













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 531-540.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.070
林金杏1( )(
)( ), 王新栋2,3, 白雪兵2, 冯丽萍1, 谢淑武1, 陈秋生2(
), 王新栋2,3, 白雪兵2, 冯丽萍1, 谢淑武1, 陈秋生2( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2023-06-05
修回日期:2023-10-12
出版日期:2023-10-25
发布日期:2023-10-25
通讯作者:
陈秋生(1963—),男,博士,教授,研究方向:动物组织细胞形态及功能研究。E-mail: chenqsh305@njau.edu.cn。ORCID: 0000-0002-6087-7029作者简介:林金杏(1983—),女,博士,研究员,研究方向:水生实验动物生理功能及标准化研究。E-mail: linjinxing@slarc.org.cn。ORCID:0000-0002-7649-9552;
基金资助:
Jinxing LIN1( )(
)( ), Xindong WANG2,3, Xuebing BAI2, Liping FENG1, Shuwu XIE1, Qiusheng CHEN2(
), Xindong WANG2,3, Xuebing BAI2, Liping FENG1, Shuwu XIE1, Qiusheng CHEN2( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-06-05
Revised:2023-10-12
Published:2023-10-25
Online:2023-10-25
Contact:
CHEN Qiusheng (ORCID: 0000-0002-6087-7029), E-mail:chenqsh305@njau.edu.cn摘要:
目的 观察和分析斑马鱼体肾的微细结构,并对其分泌的外泌体进行分离鉴定。 方法 应用光学显微镜和电子显微镜技术系统观察斑马鱼体肾的显微结构和超微结构,用纳米颗粒跟踪分析(nanoparticle tracking analysis,NTA)技术检测外泌体粒径大小。 结果 斑马鱼体肾紧贴并平行于脊椎,肾单位由肾小管和肾小体组成,其中肾小管可细分为近曲小管、远曲小管及颈段3种类型,肾小体由肾小球和肾小囊构成;经高碘酸-希夫(periodic acid-Schiff,PAS)染色后,可见近曲小管富含糖原颗粒,其游离面有明显的刷状缘结构。透射电子显微镜下,在肾小管的管腔观察到外泌体分布,上皮细胞游离面的胞质有少量多囊泡体和大量的晚期内涵体分布,肾小管的顶端和肾小球足细胞中亦观察到少量多囊泡体分布。通过CD9、CD63和TSG101免疫组织化学和免疫荧光检测显示,多囊泡体及其外泌体在肾小管管腔的游离面高表达,在肾小体和管腔内表达较弱。NTA和透射电子显微镜观察结果显示,分离获得的斑马鱼体肾外泌体呈茶托状,粒径众数为144.4 nm,符合外泌体形态和直径大小特征。 结论 斑马鱼体肾具有哺乳动物肾脏的典型结构,为体内的泌尿器官。肾小管具有分泌外泌体的能力,其形成是多囊泡体向细胞游离面释放到胞外的过程。本研究结果为水生实验动物泌尿器官的功能研究及相关模型的开发应用奠定了形态学基础。
中图分类号:
林金杏,王新栋,白雪兵,等. 成年斑马鱼体肾的微细结构及其外泌体的分布鉴定[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(5): 531-540. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.070.
Jinxing LIN,Xindong WANG,Xuebing BAI,et al. Fine Structure of the Trunk Kidney and Distribution of Its Secreted Exosomes in the Adult Zebrafish[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 531-540. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.070.
