













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 511-522.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.048
孟雨1,2( ), 梁冬丽2(
), 梁冬丽2( ), 郑琳琳2, 周园园2, 王朝霞2(
), 郑琳琳2, 周园园2, 王朝霞2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-25
修回日期:2024-06-03
出版日期:2024-10-25
发布日期:2024-10-25
通讯作者:
王朝霞(1969—),女,博士,研究员,研究方向:医学实验动物学。E-mail: zhaoxiaw@sjtu.edu.cn作者简介:孟 雨(1999—),女,硕士研究生,研究方向:实验动物。E-mail: mengyu0809@sjtu.edu.cn;
MENG Yu1,2( ), LIANG Dongli2(
), LIANG Dongli2( ), ZHENG Linlin2, ZHOU Yuanyuan2, WANG Zhaoxia2(
), ZHENG Linlin2, ZHOU Yuanyuan2, WANG Zhaoxia2( )
)
Received:2024-03-25
Revised:2024-06-03
Published:2024-10-25
Online:2024-10-25
Contact:
WANG Zhaoxia, E-mail: zhaoxiaw@sjtu.edu.cn摘要:
目的 优化通过注射人肝肿瘤细胞株构建原位癌裸小鼠模型的条件,并探索适宜的给药治疗时间。 方法 选用稳定表达萤光素酶报告基因(LUC)的人肝细胞癌Hep3B与肝母细胞瘤HepG2细胞株,使用小动物活体成像系统分析萤光素酶发光强度与肝肿瘤细胞数量之间的线性相关性,验证人源肝肿瘤细胞的发光效率。在5周龄雌性BALB/c裸小鼠的肝叶原位接种不同浓度(8×106、2.4×107、7.2×107个/mL)、不同重悬介质(PBS、Matrigel)的人肝肿瘤细胞悬液HepG2-LUC和Hep3B-LUC(共12组,每组7只),分别构建人肝肿瘤裸小鼠原位癌模型。每7 d为1个周期记录各组小鼠体重,用小动物活体成像系统定期监测原位肿瘤的生长过程,观察肿瘤生长趋势。接种肿瘤细胞后第35天 剖取小鼠肝脏,制备病理切片,进行苏木精-伊红(hematoxylin and eosin,HE)染色观察组织病理学变化。 结果 两种人肝肿瘤细胞株的发光强度均与细胞数量呈正相关(R2=0.983 1,R2=0.970 5),适宜用于原位癌模型的构建。HepG2-LUC高浓度组,HepG2-LUC+Matrigel低、中、高浓度组,Hep3B-LUC中、高浓度组与Hep3B-LUC+Matrigel低、中、高浓度组均成功造模。HepG2-LUC+Matrigel高浓度组较低浓度与中浓度组小鼠的体重显著下降(P<0.05),Hep3B-LUC+Matrigel高浓度组较低浓度与中浓度组小鼠的体重也显著下降(P<0.05)。成功造模组小鼠的荧光发光强度随时间呈指数型增长(R2>0.950 0),且在移植后14 d发光强度至少可达到1.0×107 p/(s·cm2·sr)。 HepG2-LUC低、中浓度组和Hep3B-LUC低浓度组小鼠肝脏未见明显的病理学变化,其余组肝脏肿瘤和肝细胞病变明显。 结论 对于HepG2-LUC细胞株,推荐肝叶原位注射2.4×107个/mL(50 μL)且与Matrigel重悬的混合细胞液体造模,并于造模后第7天给药或采取预后措施;而对于Hep3B-LUC细胞株,推荐肝叶原位注射7.2×107个/mL(50 μL)(不与Matrigel重悬混合)造模,并于造模后的第14天给药或采取预后措施。
中图分类号:
孟雨,梁冬丽,郑琳琳,等. 人肝肿瘤细胞的裸小鼠原位癌建模条件优化及评价[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(5): 511-522. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.048.
MENG Yu,LIANG Dongli,ZHENG Linlin,et al. Optimization and Evaluation of Conditions for Orthotopic Nude Mouse Models of Human Liver Tumor Cells[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 511-522. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.048.
