













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 243-250.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.166
• 人类疾病动物模型 • 下一篇
收稿日期:2023-11-21
修回日期:2024-04-14
出版日期:2024-07-06
发布日期:2024-06-25
通讯作者:
师长宏(1973—),男,博士,教授,博士生导师,研究方向:人类疾病动物模型。E-mail: changhong@fmmu.edu.cn。ORCID: 0000-0001-7490-3593作者简介:秦 靖(1994—),女,硕士研究生,助理实验师,研究方向:分子影像研究。E-mail: qinjingjd@fmmu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Jing QIN, Yong ZHAO, Caiqin ZHANG, Bing BAI, Changhong SHI( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-11-21
Revised:2024-04-14
Published:2024-06-25
Online:2024-07-06
Contact:
SHI Changhong (ORCID: 0000-0001-7490-3593), E-mail: changhong@fmmu.edu.cn摘要:
目的 制备基于近红外荧光(near-infrared fluorescence,NIRF)探针的新型化合物,通过活体成像实现对炎性脑水肿小鼠模型的动态监测,以及对治疗效果的实时评估。 方法 选择NIRF探针IR-783与临床脑水肿治疗药物呋塞米(furosemide,FSM)进行化学连接,获得新的化合物IR-783-FSM。通过紫外分光光度计评价该化合物的紫外荧光特性;体外细胞学实验检测小鼠巨噬细胞RAW 264.7对该化合物的摄取情况;CCK8实验评价该化合物的细胞毒性。BALB/c小鼠腹腔注射脂多糖构建炎性脑水肿模型,通过HE染色和测量脑组织干湿重法确认建模成功;将脑水肿模型小鼠分为对照组、IR-783和IR-783-FSM治疗组,分别给予PBS、IR-783和IR-783-FSM腹腔注射后进行实时活体荧光成像,并在10 h后处死各组小鼠,进行脑部离体成像和干湿重测量,观察IR-783-FSM对炎性脑水肿模型的NIRF成像特性和治疗效果。 结果 新合成的化合物IR-783-FSM保留了IR-783优良的近红外荧光特征,可以靶向小鼠巨噬细胞,IC50为48.82 μmol/L。腹腔注射脂多糖可以成功构建炎性脑水肿模型,且其脑组织含水量较空白对照组小鼠明显升高(P<0.01);小鼠活体成像显示,与IR-783相比,IR-783-FSM在脑水肿模型中具有明显较强的荧光信号;与对照组相比,2、5和8 mmol/L IR-783-FSM治疗组小鼠的脑含水量均明显减少(P<0.01)。 结论 合成的新型NIRF探针IR-783-FSM可以实现对脑水肿的动态监测和对治疗效果的实时评估。
中图分类号:
秦靖,赵勇,张彩勤,等. 靶向炎性脑水肿的诊疗一体化近红外荧光探针的构建与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(3): 243-250. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.166.
Jing QIN,Yong ZHAO,Caiqin ZHANG,et al. Construction and Evaluation of Theranostic Near-infrared Fluorescent Probe for Targeting Inflammatory Brain Edema[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 243-250. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.166.
