
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 173-179.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.102
• Animal Models of Human Diseases • Previous Articles Next Articles
Haosheng WU1( ), Hang SU1, Chao ZHU1, Wenhui WANG1, Shengbing WU2,3, Shuai CUI2,4, Meiqi ZHOU4,5(
), Hang SU1, Chao ZHU1, Wenhui WANG1, Shengbing WU2,3, Shuai CUI2,4, Meiqi ZHOU4,5( )(
)( )
)
Received:2022-07-06
Revised:2022-09-21
Online:2023-04-25
Published:2023-05-16
Contact:
Meiqi ZHOU
CLC Number:
Haosheng WU, Hang SU, Chao ZHU, Wenhui WANG, Shengbing WU, Shuai CUI, Meiqi ZHOU. Research Progress of Animal Models of Stress Cardiomyopathy[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 173-179.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.102
动物 Animal | 品种或品系 Stock or strain | 性别 Sex | 年龄或体质量 Age/weight | 药物 Drug | 剂量 Dose | 给药方案 Dosage regimen | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大鼠 Rat | SD | 雄 | 250~300 g | ISO | 50 mg/kg | 单次腹腔注射 | [ |
| SD | 雌 | 2~4月龄,241±55 g | ISO | 100 mg/kg | 单次腹腔注射 | [ | |
| SD | 雄 | 220~250 g,8周龄 | ISO | 100 mg/kg | 不同部位多点皮下注射,持续3周 | [ | |
| SD | 雌 | 300~350 g | NE | 2~4 mg/kg | 单次腹腔注射 | [ | |
| SD | 雌 | 300~350 g | NE | 4 mg/kg | 单次腹腔注射 | [ | |
| 小鼠Mice | C57BL/6J | 雄/雌 | 8~16周龄 | ISO | 200 mg/kg | 单次腹腔注射 | [ |
| C57BL/6J | / | 16周 | ISO | 400 mg/kg | 单次腹腔注射 | [ | |
| C57BL/6J | 雄性 | 7周龄,20~25 g | ISO | 50 mg/kg | 腹腔注射3周 | [ | |
| 129/Sv | / | 8周 | ISO | 25 mg/kg | 连续皮下注射5 d | [ | |
| C57BL/ 6J | 雄/雌 | 8周 | ISO | 30 mg/kg | 皮下埋置微渗透泵,连续21 d释放ISO | [ |
Table 1 Methods of constructing rat and mouse model of stress cardiomyopathy by chemical factors
动物 Animal | 品种或品系 Stock or strain | 性别 Sex | 年龄或体质量 Age/weight | 药物 Drug | 剂量 Dose | 给药方案 Dosage regimen | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大鼠 Rat | SD | 雄 | 250~300 g | ISO | 50 mg/kg | 单次腹腔注射 | [ |
| SD | 雌 | 2~4月龄,241±55 g | ISO | 100 mg/kg | 单次腹腔注射 | [ | |
| SD | 雄 | 220~250 g,8周龄 | ISO | 100 mg/kg | 不同部位多点皮下注射,持续3周 | [ | |
| SD | 雌 | 300~350 g | NE | 2~4 mg/kg | 单次腹腔注射 | [ | |
| SD | 雌 | 300~350 g | NE | 4 mg/kg | 单次腹腔注射 | [ | |
| 小鼠Mice | C57BL/6J | 雄/雌 | 8~16周龄 | ISO | 200 mg/kg | 单次腹腔注射 | [ |
| C57BL/6J | / | 16周 | ISO | 400 mg/kg | 单次腹腔注射 | [ | |
| C57BL/6J | 雄性 | 7周龄,20~25 g | ISO | 50 mg/kg | 腹腔注射3周 | [ | |
| 129/Sv | / | 8周 | ISO | 25 mg/kg | 连续皮下注射5 d | [ | |
| C57BL/ 6J | 雄/雌 | 8周 | ISO | 30 mg/kg | 皮下埋置微渗透泵,连续21 d释放ISO | [ |
| 动物Animal | 品种Stock | 性别 Sex | 月龄或体质量 Age/weight | 造模方案 Modeling process | 参考文献Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大鼠Rat | SD | 雄性 | 3~4月龄,300~350 g | 束缚2 h | [ |
| 大鼠Rat | SD | 雄性 | 300~350 g | 固定30 min,每间隔2 min给予10 s足底电刺激2 mA,每日2次,持续15 d | [ |