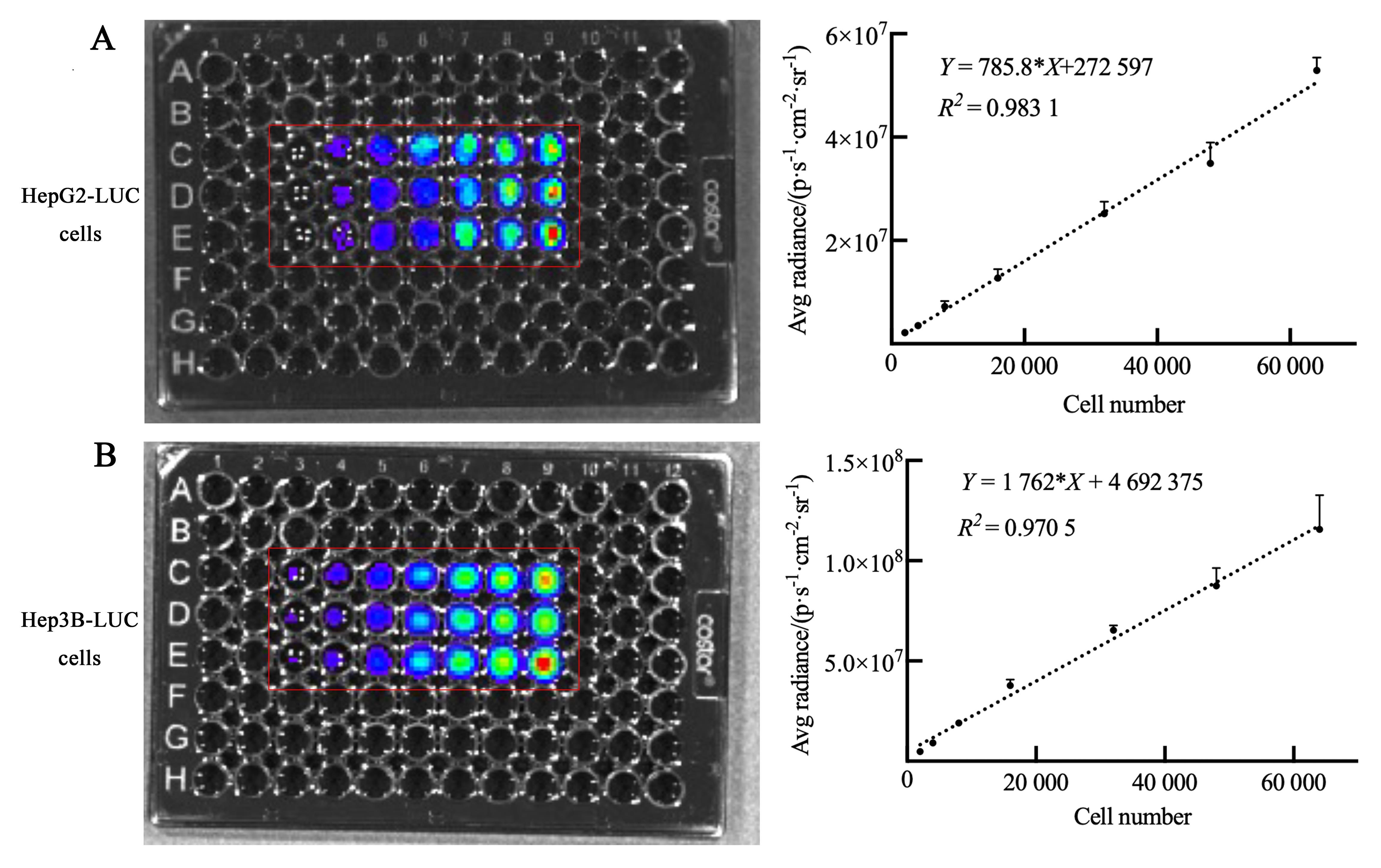
图1 人肝肿瘤细胞株的细胞生物发光效率注:A和B分别为萤光素酶报告基因(LUC)标记的人肝母细胞瘤HepG2细胞( HepG2-LUC)、人肝癌细胞Hep3B( Hep3B-LUC)细胞与D-荧光素钾底物混合孵育后的生物发光效率,一元线性回归及单因素方差分析显示各细胞数目与平均生物发光强度呈线性正相关关系。96孔板中,从左至右每孔含细胞数量依次为2×103、4×103、8×103、1.6×104、3.2×104、4.8×104和6.4×104个(n=3)。
Figure 1 Cell bioluminescence efficiency of human liver tumor cell linesNote: A, Bioluminescence efficiency of human hepatoblastoma HepG2 cells labeled with luciferase reporter gene (LUC) after incubating with D-luciferin potassium; B, Bioluminescence efficiency of human hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells labeled with LUC after incubating with D-luciferin potassium. Simple linear regression and one-way ANOVA test showed that the number of each cell was positively correlated with the average bioluminescence intensity. In the 96-well plate, the number of cells in each well from left to right was 2×103,4×103, 8×103, 1.6×104, 3.2×104, 4.8×104, and 6.4×104, n=3.
