













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 457-465.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.035
刘月琴1,2, 薛卫国1, 王淑友2, 申耀华1, 贾术永2, 王广军2, 宋晓晶2( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-04
修回日期:2025-04-13
出版日期:2025-08-25
发布日期:2025-09-01
通讯作者:
作者简介:刘月琴(1999—),女,硕士研究生,研究方向:针刺治疗脑病的机制研究。E-mail:15614330337@163.com基金资助:
LIU Yueqin1,2, XUE Weiguo1, WANG Shuyou2, SHEN Yaohua1, JIA Shuyong2, WANG Guangjun2, SONG Xiaojing2( )(
)( )
)
Received:2025-03-04
Revised:2025-04-13
Published:2025-08-25
Online:2025-09-01
Contact:
SONG Xiaojing (ORCID: 0000-0002-9382-285X), E-mail: xts2010@163.com摘要:
目的 探讨活体探头式激光共聚焦成像(probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy,pCLE)技术在快速检测与评估小鼠消化道组织形态特征中的应用价值。 方法 将12只6周龄的SPF级雄性昆明小鼠随机分为两组,其中6只使用乙醇体积分数为52%的红星牌二锅头白酒进行灌胃造模,另外6只使用生理盐水灌胃作为对照。连续灌胃28 d后,每组随机选取3只,经3%异氟烷吸入深度麻醉后颈椎脱臼处死,即刻剖取胃、十二指肠、空肠和直肠组织,浸入1%荧光素钠溶液染色,采用pCLE技术观察各组织黏膜表面的微观结构。剩余模型组和对照组小鼠经3%异氟烷吸入深度麻醉后,先后使用生理盐水、4%多聚甲醛溶液进行心脏灌流,剪取胃、十二指肠、空肠及直肠各组织进行脱水、切片和苏木精-伊红(hematoxylin-eosin,HE)染色,于光学显微镜下观察各节段组织的形态学变化。 结果 pCLE观察显示,对照组小鼠消化道黏膜组织表面荧光染色均匀,胃小凹、肠绒毛及肠隐窝形状完整,排列紧密,边缘结构清晰;而模型组小鼠消化道黏膜发生肿胀和变形,并伴有荧光染色不均匀和荧光素渗漏的现象。此外,部分组织出现缺损或细胞脱落,相邻特征结构(如胃小凹、肠隐窝)之间的边界模糊。HE染色观察显示,对照组小鼠消化道组织结构正常,细胞排列整齐、无缺损,黏膜下腺体大小一致且无增生性改变,无明显炎性细胞浸润;而模型组小鼠部分消化道组织结构缺损,细胞排列紊乱稀疏,黏膜下腺体萎缩,并伴有明显的炎性细胞浸润。pCLE观察结果与HE染色的组织学特征一致。 结论 pCLE能够实现对消化道黏膜结构特征的快速、实时、大范围、高分辨率显微成像,并且能更真实、全面地展示其生理及微观结构特征,该技术在小动物消化系统损伤的组织学评估研究中显示出良好的应用前景和实际应用价值。
中图分类号:
刘月琴,薛卫国,王淑友,等. 探头式激光共聚焦成像技术用于小鼠消化道组织形态特征分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 457-465. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.035.
LIU Yueqin,XUE Weiguo,WANG Shuyou,et al. Observation of Digestive Tract Tissue Morphology in Mice Using Probe-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 457-465. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.035.