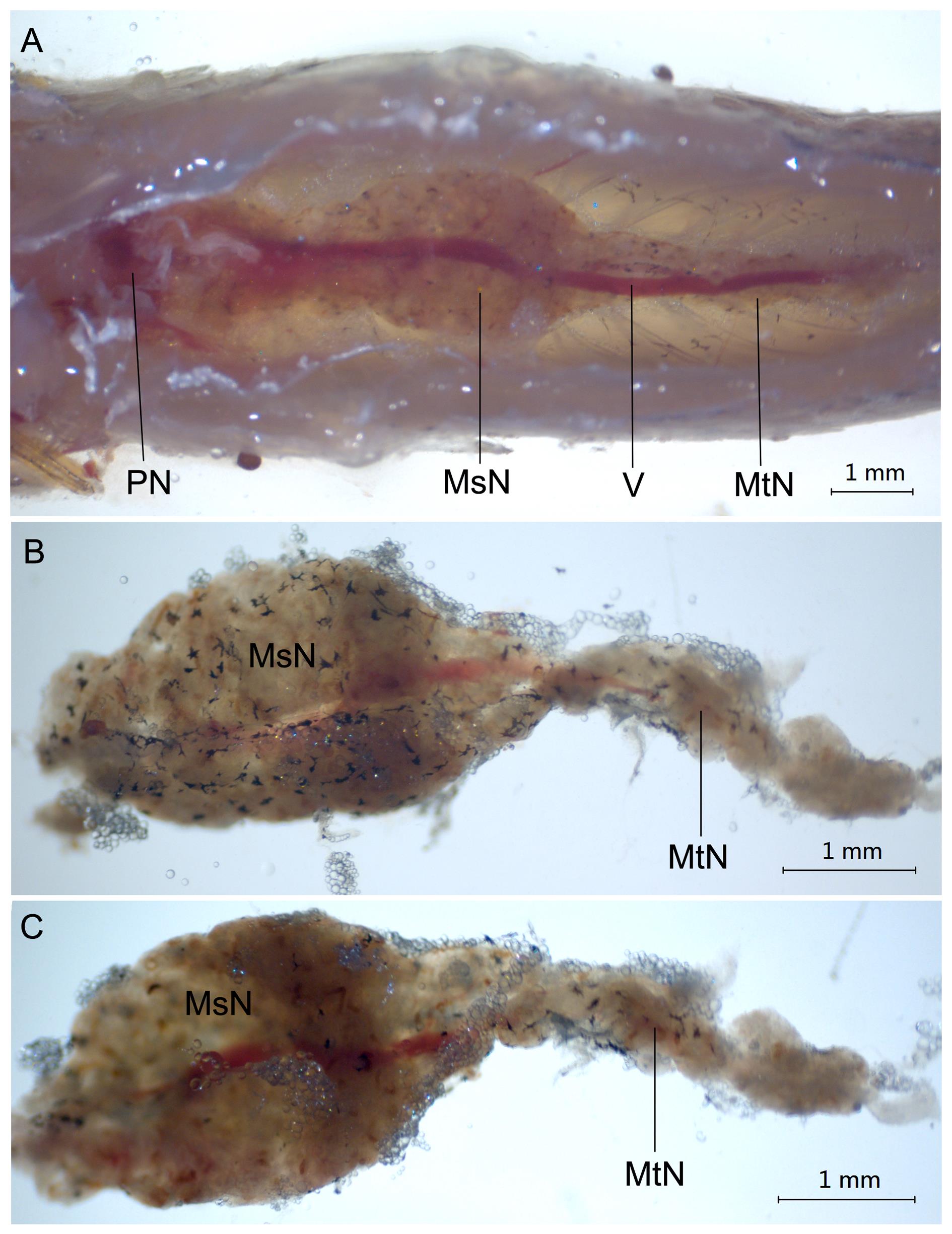
图1 体视显微镜下观察到的成年斑马鱼肾脏解剖形态注:A,斑马鱼肾脏在体内的位置;B,斑马鱼体肾的背侧面;C,斑马鱼体肾的腹侧面。标尺大小为1 mm。PN,头肾;MsN,中肾;MtN,后肾;V,静脉。
Figure 1 Anatomical structure of the kidney in adult zebrafish by stereomicroscopeNote:A, The position of kidney in zebrafish; B, Dorsal view of the trunk kidney in zebrafish; C, Ventral view of the trunk kidney in zebrafish. The scale is 1 mm. PN, Pronephros; MsN, Mesonephros; MtN, Metanephros; V, Vein.
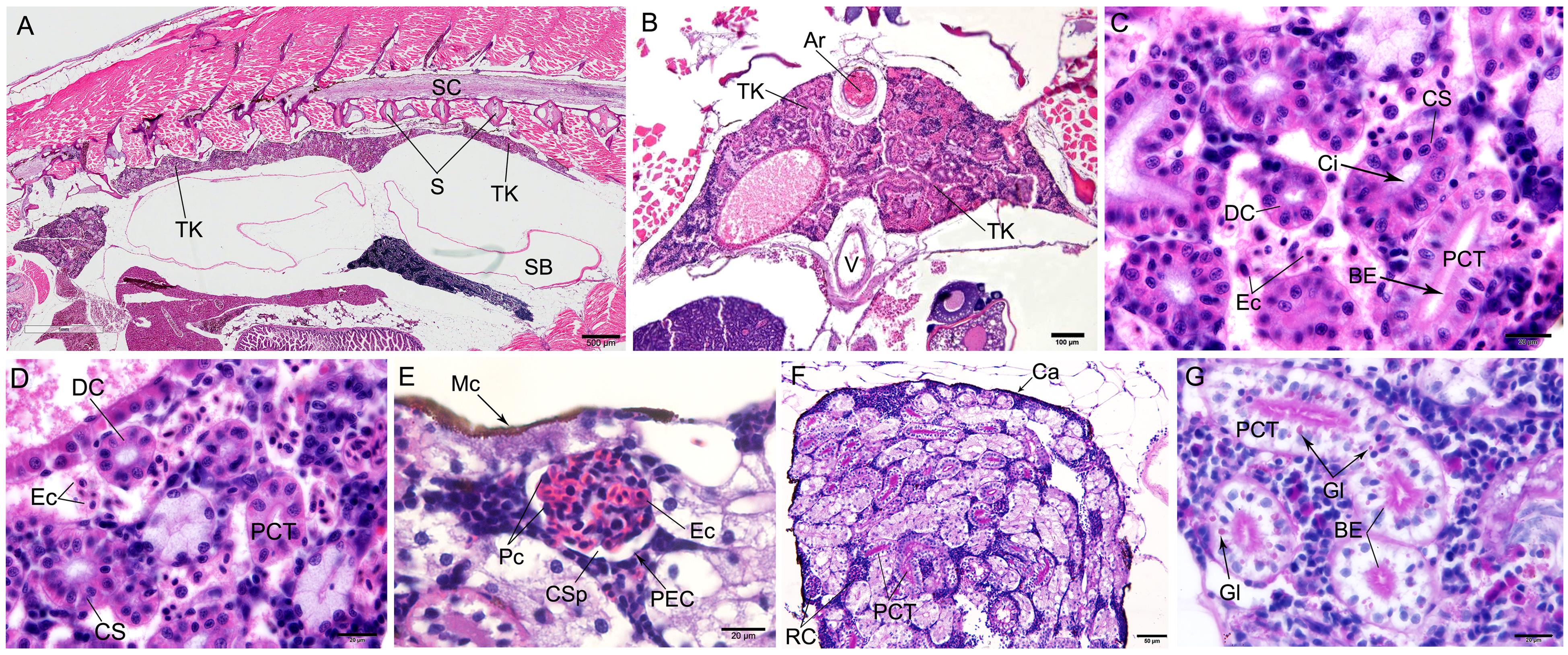
图2 HE染色(A~E)和PAS染色(F~G)后观察到的斑马鱼体肾的显微结构注:A,斑马鱼体肾纵切面形态结构,标尺大小为500 μm;B,斑马鱼体肾横切面形态结构,标尺大小为100 μm;C,斑马鱼肾小管形态结构,标尺大小为20 μm;D,斑马鱼肾小管分为近曲小管、远曲小管和颈段,标尺大小为20 μm;E,斑马鱼肾小体的形态结构,标尺大小为20 μm;F,近曲小管PAS反应呈阳性,肾小体PAS反应呈阴性,标尺大小为50 μm;G,近曲小管上皮细胞内富含糖原颗粒,游离端刷状缘清晰可见,标尺大小为20 μm。Ar,动脉;BE,刷状缘;TK,体肾;Ca,被膜;Ci,纤毛;CS,颈段;CSp,肾小囊腔;DC,远曲小管;Ec,红细胞;Gl:糖原颗粒;Mc,黑色素细胞;Pc,足细胞;PCT,近曲小管;PEC,壁层上皮细胞;RC,肾小体;S,脊柱;SB,鳔;SC,脊髓;V,静脉。
Figure 2 Microstructure of trunk kidney in the zebrafish detected by HE staining (A-E) and periodic acid-Schiff staining(F-G)Note:A, Morphological structure of zebrafish kidney in longitudinal section, the scale is 500 μm; B, Morphological structure of zebrafish kidney in cross section, the scale is 100 μm; C,Morphological structure of renal tubules of zebrafish, the scale is 20 μm; D, The renal tubules of zebrafish were divided into proximal convoluted tubules, distal convoluted tubules and cervical segments, the scale is 20 μm; E, Morphological structure of renal corpuscle, the scale is 20 μm; F, PAS reaction was positive in proximal convoluted tubules while negative in renal corpuscles, the scale is 50 μm; G, The epithelial cells of the proximal convoluted tubule were rich in glycogen particles, which were showed brush-like outline on the apical surface of the epithelial cells, the scale is 20 μm. Ar, Artery; BE, Brush-like edge; TK, Trunk kidney; Ca, Capsule; Ci, Cilia; CS, Cervical segment; CSp, Capsular space; DC, Distal convoluted tubule; Ec, Erythrocyte; Gl, Glycogen; Mc, Melanocyte; Pc, Podocyte; PCT, Proximal convoluted tubule; PEC, Parietal epithelial cell; RC, Renal corpuscle; S, Spine; SB, Swim bladder; SC, Spinal cord; V, Vein.
