













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 318-330.
胡敏1( ), 董乐轩2(
), 董乐轩2( )(
)( ), 高怡2(
), 高怡2( )(
)( ), 奚子芪2, 沈子皓2, 唐瑞阳2, 栾鑫2, 汤忞2(
), 奚子芪2, 沈子皓2, 唐瑞阳2, 栾鑫2, 汤忞2( )(
)( ), 张卫东1,2,3
), 张卫东1,2,3
收稿日期:2024-12-30
修回日期:2025-02-10
出版日期:2025-07-07
发布日期:2025-06-25
通讯作者:
汤忞(1992—),女,博士,研究员,硕士生导师,研究方向:生物3D打印在组织工程及肿瘤研究中的应用。E-mail: mit012@ shutcm.edu.cn。ORCID: 0000-0002-6084-1827作者简介:胡 敏(2000—),女,硕士研究生,研究方向:生物3D打印。E-mail: 213332692@st.usst.edu.cn。ORCID: 0009-0008-4332-8555;基金资助:
HU Min1( ), DONG Lexuan2(
), DONG Lexuan2( )(
)( ), GAO Yi2(
), GAO Yi2( )(
)( ), XI Ziqi2, SHEN Zihao2, TANG Ruiyang2, LUAN Xin2, TANG Min2(
), XI Ziqi2, SHEN Zihao2, TANG Ruiyang2, LUAN Xin2, TANG Min2( )(
)( ), ZHANG Weidong1,2,3
), ZHANG Weidong1,2,3
Received:2024-12-30
Revised:2025-02-10
Published:2025-06-25
Online:2025-07-07
Contact:
TANG Min (ORCID: 0000-0002-6084-1827), E-mail: mit012@shutcm.edu.cn摘要:
动物实验在生物医药研究中广泛用于安全性评估、毒理学分析、疗效验证以及机制探索。近年来,由于动物实验伦理审查制度日趋严格、动物福利意识不断提升,同时为了推动更高效、低成本的药物研发,美国在2022年9月通过了食品药品监督管理局(Food and Drug Administration,FDA)现代化法案2.0,首次取消了新药临床前研究必须进行动物实验的联邦强制要求。2025年4月FDA进一步提出,将在单克隆抗体等药物研发中采用人工智能计算模型、类器官毒性测试、3D微生理系统等一系列“新的替代方法”,从而逐步取代传统的动物试验模式。在这些新兴技术中,生物3D打印模型因其高仿生、高重现性和可规模化等特性,逐渐成为动物模型的重要替代和补充手段。本综述系统梳理了生物3D打印技术在生物医药领域的研究与应用进展:首先概述了生物3D打印的关键组成,包括生物材料的选择与功能化设计、多种打印策略的原理及特点,分析其在构建多细胞空间结构、微环境调控和细胞命运引导方面的优势;其次,介绍了生物3D打印模型在药物研发中的典型应用,包括通过构建肿瘤、传染病和罕见病等疾病模型实现对药效的高通量筛选,以及通过构建肝脏、心脏等器官特异性模型进行药物毒理学研究;再者,进一步探讨了生物3D打印在组织工程领域的应用范围,涵盖骨/软骨、皮肤、血管等多种功能性组织的构建,以及在再生替代等方面的最新进展。此外,本文还分析了生物3D打印模型与动物模型在疾病发生发展和药物作用机制、精准医疗、药物研发以及组织再生研究等领域的互补优势,讨论了二者交叉应用在提升建模准确性与生理相关性方面的潜力与挑战。综上,生物3D打印作为一种新兴的体外造模与制造技术,正逐步建立起涵盖疾病建模、药物筛选、毒性预测与组织再生的完整应用体系。
中图分类号:
胡敏,董乐轩,高怡,等. 生物3D打印研究及与临床前动物模型的交叉应用展望[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 318-330.
HU Min,DONG Lexuan,GAO Yi,et al. Prospects for 3D Bioprinting Research and Transdisciplinary Application to Preclinical Animal Models[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 318-330.
