













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 124-135.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.149
谭莹1,2( ), 廖文平1,2, 高启龙3, 李勇1,2, 史新辉1,2, 王京昆1,2(
), 廖文平1,2, 高启龙3, 李勇1,2, 史新辉1,2, 王京昆1,2( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2022-09-22
修回日期:2023-02-17
出版日期:2023-04-25
发布日期:2023-04-25
通讯作者:
王京昆(1969—),男,学士,正高级工程师,研究方向:新药研发和药物安全性评价研究。E-mail: wjkyimm@163.com。ORCID: 0009-0006-9724-6286作者简介:谭 莹(1979—),女,博士,正高级工程师,研究方向:药物安全性评价研究。E-mail: ty1203@163.com。ORCID: 0009-0007-3084-9020
基金资助:
Ying TAN1,2( ), Wenping LIAO1,2, Qilong GAO3, Yong LI1,2, Xinhui SHI1,2, Jingkun WANG1,2(
), Wenping LIAO1,2, Qilong GAO3, Yong LI1,2, Xinhui SHI1,2, Jingkun WANG1,2( )(
)( )
)
Received:2022-09-22
Revised:2023-02-17
Published:2023-04-25
Online:2023-04-25
Contact:
WANG Jingkun (ORCID: 0009-0006-9724-6286), E-mail: wjkyimm@163.com摘要:
目的 全面评价碘酸钠腹腔注射对SD大鼠生理指标和视网膜组织病理学特征的影响。 方法 选取64只SD大鼠随机分为阴性对照组和模型组,每组32只,雌雄各半。模型组以10 mL/kg剂量腹腔注射碘酸钠(6 mg/mL)1次,阴性对照组以10 mL/kg剂量腹腔注射生理盐水注射液1次。每天观察大鼠一般体征,注射当天(0天)和注射后第2、6、9、13、16、20、23、27、29、36、43、50、57天称量所有存活大鼠体质量;注射后第3、7、21、28、41、62天随机选取大鼠(第28天为12只/组,其余为4只/组,均为雌雄各半)进行血清生化学指标检测,系统解剖摘取脏器称重,然后对主要脏器和组织进行HE染色,以及眼HE和TUNEL染色;注射后第28、62天进行血常规指标检测。 结果 注射碘酸钠后,模型组88%的大鼠出现一过性稀便,观察期间大鼠体质量增长稍缓且以雄鼠较明显。注射后第28天模型组雌鼠红细胞容积(red blood cell volume,RDW)和雄鼠尿素氮(urea nitrogen,BUN)、网织红细胞计数(reticulocyte count,Retic#)及百分比(reticulocyte percentage,Retic%)均升高,与阴性对照组比较的差异均有统计学意义(均P<0.05)。雌雄鼠白细胞(white blood cells,WBC)、红细胞(red blood cells,RBC)、血红蛋白(hemoglobin,HGB)、红细胞比容(hematocrit,HCT)均有降低趋势,但组间差异均没有统计学意义(均P>0.05)。模型组雄鼠胸腺重量、系数除注射后第7天大于阴性对照组外,其余时间点均小于阴性对照组,但组间差异均没有统计学意义(均P>0.05)。组织病理学检查可见模型组大鼠视网膜由波浪状改变逐步发展为异常心电图样改变,各层排列紊乱,外核层局灶性变薄,视网膜外核层细胞凋亡;病变发生率、病变评分和凋亡细胞数量均明显高于或多于同时期的阴性对照组,第28天的组间差异有统计学意义(均P<0.01)。 结论 碘酸钠腹腔注射除可使大鼠视网膜变性外,对血清生化、血常规部分指标也有一定程度的影响,还出现大鼠体质量增长略缓慢和一过性粪便性状改变的现象。因此,在使用该模型开展药物安全性评价时,应关注造模试剂对动物的影响。
