













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 147-157.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.119
收稿日期:2024-08-21
修回日期:2024-12-24
出版日期:2025-04-25
发布日期:2025-04-25
通讯作者:
顾 敏(1987—),女,博士,副主任医师,研究方向:口腔菌群。E-mail:gumin106@163.com。ORCID: 0000-0001-6162-2792作者简介:潘钱家(2000—),男,硕士研究生,医师,研究方向:口腔菌群。E-mail:2743297453@qq.com
基金资助:
PAN Qianjia1, GE Junyi1, HU Nan2, HUA Fei3, GU Min1( )
)
Received:2024-08-21
Revised:2024-12-24
Published:2025-04-25
Online:2025-04-25
Contact:
GU Min (ORCID: 0000-0001-6162-2792), E-mail: gumin106@163.com摘要:
目的 研究db/db小鼠口腔菌群的改变,为探寻2型糖尿病与口腔微生态的联系提供实验基础。 方法 选取8只10周龄雄性db/db小鼠为糖尿病实验组,8只10周龄雄性db/m小鼠为正常对照组。适应性喂养5 d后,在相同饲料饲养的第6天和第37天行尾静脉采血,测定两组小鼠的空腹血糖(fasting blood glucose,FBG)水平和口服葡萄糖耐量(oral glucose tolerance test,OGTT),以验证糖尿病模型的可靠性。在相同饲料饲养的第15天采集两组小鼠两侧颊黏膜、舌背与舌腹、口底黏膜、上腭硬区黏膜、上下颌牙龈的龈上区域的口腔菌群样本,提取口腔微生物的基因组DNA后,使用GeneAmp 9700热循环仪对其中16S核糖体RNA(16S ribosomal RNA,16S rRNA)基因的V3~V4 区进行扩增,然后在Illumina MiSeq平台上通过双标引扩增和测序对口腔菌群结构进行评估,然后应用QIIME(version 1.6.0)软件进行生物信息学分析。 结果 实验开始后第6天和第37天的FBG水平和OGTT检测结果均显示db/db小鼠比db/m小鼠表现出明显的2型糖尿病症状。α多样性分析显示两组小鼠的口腔菌群在多样性上无显著差异(P>0.05),而在丰富度上差异显著(P<0.05)。主坐标分析显示db/db小鼠的口腔菌群结构与db/m小鼠存在显著差异(P<0.05),物种组成分析以及LEfSe分析显示db/db小鼠口腔菌群在门水平以变形菌门(p_Proteobacteria)为主的相对丰度显著上升(P<0.05),而在属水平上变形杆菌属(g_Proteus)和肠球菌属(g_Enterococcus)的相对丰度极显著上升(P<0.001)。 结论 2型糖尿病db/db小鼠的口腔菌群结构和丰富度均较血糖正常的对照小鼠出现了显著变化。
中图分类号:
潘钱家,葛峻沂,胡楠,等. 基于16S rRNA测序的2型糖尿病db/db小鼠模型口腔菌群差异分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(2): 147-157. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.119.
PAN Qianjia,GE Junyi,HU Nan,et al. Differential Analysis of Oral Microbiota in db/db Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes Utilizing 16S rRNA Sequencing[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 147-157. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.119.
