













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 251-258.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.014
刘芸, 冯婷婷, 佟巍, 郭智, 李夏, 孔琪, 向志光( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-23
修回日期:2024-04-12
出版日期:2024-07-06
发布日期:2024-06-25
通讯作者:
向志光(1980—),男,博士,副研究员,研究方向:免疫学。E-mail: xiangzg@cnilas.org。ORCID: 0000-0002-9317-7766作者简介:刘芸(1996—),女,硕士研究生,研究方向:免疫学。E-mail: liuyun@cnilas.org
基金资助:
Yun LIU, Tingting FENG, Wei TONG, Zhi GUO, Xia LI, Qi KONG, Zhiguang XIANG( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-01-23
Revised:2024-04-12
Published:2024-06-25
Online:2024-07-06
Contact:
XIANG Zhiguang (ORCID: 0000-0002-9317-7766), E-mail: xiangzg@cnilas.org摘要:
目的 通过小鼠肺炎病毒(pneumonia virus of mice,PVM)感染近交系BALB/c小鼠建立病毒感染肺炎动物模型,观察PVM感染过程中促炎症警报素分子高迁移率族蛋白B1(high mobility group box 1,HMGB1)的变化,以及HMGB1抑制剂甘草酸(glycyrrhizic acid,GA)对小鼠肺脏感染损伤的在体干预作用。 方法 将3周龄的雌性BALB/c小鼠随机分为3组,每组6只。一组未经PVM感染,作为对照组(Control);另外两组先以1×104半数组织培养感染剂量(50% tissue culture infective dose,TCID50)/25 μL剂量滴鼻接种PVM,然后分别给予GA生理盐水溶液灌胃(GA组)或单纯生理盐水灌胃(normal saline,NS组)处理,连续15 d。其间,观察并记录各组小鼠体重、外观等改变。在实验终点采集各组小鼠的肺脏组织样本,通过苏木精-伊红染色和免疫组织化学法检测小鼠肺脏组织内PVM和HMGB1蛋白的分布情况;通过实时荧光定量PCR法检测小鼠肺脏组织中HMGB1、Toll样受体4(Toll-like receptor 4,TLR-4)、晚期糖基化终产物特异性受体(advanced glycosylation end-product-specific receptor,AGER),以及白细胞介素(interleukin,IL)-1β、IL-2和肿瘤坏死因子α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)等炎症因子的表达水平。 结果 与Control组相比,NS组小鼠6 d后体重显著下降(P<0.05),组织病理学结果显示其肺脏有明显的炎症病变,免疫组织化学结果显示HMGB1从细胞核释放至细胞质,实时荧光定量PCR结果显示HMGB1、IL-1β和IL-2的表达水平均显著上调(P<0.05);GA干预组的临床症状和体重无明显变化。而与NS组相比,GA干预组肺组织的病理损伤明显减轻,且肺组织中HMGB1、IL-1β、IL-2和干扰素γ(interferon-γ,IFN-γ)的表达水平显著下降(P<0.05),但AGER的表达水平显著增高(P<0.05)。 结论 PVM感染能引起明显的小鼠肺部炎症性病理损伤,而GA能有效减轻其损伤,其作用机制可能与激活HMGB1信号通路相关。
中图分类号:
刘芸,冯婷婷,佟巍,等. 甘草酸能减轻小鼠肺炎病毒引起的小鼠肺脏损伤[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(3): 251-258. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.014.
Yun LIU,Tingting FENG,Wei TONG,et al. Glycyrrhizic Acid Showed Therapeutic Effects on Severe Pulmonary Damages in Mice Induced by Pneumonia Virus of Mice Infection[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 251-258. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.014.
图1 动物实验时间表注:在小鼠肺炎病毒(PVM)感染前3 d,将所有小鼠引入动物生物安全二级(ABSL-2)设施。第0天,测量小鼠体重,进行PVM滴鼻接种,同时分别灌胃给药,甘草酸(GA)或生理盐水(NS)。此后,每日给予GA或NS治疗,每3 d称重一次。每组6只小鼠。实验终点设为病毒感染后第15天。
Figure 1 Animal experiment timelineNote: Three days before pneumonia virus of mice (PVM) infection, all mice were transferred to the ABSL-2 facility. On Day 0, the body weights of mice were measured, PVM intranasal inoculation was performed, and glycyrrhizic acid (GA) or normal saline (NS) was administered via gavage. Subsequently, GA or NS treatment was given daily and body weights were measured every 3 days. Each group consisted of 6 mice. The endpoint of the experiment was set at 15 dpi (day post infection).
