
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine
• XXXX XXXX •
WANG Jiaoxiang1,2,4, ZHANG Lu1,2,3, CHEN Shuhan1,2,3, JIAO Deling1,2,3, ZHAO Heng1,2,3, WEI Taiyun1,2, GUO Jianxiong1,2,3, XU Kaixiang1,2,3, WEI HongJiang1,2,3,4( )
)
Online:2025-05-20
Contact:
WEI HongJiang
CLC Number:
WANG Jiaoxiang,ZHANG Lu,CHEN Shuhan,et al. Construction and Functional Validation of GTKO/hCD55 Gene-Edited Xenotransplant Donor Pigs[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.024.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.024
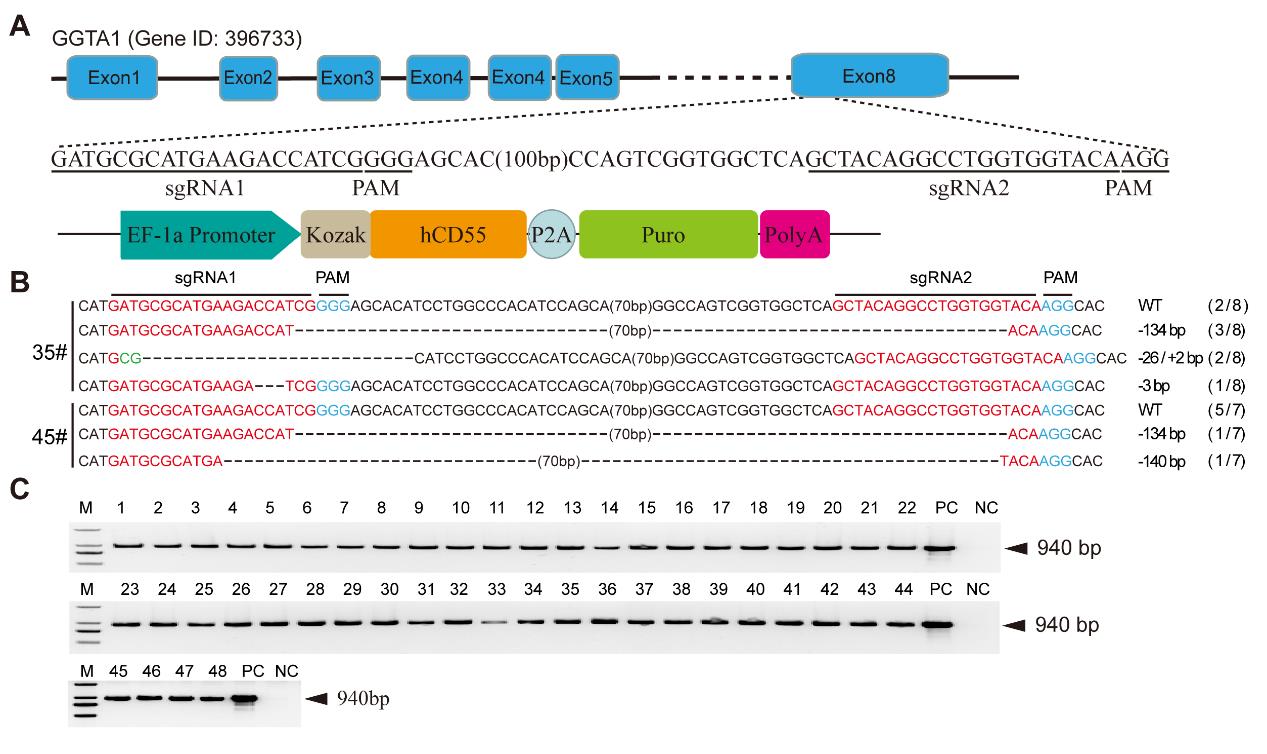
Figure 1 Screening of single-cell clone sites positive for GTKO/hCD55 gene editingNote:A, Schematic representation of the GGTA1 gene knockout and hCD55 gene overexpression vectors. B, GGTA1 target region genotype of positive single-cell clone sites; C, PCR identification of the hCD55 gene from 48 single-cell clone sites.
