLA-DMB-R | CCATACGAGACCAAATTGCC | ||
| SLA-DMA-F | GGACCTGGGTTAGCTAGTTAG | 1 028 | 55 |
| SLA-DMA-R | ACATGGCAGTGATGTCGTAGG | ||
| SLA-DOA-F | GGTTAAAACACCAGAGGGCC | 807 | 55 |
| SLA-DOA-R | GTCTCTCTCACATCCCAGCC |
表 1 主要组织相容性复合体基因的PCR扩增引物信息
Table 1 Information on PCR primers for amplification of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes
引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5' to 3') Primer sequence(5' to 3') | 扩增片段长度/bp Amplicon size /bp | 退火温度/℃ Annealing temperature/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLA-DRA-F | GCTTGTATTGCTGTCCATCC | 851 | 55 |
| SLA-DRA-R | CAAAGTCCATTCCCTGCAAG | ||
| SLA-DQA-F | ATGGTCCCAGGCCGAGTT | 768 | 55 |
| SLA-DQA-R | TCACAAGGACCCTTGGTGTC | ||
| SLA-DQB-F | CCATTACTTCTTCGTTTGCCC | 995 | 55 |
| SLA-DQB-R | GAAGAAGCTTCACAGCCAGAG | ||
| SLA-DRB-F | CACACTGTCCTCTCCTGTTC | 886 | 58 |
| SLA-DRB-R | CTCATGCTGTGAAGACGCTG | ||
| SLA-DOB-F | CCTCATTTTCTTTTTCCCCCTCC | 926 | 55 |
