













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 663-675.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.147
收稿日期:2025-09-05
修回日期:2025-12-03
出版日期:2025-12-25
发布日期:2025-12-19
通讯作者:
汪菲(1986—),女,博士,研究员,研究方向:果蝇本能行为的神经环路机制。E-mail: wangfei@ion.ac.cn。ORCID: 0000-0008-8646-2411作者简介:邓贤铭(2000—),男,博士研究生,研究方向:果蝇听觉信息编码与处理。E-mail: dengxm2022@ion.ac.cn。ORCD: 0009-0000-2402-3408
基金资助:Received:2025-09-05
Revised:2025-12-03
Published:2025-12-25
Online:2025-12-19
Contact:
WANG Fei (ORCID: 0000-0008-8646-2411), E-mail: wangfei@ion.ac.cn摘要:
近年来,黑腹果蝇(Drosophila melanogaster)的电子显微镜连接组研究取得重大突破,提供了全脑尺度下突触分辨率的神经环路图谱。本文综述果蝇电子显微镜连接组数据库从脑区局部重建到全脑完整绘制的发展历程,重点总结其在解析神经环路研究领域三大核心问题中发挥的作用:在感觉信息编码方面,以视觉系统为例揭示运动检测与颜色处理的机制;在行为决策方面,阐明雌蝇交配与产卵抉择的环路基础;在运动控制方面,解析雄蝇求偶歌曲模式生成的神经机制。这些成果揭示了结构连接与功能特化的关系和信息分级整合与并行-层级控制的机制,在极大程度上深化了对神经环路“结构-功能”关系的理解。文末展望电子显微镜连接组在跨物种比较、全脑动态网络建模及计算-实验融合等方向运用的潜力,这些探索有助于推动神经科学从局部推测转向全脑精准解析的范式革新,为复杂生物连接组研究提供技术模板与理论锚点,搭建基础神经环路与人类神经疾病的研究桥梁,并为类脑智能计算提供生物原型,为探索神经系统的进化规律和工作机制提供重要启示。
中图分类号:
邓贤铭,汪菲. 果蝇电子显微镜连接组数据库及相关神经环路功能解析的研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(6): 663-675. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.147.
DENG Xianming,WANG Fei. Research Progress on Drosophila Electron Microscopy Connectome Database and Functional Analysis of Related Neural Circuits[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 663-675. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.147.
数据库 Databases | 访问网页 Web accesses | 注释情况 Annotation notes | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|
一龄幼虫中枢神经系统电子显微镜连接组 (L1 CNS) L1 larval central nervous system (CNS) electron microscopy connectome | https://l1em.catmaid.virtualflybrain.org | 人工追踪所有神经元,共3 016个神经元 | [ |
成年雌蝇全脑电子显微镜连接组 (FAFB) Female full adult fly brain electron microscopy connectome | https://fafb.catmaid.virtualflybrain.org | 稀疏注释数据库 | [ |
FAFB的FlyWire完整注释版 FlyWire fully-annotated version of FAFB | https://codex.flywire.ai/ dataset=fafb | 密集注释数据库,共139 255个神经元 | [ |
成年雌蝇半脑电子显微镜连接组 (Hemibrain) Female adult fly hemibrain electron microscopy connectome | https://neuprint.janelia.org | 密集注释数据库,共约25 000个神经元 | [ |
成年雌蝇腹神经索电子显微镜连接组 (FANC) Female adult fly nerve cord electron microscopy connectome | https://fanc.catmaid.virtualflybrain.org | 密集注释数据库,共约14 600个神经元 | [ |
成年雄蝇腹神经索电子显微镜连接组 (MANC) Male adult fly nerve cord electron microscopy connectome | https://neuprint.janelia.org https://codex.flywire.ai/ dataset=manc | 密集注释数据库,共约23 000个神经元 | [ |
成年雌蝇脑及神经索电子显微镜连接组 (BANC) Female adult fly brain and nerve cord electron microscopy connectome | https://codex.flywire.ai/ dataset=banc | 密集注释数据库,共约115 151个神经元 | [ |