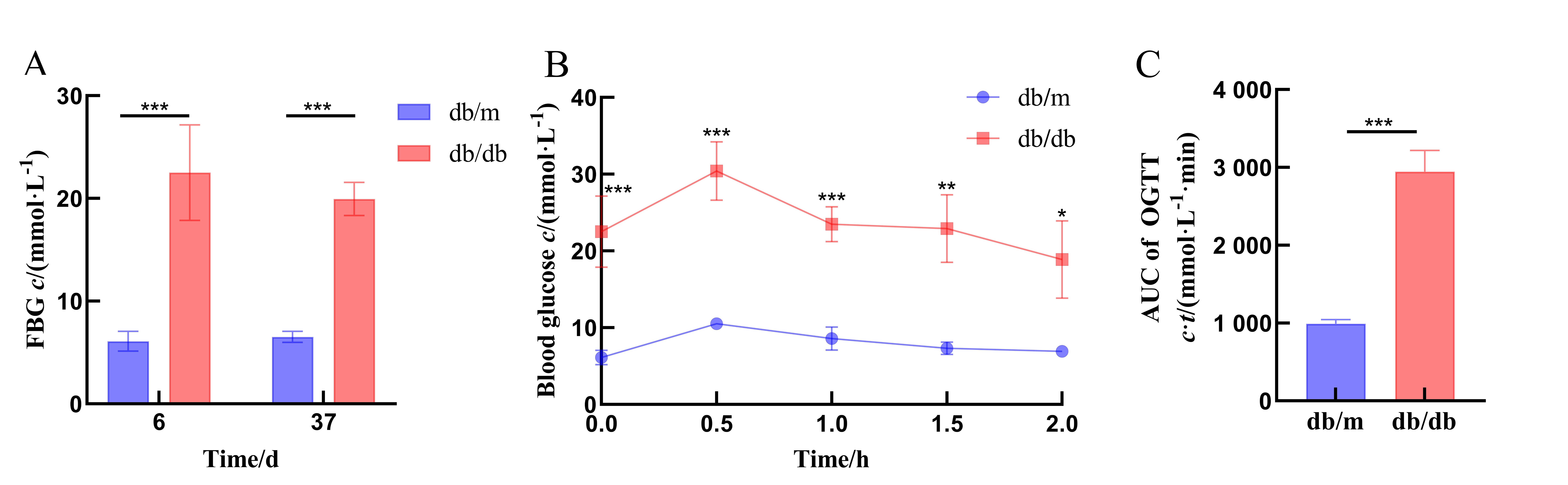
图1 db/db小鼠及db/m小鼠的血糖相关指标差异注:A,禁食12 h的空腹血糖(FBG)浓度;B,0~2 h的口服葡萄糖耐量(OGTT)分析;C,OGTT试验的曲线下面积(AUC)。db/db小鼠为糖尿病实验组;db/m小鼠为正常对照组,每组8只。*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001。
Figure 1 Comparison of blood glucose indices in db/db mice and db/m miceNote:A, The concentration of fasting blood glucose (FBG) levels after a 12-hour fasting period; B, Analysis of oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) from 0-2 hours; C, Area under the curve (AUC) of the OGTT. Db/db mice served as the diabetic group, while db/m mice were the normal controls, n=8 per group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
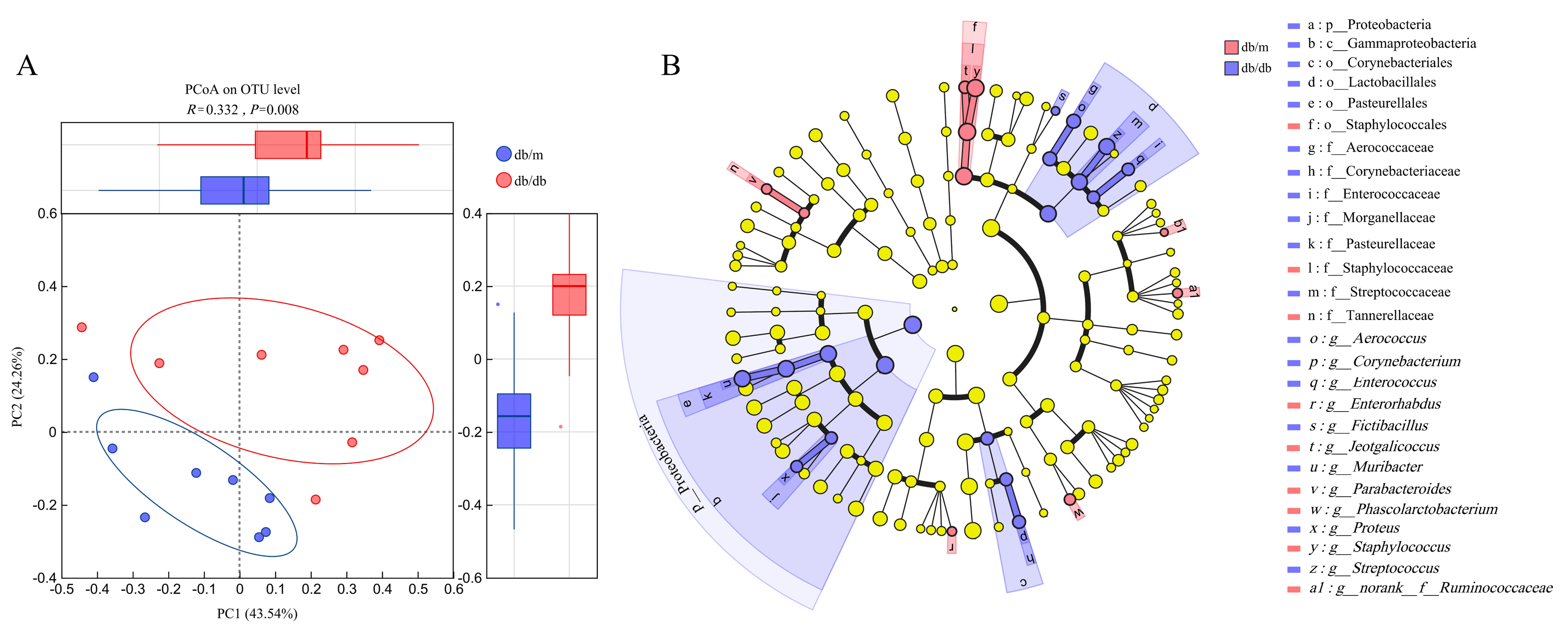
图2 db/db小鼠及db/m小鼠口腔菌群结构的PCoA分析和 LEfSe分析注:A,db/db小鼠和db/m小鼠之间的主坐标分析;B, 基于LEfSe的支系图是从门级到属级的结果(p表示门水平,c表示纲水平,o表示目水平,f表示科水平,g表示属水平)。db/db小鼠为糖尿病实验组;db/m小鼠为正常对照组,每组8只。
Figure 2 PCoA and LEfSe analysis of oral microbiota composition in db/db mice and db/m miceNote:A, Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) between db/db mice and db/m mice; B, LEfSe-derived cladogram showing taxonomic differences from phylum to genus level (p for phylum; c for class; o for order; f for family; g for genus). Db/db mice served as the diabetic model, while db/m mice were the normal controls, n=8 per group.
