
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 473-482.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.181
• Facilities and Management for Laboratory Animals • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Tingjun1, LUO Hao2, CHEN Qi1( )
)
Received:2024-12-03
Revised:2025-04-19
Online:2025-08-25
Published:2025-09-01
Contact:
CHEN Qi
CLC Number:
WANG Tingjun,LUO Hao,CHEN Qi. Discussion on AI-Based Digital Upgrade and Application Practice of Laboratory Animal Centers[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 473-482. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.181.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.181
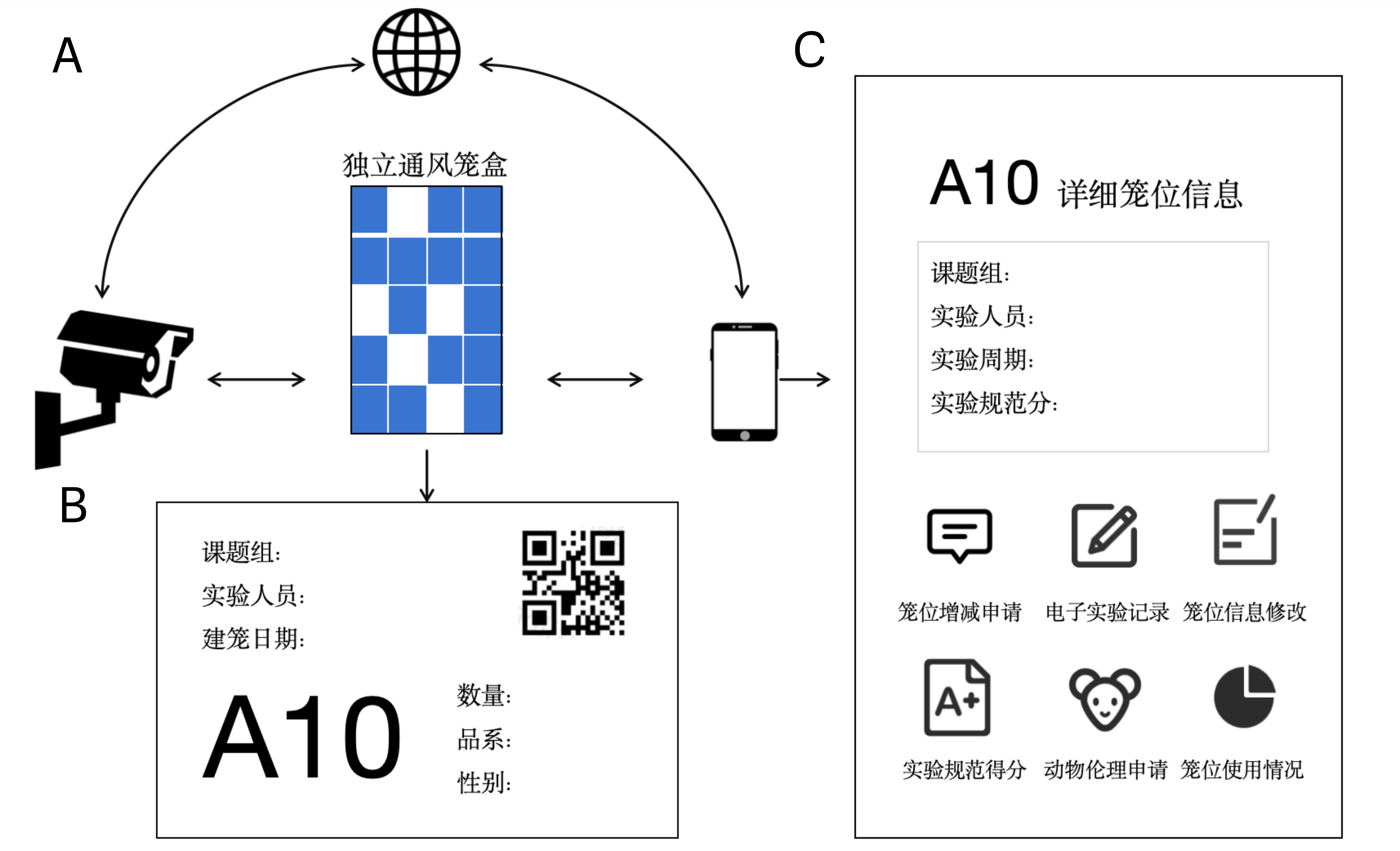
Figure 1 Composite diagram of artificial intelligence cage positioning modeNote: Artificial intelligence cage positioning system diagram (A), QR code cage positioning card (B), cage management system interface (C).
