
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 416-422.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.066
• Animal Models of Human Diseases • Previous Articles Next Articles
Bingxin XU1( )(
)( ), Kaijian FAN1,2, Tingyu WANG1, Huijin CHEN1(
), Kaijian FAN1,2, Tingyu WANG1, Huijin CHEN1( )(
)( )
)
Received:2022-05-16
Revised:2022-07-27
Online:2022-10-25
Published:2022-11-04
Contact:
Huijin CHEN
CLC Number:
Bingxin XU, Kaijian FAN, Tingyu WANG, Huijin CHEN. Effect of Dexamethasone on Cartilage Degeneration in Rats with Collagen-induced Arthritis[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 416-422.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.066
| 基因Gene | 上游引物序列Forward primer | 下游引物序列Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| MMP-9 | 5'-ATCCCTCTATGGACCTCCCAC-3' | 5'-AACAAGACTTCTCCCCGCAG-3' |
| MMP-13 | 5'-ACCCAGCCCTATCCCTTGAT-3' | 5'-TCTCGGGATGGATGCTCGTA-3' |
| ADAMTS-4 | 5'-CATCCTACGCCGGAAGAGTC-3' | 5'-AAGCGAAGCGCTTGTTTCTG-3' |
| ADAMTS-5 | 5'-GCCCACCTAACGGCAAATCT-3' | 5'-AGGACACCTGCGTATTTGGG-3' |
Table 1 Primer sequences for real-time quantitative PCR
| 基因Gene | 上游引物序列Forward primer | 下游引物序列Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| MMP-9 | 5'-ATCCCTCTATGGACCTCCCAC-3' | 5'-AACAAGACTTCTCCCCGCAG-3' |
| MMP-13 | 5'-ACCCAGCCCTATCCCTTGAT-3' | 5'-TCTCGGGATGGATGCTCGTA-3' |
| ADAMTS-4 | 5'-CATCCTACGCCGGAAGAGTC-3' | 5'-AAGCGAAGCGCTTGTTTCTG-3' |