| No. | ID | Body weight (g) | Survival time (day) | Recipients | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P01 | 500 | 3 | P516 | |
| 2 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P02 | 400 | 1 | ||
| 3 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P03 | 720 | stillbirth | P452 | |
| 4 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P04 | 380 | stillbirth | ||
| 5 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P05 | 620 | 4 | ||
| 6 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P06 | 200 | P511 | ||
| 7 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P07 | 560 | stillbirth | ||
| 8 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P08 | 300 | |||
| 9 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P09 | 400 | |||
| 10 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P10 | 480 | stillbirth | P443 | |
| 11 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P11 | 560 | 2 | ||
| 12 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P12 | 580 | 3 | ||
| 13 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P13 | 520 | 1 | ||
| 14 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P14 | 260 | weaker | 2 | |
| 15 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P15 | 320 | stillbirth | ||
| 16 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P16 | 620 | 2 | ||
| 17 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P17 | 740 | 1 | ||
| 18 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P18 | 560 | stillbirth | P525 | |
| 19 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P19 | 540 | 21 | ||
| 20 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P20 | 660 | 206 |
Table 1 The embryo transfer and generation of cloned piglets
| No. | ID | Body weight (g) | Survival time (day) | Recipients | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P01 | 500 | 3 | P516 | |
| 2 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P02 | 400 | 1 | ||
| 3 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P03 | 720 | stillbirth | P452 | |
| 4 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P04 | 380 | stillbirth | ||
| 5 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P05 | 620 | 4 | ||
| 6 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P06 | 200 | P511 | ||
| 7 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P07 | 560 | stillbirth | ||
| 8 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P08 | 300 | |||
| 9 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P09 | 400 | |||
| 10 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P10 | 480 | stillbirth | P443 | |
| 11 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P11 | 560 | 2 | ||
| 12 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P12 | 580 | 3 | ||
| 13 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P13 | 520 | 1 | ||
| 14 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P14 | 260 | weaker | 2 | |
| 15 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P15 | 320 | stillbirth | ||
| 16 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P16 | 620 | 2 | ||
