













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 112-123.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.167
马婧威( ), 李根, 杨杨, 臧彩霞, 鲍秀琦, 张丹(
), 李根, 杨杨, 臧彩霞, 鲍秀琦, 张丹( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2022-11-30
修回日期:2023-02-11
出版日期:2023-04-25
发布日期:2023-05-16
通讯作者:
张丹(1978—),女,教授,博士生导师,研究方向:新药研发与神经退行性疾病发病机制研究。E-mail:danzhang@imm.ac.cn。ORCID:0000-0001-9792-4549作者简介:马婧威(1998—),女,博士研究生,研究方向:新药活性评价及作用机制研究、神经药理学。E-mail:majingwei@imm.ac.cn
基金资助:
Jingwei MA( ), Gen LI, Yang YANG, Caixia ZANG, Xiuqi BAO, Dan ZHANG(
), Gen LI, Yang YANG, Caixia ZANG, Xiuqi BAO, Dan ZHANG( )(
)( )
)
Received:2022-11-30
Revised:2023-02-11
Published:2023-04-25
Online:2023-05-16
Contact:
ZHANG Dan (ORCID: 0000-0001-9792-4549 ), E-mail: danzhang@imm.ac.cn摘要:
目的 比较并评价环磷酰胺造模后不同恢复期小鼠生精障碍的改善程度。 方法 将48只4~5周龄体质量为18~20 g的ICR雄性小鼠随机分为3个对照组和3个模型组,每组8只。3个模型组的每只小鼠于实验第1~7天连续腹腔注射环磷酰胺60 mg/kg,处理结束后分别继续饲养7 d、14 d和21 d。每个模型组均设相应的对照组,3个对照组小鼠腹腔注射对应体积的生理盐水。各组小鼠在相应时间点通过眼眶静脉采血后处死,取睾丸、附睾和精囊,称重后计算其生殖器官指数。HE染色后比较睾丸和附睾组织病理学变化,精子质量分析测定精子相关指标。ELISA法及相关试剂盒检测血清生殖激素含量、睾丸氧化应激水平和睾丸标志性酶活性变化。 结果 与对照组相比,环磷酰胺处理结束后7 d、14 d和21 d的模型组小鼠睾丸指数均明显下降(P<0.01),7 d、14 d的附睾指数和7 d、21 d的精囊指数明显下降(P<0.05);且随着时间延长,模型组睾丸和附睾组织病理学损伤逐渐减轻。环磷酰胺处理结束后7 d、14 d的模型组精子数量明显减少(P<0.01),血清睾酮水平降低(P<0.05),睾丸中丙二醛含量明显增多(P<0.01),还原型谷胱甘肽含量和超氧化物歧化酶含量明显降低(P<0.05),睾丸标志性酶乳酸脱氢酶活力明显下降(P<0.05),γ-谷氨酰转肽酶活力明显上升(P<0.05);其中7 d的模型组小鼠精子活力明显下降(P<0.001),精子畸形率明显上升(P<0.05),血清促卵泡素和促黄体生成素明显增加(P<0.01)。