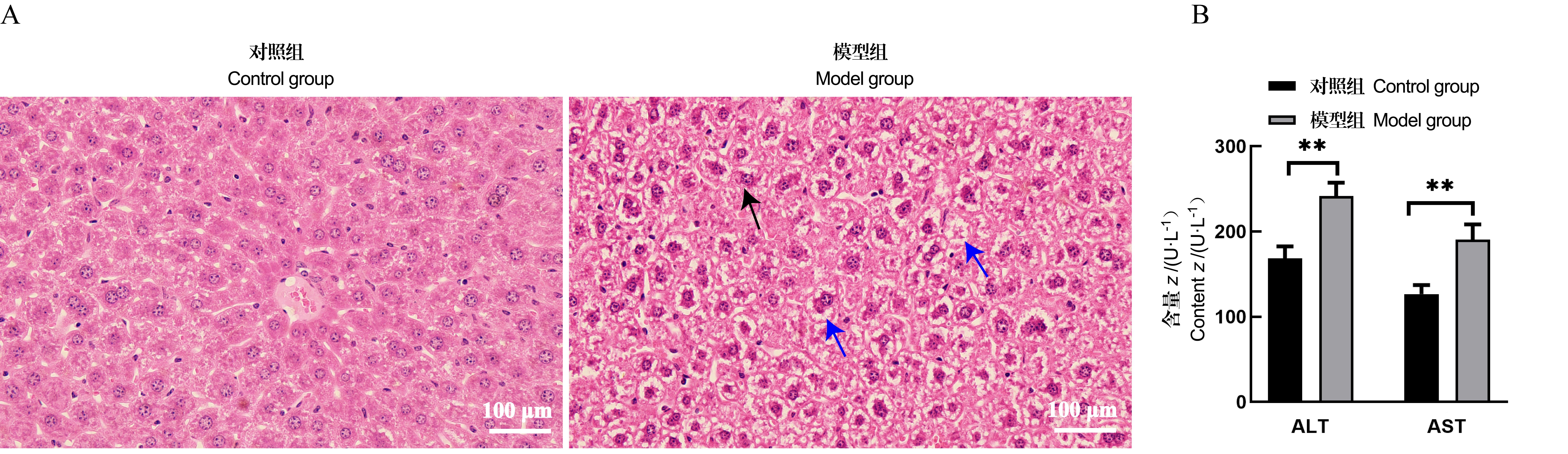
图1 小鼠肝组织HE染色结果(×40)及血清谷丙转氨酶和谷草转氨酶水平注:A为对照组和模型组小鼠肝组织HE染色结果,蓝色箭头指示肝细胞中的脂滴空泡,黑色箭头指示被挤压至边缘的细胞核;B为用紫外微孔板法检测的两组小鼠血清中的谷丙转氨酶(ALT)和谷草转氨酶(AST)水平。每组6只小鼠;与对照组比较,??P<0.01。
Figure 1 HE staining results of liver tissue (×40) and serum ALT and AST levels in miceNote: A shows HE staining images of liver tissue in control and model group mice, the blue arrows indicate the hepatocytes with macrovesicular fat, and the black arrow indicates the nuclei pushed to the edge. B shows the alanine aminotransferase(ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase(AST) levels in the two groups detected by ultraviolet microplate method. n = 6;Compared with the control group,??P<0.01.
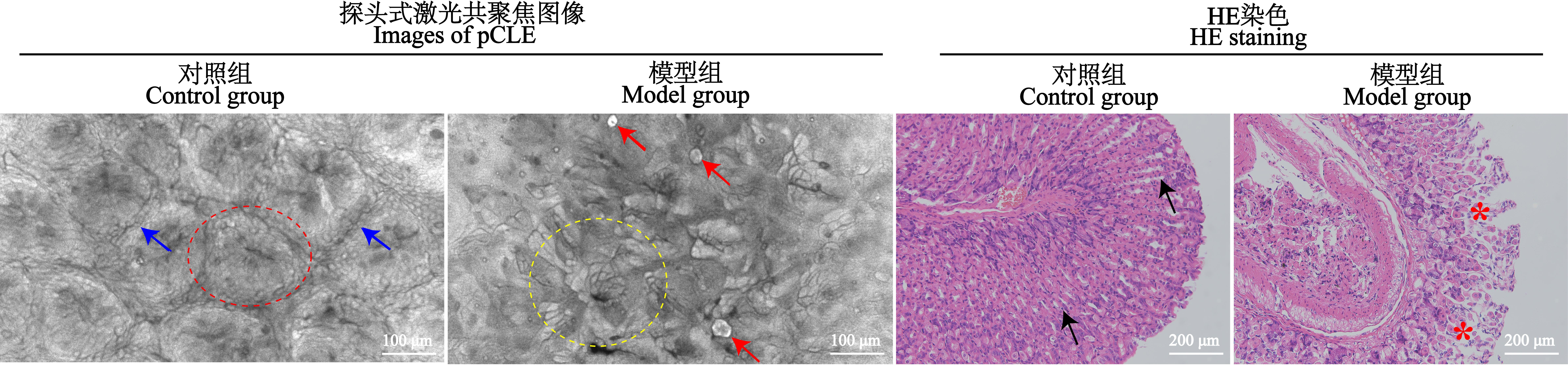
图2 小鼠胃黏膜表面pCLE图像(×1 000)和胃组织HE染色图(×20)注:对照组小鼠胃黏膜表面探头式激光共聚焦成像图中,红色虚线圈指示胃小凹,蓝色箭头指示胃小凹边界;模型组小鼠胃黏膜表面探头式激光共聚焦成像图中,黄色虚线圈指示肿胀变形的胃小凹,红色箭头指示胃黏膜表面脱落的组织细胞碎片。对照组小鼠胃组织HE染色图中,黑色箭头指示排列整齐的腺管;模型组小鼠胃组织HE染色图中,红色星号指示胃组织水肿区域。
Figure 2 pCLE images of gastric mucosa surface (×1 000) and HE staining images of gastric tissue (×20) in miceNote: In probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy(pCLE) images of the gastric mucosa surface, red dashed circle indicates gastric foveae and blue arrows indicate