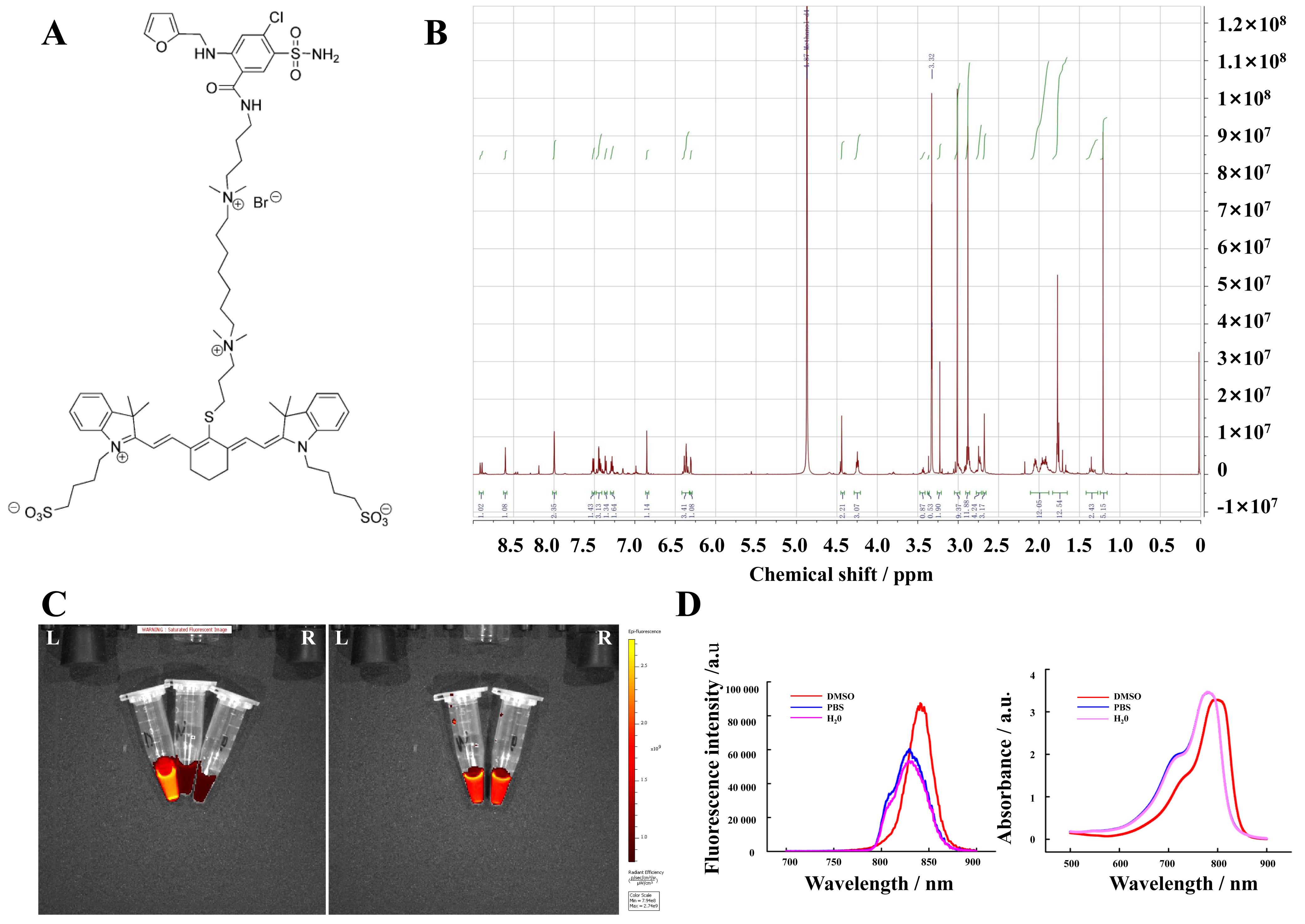
图1 IR-783-FSM探针的结构与表征注:A,IR-783-FSM结构图;B,IR-783-FSM核磁共振氢谱图;C,IR-783-FSM在不同溶剂中的荧光强度(左图从左至右的溶剂分别为DMSO、H2O、PBS,右图从左至右的溶剂分别为H2O和PBS);D,IR-783-FSM的荧光光谱(左)和吸光度光谱(右)。
Figure 1 Structure and characterization of the IR-783-FSM probeNote:A, Structure of IR-783-FSM; B, Nuclear magnetic resonance hydrogen spectrum of IR-783-FSM; C, Fluorescence intensity of IR-783-FSM in different solvents (in the left graph, the solvents from left to right are DMSO, H2O, and PBS; in the right graph, the solvents from left to right are H2O and PBS); D, Fluorescence spectra (left) and absorbance spectra (right) of IR-783-FSM.
