
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 523-530.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.056
• Animal Models of Human Diseases • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Jin1( )(
)( ), YU Shiya2, LIN Nan1,2, FANG Yongchao1, ZHAO Hu1, QIU Jinwei2, LIN Hongming2, CHEN Huiyan2, WANG Yu1, WU Weihang1,2(
), YU Shiya2, LIN Nan1,2, FANG Yongchao1, ZHAO Hu1, QIU Jinwei2, LIN Hongming2, CHEN Huiyan2, WANG Yu1, WU Weihang1,2( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-04-17
Revised:2024-07-16
Online:2024-10-25
Published:2024-10-25
Contact:
WU Weihang
CLC Number:
YANG Jin,YU Shiya,LIN Nan,et al. Effect of Modified Duodenal Exclusion Surgery on Glucose Metabolism in Rats with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 523-530. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.056.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.056
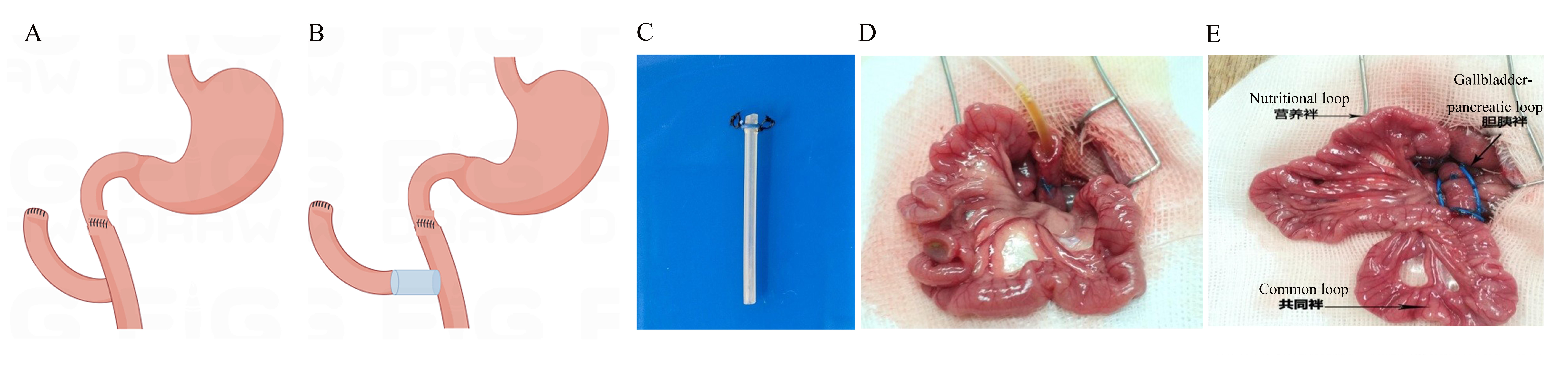
Figure 1 Surgical illustrations of rats in the duodenum exclusion (DE) group and the modified duodenal exclusion (MDE) group with anti-refluxNote:A, Schematic diagram of the surgical procedure for the DE group. B, Schematic diagram of the surgical procedure for the MDE group. C, Duodenal intestinal lumen tubes made of silicone tubing of about 2 mm in diameter and 4 cm in length, with the head end labeled with a contrast strip for easy identification in imaging. D, One end of the silicone tube was sutured to the intestinal wall, allowing biliopancreatic fluid to flow smoothly from the silicone tube. E, End of the anastomosis after simple duodenal exclusion surgery, with contrast strips marking the biliopancreatic loop and the anastomosis of biliopancreatic loop and common loop to facilitate the identification in postoperative imaging.