| 17 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P17 | 740 | 1 | ||
| 18 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P18 | 560 | stillbirth | P525 | |
| 19 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P19 | 540 | 21 | ||
| 20 | DN-GTKO-hCD55F02P20 | 660 | 206 |
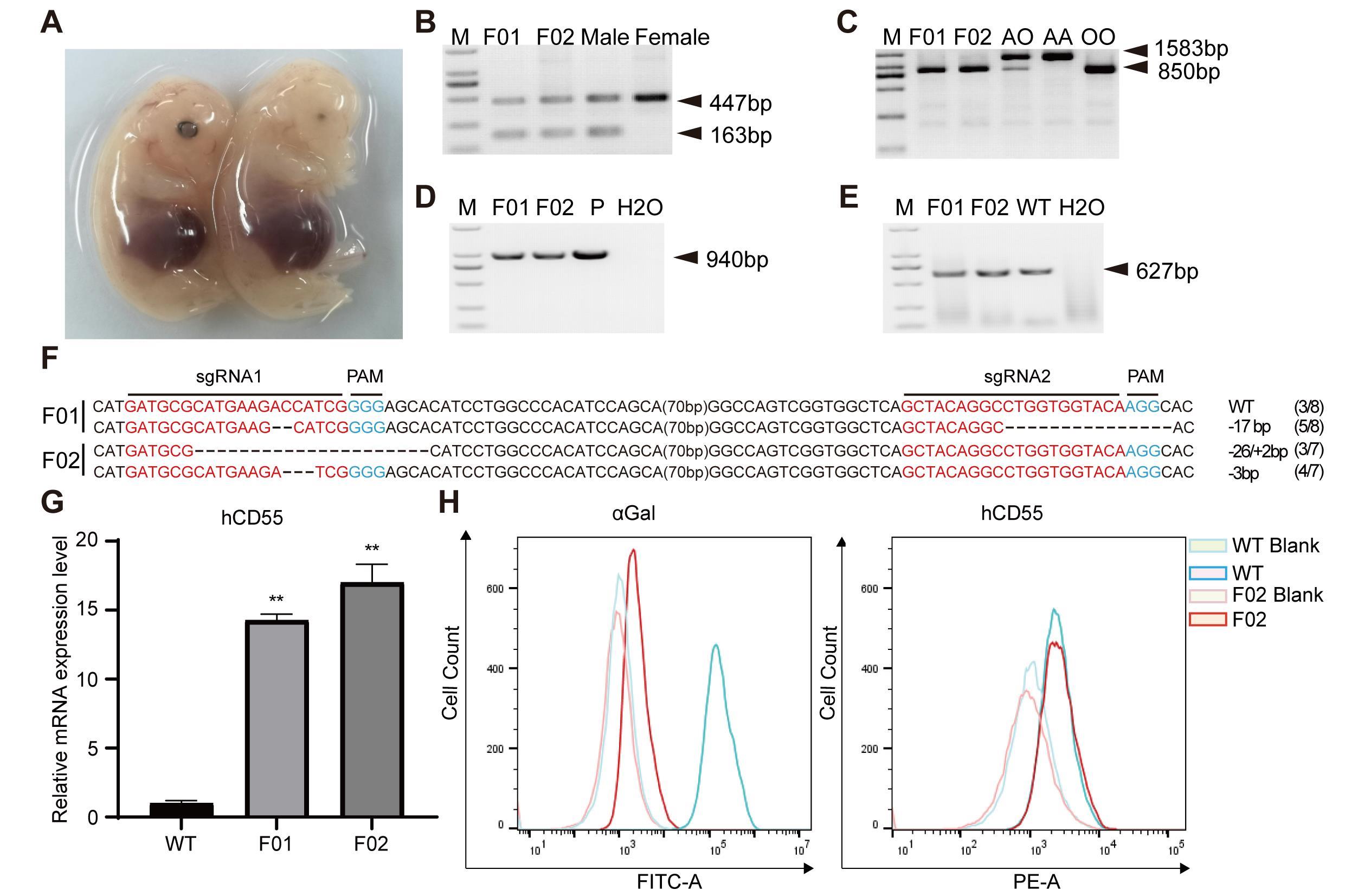
Figure 2 Identification of fetal pigs with GTKO/hCD55 gene-edited clonesNote:A, two cloned fetal pigs at 33 days; B, pig sex identification; C, Fetal pig blood typing; D, PCR identification of fetal pig hCD55; E, PCR results of the target region of the fetal pig GGTA1 gene; F, genotype of the GGTA1 target region in fetal pigs; G, hCD55 mRNA expression level in fetal pig tissues; H, Flow results of αGal and hCD55 expression in fetal porcine fibroblasts.
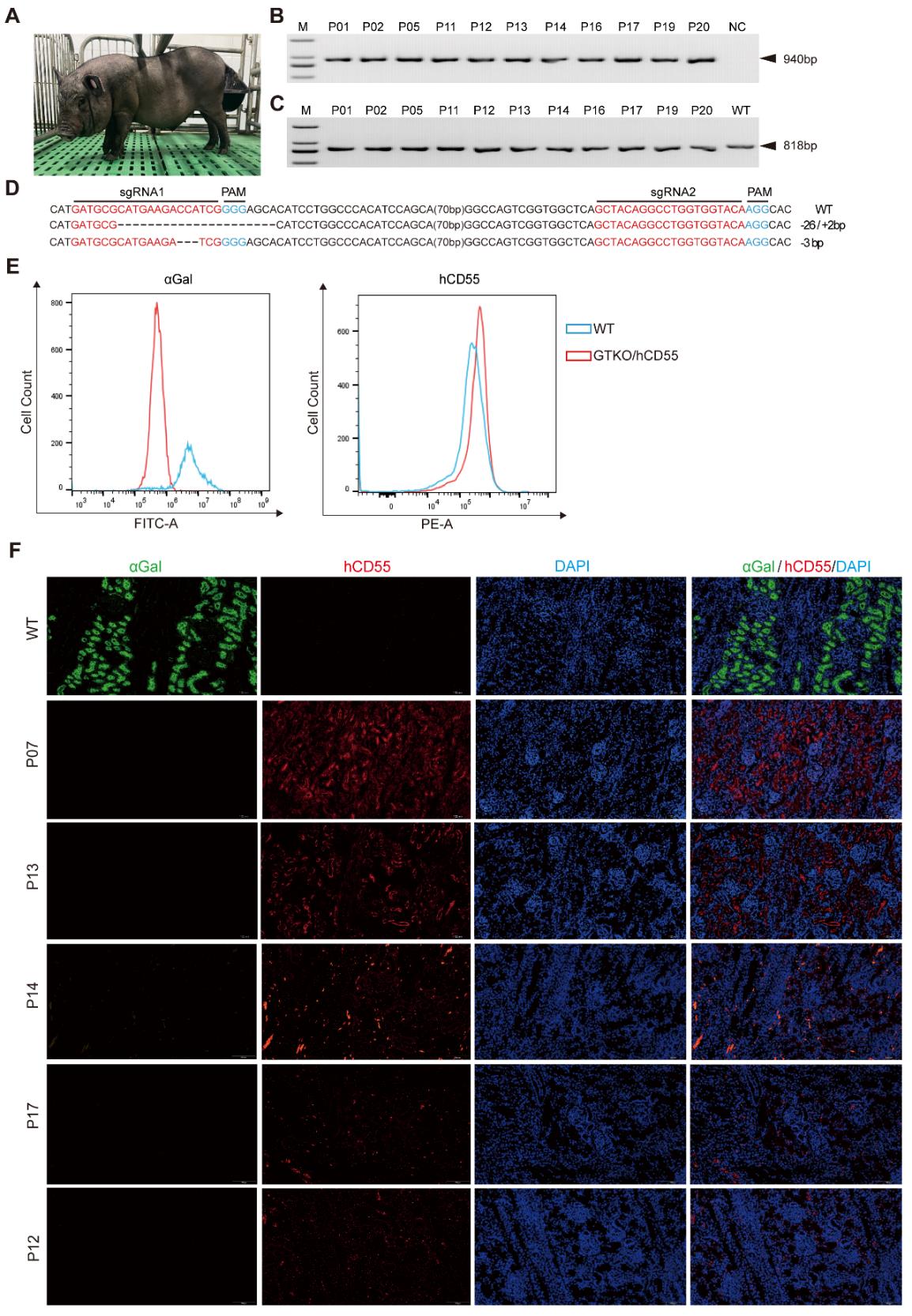
Figure 3 Identification of porcine GTKO/hCD55 gene-edited pigletsNote:A, Photo of cloned piglets of GTKO/hCD55; B, PCR identification of hCD55 in piglets; C, PCR results of the target region of GGTA1 gene in piglets; D, genotype of GGTA1 target region in piglets; E, Flow cytometry results for αGal and hCD55 expression in piglet-derived fibroblasts; F, immunofluorescence results of piglet kidneys.
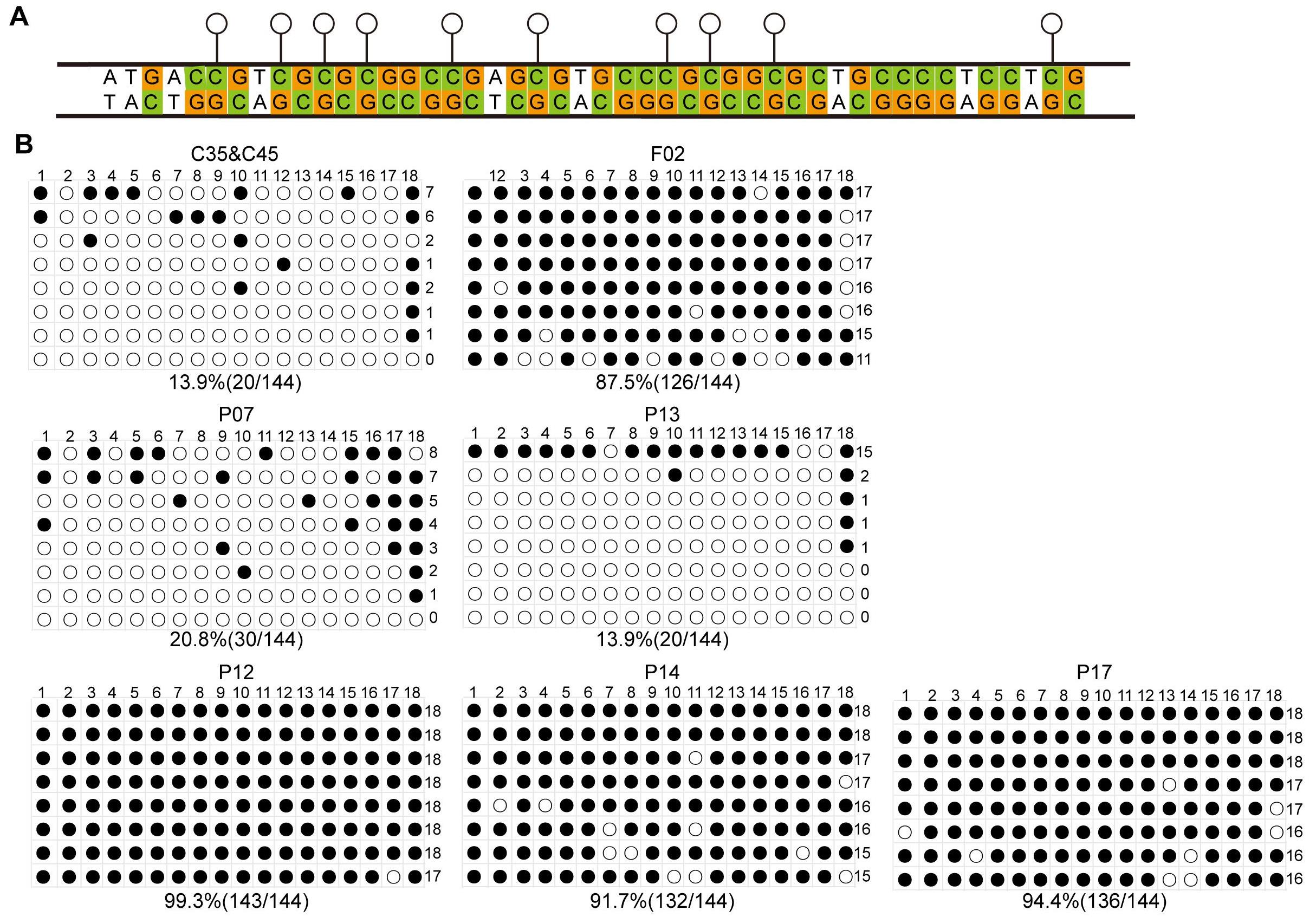
Figure 4 Methylation levels of the hCD55 gene in cell clone sites, fetal pigs, and cloned individualsNote:A, Schematic representation of CpG islands on the hCD55 gene; B, Methylation levels of hCD55 in mixed clone sites C35&C45, cloned fetal pig F02 fibroblasts, and cloned piglet (P07, P13, P12, P14, P17) kidney tissues.