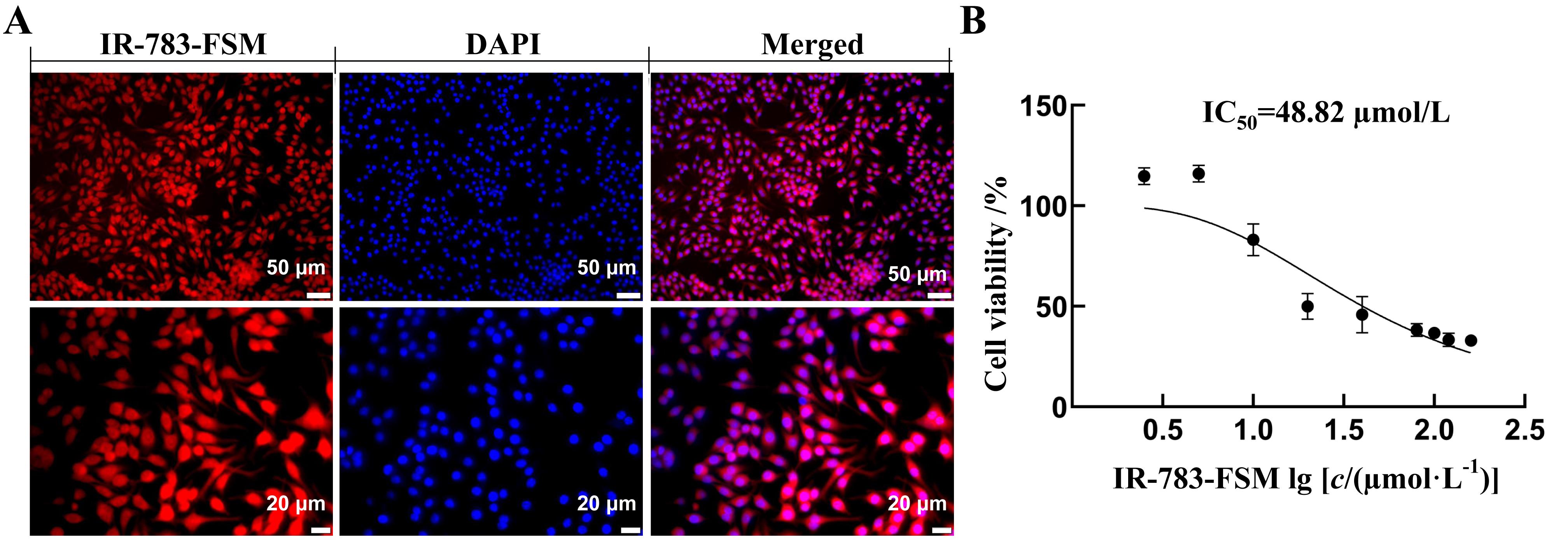
图2 IR-783-FSM探针的体外细胞摄取能力及细胞毒性注:A,近红外荧光显微镜观察小鼠巨噬细胞RAW 264.7对IR-783-FSM探针的摄取能力(红色荧光表示IR-783-FSM探针,蓝色荧光为DAPI标记的细胞核,Merged图提示IR-783-FSM探针进入细胞);B,CCK8法检测IR-783-FSM探针作用后小鼠巨噬细胞RAW 264.7的活力。
Figure 2 In vitro cellular uptake ability and cytotoxicity of IR-783-FSM probe in mouse macrophagesNote:Near-infrared fluorescence microscopy was used to observe the uptake ability of mouse macrophages RAW 264.7 to IR-783-FSM probe (Red fluorescence indicated IR-783-FSM probe. Blue fluorescence indicated the nucleus marked by DAPI. Merged plots represented the entry of the IR-783-FSM probe into cells). B, The viability of mouse macrophages RAW 264.7 treated with IR-783-FSM probe was assessed by CCK8 assay.