| SLA-DOB-R | GGAATCATCCAGAACATCGACC | ||
| SLA-DMB-F | CCGCTCAGTGTTTGGAGAT | 967 | 55 |
| SLA-DMB-R | CCATACGAGACCAAATTGCC | ||
| SLA-DMA-F | GGACCTGGGTTAGCTAGTTAG | 1 028 | 55 |
| SLA-DMA-R | ACATGGCAGTGATGTCGTAGG | ||
| SLA-DOA-F | GGTTAAAACACCAGAGGGCC | 807 | 55 |
| SLA-DOA-R | GTCTCTCTCACATCCCAGCC |
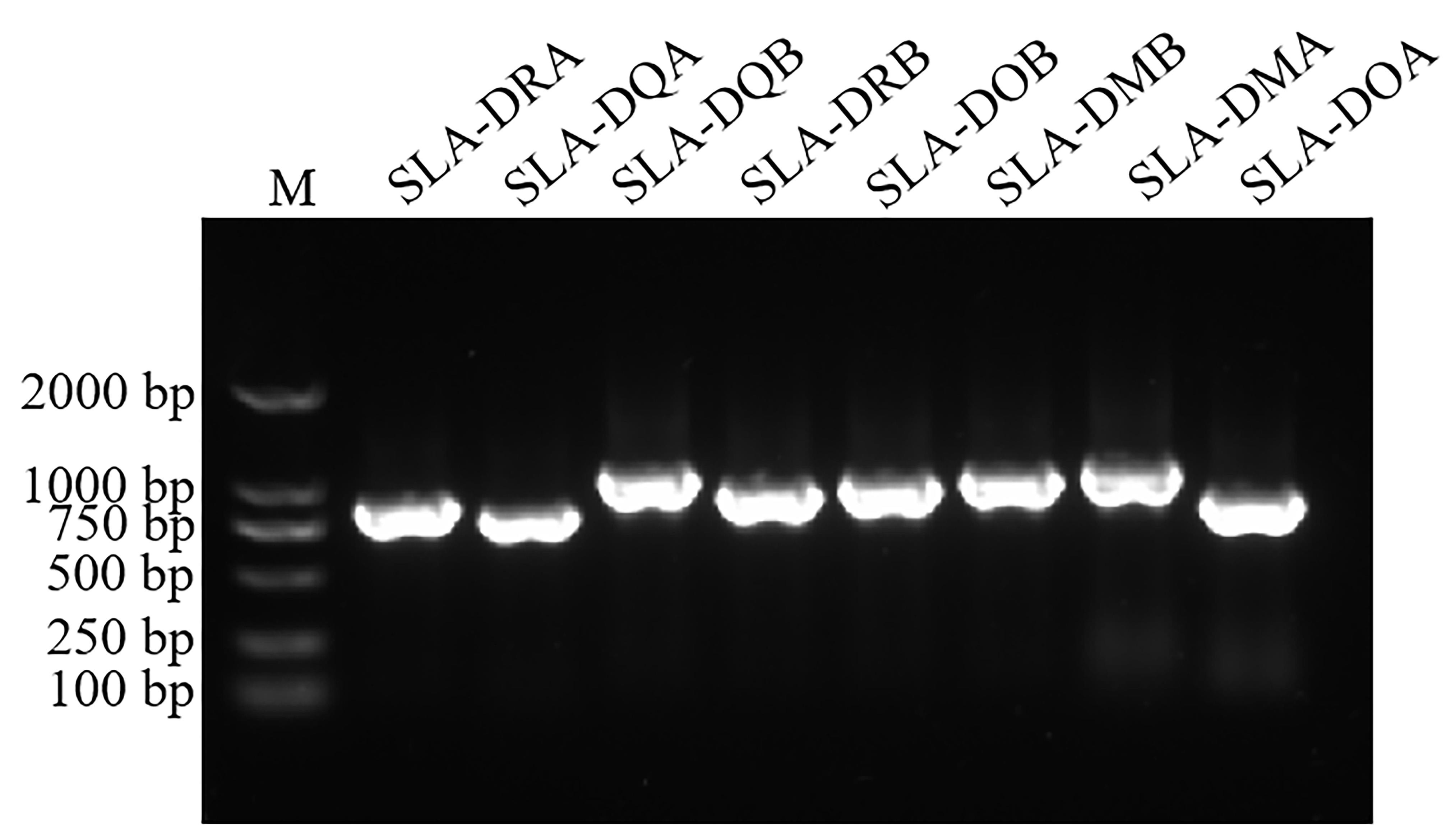
图 1 五指山猪脾脏组织中MHC Ⅱ类分子基因的PCR结果注:SLA,猪白细胞抗原,也称主要组织相容性复合体。M,DNA分子量标准2000。
Figure 1 PCR results of MHCⅡ genes in spleen tissues of Wuzhishan pigsNote: SLA refers to the swine leukocyte antigen [also named as major histocompatibility complex(MHC)]. M denotes the DNA molecular weight marker (2000 bp ladder).
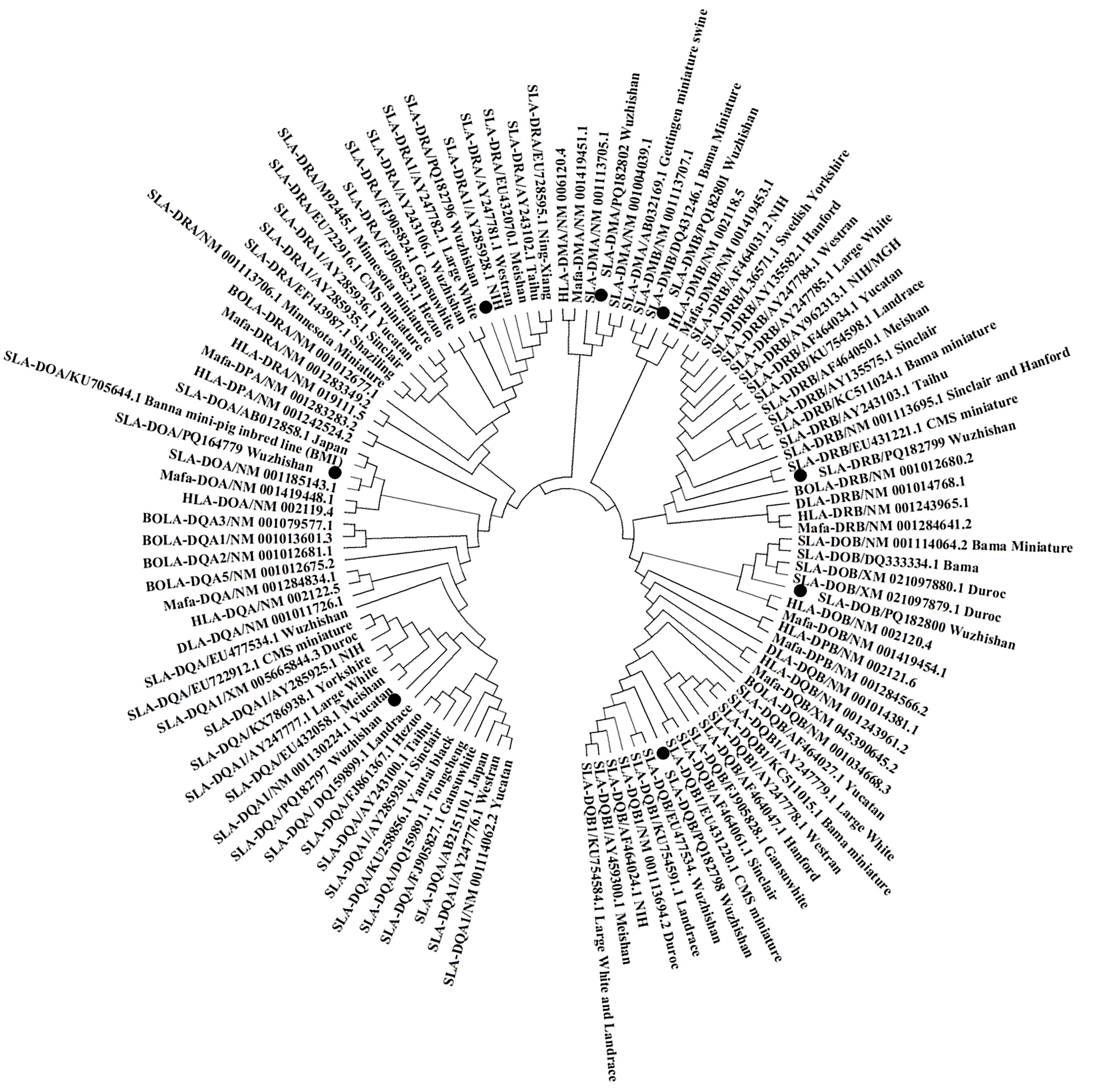

图 2 五指山猪MHC Ⅱ类分子基因的系统进化树分析注:SLA,猪白细胞抗原,也称主要组织相容性复合体。
Figure 2 Phylogenetic tree analysis of MHCⅡ genes in Wuzhishan pigsNote: SLA refers to the swine leukocyte antigen [also named as major histocompatibility complex (MHC)].