目的基因 Target gene | 上游引物(5’-3’) Forward primer | 下游引物(5’-3’) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| PVM | GCCTGCATCAACACAGTGTGT | GCCTGATGTGGCAGTGCTT |
| TLR-4 | ATGGCATGGCTTACACCACC | GAGGCCAATTTTGTCTCCACA |
| AGER | ACATGTGTGTCTGAGGGAAGC | AGCTCTGACCGCAGTGTAAAG |
| HMGB1 | CTTCGGCCTTCTTCTTGTTCT | GGCAGCTTTCTTCTCATAGGG |
| IL-2 | CCCAAGCAGGCCACAGAATTGAAA | AGTCAAATCCAGAACATGCCGCAG |
| IFN-γ | AGAGGATGGTTTGCATCTGGGTCA | ACAACGCTATGCAGCTTGTTCGTG |
| CCL2 | GGCTCAGCCAGATGCAGTTAA | CCTACTCATTGGGATCATCTTGCT |
| TNF-α | GACAAGGCTGCCCCGACTA | TTTCTCCTGGTATGAGATAGCAAATC |
| IL-1β | ATGAGGACATGAGCACCT TC | CATTGAGTTGGAGAGCTTTC |
| IL-6 | GACTTCCATCCAGTTGCCTTC TT | TCCACGATTTCCCAGAGAACA |
表1 引物序列
Table 1 Primer Sequence
目的基因 Target gene | 上游引物(5’-3’) Forward primer | 下游引物(5’-3’) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| PVM | GCCTGCATCAACACAGTGTGT | GCCTGATGTGGCAGTGCTT |
| TLR-4 | ATGGCATGGCTTACACCACC | GAGGCCAATTTTGTCTCCACA |
| AGER | ACATGTGTGTCTGAGGGAAGC | AGCTCTGACCGCAGTGTAAAG |
| HMGB1 | CTTCGGCCTTCTTCTTGTTCT | GGCAGCTTTCTTCTCATAGGG |
| IL-2 | CCCAAGCAGGCCACAGAATTGAAA | AGTCAAATCCAGAACATGCCGCAG |
