
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 551-559.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.135
• Animal Models of Human Diseases • Previous Articles Next Articles
Bin WU1( )(
)( ), Xu WANG2, Dongxu FU3, Yujun ZHU4, Jinlu HUANG5, Shunxing ZHU2(
), Xu WANG2, Dongxu FU3, Yujun ZHU4, Jinlu HUANG5, Shunxing ZHU2( )(
)( )
)
Received:2022-08-29
Revised:2022-12-09
Online:2022-12-25
Published:2023-01-04
Contact:
Shunxing ZHU
CLC Number:
Bin WU, Xu WANG, Dongxu FU, Yujun ZHU, Jinlu HUANG, Shunxing ZHU. Effect of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Shuganjieyu Formula on Constipation Type Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Brain-gut Axis in Rats[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 551-559.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.135
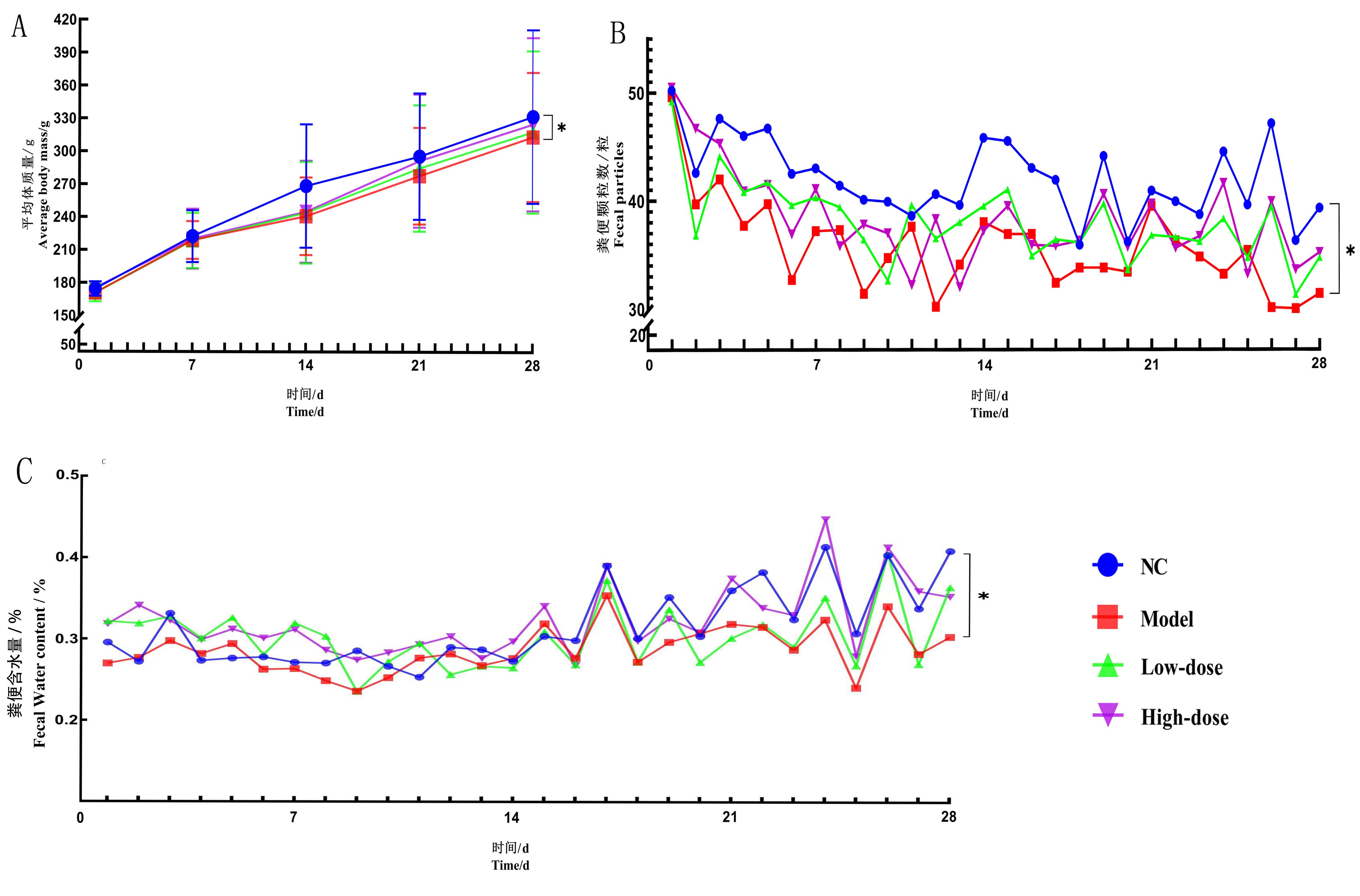
Figure 1 Change trend of body mass, fecal particles and fecal water content of rats in each groupNote: NC, normal control group; Model, model control group; Low-dose, Shuganjieyu Formula low-dose group (5 g/kg); High-dose, Shuganjieyu Formula high-dose group (20 g/kg). A: Changes in body mass of rats with time, compared to the model group, *P<0.05, n=10; B and C: Tendency of changes in daily feces and their water content in all groups of rats, compared to the normal control group, *P<0.05, n=10.