成年雄蝇中枢神经系统电子显微镜连接组 (maleCNS) Male adult fly CNS electron microscopy connectome | https://male-cns.janelia.org https://neuprint.janelia.org | 密集注释数据库,共约166 000个神经元 | [ |
表1 黑腹果蝇电子显微镜连接组数据库的资源信息
Table 1 Resource information of Drosophila melanogaster electron microscopy connectome database
数据库 Databases | 访问网页 Web accesses | 注释情况 Annotation notes | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|
一龄幼虫中枢神经系统电子显微镜连接组 (L1 CNS) L1 larval central nervous system (CNS) electron microscopy connectome | https://l1em.catmaid.virtualflybrain.org | 人工追踪所有神经元,共3 016个神经元 | [ |
成年雌蝇全脑电子显微镜连接组 (FAFB) Female full adult fly brain electron microscopy connectome | https://fafb.catmaid.virtualflybrain.org | 稀疏注释数据库 | [ |
FAFB的FlyWire完整注释版 FlyWire fully-annotated version of FAFB | https://codex.flywire.ai/ dataset=fafb | 密集注释数据库,共139 255个神经元 | [ |
成年雌蝇半脑电子显微镜连接组 (Hemibrain) Female adult fly hemibrain electron microscopy connectome | https://neuprint.janelia.org | 密集注释数据库,共约25 000个神经元 | [ |
成年雌蝇腹神经索电子显微镜连接组 (FANC) Female adult fly nerve cord electron microscopy connectome | https://fanc.catmaid.virtualflybrain.org | 密集注释数据库,共约14 600个神经元 | [ |
成年雄蝇腹神经索电子显微镜连接组 (MANC) Male adult fly nerve cord electron microscopy connectome | https://neuprint.janelia.org https://codex.flywire.ai/ dataset=manc | 密集注释数据库,共约23 000个神经元 | [ |
成年雌蝇脑及神经索电子显微镜连接组 (BANC) Female adult fly brain and nerve cord electron microscopy connectome | https://codex.flywire.ai/ dataset=banc | 密集注释数据库,共约115 151个神经元 | [ |
成年雄蝇中枢神经系统电子显微镜连接组 (maleCNS) Male adult fly CNS electron microscopy connectome | https://male-cns.janelia.org https://neuprint.janelia.org | 密集注释数据库,共约166 000个神经元 | [ |
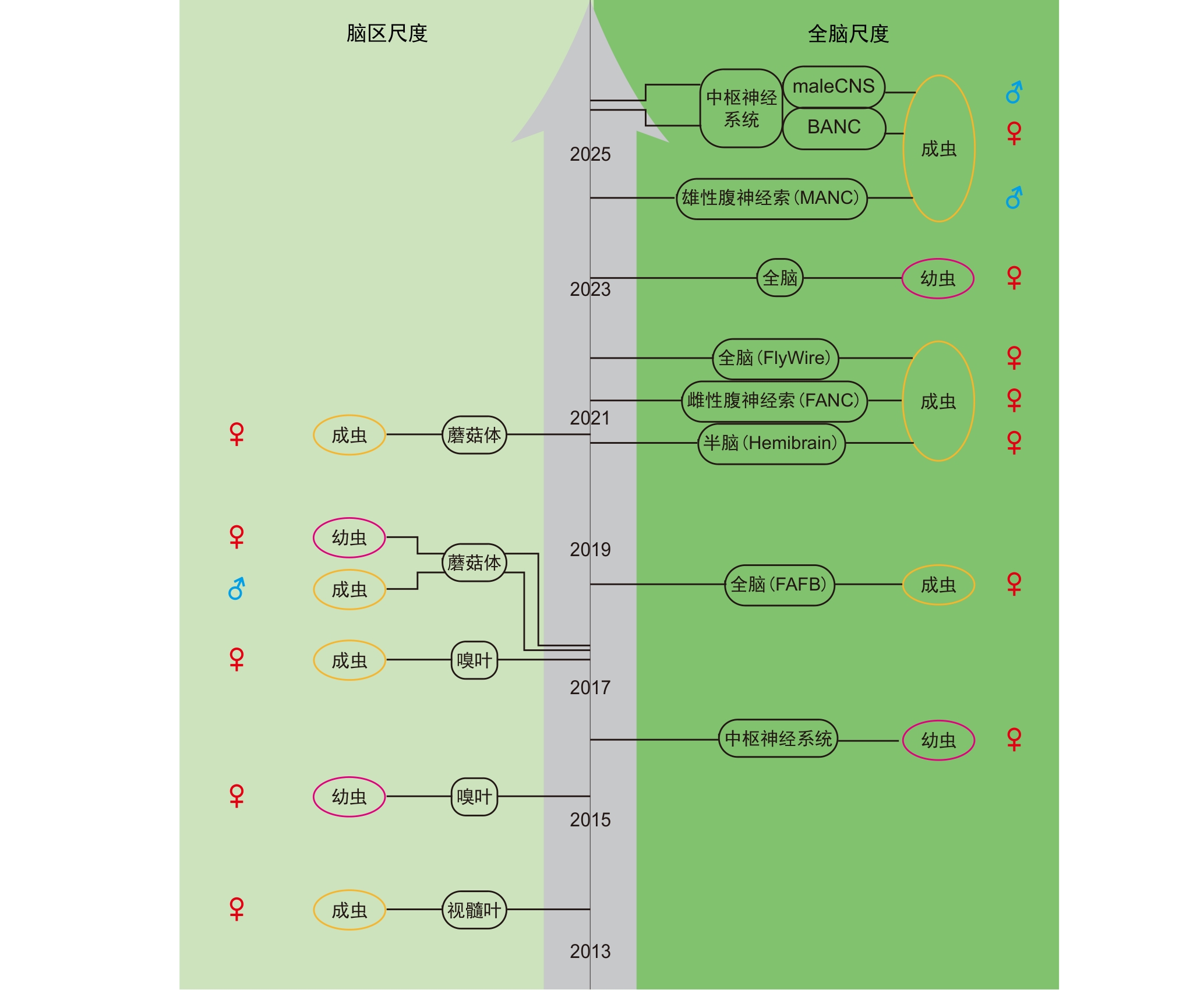
图1 黑腹果蝇电子显微镜连接组数据库的发展历程注:黑色圆框标识的是脑区尺度下(左边)和全脑尺度下(右边)黑腹果蝇的各电子显微镜连接组数据库。FAFB,成年雌蝇全脑电子显微镜连接组;Hemibrain,成年雌蝇半脑电子显微镜连接组;FANC,成年雌蝇腹神经索电子显微镜连接组;MANC,成年雄蝇腹神经索电子显微镜连接组;BANC,成年雌蝇脑及神经索电子显微镜连接组;maleCNS,成年雄蝇中枢神经系统电子显微镜连接组。
Figure 1 Development history of Drosophila melanogaster electron microscopy connectome databaseNote: Black circular frames indicate various electron microscopy connectome datasets of Drosophila melanogaster at the brain region scale (left) and the whole brain scale (right). FAFB, female full adult fly brain electron microscopy connectome; Hemibrain, female adult fly hemibrain electron microscopy connectome; FANC, female adult fly nerve cord electron microscopy connectome; MANC, male adult fly nerve cord electron microscopy connectome; BANC, female adult fly brain and nerve cord electron microscopy connectome; maleCNS, male adult fly CNS electron microscopy connectome.