| IFN-γ | AGAGGATGGTTTGCATCTGGGTCA | ACAACGCTATGCAGCTTGTTCGTG |
| CCL2 | GGCTCAGCCAGATGCAGTTAA | CCTACTCATTGGGATCATCTTGCT |
| TNF-α | GACAAGGCTGCCCCGACTA | TTTCTCCTGGTATGAGATAGCAAATC |
| IL-1β | ATGAGGACATGAGCACCT TC | CATTGAGTTGGAGAGCTTTC |
| IL-6 | GACTTCCATCCAGTTGCCTTC TT | TCCACGATTTCCCAGAGAACA |
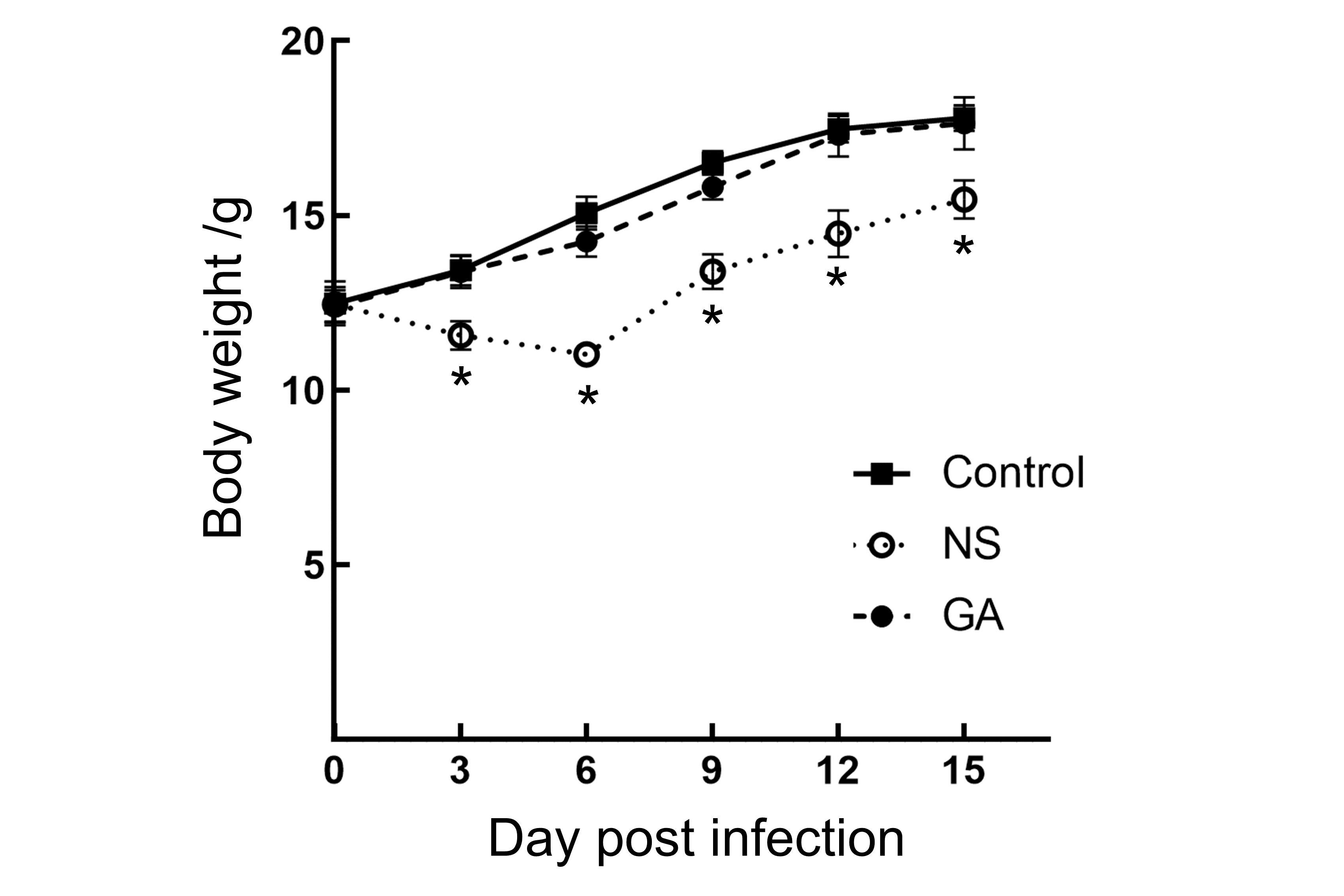
图2 PVM感染后小鼠生长曲线注:Control,未感染对照组;NS,小鼠肺炎病毒(PVM)感染后生理盐水(NS)处理组;GA,感染后(GA)甘草酸处理组。3组小鼠体重以平均值±SD表示(n=6)。与对照组相比,NS治疗组小鼠在感染后第3、6 天时体重下降,9天后体重增加,与对照组相比仍有显著差异(P<0.05);GA组小鼠与对照组相比无显著差异(P>0.05)。
Figure 2 Body weight curves of mice after PVM infectionNote:The body weights of mice in the three groups were expressed as mean value±SD (n=6). Compared with the Control group, the NS group experienced weight loss at 3 and 6 dpi. Although weight gain in the NS group could be detected after 9 dpi, there were significant differences compared to the Control group (P<0.05). There were no significant weight differences in GA group compared to the Control group (P>0.05). Control: uninfected control group; NS: group treated with normal saline (NS) after infection; GA: group treated with glycyrrhizic acid (GA) after infection.