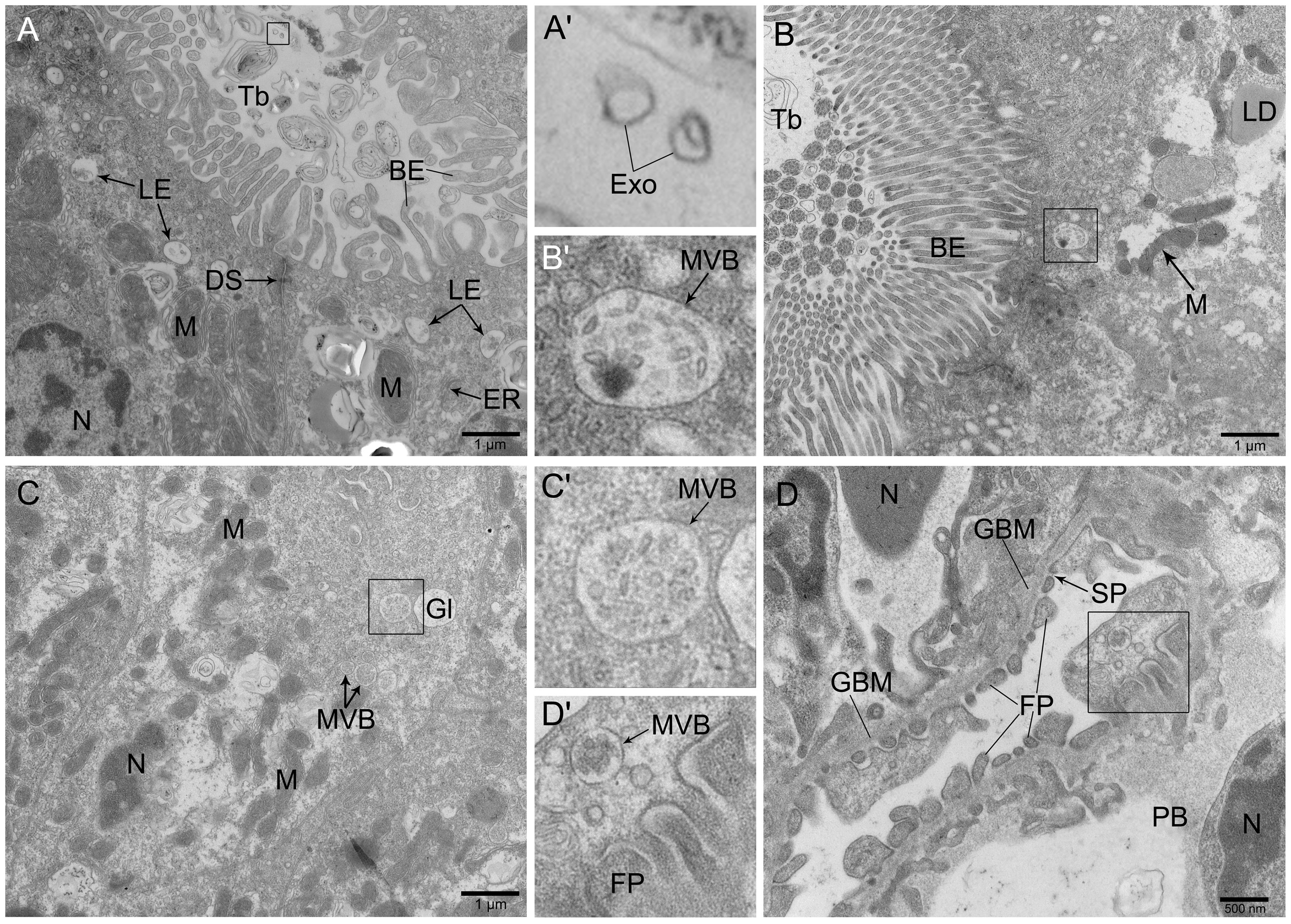
图3 透射电子显微镜下观察到的斑马鱼体肾的超微结构注:A,近曲小管的上皮细胞富含线粒体和糖原,游离端可见大量的晚期内涵体分布,标尺大小为1 μm;B,近曲小管游离端的刷状缘结构明显,呈栅栏状紧密排列,标尺大小为1 μm;C,肾小管的顶端有多囊泡体分布,标尺大小为1 μm;D,肾小球的足细胞足突结构明显,有多囊泡体分布,标尺大小为500 nm。A'、B'、C'和D'分别为A、B、C和D中方框处的放大图。BE,刷状缘;GBM,肾小球基底膜;DS,细胞桥粒;Exo,外泌体;ER,内质网;FP,足突;Gl,糖原颗粒;LE,晚期内涵体;LD,脂滴;M,线粒体;MVB,多囊泡体;N,细胞核;PB,足细胞胞体;SP,裂孔;Tb,管腔。
Figure 3 Ultrastructure of trunk kidney in zebrafish observed by transmission electron microscopeNote:A, The epithelial cells of convoluted tubule contained mitochondria and glycogen with abundant late endosomes in the apical surface, the scale is 1 μm; B, The brush-like structure at the free-end of the proximal convoluted tubule was clearly visible and arranged in a palisade shape, the scale is 1 μm; C, There were multiple vesicles distributed at the top-end of epithelial cells in the renal tubule, the scale is 1 μm; D, The structure of podocytes in the glomerulus was obvious, with multiple vesicles distributed, the scale is 500 nm. A', B', C' and D' were enlarged figures at the boxes in A, B, C and D, respectively. BE, Brush-like edge; GBM, Glomerular basement membrane; DS, Desmosome; Exo, Exosome; ER, Endoplasmic reticulum; FP, Foot process; Gl, Glycogen; LE, Late endosome; LD, Lipid droplets; M, Mitochondria; MVB, Multivesicular body; N, Nucleus; PB, Podocyte cell body; SP, Slit pore; Tb, Tube.