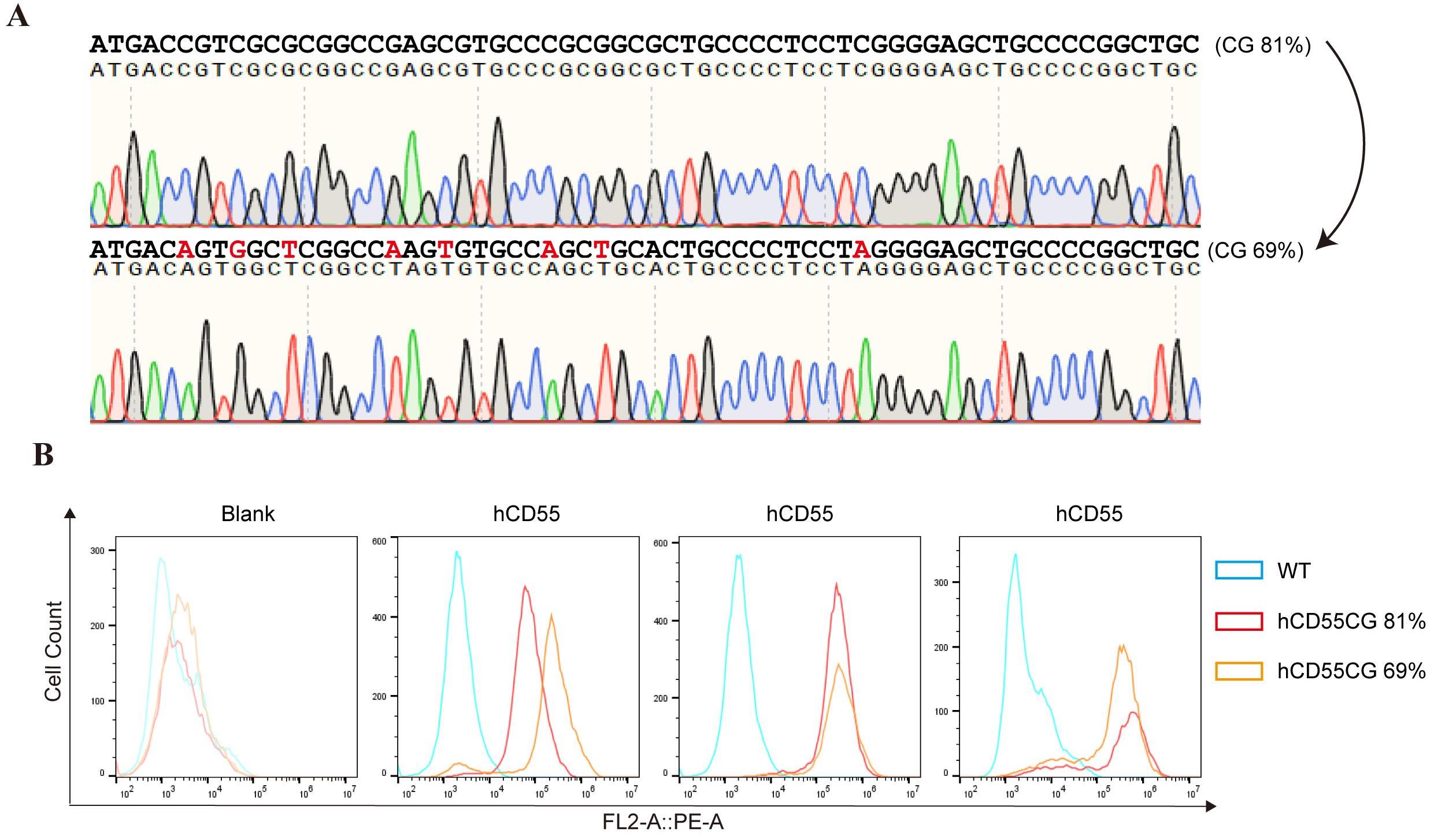
Figure 5 Expression Levels of hCD55 in Fibroblasts before and after codon optimizationNote:A, Sanger sequencing results of CpG island region of hCD55 gene before and after codon optimization; B, Porcine fibroblasts were transfected with the optimized and optimized vectors, and the expression level of hCD55 in the cells was detected by flow cytometry (triplicate experiments).