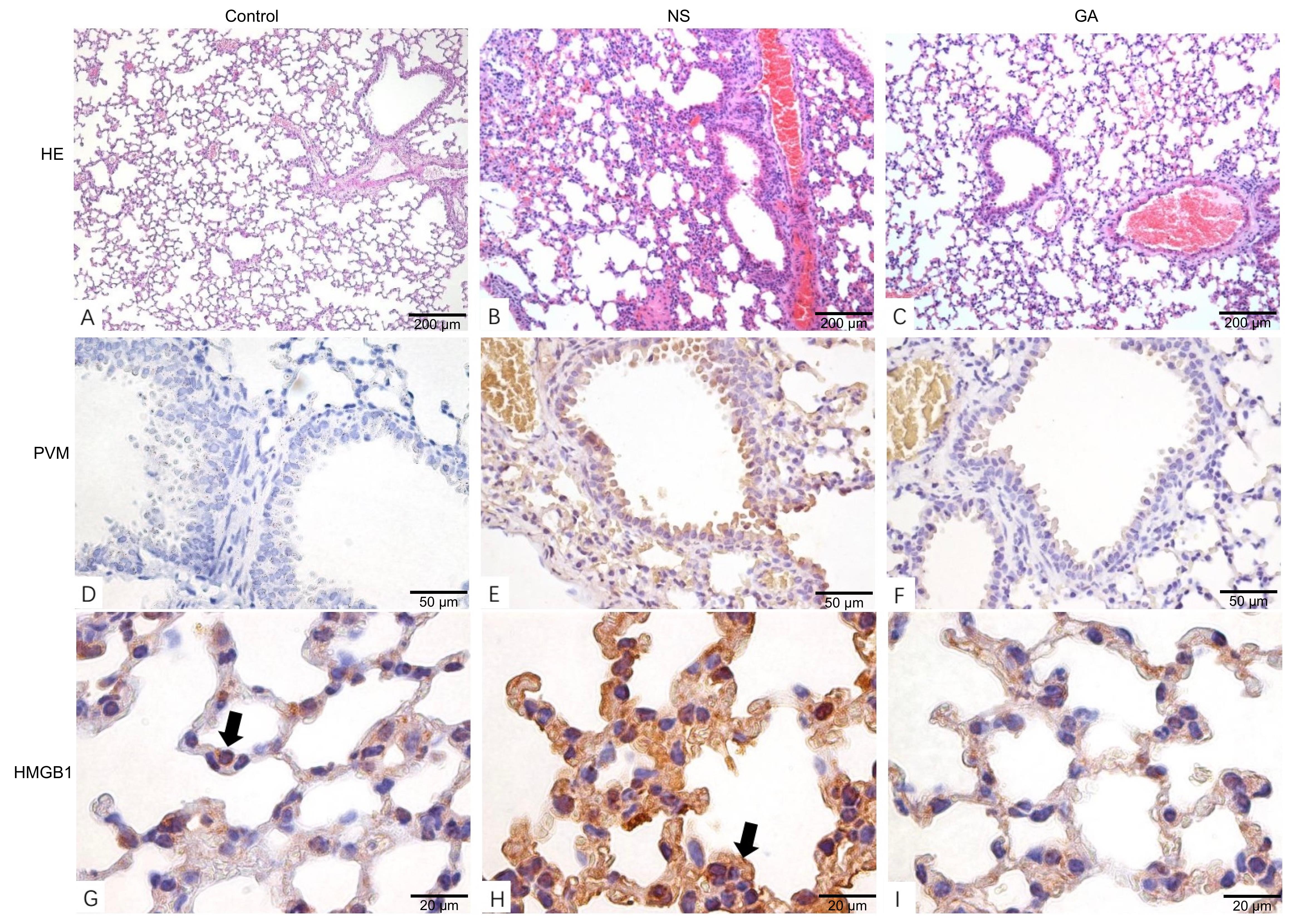
图3 PVM感染后小鼠肺部病理变化注:A~C,组织病理学分析显示PVM感染后的肺组织病理变化(苏木精-伊红染色,×10)。与Control组相比,NS组小鼠肺泡间隔增厚,肺泡腔出血,血管充血;GA组无明显的病理症状。D~F,免疫组织化学检测结果显示GA组肺组织中PVM病毒载量低于NS组(TMB染色,×40)。G~I,免疫组织化学分析显示HMGB1在肺组织中的表达(TMB染色,×100)。Control组中箭头指示HMGB1在细胞核位置;NS组可见HMGB1过表达,且分布于细胞质。Control:未感染对照组;NS:PVM感染后生理盐水处理组;GA:PVM感染后甘草酸处理组。
Figure 3 Pathological changes in the lungs of mice after PVM infection in three groupsNote:A-C, Histopathological analysis showed the pulmonary tissue pathological changes after PVM infection (HE staining, ×10). Compared with the Control group, thickened alveolar septa, hemorrhage in alveolar cavities, and vascular hyperemia were detected in the NS group; No significant pathological symptom was observed in the GA group. D-F, Immunohistochemical analysis demonstrated lower PVM viral load in pulmonary tissues in the GA group compared to the NS group (TMB staining, ×40). G-I, Immunohistochemical analysis showed the HMGB1 expression in pulmonary tissues (TMB staining, ×100). In the Control group, the cell nucleus locations of HMGB1 were indicated by arrows; in the NS group, HMGB1 was overexpressed and distributed in the cytoplasm. Control: uninfected control group; NS: group treated with normal saline(0.9%NaCl) after PVM infection; GA: group treated with glycyrrhizic acid after PVM infection. PVM: pneumonia virus of mice.
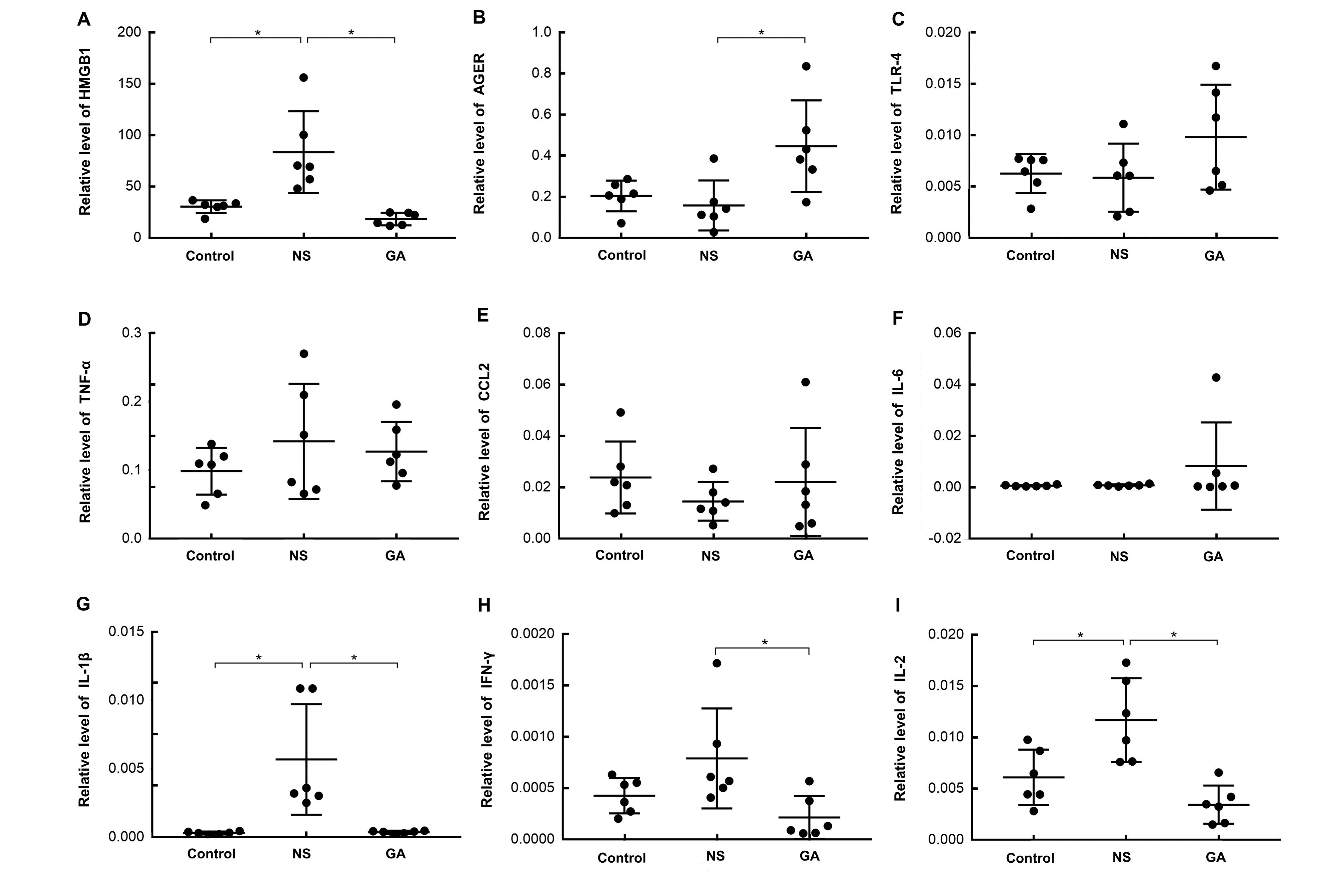
图4 PVM感染后小鼠肺组织中炎症因子与警报素HMGB1及其受体AGER的表达注:实时荧光定量PCR检测3组小鼠肺组织HMGB1、AGER、TLR-4、IL-1β、TNF-α、CCL2、IL-6、IFN-γ和IL-2相对于内参基因GAPDH的表达。n=6,*P<0.05。Control:未感染对照组;NS:PVM感染后生理盐水处理组;GA:PVM感染后甘草酸处理组。
Figure 4 Expression of inflammatory factors and the alarmin HMGB1 and its receptor AGER after PVM infection in pulmonary tissueNote:Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR was performed on the pulmonary tissues from mice in three groups. The expression of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), advanced glycosylation end-product-specific receptor (AGER), Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), IL-6, interferon-γ (IFN-γ), and IL-2 were shown as ratios to GAPDH. n=6, *P<0.05. Control: uninfected control group; NS: group treated with normal saline(0.9%NaCl) after PVM infection; GA: group treated with glycyrrhizic acid after PVM infection. PVM: pneumonia virus of mice.
