
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 53-60.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.103
Special Issue: 实验动物资源开发与利用
• Development and Utilization of Laboratory Animal Resources • Previous Articles Next Articles
Qin XU1( ), Yan NI1,2(
), Yan NI1,2( ), Wenhui SHI1, Jianying LI1, Jiangwei LIU1, Hongqiong ZHAO2, Xinming XU3(
), Wenhui SHI1, Jianying LI1, Jiangwei LIU1, Hongqiong ZHAO2, Xinming XU3( )(
)( )
)
Received:2022-07-07
Revised:2022-09-16
Online:2023-02-25
Published:2023-03-09
Contact:
Xinming XU
CLC Number:
Qin XU, Yan NI, Wenhui SHI, Jianying LI, Jiangwei LIU, Hongqiong ZHAO, Xinming XU. Analysis on Ileum and Colon Microflora of SPF Male SD Rats based on High-throughput Sequencing[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 53-60.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.103
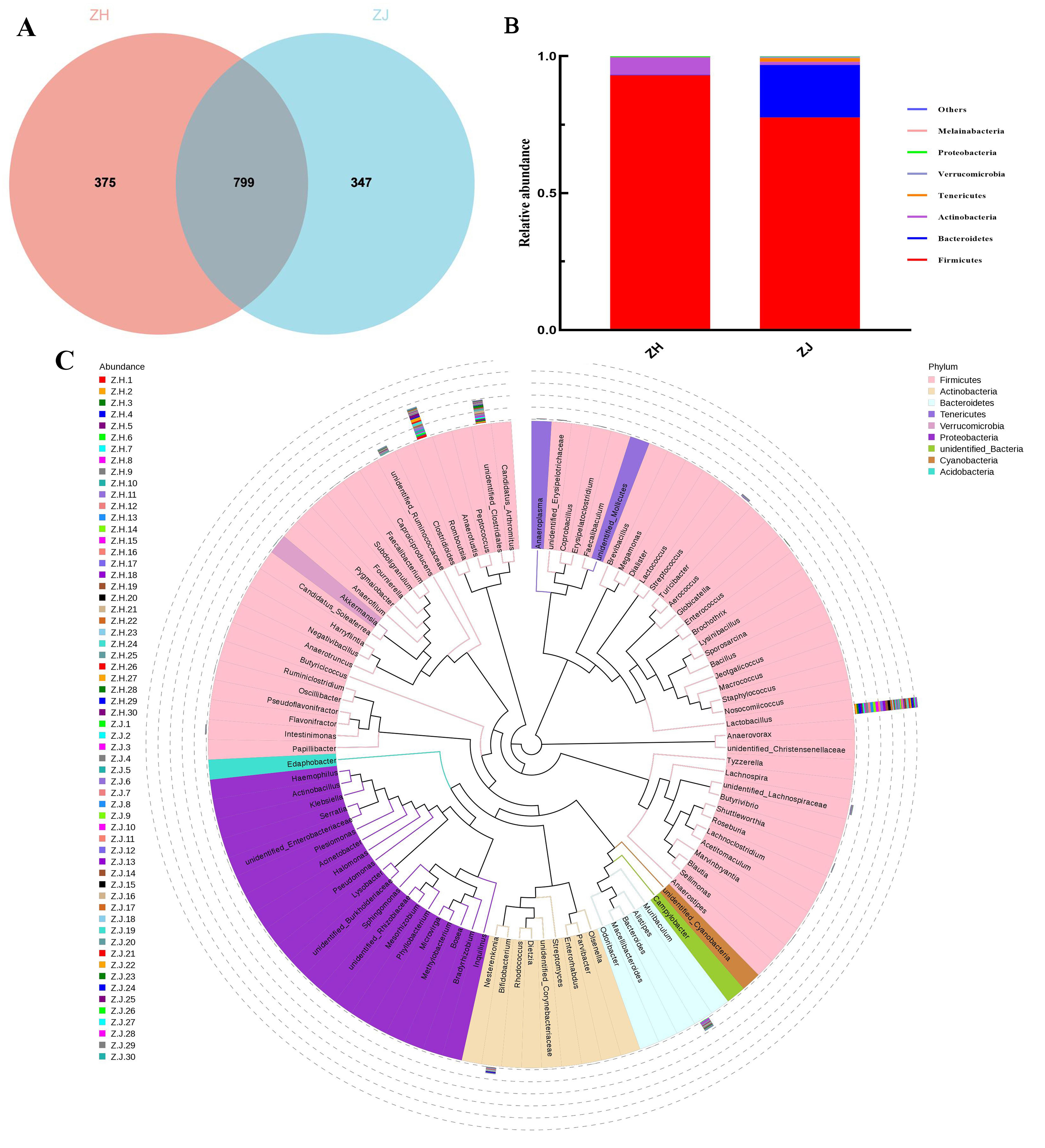
Figure 1 Classification of phylum and genus of ileum and colon microflora in rats based on operation taxonomic unitsNote:A, Venn graph, in which, the pink circle represents the number of operation taxonomic units (OTU) unique to colon (ZJ), the blue circle represents the number of OTUs unique to ileum (ZH), and the overlap part represents the number of OTUs shared by ileum and colon; B, Histogram of relative species abundance at phylum level; C, Phylogenetic graph of genus level species.