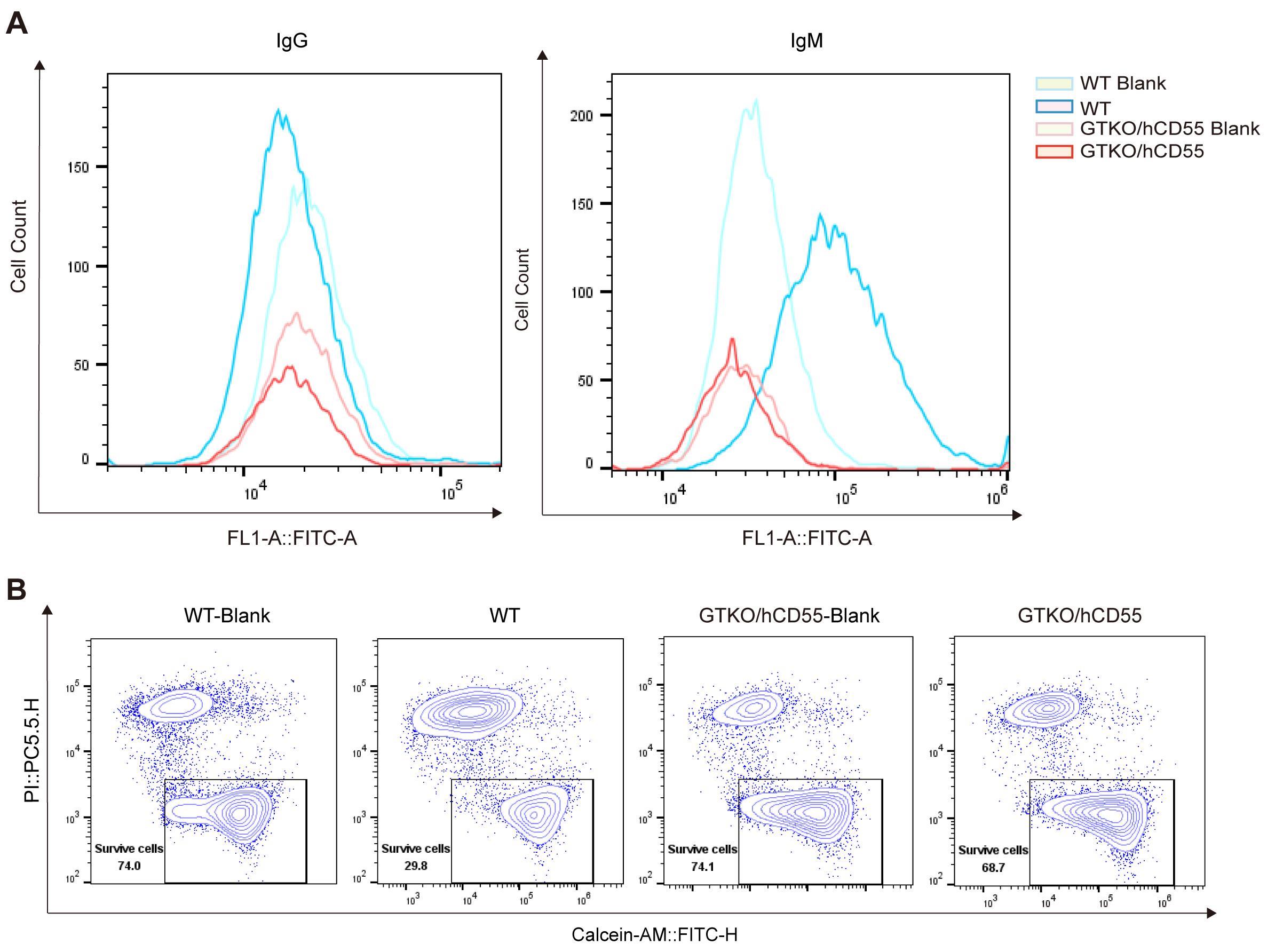
Figure 6 Evaluation of anti-immune rejection efficacy in GTKO/hCD55 gene-edited pigsNote:A, extent of binding of human IgG and IgM antibodies to porcine fibroblasts after incubation with mixed human serum; B, extent of killing of porcine cells by human complement after incubation of porcine fibroblasts with mixed human serum.