| 1 | ARANDA S S, POLACK F P. Prevention of pediatric respiratory syncytial virus lower respiratory tract illness: perspectives for the next decade[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10:1006. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01006 . |
| 2 | 侯长春, 赵海金, 蔡绍曦, 等. 呼吸道合胞病毒增加小鼠肺组织的高迁移率族蛋白B1的表达和释放[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2010, 30(4):700-703. DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2010.04.010 . |
| HOU C C, ZHAO H J, CAI S X, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus increases the expression and release of high mobility group Box-1 protein in the lung tissue of mice[J]. J South Med Univ, 2010, 30(4):700-703. DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2010.04.010 . | |
| 3 | RAYAVARA K, KUROSKY A, STAFFORD S J, et al. Proinflammatory effects of respiratory syncytial virus-induced epithelial HMGB1 on human innate immune cell activation[J]. J Immunol, 2018, 201(9):2753-2766. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800558 . |
| 4 | EASTON A J, DOMACHOWSKE J B, ROSENBERG H F. Animal pneumoviruses: molecular genetics and pathogenesis[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2004, 17(2):390-412. DOI: 10.1128/cmr.17.2.390-412.2004 . |
| 5 | TAYLOR G. Animal models of respiratory syncytial virus infection[J]. Vaccine, 2017, 35(3):469-480. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.11.054 . |
| 6 | DYER K D, GARCIA-CRESPO K E, GLINEUR S, et al. The Pneumonia Virus of Mice (PVM) model of acute respiratory infection[J]. Viruses, 2012, 4(12):3494-3510. DOI: 10.3390/v4123494 . |
| 7 | ALTAMIRANO-LAGOS M J, DÍAZ F E, MANSILLA M A, et al. Current animal models for understanding the pathology caused by the respiratory syncytial virus[J]. Front Microbiol, 2019, 10:873. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00873 . |
| 8 | SCAFFIDI P, MISTELI T, BIANCHI M E. Release of chromatin protein HMGB1 by necrotic cells triggers inflammation[J]. Nature, 2002, 418(6894):191-195. DOI: 10.1038/nature00858 . |
| 9 | LI G Q, LIANG X Y, LOTZE M T. HMGB1: the central cytokine for all lymphoid cells[J]. Front Immunol, 2013, 4:68. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00068 . |