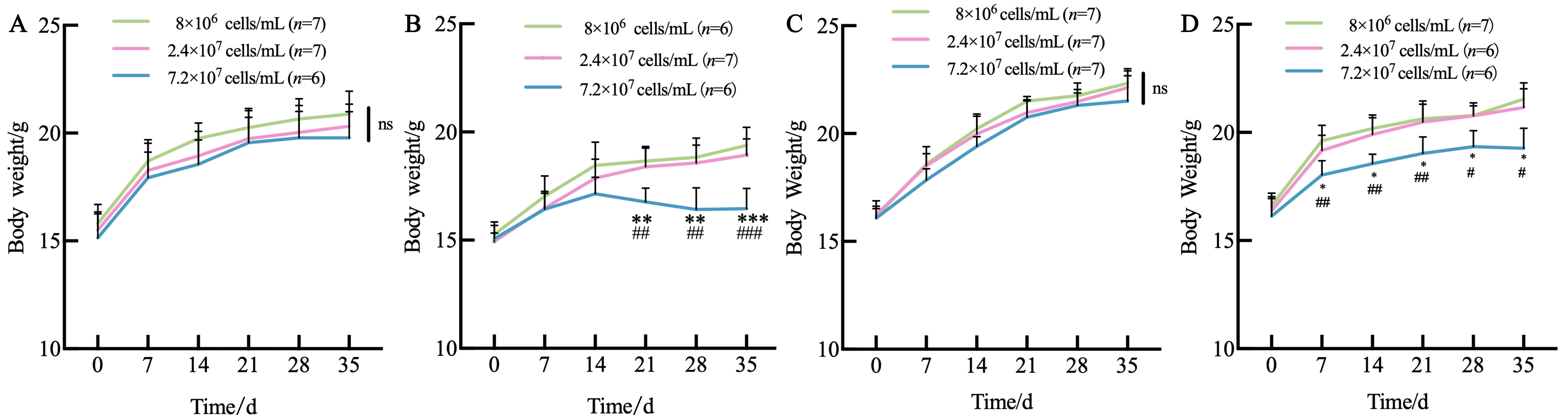
图2 不同接种细胞浓度、不同介质的肝肿瘤模型裸小鼠的体重变化注:A~D依次为HepG2-LUC[萤光素酶报告基因(LUC)标记的用PBS稀释成不同细胞浓度的人肝母细胞瘤HepG2细胞]、HepG2-LUC+Matrigel[LUC标记的与Matrigel基质胶(4 mg/mL)混合成不同细胞浓度的人肝母细胞瘤HepG2细胞]、Hep3B-LUC(LUC标记的用PBS稀释成不同细胞浓度的人肝癌Hep3B细胞)、Hep3B-LUC+Matrigel[LUC标记的与Matrigel基质胶(4 mg/mL)混合成不同细胞浓度的人肝癌Hep3B细胞]原位注射裸小鼠的体重随时间增长趋势。与低浓度(8×106个细胞/mL)组相比,#P<0.05,##P<0.01,###P=0.000 1;与中浓度(2.4×107个细胞/mL)组相比,*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P=0.000 1;3组之间比较,nsP>0.05。
Figure 2 Body weight changes of nude mouse liver tumor models with different cell concentrations and suspension mediaNote:A-D represent body weight over time in nude mouse orthotopic tumor models of HepG2-LUC [human hepatoblastoma HepG2 cells labeled with luciferase reporter gene (LUC) and diluted with PBS into different cell concentrations], HepG2-LUC+Matrigel (human hepatoblastoma HepG2 cells labeled with LUC and diluted with 4 mg/mL Matrigel into different cell concentrations), Hep3B-LUC (human hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells labeled with LUC and diluted with PBS into different cell concentrations), and Hep3B-LUC+Matrigel (human hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells labeled with LUC and diluted with 4 mg/mL Matrigel into different cell concentrations) successively. Compared with the low-concentration (8×106 cells/mL) group of the same time, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P=0.000 1; Compared with the medium-concentration (2.4×107 cells/mL) group of the same time, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P=0.000 1; Compared among the three groups of the same time, nsP>0.05.