| 大鼠Rat | SD | 雄性 | 280~300 g | 限制饮水50 mL/d,每日束缚6~8 h,连续3周 | [ |
Table 2 Methods of constructing stress cardiomyopathy model in rats by physical factors
| 动物Animal | 品种Stock | 性别 Sex | 月龄或体质量 Age/weight | 造模方案 Modeling process | 参考文献Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大鼠Rat | SD | 雄性 | 3~4月龄,300~350 g | 束缚2 h | [ |
| 大鼠Rat | SD | 雄性 | 300~350 g | 固定30 min,每间隔2 min给予10 s足底电刺激2 mA,每日2次,持续15 d | [ |
| 大鼠Rat | SD | 雄性 | 280~300 g | 限制饮水50 mL/d,每日束缚6~8 h,连续3周 | [ |
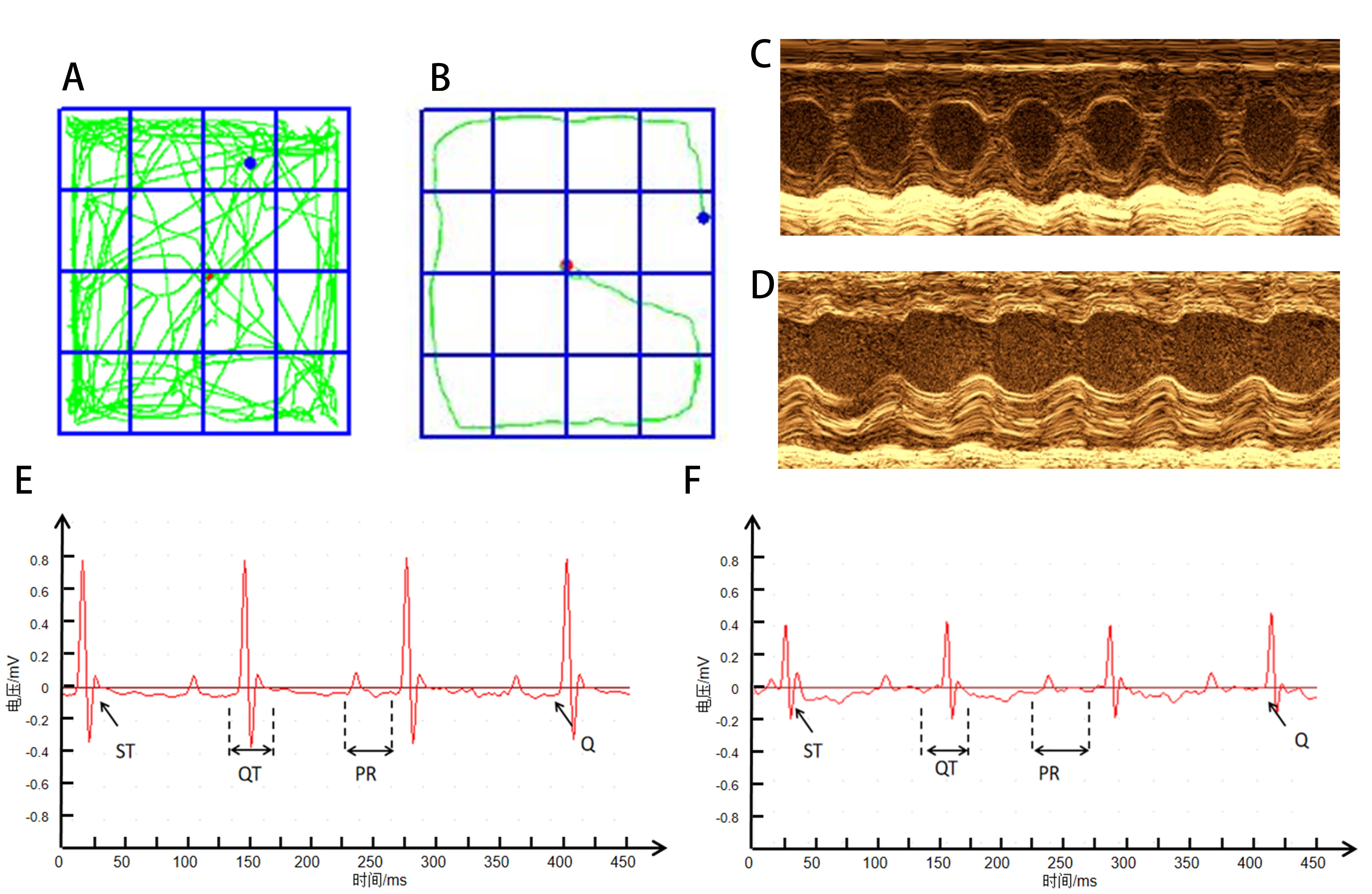
Figure 1 Representative images of evaluation index in an animal model of stress cardiomyopathyNote: A is the trajectory diagram of open field experiment in normal group; B is the open field experiment trajectory of SC model group; C is the cardiogram of the normal group; D is the cardiogram of SC model group; E is the electrocardiogram of normal group; F is the electrocardiogram of SC model group.
| 1 | SHAH R M, SHAH M, SHAH S, et al. Takotsubo syndrome and COVID-19: associations and implications[J]. Curr Probl Cardiol, 2021, 46(3):100763. DOI:10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2020. 100763 . |
| 2 | BARBIERI L, GALLI F, CONCONI B, et al. Takotsubo syndrome in COVID-19 era: is psychological distress the key? [J]. J Psychosom Res, 2021, 140:110297. DOI:10.1016/j.jpsychores. 2020.110297 . |
| 3 | CASTILLO RIVERA A M, RUIZ-BAILÉN M, RUCABADO AGUILAR L. Takotsubo cardiomyopathy - a clinical review[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2011, 17(6): RA135-RA147. DOI:10.12659/msm. 881800 . |
| 4 | OKURA H. Update of takotsubo syndrome in the era of COVID-19[J]. J Cardiol, 2021, 77(4):361-369. DOI:10.1016/j.jjcc. 2020.10.004 . |
| 5 | CHHABRA L. Prognostication in takotsubo syndrome[J]. Rev Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 23(3):110. DOI:10.31083/j.rcm2303110 . |
| 6 | TEMPLIN C, GHADRI J R, DIEKMANN J, et al. Clinical features and outcomes of takotsubo (stress) cardiomyopathy[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 373(10):929-938. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa1406761 . |
| 7 | LYON A R, CITRO R, SCHNEIDER B, et al. Pathophysiology of takotsubo syndrome[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2021, 77(7):902-921. DOI:10.1016/j.jacc.2020.10.060 . |
| 8 | LI C M, HUANG D, TANG J, et al. ClC-3 chloride channel is involved in isoprenaline-induced cardiac hypertrophy[J]. Gene, 2018, 642:335-342. DOI:10.1016/j.gene.2017.11.045 . |
| 9 | 张志红. 硫化氢对Takotsubo心肌病的保护作用及其机制探讨[D].石家庄: 河北医科大学, 2017. |
| ZHANG Z H. Protective effect of H2S on takotsubo cardiomyopathy and its mechanism[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Medical University, 2017. | |