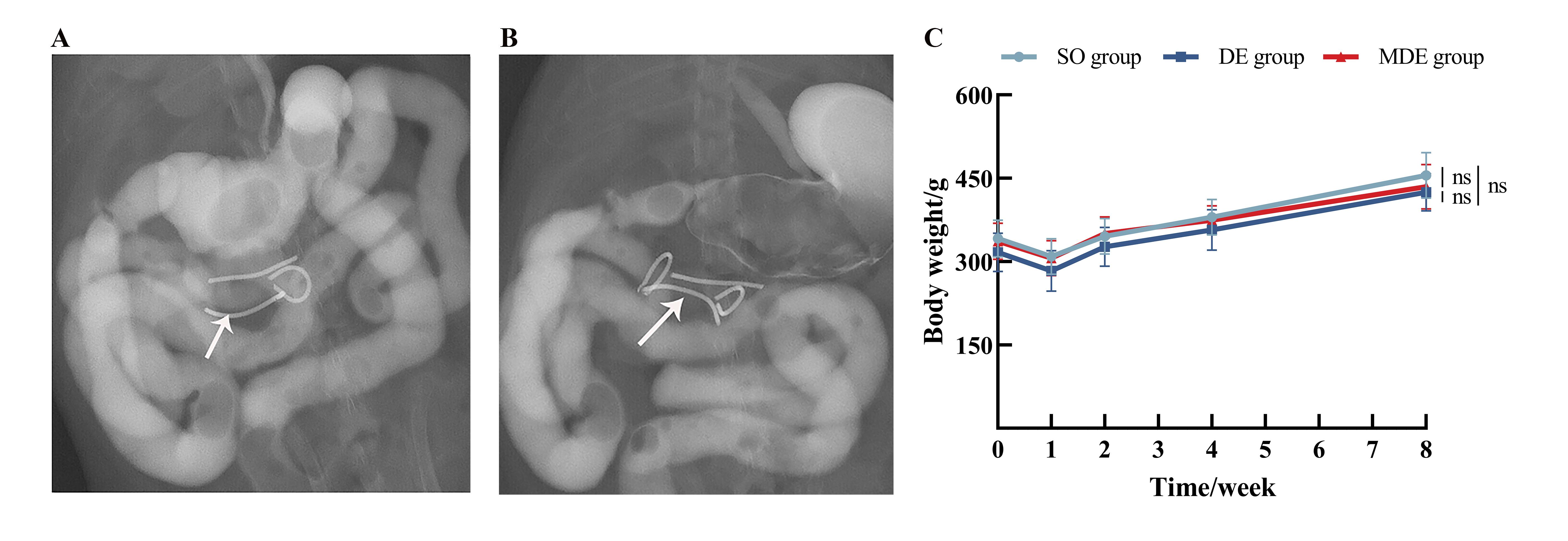
Figure 2 Postoperative gastroenterography and body weight changes in DE and MDE rat groupsNote:A, Postoperative gastroenterography of simple duodenal exclusion (DE group, n=11) (the arrow indicates the biliopancreatic loop, with visible contrast reflux into the loop). B, Postoperative gastroenterography of simple duodenal exclusion + tube placement (MDE group, n=10) (the arrow indicates the biliopancreatic loop with inserted tube, with no contrast reflux observed). C, Postoperative body weight changes in three groups of rats (SO, Sham operation, n=12; ns, No statistical difference).

Figure 3 Changes in fasting glucose and GLP-1 levels in the three groups of rats at different time points before and after surgeryNote:A, Line graphs and bar charts showing the changes in fasting glucose levels of the three groups of rats at different time points before and after surgery. B, Line graphs and bar charts of changes in GLP-1 levels at different time points pre- and post-operatively in the three groups of rats. SO group, Sham operation group, n=12; DE group, Simple duodenal exclusion group, n=11; MDE group, Simple duodenal exclusion with tube placement/anti-reflux group, n=10. ns, No statistical difference. * indicates P<0.05, **indicates P<0.01, ***indicates P<0.001,****indicates P<0.000 1.
