













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 436-444.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.004
孔垂琴, 田苗苗, 蔡利东, 吴东, 倪露, 张楚漫, 杨慧欣( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-10
修回日期:2024-07-11
出版日期:2024-09-06
发布日期:2024-08-25
通讯作者:
杨慧欣(1981—),女,硕士,中级实验师,主要从事动物遗传育种与繁育和实验动物管理工作。E-mail: yanghx@gempharmatech.com。ORCID:0009-0003-6947-8256作者简介:孔垂琴(1996—),女,硕士,兽医师,主要从事微生物检测工作。E-mail: kongcq@gempharmatech.com
基金资助:
KONG Chuiqin, TIAN Miaomiao, CAI Lidong, WU Dong, NI Lu, ZHANG Chuman, YANG Huixin( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-01-10
Revised:2024-07-11
Published:2024-08-25
Online:2024-09-06
Contact:
YANG Huixin (ORCID: 0009-0003-6947-8256), E-mail: yanghx@gempharmatech.com摘要:
目的 通过探究不同材质滤膜的微生物捕捉性能,评估其对屏障环境实验设施中啮齿类动物健康状况的监测效果。 方法 以嗜肺巴斯德杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌为代表菌株,在实验室条件下模拟滤膜捕捉微生物的过程,以捕捉粉尘质量、最低检测限度及荧光定量PCR检测的Ct值差异综合评估5种具有吸附、透气性能的自选材质滤膜(M1~M5)和商品化捕捉滤膜(T1)的微生物捕捉效果。将性能最优的自选材质滤膜置于屏障设施内笼架的通风管道中,用相应笼架的哨兵鼠作为对照组,以表皮葡萄球菌和大肠埃希菌为指示菌,计算阳性检出率和符合率,探讨其作为微生物捕捉滤膜在屏障设施内监测实验动物健康状况的可行性。 结果 从捕捉粉尘质量看,自选材质滤膜M3(滤径为0.1 μm的无纺布可作为材质)的捕捉效果仅次于T1,捕捉量达0.126 g;对于金黄色葡萄球菌,除M4外,其余材质的滤膜最低检测限度均为102 CFU/g;对于嗜肺巴斯德杆菌,所有滤膜的最低检测限度皆为102 CFU/g;但M3的荧光定量PCR扩增结果Ct值显著小于其他材质,故5种自选材质滤膜中M3的捕捉效果最好。滤膜检测验证实验中,表皮葡萄球菌在哨兵鼠粪便和M3中的阳性检出率分别为50.00%(6/12)和58.33%(7/12),符合率为92%;大肠埃希菌在哨兵鼠粪便和M3中阳性检出率均为50.00%(6/12),符合率为100%。 结论 5种自选材质滤膜中,M3捕捉效果最佳;在屏障环境设施内,M3对于表皮葡萄球菌的监测效果优于哨兵鼠。因此,滤径为0.1 μm的无纺布可作为微生物捕捉滤膜材质,为笼架排风粉尘PCR监测用微生物捕捉滤膜的材质选择和应用提供借鉴经验。
中图分类号:
孔垂琴,田苗苗,蔡利东,等. 不同材质的微生物捕捉滤膜在屏障环境设施中的应用效果初探[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(4): 436-444. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.004.
KONG Chuiqin,TIAN Miaomiao,CAI Lidong,et al. Exploration on Application Effectiveness of Microbial Capture Filter Membranes from Different Materials in Barrier Environment Facilities[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 436-444. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.004.