| 10 | ALI A, REDFORS B, ALKHOURY J, et al. Sacubitril/valsartan decreases mortality in the rat model of the isoprenaline-induced takotsubo-like syndrome[J]. ESC Heart Fail, 2021, 8(5):4130-4138. DOI:10.1002/ehf2.13530 . |
| 11 | QI C L, SHAO Y Z, LIU X S, et al. The cardioprotective effects of icariin on the isoprenaline-induced takotsubo-like rat model: involvement of reactive oxygen species and the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2019, 74:105733. DOI:10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105733 . |
| 12 | 杜志君, 蔡伟文, 张文静, 等. 典型与非典型应激性心肌病大鼠模型的制备方法[J]. 广东医学, 2016, 37(7):953-957. DOI:10.13820/j.cnki.gdyx.2016.07.001 . |
| DU Z J, CAI W W, ZHANG W J, et al. Research on the rat model establishment methods of typical and atypical stress cardiomyopathy[J]. Guangdong Med J, 2016, 37(7):953-957. DOI:10.13820/j.cnki.gdyx.2016.07.001 . | |
| 13 | GODSMAN N, KOHLHAAS M, NICKEL A, et al. Metabolic alterations in a rat model of takotsubo syndrome[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2021, 118(8):1932-1946. DOI:10.1093/cvr/cvab081 . |
| 14 | 尹元立, 高永红. 血清缺血修饰白蛋白与大鼠应激性心肌病相关性分析[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2018, 10(5):621-624. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4055.2018.05.30 . |
| YIN Y L, GAO Y H. Correlation between serum ischemia modified albumin and rat Takotsubo cardiomyopathy[J]. Chin J Evid Based Cardiovasc Med, 2018, 10(5):621-624. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4055.2018.05.30 . | |
| 15 | 蔡伟文, 杜志君, 查道刚. 大鼠应激性心肌病模型及其复发模型的制备[J]. 岭南心血管病杂志, 2016, 22(3):315-319. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9688.2016.02.18 . |
| CAI W W, DU Z J, ZHA D G. Preparation for rat model of stress-induced cardiomyopathy and its recurrence model[J]. South China J Cardiovasc Dis, 2016, 22(3):315-319. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9688.2016.02.18 . | |
| 16 | LIAO X D, CHANG E, TANG X M, et al. Cardiac macrophages regulate isoproterenol-induced takotsubo-like cardiomyo-pathy[J]. JCI Insight, 2022, 7(3): e156236. DOI:10.1172/jci.insight.156236 . |
| 17 | SHAO Y Z, REDFORS B, STÅHLMAN M, et al. A mouse model reveals an important role for catecholamine-induced lipotoxicity in the pathogenesis of stress-induced cardiomyopathy[J]. Eur J Heart Fail, 2013, 15(1):9-22. DOI:10.1093/eurjhf/hfs161 . |
| 18 | 向仕钊, 卞洲艳, 周恒, 等. 比索洛尔联合还原型谷胱甘肽改善应激性心肌病心肌重构[J]. 中国心血管杂志, 2015, 20(5):358-365. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5410.2015.05.011 . |
| XIANG S Z, BIAN Z Y, ZHOU H, et al. Combined utilization of bisoprolol and glutathione attenuates ventricular remodeling of takotsubo cardiomyopathy in mice[J]. Chin J Cardiovasc Med, 2015, 20(5):358-365. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-5410.2015.05.011 . | |