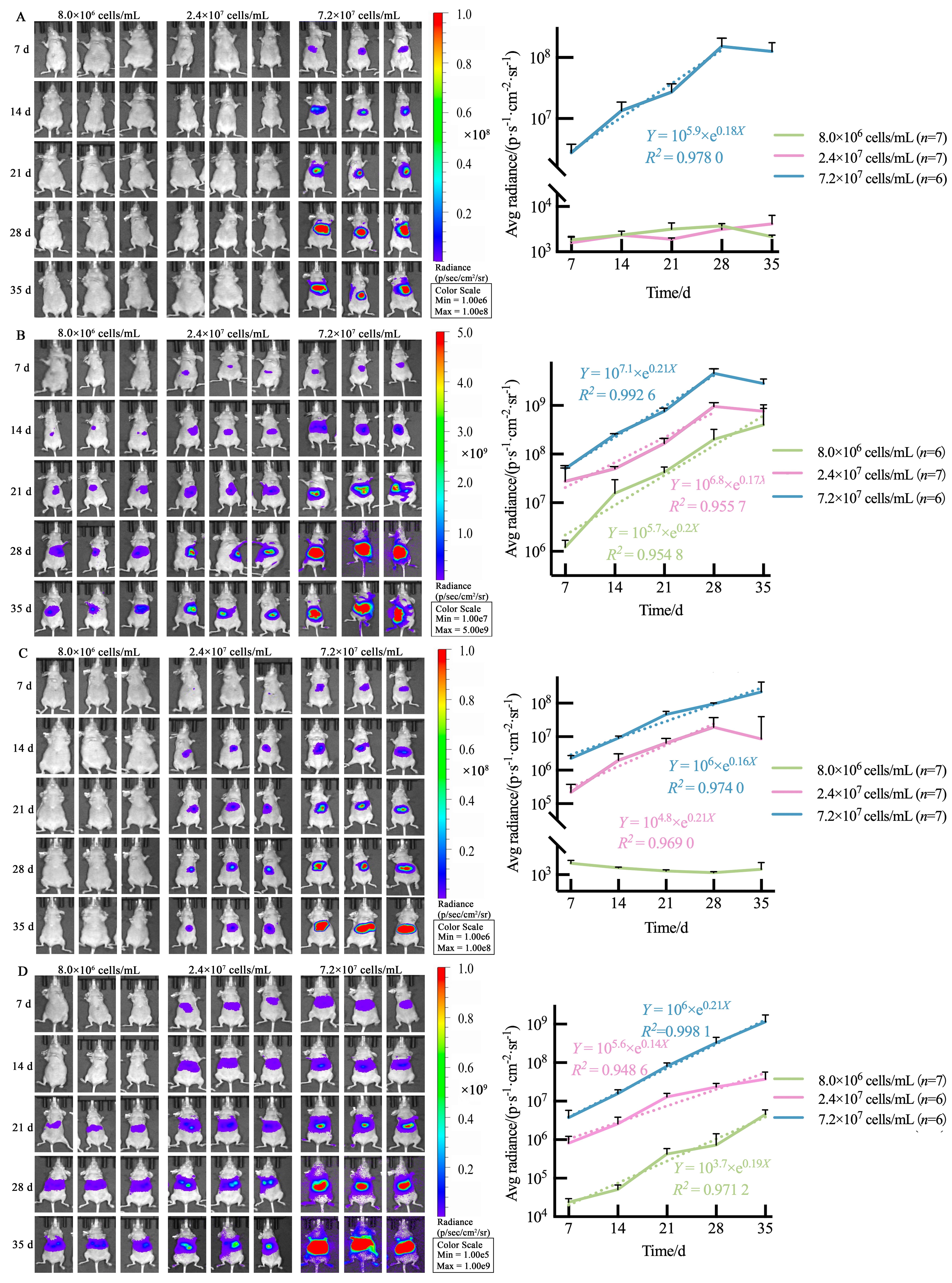
图3 不同接种细胞浓度、不同介质的肝肿瘤模型裸小鼠体内生物发光强度注:A~D依次为HepG2-LUC[萤光素酶报告基因(LUC)标记的用PBS稀释成不同细胞浓度的人肝母细胞瘤HepG2细胞]、HepG2-LUC+Matrigel(LUC标记的与Matrigel基质胶(4 mg/mL)混合成不同细胞浓度的人肝母细胞瘤HepG2细胞)、Hep3B-LUC(LUC标记的用PBS稀释成不同细胞浓度的人肝癌Hep3B细胞)、Hep3B-LUC+Matrigel(LUC标记的与Matrigel基质胶(4 mg/mL)混合成不同细胞浓度的人肝癌Hep3B细胞)原位注射裸小鼠的每周成像结果,提示造模后各组小鼠体内发光强度随时间的变化趋势(虚线提示呈指数型增长)。
Figure 3 Bioluminescence monitoring of nude mouse liver tumor models with different cell concentrations and suspension mediaNote:A-D represent the weekly bioluminescence monitoring results of nude mouse orthotopic tumor models of HepG2-LUC [human hepatoblastoma HepG2 cells labeled with luciferase reporter gene (LUC) and diluted with PBS into different cell concentrations], HepG2-LUC+Matrigel (human hepatoblastoma HepG2 cells labeled with LUC and diluted with 4 mg/mL Matrigel into different cell concentrations), Hep3B-LUC (human hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells labeled with LUC and diluted with PBS into different cell concentrations), and Hep3B-LUC+Matrigel (human hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells labeled with LUC and diluted with 4 mg/mL Matrigel into different cell concentrations) successively, which show the change trends of the luminescence intensity over time after in-situ modeling (dotted lines indicate exponential growth).