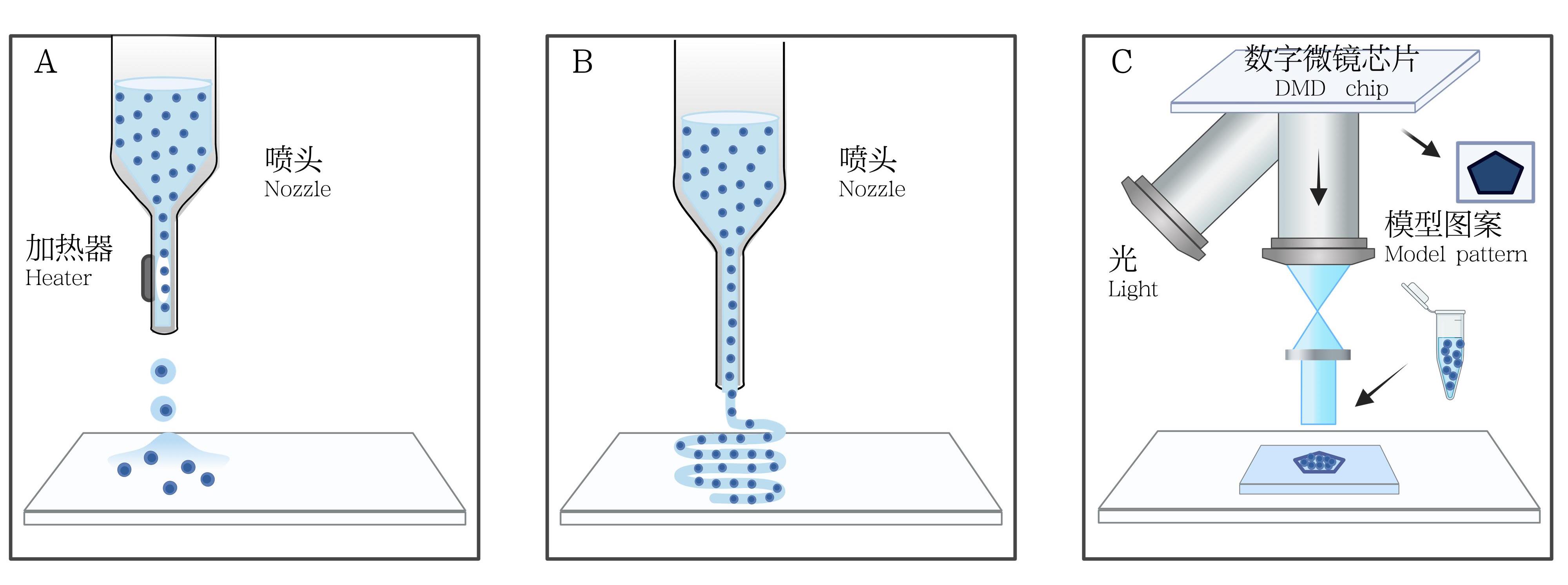
图1 3种生物3D打印工艺类型的工作机制示意图注:A,喷墨式生物3D打印(局部加热生物墨水,并膨胀一个气泡以推动液滴从喷嘴头喷出);B,挤出式生物3D打印(逐层打印连续的细丝状生物墨水);C,光固化生物3D打印[利用数字微镜装置(DMD)芯片,使得紫外光或其他光源模式化投射到生物墨水上]。
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the working principles of three types of 3D bioprinting processesNote:A, Inkjet-based 3D bioprinting, in which localized heating of the bioink inflates an air bubble to push droplets out from the nozzle; B, Extrusion-based 3D bioprinting, which prints continuous filaments of bioink layer by layer; C, Light-based 3D bioprinting, which utilizes a digital micro-mirror device (DMD) chip to project patterned UV light or other light sources onto the bioink.