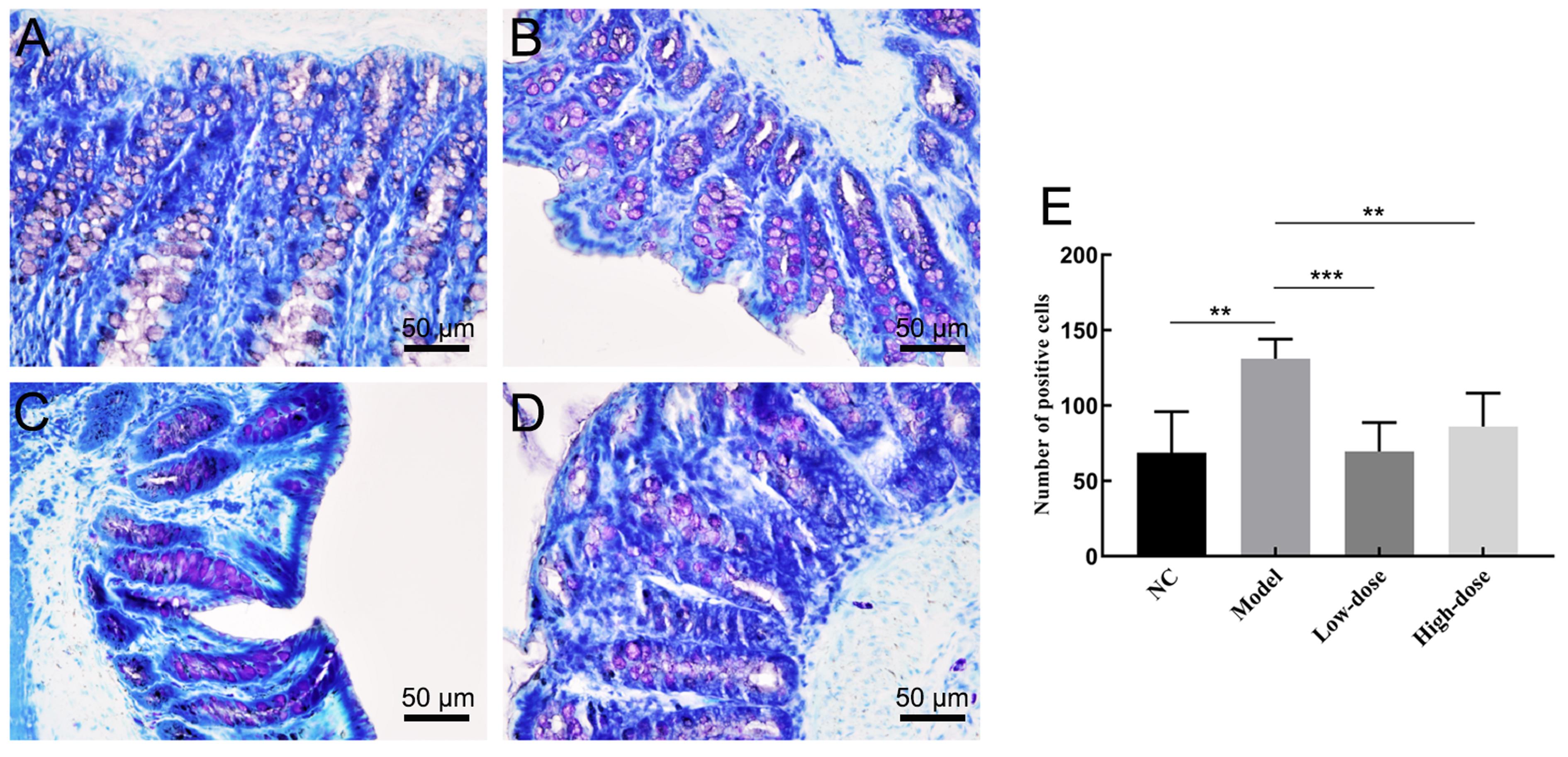
Figure 2 Histopathological changes (toloniumchloride,×200) and the number of mast cells in colon of ratsNote:Left, the results of modified toloniumchloride staining of colon tissue (the scale of each small figure was all 50 μm). A: Normal control group; B: Model control group; C and D: Low- (5 g/kg) and high- (20 g/kg) dose of Shuganjieyu Formula groups. E: The statistical data of mass cells positive cells, compared to the model group, **P<0.01,***P<0.001, n=10。
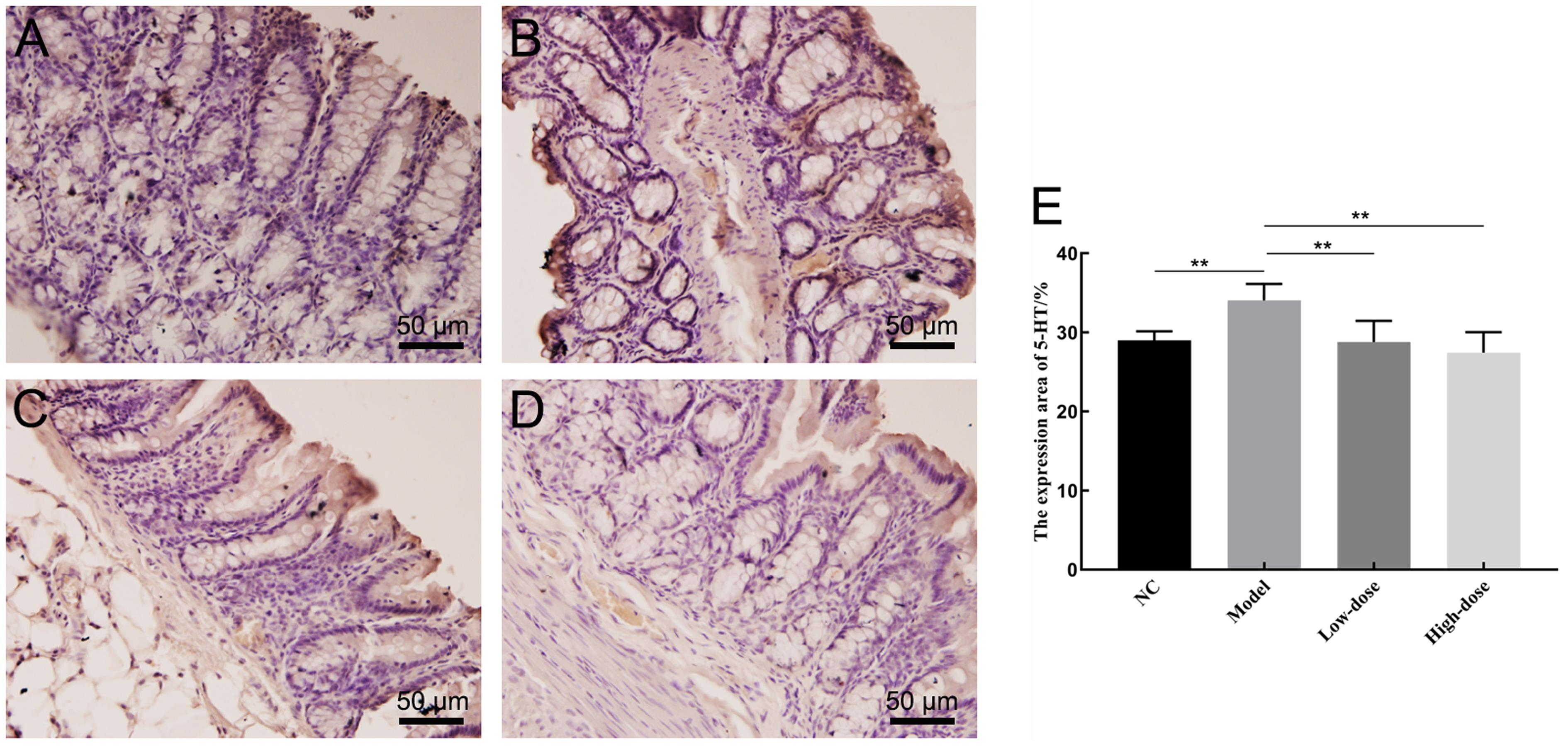