21 d的模型组小鼠精子相关指标、血清生殖激素水平、睾丸氧化应激水平和睾丸标志性酶活性变化均不明显(均P>0.05)。 结论 环磷酰胺60 mg/kg连续腹腔注射7 d,注射结束后7 d所致小鼠生殖毒性较为明显,能够构建较理想的小鼠生精障碍模型;而随着恢复期的延长,至环磷酰胺处理结束后21 d小鼠生精障碍各项指标逐渐恢复,接近正常水平。
中图分类号:
马婧威, 李根, 杨杨, 臧彩霞, 鲍秀琦, 张丹. 环磷酰胺诱导生精障碍小鼠模型不同恢复期的比较研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(2): 112-123.
Jingwei MA, Gen LI, Yang YANG, Caixia ZANG, Xiuqi BAO, Dan ZHANG. Comparative Study on Different Recovery Periods of the Spermatogenic Dysfunction Mouse Model Induced by Cyclophosphamide[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 112-123.
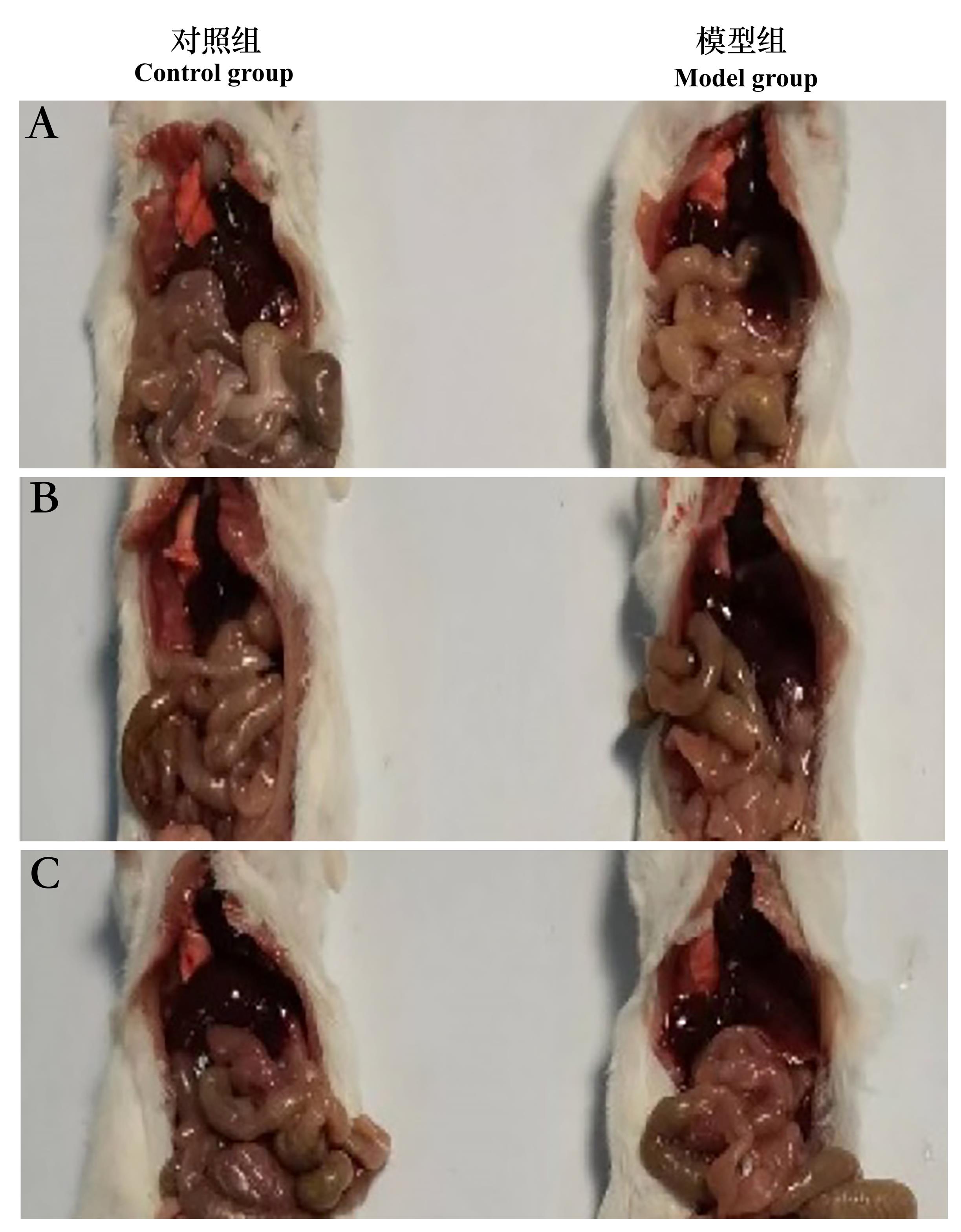
图1 环磷酰胺给药诱导生精障碍模型后7 d(A)、14 d(B)和21 d(C)的小鼠体内器官状态
Figure 1 In-vivo organ state of spermatogenic dysfunction mice on the 7th(A),14th(B) and 21st(C)day after cyclophosphamide administration
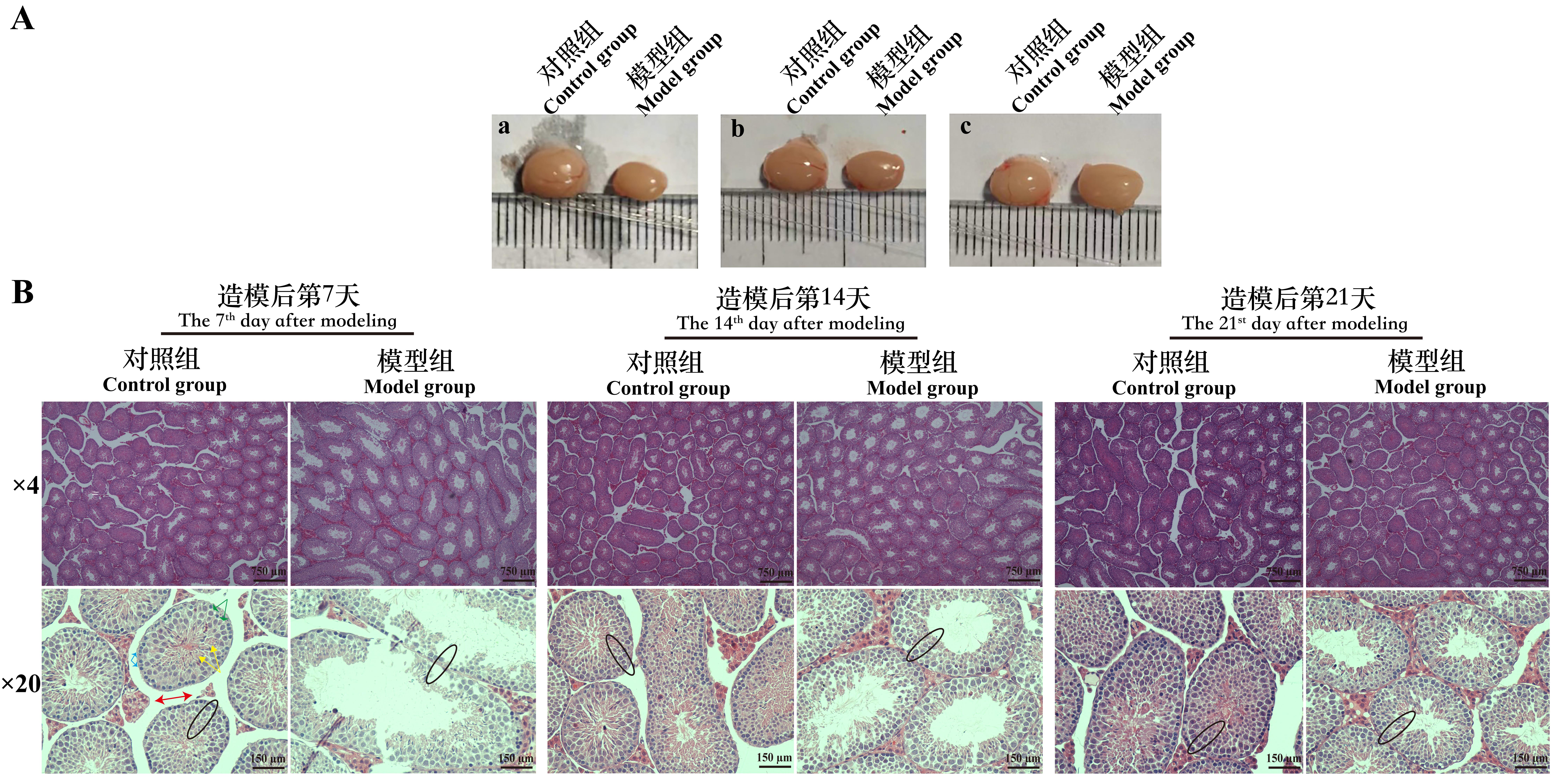
图2 环磷酰胺给药诱导生精障碍模型后7、14和21 d的小鼠睾丸外观(A)和睾丸组织病理学(B)变化(HE染色)注:红色箭头指示间质细胞;蓝色箭头指示精原细胞;绿色箭头指示精母细胞;黄色箭头指示精细胞;线圈表示生精细胞层数。
Figure 2 The changes of testicular appearance(A) and testicular histopathology (B) of spermatogenic dysfunction mice on the 7th, 14th and 21st day after cyclophosphamide administration (HE staining)Note: The red arrow indicates interstitial cells; the blue arrow indicates spermatogonium; the green arrow indicates spermatocyte; the yellow arrow indicates spermatid; the coil represents the number of spermatogenic cell layer.
