













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 271-281.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.183
成慧1( ), 方菲1, 石嘉豪1, 杨桦1, 张梦杰1, 杨平2, 费俭1,2(
), 方菲1, 石嘉豪1, 杨桦1, 张梦杰1, 杨平2, 费俭1,2( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2022-11-28
修回日期:2023-02-15
出版日期:2023-06-25
发布日期:2023-07-18
通讯作者:
费 俭(1965—),男,博士,教授、博士生导师,研究方向:基因功能的模式生物研究。E-mail: jfei@tongji.edu.cn。ORCID: 0000-0001-7755-0818作者简介:成 慧(1996—),女,硕士,研究方向:遗传与衰老。E-mail: 1931474@tongji.edu.cn
基金资助:
Hui CHENG1( ), Fei FANG1, Jiahao SHI1, Hua YANG1, Mengjie ZHANG1, Ping YANG2, Jian FEI1,2(
), Fei FANG1, Jiahao SHI1, Hua YANG1, Mengjie ZHANG1, Ping YANG2, Jian FEI1,2( )(
)( )
)
Received:2022-11-28
Revised:2023-02-15
Published:2023-06-25
Online:2023-07-18
Contact:
FEI Jian (ORCID: 0000-0001-7755-0818 ), E-mail: jfei@tongji.edu.cn摘要:
目的 揭示H1连接子组蛋白基因(H1 linker histone gene,hil-1)的生理学功能,以及其调控线虫寿命的分子机制。 方法 以秀丽隐杆线虫为模式生物,采用RNA干扰菌喂食、hil-1(gk229)突变体回交纯化以及过表达质粒显微注射技术来敲降、敲除以及过表达hil-1基因,然后观察线虫存活寿命及产卵情况,通过热耐受实验、百草枯应激实验和重金属Cr6+应激实验评价hil-1(gk229)突变体的抗逆性,利用实时荧光定量PCR实验以及构建双突变体线虫进一步确定hil-1调控寿命所关联的信号通路和作用靶点。 结果 与野生型N2线虫相比,RNA干扰后的线虫寿命以及hil-1(gk229)突变体线虫寿命明显缩短(P<0.001),而hil-1全身性过表达后线虫寿命延长(P<0.05)。与野生型N2线虫相比,hil-1(gk229)突变体线虫对热压力和氧化压力的耐受性明显降低(P<0.001,P<0.05),而对重金属的耐受能力无差异(P>0.05)。并且,相比于野生型N2线虫,hil-1(gk229)突变体线虫的发育周期缩短(P<0.001),产卵提前(P<0.001),但产卵总量没有显著变化(P>0.05)。给eat-2(ad465)突变体线虫喂食hil-1 RNA干扰菌后,hil-1表达下调不影响eat-2(ad465)突变体线虫的寿命(P>0.05)。相较于野生型N2线虫,hil-1(gk229)突变体线虫中daf-16表达水平明显下调(P<0.001),其下游基因mtl-1和ctl-1表达也下调(P<0.05,P<0.001)。与daf-2(e1370)突变体相比,daf-2(e1370);hil-1(gk229)双突变体线虫的寿命无明显变化(P>0.05);而与daf-16(mu 86)突变体相比,daf-16(mu86);hil-1(gk229)双突变线虫的寿命明显缩短(P<0.001)。与对照组相比,在表皮和肠道中RNA干扰hil-1基因表达后线虫寿命明显缩短(P<0.001)。 结论 hil-1基因缺失明显缩短线虫寿命,同时使线虫对热压力和氧化压力的耐受性降低。hil-1基因可能通过饮食限制信号通路调控秀丽隐杆线虫的寿命,且该作用主要在表皮和肠道。
中图分类号:
成慧, 方菲, 石嘉豪, 杨桦, 张梦杰, 杨平, 费俭. hil-1基因通过饮食限制通路调节秀丽隐杆线虫寿命[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(3): 271-281.
Hui CHENG, Fei FANG, Jiahao SHI, Hua YANG, Mengjie ZHANG, Ping YANG, Jian FEI. H1 Linker Histone Gene Regulates Lifespan via Dietary Restriction Pathways in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 271-281.