the border of the gastric foveae in the control group, yellow dashed circle shows swollen and deformed gastric foveae and the red arrows are detached tissue cell fragments on the gastric mucosa surface in the model group. In HE staining images of gastric tissues, black arrows indicate neatly arranged glandular ducts in the control group and the red asterisks indicate edematous areas of gastric tissues in the model group.

图3 小鼠十二指肠黏膜表面pCLE图像(×1 000)和十二指肠组织HE染色图(×20)注:小鼠十二指肠黏膜表面探头式激光共聚焦成像图中,蓝色箭头为清晰的十二指肠边界,红色箭头为十二指肠黏膜脱落的组织细胞碎片,黄色星号为荧光素渗漏的亮色区域;小鼠十二指肠HE染色图中,黑色箭头所示为炎性细胞浸润,红色星号为肠绒毛水肿,黑色星号为肠绒毛坏死脱落。
Figure 3 pCLE images of duodenal mucosa surface (×1 000) and HE staining images of duodenal tissue (×20) in miceNote: In probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy(pCLE)images of the duodenal mucosa surface in mice, blue arrow indicates a clear duodenal mucosal boundary, red arrows indicate detached tissue cell fragments on the duodenal mucosa surface, yellow asterisks indicate bright areas of fluorescein leakage. In HE staining images of mouse duodenal tissues, black arrows indicate inflammatory cell infiltration, red asterisk indicates intestinal villi edema and black asterisk indicates intestinal villi necrosis and shedding.