对比项目 Comparison items | 本方案(多模态大模型) This solution (multimodal large language model) | 人工监管方法 Manual supervision method | “信息化系统 + 传统人工智能笼位识别”方案 "Information system + You Only Look Once" solution |
|---|---|---|---|
识别技术 Recognition technology | GPT-4o大模型 | 人工目视核查 | YOLO目标检测 |
识别准确率 Recognition accuracy | 98.5%(持续优化) | 监管人员易疲劳 | > 98%*(理论推测值) |
改造要求 Upgrade requirements | 摄像头,网络系统,普通计算机 | 无 | 摄像头,网络系统,配备主流高性能显卡的计算机 |
改造成本 Upgrade cost | 低 | 无 | 高 |
使用成本 Usage cost | 低 | 高 | 低 |
工作效率 Work efficiency | 高(3.7 s/笼架) | 低(5~10 min/笼架) | 极快(1 s以内) |
适应性 Adaptability | 强(可适应多种场景) | 强 | 弱(需要与训练数据类似) |
拓展性 Scalability | 完善 | 无 | 支持的,但是成本高昂,需要重新训练模型 |
Table 1 Comparative analysis of cage location monitoring plans
对比项目 Comparison items | 本方案(多模态大模型) This solution (multimodal large language model) | 人工监管方法 Manual supervision method | “信息化系统 + 传统人工智能笼位识别”方案 "Information system + You Only Look Once" solution |
|---|---|---|---|
识别技术 Recognition technology | GPT-4o大模型 | 人工目视核查 | YOLO目标检测 |
识别准确率 Recognition accuracy | 98.5%(持续优化) | 监管人员易疲劳 | > 98%*(理论推测值) |
改造要求 Upgrade requirements | 摄像头,网络系统,普通计算机 | 无 | 摄像头,网络系统,配备主流高性能显卡的计算机 |
改造成本 Upgrade cost | 低 | 无 | 高 |
使用成本 Usage cost | 低 | 高 | 低 |
工作效率 Work efficiency | 高(3.7 s/笼架) | 低(5~10 min/笼架) | 极快(1 s以内) |
适应性 Adaptability | 强(可适应多种场景) | 强 | 弱(需要与训练数据类似) |
拓展性 Scalability | 完善 | 无 | 支持的,但是成本高昂,需要重新训练模型 |
| [1] | 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 实验动物 环境及设施: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2023. |
| State Administration for Market Regulation, National Standardization Administration. Laboratory animal—Environment and housing facilities: [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2023. | |
| [2] | 刘莲莲, 张成梅, 张海艇, 等. 高校动物房屏障系统高效管理初探[J]. 医学动物防制, 2020, 36(7):661-662, 667. DOI: 10.7629/yxdwfz202007015 . |
| LIU L L, ZHANG C M, ZHANG H T, et al. Primary study on efficient management of animal house barrier system in colleges and universities[J]. J Med Pest Contr, 2020, 36(7):661-662, 667. DOI: 10.7629/yxdwfz202007015 . | |
| [3] | 刘琪帅, 李朝, 任晓霞. "双一流"高校建设背景下新型实验动物中心的建设与管理[J]. 实验技术与管理, 2022, 39(9):266-268. DOI: 10.16791/j.cnki.sjg.2022.09.045 . |
| LIU Q S, LI Z, REN X X. Construction and management of new laboratory animal center under background of "Double First-Class" university construction[J]. Exp Technol Manag, 2022, 39(9):266-268. DOI: 10.16791/j.cnki.sjg.2022.09.045 . | |
| [4] | 陈晓娟, 李巍, 汪洌. 高校实验动物管理流程信息化探索: 以浙江大学为例[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2021, 41(6):554-558. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2021.045 . |
| CHEN X J, LI W, WANG L. Exploration on informatization of laboratory animal management process in colleges and universities: the case of Zhejiang University[J]. Lab Anim Comp Med, 2021, 41(6):554-558. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2021.045 . | |
| [5] | 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 实验动物 福利伦理审查指南: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. Laboratory animal—Guideline for ethical review of animal welfare: [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018. | |
| [6] | 陆伟, 刘家伟, 马永强, 等. ChatGPT为代表的大模型对信息资源管理的影响[J]. 图书情报知识, 2023, 40(2):6-9, 70. DOI: 10.13366/j.dik.2023.02.006 . |
| LU W, LIU J W, MA Y Q, et al. The influence of large language models represented by ChatGPT on information resources management[J]. Doc Inf Knowl, 2023, 40(2):6-9, 70. DOI: 10.13366/j.dik.2023.02.006 . | |