模型类型 Model types | 2D细胞模型 2D cell model | 生物3D打印模型 3D bioprinting model | PDX动物模型 Patient-derived xenograft animal model |
|---|---|---|---|
| 实验周期 Experimental cycle | 1周内 | 7 d | 3~6个月 |
| 成本 Cost | 1 000~2 000元/例 | 数万元/批 | 数十万元/批 |
| 建模成功率 Modeling success rate | 高 (>90%) [ | 高 (>80%) [ | 低 (>60%) [ |
| 临床相关性 Clinical relevance | 有限 | 高 | 高 |
| 遗传信息保真度Genetic information fidelity | 有限 | 高 | 高 |
| 可重复性 Reproducibility | 高 | 高 | 低 |
| 细胞种类 Cell types | 有限 | 多样化,含有多种细胞 | 多样化,但受鼠源细胞影响 |
| 系统完整性 System integrity | 低,仅细胞层面 | 中等,组织/器官层面,尚缺乏动态 循环和整体性调控 | 高,具有完整生理环境 |
| 材料可控性 Material controllability | 无 | 高 | 低 |
| 通量 Throughput | 高 | 高 | 低 |
表1 精准医疗常见模型对比
Table 1 Comparison of common models in precision medicine
模型类型 Model types | 2D细胞模型 2D cell model | 生物3D打印模型 3D bioprinting model | PDX动物模型 Patient-derived xenograft animal model |
|---|---|---|---|
| 实验周期 Experimental cycle | 1周内 | 7 d | 3~6个月 |
| 成本 Cost | 1 000~2 000元/例 | 数万元/批 | 数十万元/批 |
| 建模成功率 Modeling success rate | 高 (>90%) [ | 高 (>80%) [ | 低 (>60%) [ |
| 临床相关性 Clinical relevance | 有限 | 高 | 高 |
| 遗传信息保真度Genetic information fidelity | 有限 | 高 | 高 |
| 可重复性 Reproducibility | 高 | 高 | 低 |
| 细胞种类 Cell types | 有限 | 多样化,含有多种细胞 | 多样化,但受鼠源细胞影响 |
| 系统完整性 System integrity | 低,仅细胞层面 | 中等,组织/器官层面,尚缺乏动态 循环和整体性调控 | 高,具有完整生理环境 |
| 材料可控性 Material controllability | 无 | 高 | 低 |
| 通量 Throughput | 高 | 高 | 低 |
| [1] | AKHTAR A. The flaws and human harms of animal experimentation[J]. Camb Q Healthc Ethics, 2015, 24(4):407-419. DOI:10.1017/S0963180115000079 . |
| [2] | BALCOMBE J P. Laboratory environments and rodents' behavioural needs: a review[J]. Lab Anim, 2006, 40(3):217-235. DOI:10.1258/002367706777611488 . |
| [3] | TEBON P J, WANG B W, MARKOWITZ A L, et al. Drug screening at single-organoid resolution via bioprinting and interferometry[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1):3168. DOI:10.1038/s41467-023-38832-8 . |
| [4] | LEVATO R, DUDARYEVA O, GARCIAMENDEZ-MIJARES C E, et al. Light-based vat-polymerization bioprinting[J]. Nat Rev Meth Primers, 2023, 3:47. DOI:10.1038/s43586-023-00231-0 . |
| [5] | KANG H W, LEE S J, KO I K, et al. A 3D bioprinting system to produce human-scale tissue constructs with structural integrity[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2016, 34(3):312-319. DOI:10.1038/nbt.3413 . |
| [6] | JI S, GUVENDIREN M. Recent advances in bioink design for 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs[J]. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2017, 5:23. DOI:10.3389/fbioe.2017.00023 . |
| [7] | WANG T, HAN Y, WU Z J, et al. Tissue-specific hydrogels for three-dimensional printing and potential application in peripheral nerve regeneration[J]. Tissue Eng Part A, 2022, 28(3-4):161-174. DOI:10.1089/ten.TEA.2021.0093 . |
| [8] | XIANG Y, MILLER K, GUAN J A, et al. 3D bioprinting of complex tissues in vitro: state-of-the-art and future perspectives[J]. Arch Toxicol, 2022, 96(3):691-710. DOI:10.1007/s00204-021-03212-y . |
| [9] | TANG M, RICH J N, CHEN S C. Biomaterials and 3D bioprinting strategies to model glioblastoma and the blood-brain barrier[J]. Adv Mater, 2021, 33(5): e2004776. DOI:10.1002/adma.202004776 . |
| [10] | ZHOU L Y, FU J Z, HE Y. A review of 3D printing technologies for soft polymer materials[J]. Adv Funct Mater, 2020, 30(28):2000187. DOI:10.1002/adfm.202000187 . |
| [11] | U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Novel drug approvals for 2024[EB/OL]. (2024-05-22)[2025-06-05].. |