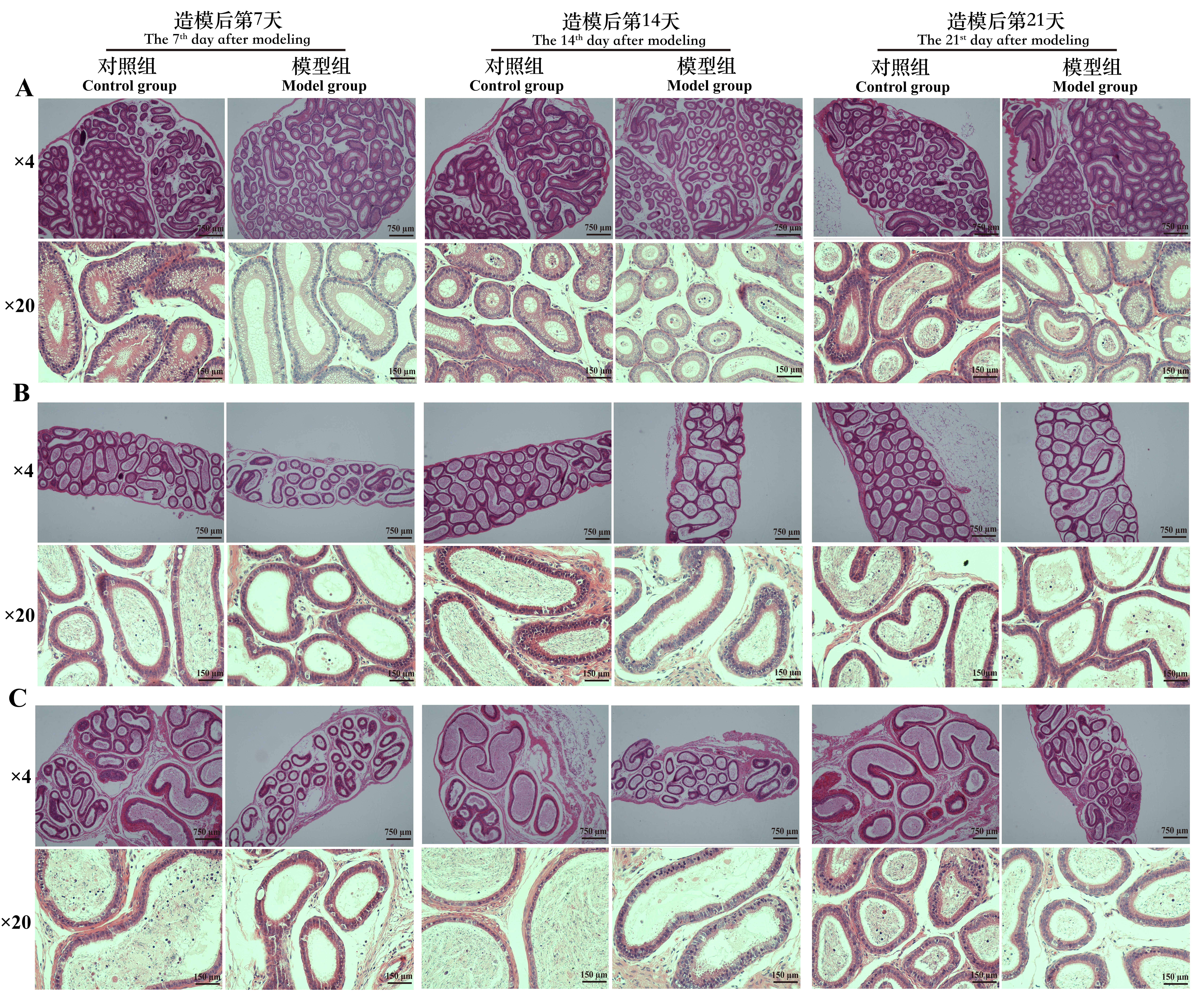
图3 环磷酰胺给药诱导生精障碍模型后7、14和21 d的小鼠附睾组织头部(A)、体部(B)和尾部(C)病理学变化(HE染色)
Figure 3 Pathological changes of epididymal head (A), body (B) and tail (C) of spermatogenic dysfunction mice on the 7th, 14th and 21st day after cyclophosphamide administration (HE staining)
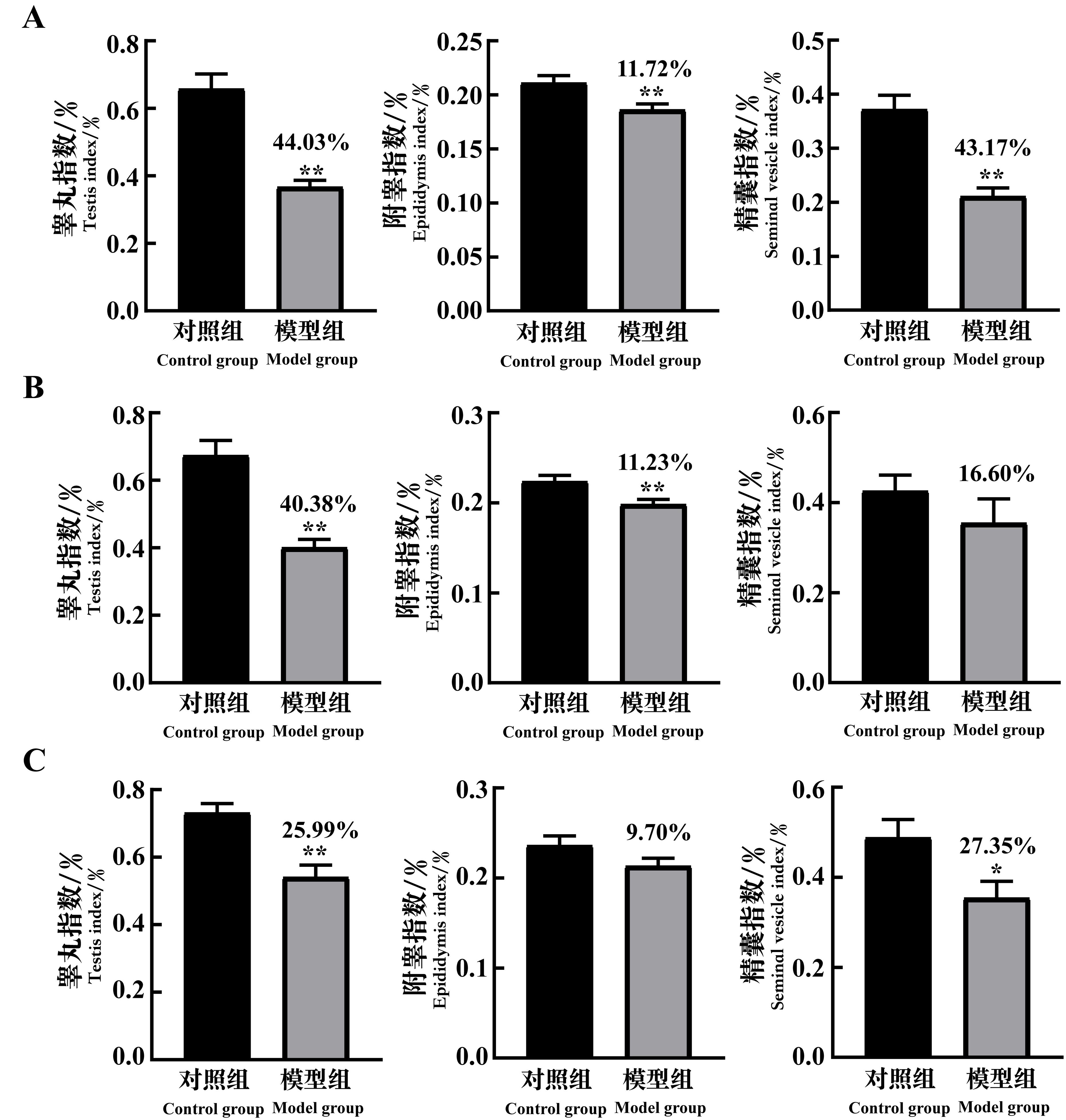
图4 环磷酰胺给药诱导生精障碍模型后7 d(A)、14 d(B)和21 d(C)的小鼠生殖器官指数变化注:每组小鼠n=8。与对照组相比,*P<0.05,**P<0.01。模型组上方数据为与对照组比较的下降百分比。
Figure 4 The changes of reproductive organ index of spermatogenic dysfunction mice on the 7th(A), 14th(B)and 21st(C)day after cyclophosphamide administrationNote: In each group, n=8. Compared with the control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. The data above the model group is the percentage decline compared with the control group.