基因ID Gene ID | 染色体定位 Chromosomal localization | 氨基酸长度/aa Amino acid length/aa | 相对分子质量,×103 Relative molecular mass, ×103 | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 亲水性平均系数 Grade average of hydropathicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLA-DRA | Chr07 | 252 | 28.4 | 5.03 | 0.029 |
| SLA-DQA | Chr07 | 255 | 28.2 | 5.53 | 0.007 |
| SLA-DQB | Chr07 | 261 | 29.5 | 6.97 | -0.222 |
| SLA-DRB | Chr07 | 266 | 30.0 | 8.59 | -0.135 |
| SLA-DOB | Chr07 | 264 | 29.8 | 5.32 | 0.024 |
| SLA-DMB | Chr07 | 272 | 29.8 | 5.69 | 0.027 |
| SLA-DMA | Chr07 | 260 | 28.9 | 4.69 | 0.152 |
| SLA-DOA | Chr07 | 250 | 27.7 | 6.18 | 0.016 |
表 2 五指山猪MHC Ⅱ类分子的理化性质分析
Table 2 Physicochemical property analysis of MHC Ⅱ molecules in Wuzhishan pigs
基因ID Gene ID | 染色体定位 Chromosomal localization | 氨基酸长度/aa Amino acid length/aa | 相对分子质量,×103 Relative molecular mass, ×103 | 等电点 Isoelectric point | 亲水性平均系数 Grade average of hydropathicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLA-DRA | Chr07 | 252 | 28.4 | 5.03 | 0.029 |