组别 Group | 材质 Material | 滤径/μm Filter diameter/μm | 规格 Specification | 厂家 Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 玻纤滤材 | 0.1 | H13高效 | 重庆再升科技股份有限公司 |
| M2 | PPK3熔喷布 | 0.1 | 90 g/m2 | 上海仁益制毡有限公司 |
| M3 | 无纺布 | 0.1 | 80 g/m2 | 东莞市佳联达无纺布有限公司 |
| M4 | 聚丙烯微孔滤膜 | 0.3 | PP-T 0.22 μm | 山东新华医疗器械股份有限公司 |
| M5 | 脱脂纱布 | 0.2 | 7.5 cm×7.5 cm | 徐州市徐卫卫生材料有限责任公司 |
| T1 | 未知 | 未知 | 未知 | 泰尼百斯 |
表1 不同材质的微生物捕捉滤膜信息
Table 1 Information of microbial capture filter membranes made from different materials
组别 Group | 材质 Material | 滤径/μm Filter diameter/μm | 规格 Specification | 厂家 Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 玻纤滤材 | 0.1 | H13高效 | 重庆再升科技股份有限公司 |
| M2 | PPK3熔喷布 | 0.1 | 90 g/m2 | 上海仁益制毡有限公司 |
| M3 | 无纺布 | 0.1 | 80 g/m2 | 东莞市佳联达无纺布有限公司 |
| M4 | 聚丙烯微孔滤膜 | 0.3 | PP-T 0.22 μm | 山东新华医疗器械股份有限公司 |
| M5 | 脱脂纱布 | 0.2 | 7.5 cm×7.5 cm | 徐州市徐卫卫生材料有限责任公司 |
| T1 | 未知 | 未知 | 未知 | 泰尼百斯 |
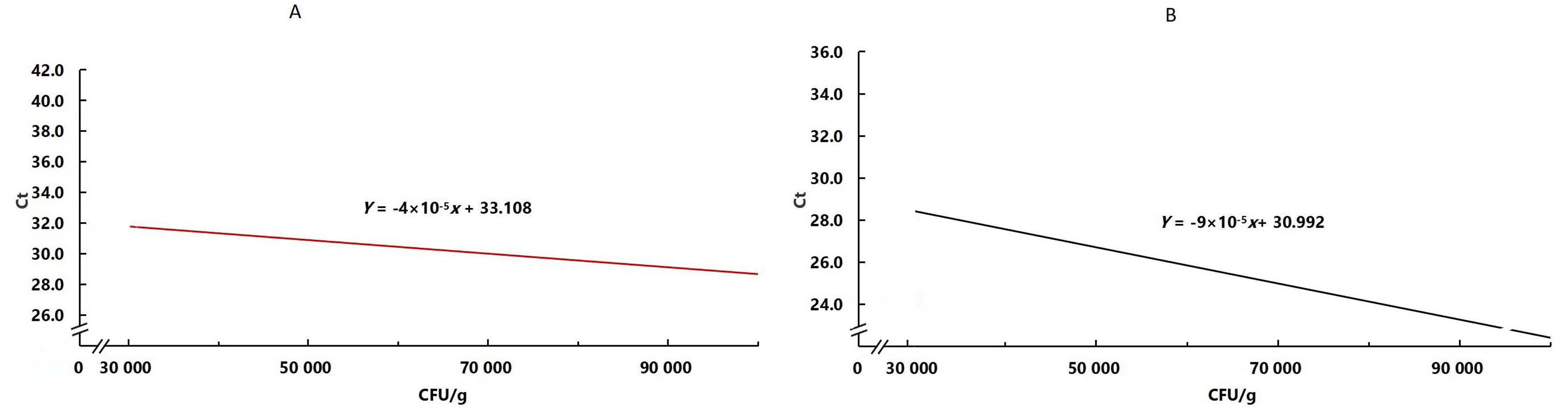
图1 金黄色葡萄球菌(A)和嗜肺巴斯德杆菌(B)污染EAD模拟样品的混合效果注:Ct为循环阈值,CFU为菌落形成单位。
Figure 1 Mixing effect of exhaust air dust (EAD) simulated samples contaminated by Staphylococcus aureus (Sa) (A) and Pasteurella pneumotropica (Pp) (B)Note:Ct, cycle threshold; CFU, colony forming unit.