| ADAMTS-5 | 5'-GCCCACCTAACGGCAAATCT-3' | 5'-AGGACACCTGCGTATTTGGG-3' |
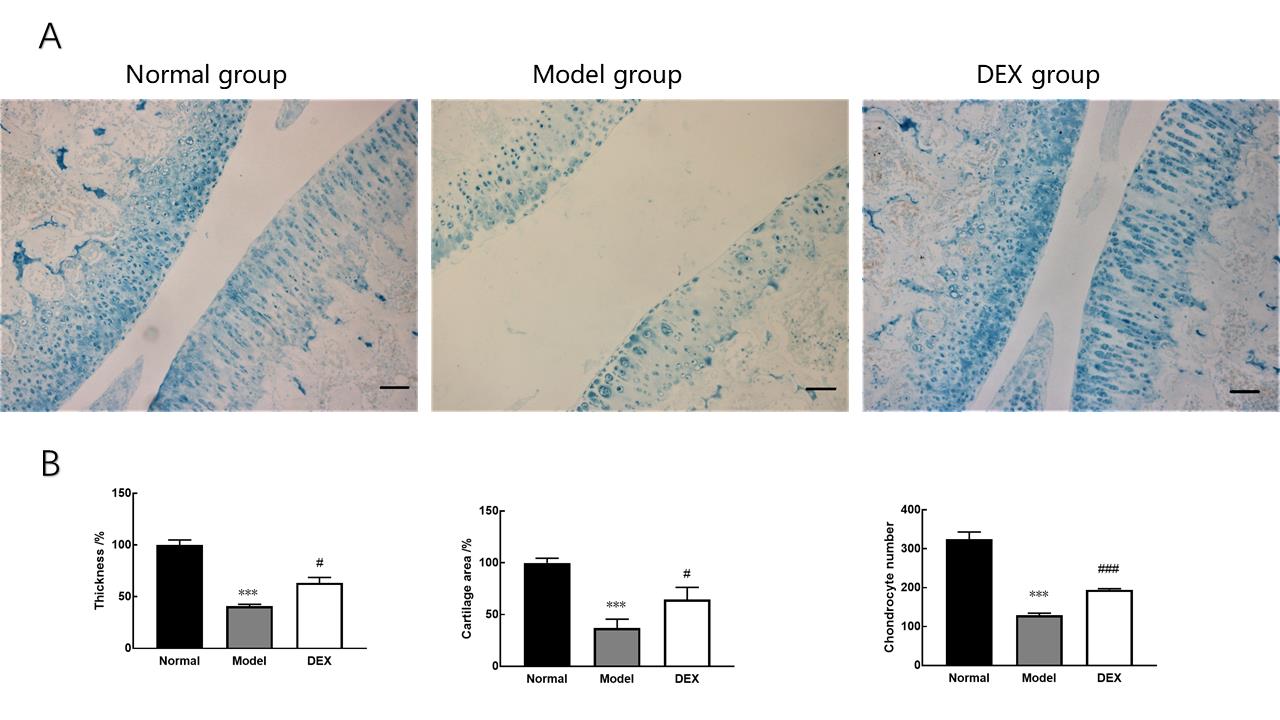
Figure 1 Inhibitory effect of dexamethasone on degeneration of knee articular cartilage in collagen-induced arthritis ratsNote: A, Alcian blue staining of knee joints of the three groups of rats; the scale bar is 100 μm and magnification is ×100. B, (left to right) Charts of cartilage thickness, cartilage area, and number of cartilage cells in each group. DEX, dexamethasone treatment group. Data are expressed as mean±SEM with 10 rats per group. Compared with the normal group, ***P<0.001; Compared with the model group, #P<0.05, ###P<0.001.
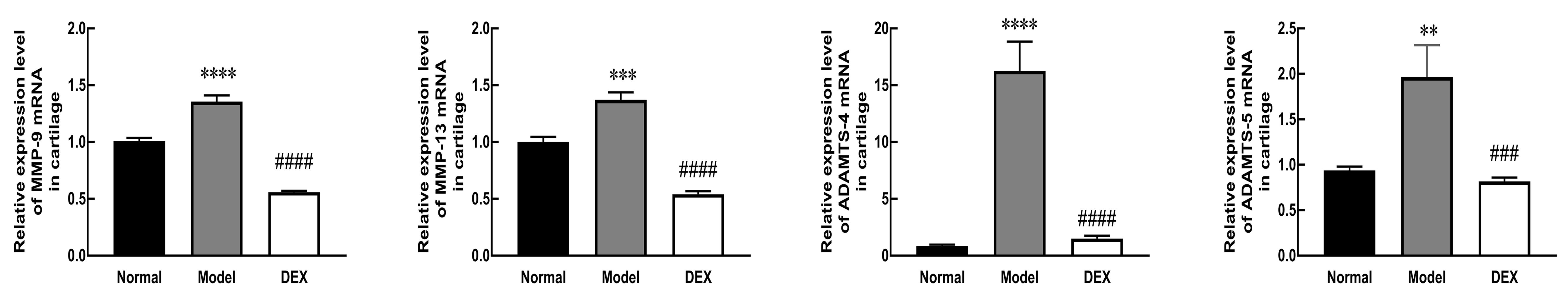
Figure 2 Inhibitory effect of dexamethasone on matrix metalloproteinases transcription in the knee cartilage tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats detected by real-time quantitative PCRNote: MMP-9 and MMP-13, matrix metalloproteinases-9 and -13; ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5, a disintegrin-like and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs-4 and -5. DEX, dexamethasone treatment group. Data are expressed as mean±SEM with 10 rats per group. Compared with the normal group, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.000 1; Compared with the model group, ###P<0.001, ####P<0.000 1.