| 1 | ALI A, KEMTER E, WOLF E. Advances in organ and tissue xenotransplantation[J]. Annual Review of Animal Biosciences, 2024, 12: 369–390. DOI:10.1146/annurev-animal-021122-102606 . |
| 2 | SINGH A K, GOERLICH C E, ZHANG T, et al. Genetically engineered pig heart transplantation in non-human primates[J]. Communications Medicine, 2025, 5: 6. DOI:10.1038/s43856-025-00731-y . |
| 3 | EISENSON D, HISADOME Y, SANTILLAN M, et al. Consistent survival in consecutive cases of life-supporting porcine kidney xenotransplantation using 10ge source pigs[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15: 3361. DOI:10.1038/s41467-024-47679-6 . |
| 4 | ANAND R P, LAYER J V, HEJA D, et al. Design and testing of a humanized porcine donor for xenotransplantation[J]. Nature, 2023, 622(7982): 393–401. DOI:10.1038/s41586-023-06594-4 . |
| 5 | MOHIUDDIN M M, SINGH A K, SCOBIE L, et al. Graft dysfunction in compassionate use of genetically engineered pig-to-human cardiac xenotransplantation: a case report[J]. Lancet, 2023, 402(10399): 397–410. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00775-4 . |
| 6 | GRIFFITH B P, GOERLICH C E, SINGH A K, et al. Genetically modified porcine-to-human cardiac xenotransplantation[J]. The New England journal of Medicine, 2022, 387(1): 35–44. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa2201422 . |
| 7 | PAN W, ZHANG W, ZHENG B, et al. Cellular dynamics in pig-to-human kidney xenotransplantation[J]. Med, 2024, 5(8): 1016-1029.e4. DOI:10.1016/j.medj.2024.05.003 . |
| 8 | KAWAI T, WILLIAMS W W, ELIAS N, et al. Xenotransplantation of a porcine kidney for end-stage kidney disease[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 2025. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa2412747 . |
| 9 | MALLAPATY S. First pig-to-human liver transplant recipient "doing very well"[J]. Nature, 2024, 630(8015): 18. DOI:10.1038/d41586-024-01613-4 . |
| 10 | KUWAKI K, Y-L TSENG, DOR F J M F, et al. Heart transplantation in baboons using alpha1,3-galactosyltransferase gene-knockout pigs as donors: initial experience[J]. Nature Medicine, 2005, 11(1): 29–31. DOI:10.1038/nm1171 . |
| 11 | AZIMZADEH A M, KELISHADI S S, EZZELARAB M B, et al. Early graft failure of galtko pig organs in baboons is reduced by expression of a human complement pathway-regulatory protein[J]. Xenotransplantation, 2015, 22(4): 310–316. DOI:10.1111/xen.12176 . |
| 12 | MOHIUDDIN M M, GOERLICH C E, SINGH A K, et al. Progressive genetic modifications of porcine cardiac xenografts extend survival to 9 months[J]. Xenotransplantation, 2022, 29(3): e12744. DOI:10.1111/xen.12744 . |
| 13 | CHABAN R, MCGRATH G, HABIBABADY Z, et al. Increased human complement pathway regulatory protein gene dose is associated with increased endothelial expression and prolonged survival during ex-vivo perfusion of gtko pig lungs with human blood[J]. Xenotransplantation, 2023, 30(4): e12812. DOI:10.1111/xen.12812 . |
| 14 | WARD T, PIPKIN P A, CLARKSON N A, et al. Decay-accelerating factor cd55 is identified as the receptor for echovirus 7 using celics, a rapid immuno-focal cloning method[J]. The EMBO Journal, 1994, 13(21): 5070–5074. DOI:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06836.x . |
| 15 | LUKACIK P, ROVERSI P, WHITE J, et al. Complement regulation at the molecular level: the structure of decay-accelerating factor[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(5): 1279–1284. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0307200101 . |