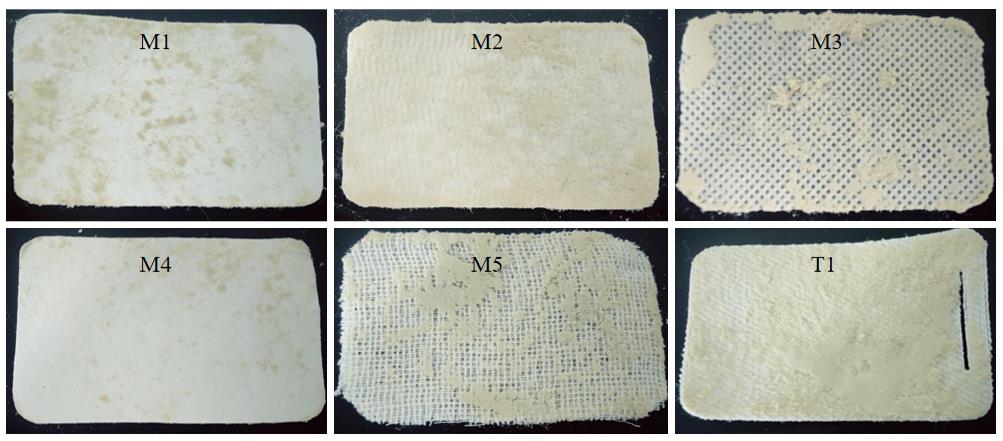

图2 不同材质滤膜的粉尘捕捉效果图注:图中M1、M2、M3、M4和M5为本次实验选用材质,T1为购买的成品。从观察结果来看,M3、M5和T1表面附着有大量粉尘,而M1、M2、M4表面附着粉尘相对较少;各滤膜材质附着粉尘前后的质量差从低到高依次为M4<M1<M2<M5<M3<T1。
Figure 2 Dust capture effectiveness of filter membranes made from different materialsNote:In the figure, M1, M2, M3, M4, and M5 were the materials selected for the experiment, and T1 was the purchased finished product. Based on visual observation, surfaces of M3, M5, and T1 had a large amount of dust attached, while surfaces of M1, M2, and M4 had relatively less dust attached. The mass differences of each filter membrane material, ranked from lowest to highest, were M4<M1<M2<M5<M3<T1.
材质种类 Material | 材质大小/cm Size/cm | 粉尘捕捉前滤膜质量/g m1/g | 粉尘捕捉后滤膜质量/g m2/g | 质量差/g m(m1-m2)/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 5×3 | 0.196±0.003 | 0.266±0.000 | 0.070±0.049 |
| M2 | 5×3 | 0.070±0.000 | 0.164±0.000 | 0.094±0.067 |
| M3 | 5×3 | 0.390±0.000 | 0.516±0.000 | 0.126±0.089* |
| M4 | 5×3 | 0.202±0.000 | 0.221±0.000 | 0.019±0.013 |
| M5 | 5×3 | 0.203±0.000 | 0.286±0.000 | 0.084±0.059 |
| T1 | 5×3 | 0.617±0.000 | 0.760±0.000 | 0.143±0.101* |
表2 不同材质滤膜的粉尘捕捉效果评价
Table 2 Evaluation of dust capturing effectiveness of filter membranes made from different materials
材质种类 Material | 材质大小/cm Size/cm | 粉尘捕捉前滤膜质量/g m1/g | 粉尘捕捉后滤膜质量/g m2/g | 质量差/g m(m1-m2)/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 5×3 | 0.196±0.003 | 0.266±0.000 | 0.070±0.049 |
| M2 | 5×3 | 0.070±0.000 | 0.164±0.000 | 0.094±0.067 |
| M3 | 5×3 | 0.390±0.000 | 0.516±0.000 | 0.126±0.089* |
| M4 | 5×3 | 0.202±0.000 | 0.221±0.000 | 0.019±0.013 |
| M5 | 5×3 | 0.203±0.000 | 0.286±0.000 | 0.084±0.059 |
| T1 | 5×3 | 0.617±0.000 | 0.760±0.000 | 0.143±0.101* |
材质 Material Bacteria | 细菌浓度/(CFU·g-1) concentration/(CFU·g-1) | 金黄色葡萄球菌 Staphylococcus aureus (Sa) | 嗜肺巴斯德杆菌 Pasteurella pneumotropica (Pp) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
循环阈值( Ct ( | 变异系数/% CV/% | 循环阈值( Ct( | 变异系数/% CV/% | ||||
M1 | 106 | 24.03±0.13 | 0.005 | 23.59±0.42 | 0.018 | ||
| 105 | 26.13±0.23 | 0.009 | 25.88±0.23 | 0.009 | |||
| 104 | 29.51±0.43 | 0.015 | 28.82±0.60 | 0.021 | |||
| 103 | 33.72±0.18 | 0.005 | 33.84±0.39 | 0.012 | |||
| 102 | 36.52±0.27 | 0.007 | 36.15±0.28 | 0.008 | |||
M2 | 106 | 23.42±1.06 | 0.045 | 19.50±0.17 | 0.009 | ||
| 105 | 26.50±0.47 | 0.018 | 22.15±0.22 | 0.010 | |||
| 104 | 28.22±0.13 | 0.005 | 25.67±0.33 | 0.013 | |||
| 103 | 32.30±0.28 | 0.009 | 30.33±0.34 | 0.011 | |||
| 102 | 35.28±0.42 | 0.012 | 35.97±0.25 | 0.007 | |||
M3 | 106 | 24.74±0.17 | 0.007 | 19.78±0.43 | 0.022 | ||
| 105 | 26.08±0.00 | 0.000 | 21.46±0.10 | 0.005 | |||
| 104 | 29.60±0.23 | 0.008 | 25.25±0.28 | 0.011 | |||
| 103 | 35.01±0.03 | 0.001 | 27.39±0.19 | 0.007 | |||
| 102 | 35.14±0.28* | 0.008 | 32.91±0.80* | 0.024 | |||