样品名称 Sample name | 观察数 Observed number | OTU数 OTU number | 香农指数 Shannon index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 测序深度 Goods_Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 回肠(ZH) | 7 969 | 1 174 | 2.49 | 0.950 | 337.61 | 0.998 |
| 结肠(ZJ) | 18 434 | 1 146 | 5.90 | 0.661 | 671.08 | 0.998 |
Table1 Alpha diversity indices statistics of microflora in ileum and colon of rats
样品名称 Sample name | 观察数 Observed number | OTU数 OTU number | 香农指数 Shannon index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 测序深度 Goods_Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 回肠(ZH) | 7 969 | 1 174 | 2.49 | 0.950 | 337.61 | 0.998 |
| 结肠(ZJ) | 18 434 | 1 146 | 5.90 | 0.661 | 671.08 | 0.998 |
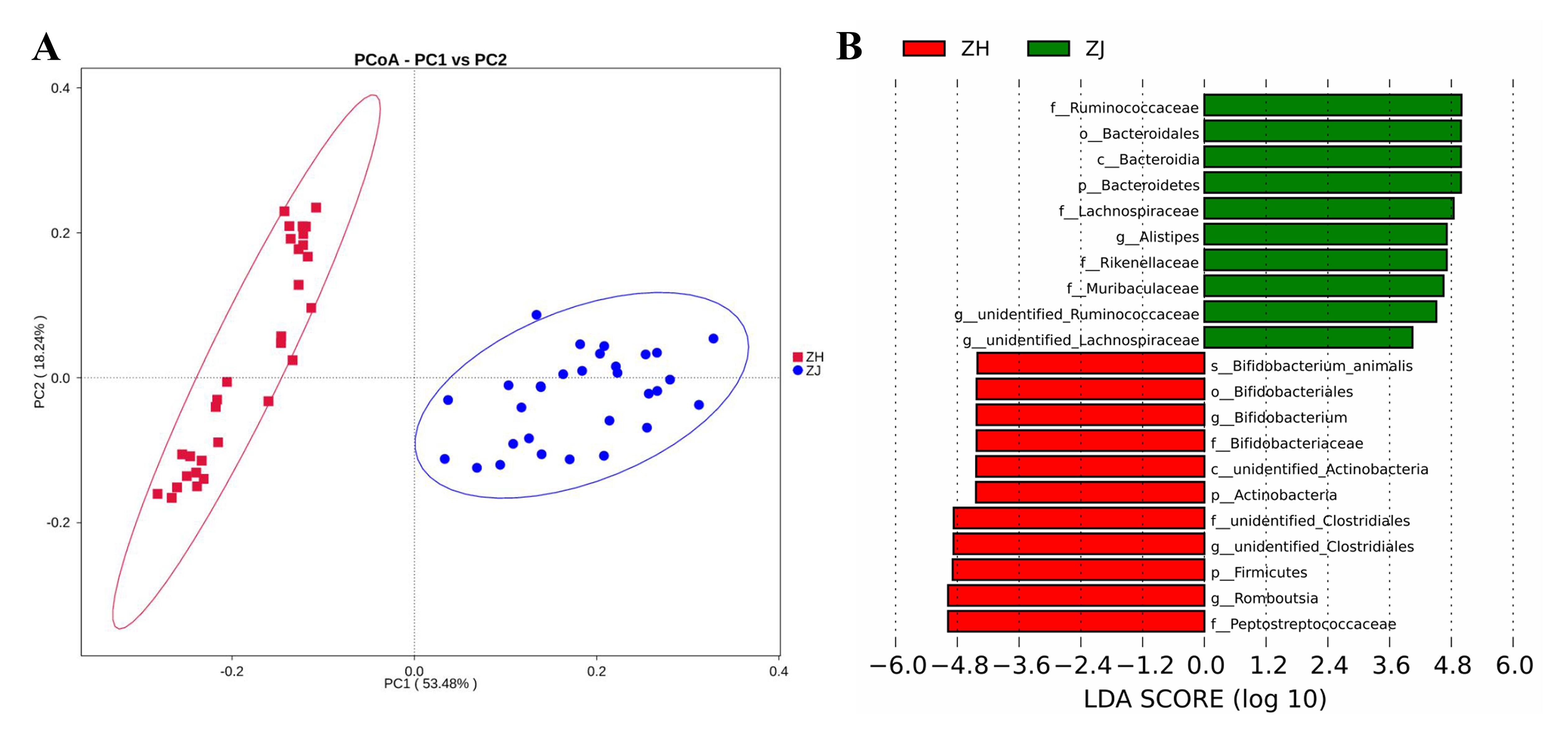
Figure 2 Diversity analysis of microflora in ileum and colon of ratsNote: A, the principal co-ordinates analysis (PCoA) based on the weighted unifrac distance. The abscissa represents one principal component (PC1), the ordinate represents another principal component (PC2), and the percentage represents the contribution value of principal component to sample difference. B, the linear discriminant analysis (LDA) value distribution. ZJ, colon; ZH, ileum.
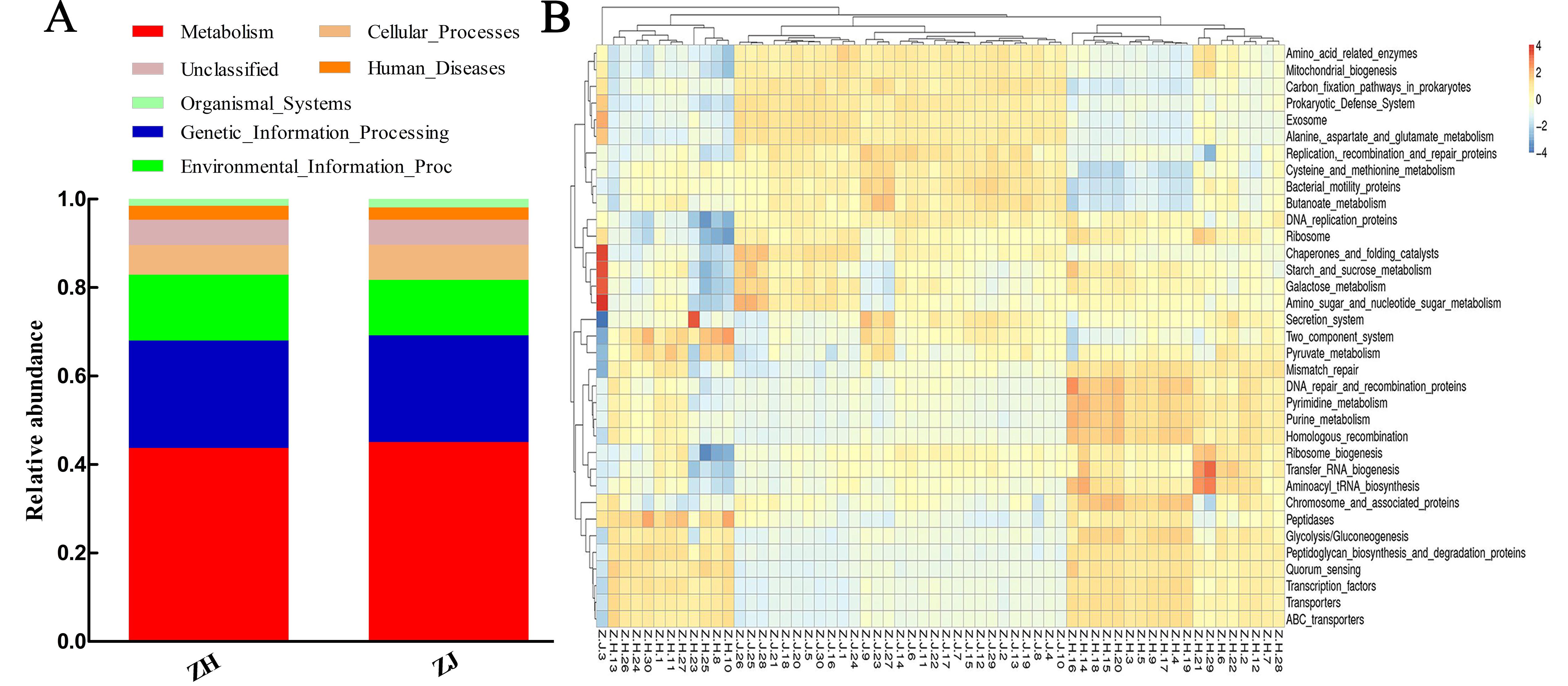
Figure 3 Functional prediction charts of microflora in ileum and colon of ratsNote:A, Tax4Fun relative abundance histogram of function annotation; B, clustering heat map of function annotation based on Tax4Fun.
| 1 | PALAU-RODRIGUEZ M, TULIPANI S, ISABEL QUEIPO-ORTUÑO M, et al. Metabolomic insights into the intricate gut microbial-host interaction in the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes[J]. Front Microbiol, 2015, 6:1151. DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2015.01151 . |
| 2 | GILL T, ASQUITH M, ROSENBAUM J T, et al. The intestinal microbiome in spondyloarthritis[J]. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 2015, 27(4):319-325. DOI:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000187 . |
| 3 | SCHAEVERBEKE T, TRUCHETET M E, RICHEZ C. Gut metagenome and spondyloarthritis[J]. Joint Bone Spine, 2013, 80(4):349-352. DOI:10.1016/j.jbspin.2013.02.005 . |
| 4 | 赵杰, 朱维铭, 李宁. 益生菌、益生元、合生元与炎症性肠病[J]. 肠外与肠内营养, 2014, 21(4):251-253, 256. DOI:10.16151/j.1007-810x.2014.04.014 . |
| ZHAO J, ZHU W M, LI N. Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics and inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Parenter Enteral Nutr, 2014, 21(4):251-253, 256. DOI:10.16151/j.1007-810x.2014.04.014 . | |