中图分类号:
谭莹,廖文平,高启龙,等. 碘酸钠诱发视网膜色素变性大鼠模型的生理指标和组织病理学分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(2): 124-135. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.149.
Ying TAN,Wenping LIAO,Qilong GAO,et al. Physiological Indexes and Histopathology Analysis of Sodium Iodate-Induced Retinitis Pigmentosa in Rats[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 124-135. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.149.
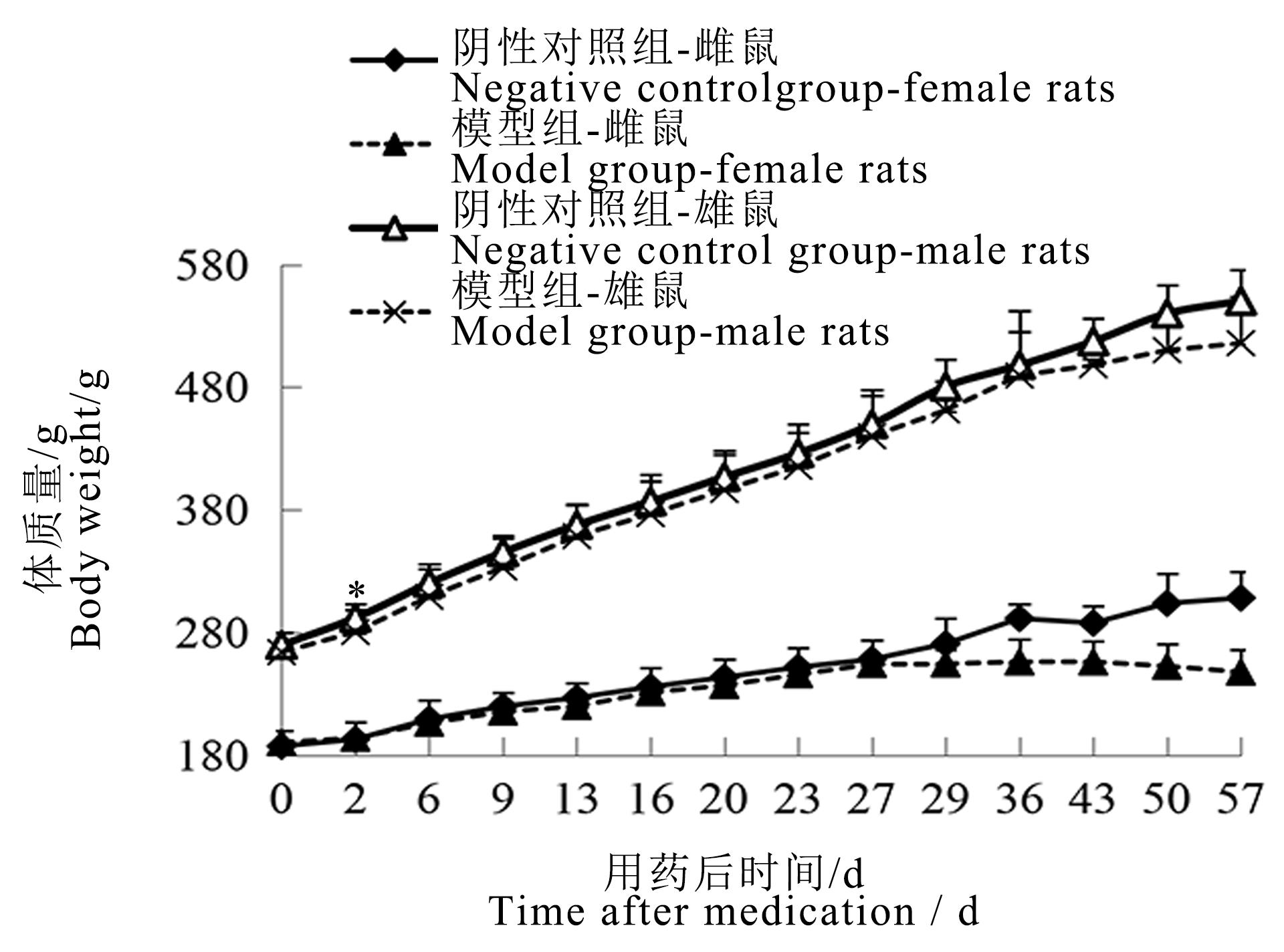
图1 碘酸钠注射后雌雄鼠体质量变化曲线图注:模型组一次性腹腔注射质量浓度为6 mg/mL碘酸钠溶液10 mL/kg;阴性对照组以相同容积和频次腹腔注射生理盐水注射液。各时间点两组大鼠数量分别为单性别16、16、14、12、12、12、12、10、10、4、4、2、2、2只;与阴性对照组间比较,?P<0.05。
Figure 1 Body weight curve of male and female rats after sodium iodate injectionNote:The model group was intraperitoneally injected with 6 mg/mL sodium iodate solution once at the dose of 10 mL/kg;the negative control group was intraperitoneally injected with normal saline at the same volume and frequency. The number of rats in the two groups at each time point was 16, 16, 14, 12,12, 12, 12, 10, 10, 4, 4, 2, 2, 2 respectively for single sex. Compared with the negative control group, ?P<0.05.
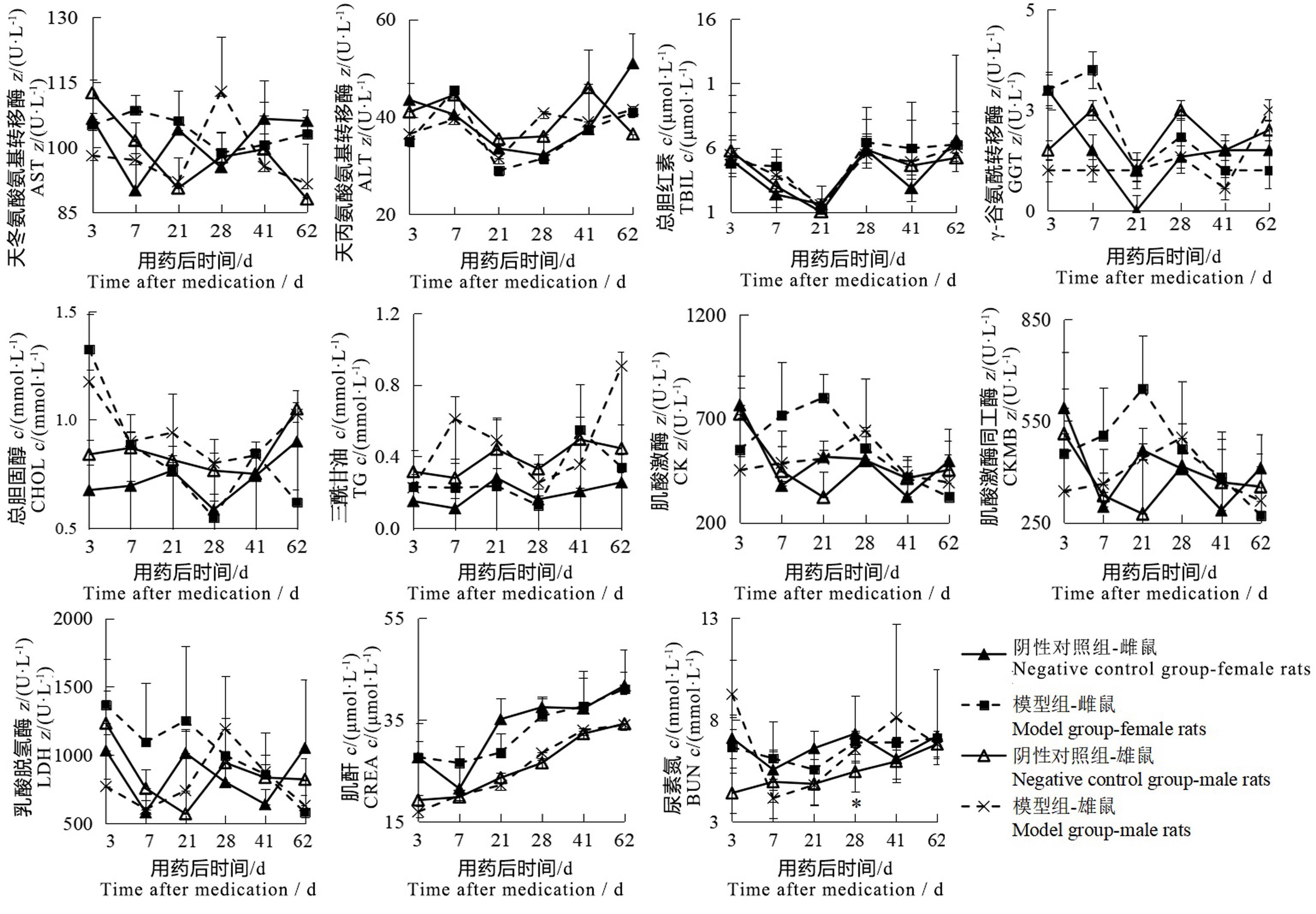
图2 碘酸钠注射后雌雄鼠血清生化指标变化注:模型组一次性腹腔注射质量浓度为6 mg/mL碘酸钠溶液10 mL/kg;阴性对照组以相同容积和频次腹腔注射生理盐水注射液。各时间点两组大鼠数量分别为单性别2、2、2、6、2、2只;与阴性对照组比较,?P<0.05。
Figure 2 Changes of serum biochemical indexes of male and female rats after sodium iodate injectionNote: The model group was intraperitoneally injected with 6 mg/mL sodium iodate solution once at the dose of 10 mL/kg; the negative control group was intraperitoneally injected with normal saline at the same volume and frequency. The number of rats in the two groups at each time point was 2, 2, 2, 6, 2, 2 respectively for single sex. Compared with the negative control group, ?P<0.05.