指标 Index | db/m | db/db | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
观察物种指数 Sobs | 10.25±8.43 | 77.25±29.33 | 0.049* |
香农指数# Shannon# | 2.40 (2.25~2.48) | 2.32 (2.23~2.51) | 0.529 |
辛普森指数 Simpson | 0.18±0.04* | 0.16±0.04 | 0.499 |
基于丰度的覆盖估计值 ACE | 105.56±8.34 | 79.49±30.06 | 0.045* |
Chao1丰富度估计量 Chao1 | 105.67±9.78 | 79.25±30.42 | 0.046* |
测序覆盖度 Coverage | 0.999 9 | 1.000 0 | 0.458 |
表1 db/db小鼠及db/m小鼠口腔菌群的α多样性分析 (n=8, xˉ±s)
Table 1 Alpha (α) diversity analysis of oral microbiota in db/db mice and db/m mice
指标 Index | db/m | db/db | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
观察物种指数 Sobs | 10.25±8.43 | 77.25±29.33 | 0.049* |
香农指数# Shannon# | 2.40 (2.25~2.48) | 2.32 (2.23~2.51) | 0.529 |
辛普森指数 Simpson | 0.18±0.04* | 0.16±0.04 | 0.499 |
基于丰度的覆盖估计值 ACE | 105.56±8.34 | 79.49±30.06 | 0.045* |
Chao1丰富度估计量 Chao1 | 105.67±9.78 | 79.25±30.42 | 0.046* |
测序覆盖度 Coverage | 0.999 9 | 1.000 0 | 0.458 |
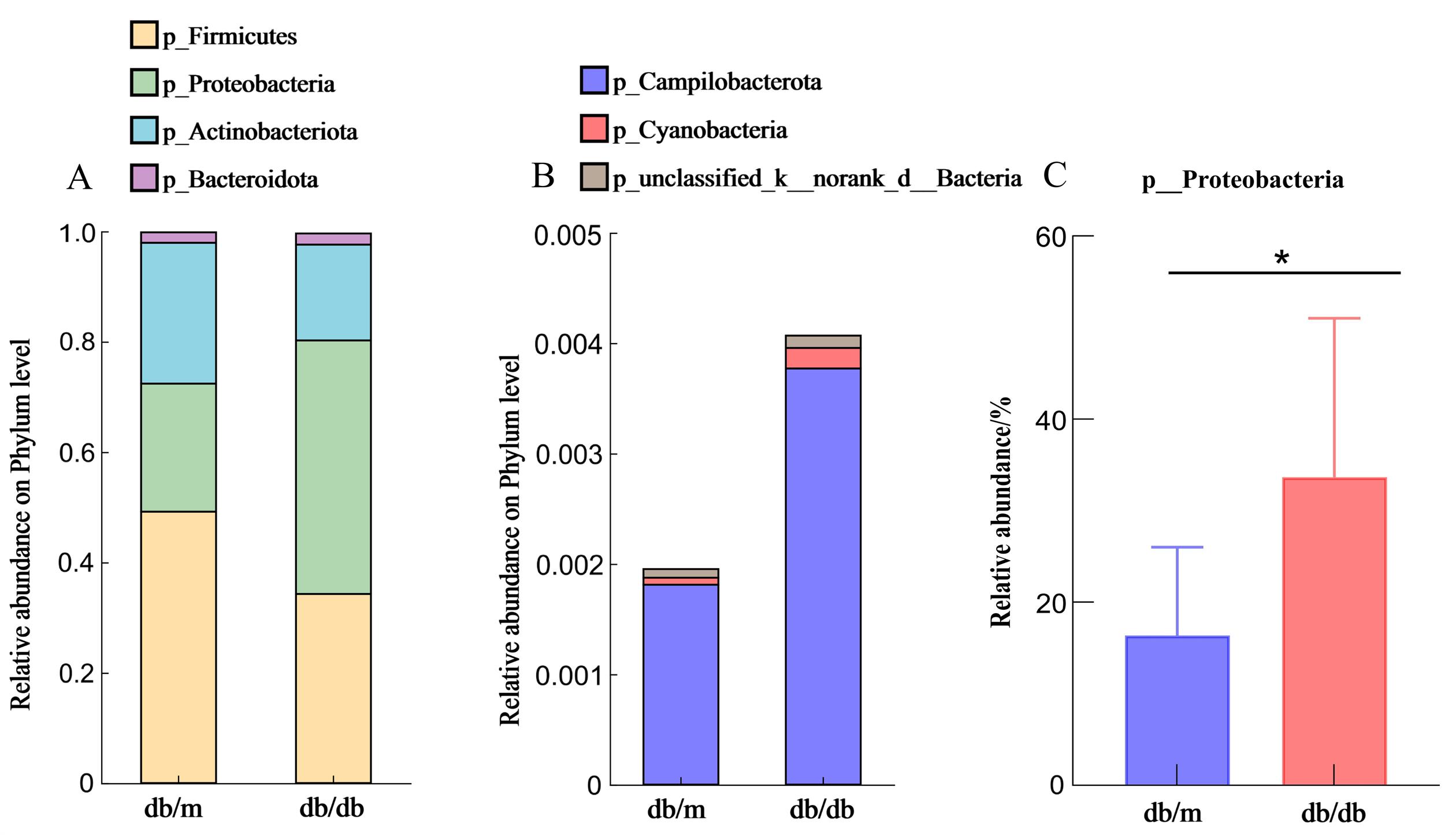
图3 db/db小鼠与db/m小鼠口腔微生物菌群在门水平上的差异注:A~B,db/db组和db/m组口腔微生物在门水平上的群落组成直方图;C,变形杆菌门的相对丰度。db/db小鼠为糖尿病实验组;db/m小鼠为正常对照组,每组8只。*P<0.05。
Figure 3 Comparison of oral microbiota between db/db mice and db/m mice at the phylum levelNote:A-B, Phylum-level community composition of oral microbiota in db/db and db/m groups; C, Relative abundance of p_Proteobacteria. db/db mice served as the diabetic model, while db/m mice were the normal controls, n=8 per group. *P<0.05.
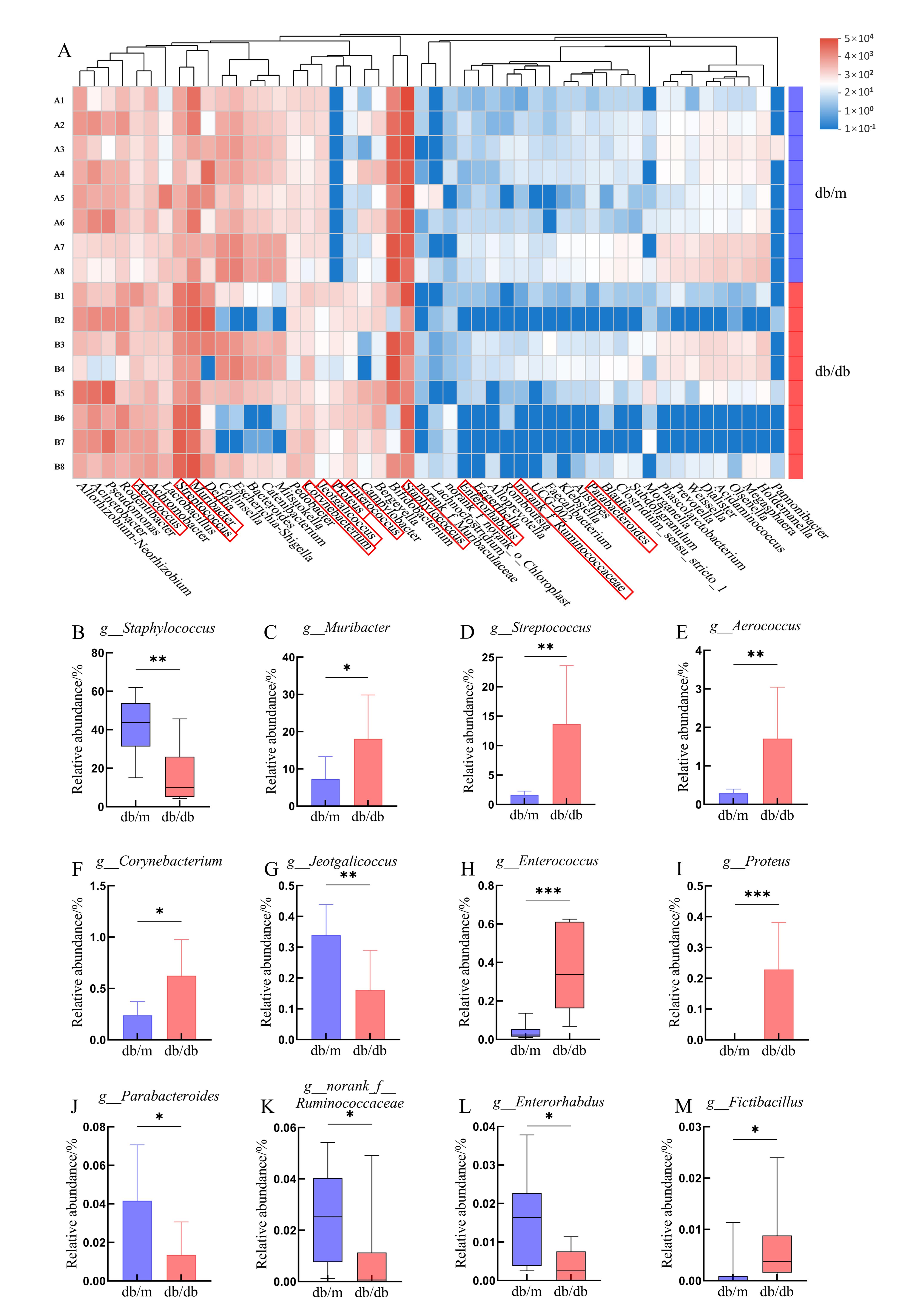
图4 db/db小鼠及db/m小鼠的口腔微生物菌群在属水平上的差异注:A,db/db和db/m组唾液微生物群中50种优势物种的相对丰度热图;B~M,葡萄球菌属、鼠杆菌属、链球菌属、气球菌属、棒杆菌属、嗜冷咸海鲜球菌属、肠球菌属、变形杆菌属、副拟杆菌属、瘤胃球菌科下未分类属、肠杆菌属、假芽孢杆菌属水平的相对丰度。正态分布的数据由条形图表示,非正态分布的数据用箱线图表示。db/db小鼠为糖尿病实验组;db/m小鼠为正常对照组,每组8只。*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001。
Figure 4 Differences in oral microbiota composition between db/db mice and db/m mice at the genus levelNote: A, Heatmap showing the relative abundance of the top 50 dominant species in the saliva microbiota (db/db vs. db/m); B-M, Relative abundance of the following genera: g_Staphylococcus, g_Muribacter, g_Streptococcus, g_Aerococcus, g_Corynebacterium, g_Jeotgalicoccus, g_Enterococcus, g_Proteus, g_Parabacteroides, g_Ruminococcaceae, g_Enterorhabdus, and g_Fictibacillus. Normally distributed data are presented as bar plots, and non-normally distributed data as box plots. Db/db mice served as the diabetic model, while db/m mice were the normal controls, n=8 per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