Figure 3 5-HT immunohistochemical staining of colon tissue of rats (DAB,×200 )Note:On the left is the colon tissue immunohistochemical staining (DAB, all of which have the same scale size, 50 μm). A is the normal control group (NC), B is the model control group (Model), C is the low-dose (5 g/kg) group of Shuganjieyu Formula (low-dose), D is the high-dose (20 g/kg) group of Shuganjieyu Formula (high-dose). E: The semi-quantitative statistical graph of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) positive expression area, compared with the model group, **P<0.01, n=10。
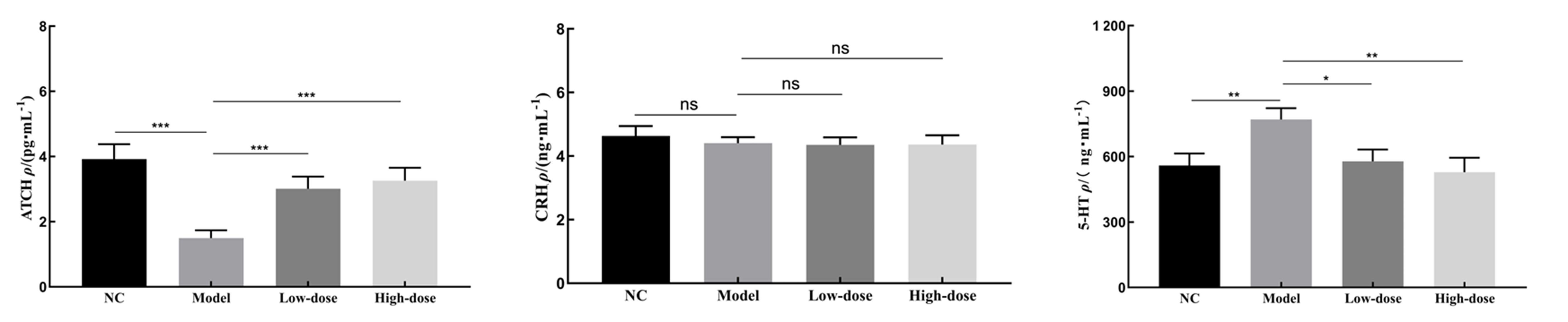
Figure 4 Comparison of 5-HT, CRH and ACTH contents in serum of rats in the four groups (ELISA)Note: ACTH, adrenocorticotropic hormone; CRH, corticotropin releasing hormone; 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine. NC, Normal control group; Model, model control group; Low-dose, Shuganjieyu Formula low-dose group (5 g/kg); High-dose, Shuganjieyu Formula high-dose group (20 g/kg). Compared to the model group,ns indicates P>0.05,*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001; n=10.