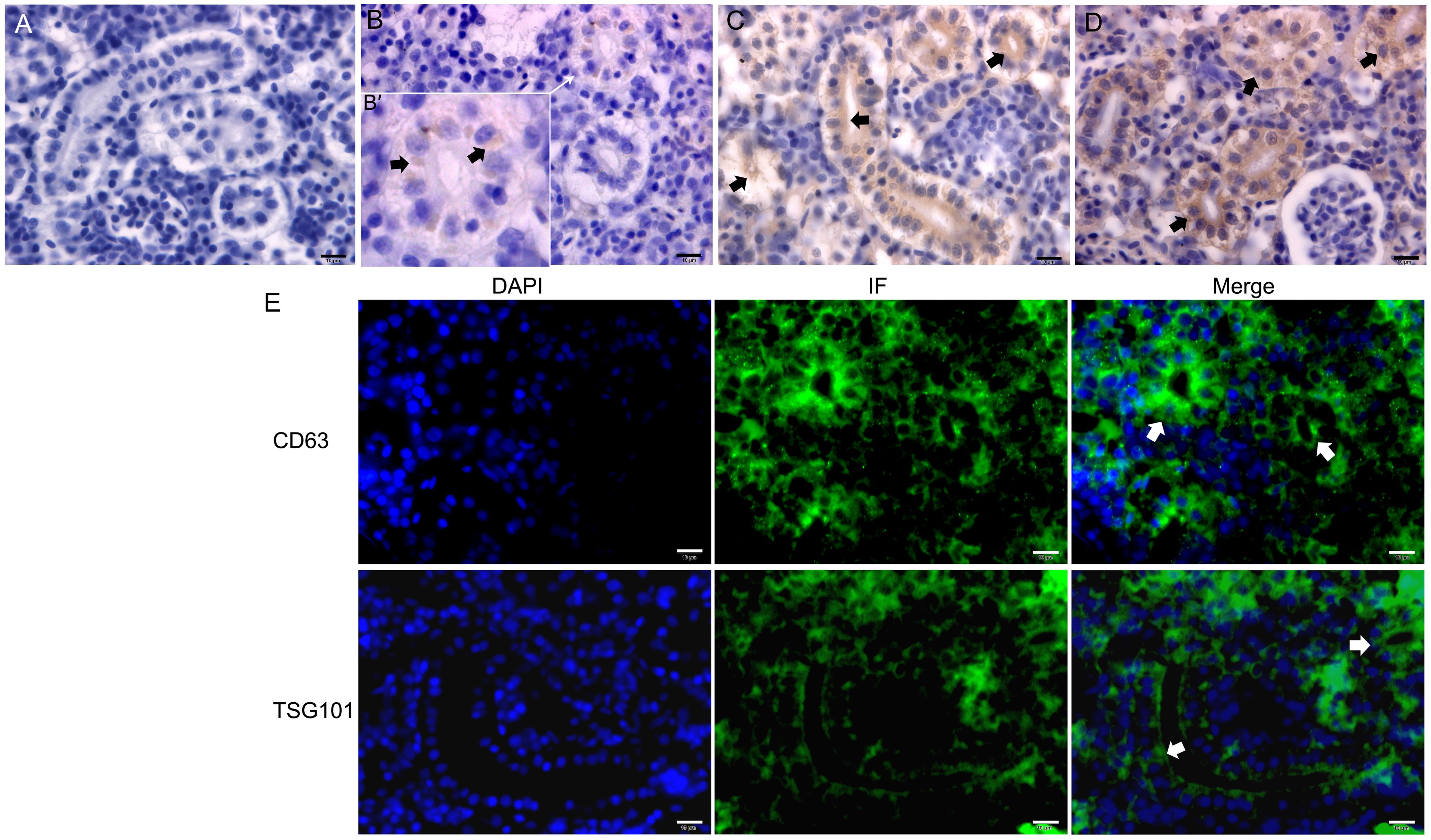
图4 免疫组织化学(A~D)和免疫荧光(E)检测斑马鱼体肾中CD9、CD63和TSG101蛋白表达注:A为免疫组织化学法(DAB染色)检测的阴性对照;B~D分别显示免疫组织化学检测CD9、CD63、TSG101在体肾中的分布情况(黑色短箭头示阳性反应,B′为B图中白色箭头所指处的放大图);E,CD63和TSG101免疫荧光(IF)法(DAPI染色)进一步检测CD63和TSG101在斑马鱼体肾中广泛分布,其中肾小管游离面(白色短箭头示)分布最为明显。标尺大小均为10 μm。
Figure 4 Immunohistochemistry (A-D) and immunofluorescence (E) of CD9、CD63 and TSG101 in the trunk kidney of zebrafishNote:A, Negative control of immunohistochemistry (DAB stain); B-D, Distribution of CD9, CD63 and TSG101 in the trunk kidney, respectively, and black short arrows showed positive reactions. The figure B' was the enlarged figure pointed by the white arrow of figure B: E, CD63 and TSG101 were widely distributed in the trunk kidney of zebrafish by immunofluorescence (IF) method (DAPI stain), particularly abundant in the apical surface of renal tubules (white short arrows). All of cale bars are 10 μm.