| 19 | KHURANA I, MAXWELL S, ROYCE S, et al. SAHA attenuates Takotsubo-like myocardial injury by targeting an epigenetic Ac/Dc axis[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2021, 6:159. DOI:10.1038/s41392-021-00546-y . |
| 20 | WALSH-WILKINSON E, ARSENAULT M, COUET J. Segmental analysis by speckle-tracking echocardiography of the left ventricle response to isoproterenol in male and female mice[J]. PeerJ, 2021, 9: e11085. DOI:10.7717/peerj.11085 . |
| 21 | 万坤铭, 孙帅, 俞超芹. 应激致功能性下丘脑性闭经动物模型研究进展[J]. 南昌大学学报(医学版), 2022, 62(1):99-104. DOI:10.13764/j.cnki.ncdm.2022.01.020 . |
| WAN K M, SUN S, YU C Q. Advances in animal models of stress-induced functional hypothalamic amenorrhea[J]. J Nanchang Univ Med Sci, 2022, 62(1):99-104. DOI:10.13764/j.cnki.ncdm.2022.01.020 . | |
| 22 | 高源, 郭翠娟, 刘仁平, 等. 束缚应激对小鼠卵巢氧化损伤的实验研究[J]. 南昌大学学报(医学版), 2022, 62(2):26-30. DOI:10.13764/j.cnki.ncdm.2022.02.005 . |
| GAO Y, GUO C J, LIU R P, et al. A study on ovarian oxidative damage caused by restraint stress in mice[J]. J Nanchang Univ Med Sci, 2022, 62(2):26-30. DOI:10.13764/j.cnki.ncdm.2022.02.005 . | |
| 23 | 齐跃, 房加雄, 董彦, 等. 束缚诱导大鼠应激性心肌病的有效性评价[J]. 武警后勤学院学报(医学版), 2016, 25(10):791-794. DOI:10.16548/j.2095-3720.2016.10.004 . |
| QI Y, FANG J X, DONG Y, et al. Evaluation of the immobilization effectiveness on inducing stress cardiomyopathy in rats[J]. J Logist Univ PAP Med Sci, 2016, 25(10):791-794. DOI:10.16548/j.2095-3720.2016.10.004 . | |
| 24 | 李永丰, 吴宇蔚, 乔海法. 足底电击应激诱发精神疾病模型的研究进展[J]. 神经解剖学杂志, 2020, 36(4):464-468. DOI:10.16557/j.cnki.1000-7547.2020.04.018 . |
| LI Y F, WU Y W, QIAO H F. Research progress of the mental illness model induced by plantar shock stress[J]. Chin J Neuroanat, 2020, 36(4):464-468. DOI:10.16557/j.cnki.1000-7547.2020.04.018 . | |
| 25 | 李凤, 李玉军, 王凯, 等. 大鼠应激性心肌病模型心肌组织BNP的表达变化[J]. 中国法医学杂志, 2015, 30(5):459-462, 467. DOI:10.13618/j.issn.1001-5728.2015.05.003 . |
| LI F, LI Y J, WANG K, et al. Expression of BNP in a rat model of stress cardiomyopathy[J]. Chin J Forensic Med, 2015, 30(5):459-462, 467. DOI:10.13618/j.issn.1001-5728.2015.05.003 . | |
| 26 | 阿兰达. 大鼠应激性心肌病神经肽Y和PGC-1α表达的实验研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2010. |
| ANANDA S. An Experimental study on the expression of Neuropeptide Y and PGC-1α in a rat model of Stress Cardiomyopathy[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2010. | |
| 27 | 石建, 曾安宁, 熊德高. 灯盏花素改善应激性心肌病大鼠心功能异常的机制[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2016, 36(15):3646-3648. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2016.15.016 . |