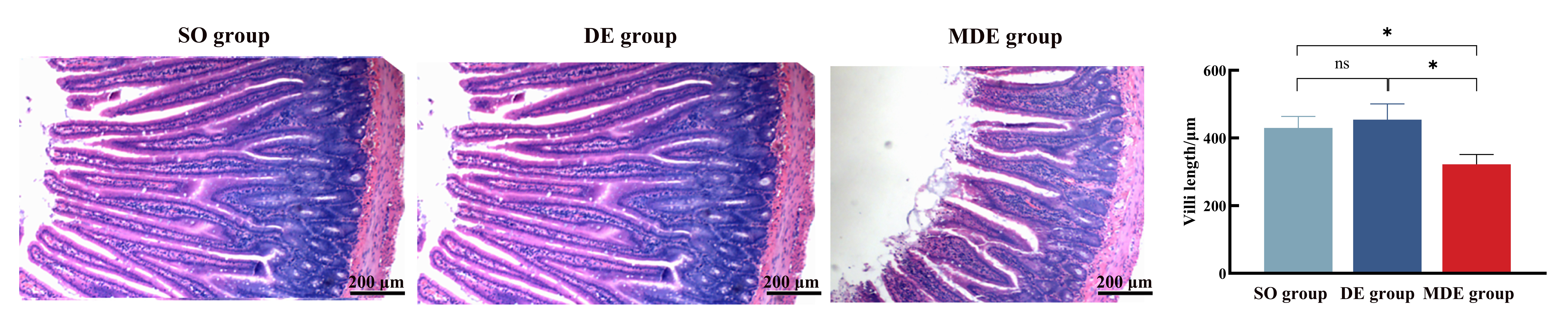
Figure 4 Morphology of intestinal mucosal villi of biliopancreatic collaterals in three groups of rats after 8 weeks (HE staining, ×100)Note:SO, Sham operation group, n=12; DE, Simple duodenal exclusion group, n=11; MDE, Simple duodenal exclusion with tube placement/anti-reflux group, n=10. ns, No statistical difference. *indicates P<0.05.
| 1 | WANG L M, GAO P, ZHANG M, et al. Prevalence and ethnic pattern of diabetes and prediabetes in China in 2013[J]. JAMA, 2017, 317(24):2515-2523. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2017.7596 . |
| 2 | MINGRONE G, PANUNZI S, GAETANO A D, et al. Metabolic surgery versus conventional medical therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: 10-year follow-up of an open-label, single-centre, randomised controlled trial[J]. Lancet, 2021, 397(10271):293-304. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32649-0 . |
| 3 | YOSHINO M, KAYSER B D, YOSHINO J, et al. Effects of diet versus gastric bypass on metabolic function in diabetes[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 383(8):721-732. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2003697 . |
| 4 | MINGRONE G, PANUNZI S, GAETANO A D, et al. Bariatric surgery versus conventional medical therapy for type 2 diabetes[J]. N Engl J Med, 2012, 366(17):1577-1585. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1200111 . |
| 5 | 高相楠, 高宏凯, 张利岩, 等. 腹腔镜胃转流术对体质指数28~35 kg/m2伴代谢综合征的2型糖尿病患者的疗效研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2015, 18(8):906-910. DOI: 10.3969/J.iSSn.1007-9572.2015.08.012 . |
| GAO X N, GAO H K, ZHANG L Y, et al. Efficacy of laparoscopic gastric bypass operation on type 2 diabetic mellitus patients with body mass index 28-35 kg/m2 accompanied by metabolic syndrome[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2015, 18(8):906-910. DOI: 10.3969/J.iSSn.1007-9572.2015.08.012 . | |
| 6 | 张振,宫轲. 外科治疗糖尿病的主要手术方式及其机制[J].首都医科大学学报, 2015, 36(2):318-323. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7795.2015.02.029 . |
| ZHANG Z, GONG K. Main surgery procedures and mechanisms for treating type 2 diabetes[J]. J Cap Med Univ, 2015, 36(2):318-323. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7795.2015.02.029 . | |
| 7 | 吴春兴, 王小芳, 谢斐. 参麦注射液治疗稳定性心绞痛合并2型糖尿病患者的临床疗效观察[J]. 医学临床研究, 2019, 36(1):148-149, 154. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7171.2019.01.050 . |
| WU C X, WANG X F, XIE F. Clinical observation of Shenmai injection in the treatment of patients with stable angina pectoris complicated with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. J Clin Res, 2019, 36(1):148-149, 154. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7171.2019.01.050 . | |
| 8 | ANGRISANI L, SANTONICOLA A, IOVINO P, et al. Bariatric surgery and endoluminal procedures: IFSO worldwide survey 2014[J]. Obes Surg, 2017, 27(9):2279-2289. DOI: 10.1007/s11695-017-2666-x . |
| 9 | THALER J P, CUMMINGS D E. Minireview: Hormonal and metabolic mechanisms of diabetes remission after gastrointestinal surgery[J]. Endocrinology, 2009, 150(6):2518-2525. DOI: 10.1210/en.2009-0367 . |
| 10 | 王瑜, 张再重, 王烈, 等. 不同肠段小肠旷置术对非肥胖型2型糖尿病大鼠的治疗作用[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2009, 47(22):1736-1740. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5815.2009.22.016 . |