| 1 | RUSSO M P, GRANDE-RATTI M F, BURGOS M A, et al. Prevalence of diabetes, epidemiological characteristics and vascular complications[J]. Arch Cardiol Mex, 2023, 93(1):30-36. DOI:10.24875/ACM.21000410 . |
| 2 | RUZE R, LIU T T, ZOU X, et al. Obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: connections in epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatments[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2023, 14:1161521. DOI:10.3389/fendo.2023.1161521 . |
| 3 | ZHENG Y, LEY S H, HU F B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2018, 14(2):88-98. DOI:10.1038/nrendo.2017.151 . |
| 4 | ZHANG Y, SONG M Y, CAO Y, et al. Incident early- and later-onset type 2 diabetes and risk of early- and later-onset cancer: prospective cohort study[J]. Diabetes Care, 2023, 46(1):120-129. DOI:10.2337/dc22-1575 . |
| 5 | MARTAGON A J, ZUBIRÁN R, GONZÁLEZ-ARELLANES R, et al. HDL abnormalities in type 2 diabetes: Clinical implications[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2024, 394:117213. DOI:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2023.117213 . |
| 6 | WANG D Y, ZHANG G S, YU Y N, et al. Imaging of sarcopenia in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Clin Interv Aging, 2024, 19:141-151. DOI:10.2147/CIA.S443572 . |
| 7 | DENNIS J M, SHIELDS B M, HENLEY W E, et al. Disease progression and treatment response in data-driven subgroups of type 2 diabetes compared with models based on simple clinical features: an analysis using clinical trial data[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2019, 7(6):442-451. DOI:10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30087-7 . |
| 8 | EDDOUKS M, CHATTOPADHYAY D, ZEGGWAGH N A. Animal models as tools to investigate antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory plants[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2012, 2012:142087. DOI:10.1155/2012/142087 . |
| 9 | 唐艺丹, 王鲜忠, 张姣姣. Ⅱ型糖尿病动物模型构建的研究进展[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2020, 28(6):870-876. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2020.06.020 . |
| TANG Y D, WANG X Z, ZHANG J J. Research progress in the construction of type Ⅱ diabetes animal models[J]. Acta Lab Animalis Sci Sin, 2020, 28(6):870-876. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2020.06.020 . | |
| 10 | 崔淼, 朱春江, 刘向荣. 糖尿病动物模型构建的研究进展[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2023, 27(2):227-230. DOI:1007-4287(2023)02-0227-04 . |
| CUI M, ZHU C J, LIU X R. Research progress on the construction of animal model of diabetes mellitus[J]. Chin J Lab Diagn, 2023, 27(2):227-230. DOI:1007-4287(2023)02-0227-04 . | |