| [12] | VAN NORMAN G A. Limitations of animal studies for predicting toxicity in clinical trials: is it time to rethink our current approach?[J]. JACC Basic Transl Sci, 2019, 4(7):845-854. DOI:10.1016/j.jacbts.2019.10.008 . |
| [13] | SCHUSTER B, JUNKIN M, KASHAF S S, et al. Automated microfluidic platform for dynamic and combinatorial drug screening of tumor organoids[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1):5271. DOI:10.1038/s41467-020-19058-4 . |
| [14] | TUNG Y T, CHEN Y C, DERR K, et al. A 3D bioprinted human neurovascular unit model of glioblastoma tumor growth[J]. Adv Healthc Mater, 2024, 13(15):e2302831. DOI:10.1002/adhm.202302831 . |
| [15] | DESIGAUX T, COMPERAT L, DUSSERRE N, et al. 3D bioprinted breast cancer model reveals stroma-mediated modulation of extracellular matrix and radiosensitivity[J]. Bioact Mater, 2024, 42:316-327. DOI:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024. 08.037 . |
| [16] | TANG M, XIE Q, GIMPLE R C, et al. Three-dimensional bioprinted glioblastoma microenvironments model cellular dependencies and immune interactions[J]. Cell Res, 2020, 30(10):833-853. DOI:10.1038/s41422-020-0338-1 . |
| [17] | TANG M, TIWARI S K, AGRAWAL K, et al. Rapid 3D bioprinting of glioblastoma model mimicking native biophysical heterogeneity[J]. Small, 2021, 17(15): e2006050. DOI:10.1002/smll.202006050 . |
| [18] | TANG M, QU Y J, HE P X, et al. Heat-inducible CAR-T overcomes adverse mechanical tumor microenvironment in a 3D bioprinted glioblastoma model[J]. Mater Today Bio, 2024, 26:101077. DOI:10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101077 . |
| [19] | JOHNSON B N, LANCASTER K Z, HOGUE I B, et al. 3D printed nervous system on a chip[J]. Lab Chip, 2016, 16(8):1393-1400. DOI:10.1039/c5lc01270h . |
| [20] | BANERJEE D, IVANOVA M M, CELIK N, et al. Biofabrication of an in-vitro bone model for Gaucher disease[J]. Biofabrication, 2023, 15(4):045023. DOI:10.1088/1758-5090/acf95a . |
| [21] | SCARIAN E, BORDONI M, FANTINI V, et al. Patients' stem cells differentiation in a 3D environment as a promising experimental tool for the study of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(10):5344. DOI:10.3390/ijms23105344 . |
| [22] | ROUSSEL R, STEG P G, MOHAMMEDI K, et al. Prevention of cardiovascular disease through reduction of glycaemic exposure in type 2 diabetes: a perspective on glucose-lowering interventions[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2018, 20(2):238-244. DOI:10.1111/dom.13033 . |
| [23] | ALI A S M, WU D W, BANNACH-BROWN A, et al. 3D bioprinting of liver models: a systematic scoping review of methods, bioinks, and reporting quality[J]. Mater Today Bio, 2024, 26:100991. DOI:10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.100991 . |
| [24] | NGUYEN D G, FUNK J, ROBBINS J B, et al. Bioprinted 3D primary liver tissues allow assessment of organ-level response to clinical drug induced toxicity in vitro [J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(7): e0158674. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0158674 . |
| [25] | JANANI G, PRIYA S, DEY S, et al. Mimicking native liver lobule microarchitecture in vitro with parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells using 3D bioprinting for drug toxicity and drug screening applications[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2022, 14(8):10167-10186. DOI:10.1021/acsami.2c00312 . |