| SLA-DQA | Chr07 | 255 | 28.2 | 5.53 | 0.007 |
| SLA-DQB | Chr07 | 261 | 29.5 | 6.97 | -0.222 |
| SLA-DRB | Chr07 | 266 | 30.0 | 8.59 | -0.135 |
| SLA-DOB | Chr07 | 264 | 29.8 | 5.32 | 0.024 |
| SLA-DMB | Chr07 | 272 | 29.8 | 5.69 | 0.027 |
| SLA-DMA | Chr07 | 260 | 28.9 | 4.69 | 0.152 |
| SLA-DOA | Chr07 | 250 | 27.7 | 6.18 | 0.016 |
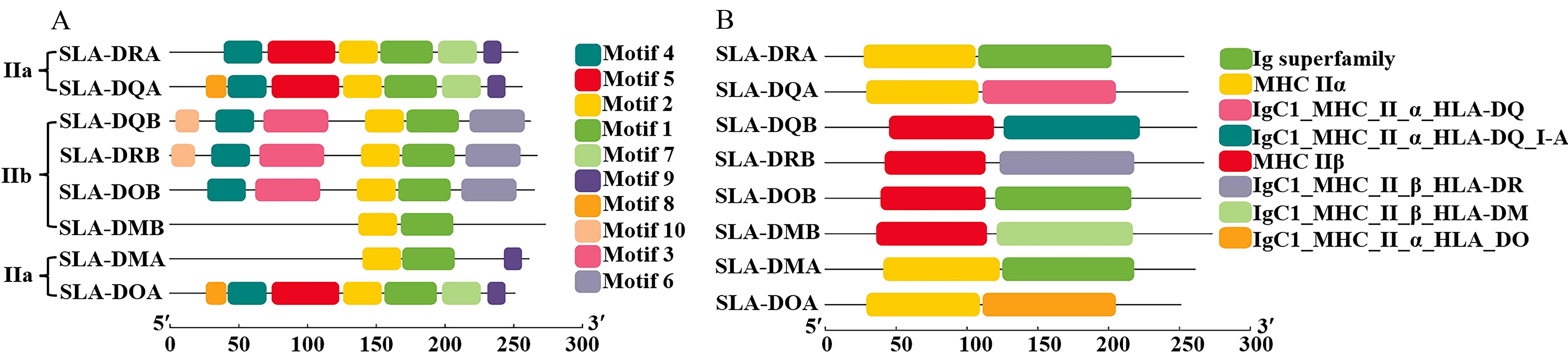
图 3 五指山猪MHC Ⅱ类分子的保守基序(A)和保守结构域(B)分析注:不同颜色的方框代表了不同的保守基序或保守结构域;横坐标为MHCⅡ类分子的氨基酸长度。SLA,猪白细胞抗原,也称主要组织相容性复合体。
Figure 3 Analysis of conserved motifs (A) and structural domains (B) of MHCⅡ molecules in Wuzhishan pigsNote: Colored boxes represent different conserved motifs or conserved domains. The x-axis denotes the amino acid length of MHC Ⅱ molecules. SLA refers to the swine leukocyte antigen [also named as major histocompatibility complex (MHC)].