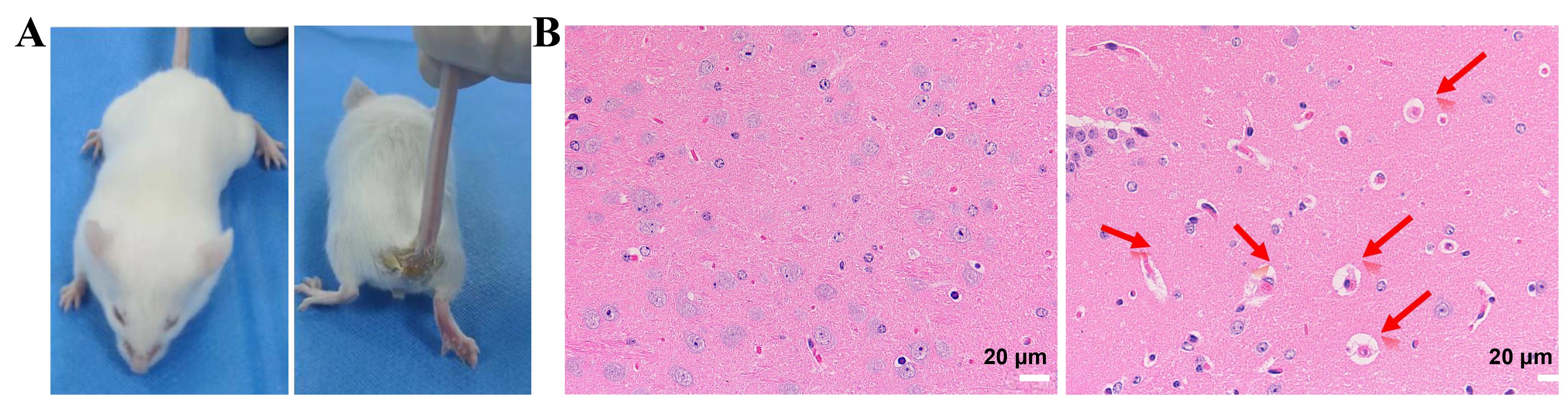
图3 脂多糖脑水肿小鼠模型构建成功注:A,脂多糖腹腔注射造模后小鼠精神萎靡(左)伴有腹泻(右);B,HE染色观察脂多糖腹腔注射造模后小鼠脑组织病理切片(左为注射生理盐水的空白组小鼠,右为注射脂多糖的小鼠,箭头所指部位血管周缝明显增宽显示脑水肿)。
Figure 3 The mouse model of lipopolysaccharide-induced brain edema was successfully constructedNote:A, After intraperitoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), mice appeared lethargic (left) with diarrhea (right). B, HE staining was used to observe the pathological sections of brain tissues in mice after model construction with LPS intraperitoneal injection (left image indicated the blank group injected with normal saline, and the right indicated the mice injected with LPS, while the arrows indicated marked widening of the perivascular spaces, indicating cerebral edema).
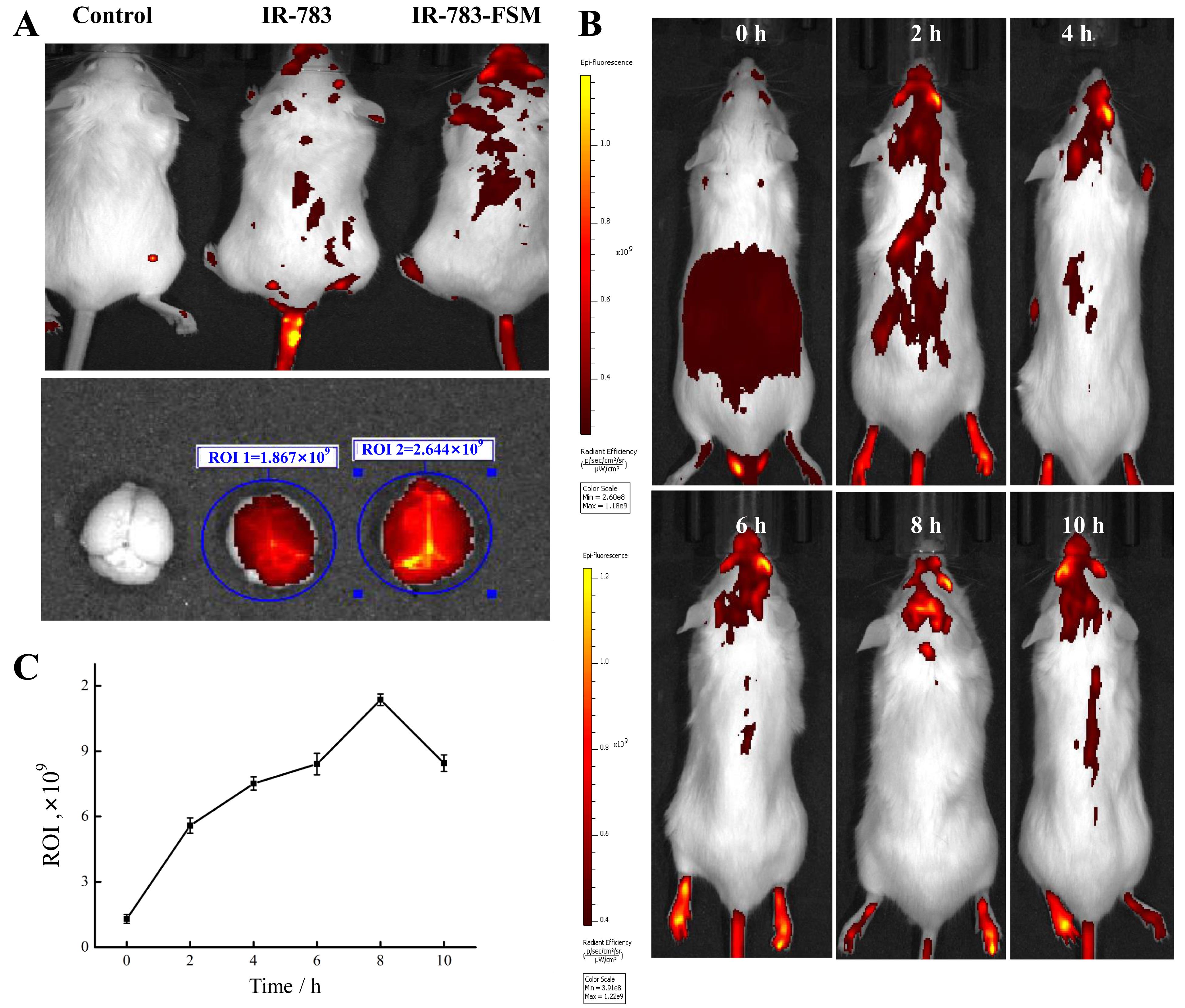
图4 脑水肿小鼠模型体内IR-783和IR-783-FSM的荧光成像结果注:A,PBS、IR-783和IR-783-FSM腹腔注射10 h后的活体和离体成像图;B,IR-783-FSM在脑水肿小鼠模型中的近红外荧光实时成像;C,IR-783-FSM在炎性脑水肿模型小鼠中的近红外荧光成像定量分析 (ROI表示感兴趣的区域)。
Figure 4 Fluorescence imaging results of IR-783 and IR-783-FSM in a mouse model of brain edemaNote: A, In vivo and ex vivo near-infrared fluorescence imaging 10 h after intraperitoneal injections of PBS, IR-783, and IR-783-FSM; B, Real-time near-infrared fluorescence imaging of IR-783-FSM in a mouse model of brain edema; C, Quantitative analysis of near-infrared fluorescence imaging of IR-783-FSM in a mouse model of brain edema (ROI represents regions of interest).
给药分组(n=5) Grouping and administration (n=5) | 脑组织含水量/% Brain water content/% |
|---|---|
| PBS | 79.511±0.483 |
| 5 mmol/L IR-783 | 78.364±0.949 |
| 2 mmol/L IR-783-FSM | 77.988±0.124** |
| 5 mmol/L IR-783-FSM | 77.276±0.816** |
| 8 mmol/L IR-783-FSM | 77.364±0.949** |
表1 脑水肿小鼠经IR-783-FSM治疗后的脑含水量变化
Table 1 Changes of brain water content in mice with brain edema treated with IR-783-FSM
给药分组(n=5) Grouping and administration (n=5) | 脑组织含水量/% Brain water content/% |
|---|---|
| PBS | 79.511±0.483 |
| 5 mmol/L IR-783 | 78.364±0.949 |
| 2 mmol/L IR-783-FSM | 77.988±0.124** |
| 5 mmol/L IR-783-FSM | 77.276±0.816** |
| 8 mmol/L IR-783-FSM | 77.364±0.949** |
| 1 | 杜安妮, 石京山. 创伤性脑损伤动物模型的新进展[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2015, 31(4):526-529. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-5519.2015.04.016 . |
| DU A N, SHI J S. New progress in animal models of traumatic brain injury[J]. J Mod Med Health, 2015, 31(4):526-529. DOI:10. 3969/j.issn.1009-5519.2015.04.016 . | |
| 2 | 吴志敏, 沈素兴. 基层训练伤康复治疗的现状与思考[J]. 西南军医, 2019, 21(3):284-286. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7193.2019.03.029 . |