| 5 | CRABBÉ P A, BAZIN H, EYSSEN H, et al. The normal microbial flora as a major stimulus for proliferation of plasma cells synthesizing IgA in the gut. The germ-free intestinal tract[J]. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol, 1968, 34(4):362-375. DOI:10.1159/000230130 . |
| 6 | WILLIAMS A M, PROBERT C S J, STEPANKOVA R, et al. Effects of microflora on the neonatal development of gut mucosal T cells and myeloid cells in the mouse[J]. Immunology, 2006, 119(4):470-478. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2567.2006.02458.x . |
| 7 | WILMORE D W, ROBINSON M K. Short bowel syndrome[J]. World J Surg, 2000, 24(12):1486-1492. DOI:10.1007/s002680010266 . |
| 8 | KABIR S I, KABIR S A, RICHARDS R, et al. Pathophysiology, clinical presentation and management of diversion colitis: a review of current literature[J]. Int J Surg, 2014, 12(10):1088-1092. DOI:10.1016/j.ijsu.2014.08.350 . |
| 9 | KLINGENSMITH N J, COOPERSMITH C M. The gut as the motor of multiple organ dysfunction in critical illness[J]. Crit Care Clin, 2016, 32(2):203-212. DOI:10.1016/j.ccc.2015.11.004 . |
| 10 | 黎介寿. 肠内营养与肠屏障功能[J]. 肠外与肠内营养, 2016, 23(5):257-259. DOI:10.16151/j.1007-810x.2016.05.001 . |
| LI J S. Enteral nutrition and intestinal barrier function[J]. Parenter Enteral Nutr, 2016, 23(5):257-259. DOI:10.16151/j.1007-810x.2016.05.001 . | |
| 11 | 孙亚鲁, 尹勇, 王晓梅. 肠道菌群与脑卒中的关系[J]. 医学综述, 2019, 25(9):1782-1786. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2019.09.022 . |
| SUN Y L, YIN Y, WANG X M. Relationship between intestinal flora and stroke[J]. Med Recapitul, 2019, 25(9):1782-1786. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2019.09.022 . | |
| 12 | 李波, 侍荣华, 李宗杰. 肠道菌群-肠-脑轴与心身疾病的相互关系[J]. 生理科学进展, 2018, 49(3):221-226. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0559-7765.2018.03.013 . |
| LI B, SHI R H, LI Z J. The correlations between microbiota-gut-brain axis and psychosomatic disorders[J]. Prog Physiol Sci, 2018, 49(3):221-226. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0559-7765.2018.03.013 . | |
| 13 | 黄小群, 廖小平. 肠道菌群与抑郁的相关性研究进展[J]. 中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2019, 22(1):112-116. DOI:10.12083/SYSJ.2019.01.023 . |
| HUANG X Q, LIAO X P. Research progress on the relationship between intestinal flora and depression[J]. Chin J Pract Nerv Dis, 2019, 22(1):112-116. DOI:10.12083/SYSJ.2019.01.023 . | |