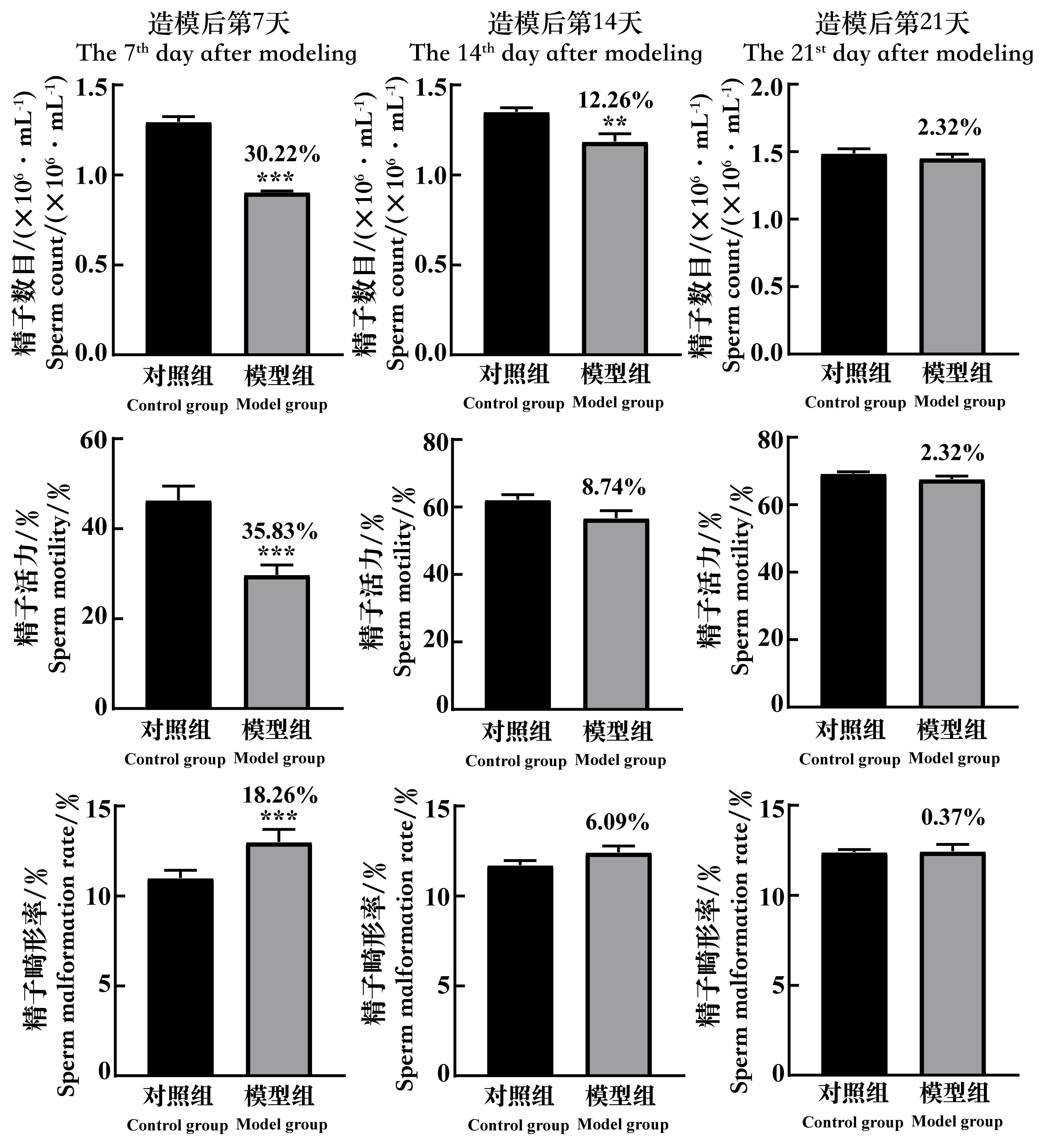
图5 环磷酰胺给药诱导生精障碍模型后7、14和21 d的小鼠精子数目、精子活力和精子畸形率的变化注:每组小鼠n=8。与对照组相比,**P<0.01,***P<0.001。模型组上方数据为与对照组比较的下降百分比。
Figure 5 The changes of the sperm count, the sperm motility and the rate of sperm malformation of spermatogenic dysfunction mice on the 7th, 14th and 21st day after cyclophosphamide administrationNote:In each group, n=8. Compared with the control group, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. The data above the model group is the percentage decline compared with the control group.