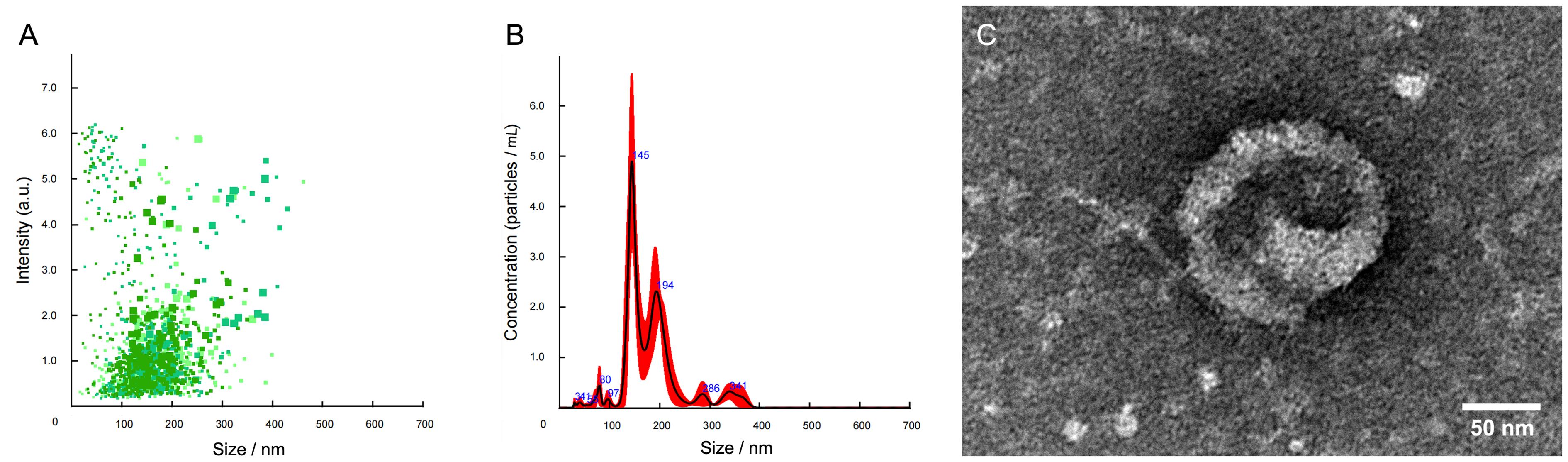
图5 纳米颗粒跟踪分析技术(A~B)和透射电子显微镜(C)鉴定成年斑马鱼的体肾外泌体注:A,斑马鱼体肾外泌体强度/粒径散点图;B,斑马鱼体肾外泌体平均浓度/粒径分布图;C,分离提取的斑马鱼体肾外泌体超微结构。
Figure 5 The trunk kidney exosomes in the adult zebrafish identified by nanoparticle tracking analysis (A-B) and transmission electron microscopy (C)Note:A, Scatter diagram of exosome strength/particle size in the trunk kidney of zebrafish; B, Distribution diagram of average exosome concentration/particle size in the trunk kidney of zebrafish; C, Ultrastructure of the trunk kidney exosome in zebrafish.