| SHI J, ZENG A N, XIONG D G. Mechanism of breviscapine in improving cardiac dysfunction in rats with stress cardiomyopathy[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2016, 36(15):3646-3648. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2016.15.016 . | |
| 28 | 孙艳荣, 富华颖. 制动联合脱水建立应激性心肌病大鼠模型[J]. 泰山医学院学报, 2017, 38(5):497-499. DOI:10. 3969 / j. issn. 1004-7115.2017.05.006 . |
| SUN Y R, FU H Y. Establishment of rat model of stress induced cardiomyopathy by combination of braking and dehydration[J]. J Taishan Med Coll, 2017, 38(5):497-499. DOI:10. 3969 / j. issn. 1004-7115.2017.05.006 . | |
| 29 | 郭瑞威, 杨丽霞, 奚银艳, 等. 电刺激迷走神经建立应激性心肌病家兔模型[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2016, 36(3):186-189. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-5817.2016.03.005 . |
| GUO R W, YANG L X, XI Y Y, et al. Establishment of stress induced cardiomyopathy model by stimulation of vagus nerve with electricity signal in rabbit[J]. Lab Anim Comp Med, 2016, 36(3):186-189. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-5817.2016.03.005 . | |
| 30 | GOULD T D, DAO D T, KOVACSICS C E. The open field test[M]//Pietropaolo P. Mood and anxiety related phenotypes in mice. Totowa: Humana Press, 2009:1-20. DOI:10.1007/978-1-60761-303-9_1 . |
| 31 | THIPPESWAMY B S, MISHRA B, VEERAPUR V P, et al. Anxiolytic activity of Nymphaea alba Linn. in mice as experimental models of anxiety[J]. Indian J Pharmacol, 2011, 43(1):50-55. DOI:10.4103/0253-7613.75670 . |
| 32 | LIPKIND D, SAKOV A, KAFKAFI N, et al. New replicable anxiety-related measures of wall vs center behavior of mice in the open field[J]. J Appl Physiol (1985), 2004, 97(1):347-359. DOI:10.1152/japplphysiol.00148.2004 . |
| 33 | YAKUPOGLU H Y, SAEED S, SENIOR R, et al. Reversible exercise-induced left ventricular dysfunction in symptomatic patients with previous Takotsubo syndrome: insights from stress echocardiography[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2020:jeaa237. DOI:10.1093/ehjci/jeaa237 . |
| 34 | LEE M. Time course of functional recovery in takotsubo (stress) cardiomyopathy: a serial speckle tracking echocardiography and electrocardiography study[J]. J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2020, 28(1):50-60. DOI:10.4250/jcvi.2019. 0083 . |
| 35 | SEMELKA R C, TOMEI E, WAGNER S, et al. Interstudy reproducibility of dimensional and functional measurements between cine magnetic resonance studies in the morphologically abnormal left ventricle[J]. Am Heart J, 1990, 119(6):1367-1373. DOI:10.1016/S0002-8703(05)80187-5 . |