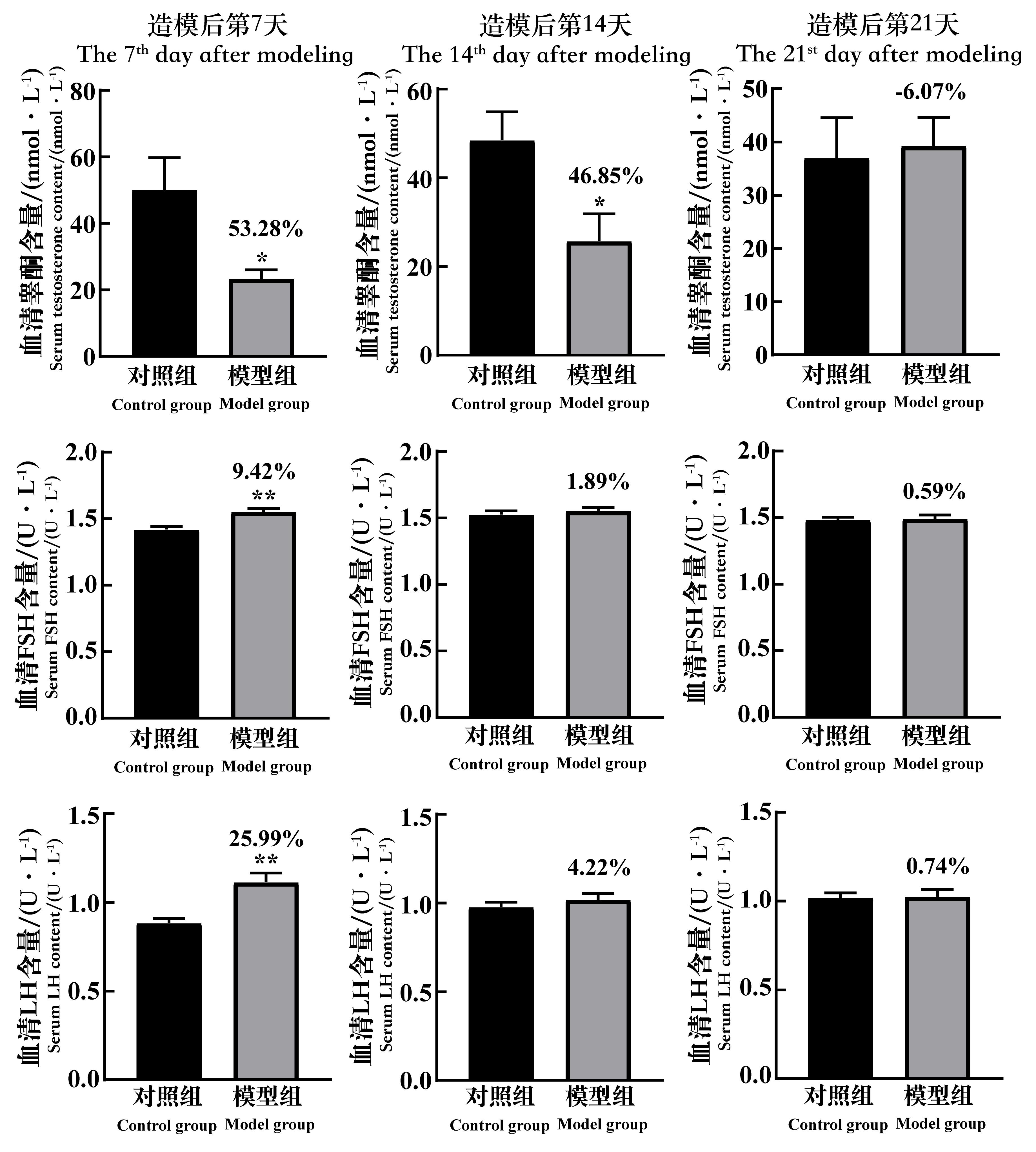
图6 环磷酰胺给药诱导生精障碍模型后7、14和21 d的小鼠血清睾酮、促卵泡素和促黄体生成素含量的变化注:FSH,促卵泡素;LH,促黄体生成素。每组小鼠n=8。与对照组相比,*P<0.05,**P<0.01。模型组上方数据为与对照组比较的下降百分比。
Figure 6 The changes of the serum testosterone content, FSH content and LH content of spermatogenic dysfunction mice on the 7th, 14th and 21st day after cyclophosphamide administrationNote:FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone; LH, luteinizing hormone. In each group, n=8. Compared with the control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01.The data above the model group is the percentage decline compared with the control group.
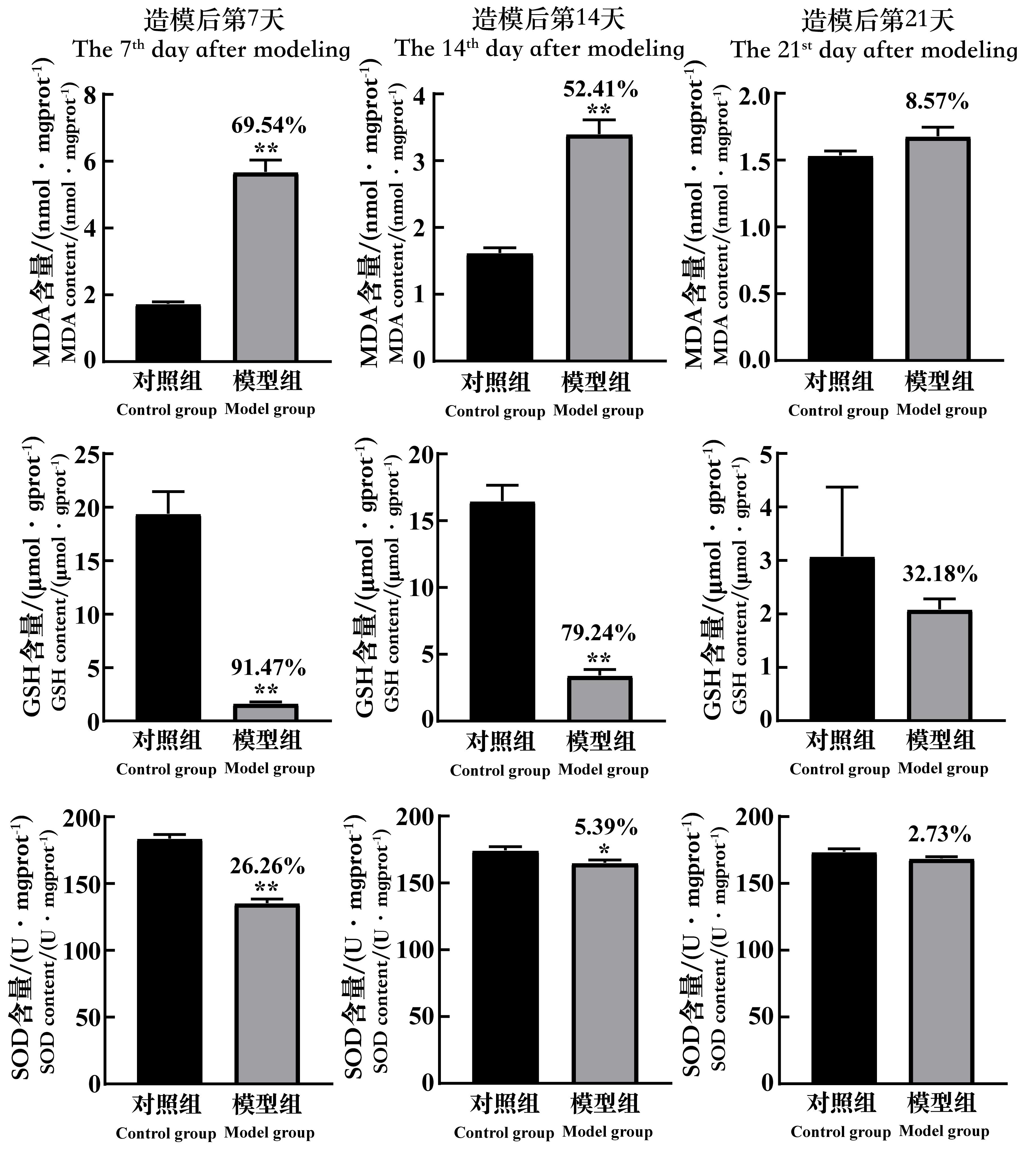
图7 环磷酰胺给药诱导生精障碍模型后7、14和21 d的小鼠睾丸组织MDA、GSH和SOD含量的变化注:MDA,丙二醛;GSH,还原型谷胱甘肽;SOD,超氧化物歧化酶;mgprot(gprot),每毫克(克)蛋白。每组小鼠n=8。与对照组相比,*P<0.05,**P<0.01。模型组上方数据为与对照组比较的下降百分比。
Figure 7 The changes of the MDA, GSH and SOD content in testicular tissue of spermatogenic dysfunction mice on the 7th, 14th and 21st day after cyclophos-phamide administrationNote:MDA,malonaldehyde;GSH,glutathione;SOD, superoxide dismutase; mgprot/gprot, per 1 mg (g) protein. In each group,n=8. Compared with the control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. The data above the model group is the percentage decline compared with the control group.