| 11 | WONG S K, CHIN K Y, SUHAIMI F H, et al. Animal models of metabolic syndrome: a review[J]. Nutr Metab, 2016, 13:65. DOI:10.1186/s12986-016-0123-9 . |
| 12 | 王松月, 依香叫, 李金诚, 等. 自发性2型糖尿病模型db/db小鼠生物学特性研究[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志, 2019, 25(7):909-912. DOI: 10.19945/j.cnki.issn.1006-3250.2019.07.019 . |
| WANG S Y, YI X J, LI J C, et al. Biological characteristics of spontaneous type 2 diabetes mellitus model db/db mice[J]. Chin J Basic Med Tradit Chin Med, 2019, 25(7):909-912. DOI: 10.19945/j.cnki.issn.1006-3250.2019.07.019 . | |
| 13 | ZHANG Y H, WANG X, LI H X, et al. Human oral microbiota and its modulation for oral health[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 99:883-893. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.146 . |
| 14 | 朱双, 汤帅, 丁刚. 口腔菌群与口腔疾病及全身性疾病关系的研究进展[J]. 中国医药导报, 2023, 20(18):35-38. DOI: 10.20047/j.issn1673-7210.2023.18.07 . |
| ZHU S, TANG S, DING G. Research progress on the relationship between oral flora and oral diseases and systemic diseases[J]. China Med Her, 2023, 20(18):35-38. DOI: 10.20047/j.issn1673-7210.2023.18.07 . | |
| 15 | MAIER T. Oral microbiome in health and disease: maintaining a healthy, balanced ecosystem and reversing dysbiosis[J]. Microorganisms, 2023, 11(6):1453. DOI:10.3390/micro-organisms11061453 . |
| 16 | LU Y B, LI Z Y, PENG X. Regulatory effects of oral microbe on intestinal microbiota and the illness[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2023, 13:1093967. DOI:10.3389/fcimb.2023.1093967 . |
| 17 | TANG B Y, YAN C X, SHEN X, et al. The bidirectional biological interplay between microbiome and viruses in periodontitis and type-2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13:885029. DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2022.885029 . |
| 18 | STÖHR J, BARBARESKO J, NEUENSCHWANDER M, et al. Bidirectional association between periodontal disease and diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1):13686. DOI:10.1038/s41598-021-93062-6 . |
| 19 | BARUTTA F, BELLINI S, DURAZZO M, et al. Novel insight into the mechanisms of the bidirectional relationship between diabetes and periodontitis[J]. Biomedicines, 2022, 10(1):178. DOI:10.3390/biomedicines10010178 . |
| 20 | SHINJO T, NISHIMURA F. The bidirectional association between diabetes and periodontitis, from basic to clinical[J]. Jpn Dent Sci Rev, 2024, 60:15-21. DOI:10.1016/j.jdsr.2023. 12.002 . |