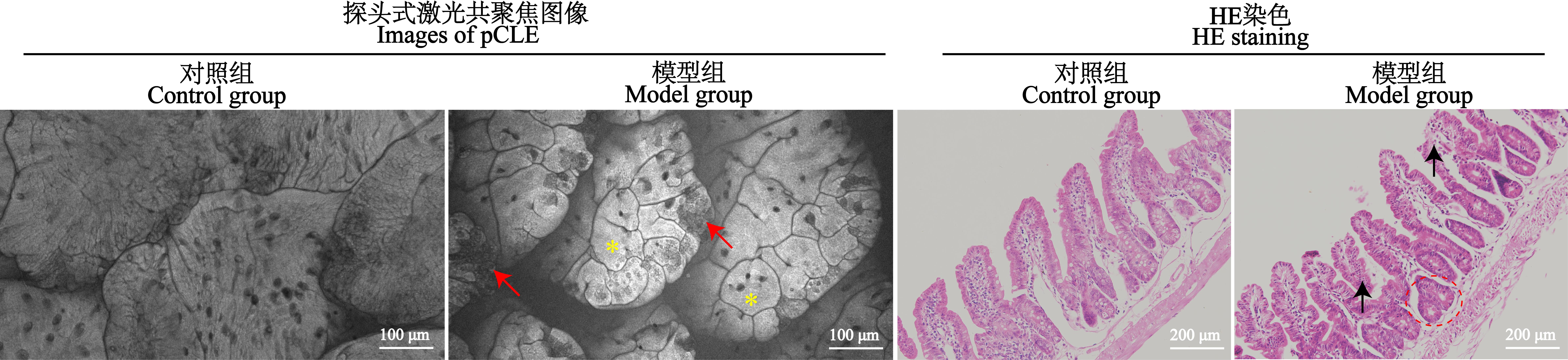
图4 小鼠空肠黏膜表面pCLE图像(×1 000)和小鼠空肠组织HE染色图(×20)注:模型组小鼠空肠黏膜表面探头式激光共聚焦成像图中,红色箭头为空肠黏膜表面组织细胞点灶状坏死区,黄色星号为荧光素渗漏的局部亮色区域;模型组小鼠空肠HE染色图中,黑色箭头所示为形态结构被破坏的肠绒毛,顶端断裂、脱落,红色虚线圈为拥挤的腺体。
Figure 4 pCLE images of jejunum mucosa surface (×1 000) and HE staining images of jejunum tissue (×20) in miceNote: In probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy(pCLE)images of the jejunum mucosa surface in the model group, red arrows indicate focal necrosis area of surface tissue cells in the jejunum mucosa, and yellow asterisks show local bright area of fluorescein leakage. In HE staining images of jejunal tissues in the model group, black arrows indicate the intestinal villi with destroyed morphological structure, exhibiting apical rupture and shedding, and red dashed circle indicates crowded glands.
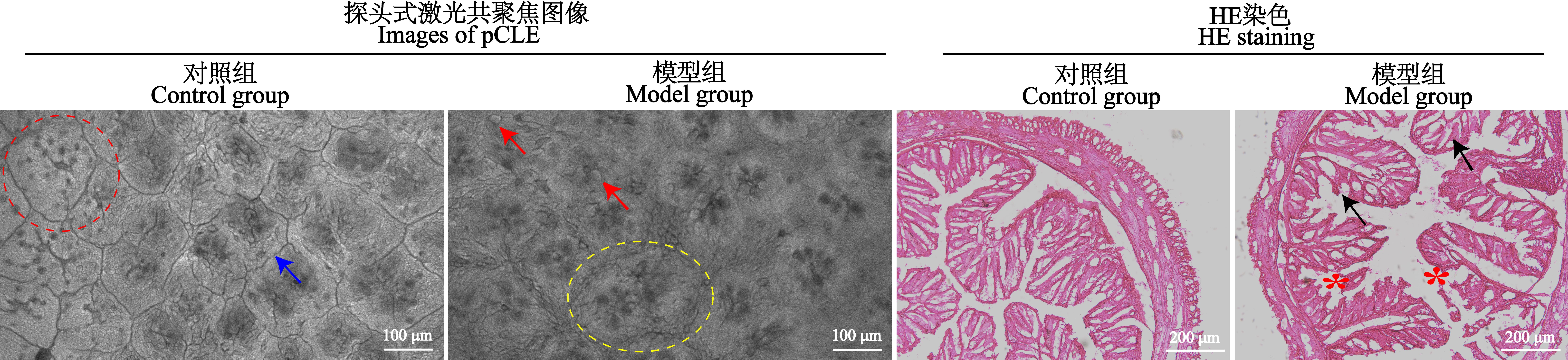
图5 小鼠直肠黏膜表面pCLE图像(×1 000)和小鼠直肠组织HE染色图(×10)注:对照组小鼠直肠黏膜表面探头式激光共聚焦成像图中,红色虚线圈指示直肠隐窝,蓝色箭头指示清晰的直肠隐窝边界;模型组小鼠直肠黏膜表面激光共聚焦图像中,黄色虚线圈指示相邻隐窝融合,红色箭头指示直肠黏膜表面组织细胞脱落处;模型组小鼠直肠组织HE染色图中,黑色箭头指示腺管排列紊乱,红色星号指示上皮结构不完整。
Figure 5 pCLE images of rectal mucosa surface (×1 000) and HE staining images of rectal tissue (×10) in miceNote: In probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy(pCLE)images of the rectal mucosa surface, red dashed circle indicates rectal crypts and blue arrow indicates clear rectal crypts boundary in the control group, yellow dashed circle shows fusion of adjacent crypts, and red arrows indicate tissue cells exfoliation on the rectal mucosa surface in the model group. In HE staining images of rectal tissues in the model group, black arrows indicate disordered arrangement of glandular ducts and red asterisks indicate that the intestinal epithelial structure is incomplete.