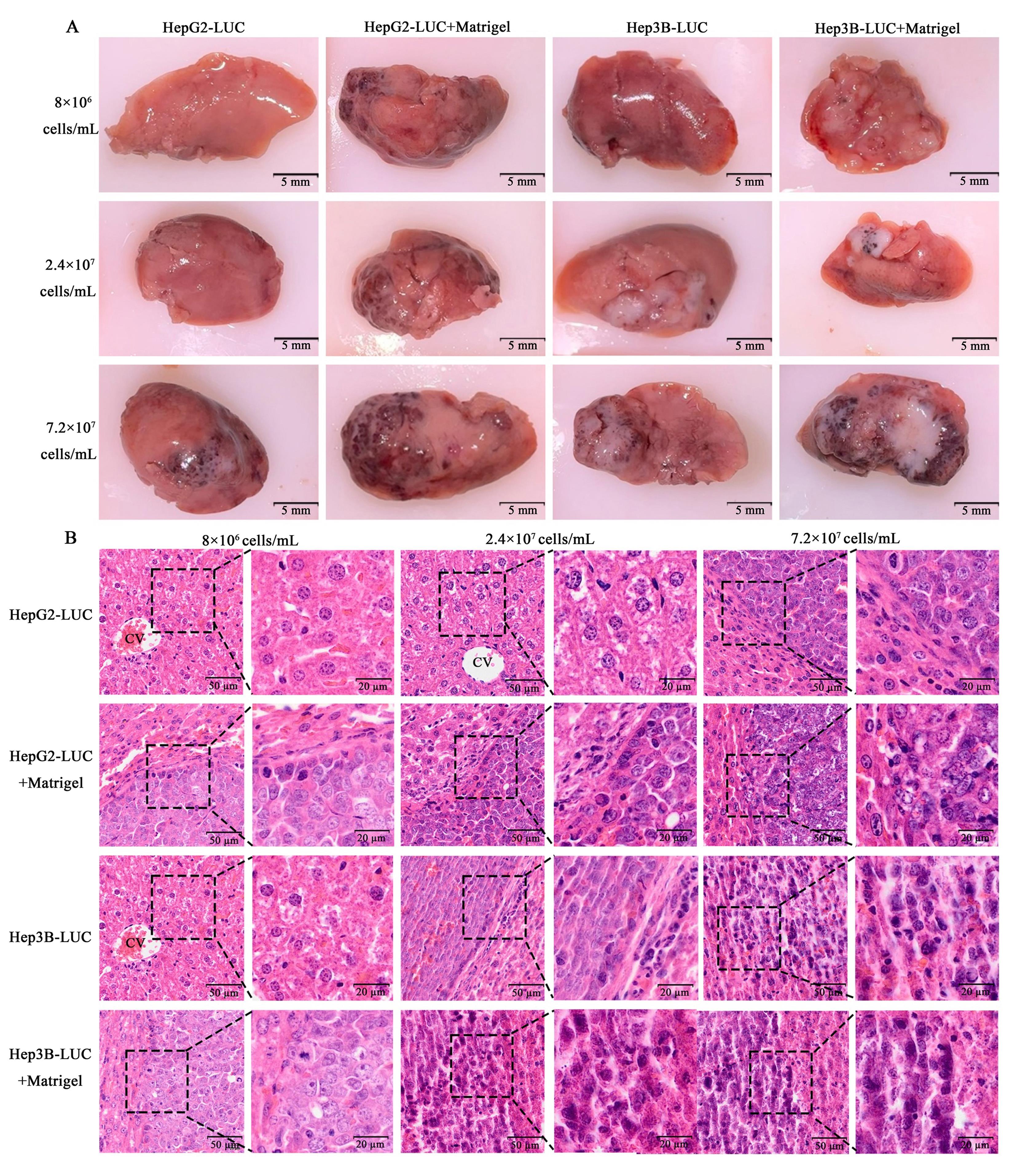
图4 不同接种细胞浓度、不同介质的肝肿瘤模型裸小鼠的肝脏组织典型图片(A)和HE染色图(B)注:HepG2-LUC,用PBS稀释成不同细胞浓度的萤光素酶报告基因(LUC)标记的人肝母细胞瘤HepG2细胞接种裸小鼠左肝叶后35 d;HepG2-LUC+Matrigel,与Matrigel基质胶(4 mg/mL)以1∶1的比例混合成不同细胞浓度的LUC标记的人肝母细胞瘤HepG2细胞接种裸小鼠左肝叶后35 d;Hep3B-LUC,用PBS稀释成不同细胞浓度的LUC标记的人肝癌细胞Hep3B接种裸小鼠左肝叶后35 d;Hep3B-LUC+Matrigel,与Matrigel基质胶(4 mg/mL)以1∶1的比例混合成不同细胞浓度的LUC标记的人肝癌细胞Hep3B接种裸小鼠左肝叶后35 d。A图中比例尺大小为5 mm,B图中各细胞浓度组内左右两图的比例尺大小分别为50 μm和20 μm。
Figure 4 Gross images (A) and HE staining (B) of liver tissue in nude mouse liver tumor models with different cell concentrations and suspension mediaNote:HepG2-LUC, left liver lobe of nude mice 35 days after in-situ modeling with human hepatoblastoma HepG2 cells labeled with luciferase reporter gene (LUC) and diluted with PBS into different cell concentrations. HepG2-LUC+Matrigel, left liver lobe of nude mice 35 days after in-situ modeling with human hepatoblastoma HepG2 cells labeled with LUC and diluted with 4 mg/mL Matrigel into different cell concentrations. Hep3B-LUC, left liver lobe of nude mice 35 days after in-situ modeling with human hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells labeled with LUC and diluted with PBS into different cell concentrations. Hep3B-LUC+Matrigel, left liver lobe of nude mice 35 days after in-situ modeling with human hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells labeled with LUC and diluted with 4 mg/mL Matrigel into different cell concentrations. The scale size is 5 mm in figure A, and the scale sizes of the left and right graphs in each cell concentration group are 50 μm and 20 μm respectively in figure B.