| WU Z M, SHEN S X. Present situation and thinking of rehabilitation treatment of training injuries at the grass-roots level[J]. J Mil Surg Southwest China, 2019, 21(3):284-286. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7193.2019.03.029 . | |
| 3 | 李慧堂, 张岱男, 张新中, 等. 黄芪甲苷对大鼠创伤性脑损伤后脑水肿、炎症反应、细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2022, 31(9):1198-1203, 1223. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2022.09.006 . |
| LI H T, ZHANG D N, ZHANG X Z, et al. Effects of astragaloside Ⅳ on brain edema, inflammatory response and cell apoptosis after traumatic brain injury in rats[J]. Mod J Integr Tradit Chin West Med, 2022, 31(9):1198-1203, 1223. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2022.09.006 . | |
| 4 | ZHANG C, LEE J Y, KEEP R F, et al. Brain edema formation and complement activation in a rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage[J]. Acta Neurochir Suppl, 2013, 118:157-161. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-7091-1434-6_29 . |
| 5 | 姚奔驰. 托拉塞米与呋塞米治疗脑出血后急性脑水肿患者的临床效果[J]. 中国药物经济学, 2021, 16(3):109-111, 119. DOI: 10.12010/j.issn.1673-5846.2021.03.028 . |
| YAO B C. Clinical effects of torasemide and furosemide in the treatment of patients with acute cerebral edema after cerebral hemorrhage[J]. China J Pharm Econ, 2021, 16(3):109-111, 119. DOI: 10.12010/j.issn.1673-5846.2021.03.028 . | |
| 6 | 郦昱琨, 尹文俊, 安晓婕, 等. 呋塞米与甘露醇联用致脑水肿患者急性肾损伤风险因素分析及预测[J]. 中国新药与临床杂志, 2022, 41(5):286-290. DOI: 10.14109/j.cnki.xyylc.2022.05.07 . |
| LI Y K, YIN W J, AN X J, et al. Risk factor analysis and prediction of acute kidney injury in patients with cerebral edema treated with furosemide and mannitol[J]. Chin J N Drugs Clin Remedies, 2022, 41(5):286-290. DOI: 10.14109/j.cnki.xyylc.2022.05.07 . | |
| 7 | HAN X Y, SONG X Y, YU F B, et al. A ratiometric near-infrared fluorescent probe for quantification and evaluation of selenocysteine-protective effects in acute inflammation[J]. Adv Funct Materials, 2017, 27(28):1700769. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201700769 . |
| 8 | HUANG J, JIANG Y, LI J, et al. A renal-clearable macromolecular reporter for near-infrared fluorescence imaging of bladder cancer[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2020, 59(11):4415-4420. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201911859 . |
| 9 | ZHANG C Q, ZHAO Y, ZHANG H, et al. The application of heptamethine cyanine dye DZ-1 and indocyanine green for imaging and targeting in xenograft models of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(6):1332. DOI: 10.3390/ijms18061332 . |