| 36 | MITSUMA W, KODAMA M, ITO M, et al. Serial electrocardiographic findings in women with takotsubo cardiomyopathy[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2007, 100(1):106-109. DOI:10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.02.062 . |
| 37 | ABRAHAM J, MUDD J O, KAPUR N, et al. Stress cardiomyopathy after intravenous administration of catecholamines and beta-receptor agonists[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2009, 53(15):1320-1325. DOI:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.02.020 . |
| 38 | GIANNI M, DENTALI F, GRANDI A M, et al. Apical ballooning syndrome or takotsubo cardiomyopathy: a systematic review[J]. Eur Heart J, 2006, 27(13):1523-1529. DOI:10.1093/eurheartj/ehl032 . |
| 39 | CHHABRA L, BUTT N, AHMAD S A, et al. Electro-cardiographic changes in takotsubo cardiomyopathy[J]. J Electrocardiol, 2021, 65:28-33. DOI:10.1016/j.jelectrocard. 2020.12.006 . |
| 40 | DJURIĆ I, OBRADOVIĆ S, GLIGIĆ B. Dynamics of electrocardiographic changes, brain-natriuretic peptide and cortisol levels in a patient with stress (takotsubo) cardiomyopathy: a case report[J]. Vojnosanit Pregl, 2013, 70(5):511-515. DOI:10.2298/vsp1305511d . |
| 41 | MADHAVAN M, BORLAUG B A, LERMAN A, et al. Stress hormone and circulating biomarker profile of apical ballooning syndrome (Takotsubo cardiomyopathy): insights into the clinical significance of B-type natriuretic peptide and troponin levels[J]. Heart, 2009, 95(17):1436-1441. DOI:10.1136/hrt.2009.170399 . |
| 42 | AHMED K A, MADHAVAN M, PRASAD A. Brain natriuretic peptide in apical ballooning syndrome (Takotsubo/stress cardiomyopathy): comparison with acute myocardial infarction[J]. Coron Artery Dis, 2012, 23(4):259-264. DOI:10.1097/MCA.0b013e3283526a57 . |
| 43 | JOHANSSON G, JONSSON L, LANNEK N, et al. Severe stress-cardiopathy in pigs[J]. Am Heart J, 1974, 87(4):451-457. DOI:10.1016/0002-8703(74)90170-7 . |
| [1] | Tianwei LIANG, Yasheng DENG, Hui HUANG, Na RONG, Xin LIU, Yujie WANG, Jiang LIN. Preparation Methods and Evaluation Criteria Analysis of Animal Models for Perimenopausal Syndrome [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 74-84. |
| [2] | Committee of Experts on Medical Animal Experiments, Chinese Research Hospital Association. Guidelines for the Selection of Animal Models and Preclinical Drug Trials for Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage (2024 Edition) [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 3-30. |
| [3] | Xin LIU, Shaobo SHI, Cui ZHANG, Bo YANG, Chuan QU. Construction and Evaluation of End-to-side Anastomosis Model of Autologous Arteriovenous Fistula in Mice [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 595-603. |