基因 Gene | 引物序列 Sequences of primers |
|---|---|
| hil-1 | Forward: 5’-AATGGAACCGGAAGCAGCAA-3’ Reverse: 5’-TCCGCGAGTCTGTTCAATGT-3’ |
| daf-16 | Forward: 5’- GCTCCCTTCACTCGACACTT-3’ Reverse: 5’- TTCGATTGAGTTCGGGGACG-3’ |
| mtl-1 | Forward: 5’- GCTTGCAAGTGTGACTGCAA-3’ Reverse: 5’- TTGATGGGTCTTGTCTCCGC-3’ |
| ctl-1 | Forward: 5’- TACCGAGGAGGGTAACTGGG-3’ Reverse: 5’- AGTCTGTGGATTGCGCTTCA-3’ |
| act-4 | Forward: 5’- GCCACCGCTGCCTCCTCATC-3’ Reverse: 5’- CCGGCAGACTCCATACCCAAGAAG-3’ |
表1 PCR引物序列
Table 1 Prime sequences for PCR
基因 Gene | 引物序列 Sequences of primers |
|---|---|
| hil-1 | Forward: 5’-AATGGAACCGGAAGCAGCAA-3’ Reverse: 5’-TCCGCGAGTCTGTTCAATGT-3’ |
| daf-16 | Forward: 5’- GCTCCCTTCACTCGACACTT-3’ Reverse: 5’- TTCGATTGAGTTCGGGGACG-3’ |
| mtl-1 | Forward: 5’- GCTTGCAAGTGTGACTGCAA-3’ Reverse: 5’- TTGATGGGTCTTGTCTCCGC-3’ |
| ctl-1 | Forward: 5’- TACCGAGGAGGGTAACTGGG-3’ Reverse: 5’- AGTCTGTGGATTGCGCTTCA-3’ |
| act-4 | Forward: 5’- GCCACCGCTGCCTCCTCATC-3’ Reverse: 5’- CCGGCAGACTCCATACCCAAGAAG-3’ |
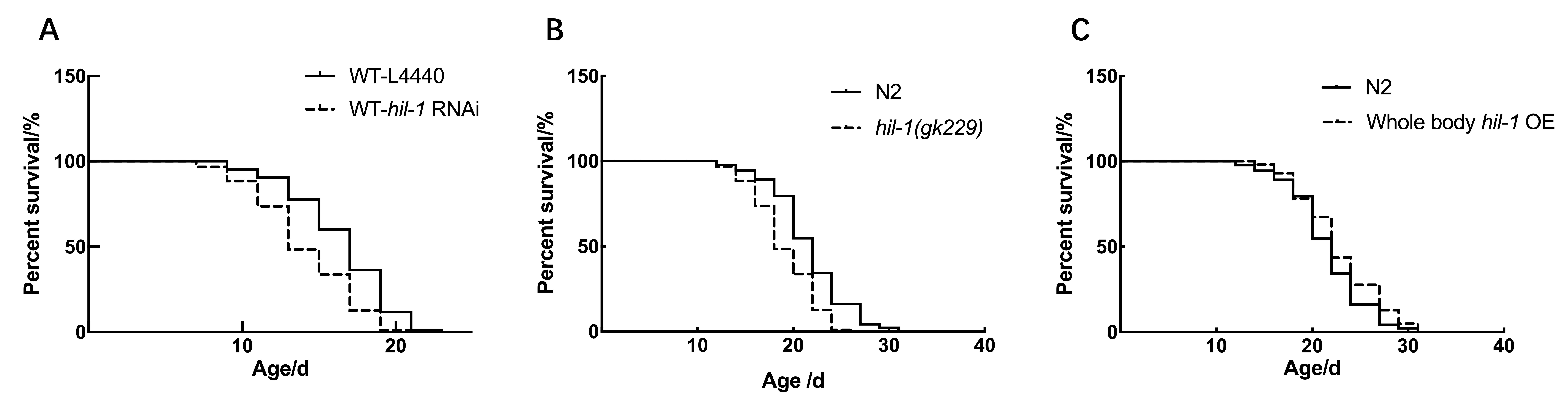
图1 hil-1参与线虫寿命的调控注:A,野生型N2线虫喂食hil-1 RNA干扰(RNAi)菌的生存曲线[与对照组(喂食L4440)相比,P<0.001];B,野生型N2线虫与hil-1(gk229)突变体线虫的生存曲线(与N2线虫相比,P<0.001);C,野生型N2线虫与hil-1全身性过表达线虫(hil-1 OE)的生存曲线(与N2线虫相比,P<0.05)。
Figure 1 hil-1 is involved in regulation of the lifespan in C. elegansNote:A, Survival curves of wild-type N2 worms fed hil-1 RNA interference (RNAi) bacteria [compared with control group (fed L4440), P<0.001]; B, Survival curves of wild-type N2 worms and hil-1(gk229) mutants (compared with N2, P<0.001); C, Survival curves between wild-type N2 nematode and hil-1 systemic overexpression worms (compared with N2 nematode, P<0.05).