| 21 | 杨忠良, 王健辉, 刘琳, 等. 实验性牙周炎对小鼠焦虑样行为及肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中华老年口腔医学杂志, 2023, 21(5):257-263. DOI: 10.19749/j.cn.cjgd.1672-2973.2023.05.001 . |
| YANG Z L, WANG J H, LIU L, et al. Effects of experimental periodontitis on anxiety-like behavior and gut microbiota in mice[J]. Chin J Geriatr Dent, 2023, 21(5):257-263. DOI: 10.19749/j.cn.cjgd.1672-2973.2023.05.001 . | |
| 22 | 刘静, 陆洁, 裴天仙, 等. 基因缺陷型2型糖尿病模型动物db/db小鼠早期生物学特性研究[J]. 药物评价研究, 2013, 36(1):8-12.DOI: 10.7501/i.issn.1674-6376.2013.01.003 . |
| LIU J, LU J, PEI T X, et al. Research on early biological characteristics of gene defect type 2 diabetes model db/db mice[J]. Drug Eval Res, 2013, 36(1):8-12. DOI: 10.7501/i.issn.1674-6376.2013.01.003 . | |
| 23 | 侯黎光, 叶宇, 苟惠清, 等. A20通过抑制自噬缓解实验性牙周炎牙槽骨吸收[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 42(4):476-483, 587. DOI: 10.7655/NYDXBNS20220403 . |
| HOU L G, YE Y, GOU H Q, et al. A20 alleviates alveolar bone loss in experimental periodontitis by inhibiting autophagy[J]. J Nanjing Med Univ (Nat Sci), 2022, 42(4):476-483, 587. DOI: 10.7655/NYDXBNS20220403 . | |
| 24 | KIM K S, HONG S M, HAN K, et al. Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: nationwide population based study[J]. BMJ, 2024, 384: e076388. DOI:10.1136/bmj-2023-076388 . |
| 25 | SEBASTIAN S A, PADDA I, JOHAL G. Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome: a state-of-the-art review[J]. Curr Probl Cardiol, 2024, 49(2):102344. DOI:10.1016/j.cpcardiol. 2023.102344 . |
| 26 | WANG Y Q, ZHU J K, TANG Y, et al. Association between pulp and periapical disease with type 2 diabetes: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization[J]. Int Endod J, 2024, 57(5):566-575. DOI:10.1111/iej.14034 . |
| 27 | NADIA A, HASSAN A, MUSHRIQ A. Oral flora and functional dysbiosis of cleft lip and palate patients: a scoping review[J]. Spec Care Dent, 2023, 44(2):255-268. DOI:10.1111/scd.12872 . |
| 28 | XU J Y, YU L, YE S R, et al. Oral microbiota-host interaction: the chief culprit of alveolar bone resorption[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15:1254516. DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1254516 . |
| 29 | 李宗泽, 赵泽, 张文菲, 等. 16S核糖体DNA Amplicon测序法分析2型糖尿病患者口腔微生物多样性[J]. 转化医学杂志, 2017, 6(3):151-156. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3097.2017.03.006 . |
| LI Z Z, ZHAO Z, ZHANG W F, et al. Analysis of oral microbial diversity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus by 16S ribosome DNA Amplicon sequencing[J]. Transl Med J, 2017, 6(3):151-156. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3097.2017.03.006 . | |