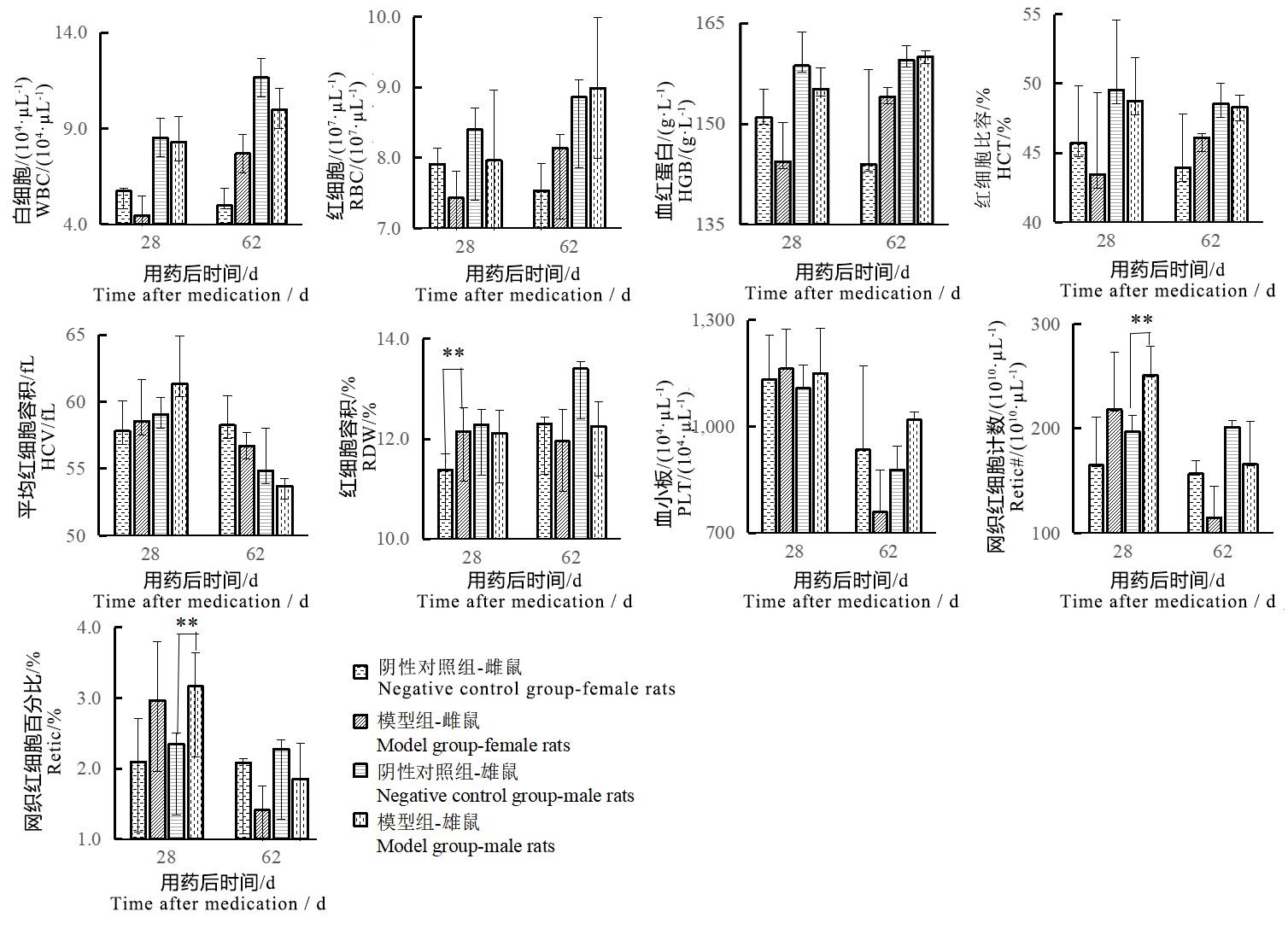
图3 碘酸钠注射后雌雄鼠血常规指标变化注:模型组一次性腹腔注射质量浓度为6 mg/mL碘酸钠溶液10 mL/kg;阴性对照组以相同容积和频次腹腔注射生理盐水注射液。各时间点两组大鼠数量分别为单性别2、2、2、6、2、2只;与阴性对照组间比较,??P<0.01。
Figure 3 Changes of blood routine indexes of male and female rats after sodium iodate injectionNote:The model group was intraperitoneally injected with 6 mg/mL sodium iodate solution once at the dose of 10 mL/kg;the negative control group was intraperitoneally injected with normal saline at the same volume and frequency. The number of rats in the two groups at each time point was 2, 2, 2, 6, 2, 2 respectively for single sex. Compared with the negative control group, ??P<0.01.