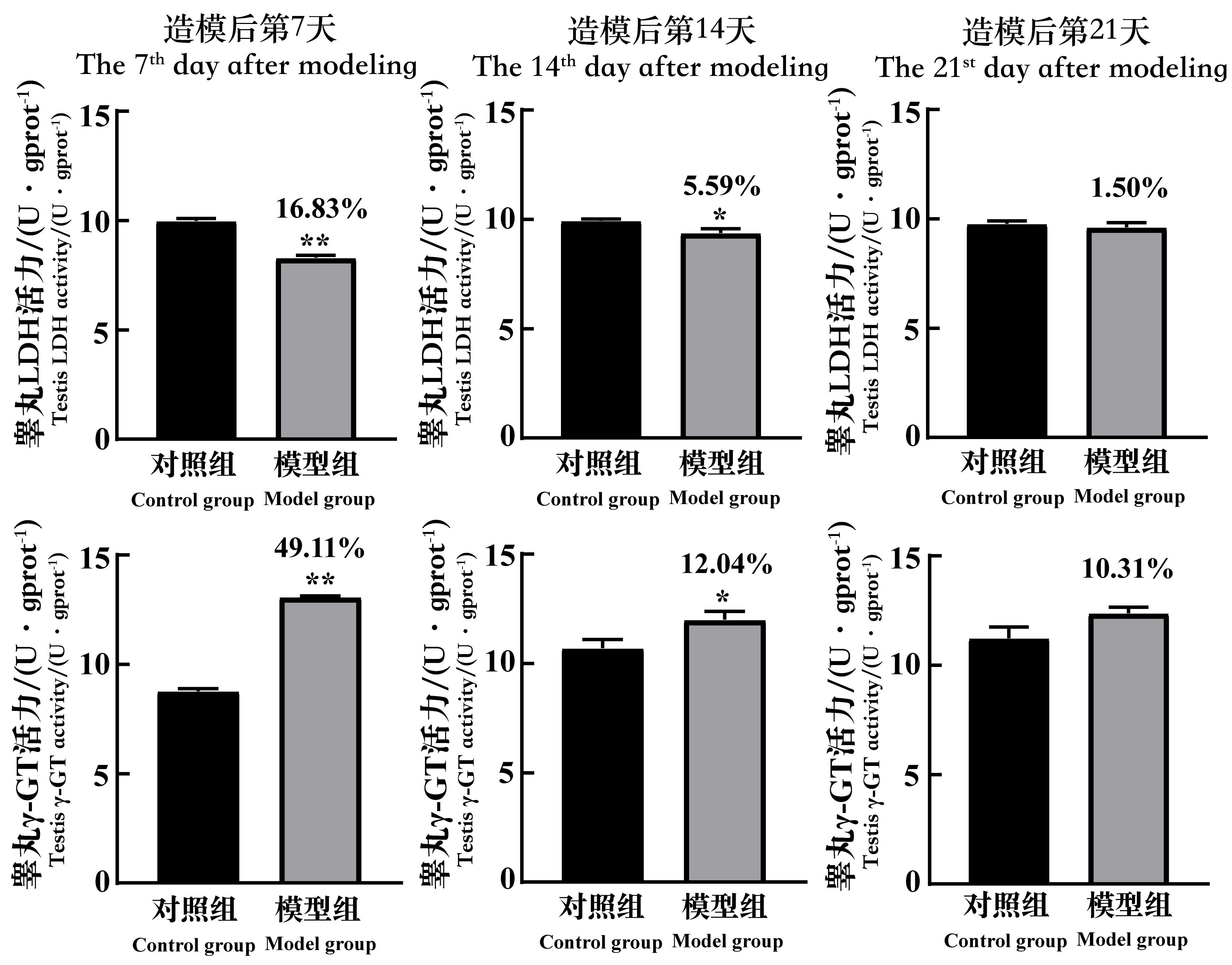
图8 环磷酰胺给药诱导生精障碍模型后7、14和21 d的小鼠睾丸组织LDH和γ-GT活力的变化注:LDH,乳酸脱氢酶;γ-GT,γ-谷氨酰基转移酶;mgprot(gprot),每毫克(克)蛋白。每组小鼠n=8。与对照组相比,*P<0.05,**P<0.01。模型组上方数据为与对照组比较的下降百分比。
Figure 8 The changes of the LDH and γ-GT activity in testicular tissue of spermatogenic dysfunction mice on the 7th, 14th and 21st day after cyclophosphamide administrationNote:LDH, lactic dehydrogenase; γ-GT, gamma-glutamyl-trans-ferase; mgprot (gprot), per 1 mg(g) protein. In each group, n=8. Compared with the control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. The data above the model group is the percentage decline compared with the control group.