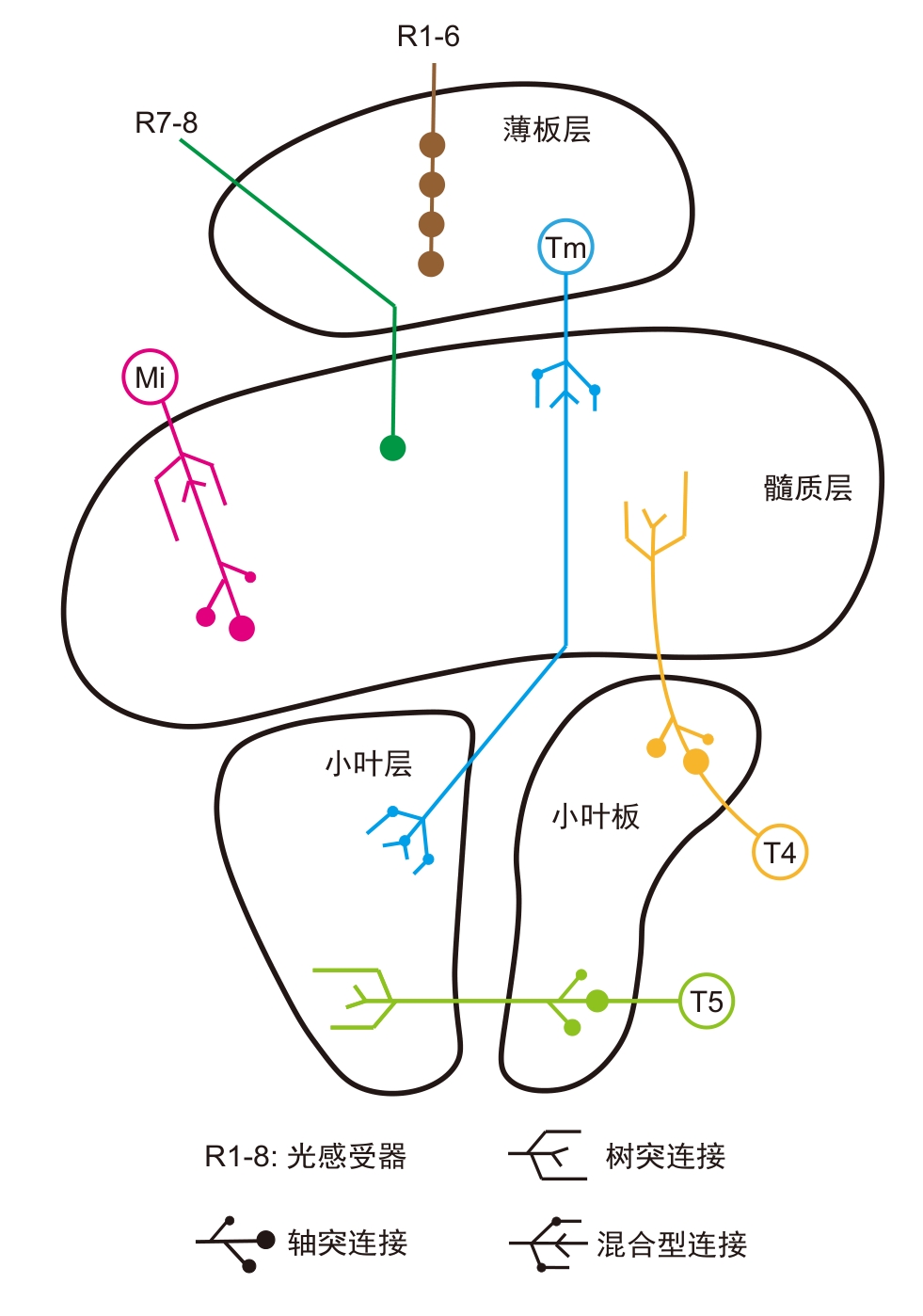
图2 果蝇视叶结构及运动检测、颜色感知相关的视觉神经元类型(改自文献[55])
Figure 2 Structure of Drosophila melanogaster optic lobe and types of visual neurons related to motion detection and color perception (adapted from reference [55])
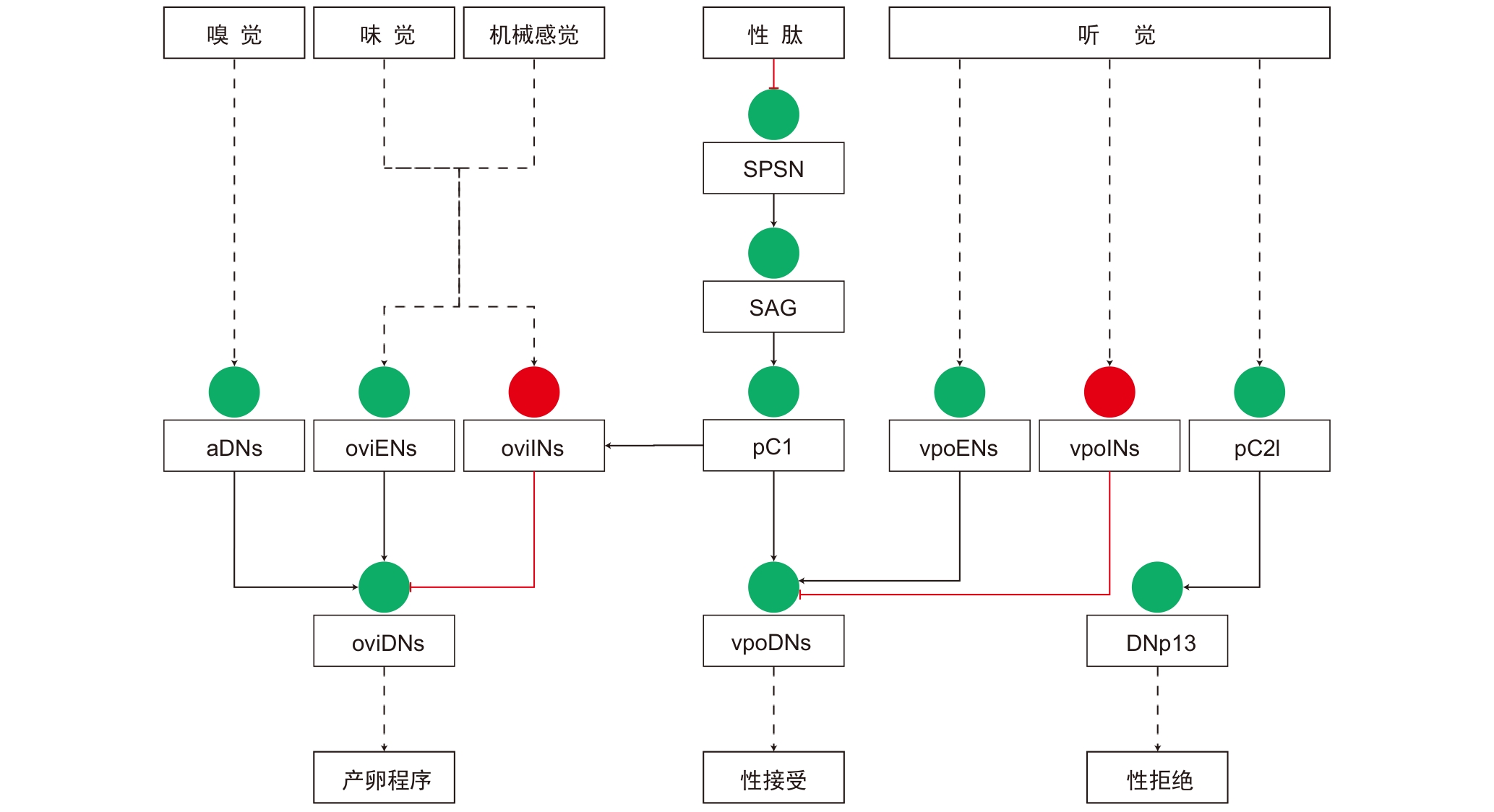
图3 雌性果蝇交配、产卵决策的神经环路注:实线表示单级突触连接,虚线表示跨多级的突触连接。红色圆圈、红色线条分别表示抑制性神经元和连接。绿色圆圈、黑色线条分别表示兴奋性神经元和连接。SPSN,性肽感觉神经元;SAG,性肽腹神经节神经元;pC1,pC1中间神经元;pC2l,pC2l中间神经元;aDNs,前背神经元;oviENs,产卵兴奋性神经元;oviINs,产卵抑制性神经元;oviDNs,产卵下行神经元;vpoENs,阴道板展开兴奋性神经元;vpoINs,阴道板展开抑制性神经元;vpoDNs,阴道板展开下行神经元;DNp13,大脑后表面的下行神经元13。
Figure 3 Neural circuits of mating and egg-laying decisions in female DrosophilaNote: Solid lines indicate monosynaptic connections, while dashed lines indicate polysynaptic connections. Red circles and red lines represent inhibitory neurons and connections, respectively. Green circles and black lines represent excitatory neurons and connections, respectively. SPSN, sex peptide sensory neuron; SAG, sex peptide abdominal ganglion neuron; pC1, pC1 interneurons; pC2l, pC2l interneurons; aDNs, anterior dorsal neurons; oviENs, oviposition excitatory neurons; oviINs, oviposition inhibitory neurons; oviDNs, oviposition descending neurons; vpoENs, vaginal plate opening excitatory neurons; vpoINs, vaginal plate opening inhibitory neurons; vpoDNs, vaginal plate opening descending neurons; DNp13, descending neurons 13 on the posterior surface of the brain.