| 1 | 刘建湘, 刘新光. 肠易激综合征的诊断与治疗[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2008, 28(7):524-526. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-2194.2008.07.006 . |
| LIU J X, LIU X G. Diagnosis and treatment of irritable bowel syndrome[J]. Chin J Pract Intern Med, 2008, 28(7):524-526. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-2194.2008.07.006 . | |
| 2 | MERTZ H R. Irritable bowel syndrome[J]. N Engl J Med, 2003, 349(22):2136-2146. DOI:10.1056/nejmra035579 . |
| 3 | 中华医学会消化病学分会胃肠功能性疾病协作组, 中华医学会消化病学分会胃肠动力学组. 中国肠易激综合征专家共识意见(2015年, 上海)[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2016, 36(5):299-312. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1432.2016.05.005 . |
| Gastrointestinal Functional Diseases Collaborative Group of Digestive Branch of Chinese Medical Association, Gastro-intestinal Dynamics Group of Digestive Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on irritable bowel syndrome in China (Shanghai, 2015) [J]. Chin J Dig, 2016(5):299-312. DOI: 10.3760/cma. j.issn. 0254-1432.2016.05.005 . | |
| 4 | 宋怡然, 梁笑楠, 李忱阳, 等. «2020年中国肠易激综合征专家共识意见»解读[J]. 临床荟萃, 2021, 36(7): 628-631. |
| SONG Y R, LIANG X N, LI C Y, et al. Interpretation on Chinese expert consensus of irritable bowel syndrome in 2020[J]. Clin Focus, 2021, 36(7): 628-631. | |
| 5 | LEE C, DOO E, CHOI J M, et al. The increased level of depression and anxiety in irritable bowel syndrome patients compared with healthy controls: systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. J Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2017, 23(3):349-362. DOI:10.5056/jnm16220 . |
| 6 | ZHANG Q E, WANG F, QIN G, et al. Depressive symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a meta-analysis of comparative studies[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2018, 14(11):1504-1512. DOI:10.7150/ijbs.25001 . |
| 7 | ZAMANI M, ALIZADEH-TABARI S, ZAMANI V. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the prevalence of anxiety and depression in patients with irritable bowel syndrome[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 50(2):132-143. DOI:10.1111/apt.15325 . |
| 8 | HU Z C, LI M X, YAO L, et al. The level and prevalence of depression and anxiety among patients with different subtypes of irritable bowel syndrome: a network meta-analysis[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2021, 21(1):23. DOI:10.1186/s12876-020-01593-5 . |
| 9 | 吴斌, 朱宇均, 黄金路. 从"气"论治法对便秘型肠易激综合征的临床疗效及对部分脑肠肽的影响[J]. 中国医药科学, 2022, 12(11):9-13, 26. |
| WU B, ZHU Y J, HUANG J L. Clinical efficacy of the Qi in treating constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome and its effect on brain-gut peptides[J]. China Med Pharm, 2022, 12(11):9-13, 26. | |
| 10 | 彭丽华, 杨云生, 孙刚, 等. 便秘型肠易激综合征新概念模型的建立[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2004, 12(1): 112-116. |
| PENG L H, YANG Y S, SUN G, et al. A new model of constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome in rats[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2004, 12(1): 112-116. | |
| 11 | QUIGLEY E M M. Microbiota-brain-gut axis and neuro-degenerative diseases[J]. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep, 2017, 17(12):94. DOI:10.1007/s11910-017-0802-6 . |
| 12 | SPIELMAN L J, GIBSON D L, KLEGERIS A. Unhealthy gut, unhealthy brain: the role of the intestinal microbiota in neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Neurochem Int, 2018, 120:149-163. DOI:10.1016/j.neuint.2018.08.005 . |
| 13 | VERMEULEN W, DE MAN J G, PELCKMANS P A, et al. Neuroanatomy of lower gastrointestinal pain disorders[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(4):1005-1020. DOI:10.3748/wjg.v20.i4.1005 . |