线虫种类 C. elegans strains | 线虫数量 Number | 平均寿命 Mean lifespan /d |
|---|---|---|
| N2 | 94 | 22±0.23 |
| hil-1(gk229) | 95 | 18±0.67*** |
| Whole body hil-1 OE | 101 | 22±0.22* |
| daf-2(e1370) | 101 | 47±0.46 |
| daf-2(e1370);hil-1(gk229) | 97 | 47±0.57 |
| daf-16(mu86) | 98 | 15±0.24 |
| daf-16(mu86);hil-1(gk229) | 82 | 14±0.26▲▲▲ |
| N2-L4440 | 85 | 17±0.23 |
| N2-hil-1 RNAi | 95 | 13±0.60△△△ |
| eat-2(ad465)-L4440 | 91 | 26±0.41 |
| eat-2(ad465)-hil-1 RNAi | 103 | 26±0.42 |
| NR350-L4440 | 90 | 16±0.56 |
| NR350-hil-1 RNAi | 95 | 16±0.57 |
| TU3311-L4440 | 101 | 13±0.28 |
| TU3311-hil-1 RNAi | 105 | 13±0.33 |
| NR222-L4440 | 105 | 22±0.27 |
| NR222-hil-1 RNAi | 91 | 17±0.34aaa |
| VP303-L4440 | 91 | 18±0.62 |
| VP303-hil-1 RNAi | 96 | 13±0.44bbb |
| AMJ345-L4440 | 99 | 15±0.21 |
| AMJ345-hil-1 RNAi | 99 | 15±0.23cc |
表2 线虫寿命实验的数据分析
Table 2 Analysis of experimental data of lifespan in C. elegans
线虫种类 C. elegans strains | 线虫数量 Number | 平均寿命 Mean lifespan /d |
|---|---|---|
| N2 | 94 | 22±0.23 |
| hil-1(gk229) | 95 | 18±0.67*** |
| Whole body hil-1 OE | 101 | 22±0.22* |
| daf-2(e1370) | 101 | 47±0.46 |
| daf-2(e1370);hil-1(gk229) | 97 | 47±0.57 |
| daf-16(mu86) | 98 | 15±0.24 |
| daf-16(mu86);hil-1(gk229) | 82 | 14±0.26▲▲▲ |
| N2-L4440 | 85 | 17±0.23 |
| N2-hil-1 RNAi | 95 | 13±0.60△△△ |
| eat-2(ad465)-L4440 | 91 | 26±0.41 |
| eat-2(ad465)-hil-1 RNAi | 103 | 26±0.42 |
| NR350-L4440 | 90 | 16±0.56 |
| NR350-hil-1 RNAi | 95 | 16±0.57 |
| TU3311-L4440 | 101 | 13±0.28 |
| TU3311-hil-1 RNAi | 105 | 13±0.33 |
| NR222-L4440 | 105 | 22±0.27 |
| NR222-hil-1 RNAi | 91 | 17±0.34aaa |
| VP303-L4440 | 91 | 18±0.62 |
| VP303-hil-1 RNAi | 96 | 13±0.44bbb |
| AMJ345-L4440 | 99 | 15±0.21 |
| AMJ345-hil-1 RNAi | 99 | 15±0.23cc |
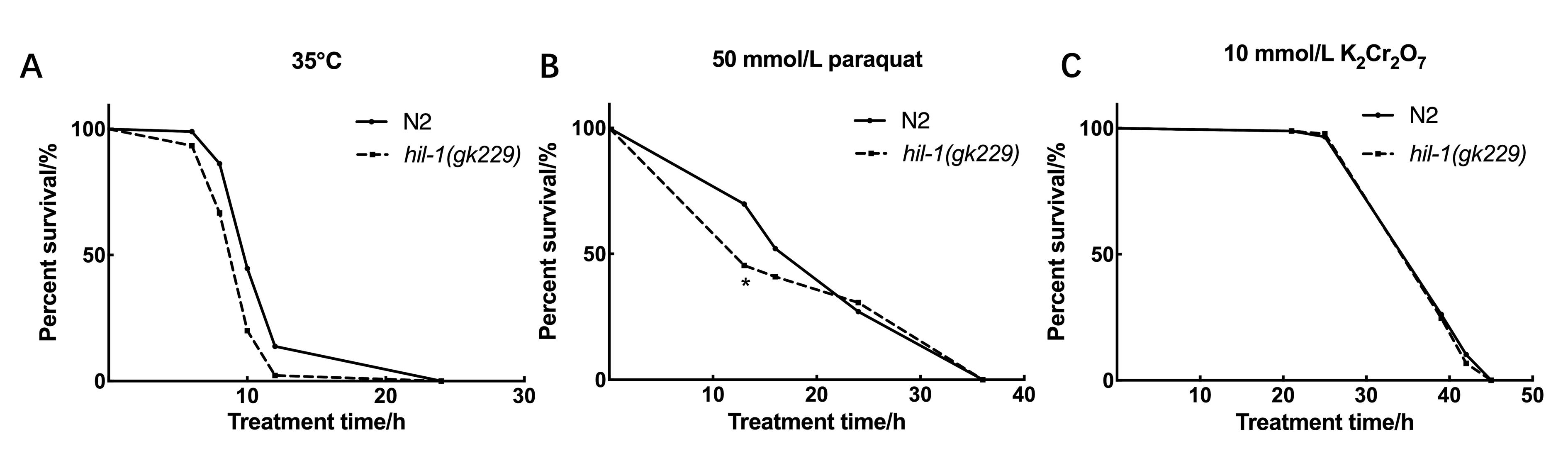
图2 hil-1缺失降低了线虫对热压力和氧化压力的耐受性注:A,野生型N2线虫与hil-1(gk229)突变体线虫从20 ℃转移至35 ℃环境中的生存曲线,P<0.001;B,野生型N2线虫与hil-1(gk229)突变体在50 mmol/L百草枯环境中的生存曲线,*P<0.05;C,野生型N2 线虫与hil-1(gk229)突变体在10 mmol/L K2Cr2O7环境中的生存曲线,P>0.05。
Figure 2 The deletion of hil-1 reduces the tolerance to heat shock and oxidative stress of C. elegansNote:A, Survival curves of wild-type N2 worms and hil-1(gk229) mutant worms transferred from 20 °C to 35 °C, P<0.001; B, Survival curves of wild-type N2 worms and hil-1(gk229) mutant worms exposed to 50 mmol/L paraquat, *P<0.05; C, Survival curves of wild-type N2 worms and hil-1(gk229) mutant worms exposed to 10 mmol/L K2Cr2O7, P>0.05.