| 10 | LOTZE M T, TRACEY K J. High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1): nuclear weapon in the immune arsenal[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2005, 5(4):331-342. DOI: 10.1038/nri1594 . |
| 11 | WANG L Q, YANG R, YUAN B C, et al. The antiviral and antimicrobial activities of licorice, a widely-used Chinese herb[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2015, 5(4):310-315. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.05.005 . |
| 12 | GOWDA P, PATRICK S, JOSHI S D, et al. Glycyrrhizin prevents SARS-CoV-2 S1 and Orf3a induced high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) release and inhibits viral replication[J]. Cytokine, 2021, 142:155496. DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155496 . |
| 13 | UTSUNOMIYA T, KOBAYASHI M, POLLARD R B, et al. Glycyrrhizin, an active component of licorice roots, reduces morbidity and mortality of mice infected with lethal doses of influenza virus[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 1997, 41(3):551-556. DOI: 10.1128/AAC.41.3.551 . |
| 14 | DENG Q P, WANG M J, ZENG X, et al. Effects of glycyrrhizin in a mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2017, 41(4):1383-1392. DOI: 10.1159/000467897 . |
| 15 | YAO D C, BROWNLEE M. Hyperglycemia-induced reactive oxygen species increase expression of the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and RAGE ligands[J]. Diabetes, 2010, 59(1):249-255. DOI: 10.2337/db09-0801 . |
| 16 | SHARMA P, SHARMA A, VISHWAKARMA A L, et al. Host lung immunity is severely compromised during tropical pulmonary eosinophilia: role of lung eosinophils and macrophages[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2016, 99(4):619-628. DOI: 10.1189/jlb.4A0715-309RR . |
| 17 | JANG S S, KIM H G, LEE J S, et al. Melatonin reduces X-ray radiation-induced lung injury in mice by modulating oxidative stress and cytokine expression[J]. Int J Radiat Biol, 2013, 89(2):97-105. DOI: 10.3109/09553002.2013.734943 . |
| 18 | DEANE R, SINGH I, SAGARE A P, et al. A multimodal RAGE-specific inhibitor reduces amyloid β-mediated brain disorder in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease[J]. J Clin Invest, 2012, 122(4):1377-1392. DOI: 10.1172/jci58642 . |