| 14 | CHRISTIANSON J A, BIELEFELDT K, ALTIER C, et al. Development, plasticity and modulation of visceral afferents[J]. Brain Res Rev, 2009, 60(1):171-186. DOI:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2008.12.004 . |
| 15 | GONDA X, PETSCHNER P, ESZLARI N, et al. Effects of different stressors are modulated by different neuro-biological systems: the role of GABA-a versus CB1 receptor gene variants in anxiety and depression[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2019, 13: 138. DOI:10.3389/fncel.2019.00138 . |
| 16 | HOUTEPEN L C, SCHÜR R R, WIJNEN J P, et al. Acute stress effects on GABA and glutamate levels in the prefrontal cortex: A 7T 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy study[J]. Neuroimage Clin, 2017, 14:195-200. DOI:10.1016/j.nicl.2017. 01.001 . |
| 17 | LIBERZON I, KRSTOV M, YOUNG E A. Stress-restress: effects on ACTH and fast feedback[J]. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 1997, 22(6):443-453. DOI:10.1016/s0306-4530(97)00044-9 . |
| 18 | SANTOS J, ALONSO C, VICARIO M, et al. Neuro-pharmacology of stress-induced mucosal inflammation: implications for inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome[J]. Curr Mol Med, 2008, 8(4):258-273. DOI:10.2174/156652408784533788 . |
| 19 | ROBLES A, PEREZ INGLES D, MYNEEDU K, et al. Mast cells are increased in the small intestinal mucosa of patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2019, 31(12): e13718. DOI:10.1111/nmo.13718 . |
| 20 | YU Y C, LI J, ZHANG M X, et al. Resveratrol improves brain-gut axis by regulation of 5-HT-dependent signaling in the rat model of irritable bowel syndrome[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2019, 13:30. DOI:10.3389/fncel.2019.00030 . |
| 21 | 刘欢, 张孟历, 于猛, 等. 醋制香附挥发油抗抑郁活性及化学成分分析[J]. 药物评价研究, 2020, 43(3):436-442. DOI:10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2020.03.012 . |
| LIU H, ZHANG M L, YU M, et al. Antidepressant activity evaluation and GC-MS analysis of volatile oil from vinegar-made Cyperi rhizome[J]. Drug Eval Res, 2020, 43(3):436-442. DOI:10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2020.03.012 . | |
| 22 | 宋美卿, 仝立国, 贾力莉, 等. 疏肝行气对药"香橼-佛手"对抑郁大鼠行为学及海马单胺类神经递质的影响[J]. 中国药物与临床, 2021, 21(5):737-740. DOI:10.11655/zgywylc2021.05.006 . |
| SONG M Q, TONG L G, JIA L L, et al. Effects of Shuxingqi medicine "Citron-bergamot" on behavior and monoamine neurotransmitters in hippocampus of depressed rats[J]. Chin Remedies Clin, 2021, 21(5):737-740. DOI:10.11655/zgywylc2021.05.006 . | |
| 23 | 方圆之, 高杰. 白芍的通便作用及其对便秘小鼠结肠AQP4、VIP表达的影响[J]. 山东中医杂志, 2017, 36(1):62-65. DOI:10.16295/j.cnki.0257-358x.2017.01.022 . |
| FANG Y Z, GAO J. Cathartic effect of Baishao and its effect on AQP4 and VIP in mice with constipation[J]. Shandong J Tradit Chin Med, 2017, 36(1):62-65. DOI:10.16295/j.cnki.0257-358x.2017.01.022 . | |
| 24 | FAN R, HUANG X, WANG Y, et al. Ethnopharmacokinetic- and activity-guided isolation of a new antidepressive compound from fructus aurantii found in the traditional Chinese medicine Chaihu-Shugan-San: a new approach and its application[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2012, 2012:607584. DOI:10.1155/2012/607584 . |
| 25 | 李陈雪, 杨玉赫, 冷德生, 等. 枳壳化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2019, 21(2):158-161. DOI:10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2019.02.043 . |
| LI C X, YANG Y H, LENG D S, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and quality evaluation of fructus aurantii[J]. J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med, 2019, 21(2):158-161. DOI:10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2019.02.043 . |