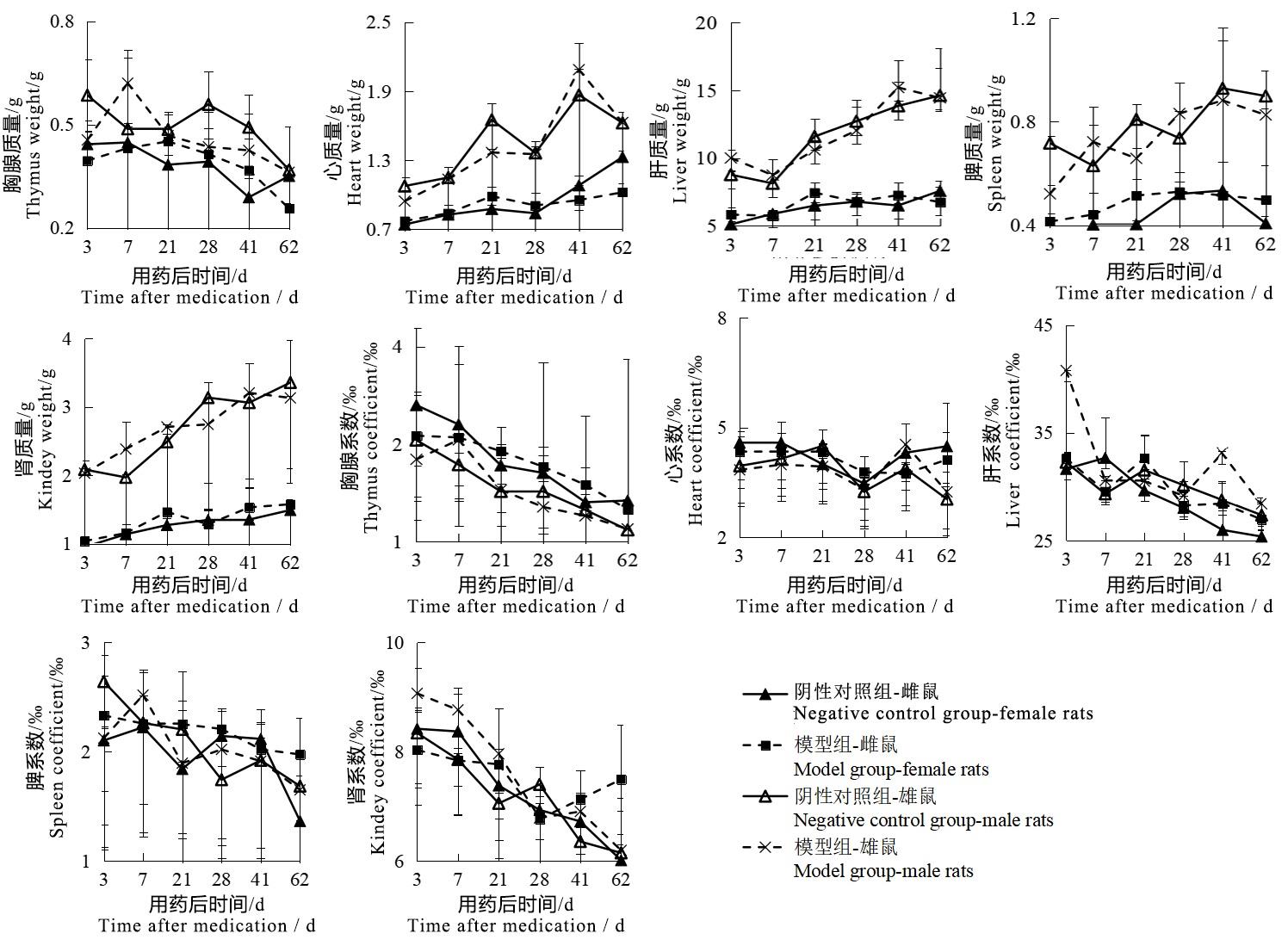
图4 碘酸钠注射后雌雄鼠各脏器质量及系数变化图注:模型组一次性腹腔注射质量浓度为6 mg/mL碘酸钠溶液10 mL/kg;阴性对照组以相同容积和频次腹腔注射生理盐水注射液。各时间点两组大鼠数量分别为单性别2、2、2、6、2、2只。
Figure 4 Changes of organ weight and coefficient of male and female rats after sodium iodate injectionNote:The model group was intraperitoneally injected with 6 mg/mL sodium iodate solution once at the dose of 10 mL/kg;the negative control group was intraperitoneally injected with normal saline at the same volume and frequency. The number of rats in the two groups at each time point was 2, 2, 2, 6, 2, 2 respectively for single sex.