| [26] | HE J Y, WANG J L, PANG Y, et al. Bioprinting of a hepatic tissue model using human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes for drug-induced hepatotoxicity evaluation[J]. Int J Bioprint, 2022, 8(3):581. DOI:10.18063/ijb.v8i3.581 . |
| [27] | DEY S, BHAT A, JANANI G, et al. Microfluidic human physiomimetic liver model as a screening platform for drug induced liver injury[J]. Biomaterials, 2024, 310:122627. DOI:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122627 . |
| [28] | FERRI N, SIEGL P, CORSINI A, et al. Drug attrition during pre-clinical and clinical development: understanding and managing drug-induced cardiotoxicity[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2013, 138(3):470-484. DOI:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.03.005 . |
| [29] | YANG K X, WANG L X, VIJAYAVENKATARAMAN S, et al. Recent applications of three-dimensional bioprinting in drug discovery and development[J]. Adv Drug Deliv Rev, 2024, 214:115456. DOI:10.1016/j.addr.2024.115456 . |
| [30] | ARAI K, MURATA D, TAKAO S, et al. Drug response analysis for scaffold-free cardiac constructs fabricated using bio-3D printer[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1):8972. DOI:10.1038/s41598-020-65681-y . |
| [31] | IWANAGA S, HAMADA Y, TSUKAMOTO Y, et al. Design and fabrication of mature engineered pre-cardiac tissue utilizing 3D bioprinting technology and enzymatically crosslinking hydrogel[J]. Materials, 2022, 15(22):7928. DOI:10.3390/ma15227928 . |
| [32] | LIU S T, WANG Z H, CHEN X Y, et al. Multiscale anisotropic scaffold integrating 3D printing and electrospinning techniques as a heart-on-a-chip platform for evaluating drug-induced cardiotoxicity[J]. Adv Healthc Mater, 2023, 12(24): e2300719. DOI:10.1002/adhm.202300719 . |
| [33] | 王梓霏, 丁雅卉, 李彦, 等. 生物3D打印在肿瘤研究及组织工程中的应用[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2024, 34(9):814-826. DOI: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2024.09.002 . |
| WANG Z F, DING Y H, LI Y, et al. Application of 3D bioprinting in cancer research and tissue engineering[J]. China Oncol, 2024, 34(9):814-826. DOI: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2024.09.002 . | |
| [34] | BAI Y X, WANG Z J, HE X L, et al. Application of bioactive materials for osteogenic function in bone tissue engineering[J]. Small Methods, 2024, 8(8): e2301283. DOI:10.1002/smtd.202301283 . |
| [35] | YAN Y F, CHEN H, ZHANG H B, et al. Vascularized 3D printed scaffolds for promoting bone regeneration[J]. Biomaterials, 2019, 190-191:97-110. DOI:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.10.033 . |
| [36] | VEGA S L, KWON M Y, BURDICK J A. Recent advances in hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering[J]. Eur Cell Mater, 2017, 33:59-75. DOI:10.22203/eCM.v033a05 . |
| [37] | WENG T T, ZHANG W, XIA Y L, et al. 3D bioprinting for skin tissue engineering: Current status and perspectives[J]. J Tissue Eng, 2021, 12:20417314211028574. DOI:10.1177/204173 14211028574 . |
| [38] | SHI Y, XING T L, ZHANG H B, et al. Tyrosinase-doped bioink for 3D bioprinting of living skin constructs[J]. Biomed Mater, 2018, 13(3):035008. DOI:10.1088/1748-605X/aaa5b6 . |
| [39] | JIN R H, CUI Y C, CHEN H J, et al. Three-dimensional bioprinting of a full-thickness functional skin model using acellular dermal matrix and gelatin methacrylamide bioink[J]. Acta Biomater, 2021, 131:248-261. DOI:10.1016/j.actbio.2021. 07.012 . |