M4 | 106 | 28.40±0.05 | 0.002 | 24.96±0.43 | 0.017 | ||
| 105 | 29.59±0.02 | 0.001 | 28.39±0.34 | 0.012 | |||
| 104 | 35.70±0.62 | 0.017 | 30.83±0.51 | 0.017 | |||
| 103 | 36.24±0.21 | 0.006 | 33.64±0.45 | 0.013 | |||
| 102 | / | / | 36.56±0.00 | 0.012 | |||
M5 | 106 | 23.31±0.41 | 0.018 | 18.04±0.70 | 0.039 | ||
| 105 | 25.96±0.16 | 0.006 | 21.76±0.49 | 0.023 | |||
| 104 | 28.85±0.25 | 0.009 | 25.08±0.23 | 0.009 | |||
| 103 | 33.23±0.36 | 0.011 | 28.11±0.46 | 0.016 | |||
| 102 | 35.56±0.45 | 0.013 | 32.94±0.40 | 0.012 | |||
T1 | 106 | 22.92±0.31 | 0.014 | 16.88±0.43 | 0.025 | ||
| 105 | 25.36±0.23 | 0.009 | 21.62±0.34 | 0.016 | |||
| 104 | 28.93±0.13 | 0.004 | 23.68±0.44 | 0.019 | |||
| 103 | 31.98±0.37 | 0.012 | 27.46±0.75 | 0.027 | |||
| 102 | 33.14±0.00* | 0.024 | 32.10±0.28* | 0.009 | |||
表3 不同材质滤膜捕捉金黄色葡萄球菌和嗜肺巴斯德杆菌和检测灵敏度和变异系数
Table 3 Detection sensitivity and coefficient of variation (CV) for Staphylococcus aureus (Sa) and Pasteurella pneumotropica (Pp) using filter membranes made from different materials
材质 Material Bacteria | 细菌浓度/(CFU·g-1) concentration/(CFU·g-1) | 金黄色葡萄球菌 Staphylococcus aureus (Sa) | 嗜肺巴斯德杆菌 Pasteurella pneumotropica (Pp) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
循环阈值( Ct ( | 变异系数/% CV/% | 循环阈值( Ct( | 变异系数/% CV/% | ||||
M1 | 106 | 24.03±0.13 | 0.005 | 23.59±0.42 | 0.018 | ||
| 105 | 26.13±0.23 | 0.009 | 25.88±0.23 | 0.009 | |||
| 104 | 29.51±0.43 | 0.015 | 28.82±0.60 | 0.021 | |||
| 103 | 33.72±0.18 | 0.005 | 33.84±0.39 | 0.012 | |||
| 102 | 36.52±0.27 | 0.007 | 36.15±0.28 | 0.008 | |||
M2 | 106 | 23.42±1.06 | 0.045 | 19.50±0.17 | 0.009 | ||
| 105 | 26.50±0.47 | 0.018 | 22.15±0.22 | 0.010 | |||
| 104 | 28.22±0.13 | 0.005 | 25.67±0.33 | 0.013 | |||
| 103 | 32.30±0.28 | 0.009 | 30.33±0.34 | 0.011 | |||
| 102 | 35.28±0.42 | 0.012 | 35.97±0.25 | 0.007 | |||
M3 | 106 | 24.74±0.17 | 0.007 | 19.78±0.43 | 0.022 | ||
| 105 | 26.08±0.00 | 0.000 | 21.46±0.10 | 0.005 | |||
| 104 | 29.60±0.23 | 0.008 | 25.25±0.28 | 0.011 | |||
| 103 | 35.01±0.03 | 0.001 | 27.39±0.19 | 0.007 | |||
| 102 | 35.14±0.28* | 0.008 | 32.91±0.80* | 0.024 | |||
M4 | 106 | 28.40±0.05 | 0.002 | 24.96±0.43 | 0.017 | ||
| 105 | 29.59±0.02 | 0.001 | 28.39±0.34 | 0.012 | |||
| 104 | 35.70±0.62 | 0.017 | 30.83±0.51 | 0.017 | |||
| 103 | 36.24±0.21 | 0.006 | 33.64±0.45 | 0.013 | |||
| 102 | / | / | 36.56±0.00 | 0.012 | |||
M5 | 106 | 23.31±0.41 | 0.018 | 18.04±0.70 | 0.039 | ||
| 105 | 25.96±0.16 | 0.006 | 21.76±0.49 | 0.023 | |||
| 104 | 28.85±0.25 | 0.009 | 25.08±0.23 | 0.009 | |||
| 103 | 33.23±0.36 | 0.011 | 28.11±0.46 | 0.016 | |||
| 102 | 35.56±0.45 | 0.013 | 32.94±0.40 | 0.012 | |||
T1 | 106 | 22.92±0.31 | 0.014 | 16.88±0.43 | 0.025 | ||
| 105 | 25.36±0.23 | 0.009 | 21.62±0.34 | 0.016 | |||