| 1 | RASOOLY R S, HENKEN D, FREEMAN N, et al. Genetic and genomic tools for zebrafish research: the NIH zebrafish initiative[J]. Dev Dyn, 2003, 228(3):490-496. DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.10366 . |
| 2 | LUBIN A, OTTERSTROM J, HOADE Y, et al. A versatile, automated and high-throughput drug screening platform for zebrafish embryos[J]. Biol Open, 2021, 10(9): bio058513. DOI: 10.1242/bio.058513 . |
| 3 | PATTON E E, ZON L I, LANGENAU D M. Zebrafish disease models in drug discovery: from preclinical modelling to clinical trials[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2021, 20(8):611-628. DOI: 10.1038/s41573-021-00210-8 . |
| 4 | 熊凤, 谢训卫, 潘鲁媛, 等. 国家斑马鱼资源中心的资源、技术和服务建设[J]. 遗传, 2018, 40(8):683-692. DOI: 10.16288/j.yczz.18-151 . |
| XIONG F, XIE X W, PAN L Y, et al. Development of resources, technologies and services at the China Zebrafish Resource Center[J]. Hereditas, 2018, 40(8):683-692. DOI: 10.16288/j.yczz.18-151 . | |
| 5 | 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 实验动物 实验鱼质量控制: GB/T 39649—2020[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2020. |
| State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Laboratory animal-Quality control of laboratory fish: GB/T 39649-2020[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2020. | |
| 6 | WALLACE M A. Anatomy and physiology of the kidney[J]. AORN J, 1998, 68(5):800, 803-16, 819-20; quiz 821-824. DOI: 10.1016/s0001-2092(06)62377-6 . |
| 7 | LIN J X, CHEN Q S, HU J H. Color atlas of zebrafish histology and cytology[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2022. DOI:10.1007/978-981-16-9852-1 . |
| 8 | THÉRY C, WITWER K W, AIKAWA E, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines[J]. J Extracell Vesicles, 2018, 7(1):1535750. DOI: 10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750 . |
| 9 | YANG D B, ZHANG W H, ZHANG H Y, et al. Progress, opportunity, and perspective on exosome isolation - efforts for efficient exosome-based theranostics[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(8):3684-3707. DOI: 10.7150/thno.41580 . |
| 10 | BAI X B, GUO Y N, SHI Y H, et al. In vivo multivesicular bodies and their exosomes in the absorptive cells of the zebrafish (Danio Rerio) gut[J]. Fish Shellfish Immunol, 2019, 88:578-586. DOI: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.03.030 . |
| 11 | BAI X B, SHI Y H, TARIQUE I, et al. Multivesicular bodies containing exosomes in immune-related cells of the intestine in zebrafish (Danio rerio): Ultrastructural evidence[J]. Fish Shellfish Immunol, 2019, 95:644-649. DOI: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.10.044 . |
| 12 | LÄSSER C, ELDH M, LÖTVALL J. Isolation and characterization of RNA-containing exosomes[J]. J Vis Exp, 2012(59): e3037. DOI: 10.3791/3037 . |
| 13 | WEN J, ZENG M R, YANG Y Y, et al. Exosomes in diabetic kidney disease[J]. Kidney Dis, 2023, 9(3):131-142. DOI: 10.1159/000529709 . |
| 14 | AGBORBESONG E, BISSLER J, LI X G. Liquid biopsy at the frontier of kidney diseases: application of exosomes in diagnostics and therapeutics[J]. Genes, 2023, 14(7):1367. DOI: 10.3390/genes14071367 . |
| 15 | RESENDE A D, LOBO-DA-CUNHA A, ROCHA E. Comparative summary of the fish renal structure, using the brown trout (Salmo trutta) as the reference model[J]. Microsc Microanal, 2012, 18(S5):47-48. DOI: 10.1017/s1431927612012895 . |
| 16 | 林国辉, 邱玫, 方展强. 剑尾鱼肾脏组织的超微结构观察[J]. 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 43(1): 105-108. |
| LIN G H, QIU M, FANG Z Q. Observation on the histology and ultrastructure of the kidney in xiphophorus helleri [J]. J South China Norm Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2011, 43(1): 105-108. | |
| 17 | VAN NIEL G, D'ANGELO G, RAPOSO G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2018, 19(4):213-228. DOI: 10.1038/nrm.2017.125 . |
| 18 | KALLURI R, LEBLEU V S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes[J]. Science, 2020, 367(6478): eaau6977. DOI: 10.1126/science.aau6977 . |
| 19 | BANG C, THUM T. Exosomes: new players in cell-cell communication[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2012, 44(11):2060-2064. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.08.007 . |
| 20 | VAN NIEL G, CARTER D R F, CLAYTON A, et al. Challenges and directions in studying cell-cell communication by extracellular vesicles[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2022, 23(5):369-382. DOI: 10.1038/s41580-022-00460-3 . |