| [40] | GOLD K A, SAHA B, RAJEEVA PANDIAN N K, et al. 3D bioprinted multicellular vascular models[J]. Adv Healthc Mater, 2021, 10(21): e2101141. DOI:10.1002/adhm.202101141 . |
| [41] | WU X F, CHEN K, CHAI Q, et al. Freestanding vascular scaffolds engineered by direct 3D printing with Gt-Alg-MMT bioinks[J]. Biomater Adv, 2022, 133:112658. DOI:10.1016/j.msec. 2022.112658 . |
| [42] | LÓPEZ-CARRASCO A, MARTÍN-VAÑÓ S, BURGOS-PANADERO R, et al. Impact of extracellular matrix stiffness on genomic heterogeneity in MYCN-amplified neuro-blastoma cell line[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2020, 39(1):226. DOI:10.1186/s13046-020-01729-1 . |
| [43] | REN X X, HUANG M L, WENG W X, et al. Personalized drug screening in patient-derived organoids of biliary tract cancer and its clinical application[J]. Cell Rep Med, 2023, 4(11):101277. DOI:10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101277 . |
| [44] | LUCÀ R, ASSENZA M R, MAIULLARI F, et al. Inhibition of the mTOR pathway and reprogramming of protein synthesis by MDM4 reduce ovarian cancer metastatic properties[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(6):558. DOI:10.1038/s41419-021-03828-z . |
| [45] | ZHAO Z Y, FENG X Q, WU H J, et al. Construction of a lung cancer 3D culture model based on alginate/gelatin micro-beads for drug evaluation[J]. Transl Lung Cancer Res, 2024, 13(10):2698-2712. DOI:10.21037/tlcr-24-490 . |
| [46] | SHIHABI A AL, TEBON P J, NGUYEN H T L, et al. The landscape of drug sensitivity and resistance in sarcoma[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2024, 31(10):1524-1542.e4. DOI:10.1016/j.stem. 2024.08.010 . |
| [47] | SUN H, SUN L J, KE X D, et al. Prediction of clinical precision chemotherapy by patient-derived 3D bioprinting models of colorectal cancer and its liver metastases[J]. Adv Sci, 2024, 11(2): e2304460. DOI:10.1002/advs.202304460 . |
| [48] | PERRON U, GRASSI E, CHATZIPLI A, et al. Integrative ensemble modelling of cetuximab sensitivity in colorectal cancer patient-derived xenografts[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1):9139. DOI:10.1038/s41467-024-53163-y . |
| [49] | LI S, LV J, LI Z, et al. Overcoming multi-drug resistance in SCLC: A synergistic approach with venetoclax and hydroxychloroquine targeting the lncRNA LYPLAL1-DT/BCL2/BECN1 pathway[J]. Mol Cance, 2024, 23(1): 243. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-024-02145-1 . |
| [50] | HASHIMOTO T, NAKAMURA Y, FUJISAWA T, et al. The SCRUM-MONSTAR cancer-omics ecosystem: striving for a quantum leap in precision medicine[J]. Cancer Discov, 2024, 14(11):2243-2261. DOI:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-0206 . |
| [51] | 邹晟.基于3D生物打印技术构建肺癌体外模型[D].南昌: 南昌大学, 2023. DOI: 10.27232/d.cnki.gnchu.2023.000153 . |
| ZOU S. A lung cancer model in vitro was constructed based on 3D bioprinting[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2023. DOI:10.27232/d.cnki.gnchu.2023.000153 . | |
| [52] | 孙航. 基于3D生物打印技术构建人源消化系恶性肿瘤临床前模型及其临床应用研究[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院, 2024.DOI:10.27648/d.cnki.gzxhu.2024.000117 . |
| SUN H. Construction and clinical application research on human-derived preclinical models of gastrointestinal cancer based on 3D bioprinting technology[D]. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College, 2024. DOI:10.27648/d.cnki.gzxhu.2024. 000117 . | |
| [53] | 肖瑞英, 鲍伟, 祝亚平. PDX模型在妇科肿瘤中的研究进展[J].中国计划生育和妇产科,2023,15(7):10-13. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4020.2023.07.03 . |