| [1] | SCHLEGEL P, YIN Y J, BATES A S, et al. Whole-brain annotation and multi-connectome cell typing of Drosophila [J]. Nature, 2024, 634(8032):139-152. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07686-5 . |
| [2] | ASINOF S K, CARD G M. Neural control of naturalistic behavior choices[J]. Annu Rev Neurosci, 2024, 47(1): 369-388. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-111020-094019 . |
| [3] | PAREKH R, ASCOLI G A. Neuronal morphology goes digital: a research hub for cellular and system neuroscience[J]. Neuron, 2013, 77(6):1017-1038. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013. 03.008 . |
| [4] | FEINBERG E H, VANHOVEN M K, BENDESKY A, et al. GFP Reconstitution Across Synaptic Partners (GRASP) defines cell contacts and synapses in living nervous systems[J]. Neuron, 2008, 57(3):353-363. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007. 11.030 . |
| [5] | LILLVIS J L, OTSUNA H, DING X Y, et al. Rapid reconstruction of neural circuits using tissue expansion and light sheet microscopy[J]. eLife, 2022, 11: e81248. DOI: 10.7554/eLife. 81248 . |
| [6] | LICHTMAN J W, SANES J R. Ome sweet ome: what can the genome tell us about the connectome?[J]. Curr Opin Neurobiol, 2008, 18(3): 346-353. DOI: 10.1016/j.conb. 2008. 08.010 . |
| [7] | SCHNEIDER-MIZELL C M, GERHARD S, LONGAIR M, et al. Quantitative neuroanatomy for connectomics in Drosophila [J]. eLife, 2016, 5: e12059. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.12059 . |
| [8] | CARDONA A, SAALFELD S, PREIBISCH S, et al. An integrated micro- and macroarchitectural analysis of the Drosophila brain by computer-assisted serial section electron microscopy[J]. PLoS Biol, 2010, 8(10): e1000502. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000502 . |
| [9] | LEE T J, KUMAR A, BALWANI A H, et al. Large-scale neuroanatomy using LASSO: loop-based automated serial sectioning operation[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(10): e0206172. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206172 . |
| [10] | SULOWAY C, PULOKAS J, FELLMANN D, et al. Automated molecular microscopy: the new Leginon system[J]. J Struct Biol, 2005, 151(1):41-60. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsb.2005.03.010 . |
| [11] | LU Z Y, XU C S, HAYWORTH K J, et al. En bloc preparation of Drosophila brains enables high-throughput FIB-SEM connectomics[J]. Front Neural Circuits, 2022, 16:917251. DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2022.917251 . |
| [12] | PLAZA S M, CLEMENTS J, DOLAFI T, et al. neuPrint: an open access tool for EM connectomics[J]. Front Neuroinform, 2022, 16:896292. DOI: 10.3389/fninf.2022.896292 . |
| [13] | DORKENWALD S, MCKELLAR C E, MACRINA T, et al. FlyWire: online community for whole-brain connectomics[J]. Nat Methods, 2022, 19(1):119-128. DOI: 10.1038/s41592-021-01330-0 . |
| [14] | DORKENWALD S, SCHNEIDER-MIZELL C M, BRITTAIN D, et al. CAVE: connectome annotation versioning engine[J]. Nat Methods, 2025, 22(5):1112-1120. DOI: 10.1038/s41592-024-02426-z . |
| [15] | CARDONA A, SAALFELD S, SCHINDELIN J, et al. TrakEM2 software for neural circuit reconstruction[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(6): e38011. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038011 . |
| [16] | BATES A S, MANTON J D, JAGANNATHAN S R, et al. The natverse, a versatile toolbox for combining and analysing neuroanatomical data[J]. eLife, 2020, 9: e53350. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.53350 . |
| [17] | SAALFELD S, CARDONA A, HARTENSTEIN V, et al. CATMAID: collaborative annotation toolkit for massive amounts of image data[J]. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(15):1984-1986. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp266 . |
| [18] | ECKSTEIN N, BATES A S, CHAMPION A, et al. Neurotransmitter classification from electron microscopy images at synaptic sites in Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Cell, 2024, 187(10):2574-2594.e23. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.03.016 . |
| [19] | BUHMANN J, SHERIDAN A, MALIN-MAYOR C, et al. Automatic detection of synaptic partners in a whole-brain Drosophila electron microscopy data set[J]. Nat Methods, 2021, 18(7):771-774. DOI: 10.1038/s41592-021-01183-7 . |
| [20] | TAKEMURA S Y, BHARIOKE A, LU Z Y, et al. A visual motion detection circuit suggested by Drosophila connectomics[J]. Nature, 2013, 500(7461):175-181. DOI: 10.1038/nature12450 . |
| [21] | TAKEMURA S Y, XU C S, LU Z Y, et al. Synaptic circuits and their variations within different columns in the visual system of Drosophila [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2015, 112(44):13711-13716. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1509820112 . |
| [22] | OHYAMA T, SCHNEIDER-MIZELL C M, FETTER R D, et al. A multilevel multimodal circuit enhances action selection in Drosophila [J]. Nature, 2015, 520(7549):633-639. DOI: 10.1038/nature14297 . |
| [23] | BERCK M E, KHANDELWAL A, CLAUS L, et al. The wiring diagram of a glomerular olfactory system[J]. eLife, 2016, 5: e14859. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.14859 . |
| [24] | SCHLEGEL P, TEXADA M J, MIROSCHNIKOW A, et al. Synaptic transmission parallels neuromodulation in a central food-intake circuit[J]. eLife, 2016, 5: e16799. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.16799 . |