| [1] | 曾锦树, 汤晓琼, 阮炜炜, 等. 前列腺肿瘤组织的超声弹性与原子力显微成像[J]. 福建师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 37(2):51-56. DOI: 10.12046/j.issn.1000-5277.2021.02.008 . |
| ZENG J S, TANG X Q, RUAN W W, et al. Ultrasound elastography and atomic force microscopy of prostate tumor tissue[J]. J Fujian Norm Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2021, 37(2):51-56. DOI: 10.12046/j.issn.1000-5277.2021.02.008 . | |
| [2] | 梁忠泉, 刘畅, 杨志娜, 等. 脂肪组织石蜡切片制作方法探讨[J]. 中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志, 2019, 28(2): 170-173. DOI: 10.16705/j.cnki.1004-1850.2019.02.012 . |
| LIANG Z Q, LIU C, YANG Z N, et al. Discussion on preparation method for paraffin section of adipose tissues [J]. Chin J Histochem Cytochem, 2019, 28 (2): 170-173. DOI: 10.16705/j.cnki.1004-1850.2019.02.012 . | |
| [3] | 王贵龙, 王爱瑶. 共聚焦激光显微内镜与普通结肠镜对溃疡性结肠炎患者炎症活动度及黏膜屏障功能改变的判定价值比较[J]. 上海医药, 2021, 42(7):60-63, 71. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1533.2021.07.017 . |
| WANG G L, WANG A Y. The comparison of confocal laser microscopy and common colonoscopy to determine changes in inflammatory activity and mucosal barrier function in ulcerative colitis patients[J]. Shanghai Med Pharm J, 2021, 42(7):60-63, 71. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1533.2021.07.017 . | |
| [4] | 薛培婷. 共聚焦激光显微内镜下溃疡性结肠炎炎症分级的人工智能辅助诊断模型建立与验证 [D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2023. DOI: 10.27272/d.cnki.gshdu.2023.002239 . |
| XUE P T. Artificial intelligence-assisted confocal laser endomicroscopy for grading the inflammation degree of ulcerative colitis [D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2023. DOI: 10.27272/d.cnki.gshdu.2023.002239 . | |
| [5] | 刘志美, 张静. 共聚焦激光显微内镜在早期胃癌诊断中的应用进展[J]. 中国微创外科杂志, 2024, 24(9):623-627.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6604.2024.09.006 . |
| LIU Z M, ZHANG J. Application progress of confocal laser microscopic endoscopy in the diagnosis of early gastric cancer[J]. Chin J Minim Invasive Surg, 2024, 24(9):623-627.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6604.2024.09.006 . | |
| [6] | 王羽宸. 原位实时光学活检改善低位直肠癌肛门功能的对照研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2024. DOI: 10.27003/d.cnki.gojyu.2024.000947 . |
| WANG Y C. In situ real-time optical biopsy improves anal function in low rectal cancer: a controlled study[D]. Gangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2024. DOI: 10.27003/d.cnki.gojyu.2024.000947 . | |
| [7] | 丁慧, 陈慧敏, 李晓波, 等. 十二指肠镜联合探头式共聚焦激光显微内镜对十二指肠疾病的观察研究[J]. 临床内科杂志, 2024, 41(7): 446-450. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9057.2024.07.003 . |
| DING H, CHEN H M, LI X B, et al. Observation study of small bowel diseases by enteroscopy combined with probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy[J]. J Clin Intern Med, 2024, 41(7): 446-450. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9057.2024.07.003 . | |
| [8] | 刘凯. 激光共聚焦显微内镜在上消化道早癌和癌前病变中的应用进展[J]. 胃肠病学, 2024, 29(3):186-192. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7125.2024.03.006 . |