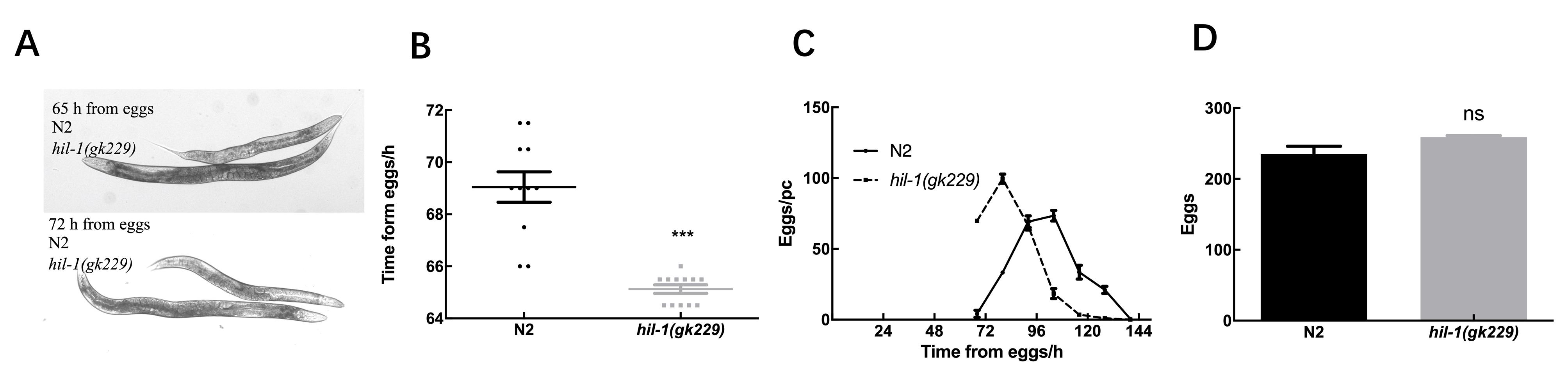
图3 hil-1缺失影响线虫发育注:A,分别在卵发育65 h和72 h 时在显微镜下观察野生型N2线虫和hil-1(gk229)突变体线虫(放大倍数100X);B,野生型N2线虫与hil-1(gk229)突变体线虫从卵发育到产下第一颗卵所用时间,每组各10条线虫,***P<0.001;C,野生型N2线虫与hil-1(gk229)突变体从卵发育开始每12 h平均产卵量,每组均不少于10条线虫;D,野生型N2线虫与hil-1(gk229)突变体平均产卵总量,每组均不少于10条线虫,P>0.05。
Figure 3 The deletion of hil-1 affects the development of C. elegansNote:A, Observing the morphology of eggs of wild-type N2 worms and hil-1(gk229) mutant worms at 65 h and 72 h of development under microscope, with magnification of 100X; B, The duration of wild-type N2 worms and hil-1(gk229) mutant worms from egg to the laying of the first egg, n =10 in each group, ***P<0.001; C, The average number of eggs production every 12 h from egg development in wild-type N2 worms and hil-1(gk229) mutant worms, n > 10 in each group; D, The total number of eggs in wild-type N2 worms and hil-1(gk229) mutant worms. n > 10 in each group, nsP>0.05.