| 14 | 王林洁, 袁建玲, 鲍波. 肠道菌群对帕金森病影响的研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2019, 25(8):1501-1505. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2019.08.009 . |
| WANG L J, YUAN J L, BAO B. Research progress in influence of gut Microbiota on Parkinson's disease[J]. Med Recapitul, 2019, 25(8):1501-1505. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2019.08.009 . | |
| 15 | 孙功鹏, 高月兰, 魏家燕, 等. 氧化三甲胺与常见慢性疾病相关研究进展[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2019, 40(11):1377-1381. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2019.11.023 . |
| SUN G P, GAO Y L, WEI J Y, et al. Research progress on trimethylamine oxide and common chronic diseases[J]. Int J Lab Med, 2019, 40(11):1377-1381. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2019.11.023 . | |
| 16 | 王晓钰, 蒋升瑶, 蔺智兵, 等. 基于糖尿病-肿瘤小鼠模型研究糖尿病对结直肠癌/乳腺癌进展及肠道菌群的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2021, 41(6):469-479. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5817.2018.06.007 . |
| WANG X Y, JIANG S Y, LIN Z B, et al. Effects of diabetes on colorectal cancer/breast cancer progression and intestinal flora based on a diabetes-tumor mouse model[J]. Lab Anim Comp Med, 2021, 41(6):469-479. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5817.2018.06.007 . | |
| 17 | 陈梅佳, 沈楠, 杜青. 肠道菌群在风湿免疫性疾病中作用的研究进展[J]. 中华全科医师杂志, 2019, 18(3):279-282. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-7368.2019.03.018 . |
| CHEN M J, SHEN N, DU Q. Research progress of intestinal flora in rheumatic immune diseases[J]. Chin J Gen Pract, 2019, 18(3):279-282. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-7368.2019.03.018 . | |
| 18 | MAGOČ T, SALZBERG S L. FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies[J]. Bioinfor-matics, 2011, 27(21):2957-2963. DOI:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr507 . |
| 19 | CAPORASO J G, KUCZYNSKI J, STOMBAUGH J, et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data[J]. Nat Methods, 2010, 7(5):335-336. DOI:10.1038/nmeth.f.303 . |
| 20 | MINCHIN P R. An evaluation of the relative robustness of techniques for ecological ordination[J]. Vegetatio, 1987, 69(1):89-107. DOI:10.1007/BF00038690 . |
| 21 | BROOKS A W, PRIYA S, BLEKHMAN R, et al. Gut microbiota diversity across ethnicities in the United States[J]. PLoS Biol, 2018, 16(12): e2006842. DOI:10.1371/journal.pbio.2006842 . |