| 10 | GUSDON A M, GIALDINI G, KONE G, et al. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and perihematomal edema growth in intracerebral hemorrhage[J]. Stroke, 2017, 48(9):2589-2592. DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.018120 . |
| 11 | RENDEVSKI V, ALEKSOVSKI B, MIHAJLOVSKA RENDEVSKA A, et al. Inflammatory and oxidative stress markers in intracerebral hemorrhage: relevance as prognostic markers for quantification of the edema volume[J]. Brain Pathol, 2023, 33(2): e13106. DOI: 10.1111/bpa.13106 . |
| 12 | SHI C H, WU J B, CHU G C Y, et al. Heptamethine carbocyanine dye-mediated near-infrared imaging of canine and human cancers through the HIF-1α/OATPs signaling axis[J]. Oncotarget, 2014, 5(20):10114-10126. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2464 . |
| 13 | ZHANG C Q, ZHAO Y, ZHAO N N, et al. NIRF optical/PET dual-modal imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma using heptamethine carbocyanine dye[J]. Contrast Media Mol Imaging, 2018, 2018:4979746. DOI: 10.1155/2018/4979746 . |
| 14 | YANG X J, SHI C M, TONG R, et al. Near IR heptamethine cyanine dye-mediated cancer imaging[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2010, 16(10):2833-2844. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0059 . |
| 15 | QIN J, ZHANG C Q, ZHAO Y, et al. Small mitochondria-targeting fluorophore with multifunctional therapeutic activities against prostate cancer via the HIF1α/OATPs pathway[J]. Mol Pharmaceutics, 2023, 20(12):6226-6236. DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.3c00621 . |
| 16 | 曹传顶. 3%氯化钠对脂多糖小鼠脑水肿的保护作用及非渗透机制研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2014. |
| CAO C D. Protective effect of 3% sodium chloride on brain edema in lipopolysaccharide mice and its non-osmotic mechanism [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2014. | |
| 17 | 吴俊杰. 基于活体成像的大鼠脑水肿模型评价指标体系的建立及冰片对脂多糖致大鼠脑水肿的改善作用机制研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2019. |
| WU J J. Establishment of evaluation index system of rat brain edema model based on in vivo imaging and the mechanism of borneol in improving lipopolysaccharide induced brain edema in rats[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2019. | |
| 18 | 宁雪, 刘洋洋, 李韪韬. 甘露醇对脂多糖致小鼠脑水肿治疗的多参数评估[J]. 生物医学工程研究, 2021, 40(1):43-48. DOI: 10.19529/j.cnki.1672-6278.2021.01.08 . |
| NING X, LIU Y Y, LI W T. Multi parameter evaluation of mannitol in the treatment of lipopolysaccharide induced brain edema in mice[J]. J Biomed Eng Res, 2021, 40(1):43-48. DOI: 10.19529/j.cnki.1672-6278.2021.01.08 . | |
| 19 | MAAS A I R, MENON D K, ADELSON P D, et al. Traumatic brain injury: integrated approaches to improve prevention, clinical care, and research[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2017, 16(12):987-1048. DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30371-X . |