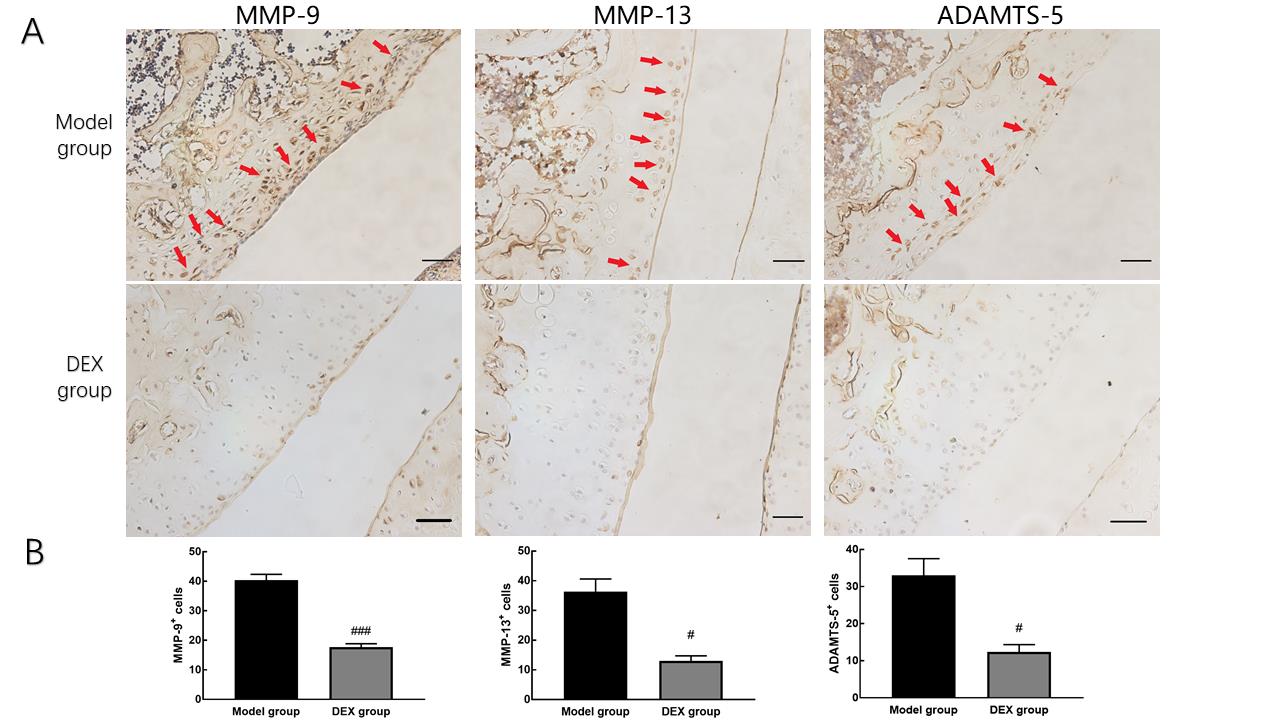
Figure 3 Inhibitory effect of dexamethasone on MMP-9, MMP-13 and ADAMTS-5 expression in the knee cartilage of collagen-induced arthritis rats detected by immunohistochemistryNote:A shows immunohistochemical results (DAB staining; the scale bar is 50 μm and magnification is ×400). Red arrows indicate matrix metalloproteinases-9 (MMP-9), matrix metalloproteinases-9 (MMP-13), and a disintegrin-like and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs--5 (ADAMTS-5) positive chondrocytes, respectively. B shows semi-quantitative results of MMP-9, MMP-13, and ADAMTS-5. Data are expressed as mean±SEM with 10 rats per group. Compared with the model group, #P<0.05, ###P<0.001.
| 1 | DEANE K D, DEMORUELLE M K, KELMENSON L B, et al. Genetic and environmental risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol, 2017, 31(1):3-18. DOI:10.1016/j.berh.2017.08.003 . |
| 2 | HARRE U, SCHETT G. Cellular and molecular pathways of structural damage in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Semin Immunopathol, 2017, 39(4):355-363. DOI:10.1007/s00281-017-0634-0 . |
| 3 | SHI W J, TJOUMAKARIS F P, LENDNER M, et al. Biologic injections for osteoarthritis and articular cartilage damage: can we modify disease? [J]. Physician Sportsmed, 2017, 45(3):203-223. DOI:10.1080/00913847.2017.1357421 . |
| 4 | BISHNOI M, JAIN A, HURKAT P, et al. Chondroitin sulphate: a focus on osteoarthritis[J]. Glycoconj J, 2016, 33(5):693-705. DOI:10.1007/s10719-016-9665-3 . |
| 5 | LORSCHEIDER M, TSAPIS N, UR-REHMAN M, et al. Dexamethasone palmitate nanoparticles: an efficient treatment for rheumatoid arthritis[J]. J Control Release, 2019, 296:179-189. DOI:10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.01.015 . |
| 6 | FORMICA F A, BARRETO G, ZENOBI-WONG M. Cartilage-targeting dexamethasone prodrugs increase the efficacy of dexamethasone[J]. J Control Release, 2019, 295:118-129. DOI:10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.12.025 . |
| 7 | JENSEN T W, HANSEN M S, HØRSLEV-PETERSEN K, et al. Periarticular and generalised bone loss in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: influence of alendronate and intra-articular glucocorticoid treatment. Post hoc analyses from the CIMESTRA trial[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2014, 73(6):1123-1129. DOI:10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-203171 . |
| 8 | 许冰馨, 王琪珊, 李钦, 等. 地塞米松对CIA大鼠DRG中炎症因子的抑制和关节疼痛的改善作用[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2020, 36(12):1691-1696. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2020.12.012 . |
| XU B X, WANG Q S, LI Q, et al. Dexamethasone inhibits inflammatory factors in DRG and improves joint pain of CIA rats[J]. Chin Pharmacol Bull, 2020, 36(12):1691-1696. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2020.12.012 . | |
| 9 | 许冰馨, 王琪珊, 范凯健, 等. 地塞米松改善胶原性关节炎大鼠免疫功能与其血药浓度的相关性研究[J]. 实用药物与临床, 2021, 24(3):198-203. DOI:10.14053/j.cnki.ppcr.202103002 . |
| XU B X, WANG Q S, FAN K J, et al. Correlation between dexamethasone's improving immune function and blood concentration in rats with collagen-induced arthritis[J]. Pract Pharm Clin Remedies, 2021, 24(3):198-203. DOI:10.14053/j.cnki.ppcr.202103002 . | |