| [25] | TOBIN W F, WILSON R I, LEE W A. Wiring variations that enable and constrain neural computation in a sensory microcircuit[J]. eLife, 2017, 6: e24838. DOI: 10.7554/eLife. 24838 . |
| [26] | TAKEMURA S Y, ASO Y, HIGE T, et al. A connectome of a learning and memory center in the adult Drosophila brain[J]. eLife, 2017, 6: e26975. DOI: 10.7554/elife.26975 . |
| [27] | EICHLER K, LI F, LITWIN-KUMAR A, et al. The complete connectome of a learning and memory centre in an insect brain[J]. Nature, 2017, 548(7666):175-182. DOI: 10.1038/nature 23455 . |
| [28] | GERHARD S, ANDRADE I, FETTER R D, et al. Conserved neural circuit structure across Drosophila larval development revealed by comparative connectomics[J]. eLife, 2017, 6: e29089. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.29089 . |
| [29] | ZHENG Z H, LAURITZEN J S, PERLMAN E, et al. A complete electron microscopy volume of the brain of adult Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Cell, 2018, 174(3):730-743.e22. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.06.019 . |
| [30] | SCHEFFER L K, XU C S, JANUSZEWSKI M, et al. A connectome and analysis of the adult Drosophila central brain[J]. eLife, 2020, 9: e57443. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.57443 . |
| [31] | MAISAK M S, HAAG J, AMMER G, et al. A directional tuning map of Drosophila elementary motion detectors[J]. Nature, 2013, 500(7461):212-216. DOI: 10.1038/nature12320 . |
| [32] | WINDING M, PEDIGO B D, BARNES C L, et al. The connectome of an insect brain[J]. Science, 2023, 379(6636): eadd9330. DOI: 10.1126/science.add9330 . |
| [33] | LIN A, YANG R Z, DORKENWALD S, et al. Network statistics of the whole-brain connectome of Drosophila [J]. Nature, 2024, 634(8032):153-165. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07968-y . |
| [34] | SEUNG H S. Predicting visual function by interpreting a neuronal wiring diagram[J]. Nature, 2024, 634(8032):113-123. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07953-5 . |
| [35] | SHIU P K, STERNE G R, SPILLER N, et al. A Drosophila computational brain model reveals sensorimotor processing[J]. Nature, 2024, 634(8032):210-219. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07763-9 . |
| [36] | BATES A S, PHELPS J S, KIM M, et al. Distributed control circuits across a brain-and-cord connectome[J]. bioRxiv, 2025. DOI: 10.1101/2025.07.31.667571. DOI: 10.1101/2025.07. 31.667571 . |
| [37] | TASTEKIN I, DE HAAN VICENTE I, BERESFORD R J, et al. From sensory detection to motor action: the comprehensive Drosophila taste-feeding connectome[J]. bioRxiv, 2025. DOI: 10.1101/2025.08.25.671814 . |
| [38] | BERG S, BECKETT I R, COSTA M, et al. Sexual dimorphism in the complete connectome of the Drosophila male central nervous system[J]. bioRxiv, 2025. DOI: 10.1101/2025.10.09. 680999 . |
| [39] | TAKEMURA S Y, HAYWORTH K J, HUANG G B, et al. A connectome of the male Drosophila ventral nerve cord[J]. bioRxiv, 2023. DOI: 10.1101/2023.06.05.543757 . |
| [40] | AZEVEDO A, LESSER E, PHELPS J S, et al. Connectomic reconstruction of a female Drosophila ventral nerve cord[J]. Nature, 2024, 631(8020):360-368. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07389-x . |
| [41] | NERN A, LOESCHE F, TAKEMURA S Y, et al. Connectome-driven neural inventory of a complete visual system[J]. Nature, 2025, 641(8065):1225-1237. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-08746-0 . |
| [42] | FISCHBACH K F, DITTRICH A P M. The optic lobe of Drosophila melanogaster. I. A Golgi analysis of wild-type structure[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 1989, 258(3): 441-475. DOI: 10.1007/BF00218858 . |
| [43] | KIM S, CASSIDY J J, YANG B Y, et al. Hexagonal patterning of the insect compound eye: facet area variation, defects, and disorder[J]. Biophys J, 2016, 111(12):2735-2746. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.11.004 . |
| [44] | SHARKEY C R, BLANCO J, LEIBOWITZ M M, et al. The spectral sensitivity of Drosophila photoreceptors[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 18242. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-74742-1 . |
| [45] | CURRIER T A, PANG M M, CLANDININ T R. Visual processing in the fly, from photoreceptors to behavior[J]. Genetics, 2023, 224(2): iyad064. DOI: 10.1093/genetics/iyad064 . |
| [46] | TAKEMURA S Y, NERN A, CHKLOVSKII D B, et al. The comprehensive connectome of a neural substrate for 'ON' motion detection in Drosophila [J]. eLife, 2017, 6: e24394. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.24394 . |
| [47] | SHINOMIYA K, HUANG G, LU Z Y, et al. Comparisons between the ON- and OFF-edge motion pathways in the Drosophila brain[J]. eLife, 2019, 8: e40025. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.40025 . |
| [48] | SHINOMIYA K, NERN A, MEINERTZHAGEN I A, et al. Neuronal circuits integrating visual motion information in Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Curr Biol, 2022, 32(16):3529-3544.e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.06.061 . |
| [49] | CHRISTENSON M P, SANZ DIEZ A, HEATH S L, et al. Hue selectivity from recurrent circuitry in Drosophila [J]. Nat Neurosci, 2024, 27(6):1137-1147. DOI: 10.1038/s41593-024-01640-4 . |
| [50] | SCHLEGEL P, BATES A S, STÜRNER T, et al. Information flow, cell types and stereotypy in a full olfactory connectome[J]. eLife, 2021, 10: e66018. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.66018 . |