| [7] | 徐敏, 张振建, 许景东, 等. "一院多区"医院管理的探索与思考[J]. 中国卫生质量管理, 2017, 24(4):107-109. DOI: 10.13912/j.cnki.chqm.2017.24.4.35 . |
| XU M, ZHANG Z J, XU J D, et al. Exploration and thinking of hospital management in "one hospital with multi-district"[J]. Chin Health Qual Manag, 2017, 24(4):107-109. DOI: 10.13912/j.cnki.chqm.2017.24.4.35 . | |
| [8] | 陈玲. 高校实验室安全管理面临的问题与对策[J]. 实验室研究与探索, 2017, 36(1):283-286. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7167.2017.01.070 . |
| CHEN L. Problems and countermeasures of laboratory safety management in colleges and universities in the new era[J]. Res Explor Lab, 2017, 36(1):283-286. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7167.2017.01.070 . | |
| [9] | 胡永艳, 陶迎红, 孔申申. 一种基于互联网的实验动物管理系统介绍[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2020, 40(3):257-261. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5817.2020.03.015 . |
| HU Y Y, TAO Y H, KONG S S. Introduction of a web-based novel laboratory animal management system[J]. Lab Anim Comp Med, 2020, 40(3):257-261. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5817.2020.03.015 . | |
| [10] | 宋予震, 郭素琴, 史洪涛, 等. 动物医学虚拟仿真实验教学平台的建设与应用[J]. 高教学刊, 2020, 6(21):79-81. DOI: 10.19980/j.cn23-1593/g4.2020.21.023 . |
| SONG Y Z, GUO S Q, SHI H T, et al. Construction and application of virtual simulation experimental teaching platform for animal medicine[J]. J High Educ, 2020, 6(21):79-81. DOI: 10.19980/j.cn23-1593/g4.2020.21.023 . | |
| [11] | 黄术兵, 姚文茜, 侯豹, 等. 高校实验动物管理工作的现状和对策研究[J]. 实验室科学, 2023, 26(6):147-150. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4305.2023.06.035 . |
| HUANG S B, YAO W X, HOU B, et al. Current situation and countermeasures on the management of laboratory animals in universities[J]. Lab Sci, 2023, 26(6):147-150. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4305.2023.06.035 . | |
| [12] | 李秀, 陈晓梅, 商可心, 等. 使用型高校实验动物中心信息化管理模式开发应用[J]. 上海畜牧兽医通讯, 2020(4):61-65, 68. DOI: 10.14170/j.cnki.cn31-1278/s.2020.04.025 . |
| LI X, CHEN X M, SHANG K X, et al. Development and application of information management mode of experimental animal center in using university[J]. Shanghai J Anim Husb Vet Med, 2020(4):61-65, 68. DOI: 10.14170/j.cnki.cn31-1278/s.2020.04.025 . | |
| [13] | 胡瑚. 基于MySQL的科研信息管理系统数据库设计[J]. 信息与电脑(理论版), 2024, 36(4):169-171. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9767.2024.04.054 . |
| HU H. Database design of scientific research information management system based on MySQL[J]. Inf Comput, 2024, 36(4):169-171. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9767.2024.04.054 . | |
| [14] | 郭全中, 苏刘润薇. 作为新基础设施的AGI: 以GPT-4O等新一代生成式人工智能为例[J]. 新闻爱好者, 2024(7):16-21. DOI: 10.16017/j.cnki.xwahz.20240527.001 . |
| GUO Q Z, SU L R W. AGI as a new infrastructure: Taking GPT-4O and other new generation of generative artificial intelli-gence as an example[J]. Jour Lov, 2024(7):16-21. DOI: 10.16017/j.cnki.xwahz.20240527.001 . | |
| [15] | 郭全中, 张金熠. ChatGPT的技术特征与应用前景[J]. 中国传媒科技, 2023(1):159-160. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0134.2023.01.032 . |
| GUO Q Z, ZHANG J Y. Technical characteristics and application prospect of ChatGPT[J]. Media Sci Technol China, 2023(1):159-160. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0134.2023.01.032 . | |