| 19 | ORSATTI C L, MISSIMA F, PAGLIARONE A C, et al. Th1/Th2 cytokines' expression and production by propolis-treated mice[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2010, 129(3):314-318. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.03.030 . |
| 20 | TRACEY L, PÉREZ-ROSADO A, ARTIGA M J, et al. Expression of the NF-kappaB targets BCL2 and BIRC5/Survivin characterizes small B-cell and aggressive B-cell lymphomas, respectively[J]. J Pathol, 2005, 206(2):123-134. DOI: 10.1002/path.1768 . |
| 21 | HOU C H, FONG Y C, TANG C H. HMGB-1 induces IL-6 production in human synovial fibroblasts through c-Src, Akt and NF-κB pathways[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2011, 226(8):2006-2015. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.22541 . |
| 22 | CHEN R C, KANG R, TANG D L.The mechanism of HMGB1 secretion and release[J].Exp Mol Med, 2022, 54(2):91-102. DOI:10.1038/s12276-022-00736-w . |
| 23 | MAGNA M, PISETSKY D S.The role of HMGB1 in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases[J]. Mol Med, 2014, 20(1):138-146. DOI:10.2119/molmed.2013.00164 . |
| 24 | NI Y F, KUAI J K, LU Z F, et al. Glycyrrhizin treatment is associated with attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression[J]. J Surg Res, 2011, 165(1): e29-e35. DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2010.10.004 . |
| 25 | SITIA G, IANNACONE M, MÜLLER S, et al. Treatment with HMGB1 inhibitors diminishes CTL-induced liver disease in HBV transgenic mice[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2007, 81(1):100-107. DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0306173 . |
| 26 | INGRAHAM N E, LOTFI-EMRAN S, THIELEN B K, et al. Immunomodulation in COVID-19[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2020, 8(6):544-546. DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30226-5 . |
| 27 | MURCK H. Symptomatic protective action of glycyrrhizin (licorice) in COVID-19 infection?[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11:1239. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01239 . |
| 28 | SEO E H, SONG G Y, KWAK B O, et al. Effects of glycyrrhizin on the differentiation of myeloid cells of the heart and lungs in lipopolysaccharide-induced septic mice[J]. Shock, 2017, 48(3):371-376. DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000850 . |