| [4] | Shuwu XIE, Ruling SHEN, Jinxing LIN, Chun FAN. Progress in Establishment and Application of Laboratory Animal Models Related to Development of Male Infertility Drugs [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 504-511. |
| [5] | Yanjuan CHEN, Ruling SHEN. Progress in the Application of Animal Disease Models in the Medical Research on Colorectal Cancer [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 512-523. |
| [6] | Rui ZHANG, Meiyu LÜ, Jianjun ZHANG, Jinlian LIU, Yan CHEN, Zhiqiang HUANG, Yao LIU, Lanhua ZHOU. Research Progress on Establishing and Evaluation of Acne Animal Models [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 398-405. |
| [7] | Jin LU, Jian WANG, Lian ZHU, Guofeng YAN, Zhengwen MA, Yao LI, Jianjun DAI, Yinqiu ZHU, Jing ZHOU. Establishment of Preeclampsia Model in Goat and Evaluation on Maternal Biological Characteristics [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 371-380. |
| [8] | Jiahui YU, Qian GONG, Lenan ZHUANG. Animal Models of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Their Application in Drug Research [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 381-397. |
| [9] | Yasheng DENG, Jiang LIN, Chiling GAN, Guanfeng ZENG, Jiayin HUANG, Huifang DENG, Yingxian MA, Siyin HAN. Literature Analysis of the Preparation Elements of Animal Models of Skin Photoaging and the Data of Subjects [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 406-414. |
| [10] | Xue WANG, Yonghe HU. Analysis of Common Types and Construction Elements of Diabetic Mouse Models [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 415-421. |
| [11] | Hui HUANG, Yasheng DENG, Tianwei LIANG, Yiqing ZHENG, Yanping FAN, Na RONG, Jiang LIN. Evaluation and Analysis of Modeling Methods for Animal Models with Diminished Ovarian Reserve [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 422-428. |
| [12] | Lei XIANG, Jinzhu JING, Zhen LIANG, Guoqiang YAN, Wenfeng GUO, Meng ZHANG, Wei ZHANG, Yajun LIU. A Visual Analysis on Animal Model of Sarcopenia Based on VOSviewer [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 429-439. |
| [13] | Zhigang TAN, Jinxin LIU, Chuya ZHENG, Wenfeng LIAO, Luping FENG, Hongli PENG, Xiu YAN, Zhenjian ZHUO. Advances and Applications in Animal Models of Neuroblastoma [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 288-296. |
| [14] | Can LAI, Lele LI, Tala HU, Yan MENG. Recent Advances of Animal Models of Renal Interstitial Fibrosis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 163-172. |
| [15] | Ling HU, Zhibin HU, Yunqing HU, Yuqiang DING. Overview of Studies in Animal Models of Schizophrenia [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 145-155. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||