| 10 | WU J, FAN K J, WANG Q S, et al. DMY protects the knee joints of rats with collagen-induced arthritis by inhibition of NF-1B signaling and osteoclastic bone resorption[J]. Food Funct, 2020, 11(7):6251-6264. DOI:10.1039/D0FO00396D . |
| 11 | FAN K J, WU J, WANG Q S, et al. Metformin inhibits inflammation and bone destruction in collagen- induced arthritis in rats[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2020, 8(23):1565. DOI:10.21037/atm-20-3042 . |
| 12 | 曾光, 陈芳, 熊新贵, 等. 熊果酸对CIA大鼠关节炎症及骨质破坏的影响[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报, 2013, 33(7):3-7. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-070X.2013.07.001.003.05 . |
| ZENG G, CHEN F, XIONG X G, et al. Effects of ursolic acid on arthritis and bone destruction in collagen-induced CIA rats[J]. J Tradit Chin Med Univ Hunan, 2013, 33(7):3-7. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-070X.2013.07.001.003.05 . | |
| 13 | 王琪珊, 范凯健, 许冰馨, 等. DLTH通过调节免疫功能和软骨降解从而抑制RA的作用[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2021, 37(5):624-630. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2021.05.007 |
| WANG Q S, FAN K J, XU B X, et al. Study of DLTH inhibiting RA by regulating immune function and cartilage degradation[J]. Chin Pharmacol Bull, 2021, 37(5):624-630. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2021.05.007 | |
| 14 | YANG C Y, CHANALARIS A, TROEBERG L. ADAMTS and ADAM metalloproteinases in osteoarthritis - looking beyond the 'usual suspects'[J]. Osteoarthr Cartil, 2017, 25(7):1000-1009. DOI:10.1016/j.joca.2017.02.791 . |
| 15 | MALEMUD C J. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in health and disease: an overview[J]. Front Biosci, 2006, 11:1696-1701. DOI:10.2741/1915 . |
| 16 | KOVÁCS B, VAJDA E, NAGY E E. Regulatory effects and interactions of the Wnt and OPG-RANKL-RANK signaling at the bone-cartilage interface in osteoarthritis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(18):4653. DOI:10.3390/ijms20184653 . |
| 17 | BURRAGE P S, MIX K S, BRINCKERHOFF C E. Matrix metalloproteinases: role in arthritis[J]. Front Biosci, 2006, 11:529-543. DOI:10.2741/1817 . |
| 18 | ZHANG J F, WANG G L, ZHOU Z J, et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases, and interleukins in vertebral cartilage endplate[J]. Orthop Surg, 2018, 10(4):306-311. DOI:10.1111/os.12409 . |
| 19 | 冀全博, 张强, 王岩. 带有血小板凝血酶敏感蛋白结构域的解聚素与金属蛋白酶4、5在骨关节炎中作用的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2013, 27(9): 1080-1084. DOI: 10.7507/1002-1892.20130236 . |
| JI Q B, ZHANG Q, WANG Y. Research progress of a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motif 4 and 5 in osteoarthritis[J]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2013, 27(9):1080-1084. DOI: 10.7507/1002-1892.20130236 . | |
| 20 | MALFAIT A M, TORTORELLA M D. The elusive DMOAD: Aggrecanase inhibition from laboratory to clinic[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2019, 37 Suppl 120(5):130-134. |
| 21 | MIYOSHI M, LIU S. Collagen-induced arthritis models[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2018, 1868:3-7. DOI:10.1007/978-1-4939-8802-0_1 . |