| 29 | YU Z Q, OHTAKI Y, KAI K Z, et al. Critical roles of platelets in lipopolysaccharide-induced lethality: effects of glycyrrhizin and possible strategy for acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2005, 5(3):571-580. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2004.11.004 . |
| [1] | 王丹, 张晓璐, 王妍, 傅博, 王文栋, 刘京, 张甦寅, 武怡荷, 吴德国, 杜小燕, 战大伟, 章秀林, 李长龙. Big-BALB/c小鼠亚系选育前后的抗体制备效率比较研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(6): 612-618. |
| [2] | 程继帅, 牟唐维, 柳蕾, 吴化叶, 李琦涵. BALB/c小鼠经不同途径感染单纯疱疹病毒Ⅱ型的病理学比较分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2020, 40(1): 15-21. |
| [3] | 雷山, 刘强, 黄维金, 王佑春. 小鼠品系、性别和被毛对可视化假病毒感染模型的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2019, 39(6): 423-428. |
| [4] | 邹芦, 戴天娥, 卢晓, 艾晓杰. 替来他明/唑拉西泮联合右美托咪定对BALB/c小鼠麻醉效果观察[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2019, 39(4): 310-313. |
| [5] | 李迎, 杜小燕, 崔晓霞, 马兰芝, 尚世臣, 赵志兵, 赵权, 李桂军, 王冬平, 陈振文. CMU/1和CMU/2长爪沙鼠与F344大鼠及BALB/c小鼠4项凝血指标分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2018, 38(1): 57-59. |
| [6] | 顾剑洁, 葛蓉, 徐伟超, 刘丽均. 不同超排卵方案对BALB/c小鼠超排卵效果的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2017, 37(6): 482-484. |
| [7] | 邵宝珠, 唐其凤, 曹丽丽. BALB/c小鼠不同体质量范围对重组人促红素注射液体内活性测定的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2016, 36(3): 216-218. |
| [8] | 陈美莲, 赖国祥, 柳德灵, 卓惠长. 沙丁胺醇对老年大鼠呼吸机相关肺损伤的干预作用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2014, 34(4): 283-287. |
| [9] | 卢光新, 吕飞, 杜勇, 杨艳果, 周春芳, 金灵莉, 杨建业. 复方甘草酸苷对溃疡性结肠炎大鼠结肠组织NF-κB p65及COX-2表达的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2014, 34(2): 98-101. |
| [10] | 郑海明, 赵航, 郑萍. 葡聚糖硫酸钠和偶氮氧甲烷建立小鼠溃疡性结肠炎癌变模型[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2012, 32(1): 47-50. |
| [11] | 李吉达,徐守振,王建琳,尹燕博. 猪高致病性蓝耳病病毒诱发病毒性肺损伤动物模型初探[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2010, 30(5): 340-343. |
| [12] | 武珊珊1,刘吉福1,梁海龙1,张宪成2,黄春倩2,赵建2. 全氟异丁烯诱发大鼠急性肺损伤的初步观察[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2010, 30(4): 257-260. |
| [13] | 顾卫忠1,王晓东1,鲍世民2,邢正弘1,陈国强1. 玩具对小鼠生长繁育性能影响初探[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2008, 28(2): 131-132. |
| [14] | 敖红1,许兰文1,杨萍1,金玫蕾2. 4个与营养代谢相关基因对小鼠的血清生化指标的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2007, 27(3): 186-189. |
| [15] | 姚健, 胡樱, 夏萍, 李春生. 三种处理饲料饲喂BALB/c小鼠的效价分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2005, 25(1): 47-48. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||