| LIU K. Progress of confocal laser endomicroscopy in early cancer and precancerous lesions of upper gastrointestinal tract[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol, 2024, 29(3):186-192. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7125.2024.03.006 . | |
| [9] | 左秀丽, 许树长, 王林恒, 等. 中国显微内镜消化系统疾病临床应用共识意见[J]. 胃肠病学, 2023, 28(2):91-106. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7125.2023.02.005 . |
| ZUO X L, XU S C, WANG L H, et al. Chinese expert consensus on clinical application of endomicroscopy in digestive diseases[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol, 2023, 28(2):91-106. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7125.2023.02.005 . | |
| [10] | SONG X J, WANG S Y, ZHAO C, et al. Visual method for evaluating liver function: targeted in vivo fluorescence imaging of the asialoglycoprotein receptor[J]. Biomed Opt Express, 2019, 10(10):5015-5024. DOI: 10.1364/BOE.10.005015 . |
| [11] | 李丽. 探头式共聚焦激光显微内镜对早期胃癌及癌前病变诊断价值的研究[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学, 2020. DOI: 10.27157/d.cnki.ghzku.2020.006230 . |
| LI L. The study on the diagnostic value of probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy in early gastric cancer and precancerous lesions[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2020. DOI: 10.27157/d.cnki.ghzku.2020.006230 . | |
| [12] | 杨静. 探头式共聚焦激光显微内镜在胆管良恶性狭窄鉴别诊断中的研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2016. DOI: 10.7666/d.Y3032821 . |
| YANG J. Research on the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant bile duct stenosis by probe-type confocal laser endoscopy[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2016. DOI: 10.7666/d.Y3032821 . | |
| [13] | 张燕萍. 探头式共聚焦激光显微内镜对大肠息肉的诊断价值[D]. 北京: 首都医科大学, 2015. |
| ZHANG Y P. Diagnostic value of probe-type confocal laser endomicroscopy for colorectal polyps[D]. Beijing: Capital Medical University, 2015. | |
| [14] | 杨雪芳, 刘哲晰, 王璞. 共聚焦内窥显微成像技术及其应用[J]. 中国激光, 2022, 49(19):1907002. DOI: 10.3788/CJL202249.1907002 . |
| YANG X F, LIU Z X, WANG P. Confocal endoscopic microscopy and its applications[J]. Chin J Lasers, 2022, 49(19):1907002. DOI: 10.3788/CJL202249.1907002 . | |
| [15] | MOUSSATA D, GOETZ M, GLOECKNER A, et al. Confocal laser endomicroscopy is a new imaging modality for recognition of intramucosal bacteria in inflammatory bowel disease in vivo [J]. Gut, 2011, 60(1):26-33. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2010.213264 . |
| [16] | RASMUSSEN D N, KARSTENSEN J G, RIIS L B, et al. Confocal laser endomicroscopy in inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2015, 9(12):1152-1159. DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjv131 . |
| [17] | BUCHNER A M. Confocal laser endomicroscopy in the evaluation of inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2019, 25(8):1302-1312. DOI: 10.1093/ibd/izz021 . |
| [18] | IMAEDA A. Confocal laser endomicroscopy for the detection of atrophic gastritis: a new application for confocal endomicroscopy?[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2015, 49(5):355-357. DOI:10.1097/MCG.0000000000000309 . |