| [51] | ZHENG Z H, LI F, FISHER C, et al. Structured sampling of olfactory input by the fly mushroom body[J]. Curr Biol, 2022, 32(15):3334-3349.e6. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.06.031 . |
| [52] | KIM H, HORIGOME M, ISHIKAWA Y, et al. Wiring patterns from auditory sensory neurons to the escape and song-relay pathways in fruit flies[J]. J Comp Neurol, 2020, 528(12):2068-2098. DOI: 10.1002/cne.24877 . |
| [53] | BAKER C A, MCKELLAR C, PANG R, et al. Neural network organization for courtship-song feature detection in Drosophila [J]. Curr Biol, 2022, 32(15):3317-3333.e7. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.06.019 . |
| [54] | DEUTSCH D, CLEMENS J, THIBERGE S Y, et al. Shared song detector neurons in Drosophila male and female brains drive sex-specific behaviors[J]. Curr Biol, 2019, 29(19):3200-3215.e5. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.08.008 . |
| [55] | MATSLIAH A, YU S C, KRUK K, et al. Neuronal parts list and wiring diagram for a visual system[J]. Nature, 2024, 634(8032):166-180. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07981-1 . |
| [56] | ARANHA M M, VASCONCELOS M L. Deciphering Drosophila female innate behaviors[J]. Curr Opin Neurobiol, 2018, 52:139-148. DOI: 10.1016/j.conb.2018.06.005 . |
| [57] | BUSSELL J J, YAPICI N, ZHANG S X, et al. Abdominal-B neurons control Drosophila virgin female receptivity[J]. Curr Biol, 2014, 24(14): 1584-1595. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.06.011 . |
| [58] | VON PHILIPSBORN A C. Neuroscience: the female art of saying no. Curr Biol, 2020, 30(19): R1080-R1083. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.08.023 . |
| [59] | WANG K Y, WANG F, FORKNALL N, et al. Neural circuit mechanisms of sexual receptivity in Drosophila females[J]. Nature, 2021, 589(7843): 577-581. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2972-7 . |
| [60] | WANG F, WANG K Y, FORKNALL N, et al. Circuit and behavioral mechanisms of sexual rejection by Drosophila females[J]. Curr Biol, 2020, 30(19): 3749-3760.e3. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.07.083 . |
| [61] | STÜRNER T, BROOKS P, SERRATOSA CAPDEVILA L, et al. Comparative connectomics of Drosophila descending and ascending neurons[J]. Nature, 2025, 643(8070): 158-172. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-08925-z . |
| [62] | ZHOU C, PAN Y F, ROBINETT C C, et al. Central brain neurons expressing doublesex regulate female receptivity in Drosophila [J]. Neuron, 2014, 83(1): 149-163. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.05.038 . |
| [63] | KUBLI E. Sex-peptides: seminal peptides of the Drosophila male[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS, 2003, 60(8): 1689-1704. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-003-3052 . |
| [64] | LIU H F, KUBLI E. Sex-peptide is the molecular basis of the sperm effect inDrosophila melanogaster [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2003, 100(17): 9929-9933. DOI: 10.1073/pnas. 1631700100 . |
| [65] | YANG C H, RUMPF S, XIANG Y, et al. Control of the postmating behavioral switch in Drosophila females by internal sensory neurons[J]. Neuron, 2009, 61(4): 519-526. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.12.021 . |
| [66] | YAPICI N, KIM Y J, RIBEIRO C, et al. A receptor that mediates the post-mating switch in Drosophila reproductive behaviour[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7174): 33-37. DOI: 10.1038/nature06483 . |
| [67] | HÄSEMEYER M, YAPICI N, HEBERLEIN U, et al. Sensory neurons in the Drosophila genital tract regulate female reproductive behavior[J]. Neuron, 2009, 61(4): 511-518. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.01.009 . |
| [68] | KUBLI E, BOPP D. Sexual behavior: how sex peptide flips the postmating switch of female flies. Curr Biol, 2012, 22(13): R520-R522. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.04.058 . |
| [69] | CHAPMAN T, BANGHAM J, VINTI G, et al. The sex peptide of Drosophila melanogaster: female post-mating responses analyzed by using RNA interference[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2003, 100(17): 9923-9928. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1631635100 . |
| [70] | FENG K, PALFREYMAN M T, HÄSEMEYER M, et al. Ascending SAG neurons control sexual receptivity of Drosophila females[J]. Neuron, 2014, 83(1): 135-148. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014. 05.017 . |
| [71] | CHIU H, ROBIE A A, BRANSON K, et al. Cell type-specific contributions to a persistent aggressive internal state in female Drosophila [J]. eLife, 2025, 12: RP88598. DOI: 10.7554/elife.88598 . |
| [72] | SCHRETTER C E, ASO Y, ROBIE A A, et al. Cell types and neuronal circuitry underlying female aggression in Drosophila [J]. eLife, 2020, 9: e58942. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.58942 . |
| [73] | DEUTSCH D, PACHECO D, ENCARNACION-RIVERA L, et al. The neural basis for a persistent internal state in Drosophila females[J]. eLife, 2020, 9: e59502. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.59502 . |
| [74] | WANG F, WANG K Y, FORKNALL N, et al. Neural circuitry linking mating and egg laying in Drosophila females[J]. Nature, 2020, 579(7797): 101-105. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2055-9 . |
| [75] | VIJAYAN V, WANG Z, CHANDRA V, et al. An internal expectation guides Drosophila egg-laying decisions[J]. Sci Adv, 2022, 8(43): 19. DOI:10.1126/sciadv.abn3852 . |