| 104 | 28.93±0.13 | 0.004 | 23.68±0.44 | 0.019 | |||
| 103 | 31.98±0.37 | 0.012 | 27.46±0.75 | 0.027 | |||
| 102 | 33.14±0.00* | 0.024 | 32.10±0.28* | 0.009 | |||
检测项目 Testing item | M3滤膜 M3 filter | 哨兵鼠粪便样品 Sentinel mouse faeces | 符合率/% Coincidence rate/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
阳性 Positive | 阴性 Negative | 汇总 Summary | |||
表皮葡萄球菌 Staphylococcus epidermidis | 阳性 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 92 |
| 阴性 | 0 | 5 | 5 | ||
| 汇总 | 6 | 6 | 12 | ||
大肠埃希菌 Escherichia coli | 阳性 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 100 |
| 阴性 | 0 | 6 | 6 | ||
| 汇总 | 6 | 6 | 12 | ||
表4 滤膜M3的检测验证结果
Table 4 Detection validation results for filter membrane M3
检测项目 Testing item | M3滤膜 M3 filter | 哨兵鼠粪便样品 Sentinel mouse faeces | 符合率/% Coincidence rate/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
阳性 Positive | 阴性 Negative | 汇总 Summary | |||
表皮葡萄球菌 Staphylococcus epidermidis | 阳性 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 92 |
| 阴性 | 0 | 5 | 5 | ||
| 汇总 | 6 | 6 | 12 | ||
大肠埃希菌 Escherichia coli | 阳性 | 6 | 0 | 6 | 100 |
| 阴性 | 0 | 6 | 6 | ||
| 汇总 | 6 | 6 | 12 | ||
| 1 | LIPMAN N S, HOMBERGER F R. Rodent quality assurance testing: use of sentinel animal systems[J]. Lab Anim, 2003, 32(5):36-43. DOI: 10.1038/laban0503-36 . |
| 2 | LIVINGSTON R S, RILEY L K. Diagnostic testing of mouse and rat colonies for infectious agents[J]. Lab Anim, 2003, 32(5):44-51. DOI: 10.1038/laban0503-44 . |
| 3 | O'CONNELL K A, TIGYI G J, LIVINGSTON R S, et al. Evaluation of in-cage filter paper as a replacement for sentinel mice in the detection of murine pathogens[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2021, 60(2):160-167. DOI: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-20-000086 . |
| 4 | 于灵芝, 魏晓锋, 黎明, 等. 啮齿类实验动物健康监测用脏垫料哨兵动物法和排风粉尘PCR法比较[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(3): 321-327. DOI:10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.168 . |
| YU L Z, WEI X F, LI M, et al. Comparison of methods between soiled bedding sentinels and exhaust air dust PCR for health monitoring of rodent laboratory animals[J]. Lab Anim Comp Med, 2024, 44(3): 321-327. DOI:10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.168 . | |
| 5 | MILLER M, BRIELMEIER M. Environmental samples make soiled bedding sentinels dispensable for hygienic monitoring of IVC-reared mouse colonies[J]. Lab Anim, 2018, 52(3):233-239. DOI: 10.1177/0023677217739329 . |
| 6 | COMPTON S R, HOMBERGER F R, PATURZO F X, et al. Efficacy of three microbiological monitoring methods in a ventilated cage rack[J]. Comp Med, 2004, 54(4):382-392. |
| 7 | HENDERSON K S, PERKINS C L, HAVENS R B, et al. Efficacy of direct detection of pathogens in naturally infected mice by using a high-density PCR array[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2013, 52(6):763-772. DOI: 10.1136/vr.f6532 . |