| WANG Y, ZHANG Z C, WANG L, et al. Effect of diabetes control after small intestine exclusion surgery in Goto-Kakizaki rat with non-obese type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Chin J Surg, 2009, 47(22):1736-1740. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5815.2009.22.016 . | |
| 11 | DE JONGE C, RENSEN S S, VERDAM F J, et al. Endoscopic duodenal-jejunal bypass liner rapidly improves type 2 diabetes[J]. Obes Surg, 2013, 23(9):1354-1360. DOI: 10.1007/s11695-013-0921-3 . |
| 12 | 陈济华, 陈鑫. 十二指肠空肠套管治疗肥胖和2型糖尿病的研究进展[J]. 中华消化内镜杂志, 2021, 38(6):496-500. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn321463-20200716-00325 . |
| CHEN J H, CHEN X. The researching progress of duodenal-jejunal bypass sleeve in treating obesity and type 2 diabetes[J]. Chin J Dig Endosc, 2021, 38(6):496-500. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn321463-20200716-00325 . | |
| 13 | 陈鑫, 刘彬, 喻敏, 等. 十二指肠腔内套管置入术改善非肥胖型2型糖尿病大鼠糖代谢的作用[J]. 中华内分泌外科杂志, 2013, 7(6):447-450, 477. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-6090.2013.06.002 . |
| CHEN X, LIU B, YU M, et al. Duodenal endoluminal sleeve improves glucose metabolism of non-obese type 2 diabetic rats[J]. Chin J Endocr Surg, 2013, 7(6):447-450, 477. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-6090.2013.06.002 . | |
| 14 | 黄盛, 焦亚彬, 王瑜, 等. 胃转流术治疗非肥胖型2型糖尿病大鼠的长期疗效观察[J]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2011, 5(5):1313-1317. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2011.05.011 . |
| HUANG S, JIAO Y B, WANG Y, et al. Long-term efficacy of gastric bypass on non-obese type 2 diabetes mellitus in Goto-Kakizaki rat[J]. Chin J Clin Electron Ed, 2011, 5(5):1313-1317. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2011.05.011 . | |
| 15 | SUN D, LIU S Z, ZHANG G Y, et al. Type 2 diabetes control in a nonobese rat model using sleeve gastrectomy with duodenal-jejunal bypass (SGDJB)[J]. Obes Surg, 2012, 22(12):1865-1873. DOI: 10.1007/s11695-012-0744-7 . |
| 16 | 李贝贝. GLP1药物治疗2型糖尿病与早期胰岛素治疗2型糖尿病的临床效果及对血糖影响的比较[J]. 中文科技期刊数据库(全文版)医药卫生, 2022(7):52-55. |
| LI B B. Comparison of clinical effects and blood sugar effects between GLP1 drugs and early insulin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Chinese Science and Technology Journal Database (Full-text Edition) Medical and Health, 2022(7):52-55. | |
| 17 | 梅承翰, 陈蓓蓓. 胰高血糖素样肽1类似物对阿尔兹海默症的神经保护作用及机制研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(2): 186-193. DOI:10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.136 . |
| MEI C H, CHEN B B. Research progress on neuroprotective effects and mechanisms of glucagon-likepeptide 1 analogues in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Lab Anim Comp Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 186-193. DOI:10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.136 . |
| [1] | QIN Chao, LI Shuangxing, ZHAO Tingting, JIANG Chenchen, ZHAO Jing, YANG Yanwei, LIN Zhi, WANG Sanlong, WEN Hairuo. Study on the 90-day Feeding Experimental Background Data of SD Rats for Drug Safety Evaluation [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 439-448. |
| [2] | LIU Liyu, JI Bo, LIU Xiaoxuan, FANG Yang, ZHANG Ling, GUO Tingting, QUAN Ye, LI Hewen, LIU Yitian. Exploration of Rat Fetal Lung Tissue Fixation Methods [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 432-438. |