| 1 | SELVAGGI F, CATALANO T, COTELLESE R, et al. Targeting Wnt/β-catenin pathways in primary liver tumours: from microenvironment signaling to therapeutic agents[J]. Cancers, 2022, 14(8):1912. DOI: 10.3390/cancers14081912 . |
| 2 | ZHENG H C, XUE H, YUN W J. An overview of mouse models of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Infect Agent Cancer, 2023, 18(1):49. DOI: 10.1186/s13027-023-00524-9 . |
| 3 | MARRERO J A, KULIK L M, SIRLIN C B, et al. Diagnosis, staging, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2018 practice guidance by the American association for the study of liver diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 68(2):723-750. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29913 . |
| 4 | EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE STUDY OF THE LIVER. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69(1):182-236. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.019 . |
| 5 | MOLINA-SÁNCHEZ P, LUJAMBIO A. Experimental models for preclinical research in hepatocellular carcinoma[M]//Molecular and Translational Medicine. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2019:333-358. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-21540-8_16 . |
| 6 | KALYAN A, NIMEIRI H, KULIK L. Systemic therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma: current and promising[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2015, 19(2):421-432. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2015.01.009 . |
| 7 | CZAUDERNA P, ZBRZEZNIAK G, NAROZANSKI W, et al. Preliminary experience with arterial chemoembolization for hepatoblastoma and hepatocellular carcinoma in children[J]. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 2006, 46(7):825-828. DOI: 10.1002/pbc.20422 . |
| 8 | BROWN Z J, HEINRICH B, GRETEN T F. Mouse models of hepatocellular carcinoma: an overview and highlights for immunotherapy research[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 15(9):536-554. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-018-0033-6 . |
| 9 | 雷会霞, 苗明三. 基于数据挖掘的肝癌动物模型应用分析[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2022, 38(3):186-190. DOI: 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.20210615.006 . |
| LEI H X, MIAO M S. Application analysis of liver cancer animal model based on data mining[J]. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Med, 2022, 38(3):186-190. DOI: 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.20210615.006 . | |
| 10 | 陈志刚, 纪志刚, 石冰冰, 等. 荧光素酶在膀胱肿瘤动物模型中的应用[J]. 北京医学, 2015, 37(11):1101-1103. DOI: 10.15932/j.0253-9713.2015.11.027 . |
| CHEN Z G, JI Z G, SHI B B, et al. Application of luciferase in animal model of bladder tumor[J]. Beijing Med J, 2015, 37(11):1101-1103. DOI: 10.15932/j.0253-9713.2015.11.027 . | |
| 11 | WU T, HEUILLARD E, LINDNER V, et al. Multimodal imaging of a humanized orthotopic model of hepatocellular carcinoma in immunodeficient mice[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6:35230. DOI: 10.1038/srep35230 . |
| 12 | GU C Y, LEE T K W. Preclinical mouse models of hepatocellular carcinoma: an overview and update[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2022, 412(2):113042. DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2022.113042 . |
| 13 | ZHOU Z F, PENG F, LI J Y, et al. Intratumoral IL-12 gene therapy inhibits tumor growth in A HCC-hu-PBL-NOD/SCID murine model[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12:7773-7784. DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S222097 . |
| 14 | HUANG Q X, HE S S, ZHAN D A. Osimertinib is a dual inhibitor of hepatocellular carcinoma and angiogenesis in an EGFR-independent manner, and synergizes with venetoclax[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2023, 149(12):10727-10735. DOI: 10.1007/s00432-023-04926-5 . |
| 15 | 黎凤明, 王静妮, 王春苗, 等. 人肝癌HepG2和Hep3B细胞的异质性与生物学行为关系的初探[J]. 广西医科大学学报, 2023, 40(3):398-405. DOI: 10.16190/j.cnki.45-1211/r.2023.03.009 . |
| LI F M, WANG J N, WANG C M, et al. Preliminary research on the relationship between heterogeneity and biological behavior of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 and Hep3B cells[J]. J Guangxi Med Univ, 2023, 40(3):398-405. DOI: 10.16190/j.cnki.45-1211/r.2023.03.009 . | |
| 16 | 敬文宪, 张伶俐. 肿瘤研究中的实验动物福利问题探讨[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2023, 31(9):1234-1240. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2023.09.015 . |
| JING W X, ZHANG L L. Discussing the welfare of laboratory animals in tumor research[J]. Acta Lab Animalis Sci Sin, 2023, 31(9):1234-1240. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2023.09.015 . | |