| 8 | BESSELSEN D G, MYERS E L, FRANKLIN C L, et al. Transmission probabilities of mouse parvovirus 1 to sentinel mice chronically exposed to serial dilutions of contaminated bedding[J]. Comp Med, 2008, 58(2):140-144. DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.2008.00260.x . |
| 9 | JENSEN E S, ALLEN K P, HENDERSON K S, et al. PCR testing of a ventilated caging system to detect murine fur mites[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2013, 52(1):28-33. DOI: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2013.01.001 . |
| 10 | KÖRNER C, MILLER M, BRIELMEIER M. Detection of Murine Astrovirus and Myocoptes musculinus in individually ventilated caging systems: investigations to expose suitable detection methods for routine hygienic monitoring[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(8): e0221118. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221118 . |
| 11 | MILLER M, RITTER B, ZORN J, et al. Exhaust air dust monitoring is superior to soiled bedding sentinels for the detection of Pasteurella pneumotropica in individually ventilated cage systems[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2016, 55(6):775-781. |
| 12 | NIIMI K, MARUYAMA S, SAKO N, et al. The SentinelTM EADR program can detect more microorganisms than bedding sentinel animals[J]. Jpn J Vet Res, 2018, 66(2): 125-129. DOI: 10.14943/jjvr.66.2.125 . |
| 13 | PETTAN-BREWER C, TROST R J, MAGGIO-PRICE L, et al. Adoption of exhaust air dust testing in SPF rodent facilities[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2020, 59(2):156-162. DOI: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-19-000079 . |
| 14 | WHARY M T, CLINE J H, KING A E, et al. Monitoring sentinel mice for Helicobacter hepaticus, H rodentium, and H bilis infection by use of polymerase chain reaction analysis and serologic testing[J]. Comp Med, 2000, 50(4):436-443. |
| 15 | DUBELKO A R, ZUWANNIN M, MCINTEE S C, et al. PCR testing of filter material from IVC lids for microbial monitoring of mouse colonies[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2018, 57(5):477-482. DOI: 10.30802/aalas-jaalas-18-000008 . |
| 16 | GERWIN P M, RICART ARBONA R J, RIEDEL E R, et al. PCR testing of IVC filter tops as a method for detecting murine pinworms and fur mites[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2017, 56(6):752-761. |
| 17 | ZORN J, RITTER B, MILLER M, et al. Murine norovirus detection in the exhaust air of IVCs is more sensitive than serological analysis of soiled bedding sentinels[J]. Lab Anim, 2017, 51(3):301-310. DOI: 10.1177/0023677216661586 . |