| 1 | 王梦梦, 克迎迎, 李亚格, 等. 杜仲补天素胶囊改善环磷酰胺诱导的小鼠生精障碍研究[J]. 中草药, 2019, 50(11): 2625-2631. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2019.11.018 . |
| WANG M M, KE Y Y, LI Y G, et al. Effect of Duzhong Butiansu Capsule on improving spermatogenesis obstacle in mice induced by cyclophosphamide[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2019, 50(11): 2625-2631. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2019.11.018 . | |
| 2 | 阚玉璇, 曾梦楠, 张贝贝, 等. 杜仲补天素胶囊对己烯雌酚诱导雄性小鼠生精障碍的实验研究[J]. 中成药, 2020, 42(9):2445-2451. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2020.09.037 . |
| KAN Y X, ZENG M N, ZHANG B B, et al. Experimental study of Eucommia ulmoides Butiansu capsule on spermatogenic disorder induced by diethylstilbestrol in male mice[J]. Chin Tradit Pat Med, 2020, 42(9):2445-2451. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2020.09.037 . | |
| 3 | 李环, 曲振廷, 钱鸿昊, 等. 人参皂苷Rg1联合人参皂苷Rg3对雄性生殖功能损伤模型小鼠生殖功能的改善作用[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2020, 46(4):707-713. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20200407 . |
| LI H, QU Z T, QIAN H H, et al. Improvement effect of ginsenoside Rg1 combined with ginsenoside Rg3 on reproductive function in male model mice with reproductive function injury[J]. J Jilin Univ Med Ed, 2020, 46(4):707-713. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20200407 . | |
| 4 | 陈指龙, 张晓春, 薛立群, 等. 环磷酰胺致小鼠生精障碍作用研究[J]. 动物医学进展, 2017, 38(5):34-38. DOI: 10.16437/j.cnki.1007-5038.2017.05.008 . |
| CHEN Z L, ZHANG X C, XUE L Q, et al. Effect of cyclophosphamide on mouse spermatogenic obstacles[J]. Prog Vet Med, 2017, 38(5):34-38. DOI: 10.16437/j.cnki.1007-5038.2017.05.008 . | |
| 5 | 舒淇琳, 王梅, 曹国琼, 等. 杜仲补天素丸对环磷酰胺诱导的生精障碍保护作用[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2022, 33(9):2119-2121. |
| SHU Q L, WANG M, CAO G Q, et al. Protective effect of Duzhongbutiansuwan on spermatogenesis induced by cyclophosphamide[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2022, 33(9):2119-2121. | |
| 6 | FAN Q G, ZHAO Z Y, MENG Q, et al. Improvement of astragalin on spermatogenesis in oligoasthenozoospermia mouse induced by cyclophosphamide[J]. Reprod Sci, 2022, 29(6):1738-1748. DOI: 10.1007/s43032-021-00808-8 . |
| 7 | DOHLE G R. Male infertility in cancer patients: review of the literature[J]. Int J Urol, 2010, 17(4):327-331. DOI: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2010.02484.x . |
| 8 | ELANGOVAN, CHIOU T J W., TZENG W F, et al.Cyclo-phosphamide treatment causes impairment of sperm and its fertilizing ability in mice[J]. Toxicology, 2006, 222(1-2):60-70. DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2006.01.027 . |
| 9 | SELVAKUMAR E, PRAHALATHAN C, SUDHARSAN P T, et al. Protective effect of lipoic acid on cyclophosphamide-induced testicular toxicity[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2006, 367(1-2):114-119. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2005.11.034 . |
| 10 | FUKUTANI K, ISHIDA H, SHINOHARA M, et al. Suppression of spermatogenesis in patients with Behçet's disease treated with cyclophosphamide and colchicine[J]. Fertil Steril, 1981, 36(1):76-80. DOI: 10.1016/S0015-0282(16)45622-0 . |
| 11 | SAPKOTA Y, WILSON C L, ZAIDI A K, et al. A novel locus predicts spermatogenic recovery among childhood cancer survivors exposed to alkylating agents[J]. Cancer Res, 2020, 80(17):3755-3764. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-0093 . |
| 12 | SIMON, HOWELL, MRCP, et al. Gonadal damage from chemotherapy and radiotherapy[J]. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am, 1998, 27(4):927-943. DOI: 10.1016/S0889-8529(05)70048-7 . |
| 13 | EN L T, BROUGHAM M F H, WALLACE W H B, et al. Impacts of platinum-based chemotherapy on subsequent testicular function and fertility in boys with cancer[J]. Hum Reprod Update, 2020, 26(6):874-885. DOI: 10.1093/humupd/dmaa041 . |
| 14 | SUN Y M, GAO F, XU D, et al. Wenshen Shengjing Decoction improves early embryo development by maintaining low H3K27me3 levels in sperm and pronuclear embryos of spermatogenesis impaired mice[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2021, 2021:8035997. DOI: 10.1155/2021/8035997 . |
| 15 | 刘建国, 赵红乐, 李姣姣, 等. 补肾活血方对环磷酰胺所致小鼠睾丸生精细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中华男科学杂志, 2020, 26(9):826-831. DOI: 10.13263/j.cnki.nja.2020.09.012 . |
| LIU J G, ZHAO H L, LI J J, et al. Bushen Huoxue Recipe reduces cyclophosphamide-induced apoptosis of spermatogenic cells in mice[J]. Natl J Androl, 2020, 26(9):826-831. DOI: 10.13263/j.cnki.nja.2020.09.012 . | |
| 16 | 范红艳, 江素鑫, 李乐乐, 等. CTX对雄性小鼠生殖功能的影响及杨梅素的干预研究[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2019, 35(5):43-46. DOI: 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2019.05.010 . |
| FAN H Y, JIANG S X, LI L L, et al. Influence of cyclophosphamide on reproductive function of male mice and intervention of myricetin[J]. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Med, 2019, 35(5):43-46. DOI: 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2019.05.010 . | |
| 17 | YAN G, TIAN F, LIU P, et al. Sheng Jing Decoction can promote spermatogenesis and increase sperm motility of the oligozoospermia mouse model[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2021, 2021:3686494. DOI: 10.1155/2021/3686494 . |
| 18 | 李勋, 陈建设, 门波, 等. 益肾通络方调控PI3K/Akt通路对环磷酰胺诱导无精/少精症大鼠模型的保护作用研究[J]. 天津医药, 2020, 48(12):1159-1164. DOI: 10.11958/20201749 . |
| LI X, CHEN J S, MEN B, et al. The protective effect of Yishen Tongluo Fang regulating PI3K/Akt pathway on the azoospermia/oligozoospermia model rats induced by cyclophosphamide[J]. Tianjin Med J, 2020, 48(12):1159-1164. DOI: 10.11958/20201749 . | |