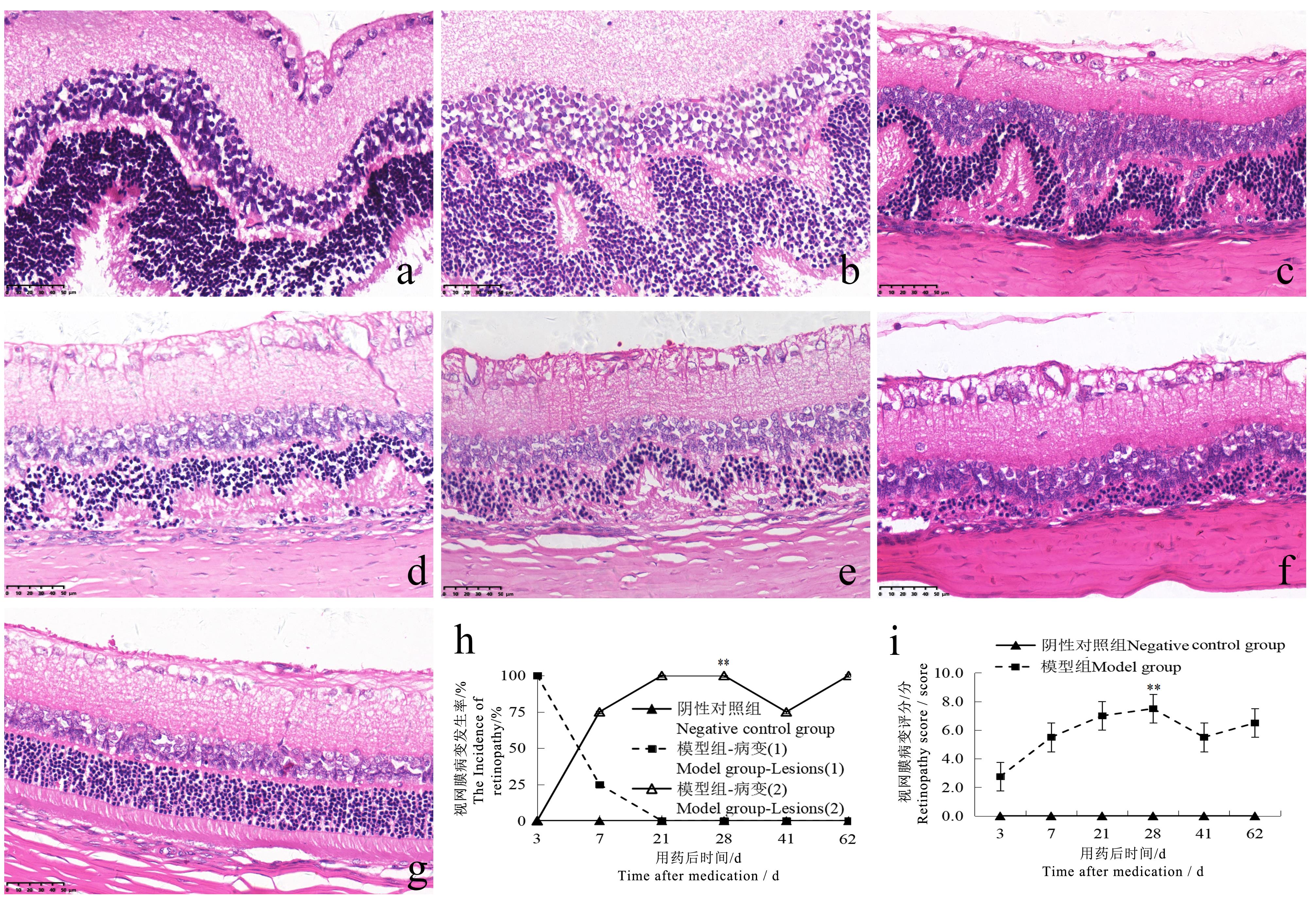
图5 碘酸钠注射后不同时间点的大鼠眼视网膜病变情况(HE染色, ×400)注:模型组一次性腹腔注射质量浓度为6 mg/mL碘酸钠溶液10 mL/kg;阴性对照组以相同容积和频次腹腔注射生理盐水注射液。各时间点两组大鼠数量分别为单性别2、2、2、6、2、2只。a示模型组注射后第3天视网膜呈波浪样改变;b示模型组注射后第7天视网膜呈异常心电图样改变,各层排列紊乱;图c~f分别示模型组注射后第21、28、41、62天视网膜呈异常心电图样改变,各层排列紊乱、外核层局灶变薄;g示阴性对照组视网膜正常;h-i为两组大鼠的视网膜病变发生率及HE评分比较(病变1为视网膜呈波浪样改变,病变2为视网膜呈心电图样改变)与阴性对照组比较,??P<0.01。图中比例尺大小均为50 μm。
Figure 5 Retinopathy in rats at different time points after sodium iodate injection (HE staining, ×400)Note:The model group was intraperitoneally injected with 6 mg/mL sodium iodate solution once at the dose of 10 mL/kg; the negative control group was intraperitoneally injected with normal saline at the same volume and frequency. The number of rats in the two groups at each time point was 2, 2, 2, 6, 2, 2 respectively for single sex. a shows the retina of the model group appeared wave-like changes on the 3rd day after injection; b shows the retina of the model group appeared abnormal electrocardiogram (ECG)-like changes on the 7th day after injection, and the arrangement of each layer was disordered; c-f show the retina of the model group appeared abnormal ECG-like changes on the 21st, 28th, 41st and 62nd days after injection, with disordered arrangement of each layer and focal thinning of the outer nuclear layer. g shows normal retina in negative control group; h-i show the comparison of the incidence of retinopathy and HE score between the two groups (Lesion 1 shows wave-like changes in the retina, lesion 2 shows ECG-like changes in the retina). ??P<0.01, vs the negative control group. The scale size in the figure are 50 μm.
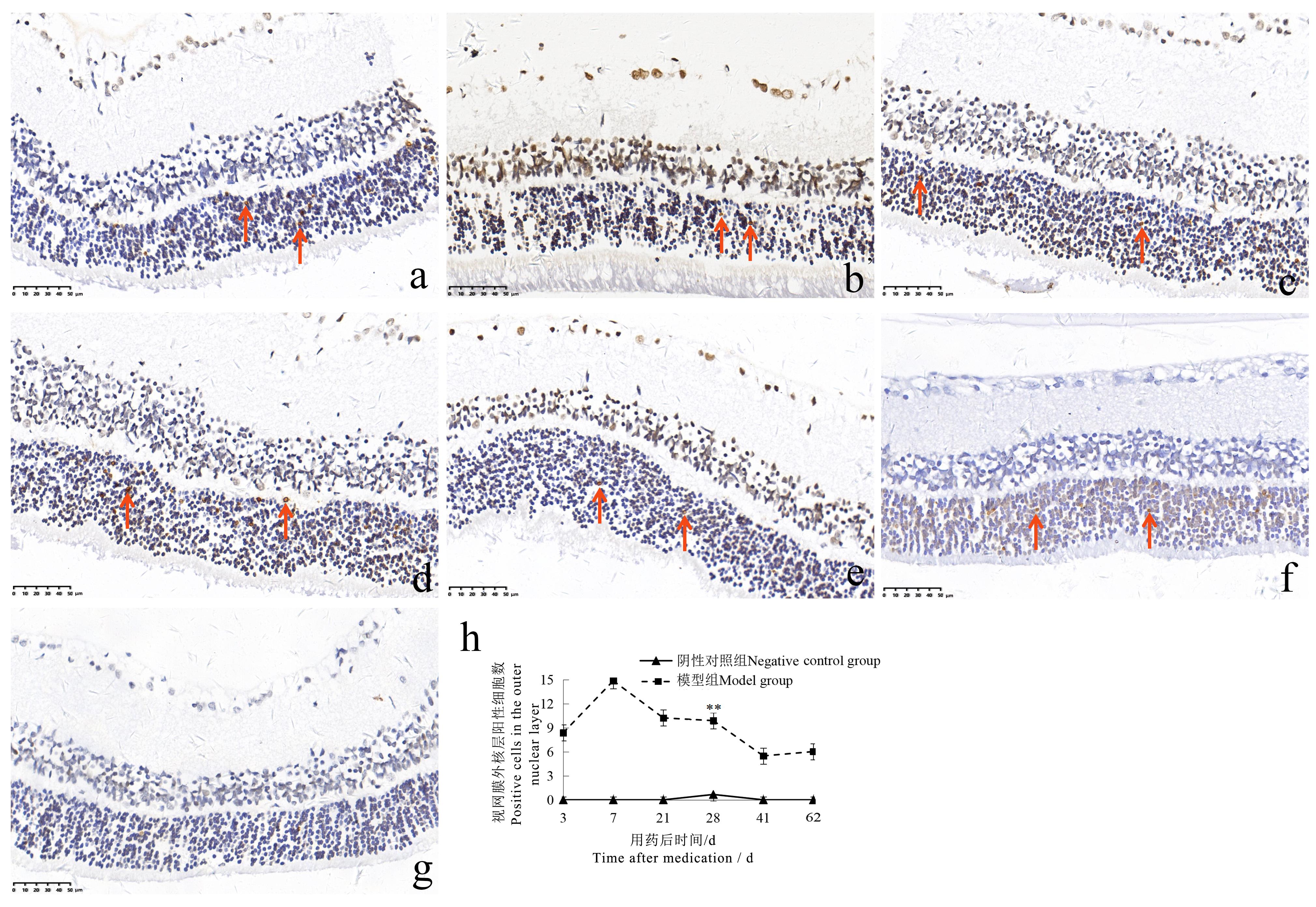
图6 碘酸钠注射后不同时间点的大鼠眼视网膜TUNEL染色情况(×400)注:模型组一次性腹腔注射质量浓度为6 mg/mL碘酸钠溶液10 mL/kg;阴性对照组以相同容积和频次腹腔注射生理盐水注射液。各时间点两组大鼠数量分别为单性别2、2、2、6、2、2只。a~f分别示模型组注射后第3、7、21、28、41、62天视网膜外核层细胞TUNEL染色阳性(箭头所示为TUNEL染色阳性细胞);g示阴性对照组视网膜TUNEL染色阴性;h为两组大鼠的视网膜外核层TUNEL染色阳性细胞数比较,与阴性对照组比较,??P<0.01。图中比例尺大小均为50 μm。
Figure 6 TUNEL staining of rat retina at different time points after sodium iodate injection (×400 )Note:The model group was intraperitoneally injected with 6 mg/mL sodium iodate solution once at the dose of 10 mL/kg;the negative control group was intraperitoneally injected with normal saline at the same volume and frequency. The number of rats in the two groups at each time point was 2, 2, 2, 6, 2, 2 respectively for single sex. a-f show that TUNEL staining was positive in the outer nuclear layer of the retina on the 3rd, 7th, 21st, 28th, 41st and 62nd days after injection in the model group (the arrows show TUNEL staining positive cells); g shows that the TUNEL staining of the retina in the negative control group was negative; h shows the comparison of the number of TUNEL staining positive cells in the outer nuclear layer of the two groups of rats. ??P<0.01, vs the negative control group. The scale size in the figure are 50 μm.
| 1 | 国家食品药品监督管理总局.«药物非临床研究质量管理规范»(国家食品药品监督管理总局令第34号)[EB/OL]. (2017-08-02)[2023-01-13]. . |
| 2 | ICH. M3(R2) Guidance on Nonclinical Safety Studies for the Conduct of Human Clinical Trials and Marketing Authori-zation for Pharmaceuticals[EB/OL]. (2009-06-11)[2023-01-13]. . |
| 3 | 范美花. 碘酸钠诱发的视网膜色素变性动物模型研究进展[J]. 中华实验眼科杂志, 2016, 34(9):860-864. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-0160.2016.09.018 . |
| FAN M H. Progress in developing a sodium iodate-induced retinitis pigmentosa animal model[J]. Chin J Exp Ophthalmol, 2016, 34(9):860-864. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-0160.2016.09.018 . | |
| 4 | 茅佩瑶, 茅希颖, 陈雪, 等. 碘酸钠诱导小鼠视网膜色素上皮变性模型的研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2020, 20(9):1636-1641, 1662. DOI: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2020.09.007 . |