| 20 | 冯华, 李文, 谭亮, 等. 颅脑创伤病情评估多模态监测系统[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志, 2020, 20(7):568-576. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6731.2020.07.002 . |
| FENG H, LI W, TAN L, et al. Multimodal monitoring system in traumatic brain injury[J]. Chin J Contemp Neurol Neurosurg, 2020, 20(7):568-576. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6731.2020.07.002 . | |
| 21 | 亢璐, 郑瑞, 杨智航, 等. 银杏叶提取物通过VEGF/PI3 K/Akt1信号通路改善大鼠创伤性脑水肿[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2021, 41(1):157-160. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2021.01.045 . |
| KANG L, ZHENG R, YANG Z H, et al. Ginkgo biloba extract improves traumatic brain edema in rats through VEGF/PI3K/Akt1 signaling pathway[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2021, 41(1):157-160. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2021.01.045 . | |
| 22 | 张建海, 黄生炫, 康泽辉, 等. 甘露醇、呋塞米联合白蛋白治疗脑外伤后脑水肿的临床价值[J]. 中国药物滥用防治杂志, 2022, 28(11):1646-1649. DOI: 10.15900/j.cnki.zylf1995.2022.11.026 . |
| ZHANG J H, HUANG S X, KANG Z H, et al. Clinical value of mannitol, furosemide combined with albumin in the treatment of cerebral edema after traumatic brain injury[J]. Chin J Drug Abuse Prev Treat, 2022, 28(11):1646-1649. DOI: 10.15900/j.cnki.zylf1995.2022.11.026 . | |
| 23 | 霍学智. 观察呋塞米治疗急性脑出血并脑水肿患者的疗效与不良反应[J]. 医学食疗与健康, 2021, 19(3):58-59. |
| HUO X Z. To observe the efficacy and side effects of furosemide in the treatment of patients with acute cerebral hemorrhage complicated with cerebral edema[J]. Med Diet Health, 2021, 19(3):58-59. | |
| 24 | HU Z H, CHEN W H, TIAN J, et al. NIRF nanoprobes for cancer molecular imaging: approaching clinic[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2020, 26(5):469-482. DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2020.02.003 . |
| 25 | LI W X, LI R, CHEN R, et al. Activatable fluorescent-photoacoustic integrated probes with deep tissue penetration for pathological diagnosis and therapeutic evaluation of acute inflammation in mice[J]. Anal Chem, 2022, 94(22):7996-8004. DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c01048 . |
| 26 | SUZUKI Y, KAJITA H, KONISHI N, et al. Subcutaneous lymphatic vessels in the lower extremities: comparison between photoacoustic lymphangiography and near-infrared fluorescence lymphangiography[J]. Radiology, 2020, 295(2):469-474. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2020191710 . |