| [16] | LI J J, GUAN Z Y, WANG J, et al. Integrated image-based deep learning and language models for primary diabetes care[J]. Nat Med, 2024, 30(10):2886-2896. DOI:10.1038/s41591-024-03139-8 . |
| [17] | 大经中医. 岐黄问道大模型[EB/OL]. (2023-08-01)[2024-12-10]. . |
| Dajing Chinese Medicine. Qihuang wendao large model[EB/OL]. (2023-08-01)[2024-12-10]. . | |
| [18] | YANG S H, ZHAO H J, ZHU S B, et al. Zhongjing: enhancing the Chinese medical capabilities of large language model through expert feedback and real-world multi-turn dialogue[C]//AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2025. |
| [19] | Interpreter X-Ray. Empower your medical choices with instant a X-ray insights[Z/OL]. [2025-08-01]. . |
| [20] | LI C Y, WONG C, ZHANG S, et al. LLaVA-med: training a large language-and-vision assistant for biomedicine in one day[C]. Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems Article, 2023. |
| [21] | 马驰, 袁粒星, 林玲, 等. 基于信息化的实验动物中心管理新模式实践[J]. 实验室研究与探索, 2020, 39(6):253-255, 277. |
| MA C, YUAN L X, LIN L, et al. Practice of a new management model for laboratory animal centers based on information technology[J]. Res Explor Lab, 2020, 39(6): 253-255, 277. | |
| [22] | 朱玉, 秦嫘, 辛丹, 等. 高等院校实验动物的信息化管理体系建设探讨[J]. 畜牧兽医科技信息, 2022(6):19-21. DOI: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1671-6027.2022.06.007 . |
| ZHU Y, QIN L, XIN D, et al. Discussion on the construction of information management system of experimental animals in colleges and universities[J]. Chin J Anim Husb Vet Med, 2022(6):19-21. DOI: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1671-6027.2022.06.007 . | |
| [23] | 赵朝阳, 朱贵波, 王金桥. ChatGPT给语言大模型带来的启示和多模态大模型新的发展思路[J]. 数据分析与知识发现, 2023, 7(3):26-35. DOI: 10.11925/infotech.2096-3467.2023.0216 . |
| ZHAO C Y, ZHU G B, WANG J Q. The inspiration brought by ChatGPT to LLM and the new development ideas of multi-modal large model[J]. Data Anal Knowl Discov, 2023, 7(3):26-35. DOI: 10.11925/infotech.2096-3467.2023.0216 . | |
| [24] | 郭君斌, 于琳, 于传强. 改进YOLOv5s算法在交通标志检测识别中的应用[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2024, 46(6):123-130. DOI: 10.11887/j.cn.202406013 . |
| GUO J B, YU L, YU C Q. Application of improved YOLOv5s algorithm in traffic sign detection and recognition[J]. J Natl Univ Def Technol, 2024, 46(6):123-130. DOI: 10.11887/j.cn.202406013 . | |
| [25] | 韩冬, 李其花, 蔡巍, 等. 人工智能在医学影像中的研究与应用[J]. 大数据, 2019, 5(1):39-67. DOI: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-0271.2019004 . |
| HAN D, LI Q H, CAI W, et al. Research and application of artificial intelligence in medical imaging[J]. Big Data Res, 2019, 5(1):39-67. DOI: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-0271.2019004 . | |
| [26] | WANG C Y, BOCHKOVSKIY A, LIAO H M. YOLOv7: trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors[C] //2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). June 17-24,2023,Vancouver,BC,Canada.IEEE,2023:7464-7475. DOI:10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00721 . |
| [1] | WANG Hanyue, CHEN Jiawei, GAO Xiangbin, LUO Wei, LIU Suning. Research Overview on Corpora Cardiaca Function of Model Animal Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, (): 1-14. |
| [2] | ZHENG Qingyong, YANG Donghua, MA Zhichao, ZHOU Ziyu, LU Yang, WANG Jingyu, XING Lina, KANG Yingying, DU Li, ZHAO Chunxiang, DI Baoshan, TIAN Jinhui. Recommendations for Standardized Reporting of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis of Animal Experiments [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 496-507. |