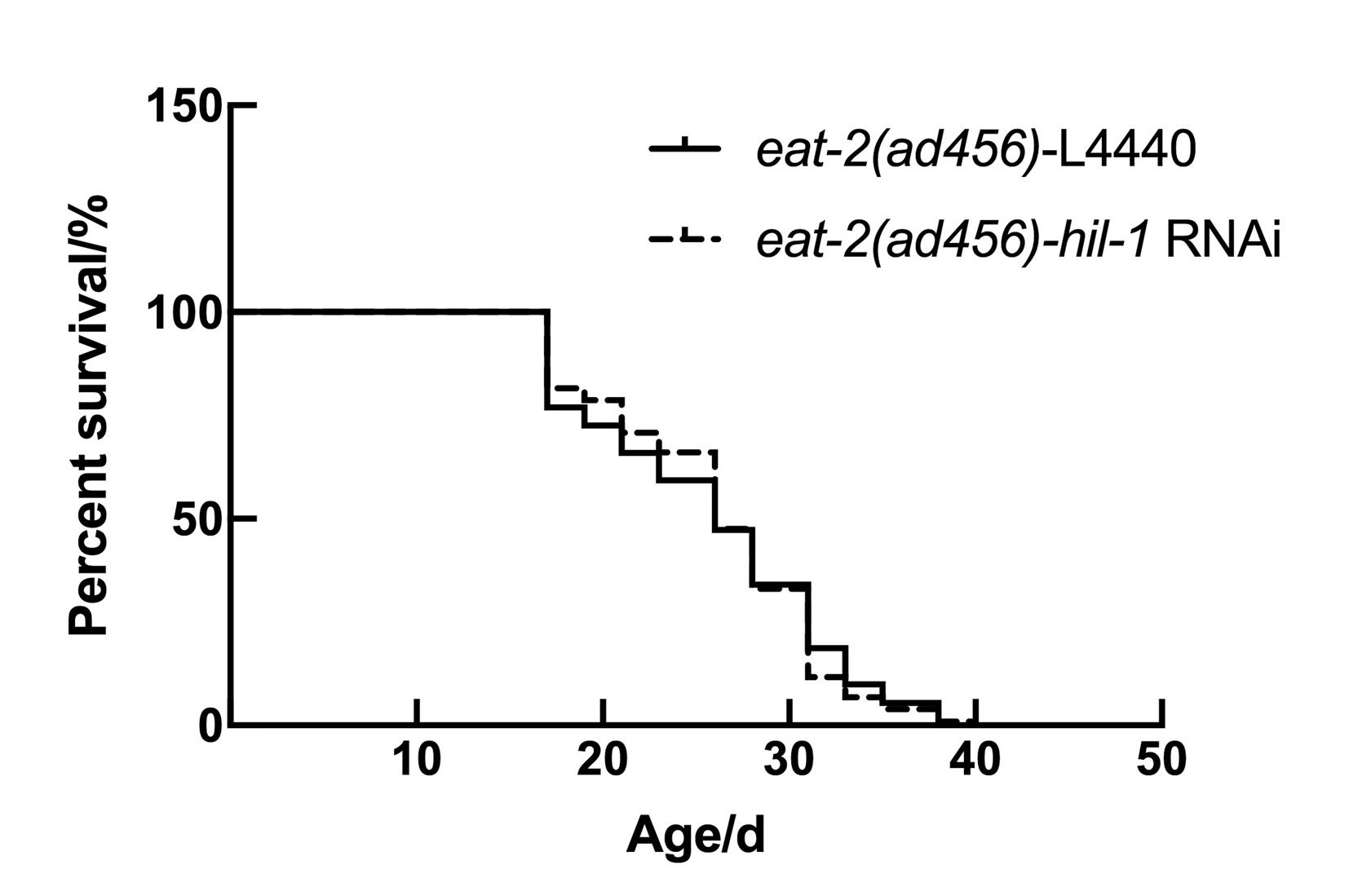
图4 hil-1 敲降不影响eat-2(ad465)突变体寿命注:eat-2(ad465)突变体喂食hil-1 RNA干扰(RNAi)菌的生存曲线。与对照组(喂食L4440)相比,P>0.05。
Figure 4 The knockdown of hil-1 has no significant effect on the lifespan of eat-2(ad465)Note: Survival curves of eat-2(ad465) mutants fed hil-1 RNA interference (RNAi) bacteria. Compared with control group (fed L4440), P>0.05.
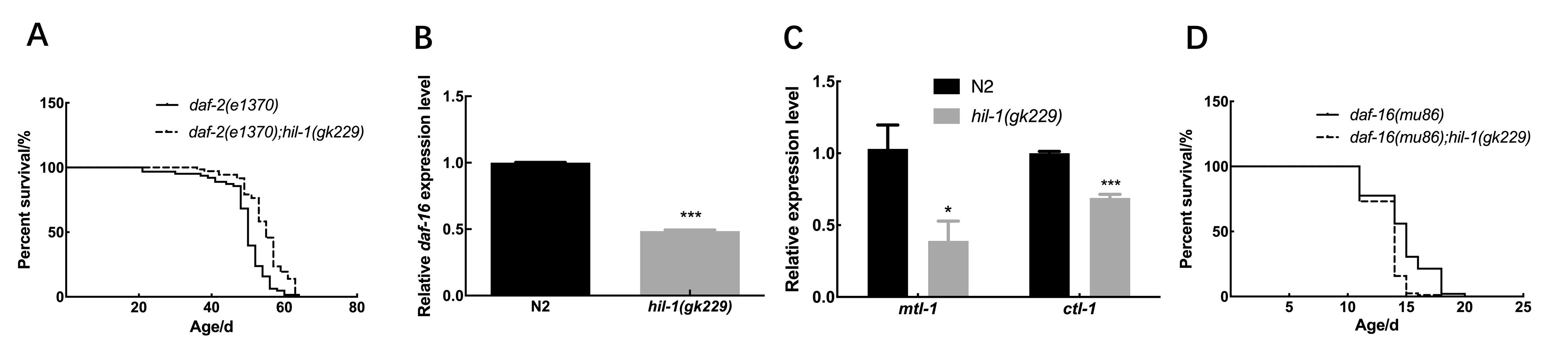
图5 hil-1不完全依赖胰岛素信号通路调控线虫寿命注:A,daf-2(e1370)突变体和daf-2(e1370);hil-1(gk229)双突变体线虫的生存曲线,P>0.05;B,野生型N2线虫和hil-1(gk229)突变体线虫中daf-16的表达量(与N2相比,***P<0.001);C,野生型N2线虫和hil-1(gk229)突变体线虫中daf-16下游靶基因mtl-1和ctl-1的表达(与N2相比,*P<0.05,***P<0.001);D,daf-16 (mu86)突变体和daf-16(mu86);hil-1(gk229)双突变体线虫的生存曲线,P<0.001。
Figure 5 hil-1 is not completely dependent on insulin signaling pathway to regulate lifespan of C. elegansNote:A, Survival curves of daf-2(e1370) mutant worms and daf-2(e1370);hil-1(gk229) mutant worms, P>0.05; B, Analysis of the expression levels of daf-16 gene in wild-type N2 worms and hil-1(gk229) mutant worms(Compared with wild-type N2 worms, ***P<0.001); C, Analysis of the expression levels of daf-16 target genes mtl-1 and ctl-1 in wild-type N2 and hil-1(gk229) mutant worms(compared with wild-type N2 worms *P<0.05,***P<0.001); D, Survival curves of daf-16(mu86) mutant worms and daf-16 (mu86); hil-1(gk229) mutant worms, P<0.001.