| XIAO R Y, BAO W, ZHU Y P. Research progress of PDX model in gynecological tumors[J]. Chin J Fam Plan Gynecol, 2023, 15(7):10-13. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4020.2023.07.03 . | |
| [54] | HERPERS B, EPPINK B, JAMES M I, et al. Functional patient-derived organoid screenings identify MCLA-158 as a therapeutic EGFR × LGR5 bispecific antibody with efficacy in epithelial tumors[J]. Nat Cancer, 2022, 3(4):418-436. DOI:10.1038/s43018-022-00359-0 . |
| [55] | CHOI J, JUNG T Y, KIM J H, et al. Efficacy of recombinant Bacillus Calmette-Guérin containing dltA in in vivo three-dimensional bio-printed bladder cancer-on-a-chip and ex vivo orthotopic mouse model[J]. Investig Clin Urol, 2023, 64(3):296-305. DOI:10.4111/icu.20220293 . |
| [56] | HONG G, KIM J, OH H, et al. Production of multiple cell-laden microtissue spheroids with a biomimetic hepatic-lobule-like structure[J]. Adv Mater, 2021, 33(36): 2102624. DOI:10.1002/adma.202102624 . |
| [57] | LOPEZ M A, HUTTER L, PAGIN E, et al. In vivo efficacy proof of concept of a large-size bioprinted dermo-epidermal substitute for permanent wound coverage[J]. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2023, 11:1217655. DOI:10.3389/fbioe.2023.1217655 . |
| [58] | LIU Y, ZHANG Y F, MEI T X, et al. hESCs-derived early vascular cell spheroids for cardiac tissue vascular engineering and myocardial infarction treatment[J]. Adv Sci, 2022, 9(9): e2104299. DOI:10.1002/advs.202104299 . |
| [59] | JIANG Z R, JIN B, LIANG Z, et al. Liver bioprinting within a novel support medium with functionalized spheroids, hepatic vein structures, and enhanced post-transplantation vascularization[J]. Biomaterials, 2024, 311:122681. DOI:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122681 . |
| [60] | SUN Y Y, HUO Y Y, RAN X Y, et al. Instant Trachea reconstruction using 3D-bioprinted C-shape biomimetic Trachea based on tissue-specific matrix hydrogels[J]. Bioact Mater, 2023, 32:52-65. DOI:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.09.011 . |
| [61] | SUN Z W, YUE X L, LIU L, et al. Bioprinted Notch ligand to function as stem cell niche improves muscle regeneration in dystrophic muscle[J]. Int J Bioprint, 2023, 9(3):711. DOI:10.18063/ijb.711 . |
| [62] | SUN B B, LIAN M F, HAN Y, et al. A 3D-Bioprinted dual growth factor-releasing intervertebral disc scaffold induces nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus reconstruction[J]. Bioact Mater, 2020, 6(1):179-190. DOI:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.06.022 . |
| [63] | XU Z Y, HUANG J J, LIU Y, et al. Extracellular matrix bioink boosts stemness and facilitates transplantation of intestinal organoids as a biosafe Matrigel alternative[J]. Bioeng Transl Med, 2022, 8(1): e10327. DOI:10.1002/btm2.10327 . |
| [64] | NANMO A, YAN L, ASABA T, et al. Bioprinting of hair follicle germs for hair regenerative medicine[J]. Acta Biomater, 2023, 165:50-59. DOI:10.1016/j.actbio.2022.06.021 . |
| [65] | NG W L, GOH G L, GOH G D, et al. Progress and opportunities for machine learning in materials and processes of additive manufacturing[J]. Adv Mater, 2024, 36(34): e2310006. DOI:10.1002/adma.202310006 . |
| [1] | 万颖寒, 顾也欣, 袁雨浓, 汤忞, 鲁立. FDA现代化法案2.0给疾病动物模型发展带来的启示和思考[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(5): 472-481. |
| [2] | 谢淑武, 沈如凌, 林金杏, 范春. 雄性不育药物研发相关实验动物模型建立和应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(5): 504-511. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||