| [3] | LIU Wentao, LUO Yanhong, LONG Yongxia, LUO Qihui, CHEN Zhengli, LIU Lida. Common Environmental Problems and Testing Experiences in Laboratory Animal Facilities in Sichuan Province [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 483-489. |
| [4] | LIN Zhenhua, CHU Xiangyu, WEI Zhenxi, DONG Chuanjun, ZHAO Zenglin, SUN Xiaoxia, LI Qingyu, ZHANG Qi. Evaluation of the Safety and Efficacy of Bone Cement in Experimental Pigs Using Vertebroplasty [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 466-472. |
| [5] | LIU Yueqin, XUE Weiguo, WANG Shuyou, SHEN Yaohua, JIA Shuyong, WANG Guangjun, SONG Xiaojing. Observation of Digestive Tract Tissue Morphology in Mice Using Probe-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 457-465. |
| [6] | LIU Kun, LAN Qing, YI Bing, XIE Xiaojie. Key Challenges and Mitigation Strategies for Animal Pregnancy in Non-clinical Reproductive Toxicity Testing of Drugs [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 449-456. |
| [7] | QIN Chao, LI Shuangxing, ZHAO Tingting, JIANG Chenchen, ZHAO Jing, YANG Yanwei, LIN Zhi, WANG Sanlong, WEN Hairuo. Study on the 90-day Feeding Experimental Background Data of SD Rats for Drug Safety Evaluation [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 439-448. |
| [8] | ZHAO Xin, WANG Chenxi, SHI Wenqing, LOU Yuefen. Advances in the Application of Zebrafish in the Research of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Mechanisms and Drug Development [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 422-431. |
| [9] | GONG Leilei, WANG Xiaoxia, FENG Xuewei, LI Xinlei, ZHAO Han, ZHANG Xueyan, FENG Xin. A Mouse Model and Mechanism Study of Premature Ovarian Insufficiency Induced by Different Concentrations of Cyclophosphamide [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 403-410. |
| [10] | JIANG Juan, SONG Ning, LIAN Wenbo, SHAO Congcong, GU Wenwen, SHI Yan. Comparison of Histopathological and Molecular Pathological Phenotypes in Mouse Models of Intrauterine Adhesions Induced by Two Concentrations of Ethanol Perfusion [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 393-402. |
| [11] | JIAO Qingzhen, WU Guihua, TANG Wen, FAN Fan, FENG Kai, YANG Chunxiang, QIAO Jian, DENG Sufang. Dynamic Monitoring and Analysis of Ammonia Concentration in Laboratory Animal Facilities Under Suspension of Heating Ventilation and Air Conditioning System [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 490-495. |
| [12] | WANG Jiaoxiang, ZHANG Lu, CHEN Shuhan, JIAO Deling, ZHAO Heng, WEI Taiyun, GUO Jianxiong, XU Kaixiang, WEI Hongjiang. Construction and Functional Validation of GTKO/hCD55 Gene-Edited Xenotransplant Donor Pigs [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 379-392. |
| [13] | . [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 508-514. |
| [14] | CHEN Ziyi, SUN Hongyan, KANG Pinfang, WU Wenjuan. Research Advances in Animal Experimental Models of Pulmonary Hypertension [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, (): 1-12. |
| [15] | XU Yingtao, WANG Mengmeng, LIN Ping, CHI Haitao, WANG Yi, BAI Ying. Exosomes Improve Ischemic Stroke by Regulation of Ferroptosis Through the NRF2/SLC7A11/GPX4 Pathway in Mice [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, (): 1-11. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||