| 22 | WANG Q S, XU B X, FAN K J, et al. Inflammation suppression by dexamethasone via inhibition of CD147-mediated NF-κB pathway in collagen-induced arthritis rats[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2020, 473(1):63-76. DOI:10.1007/s11010-020-03808-5 . |
| [1] | Ruolin CUI, Qing WANG, Ling YANG, Wenchang FENG, Zhiwei LIU, Weiran TENG, Bitao MA, Leyang WANG, Liping QIN, Lilun JIN. Repair Effects of Xiaoyusan New Formula on Cartilage Injury and MMP-13 Expression in Knee Osteoarthritis Model Rabbits [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 30-38. |
| [2] | WEI Jie, ZUO Qin, WANG Hong, LI Huan, ZHOU Jiaqi, GUANG Jiaona, FAN Tao, LIU Zuomin, FU Rui, YUE Bingfei. Population Genetic Quality Analysis of Microsatellite DNA in Wistar Rats Based on T/CALAS 21—2017 [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 528-534. |
| [3] | LV Xiaojun, WU Sen, ZHANG Ju, XU Xiaoling, PAN Wangping, LI Hougang, WANG Pinghui, HE Kaiyong. Experimental Study on Establishment of Obesity Model in Rats Induced by High-Calorie Diet [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2020, 40(5): 374-. |
| [4] | XIAO Kunlin, ZHANG Rui, Sun Hong, XIAO Kuntai, MA Jianbing. Evaluation of Monoiodoacetic Acid-induced Knee Osteoarthritis SD Rats with Diseasse Progression at Different Time Points [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2020, 40(1): 47-52. |
| [5] | DING Guang-yu, PAN Mian-li, HU Han, LIU Yi, SHEN Long-hai. Comparative Study on Iron Deficiency Anemia Rats Model by Three Different Formula Feeds [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2016, 36(6): 433-436. |
| [6] | FENG Yan-qin, AO Ji-bo, YANG Min, CHEN Jian-ming, CHEN De-sen. Experimental Study on Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Rabbits by Injection of Deer Melon Polypeptide [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2016, 36(3): 204-207. |
| [7] | XIAO Cheng-rong, TAN Hong-ling, MA Zeng-chun, WANG Yu-guang, WANG De-wen, SUN Jing-xiang, GAO Yue. Spontaneous Tumorigenesis, Hematological and Serum Biochemical Parameters of Senile Wistar Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2014, 34(4): 324-329. |
| [8] | XIAO Ping, WANG Ning, FAN Yu-lan, DONG Miao-zhu, HONG Xing-yu, ZHONG Wei-jian. Effect of Glucosamine and Chondroitin Sulfate on Histopathological, Histochemical Features and Glycosaminoglycan Content of Articular Cartilage in Guinea Pigs [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2011, 31(3): 193-197. |
| [9] | LI Hai-yan,LI Jia-min,LI Jing-xiao,WANG Xin-xing,DAI Jie-jie,SUN Xiao-mei. Insulin-Resistance Tree Shrew Model Induced by High-glucose-fat-diet with Dexamethasone [J]. , 2010, 30(3): 197-200. |
| [10] | LIU Na-xin1,LIU Cun-li2,CHEN Zhou-Xun1,SHI Hong-Qi1. Influence of Dexamethasone on Blood TNF-α,IL-10,GR in Rats Models of Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis [J]. , 2008, 28(4): 230-233. |
| [11] | XIA Chun-mei, DING Shuang-shuang,ZHANG Zhou. Establishment of Diabetic Nephropathy Model in Rat [J]. , 2002, 22(2): 78-82. |
| [12] | CUI Shi-Tao, ZHU Hong-Sheng. Mechanism of Protective Effect of Dexamethasone on Myocardial Reperfusion Injury in Isolated Working Rat Heart [J]. , 1998, 18(2): 69-72. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||