| [1] | Liya ZHAO, Liju NI, Caiqin ZHANG, Jianping TANG, Yangzheng YAO, Yanyan NIE, Xiaoxue GU, Ying ZHAO. Establishing a Genetic Detection Protocol of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Panels in Inbred Rats Based on Multiplex PCR-LDR [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 548-558. |
| [2] | Lingzhi YU, Jianyun XIE, Liping FENG, Xiaofeng WEI. Establishment of Fluorescence qPCR Method for Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus and Its Application in Feces Detection of Rats and Mice [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 566-573. |
| [3] | Ziyin XIA, Yuanyuan CHAI, Yunxia XU, Qinwei YU, Xin HUANG, Luyong ZHANG, Zhenzhou JIANG. Quantification of Uric Acid of Rat Serum by Liquid Chromatography-ultraviolet Detection and Its Comparison Study [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 314-322. |
| [4] | Ying TAN, Wenping LIAO, Qilong GAO, Yong LI, Xinhui SHI, Jingkun WANG. Physiological Indexes and Histopathology Analysis of Sodium Iodate-Induced Retinitis Pigmentosa in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 124-135. |
| [5] | Jian GE, Jingfen SUN, Yongjie WU. Taurine Has no Protective Effect on Rat Corneal Endothelial Cells Injured by Benzalkonium Chloride [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 39-43. |
| [6] | Qin XU, Yan NI, Wenhui SHI, Jianying LI, Jiangwei LIU, Hongqiong ZHAO, Xinming XU. Analysis on Ileum and Colon Microflora of SPF Male SD Rats based on High-throughput Sequencing [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 53-60. |
| [7] | Chen GAO, Chunling FAN, Yurong LI, Wenjuan PEI, Caiping GUAN. Changes in Expression of Monocarboxylate Transporters in the Rat Cerebral Cortex after Exercise-induced Fatigue Under Simulated High-altitude Hypoxia and its Significance [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 384-392. |
| [8] | Bingxin XU, Kaijian FAN, Tingyu WANG, Huijin CHEN. Effect of Dexamethasone on Cartilage Degeneration in Rats with Collagen-induced Arthritis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 416-422. |
| [9] | Huiyan QIN, Huafeng CHEN, Hui YANG, Hailan LUO, Weizhong FU, Qingbo LI, Jiehong ZHANG. The Capacity of Silkworm Cocoon Water to Mitigate the Level of Oxidative Stress in Aged Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 393-400. |
| [10] | Xiaorui ZHANG, Jing CAO, Qianqian WU, Jijun LIU, Guoyuan CHEN, Baojin WU. Effects of Probucol Formulations on Mesenteric Lymphatic Trans-port Efficiency and Pharmacokinetics in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 275-283. |
| [11] | Sijia ZHAO, Xinyu HE, Quan JING, Lin MA, Chunlan GUO, Kuo WAN. Evaluation of Pain in Acute Pulpitis Hyperalgesia Model Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 333-341. |
| [12] | Yiru WANG, Xiaoying JIANG, Ruoxi DONG, Yibin PAN, Xianghui HAN, Yongqing CAO. Modified Method for Inducing Acute Intestinal Fibrosis in Rats Using 2,4,6-Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 284-293. |
| [13] | Xiaorui ZHANG, Jing CAO, Qianqian WU, Kang KANG, Guoyuan CHEN, Baojin WU. A Preliminary Method for Continuous Drainage of Mesenteric Lymph Fluid in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 267-274. |
| [14] | Dingshan FENG, Yeyu HUANG, Xiaoxin ZHANG, Aiqin WU, Zhan WANG, Linliang SU. Effects of Storage Time on Electrolyte Content and pH Value in Rat Serum Samples [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 301-305. |
| [15] | Xiao LU, Lin ZHANG, Hui JI, Shanxiang JIANG. Efficacy of DZ1462, a Novel Sodium-phosphate Transporter Inhibitor, on 5/6 Nephrectomy-induced Hyperphosphatemia Model Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 187-193. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||