| [76] | YANG C H, BELAWAT P, HAFEN E, et al. Drosophila egg-laying site selection as a system to study simple decision-making processes[J]. Science, 2008, 319(5870): 1679-1683. DOI: 10.1126/science.1151842 . |
| [77] | VIJAYAN V, WANG F, WANG K Y, et al. A rise-to-threshold process for a relative-value decision[J]. Nature, 2023, 619(7970): 563-571. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06271-6 . |
| [78] | LOUIS M, DE POLAVIEJA G. Collective behavior: social digging in Drosophila larvae[J]. Curr Biol, 2017, 27(18): R1010-R1012. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.08.023 . |
| [79] | LIN C C, PROKOP-PRIGGE K A, PRETI G, et al. Food odors trigger Drosophila males to deposit a pheromone that guides aggregation and female oviposition decisions[J]. eLife, 2015, 4: e08688. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.08688 . |
| [80] | DUMÉNIL C, WOUD D, PINTO F, et al. Pheromonal cues deposited by mated females convey social information about egg-laying sites in Drosophila melanogaster [J]. J Chem Ecol, 2016, 42(3): 259-269. DOI: 10.1007/s10886-016-0681-3 . |
| [81] | NOJIMA T, RINGS A, ALLEN A M, et al. A sex-specific switch between visual and olfactory inputs underlies adaptive sex differences in behavior[J]. Curr Biol, 2021, 31(6): 1175-1191.e6. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.12.047 . |
| [82] | VON SCHILCHER F. The role of auditory stimuli in the courtship of Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Anim Behav, 1976, 24(1): 18-26. DOI: 10.1016/s0003-3472(76)80095-4 . |
| [83] | VON SCHILCHER F. The function of pulse song and sine song in the courtship of Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Anim Behav, 1976, 24(3): 622-625. DOI: 10.1016/s0003-3472(76)80076-0 . |
| [84] | HINDMARSH STEN T, LI R F, HOLLUNDER F, et al. Male-male interactions shape mate selection in Drosophila [J]. Cell, 2025, 188(6): 1486-1503.e25. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.01.008 . |
| [85] | ROEMSCHIED F A, PACHECO D A, ARAGON M J, et al. Flexible circuit mechanisms for context-dependent song sequencing[J]. Nature, 2023, 622(7984): 794-801. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06632-1 . |
| [86] | VON PHILIPSBORN A C, LIU T X, YU J Y, et al. Neuronal control of Drosophila courtship song[J]. Neuron, 2011, 69(3): 509-522. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.01.011 . |
| [87] | KOHATSU S, KOGANEZAWA M, YAMAMOTO D. Female contact activates male-specific interneurons that trigger stereotypic courtship behavior in Drosophila [J]. Neuron, 2011, 69(3): 498-508. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.12.017 . |
| [88] | CLOWNEY E J, IGUCHI S, BUSSELL J J, et al. Multimodal chemosensory circuits controlling male courtship in Drosophila [J]. Neuron, 2015, 87(5): 1036-1049. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.07.025 . |
| [89] | SHIRANGI T R, STERN D L, TRUMAN J W. Motor control of Drosophila courtship song[J]. Cell Rep, 2013, 5(3): 678-686. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.09.039 . |
| [90] | SHIRANGI T R, WONG A M, TRUMAN J W, et al. Doublesex regulates the connectivity of a neural circuit controlling Drosophila male courtship song[J]. Dev Cell, 2016, 37(6): 533-544. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.05.012 . |
| [91] | O'SULLIVAN A, LINDSAY T, PRUDNIKOVA A, et al. Multifunctional wing motor control of song and flight[J]. Curr Biol, 2018, 28(17): 2705-2717.e4. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.06.038 . |
| [92] | LILLVIS J L, WANG K Y, SHIOZAKI H M, et al. Nested neural circuits generate distinct acoustic signals during Drosophila courtship[J]. Curr Biol, 2024, 34(4): 808-824.e6. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.01.015 . |
| [93] | SHIOZAKI H M, WANG K Y, LILLVIS J L, et al. Activity of nested neural circuits drives different courtship songs in Drosophila [J]. Nat Neurosci, 2024, 27(10): 1954-1965. DOI: 10.1038/s41593-024-01738-9 . |
| [1] | 王晗玥, 陈嘉玮, 高湘滨, 罗威, 刘素宁. 黑腹果蝇心侧体功能的研究概述[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(6): 705-718. |
| [2] | 王明珠, 高英豪, 谭霜霜, 吴薇. UAS-Irk3-EGFP转基因果蝇品系的构建与鉴定[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(6): 656-662. |
| [3] | 陈浩田, 刘竞男. 果蝇在肥胖及相关代谢性疾病研究中的应用与进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(6): 688-704. |
| [4] | 王也, 王露. 黑腹果蝇转座子的特性、调控及其在基因组进化中的作用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(6): 676-687. |
| [5] | 李会萍, 高洪彬, 温金银, 杨锦淳. 疾病动物模型数字化图谱数据库平台的构建与初步应用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 300-308. |
| [6] | 徐龙梅, 沈如凌, 范春, 吴薇. 基于ΦC31整合酶和载体质粒pUASTattB的12株果蝇转基因阴性对照品系的建立[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(5): 541-547. |
| [7] | 唐润东, 宋思远, 吴薇. 饮食中糖分控制对雌黑腹果蝇寿命和中肠干细胞的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2019, 39(2): 118-123. |
| [8] | 乔明, 杨正明, 黄谦, 刘兰英. 穴位贴敷对哮喘大鼠嗜酸粒细胞及肺组织超微结构的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2016, 36(4): 276-279. |
| [9] | 陈颖, 潘华, 周光兴. 六种常用实验动物比较组织学共享数据库的初步建立[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2014, 34(6): 463-466. |
| [10] | 赵文, 张婀娜, 赵强. 水溶性四氧化三铁纳米粒子制备及其在大鼠体内分布[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2014, 34(3): 219-222. |
| [11] | 王晓明, 刘万策, 陈梅丽, 李会萍, 黄韧. 可定制数据项的数据采集系统的设计与实现[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2013, 33(3): 229-233. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