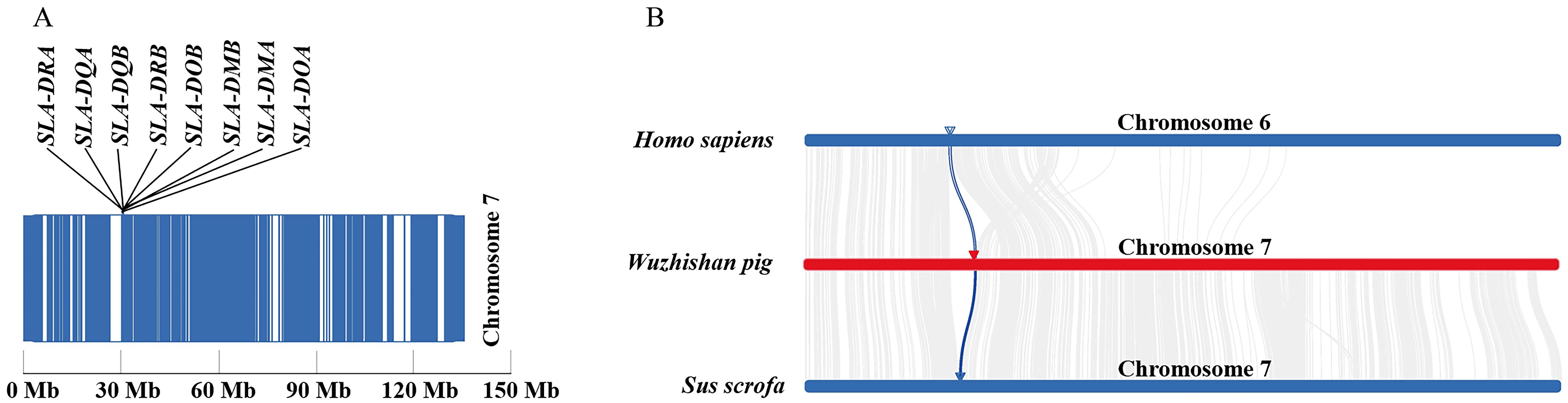
图 4 MHC Ⅱ类分子基因在五指山猪7号染色体上的分布(A)和五指山猪与人及杜洛克猪的MHC Ⅱ类分子基因共线性分析(B)注:人类基因组组装GRCh38.p12;杜洛克猪基因组组装Sscrofa11.1;具有共线性的MHC Ⅱ类分子基因为蓝色线条,具有共线性的其他基因为灰色线条。SLA,猪白细胞抗原,也称主要组织相容性复合体。
Figure 4 Chromosomal localization of MHCⅡ genes on chromosome 7 in Wuzhishan pigs(A)and syntenic relationship analysis of MHCⅡ genes between Wuzhishan pigs, Homo sapiens and Sus scrofa(B)Note: The human genome assembly used is GRCh38.p12; the Duroc pig genome assembly used is Sscrofa11.1. Genes exhibiting syntenic relationships with MHC class II molecules are depicted as blue lines, while other syntenic genes are represented by gray lines. SLA refers to the swine leukocyte antigen [also named as major histocompatibility complex (MHC)].
| [1] | SWINDLE M M, MAKIN A, HERRON A J, et al. Swine as models in biomedical research and toxicology testing[J]. Vet Pathol, 2012, 49(2):344-356. DOI:10.1177/0300985811402846 . |
| [2] | 兰宗宝, 王修文, 许惠艳. 猪器官异种移植研究进展[J]. 广西农业科学, 2008, 39(3):380-384. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2008.03.030 . |
| LAN Z B, WANG X W, XU H Y. Progress of porcine organs xenotransplantation[J]. Guangxi Agric Sci, 2008, 39(3):380-384. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2008.03.030 . | |
| [3] | CARRIER A N, VERMA A, MOHIUDDIN M, et al. Xenotransplantation: a new era[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 900594. DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2022.900594 . |
| [4] | PROSSER A, HUANG W H, LIU L, et al. Dynamic changes to tissue-resident immunity after MHC-matched and MHC-mismatched solid organ transplantation[J]. Cell Rep, 2021, 35(7):109141. DOI:10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109141 . |
| [5] | 冯书堂, 戴一凡, 章金刚, 等. 五指山小型猪近交系异种移植产业化研发进展[J]. 器官移植, 2018, 9(6):469-473. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2018.06.014 . |
| FENG S T, DAI Y F, ZHANG J G, et al. The progress of xenograft industrialization on Wuzhishan miniature pig inbred line[J]. Organ Transplant, 2018, 9(6):469-473. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2018.06.014 . | |
| [6] | 晁哲, 李娇伦, 秦烨, 等. 五指山猪SLA-DQA和SLA-DQB基因SNP检测及生物信息学分析[J]. 养猪, 2017(6):57-60. DOI: 10.13257/j.cnki.21-1104/s.2017.06.018 . |
| CHAO Z, LI J L, QIN Y, et al. Detection of single nucleotide polymorphism and bioinformatics analysis of SLA-DQA and SLA-DQB genes in Wuzhishan pig[J]. Swine Prod, 2017(6):57-60. DOI: 10.13257/j.cnki.21-1104/s.2017.06.018 . | |
| [7] | NIU M M, LIU Y Q, XIANG L, et al. Long-term case study of a Wuzhishan miniature pig with diabetes[J]. Animal Model Exp Med, 2020, 3(1):22-31. DOI:10.1002/ame2.12098 . |
| [8] | ZHAO Y Q, XIANG L, LIU Y Q, et al. Atherosclerosis induced by a high-cholesterol and high-fat diet in the inbred strain of the Wuzhishan miniature pig[J]. Anim Biotechnol, 2018, 29(2):110-118. DOI:10.1080/10495398.2017.1322974 . |