| 27 | ZHANG Y, LI W, CHEN X Q, et al. Liver-targeted near-infrared fluorescence/photoacoustic dual-modal probe for real-time imaging of In situ hepatic inflammation[J]. Anal Chem, 2023, 95(4):2579-2587. DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c05476 . |
| 28 | SONG J W, NAM H S, AHN J W, et al. Macrophage targeted theranostic strategy for accurate detection and rapid stabilization of the inflamed high-risk plaque[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(18):8874-8893. DOI: 10.7150/thno.59759 . |
| 29 | IKEDA H, ISHII A, SANO K, et al. Activatable fluorescence imaging of macrophages in cerebral aneurysms using iron oxide nanoparticles conjugated with indocyanine green[J]. Front Neurosci, 2020, 14:370. DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00370 . |
| [1] | 刘荣乐, 程灏, 尚付生, 常书福, 徐平. SHJH hr 小鼠的心脏衰老表型研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(1): 13-20. |
| [2] | 吴志浩, 曹舒扬, 周正宇. 肝螺杆菌感染引起VDR-/-小鼠炎性肠病相关肠纤维化模型的建立及机制探讨[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(1): 37-46. |
| [3] | 张楠, 李怀银, 连晓娣, 魏娟鹏, 高明. 不同光照时长对NIH小鼠体重和学习记忆能力的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(1): 73-78. |
| [4] | 王芊芊, 陶斯珏, 卫振, 金晖晖, 刘平, 汪洌. 利用辅助生殖技术挽救基因修饰小鼠的实例分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(1): 79-86. |
| [5] | 赵赫, 张帆, 肖宇宙, 安学芳, 张涛, 李丽. 一例干扰素受体缺失小鼠自发未成熟型睾丸畸胎瘤诊断[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 691-694. |
| [6] | 赵小娜, 王鹏, 叶茂青, 曲新凯. 应用Triacsin C构建新型高血糖肥胖小鼠心功能减退模型[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 605-612. |
| [7] | 谭贺, 杨晓辉, 张大秀, 王贵成. 不同发育时期小鼠代谢笼实验的最佳适应期探讨[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 502-510. |
| [8] | 孟雨, 梁冬丽, 郑琳琳, 周园园, 王朝霞. 人肝肿瘤细胞的裸小鼠原位癌建模条件优化及评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 511-522. |
| [9] | 张一粟, 刘欣茹, 武若杰, 刘睿, 欧阳红, 李晓红. 慢性不可预知性应激与完全弗氏佐剂、福尔马林诱导的妊娠期疼痛-抑郁共病小鼠模型的构建与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(3): 259-269. |
| [10] | 吴东, 石蕊, 罗珮珊, 李灵恩, 盛席静, 王梦阳, 倪露, 王素娟, 杨慧欣, 赵静. 不同颗粒饲料硬度对实验小鼠生长繁殖、饲料利用率及环境粉尘量的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(3): 313-320. |
| [11] | 刘芸, 冯婷婷, 佟巍, 郭智, 李夏, 孔琪, 向志光. 甘草酸能减轻小鼠肺炎病毒引起的小鼠肺脏损伤[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(3): 251-258. |
| [12] | 胡锦华, 韩菁婕, 金旻, 胡滨, 娄月芬. 葛根素对大鼠和小鼠骨密度影响的Meta分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(2): 149-161. |
| [13] | 梁敏, 郭洋, 王津津, 朱梦妍, 池骏, 陈艳娟, 王成稷, 喻智澜, 沈如凌. Dmd基因突变小鼠构建及在肌肉及免疫系统的表型验证[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(1): 42-51. |
| [14] | 郑建华, 法云智, 董巧燕, 邱业峰, 陈菁青. 高原急性缺氧肠道应激损伤小鼠模型的构建与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(1): 31-41. |
| [15] | 唐倩倩, 张秀莉, 常在. 清华大学实验动物中心小鼠自动饮水系统漏水情况统计分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(1): 85-91. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||