| 22 | 刘玉婷, 郝微微, 温红珠, 等. 肠道菌群的检测方法及研究进展[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2016, 24(20):3142-3148. DOI:10.11569/wcjd.v24.i20.3142 . |
| LIU Y T, HAO W W, WEN H Z, et al. Intestinal flora: detection methods and research advances[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2016, 24(20):3142-3148. DOI:10.11569/wcjd.v24.i20.3142 . | |
| 23 | 李旖旎. 粪菌移植联合小儿化食丸对高热量饮食模型大鼠肠道菌群-SCFAs-GPR43-IL1-8通路的影响[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2019. |
| LI Y N. Effects of bacteria transplantation combined with Xiaoerhuashi Pill on "intestinal flora- SCFAs-GPR43-IL18" pathway in high-calorie diet model rats[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2019. | |
| 24 | COSTELLO E K, LAUBER C L, HAMADY M, et al. Bacterial community variation in human body habitats across space and time[J]. Science, 2009, 326(5960):1694-1697. DOI:10.1126/science.1177486 . |
| 25 | 李宁. 肠道菌群紊乱与粪菌移植[J]. 肠外与肠内营养, 2014, 21(4):193-197. DOI:10.16151/j.1007-810x.2014.04.015 . |
| LI N. Intestinal flora disorder and fecal bacteria transplantation[J]. Parenter Enteral Nutr, 2014, 21(4):193-197. DOI:10.16151/j.1007-810x.2014.04.015 . | |
| 26 | 朱华, 肖冲, 尚海泉, 等. 基于高通量测序的不同年龄恒河猴肠道菌群结构差异分析[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2019, 27(1):72-78. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2019.01.012 . |
| ZHU H, XIAO C, SHANG H Q, et al. Analysis of gut microbiomes of Rhesus macaques of different ages by high-throughput sequencing[J]. Acta Lab Anim Sci Sin, 2019, 27(1):72-78. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2019.01.012 . | |
| 27 | 翟子豪, 宋飏, 王俊茵, 等. 峨眉山与黄山藏酋猴肠道菌群组成的比较[J]. 四川动物, 2019, 38(1):1-10. DOI:10.11984/j.issn.1000-7083.20180183 . |
| ZHAI Z H, SONG Y, WANG J Y, et al. Comparison of gut microbiome in Macaca thibetana between mount Emei and mount Huangshan[J]. Sichuan J Zool, 2019, 38(1):1-10. DOI:10.11984/j.issn.1000-7083.20180183 . | |
| 28 | 黄树武, 闵凡贵, 王静, 等. 常见SPF级小鼠和大鼠肠道菌群多样性研究[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2019, 27(2):229-235. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2019.02.016 . |
| HUANG S W, MIN F G, WANG J, et al. Diversity of intestinal flora in commonly used SPF mice and rats[J]. Acta Lab Anim Sci Sin, 2019, 27(2):229-235. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2019.02.016 . | |
| 29 | 简平, 王强, 王剑, 等. 不同年龄段川金丝猴肠道菌群结构差异分析[J]. 动物营养学报, 2015, 27(4):1302-1309. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2015.04.037 . |