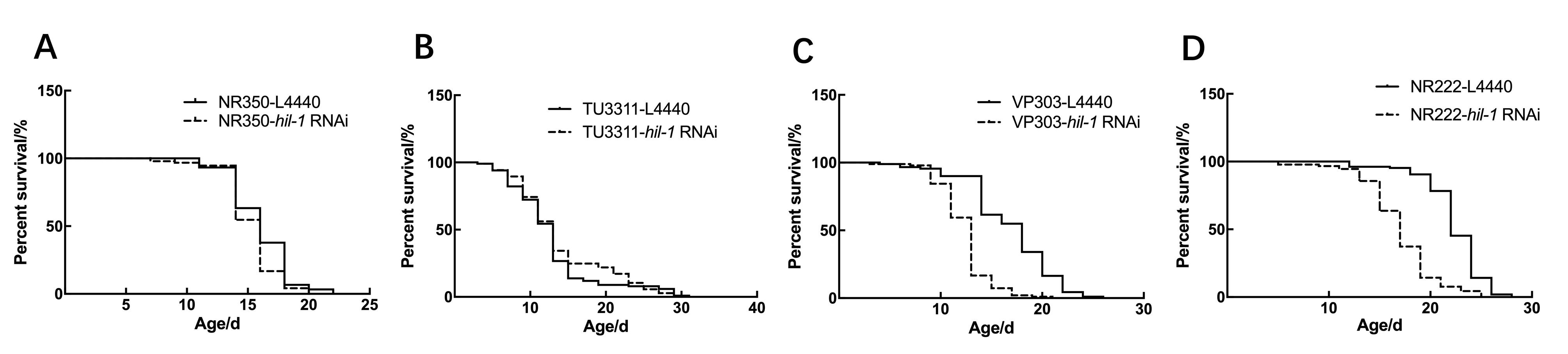
图6 hil-1作用于表皮和肠道调控线虫寿命注:A~D分别为肌肉(A)、神经(B)、表皮(C)和肠道(D)组织特异性RNA干扰(RNAi)线虫饲喂hil-1 RNA干扰菌株后的生存曲线。仅在表皮或者肠道组织降敲hil-1基因表达会显著缩短线虫寿命。
Figure 6 hil-1 acts in the hypodermis or intestine to regulate lifespanNote:A-D, Survival curves of worms with tissue-specific knockdown of hil-1in muscle(A), neuron(B), hypodermis(C) and intestine(D), respectively. Lifespan is shortened only in hypodermis-specific RNA interference (RNAi) or intestine-specific RNAi worms.