| 30 | 程梦蓉, 秦立果, 姜大昭, 等. β-羟基丁酸对糖尿病患者口腔菌群结构和丰度的调节作用[J]. 中国科技论文, 2020, 15(12):1377-1385. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2020.12.006 . |
| CHENG M R, QIN L G, JIANG D Z, et al. Modulatory effect of β-hydroxybutyrate on the structure and abundance of oral microbiota in diabetic populations[J]. China Sci, 2020, 15(12):1377-1385. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2020.12.006 . | |
| 31 | GAO C, GUO Y, CHEN F. Cross-cohort microbiome analysis of salivary biomarkers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12:816526. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.816526 . |
| 32 | 赵玉兰, 杨艺, 李进涛, 等. 2型糖尿病db/db小鼠骨强度和肠道内容物菌群的变化[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2023, 33(6):1-7. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2023.06.001 . |
| ZHAO Y L, YANG Y, LI J T, et al. Changes of bone strength and gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic db/db mice[J]. Chin J Comp Med, 2023, 33(6):1-7. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2023.06.001 . | |
| 33 | 朱洪杨, 刘烨, 李家荣, 等. 基于肠道菌群分析探讨葛根减轻T2DM db/db小鼠胰岛素抵抗的作用及机制[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2023, 48(17):4693-4701. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230418.402 . |
| ZHU H Y, LIU Y, LI J R, et al. Effect and mechanism of Puerariae Lobatae Radix in alleviating insulin resistance in T2DM db/db mice based on intestinal flora[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2023, 48(17):4693-4701. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230418.402 . | |
| 34 | 彭川, 胡学芳, 陈正涛, 等. 基于16S rRNA技术研究蒌连丸对2型糖尿病db/db小鼠肠道菌群的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2023, 29(12): 63-70. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20222107 . |
| PENG C, HU X F, CHEN Z T, et al. Effect of Loulianwan on gut microbiota in db/db mice with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on 16S rRNA sequencing technology[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form, 2023, 29(12): 63-70. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20222107 . | |
| 35 | 刘军, 丁登峰, 高伟, 等. 应用16S rRNA基因测序比较分析不同品系1型糖尿病小鼠肠道菌群的异同[J]. 实验动物科学, 2023, 40(5):24-32. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6179.2023.05.005 . |
| LIU J, DING D F, GAO W, et al. Use of 16S rRNA sequencing for comparative analysis of gut microbiome in different strains of type 1 diabetic mice[J]. Lab Anim Sci, 2023, 40(5):24-32. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6179.2023.05.005 . | |