| 17 | 罗晓琴, 丁冠茗, 郑旭, 等. 小鼠肝癌原位移植性肿瘤动物模型的改良[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2021, 31(6):16-22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2021.06.003 . |
| LUO X Q, DING G M, ZHENG X, et al. Improved mouse model of orthotopic transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chin J Comp Med, 2021, 31(6):16-22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2021.06.003 . | |
| 18 | ZHANG Y T, ZHONG A X, MIN J, et al. Biomimetic responsive nanoconverters with immune checkpoint blockade plus antiangiogenesis for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treatment[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2024, 16(6):6894-6907. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.3c18140 . |
| 19 | 李泽山, 刘超, 申东方, 等. 虎杖提取物对小鼠肝癌原位移植瘤及miRNA-204-5p/Jarid2/PTEN信号通路的影响[J]. 智慧健康, 2022, 8(10):179-182, 192. DOI: 10.19335/j.cnki.2096-1219.2022.10.054 . |
| LI Z S, LIU C, SHEN D F, et al. Effects of Polygonum cuspidatum extract on orthotopic transplanted liver cancer and miRNA-204-5p/Jarid2/PTEN signaling pathway in mice[J]. Smart Healthc, 2022, 8(10):179-182, 192. DOI: 10.19335/j.cnki.2096-1219.2022.10.054 . | |
| 20 | 潘蕊, 喻锟, 张海亮, 等. 不同方法建立小鼠肝癌原位移植瘤模型差异性的探讨[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2024, 32(3):329-336. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2024.03.006 . |
| PAN R, YU K, ZHANG H L, et al. Different transplantation models of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice[J]. Acta Lab Animalis Sci Sin, 2024, 32(3):329-336. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005- 4847.2024.03.006 . | |
| 21 | 赵然, 刘羽, 高丽丽, 等. HepG2细胞系皮下接种与肝原位接种成瘤的比较研究[J]. 哈尔滨医科大学学报, 2010, 44(3):205-207, 211. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1905.2010.03.002 . |
| ZHAO R, LIU Y, GAO L L, et al. Comparative study of subcutaneous injection and liver injection of HepG2 cells to develop tumor model[J]. J Harbin Med Univ, 2010, 44(3):205-207, 211. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1905.2010.03.002 . | |
| 22 | 尹君, 李景丁莎, 左从林, 等. 人源性肝癌细胞小鼠原位移植瘤模型的建立及特点的比较研究[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2018, 28(12):68-74. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2018.12.012 . |
| YIN J, LIJING D S, ZUO C L, et al. Establishment of mouse orthotopic transplantation tumor models of human hepatoma and comparison of their characteristics[J]. Chin J Comp Med, 2018, 28(12):68-74. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2018.12.012 . | |
| 23 | 农宜熙, 黄俊玲, 黄赞松, 等. 人肝癌细胞株的特性及其实验应用[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2017, 25(2):159-165. DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v25.i2.159 . |
| NONG Y X, HUANG J L, HUANG Z S, et al. Characteristics and experimental applications of human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2017, 25(2):159-165. DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v25.i2.159 . | |
| 24 | ARZUMANIAN V A, KISELEVA O I, POVERENNAYA E V. The curious case of the HepG2 cell line: 40 years of expertise[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(23):13135. DOI: 10.3390/ijms222313135 . |
| 25 | ŠTAMPAR M, TOMC J, FILIPIČ M, et al. Development of in vitro 3D cell model from hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cell line and its application for genotoxicity testing[J]. Arch Toxicol, 2019, 93(11):3321-3333. DOI: 10.1007/s00204-019-02576-6 . |
| 26 | KNOWLTON S, TASOGLU S. A bioprinted liver-on-a-chip for drug screening applications[J]. Trends Biotechnol, 2016, 34(9):681-682. DOI: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.05.014 . |
| 27 | BENTON G, ARNAOUTOVA I, GEORGE J, et al. Matrigel: from discovery and ECM mimicry to assays and models for cancer research[J]. Adv Drug Deliv Rev, 2014, 79-80:3-18. DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2014.06.005 . |
| 28 | MULLEN P. The use of Matrigel to facilitate the establishment of human cancer cell lines as xenografts[J]. Methods Mol Med, 2004, 88:287-292. DOI: 10.1385/1-59259-406-9:287 . |
| 29 | MORENO J A, SANCHEZ A, HOFFMAN R M, et al. Fluorescent orthotopic mouse model of pancreatic cancer[J]. J Vis Exp, 2016(115):54337. DOI: 10.3791/54337 . |
| 30 | QUINTANA E, SHACKLETON M, SABEL M S, et al. Efficient tumour formation by single human melanoma cells[J]. Nature, 2008, 456(7222):593-598. DOI: 10.1038/nature07567 . |