| [9] | HUANG Q, XU H B, YU Z, et al. Inbred Chinese Wuzhishan (WZS) minipig model for soybean glycinin and beta-conglycinin allergy[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2010, 58(8):5194-5198. DOI:10.1021/jf904536v . |
| [10] | LI X, HUANG Y, LIANG Q F, et al. Local immunosuppression in Wuzhishan pig to Rhesus monkey descemet's stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty: an innovative method to promote the survival of xenografts[J]. Ophthalmic Res, 2022, 65(2):196-209. DOI:10.1159/000521193 . |
| [11] | 韦习会, 王林云, 徐银学, 等. 五指山猪白细胞抗原血清学研究[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 1996(3): 199-206. |
| WEI X H, WANG L Y, XU Y X, et al. Preliminary serological study on swine lymphocyte antigen (sla) of the Wuzhishan pig[J]. Acta Vet Zootechnica Sin, 1996(3): 199-206. | |
| [12] | 孙俊丽. 五指山猪近交系群体三个白细胞抗原基因序列和功能分析[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2005. |
| SUN J L. Analysis of sequence and its function on three swine leutocyte antigen gene in inbreeding line of wuzhishan pig population[D]. Xianyang: Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, 2005. | |
| [13] | RABIN M, FRIES R, SINGER D, et al. Assignment of the porcine major histocompatibility complex to chromosome 7 by in situ hybridization[J]. Cytogenet Cell Genet, 1985, 39(3):206-209. DOI:10.1159/000132136 . |
| [14] | BARBOSA A, DEMEURE O, URIEN C, et al. A physical map of large segments of pig chromosome 7q11-q14: comparative analysis with human chromosome 6p21[J]. Mamm Genome, 2004, 15(12):982-995. DOI:10.1007/s00335-004-3008-6 . |
| [15] | HAMMER S E, HO C S, ANDO A, et al. Importance of the major histocompatibility complex (swine leukocyte antigen) in swine health and biomedical research[J]. Annu Rev Anim Biosci, 2020, 8:171-198. DOI:10.1146/annurev-animal-020518-115014 . |
| [16] | VAIMAN M, CHARDON P, ROTHSCHILD M F. Porcine major histocompatibility complex[J]. Rev Sci Tech, 1998, 17(1):95-107. DOI:10.20506/rst.17.1.1093 . |
| [17] | MERKENSCHLAGER J, EKSMOND U, DANELLI L, et al. MHC class II cell-autonomously regulates self-renewal and differentiation of normal and malignant B cells[J]. Blood, 2019, 133(10):1108-1118. DOI:10.1182/blood-2018-11-885467 . |
| [18] | CHARDON P, RENARD C, VAIMAN M. The major histocompatibility complex in swine[J]. Immunol Rev, 1999, 167:179-192. DOI:10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01391.x . |
| [19] | 刘丽霞. 三个猪种SLA-DQA和DRA基因分子遗传特征及其与仔猪腹泻的关联研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2015. |
| LIU L X. Molecular genetic characteristics of SLA-DQA and DRA genes and their association with piglet diarrhea in three pig breeds[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2015. | |
| [20] | VIRET C, JANEWAY C A Jr. MHC and T cell development[J]. Rev Immunogenet, 1999, 1(1):91-104. |
| [21] | 吴群, 熊平, 陈实, 等. 近交系海南五指山猪SLA经典I类和II类分子序列分析[J]. 现代免疫学, 2004(1):23-26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2478.2004.01.007 . |