| 36 | AEMAIMANAN P, AMIMANAN P, TAWEECHAISUPAPONG S. Quantification of key periodontal pathogens in insulin-dependent type 2 diabetic and non-diabetic patients with generalized chronic periodontitis[J]. Anaerobe, 2013, 22:64-68. DOI:10.1016/j.anaerobe.2013.06.010 . |
| 37 | GU M, WANG P P, XIANG S K, et al. Effects of type 2 diabetes and metformin on salivary microbiota in patients with chronic periodontitis[J]. Microb Pathog, 2021, 161(Pt B):105277. DOI:10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105277 . |
| 38 | HE J, SHEN X, FU D, et al. Human periodontitis-associated salivary microbiome affects the immune response of diabetic mice[J]. J Oral Microbiol, 2022, 14(1):2107814. DOI:10.1080/20002297.2022.2107814 . |
| 39 | 李丽丽, 谢晓婷, 吴贇, 等. 牙周炎与糖尿病关联机制的研究进展[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2023, 54(1):71-76.DOI: 10.12182/20230160203 . |
| LI L L, XIE X T, WU Y, et al. Advances in research on the mechanism of association between periodontitis and diabetes mellitus[J]. J Sichuan Univ (Med Sci), 2023, 54(1):71-76. DOI: 10.12182/20230160203 . |
| [1] | 杨劲, 俞诗雅, 林楠, 方永超, 赵虎, 邱锦维, 林鸿铭, 陈惠燕, 王瑜, 吴伟航. 改良型十二指肠旷置术对2型糖尿病大鼠糖代谢的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 523-530. |
| [2] | 王晓钰, 蒋升瑶, 蔺智兵, 崔立. 基于糖尿病-肿瘤小鼠模型研究糖尿病对结直肠癌/乳腺癌进展及肠道菌群的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2021, 41(6): 469-479. |
| [3] | 江霞, 钱豪杰, 魏迅, 郑羽旋, 周正宇. 斑马鱼糖尿病模型的构建及应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2020, 40(6): 547-552. |
| [4] | 李银银, 龚菁菁, 吴绍亮, 李小红, 王存龙, 霍学云, 路静, 吕建祎, 刘欣, 郭萌, 李长龙, 陈振文, 杜小燕. ND3在自发性糖尿病长爪沙鼠5种组织中的表达[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2017, 37(1): 6-10. |
| [5] | 郑晋华, 何敏珠, 奚骏, 庄华, 王铸钢, 匡颖. Leprtm1Srcmo 基因敲入小鼠模型的建立及表型分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2014, 34(5): 345-352. |
| [6] | 朱延涛, 金蓉家, 钟杰敏, 李守业, 徐志伟, 寿旗扬, 蔡月琴, 王辉. II型糖尿病大鼠血糖波动模型的初步建立及其特点[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2012, 32(6): 512-516. |
| [7] | 唐慧青, 陈立新, 梁磊, 符杰, 顾坚忠, 徐平. II型糖尿病模型C57BL/KsJ-db/db小鼠的生物学特性研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2011, 31(1): 62-65. |
| [8] | 温航远1,陈红艳2,杨新波2,黄正明3. 两种方法建立2型糖尿病肾病大鼠模型肾损伤相关指标的对比分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2010, 30(5): 349-353. |
| [9] | 李娜,张周,冯颖. 自发性Ⅱ型糖尿病模型db/db小鼠生物学特性研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2010, 30(1): 33-38. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||