| JIAN P, WANG Q, WANG J, et al. Difference analysis of gut microbiome of Rhinopithecus roxellana in different ages[J]. Chin J Anim Nutr, 2015, 27(4):1302-1309. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2015.04.037 . | |
| 30 | KIMBLE R, GOUINGUENET P, ASHOR A, et al. Effects of a mediterranean diet on the gut microbiota and microbial metabolites: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials and observational studies[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2022:1-22. DOI: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2057416 . |
| 31 | 王保宁, 陈昱作, 贡嘎, 等. 不同海拔区域内牦牛肠道菌群结构组成多样性研究[J]. 四川大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 58(5):152-158. DOI:10.19907/j.0490-6756.2021.056003 . |
| WANG B N, CHEN Y Z, GONG G, et al. Study on diversity of structural composition of yaks intestinal flora in different altitudes[J]. J Sichuan Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2021, 58(5):152-158. DOI:10.19907/j.0490-6756.2021.056003 . |
| [1] | Jian GE, Jingfen SUN, Yongjie WU. Taurine Has no Protective Effect on Rat Corneal Endothelial Cells Injured by Benzalkonium Chloride [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 39-43. |
| [2] | Chenyin REN, Siqi GAO, Hao LI, Biao TANG, Hua YANG, Yuehuan LIU. In Vivo Colonization Test of Two CRISPR-Engineered Escherichiacoli in Mice [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 541-550. |
| [3] | Chang WU, Xiaojie LI, Yinnan WU, Yao WANG, Yuxin WANG, Weifeng ZONG, Changhong MENG, Yihong LU. Application of Isolated Guinea Pig Ileum Method for Detection of Histamine Substances in Osteopeptide Injections [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 159-165. |
| [4] | ZHANG Boyang, CHEN Huanpeng, YU Wenlan, LIU Zhonghua, HUANG Chaofeng. Dynamic Changes of Tumor-infiltrating Immune Cells in Mice with MC38 Colon Cancer [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2021, 41(5): 409-417. |
| [5] | ZUO Ximeng, SHI Xiaoguang, LIU Jieli, YANG Zhenrui, GAO Xiang, LAI Rui, ZHAO Ze, WANG Tangshun. Establishment of a Rat Model of Granulomatous Lobular Mastitis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2021, 41(4): 299-304. |
| [6] | XU Qin, WANG Wei, DONG Xiang, LI Jianying, SHI Wenhui, LIU Xiaolu, LIU Aizhong, MA Na, SONG Laiyang, LIU Jiangwei. Chronic Toxicity Study on Deinococcus Radiodurans R1 in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2021, 41(4): 333-342. |