| 18 | MAILHIOT D, OSTDIEK A M, LUCHINS K R, et al. Comparing mouse health monitoring between soiled-bedding sentinel and exhaust air dust surveillance programs[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2020, 59(1):58-66. DOI: 10.30802/aalas-jaalas-19-000061 . |
| 19 | LUCHINS K R, MAILHIOT D, THERIAULT B R, et al. Detection of lactate dehydrogenase elevating virus in a mouse vivarium using an exhaust air dust health monitoring program[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2020, 59(3):328-333. DOI: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-19-000107 . |
| 20 | BAUER B A, BESCH-WILLIFORD C, LIVINGSTON R S, et al. Influence of rack design and disease prevalence on detection of rodent pathogens in exhaust debris samples from individually ventilated caging systems[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2016, 55(6):782-788. |
| 21 | LUPINI L, BASSI C, GUERRIERO P, et al. Microbiota and environmental health monitoring of mouse colonies by metagenomic shotgun sequencing[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2022, 39(1):37. DOI: 10.1007/s11274-022-03469-0 . |
| 22 | 王立鹏, 李永旺, 王晨娟, 等. Dole qPCR检测嗜肺巴斯德杆菌的可靠性研究及在啮齿类实验动物质量监测中的应用[J]. 现代检验医学杂志, 2019, 34(5):109-114. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7414.2019.05.027 . |
| WANG L P, LI Y W, WANG C J, et al. Reliability research of Dole qPCR method on Pasteurella pneumotropica and application in health screening of laboratory rodents[J]. J Mod Lab Med, 2019, 34(5):109-114. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7414.2019.05.027 . | |
| 23 | 于灵芝, 谢建芸, 冯丽萍, 等. 金黄色葡萄球菌荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立及其在大鼠、小鼠粪便检测中的应用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023(5):566-573. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.022 . |
| YU L Z, XIE J Y, FENG L P, et al. Establishment of fluorescence qPCR method for detection of Staphylococcus aureus and its application in feces detection of rats and mice[J]. Lab Anim Comp Med, 2023(5):566-573. DOI: 10.12300/j. issn.1674-5817.2023.022 . | |
| 24 | RAGLAND N H, MIEDEL E L, GOMEZ J M, et al. Staphylococcus xylosus PCR-validated decontamination of murine individually ventilated cage racks and air handling units by using 'active-closed' exposure to vaporized hydrogen peroxide[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2017, 56(6):742-751. |
| 25 | WON Y S, KWON H J, OH G T, et al. Identification of Staphylococcus xylosus isolated from C57BL/6J-Nos2(tm1Lau) mice with dermatitis[J]. Microbiol Immunol, 2002, 46(9):629-632. DOI: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2002.tb02744.x . |
| 26 | 史志远, 陈璐萍, 李博星, 等. 不同粪便DNA提取方法比较分析[J]. 生物工程学报, 2022, 38(9):3542-3550. DOI: 10.13345/j.cjb.220085 . |
| SHI Z Y, CHEN L P, LI B X, et al. Comparative analysis of different fecal DNA extraction methods[J]. Chin J Biotechnol, 2022, 38(9):3542-3550. DOI: 10.13345/j.cjb.220085 . | |