| [3] | LIU Zhiwei, YANG Ran, LIAN Hao, ZHANG Yu, JIN Lilun. Cartilage Protection and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fraxetin on Monosodium Iodoacetate-Induced Rat Model of Osteoarthritis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 259-268. |
| [4] | JIANG Meng, HAO Shulan, TONG Liguo, ZHONG Qiming, GAO Zhenfei, WANG Yonghui, WANG Xixing, JI Haijie. Dynamic Evaluation of Vinorelbine-Induced Phlebitis of Dorsalis Pedis Vein in a Rat Model [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 251-258. |
| [5] | PAN Yicong, JIANG Wenhong, HU Ming, QIN Xiao. Optimization of Surgical Procedure and Efficacy Evaluation of Aortic Calcification Model in Rats with Chronic Kidney Disease [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 279-289. |
| [6] | LIAN Hui, JIANG Yanling, LIU Jia, ZHANG Yuli, XIE Wei, XUE Xiaoou, LI Jian. Construction and Evaluation of a Rat Model of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 130-146. |
| [7] | WEI Yanye, SHEN Guo, ZHANG Pengfei, SHI Songping, HU Jiahao, ZHANG Xuzhe, HUA Huiyuan, HUA Guanyang, LU Hongzheng, ZENG Yong, JI Feng, WEI Zhumei. Dynamic Monitoring and Correlation Analysis of General Body Indicators, Blood Glucose, and Blood Lipid in Obese Cynomolgus Monkeys [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 30-36. |
| [8] | YIN Yulian, MA Lina, TU Siyuan, CHEN Ling, YE Meina, CHEN Hongfeng. Establishment and Evaluation of a Rat Model of Non-Puerperal Mastitis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 587-596. |
| [9] | QI Longju, CHEN Shiyuan, LIAO Zehua, SHI Yuanhu, SUN Yuyu, WANG Qinghua. Transcriptomic Analysis of Menstrual Blood-Derived Stem Cells Transplantation Combined with Exercise Training in Promoting Spinal Cord Injury Recovery in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 531-542. |
| [10] | ZHANG Naiqun, YUAN Piaopiao, CAO Linrong, YING Na, YANG Taotao. Application of PNR Detection in the Diagnosis and Drug-efficacy Evaluation of Diabetic Kidney Disease in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 543-549. |
| [11] | ZHENG Yiqing, DENG Yasheng, FAN Yanping, LIANG Tianwei, HUANG Hui, LIU Yonghui, NI Zhaobing, LIN Jiang. Application Analysis of Animal Models for Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Based on Data Mining [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 405-418. |
| [12] | XIAO Pan, WANG Hongyi, LU Lu, ZHANG Mei, CHEN Keming, SHEN Dongshuai, NIU Tingxian. Screening of Hypoxia-Sensitive and Hypoxia-Tolerant Wistar Rats and Preliminary Exploration of Hypoxia Sensitivity in Their G1 Generation [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 374-383. |
| [13] | Xiaoyu ZHU, Hantao YUAN, Sibo LI. MicroRNA-887-3p Inhibited MDM4 Expression and Proliferation but Promoted Apoptosis of Intervertebral Disc Annulus Fibrosus Cells in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 270-278. |
| [14] | Jinhua HU, Jingjie HAN, Min JIN, Bin HU, Yuefen LOU. Effects of Puerarin on Bone Density in Rats and Mice: A Meta-analysis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 149-161. |
| [15] | Liya ZHAO, Liju NI, Caiqin ZHANG, Jianping TANG, Yangzheng YAO, Yanyan NIE, Xiaoxue GU, Ying ZHAO. Establishing a Genetic Detection Protocol of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Panels in Inbred Rats Based on Multiplex PCR-LDR [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 548-558. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||