| [7] | LV Xiaojun, WU Sen, ZHANG Ju, XU Xiaoling, PAN Wangping, LI Hougang, WANG Pinghui, HE Kaiyong. Experimental Study on Establishment of Obesity Model in Rats Induced by High-Calorie Diet [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2020, 40(5): 374-. |
| [8] | HAO Lixia, LU Rong, MA Xiaxia, FAN Shujuan. Effect of Diosmetin on Acute Lung Injury Induced by Meconium and Its Mechanism in Neonatal Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2020, 40(5): 384-. |
| [9] | ZHOU Xiaoli, ZHANG Qian, GAO Zheng, QIAN Zhiyong. Pathological Observation of Spontaneous Tumor in Aged SD Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2020, 40(5): 420-. |
| [10] | YING Yong, XIA Yujie, TANG Liansheng, JIA Chanyuan, ZHANG Haijing, HU Jianting. Pathologic Change of Spontaneous Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the Ileum in a Sprague-Dawley Rat#br# [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2020, 40(3): 223-. |
| [11] | SUN Xia, LIU Xiang-mei, PANG Zeng-xiong, LIU Dong-hong, XU Ying-yu, JIANG Yi, LI Min, QIU Zhi-feng, HUANG Yu-feng. Phototoxic Effects of Ultraviolet Irradiation with Different Time Course on Skin of SD Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2019, 39(2): 124-130. |
| [12] | XU Qin, DONG Xiang, LI Jian-ying, ZHANG Dong-hui, LI Jia-jia, YANG Ya-ping, YANG Qiu-yue, SHI Wen-hui, MA Na, SONG Lai-yang, LIU Jiang-wei. The Effect of Curcumin Pretreatment on Flora Expression of Ileum and Colon Contents in Heatstroke Rats with Simulated Desert Environment [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2018, 38(6): 440-445. |
| [13] | ZHANG Wei, TANG Bin, LI Fu-rong, ZHAO Yong. Preliminary Observation on Micro-electrolyzed Water as Drinking Water in SPF Animals [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2018, 38(5): 394-398. |
| [14] | QIU Bo, WANG Yan, HU Jian-ting. Case Report on Pathomorphological Changes of Kidney in Spontaneous Nephroblastoma Occurring in SD Rat [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2018, 38(4): 314-317. |
| [15] | LIU Cheng-xiu, LI Na, TONG Pin-fen, WANG Wen-guang, LU Cai-xia, HAN Yuan-yuan, KUANG De-xuan, SUN Xiao-mei, DAI Jie-jie. Analysis of Microsatellite Genetic Characteristics in of Closed Colony of Tree Shrews [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2018, 38(1): 1-9. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||