| 27 | WINN C B, ROGERS R N, KEENAN R A, et al. Using filter media and soiled bedding in disposable individually ventilated cages as a refinement to specific pathogen-free mouse health monitoring programs[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2022, 61(4):361-369. DOI: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-22-000013 . |
| 28 | MANUEL C A, PUGAZHENTHI U, SPIEGEL S P, et al. Detection and elimination of Corynebacterium bovis from barrier rooms by using an environmental sampling surveillance program[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2017, 56(2):202-209. |
| 29 | KIM E, YANG S M, WON J E, et al. Real-time PCR method for the rapid detection and quantification of pathogenic Staphylococcus species based on novel molecular target genes[J]. Foods, 2021, 10(11):2839. DOI: 10.3390/foods10112839 . |
| [1] | 孙强. NOD小鼠的培育接力赛[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, (): 1-4. |
| [2] | 吴贤生, 黄威, 梁勇芬, 邓卉, 翟永欢, 杨嘉俊, 黄甘泉, 王刚. 实验用猫繁育与应用相关数据的检测分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(4): 428-435. |
| [3] | 吴玥, 李璐, 张阳, 王珏, 冯婷婷, 李依桐, 王凯, 孔琪. 冠状病毒感染动物模型组学数据集成分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(4): 357-373. |
| [4] | 孙强. 中国实验猴产业的历史、现状、挑战与机遇[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(4): 343-356. |
| [5] | 赵勇. 动物实验伦理的三个维度:基于生命价值、动物福利和风险防范的阐析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(4): 445-454. |
| [6] | 孙强. 趣谈实验小鼠的毛色形成[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(4): 463-466. |
| [7] | 邓少嫦, 林丹荣, 梁楚军, 雷伟侨, 杨锦淳, 赵维波. 《广东省实验动物管理条例》制度特点及近十年实施情况分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(4): 455-462. |
| [8] | 孙强. 近交系小鼠培育及其背后的故事[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(3): 335-338. |
| [9] | 刘美佟, 陈长, 张兆强, 范荻, 胡旃, 马海玲. 湖南省实验动物生物安全突发事件应急预案的编制说明[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(3): 328-334. |
| [10] | 于灵芝, 魏晓锋, 黎明, 孔志豪. 啮齿类实验动物健康监测用脏垫料哨兵动物法和排风粉尘PCR法比较[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(3): 321-327. |
| [11] | 吴东, 石蕊, 罗珮珊, 李灵恩, 盛席静, 王梦阳, 倪露, 王素娟, 杨慧欣, 赵静. 不同颗粒饲料硬度对实验小鼠生长繁殖、饲料利用率及环境粉尘量的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(3): 313-320. |
| [12] | 刘芸, 冯婷婷, 佟巍, 郭智, 李夏, 孔琪, 向志光. 甘草酸能减轻小鼠肺炎病毒引起的小鼠肺脏损伤[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(3): 251-258. |
| [13] | 王梦杰, 马文杰, 潘喻, 陈见兴, 张贺, 夏长友, 王玉娥. SPF鸡的主要垂直传播性病原体及其检测标准分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(3): 305-312. |
| [14] | 刘美佟, 陈长, 张兆强, 范荻, 胡旃, 马海玲. 湖南省实验动物机构生物安全管理现状调查[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(2): 202-208. |
| [15] | 曾龙, 李俊鹏, 王晓炜, 陈宁, 王平, 秦美蓉. 实验动物设施智能控制系统建设与运行经验探讨:以深圳市药品检验研究院为例[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(2): 220-226. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||