| 31 | BEYREUTHER E, BRÜCHNER K, KRAUSE M, et al. An optimized small animal tumour model for experimentation with low energy protons[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(5): e0177428. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177428 . |
| 32 | BROUTIER L, MASTROGIOVANNI G, VERSTEGEN M M, et al. Human primary liver cancer-derived organoid cultures for disease modeling and drug screening[J]. Nat Med, 2017, 23(12):1424-1435. DOI: 10.1038/nm.4438 . |
| 33 | NUCIFORO S, FOFANA I, MATTER M S, et al. Organoid models of human liver cancers derived from tumor needle biopsies[J]. Cell Rep, 2018, 24(5):1363-1376. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.07.001 . |
| 34 | LI L, KNUTSDOTTIR H, HUI K, et al. Human primary liver cancer organoids reveal intratumor and interpatient drug response heterogeneity[J]. JCI Insight, 2019, 4(2): e121490. DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.121490 . |
| 35 | 郑南南, 黄钢. 小动物活体光学三维成像系统及其对乳腺癌的定量分析[J]. 激光生物学报, 2022, 31(3):215-223. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7146.2022.03.004 . |
| ZHENG N N, HUANG G. Small animal living three-dimensional optical imaging system and its quantitative analysis of breast cancer[J]. Acta Laser Biol Sin, 2022, 31(3):215-223. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7146.2022.03.004 . | |
| 36 | LI G, CHI C W, SHAO X F, et al. Application of molecular imaging technology in evaluating the inhibiting effect of apigenin in vivo on subcutaneous hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2017, 487(1): 122-7. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.04.029 . |
| 37 | 夏猛, 孙玉浩, 王萌, 等. 原发性肝癌常见动物模型的研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37(8):1938-1942. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.08.042 . |
| XIA M, SUN Y H, WANG M, et al. Research advances in commonly used animal models of primary hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(8):1938-1942. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.08.042 . | |
| 38 | BHATTACHARYA S D, MI Z Y, KIM V M, et al. Osteopontin regulates epithelial mesenchymal transition-associated growth of hepatocellular cancer in a mouse xenograft model[J]. Ann Surg, 2012, 255(2):319-325. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31823e3a1c . |
| 39 | XU Q R, LIU X, LIU Z K, et al. MicroRNA-1296 inhibits metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SRPK1-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Mol Cancer, 2017, 16(1):103. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-017-0675-y . |
| [1] | 王爱红, 王明全, 杜娟. O-N-乙酰葡萄糖胺糖基化水平正调控促血管生成素-2表达从而促进小鼠肝癌中肿瘤新生血管形成[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2020, 40(1): 39-46. |
| [2] | 贾欢欢, 曾业文, 罗挺, 龚宝勇, 麦冬梅, 潘迎春, 赵维波. 不同浓度含铬垫料对小鼠血液学及脏器的毒性观察[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2019, 39(6): 454-461. |
| [3] | 谢蓓, 赵磊, 孙婧, 张丽娟, 库本高志, 魏虎来. 二乙基亚硝胺诱导建立Apc基因突变大鼠与F344大鼠肝癌模型的比较[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2017, 37(3): 191-197. |
| [4] | 刘乾, 刘松, 韩锋锋, 郭雪君. 人肺癌原位移植瘤模型的建立及活体成像观察[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2016, 36(4): 250-256. |
| [5] | 赵永江, 朱淼鑫, 袁立新, 孙磊, 耿沁, 李静, 姚明, 闫明霞. 人结肠癌原位移植瘤裸小鼠模型的活体成像观察[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2016, 36(3): 174-179. |
| [6] | 杨喜花, 李耀平, 任连生, 赵莉莉, 杨永明, 阎磊, 白喜花. 一种制备结直肠癌原位移植瘤动物模型的方法[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2015, 35(4): 305-307. |
| [7] | 周洁, 赵莉, 胡建华, 高诚. 表达绿色荧光蛋白的重组1型禽腺病毒的构建[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2013, 33(4): 249-255. |
| [8] | 张燕, 范文玺, 徐艺玫, 史深, 贵友军, 燕顺生. β-咔啉类衍生物对BALB/c裸小鼠肝癌皮下移植瘤生长的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2013, 33(4): 290-295. |
| [9] | 万伯顺, 于静娴, 陈跃宇, 王晓敏, 赵方瑜, 姚明, 闫明霞. 人结肠癌移植瘤小鼠模型的建立及初步研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2013, 33(2): 99-105. |
| [10] | 许文静, 郭建光, 吴艳秋, 高静华, 施美莲, 徐平. SPF级SCID.BG小鼠与BALB/c裸小鼠、SCID小鼠部分免疫指标的测定与比较[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2013, 33(2): 153-156. |
| [11] | 桂博, 刘向云, 潘琦, 王玖玖, 孟祥, 孙祖越. 大、小鼠腹部手术无需使用抗生素[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2011, 31(6): 462-463. |
| [12] | 彭秀华, 沈艳, 徐春华, 杨玉琴, 周文江. 采用小动物活体荧光成像对胃癌皮下和原位移植肿瘤生长的动态观察[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2011, 31(5): 371-375. |
| [13] | 彭秀华, 沈艳, 徐春华, 周文江. 裸大鼠人高转移肝癌皮下和原位移植模型的建立[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2011, 31(1): 33-37. |
| [14] | 闫明霞,刘蕾,朱淼鑫,赵方瑜,萨冰清,梁琳慧,姚明. 人肝癌原位移植瘤的活体动态观察[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2010, 30(6): 401-405. |
| [15] | 沈艳1,彭秀华1,徐春华1,周文江1,2. 裸大鼠人肝癌原位模型的建立及其生物学特性的初步观察[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2010, 30(6): 428-431. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||