| 1 | LÓPEZ-OTÍN C, BLASCO M A, PARTRIDGE L, et al. The hallmarks of aging[J]. Cell, 2013, 153(6):1194-1217. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.039 . |
| 2 | NIGON V M, FÉLIX M A. History of research on C. elegans and other free-living nematodes as model organisms[J]. WormBook, 2017, 2017:1-84. DOI: 10.1895/wormbook.1.181.1 . |
| 3 | HONJOH S, YAMAMOTO T, UNO M, et al. Signalling through RHEB-1 mediates intermittent fasting-induced longevity in C. elegans [J]. Nature, 2009, 457(7230):726-730. DOI: 10.1038/nature07583 . |
| 4 | KENYON C, CHANG J, GENSCH E, et al. A C. elegans mutant that lives twice as long as wild type[J]. Nature, 1993, 366(6454):461-464. DOI: 10.1038/366461a0 . |
| 5 | VELLAI T, TAKACS-VELLAI K, ZHANG Y, et al. Genetics: influence of TOR kinase on lifespan in C. elegans [J]. Nature, 2003, 426(6967):620. |
| 6 | HARRISON D E, STRONG R, DAVE SHARP Z, et al. Rapamycin fed late in life extends lifespan in genetically heterogeneous mice[J]. Nature, 2009, 460(7253):392-395. DOI: 10.1038/nature08221 . |
| 7 | KAEBERLEIN M, POWERS R W 3rd, STEFFEN K K, et al. Regulation of yeast replicative life span by TOR and Sch9 in response to nutrients[J]. Science, 2005, 310(5751):1193-1196. |
| 8 | KENYON C. The plasticity of aging: insights from long-lived mutants[J]. Cell, 2005, 120(4):449-460. |
| 9 | KAPAHI P, ZID B M, HARPER T, et al. Regulation of lifespan in Drosophila by modulation of genes in the TOR signaling pathway[J]. Curr Biol, 2004, 14(10):885-890. |
| 10 | NOLL M, KOROBERG R D. Action of micrococcal nuclease on chromatin and the location of histone H1[J]. J Mol Biol, 1977, 109(3):393-404. DOI: 10.1016/S0022-2836(77)80019-3 . |
| 11 | ALLAN J, HARTMAN P G, CRANE-ROBINSON C, et al. The structure of histone H1 and its location in chromatin[J]. Nature, 1980, 288(5792):675-679. DOI: 10.1038/288675a0 . |
| 12 | HERGETH S P, SCHNEIDER R. The H1 linker histones: multifunctional proteins beyond the nucleosomal core particle[J]. EMBO Rep, 2015, 16(11):1439-1453. DOI: 10.15252/embr.201540749 . |
| 13 | HAO F F, KALE S, DIMITROV S, et al. Unraveling linker histone interactions in nucleosomes[J]. Curr Opin Struct Biol, 2021, 71: S0959-S440X(21)00083-X. DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2021.06.001 . |
| 14 | BHAN S, MAY W, WARREN S L, et al. Global gene expression analysis reveals specific and redundant roles for H1 variants, H1c and H1(0), in gene expression regulation[J]. Gene, 2008, 414(1-2):10-18. DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2008.01.025 . |
| 15 | DI LIEGRO C, SCHIERA G, DI LIEGRO I. H1.0 linker histone as an epigenetic regulator of cell proliferation and differentiation[J]. Genes, 2018, 9(6):310. DOI: 10.3390/genes9060310 . |
| 16 | 石锦平, 任长虹, 李媛, 等. 秀丽隐杆线虫双突变株系hif-1(ia04);glb-13(tm2825)的制备与鉴定[J]. 军事医学, 2011, 35(4):253-257. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-9960.2011.04.004 . |
| SHI J P, REN C H, LI Y, et al. Construction and characterization of double mutant strain hif-1(ia04);glb-13(tm2825) in C.elegans [J]. Military Medical Sciences, 2011, 35(4):253-257. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-9960.2011.04.004 . | |
| 17 | ZHAO Y, GILLIAT A F, ZIEHM M, et al. Two forms of death in ageing Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8:15458. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms15458 . |
| 18 | YANG P, SUN R L, YAO M H, et al. A C-terminal truncated mutation of spr-3 gene extends lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2013, 45(7):540-548. DOI: 10.1093/abbs/gmt048 . |
| 19 | LARANCE M, POURKARIMI E, WANG B, et al. Global proteomics analysis of the response to starvation in C. elegans [J]. Mol Cell Proteomics, 2015, 14(7):1989-2001. DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M114.044289 . |
| 20 | JEDRUSIK M A, VOGT S, CLAUS P, et al. A novel linker histone-like protein is associated with cytoplasmic filaments in Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. J Cell Sci, 2002, 115(Pt 14):2881-2891. |
| 21 | HUANG C, XIONG C J, KORNFELD K. Measurements of age-related changes of physiological processes that predict lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2004, 101(21):8084-8089. |
| 22 | LEE S S, KENNEDY S, TOLONEN A C, et al. DAF-16 target genes that control C. elegans life-span and metabolism[J]. Science, 2003, 300(5619): 644-7. DOI: 10.1126/science.1083614 . |
| 23 | SUN X, CHEN W D, WANG Y D. DAF-16/FOXO transcription factor in aging and longevity [J]. Front Pharmacol, 2017, 8: 548. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00548 . |
| 24 | 尹丹阳, 胡怡, 史仍飞. 动物衰老模型的研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(2): 156-162. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.094 . |