| 21 | SHEHZAD A, ISLAM S U, SHAHZAD R, et al. Extracellular vesicles in cancer diagnostics and therapeutics[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2021, 223:107806. DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera. 2021.107806 . |
| 22 | ZHENG R, ZHANG K, TAN S Y, et al. Exosomal circLPAR1 functions in colorectal cancer diagnosis and tumorigenesis through suppressing BRD4 via METTL3-eIF3h interaction[J]. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21(1):49. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-021-01471-y . |
| 23 | WITWER K W, WOLFRAM J. Extracellular vesicles versus synthetic nanoparticles for drug delivery[J]. Nat Rev Mater, 2021, 6(2):103-106. DOI: 10.1038/s41578-020-00277-6 . |
| 24 | DUTTA D, KHAN N, WU J F, et al. Extracellular vesicles as an emerging frontier in spinal cord injury pathobiology and therapy[J]. Trends Neurosci, 2021, 44(6):492-506. DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2021.01.003 . |
| 25 | FAN M, LIU H F, YAN H Y, et al. A CAR T-inspiring platform based on antibody-engineered exosomes from antigen-feeding dendritic cells for precise solid tumor therapy[J]. Biomaterials, 2022, 282:121424. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials. 2022.121424 . |
| 26 | 白雨, 刁宗礼, 刘文虎. 外泌体在糖尿病肾脏疾病发病机制中的作用研究进展[J]. 当代医学, 2022, 28(10): 190-194. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4393.2022.10.072 . |
| BAI Y, DIAO Z L, LIU W H. Advance of the role of exosomes in the pathogenesis of diabetic kidney disease[J]. Contemp Med, 2022, 28(10): 190-194. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4393.2022.10.072 . | |
| 27 | CHEN Q H, TAKADA R, NODA C, et al. Different populations of Wnt-containing vesicles are individually released from polarized epithelial cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6:35562. DOI: 10.1038/srep35562 . |
| 28 | FÉVRIER B, RAPOSO G. Exosomes: endosomal-derived vesicles shipping extracellular messages[J]. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2004, 16(4):415-421. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2004.06.003 . |
| 29 | KLUMPERMAN J, RAPOSO G. The complex ultrastructure of the endolysosomal system[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2014, 6(10): a016857. DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016857 . |
| 30 | DENG F Y, MILLER J. A review on protein markers of exosome from different bio-resources and the antibodies used for characterization[J]. J Histotechnol, 2019, 42(4):226-239. DOI: 10.1080/01478885.2019.1646984 . |
| [1] | 赵鑫, 王晨曦, 石文清, 娄月芬. 斑马鱼在炎症性肠病机制及药物研究中的应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(4): 422-431. |
| [2] | 杨晋娴, 王淑娟, 翟金云, 朱顺星. Micall2a基因表达下调抑制斑马鱼血管发育[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(3): 282-287. |
| [3] | 谭志刚, 刘锦信, 郑楚雅, 廖文峰, 冯露平, 彭红丽, 严秀, 卓振建. 神经母细胞瘤动物模型研究进展与应用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(3): 288-296. |
| [4] | 金仕容, 华叶, 訾化星, 杜旭飞, 卜纪雯. 一种显著提高实验用斑马鱼繁殖效率和使用寿命的优化养殖方案[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(3): 297-306. |
| [5] | 冯延, 武文卿, 张静远, 李煜, 李壘辰, 袁征, 崔淑芳. 裸鼹鼠皮肤成纤维细胞外泌体的分离及鉴定[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2020, 40(6): 506-512. |
| [6] | 江霞, 钱豪杰, 魏迅, 郑羽旋, 周正宇. 斑马鱼糖尿病模型的构建及应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2020, 40(6): 547-552. |
| [7] | 邸亚男, 朱丽英, 钱雯, 潘卫. 斑马鱼作为模式动物在人类眼睛疾病研究中的应用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2020, 40(5): 440-. |
| [8] | 王 雪, 刘可春, 杨学亮, 马玉奎, 张 云. 冈田酸对斑马鱼幼鱼神经行为功能的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2020, 40(3): 190-. |
| [9] | 李英娘, 戴玮, 盛健. 斑马鱼甲状腺肿大病例分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2019, 39(6): 462-466. |
| [10] | 王俐梅, 张建, 刘忠华, 杨威. 视网膜母细胞瘤斑马鱼模型及rb1基因研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2019, 39(3): 244-248. |
| [11] | 周斌, 盛哲津, 冯琛卓, 李利妹. 一种体内实时观察黑色素瘤的斑马鱼模型[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2018, 38(1): 22-28. |
| [12] | 田芳, 王玉柱, 夏敏杰, 孙冰, 丁训城, 李卫华, 许慧慧, 胡晶莹. 实验用斑马鱼成鱼内脏组织病理学检查方法的优化[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2017, 37(6): 465-469. |
| [13] | 傅婷婷, 刘艳. 大鼠离体肾脏灌流模型在筛选慢性肾病药物的初步应用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2017, 37(5): 357-362. |
| [14] | 金璐, 李燕, 李志操, 吴西军, 周艳华, 何志旭, 舒莉萍. Irx5a基因过表达对斑马鱼胚胎早期造血的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2017, 37(4): 309-314. |
| [15] | 林金杏, 冯丽萍, 胡建华, 高诚. 斑马鱼鳍和鳞片色素细胞的显微观察[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2017, 37(2): 94-101. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||