| MAO P Y, MAO X Y, CHEN X, et al. Study on a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa induced by sodium iodate[J]. Prog Mod Biomed, 2020, 20(9):1636-1641, 1662. DOI: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2020.09.007 . | |
| 5 | LIU Y, LI Y, WANG C G, et al. Morphologic and histopathologic change of sodium iodate-induced retinal degeneration in adult rats[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2019, 12(2):443-454. |
| 6 | 李鑫, 洪萌, 侯铁奇. 骨髓间充质干细胞对视网膜色素变性大鼠视网膜的修复作用[J]. 新乡医学院学报, 2021, 38(6):511-515. DOI: 10.7683/xxyxyxb.2021.06.003 . |
| LI X, HONG M, HOU T Q. Repair effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on the retina of rats with retinitis pigmentosa[J]. J Xinxiang Med Univ, 2021, 38(6):511-515. DOI: 10.7683/xxyxyxb.2021.06.003 . | |
| 7 | 蔡曾晓瑞, 胡相卡, 桂留铭, 等. 三七总皂苷对碘酸钠所致视网膜损伤的保护作用及机制研究[J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 41(1):113-119. DOI:10.13880/j.cnki.65-1174/n.2023.22.005 . |
| CAI Z X R, HU X K, GUI L M, et al. Study on protective effect and mechanism of panax notoginseng saponins on retina injury induced by sodium iodate[J]. Journal of Shihezi University(Natural Science),2023,41(1):113-119.DOI:10.13880/j.cnki.65-1174/n.2023.22.005 . | |
| 8 | 杜柏荣, 许衍峰, 韦志强. 维生素C通过调节巨噬细胞功能缓解大鼠黄斑变性的研究[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2022, 26(17):130-134. DOI: 10.7619/jcmp.20220296 . |
| DU B R, XU Y F, WEI Z Q. Vitamin C alleviates macular degeneration in rats by regulating function of macrophages[J]. J Clin Med Pract, 2022, 26(17):130-134. DOI: 10.7619/jcmp.20220296 . | |
| 9 | 许凯. 黄芪甲苷纳米乳眼用凝胶对实验性大鼠干性年龄相关性黄斑变性的作用研究[D]. 北京: 中国中医科学院, 2018. |
| XU K. Study on the effect of astragaloside IV nanoemulsion gel onexperimental dry age-related macular degeneration rat model[D]. Beijing: China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, 2018. | |
| 10 | 朱颖婷, 邓新国, 高杨, 等. 碘酸钠诱导大鼠视网膜损伤的病理改变和SOD、CAT的变化[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2010, 26(9):1851-1854. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2010.09.038 . |
| ZHU Y T, DENG X G, GAO Y, et al. Pathological changes and activity of SOD and CAT in the damaged retina induced by sodium iodate in rats[J]. Chin J Pathophysiol, 2010, 26(9):1851-1854. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2010.09.038 . | |
| 11 | 王立春, 刘建宗, 郭莹. 碘酸钠诱导兔视网膜色素上皮变性模型的研究[J]. 眼科新进展, 2015, 35(11):1032-1035. DOI: 10.13389/j.cnki.rao.2015.0282 . |
| WANG L C, LIU J Z, GUO Y. Experimental study on rabbit retinal pigment epithelial degeneration induced by sodium iodate[J]. Recent Adv Ophthalmol, 2015, 35(11):1032-1035. DOI: 10.13389/j.cnki.rao.2015.0282 . | |
| 12 | AHN S M, AHN J, CHA S, et al. Morphologic and electrophysiologic findings of retinal degeneration after intravitreal sodium iodate injection following vitrectomy in canines[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1):3588. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-60579-1 . |
| 13 | 陈若冰, 吴素琴, 姜玥, 等. 薯蓣皂苷元抑制碘酸钠诱发ARPE-19细胞氧化应激反应[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2022, 42(11):2783-2786. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2022.11.053 . |
| CHEN R B, WU S Q, JIANG Y, et al. Diosgenin inhibits oxidative stress induced by sodium iodate in ARPE-19 cells[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2022, 42(11): 2783-2786. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2022.11.053 . | |
| 14 | GRIGNOLO A, ORZALESI N, CALABRIA G A. Studies on the fine structure and the rhodopsin cycle of the rabbit retina in experimental degeneration induced by sodium iodate[J]. Exp Eye Res, 1966, 5(1):86-97. DOI: 10.1016/S0014-4835(66)80024-6 . |