| 19 | 伍欢, 李其闯, 贾欣, 等. 环磷酰胺对小鼠精子质量及相关酶的影响[J]. 科教文汇(上旬刊), 2018(9):181-183. DOI: 10.16871/j.cnki.kjwha.2018.09.076 . |
| WU H, LI Q C, JIA X, et al. Effect of cyclophosphamide on sperm quality and related enzymes in mice[J]. Sci Educ Article Collects, 2018(9):181-183. DOI: 10.16871/j.cnki.kjwha.2018.09.076 . | |
| 20 | 王慧慧, 张莉, 徐瑞豪, 等. 杜仲补天素胶囊对白消安诱导的生精障碍小鼠的影响[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2020, 31(2):169-178. DOI: 10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2020.02.008 . |
| WANG H H, ZHANG L, XU R H, et al. Effect of Duzhong Butiansu capsule on busulfan-induced spermatogenic impairment in mice[J]. Tradit Chin Drug Res Clin Pharmacol, 2020, 31(2):169-178. DOI: 10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2020.02.008 . | |
| 21 | 曹兵, 孙亚萍, 司彦坡, 等. 杜仲补天素胶囊对双酚A诱导小鼠生精障碍的保护作用研究[J]. 中国新药杂志, 2020, 29(3):343-351. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3734.2020.03.018 . |
| CAO B, SUN Y P, SI Y P, et al. Protective effect of Duzhong Butiansu capsules on bisphenol A-induced spermatogenic disorder in mice[J]. Chin J New Drugs, 2020, 29(3):343-351. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3734.2020.03.018 . | |
| 22 | 蒋福兴. 血睾屏障体内动态变化细胞生物学机制的研究[D]. 北京: 首都师范大学, 2008. |
| JIANG F X. A study on the cellular biological mechanisms of dynamic changes in the blood testis barrier in vivo [D]. Beijing: Capital Normal University, 2008. | |
| 23 | QIAN L, YU S J. Protective effect of polysaccharides from Lycium barbarum on spermatogenesis of mice with impaired reproduction system induced by cyclophosphamide[J]. Am J Reprod Immunol, 2016, 76(5):383-385. DOI: 10.1111/aji.12558 . |
| 24 | NOOH M M, RIZK S M, SAIED N M, et al. Carnosine remedial effect on fertility of male rats receiving cyclophosphamide, hydroxydaunomycin, oncovin and prednisone (CHOP)[J]. Andrologia, 2021, 53(11): e14233. DOI: 10.1111/and.14233 . |
| 25 | 龚晓娟, 马盼, 孙敏, 等. DRD1基因敲除影响雄鼠生育的分子机理研究[J]. 实验动物科学, 2021, 38(2):53-56, 60. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6179.2021.02.009 . |
| GONG X J, MA P, SUN M, et al. Study on molecular mechanism of male mice reproduction in DRD1 knockout[J]. Lab Anim Sci, 2021, 38(2):53-56, 60. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6179.2021.02.009 . | |
| 26 | SOLOMON R, ABUMADIGHEM A, KAPELUSHNIK J, et al. Involvement of cytokines and hormones in the development of spermatogenesis in vitro from spermatogonial cells of cyclophosphamide-treated immature mice[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(4):1672. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22041672 . |
| 27 | CAO Y C, WANG X S, LI S Q, et al. The effects of l-carnitine against cyclophosphamide-induced injuries in mouse testis[J]. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol, 2017, 120(2):152-158. DOI: 10.1111/bcpt.12679 . |
| 28 | 乐小炎, 原林, 林少杰, 等. 乌贼墨多糖的制备及对睾丸化疗性损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品工业科技, 2013, 34(17):342-344, 348. DOI: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2013.17.003 . |
| LE X Y, YUAN L, LIN S J, et al. Preparation of squid ink polysaccharides and its protection against chemo-therapeutic injury on testis[J]. Sci Technol Food Ind, 2013, 34(17):342-344, 348. DOI: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2013.17.003 . | |
| 29 | 范红艳, 王艳春, 顾饶胜, 等. 生精障碍动物模型的研究进展[J]. 吉林医药学院学报, 2013, 34(2):120-123. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2995.2013.02.017 . |
| FAN H Y, WANG Y C, GU R S, et al. Research of the animal model of spermatogenic abnormalities[J]. J Jilin Med Coll, 2013, 34(2):120-123. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2995.2013.02.017 . | |
| 30 | 宿文辉, 张天彪, 张丽雁, 等. Rab13 GTPase在大鼠睾丸中的表达及其与生精上皮周期的关系[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2010, 18(5):402-405, 358. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2010.05.09 . |
| SU W H, ZHANG T B, ZHANG L Y, et al. Expression of Rab13 GTPase in rat testis and its relation with seminiferous epithelium cycle[J]. Acta Lab Anim Sci Sin, 2010, 18(5):402-405, 358. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2010.05.09 . |
| [1] | 任晨吟, 高思琦, 李浩, 唐标, 杨华, 刘月环. 两株CRISPR工程大肠埃希菌在小鼠体内的定植实验研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2022, 42(6): 541-550. |
| [2] | 宋莹, 郭雅娟, 黄铭倩, 梁金强, 黄芝瑛. 不同因素对环磷酰胺诱导的免疫抑制小鼠模型效果的影响[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2017, 37(1): 36-39. |
| [3] | 顾云浩, 曹晨洁, 胡碧原, 王俊, 韩东冬, 许爱华. PFC体内递增诱导建立S180肿瘤多药耐药模型及其稳定性观察[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2015, 35(5): 367-373. |
| [4] | 李浩, 籍国霞, 王可洲, 嵇传良, 李兰波, 张燕, 冯墨竹, 李建梅, 刘涛. 阿胶对环磷酰胺所致血虚证模型小鼠毛发生长及发质影响的研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2015, 35(1): 17-22. |
| [5] | 隋在云, 刘瑾, 李晓晶. 莱阳沙参茎叶不同提取物对环磷酰胺损伤小鼠的免疫调节作用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2012, 32(5): 411-413. |
| [6] | 黄彩玲1,林勇1,肖柳英2,潘竞锵2,张丹2. 青蒿琥酯对S180荷瘤小鼠免疫调节的作用及机制初探[J]. , 2010, 30(2): 145-148. |
| [7] | 寿旗扬,应华忠,周卫民,陈民利,林琳. 两种方法注射环磷酰胺致小鼠白细胞减少症模型的比较[J]. , 2008, 28(4): 266-268. |
| [8] | 刘香梅,张钰,闵凡贵,赵维波,刘忠华,黄韧,HUANG Ren. 环磷酰胺对近平滑念珠菌感染小鼠白细胞的影响[J]. , 2007, 27(2): 116-118. |
| [9] | 潘华,杨丽萍,周文江. 金高尔胶囊对ICR小鼠食物利用率和生长发育的影响[J]. , 2003, 23(2): 99-102. |
| [10] | 王胜昌,谢建云,邵伟娟,高诚. 弓形虫PCR检测方法的建立及初步应用[J]. , 2003, 23(1): 15-17. |
| [11] | 王仁礼, 蒋秀蓉, 张燕林, 张忠恕. 诱变剂诱导的精子染色体异常及其对胚胎发育的影响[J]. , 1999, 19(1): 18-21. |
| [12] | 赵喜新1, 阎杜海1, 王和平2, 田开宇1, 杜彩霞1. 环磷酰胺引致的小鼠白细胞减少模型及动力学分析[J]. , 1998, 18(1): 12-14. |
| [13] | 章凌1, 龚华明1, 潘振业1, 朱晴晖2, 段玲琴2. 不同品系小鼠脾细胞中膜白细胞介素-2受体阳性细胞的检测和参考值[J]. , 1994, 14(3,4): 170-172. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||