| WU Q, XIONG P, CHEN S, et al. Sequence analysis of classical swine leukocyte antigens (SLA) class I and class II molecules in inbred strain of Chinese Wuzhishan pigs[J]. Curr Immunol, 2004(1):23-26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2478.2004.01.007 . | |
| [22] | 常瑞刚, 舒丹, 刘丽霞. SLA-DRB基因多态性与仔猪腹泻的关联性研究进展[J]. 甘肃畜牧兽医, 2017, 47(6):20-21. DOI: 10.15979/j.cnki.cn62-1064/s.2017.06.002 . |
| CHANG R G, SHU D, LIU L X. Research progress on the correlation between SLA-DRB gene polymorphism and piglet diarrhea[J]. Gansu Anim Husb Vet, 2017, 47(6):20-21. DOI: 10.15979/j.cnki.cn62-1064/s.2017.06.002 . | |
| [23] | 顾茂松. 五指山小型猪SLA-DQA基因的SNPs及猪人MHC Ⅰ类区自然杀伤细胞KIRs结合区氨基酸变异的比较分析[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2005. |
| GU M S. Single nucleotide polymorphism of SLA-DQA gene in wuzhishan miniature pigs and comparision of amino acids variability of NK cell KIRs binding sites between swine and human MHC class Ⅰ region[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2005. |
| [1] | 孙强. 无替代,何谈取消[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 376-378. |
| [2] | 孔志豪, 魏晓锋, 于灵芝, 冯丽萍, 朱琦, 施国君, 王晨. 鳞状皮屑裸小鼠木糖葡萄球菌的分离鉴定[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 368-375. |
| [3] | 王晨娟, 杨玲焰, 王立鹏, 孙雪萍, 李静文, 郭连香, 荣荣, 时长军. 2019年某实验猴养殖场食蟹猴犬瘟热暴发的诊断[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 360-367. |
| [4] | 李会萍, 高洪彬, 温金银, 杨锦淳. 疾病动物模型数字化图谱数据库平台的构建与初步应用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 300-308. |
| [5] | 潘颐聪, 蒋汶洪, 胡明, 覃晓. 慢性肾脏病大鼠主动脉钙化模型的术式优化及效果评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 279-289. |
| [6] | 刘文涛, 罗艳红, 龙永霞, 罗启慧, 陈正礼, 刘丽达. 四川省实验动物设施常见环境问题及检测经验[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, (): 1-7. |
| [7] | 焦青贞, 吴桂华, 唐雯, 樊帆, 冯凯, 杨春响, 乔建, 邓素芳. 暖通系统暂停送风下实验动物设施氨浓度的动态监测与分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, (): 1-6. |
| [8] | 刘智伟, 杨然, 连浩, 张玉, 金立伦. 秦皮素对碘乙酸钠诱导骨关节炎模型大鼠的软骨保护与抗炎作用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 259-268. |
| [9] | 姜萌, 郝淑兰, 仝立国, 仲启明, 高振飞, 王永辉, 王晞星, 吉海杰. 长春瑞滨诱导大鼠足背静脉炎模型的动态评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 251-258. |
| [10] | 胡敏, 董乐轩, 高怡, 奚子芪, 沈子皓, 唐瑞阳, 栾鑫, 汤忞, 张卫东. 生物3D打印研究及与临床前动物模型的交叉应用展望[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 318-330. |
| [11] | 刘鹍, 兰青, 易兵, 谢晓婕. 药物非临床生殖毒性试验中动物妊娠的主要难点及应对方法[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, (): 1-8. |
| [12] | 秦超, 李双星, 赵婷婷, 蒋晨晨, 赵晶, 杨艳伟, 林志, 王三龙, 文海若. SD大鼠90 d喂养试验的历史背景数据[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, (): 1-10. |
| [13] | 王娇祥, 张璐, 陈姝含, 角德灵, 赵恒, 魏太云, 郭建雄, 徐凯祥, 魏红江. GTKO/hCD55基因编辑异种器官移植供体猪的构建及功能验证[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, (): 1-12. |
| [14] | 王庭君, 罗浩, 陈琦. 基于人工智能的实验动物中心信息化升级及应用实践探讨[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, (): 1-10. |
| [15] | 郑卿勇, 杨冬华, 马智超, 周姿余, 陆洋, 王晶宇, 邢丽娜, 康迎英, 杜莉, 赵春香, 狄宝山, 田金徽. 动物实验系统评价与Meta分析规范及撰写注意事项[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, (): 1-11. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||