| 15 | WANG J M, IACOVELLI J, SPENCER C, et al. Direct effect of sodium iodate on neurosensory retina[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2014, 55(3):1941-1953. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.13-13075 . |
| 16 | CHOWERS G, COHEN M, MARKS-OHANA D, et al. Course of sodium iodate-induced retinal degeneration in albino and pigmented mice[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2017, 58(4):2239-2249. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.16-21255 . |
| 17 | 黄文金, 陈志辉. 碘酸盐的毒理学研究进展[J]. 海峡预防医学杂志, 2002, 8(1):79-80. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2705.2002.01.053 . |
| HUANG W J, CHEN Z H. Research progress in toxicology of iodate[J]. Strait J Prev Med, 2002, 8(1): 79-80. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2705.2002.01.053 . | |
| 18 | 黄越, 陈乃耀, 赵雪聪, 等. 氧化应激参与放射性脑损伤的研究进展[J]. 神经解剖学杂志, 2019, 35(2):221-224. DOI: 10.16557/j.cnki.1000-7547.2019.02.019 . |
| HUANG Y, CHEN N Y, ZHAO X C, et al. Advances in research on oxidative stress involved in radiation-induced brain injury[J]. Chin J Neuroanat, 2019, 35(2):221-224. DOI: 10.16557/j.cnki.1000-7547.2019.02.019 . | |
| 19 | 廖月, 何毅怀, 罗亚文. 氧化应激在急性肝损伤中的作用[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38(10):2402-2407. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.10.039 . |
| LIAO Y, HE Y H, LUO Y W. Role of oxidative stress in acute liver injury[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38(10):2402-2407. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.10.039 . | |
| 20 | 胡英华, 贾炳超, 尚鑫, 等. 基于氧化应激通路的朱砂肾毒性机理研究及针灸对氧化应激的缓解作用[J]. 长春中医药大学学报, 2022, 38(5):513-517. DOI: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2022.05.012 . |
| HU Y H, JIA B C, SHANG X, et al. Study on the mechanism of cinnabar nephrotoxicity based on the oxidative stress pathway and the alleviating effect of acupuncture on oxidative stress[J]. J Chang Univ Chin Med, 2022, 38(5):513-517. DOI: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2022.05.012 . | |
| 21 | 刘和亮, 赵金垣. 氧化应激和肺损伤[J]. 中国职业医学, 2002, 29(5):49-51. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6486.2002.05.024 . |
| LIU H L, ZHAO J Y. Oxidative stress and lung injury[J]. China Occup Med, 2002, 29(5):49-51. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6486.2002.05.024 . | |
| 22 | 李敏启, 杜娟, 杨盼盼, 等. 氧化应激调控骨质疏松症的研究进展[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版), 2021, 59(6):16-24. DOI: 10.6040/j.issn.1671-7554.0.2021.0295 . |
| LI M Q, DU J, YANG P P, et al. Research progress of oxidative stress regulating osteoporosis[J]. J Shandong Univ Health Sci, 2021, 59(6):16-24. DOI: 10.6040/j.issn.1671-7554.0.2021.0295 . | |
| 23 | 宁佳, 胡欣, 程兴群. 变异链球菌氧化应激调控机制的研究进展[J]. 口腔疾病防治, 2023, 31(4):295-300. DOI:10.12016/j.issn.2096-1456.2023.04.012 . |
| NING J, HU X, CHENG X Q. Research progress on oxidative stress regulatory mechanisms in Streptococcus mutans[J]. J Prev Treat Stomatol Dis, 2023, 31(4):295-300. DOI: 10.12016/j. issn.2096-1456.2023.04.012 . | |
| 24 | WU N, ZHENG F, LI N, et al. RND3 attenuates oxidative stress and vascular remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rat via inhibiting ROCK1 signaling[J]. Redox Biol, 2021, 48:102204. DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102204 . |
| 25 | 李楠, 王保和, 张晨, 等. 淫羊藿苷对心血管疾病作用机制研究进展[J]. 天津中医药, 2023, 40(1):126-130. DOI: 10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2023.01.22 . |
| LI N, WANG B H, ZHANG C, et al. Research progress on the mechanism of icariin on cardiovascular diseases[J]. Tianjin J Tradit Chin Med, 2023, 40(1):126-130. DOI: 10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2023.01.22 . | |
| 26 | 王香香, 孙建军, 刁明芳. 氧化应激在感音神经性耳聋中的作用机制[J]. 中国听力语言康复科学杂志, 2023, 21(1):56-60. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4933.2023.01.014 . |