| YIN D Y, HU Y, SHI R F. Advances in animal aging models[J]. Lab Anim Comp Med, 2023, 43(2): 156-162. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.094 . | |
| 25 | HARSHMAN S W, YOUNG N L, PARTHUN M R, et al. H1 histones: current perspectives and challenges[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2013, 41(21):9593-9609. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt700 . |
| 26 | PAN C Y, FAN Y H. Role of H1 linker histones in mammalian development and stem cell differentiation[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2016, 1859(3): S1874-S9399(15)00266-7. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.12.002 . |
| 27 | SUN J, WEI H M, XU J, et al. Histone H1-mediated epigenetic regulation controls germline stem cell self-renewal by modulating H4K16 acetylation[J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6:8856. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9856 . |
| 28 | YANASE S, YASUDA K, ISHII N. Adaptive responses to oxidative damage in three mutants of Caenorhabditis elegans (age-1, mev-1 and daf-16) that affect life span[J]. Mech Ageing Dev, 2002, 123(12):1579-1587. |
| 29 | ANBALAGAN C, LAFAYETTE I, ANTONIOU-KOUROUNIOTI M, et al. Transgenic nematodes as biosensors for metal stress in soil pore water samples[J]. Ecotoxicology, 2012, 21(2):439-455. DOI: 10.1007/s10646-011-0804-0 . |
| 30 | MOILANEN L H, FUKUSHIGE T, FREEDMAN J H. Regulation of metallothionein gene transcription[J]. J Biol Chem, 1999, 274(42):29655-29665. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.274.42.29655 . |
| 31 | LIN C X, ZHANG X Y, SU Z X, et al. Carnosol improved lifespan and healthspan by promoting antioxidant capacity in Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, 2019:5958043. DOI: 10.1155/2019/5958043 . |
| 32 | GREEN C L, LAMMING D W, FONTANA L. Molecular mechanisms of dietary restriction promoting health and longevity[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2022, 23(1):56-73. DOI: 10.1038/s41580-021-00411-4 . |
| 33 | ZHANG Y P, ZHANG W H, ZHANG P, et al. Intestine-specific removal of DAF-2 nearly doubles lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans with little fitness cost[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1):6339. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-33850-4 . |
| 34 | HAHM J H, JEONG C, NAM H G. Diet restriction-induced healthy aging is mediated through the immune signaling component ZIP-2 in Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Aging Cell, 2019, 18(5): e12982. DOI: 10.1111/acel.12982 . |
| 35 | WEIR H J, YAO P, HUYNH F K, et al. Dietary restriction and AMPK increase lifespan via mitochondrial network and peroxisome remodeling[J]. Cell Metab, 2017, 26(6): S1550-S4131(17)30612-5. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.09.024 . |
| 36 | CAI H H, RASULOVA M, VANDEMEULEBROUCKE L, et al. Life-span extension by axenic dietary restriction is independent of the mitochondrial unfolded protein response and mitohormesis in Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2017, 72(10):1311-1318. DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glx013 . |
| 37 | SMITH-VIKOS T, DE LENCASTRE A, INUKAI S, et al. MicroRNAs mediate dietary-restriction-induced longevity through PHA-4/FOXA and SKN-1/Nrf transcription factors[J]. Curr Biol, 2014, 24(19): S0960-S9822(14)00991-9. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.08.013 . |
| [1] | 尹丹阳, 胡怡, 史仍飞. 动物衰老模型的研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(2): 156-162. |
| [2] | 唐慧青, 常书福, 于志锋, 张雷, 谈小倩, 瞿伟, 李亮, 钱珍, 顾坚忠, 徐平. SHJH hr 小鼠部分生物学特性及衰老表型的测定与分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(1): 44-52. |
| [3] | 唐润东, 宋思远, 吴薇. 饮食中糖分控制对雌黑腹果蝇寿命和中肠干细胞的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2019, 39(2): 118-123. |
| [4] | 潘永明, 刘瑞敏, 吴蔚, 王辉, 贾临超, 徐孝平, 朱科燕, 陈民利. 心率变异性分析评估不同因素致亚健康大鼠自主神经功能的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2012, 32(6): 467-472. |
| [5] | 贾临超, 冷晓霞, 陈民利, 潘永明, 寿旗扬, 周卫民, 陶涛, 朱科燕. 抗衰老片对肾虚小鼠空间学习记忆和脑自由基代谢的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2011, 31(6): 432-435. |
| [6] | 谢日青,冷晓霞,陈民利,朱科燕,林琳,陶涛,余佳,潘永明. 束缚应激致亚健康状态大鼠氧自由基变化及中药干预作用[J]. , 2010, 30(2): 121-123. |
| [7] | 沈志祥1, 乔伟伟2, 刘翠鲜1. 营养摄入限制对老年小鼠血甘油三酯及骨密度的影响[J]. , 2006, 26(1): 28-30. |
| [8] | 庄明1,王健2. SD大鼠股外侧肌形态结构及其酶活性的年龄性改变[J]. , 2002, 22(1): 53-55. |
| [9] | 陈冠敏, 林升清, 黄宗锈, 郑丽红, 何聆, 刘少娟. 去氢表雄酮抗衰老作用初探[J]. , 2000, 20(3): 151-153. |
| [10] | 杨斐, 丁宁, 杨昊, 桂立英. 老年雄性大鼠血清总超氧化物歧化酶活性、丙二醛含量和血浆雌二醇、睾酮含量的测定[J]. , 2000, 20(1): 49-51. |
| [11] | 顾德官, 张玉珍. 易卒中自发性高血压大鼠观察[J]. , 1996, 16(3,4): 167-169. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||