| [19] | 宋晓晶, 熊枫, 贾术永, 等. 大鼠腹内壁中线间质通道微观结构的活体激光共聚焦成像观察[J]. 激光生物学报, 2021, 30(5):435. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7146.2021.05.008 . |
| SONG X J, XIONG F, JIA S Y, et al. Observation of microstructure of midline interstitial channels of the inner abdominal wall in rat for in vivo confocal laser imaging[J]. Acta Laser Biol Sin, 2021, 30(5):435. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7146.2021.05.008 . | |
| [20] | 刘婷婷, 杨宁江. 消化道内镜活检标本石蜡切片制作分析[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2019, 11(31):99-101. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9308.2019.31.041 . |
| LIU T T, YANG N J. Analysis in making paraffin sections from gastrointestinal endoscopic biopsy specimens[J]. China Continuing Med Educ, 2019, 11(31):99-101. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9308.2019.31.041 . | |
| [21] | 王梓义, 陈静, 周学谦, 等. 探头式共聚焦激光显微内镜对胃底腺息肉的诊断价值[J]. 陆军军医大学学报, 2024, 46(10):1150-1157. DOI: 10.16016/j.2097-0927.202310082 . |
| WANG Z Y, CHEN J, ZHOU X Q, et al. Diagnostic value of probe-based confocal laser microendoscopy in differential diagnosis of fundic gland polyps[J]. J Army Med Univ, 2024, 46(10):1150-1157. DOI: 10.16016/j.2097-0927.202310082 . |
| [1] | 贡磊磊, 王晓霞, 封学伟, 李心蕾, 赵涵, 张雪艳, 冯欣. 不同浓度环磷酰胺诱导早发性卵巢功能不全小鼠模型及作用机制研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 403-410. |
| [2] | 姜娟, 宋宁, 连文博, 邵丛丛, 顾文文, 石燕. 两种浓度乙醇溶液灌注建立小鼠宫腔粘连模型的组织病理和分子病理表型比较[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 393-402. |
| [3] | 罗莲莲, 袁艳春, 王俊岭, 时广森. 肌萎缩侧索硬化症小鼠模型研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 290-299. |
| [4] | 孔志豪, 魏晓锋, 于灵芝, 冯丽萍, 朱琦, 施国君, 王晨. 鳞状皮屑裸小鼠木糖葡萄球菌的分离鉴定[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 368-375. |
| [5] | 许秋雨, 严国锋, 付丽, 范文华, 周晶, 朱莲, 仇淑雯, 张洁, 吴铃. 来曲唑缓释片皮下给药构建小鼠多囊卵巢综合征模型及其肝脏转录组学分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 119-129. |
| [6] | 潘钱家, 葛峻沂, 胡楠, 华飞, 顾敏. 基于16S rRNA测序的2型糖尿病db/db小鼠模型口腔菌群差异分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 147-157. |
| [7] | 刘荣乐, 程灏, 尚付生, 常书福, 徐平. SHJH hr 小鼠的心脏衰老表型研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(1): 13-20. |
| [8] | 吴志浩, 曹舒扬, 周正宇. 肝螺杆菌感染引起VDR-/-小鼠炎性肠病相关肠纤维化模型的建立及机制探讨[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(1): 37-46. |
| [9] | 张楠, 李怀银, 连晓娣, 魏娟鹏, 高明. 不同光照时长对NIH小鼠体重和学习记忆能力的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(1): 73-78. |
| [10] | 王芊芊, 陶斯珏, 卫振, 金晖晖, 刘平, 汪洌. 利用辅助生殖技术挽救基因修饰小鼠的实例分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(1): 79-86. |
| [11] | 赵赫, 张帆, 肖宇宙, 安学芳, 张涛, 李丽. 一例干扰素受体缺失小鼠自发未成熟型睾丸畸胎瘤诊断[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 691-694. |
| [12] | 赵小娜, 王鹏, 叶茂青, 曲新凯. 应用Triacsin C构建新型高血糖肥胖小鼠心功能减退模型[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 605-612. |
| [13] | 谭贺, 杨晓辉, 张大秀, 王贵成. 不同发育时期小鼠代谢笼实验的最佳适应期探讨[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 502-510. |
| [14] | 孟雨, 梁冬丽, 郑琳琳, 周园园, 王朝霞. 人肝肿瘤细胞的裸小鼠原位癌建模条件优化及评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 511-522. |
| [15] | 秦靖, 赵勇, 张彩勤, 白冰, 师长宏. 靶向炎性脑水肿的诊疗一体化近红外荧光探针的构建与评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(3): 243-250. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||