| WANG X X, SUN J J, DIAO M F. Mechanisms of oxidative stress in sensorineural deafness[J]. Chin Sci J Hear Speech Rehabil, 2023, 21(1):56-60. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4933.2023.01.014 . | |
| 27 | 江楠, 马瑞红, 赵晓丽, 等. 氧化应激与生殖相关疾病研究进展[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2021, 40(5):402-406. DOI:10.12280/gjszjk.20210042 . |
| JIANG N, MA R H, ZHAO X L, et al. Research progress on oxidative stress and reproductive related diseases[J]. J Int Reproductive Health/family Plan, 2021, 40(5):402-406.DOI:10.12280/gjszjk.20210042 . | |
| 28 | 赵金枫, 颜士玉, 王瑞, 等. 氧化应激在三氯乙烯所致毒性效应中的作用[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2022, 39(12):1423-1429. DOI: 10.11836/JEOM22259 . |
| ZHAO J F, YAN S Y, WANG R, et al. Role of oxidative stress in trichloroethylene-induced toxicity[J]. J Environ Occup Med, 2022, 39(12):1423-1429. DOI: 10.11836/JEOM22259 . | |
| 29 | CARIDO M, ZHU Y, POSTEL K, et al. Characterization of a mouse model with complete RPE loss and its use for RPE cell transplantation[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2014, 55(8):5431-5444. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.14-14325 . |
| 30 | KIM H L, NAM S M, CHANG B J, et al. Ultrastructural changes and expression of PCNA and RPE65 in sodium iodate-induced acute retinal pigment epithelium degeneration model[J]. Neurochem Res, 2018, 43(5):1010-1019. DOI: 10.1007/s11064-018-2508-9 . |
| 31 | KIUCHI K, YOSHIZAWA K, SHIKATA N, et al. Morphologic characteristics of retinal degeneration induced by sodium iodate in mice[J]. Curr Eye Res, 2002, 25(6):373-379. DOI: 10.1076/ceyr.25.6.373.14227 . |
| [1] | 秦超, 李双星, 赵婷婷, 蒋晨晨, 赵晶, 杨艳伟, 林志, 王三龙, 文海若. 药物安全评价用SD大鼠90 d喂养试验的背景数据研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 439-448. |
| [2] | 刘力瑜, 嵇波, 刘小玄, 方洋, 张玲, 郭亭廷, 全烨, 李鹤文, 刘翼天. 大鼠胎儿期肺组织固定方法的探索[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 432-438. |
| [3] | 刘智伟, 杨然, 连浩, 张玉, 金立伦. 秦皮素对碘乙酸钠诱导骨关节炎模型大鼠的软骨保护与抗炎作用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 259-268. |
| [4] | 姜萌, 郝淑兰, 仝立国, 仲启明, 高振飞, 王永辉, 王晞星, 吉海杰. 长春瑞滨诱导大鼠足背静脉炎模型的动态评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 251-258. |
| [5] | 肖林林, 杨逸萱, 黎珊杉, 罗兰诗雨, 尹思威, 孙俊铭, 施维, 欧阳轶强, 李习艺. 利用脑立体定位技术将人源三突变APP基因导入海马区构建阿尔茨海默病大鼠模型[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 269-278. |
| [6] | 潘颐聪, 蒋汶洪, 胡明, 覃晓. 慢性肾脏病大鼠主动脉钙化模型的术式优化及效果评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 279-289. |
| [7] | 连辉, 姜艳玲, 刘佳, 张玉立, 谢伟, 薛晓鸥, 李健. 异常子宫出血大鼠模型的构建与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 130-146. |
| [8] | 孙效容, 苏丹, 贵文娟, 陈玥. 手术诱导大鼠中重度膝骨关节炎模型的建立与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 597-604. |
| [9] | 殷玉莲, 马丽娜, 屠思远, 陈玲, 叶媚娜, 陈红风. 非哺乳期乳腺炎大鼠模型的建立及评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 587-596. |
| [10] | 杨劲, 俞诗雅, 林楠, 方永超, 赵虎, 邱锦维, 林鸿铭, 陈惠燕, 王瑜, 吴伟航. 改良型十二指肠旷置术对2型糖尿病大鼠糖代谢的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 523-530. |
| [11] | 戚龙菊, 陈世园, 廖泽华, 石袁虎, 孙郁雨, 王庆华. 经血干细胞移植联合运动训练促进大鼠脊髓损伤康复的转录组学分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 531-542. |
| [12] | 张乃群, 袁飘漂, 曹琳茸, 应娜, 杨涛涛. PNR检测在糖尿病肾脏疾病模型大鼠诊断及药效评价中的应用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 543-549. |
| [13] | 郑艺清, 邓亚胜, 范燕萍, 梁天薇, 黄慧, 刘永辉, 倪召兵, 林江. 基于数据挖掘的盆腔炎性疾病动物模型应用分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(4): 405-418. |
| [14] | 肖攀, 王红义, 陆璐, 张梅, 陈克明, 申栋帅, 牛廷献. 低氧敏感和低氧耐受型Wistar大鼠筛选及其G1代的低氧敏感性初探[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(4): 374-383. |
| [15] | 朱晓雨, 袁韩涛, 李四波. 微RNA-887-3p能抑制大鼠椎间盘纤维环细胞中 MDM4表达和细胞增殖并促进细胞凋亡[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(3): 270-278. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||