| 16 | MURAKAMI H, NAGASHIMA H, TAKAHAGI Y, et al. Transgenic pigs expressing human decay-accelerating factor regulated by porcine mcp gene promoter[J]. Molecular Reproduction and Development, 2002, 61(3): 302–311. DOI:10.1002/mrd.10043 . |
| 17 | KIM S C, MATHEWS D V, BREEDEN C P, et al. Long-term survival of pig-to-rhesus macaque renal xenografts is dependent on cd4 t cell depletion[J]. American Journal of Transplantation: Official Journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons, 2019, 19(8): 2174–2185. DOI:10.1111/ajt.15329 . |
| 18 | 李欣, 潘登科, 周佳, 等. 表达人源补体调节蛋白hCD55对异种胰岛移植的保护作用[J]. 器官移植, 2022, 13(4): 475–482. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2022.04.010 . |
| 19 | 夏强兵, 冯豪, 王璐, 等. GTKO/hcd55基因工程猪到人异种移植cdc技术的探讨[J]. 中华器官移植杂志, 2022, 43(06): 364–369. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn421203-20220505-00096 . |
| 20 | YUE Y, XU W, KAN Y, et al. Extensive germline genome engineering in pigs[J]. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2021, 5(2): 134–143. DOI:10.1038/s41551-020-00613-9 . |
| 21 | LETI F, LLACI L, MALENICA I, et al. Chapter 13: methods for cpg methylation array profiling via bisulfite conversion[J]. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 2018, 1706: 233–254. DOI:10.1007/978-1-4939-7471-9_13 . |
| 22 | MOAZAMI N, STERN J M, KHALIL K, et al. Pig-to-human heart xenotransplantation in two recently deceased human recipients[J]. Nature Medicine, 2023, 29(8): 1989–1997. DOI:10.1038/s41591-023-02471-9 . |
| 23 | LOCKE J E, KUMAR V, ANDERSON D, et al. Normal graft function after pig-to-human kidney xenotransplant[J]. JAMA Surgery, 2023, 158(10): 1106–1108. DOI:10.1001/jamasurg.2023.2774 . |
| 24 | WANG J, XU K, LIU T, et al. Production and functional verification of 8-gene (ggta1, cmah, β4galnt2, hcd46, hcd55, hcd59, htbm, hcd39)-edited donor pigs for xenotransplantation[J]. Cell Proliferation, 2025: e70028. DOI:10.1111/cpr.70028 . |
| 25 | MANOOK M, OLASO D, ANWAR I, et al. Prolonged xenokidney graft survival in sensitized nhp recipients by expression of multiple human transgenes in a triple knockout pig[J]. Science translational Medicine, 2024, 16(751): eadk6152. DOI:10.1126/scitranslmed.adk6152 . |
| 26 | YANG C, WEI Y, LI X, et al. Production of four-gene (gtko/hcd55/htbm/hcd39)-edited donor pigs and kidney xenotransplantation[J]. Xenotransplantation, 2024, 31(4): e12881. DOI:10.1111/xen.12881 . |
| 27 | ZHAO H, LI Y, WIRIYAHDAMRONG T, et al. Improved production of gtko/hcd55/hcd59 triple-gene-modified diannan miniature pigs for xenotransplantation by recloning[J]. Transgenic Research, 2020, 29(3): 369–379. DOI:10.1007/s11248-020-00201-2 . |
| [1] | ZHU Chan, ZHANG Dongliang, ZHAO Deli, SHI Xueqin, QIAN Lei, ZHANG Xuan, JIN Yan, DUAN Wei, QI Ruocheng, LIU Chaohua, YANG Xuekang, HAN Juntao, PAN Dengke. Perioperative Animal Care for Xenotransplantation from Genetically Edited Pigs to Monkeys [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 495-501. |
| [2] | Jiaoxiang WANG, Yan WANG, Ke HU, Kaixiang XU, Taiyun WEI, Deling JIAO, Heng ZHAO, Hongye ZHAO, HongJiang WEI. Establishment of PCR Identification Method for Pig Blood Type [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 585-594. |
| [3] | ZHANG Qi, WANG Jian-fei. Progress and Perspective for Xenotransplantation [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2018, 38(6): 407-411. |
| [4] | ZHANG Zhen-hua, SHEN Zeng-li, HOU Chuan-ling, SONG Chun-jiao, SUN Ai-jing. Establishment of Different Malignant Potential Prostate Cancer Animal Model from Same Origination [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2014, 34(2): 83-88. |
| [5] | YE Wen-xue,SHEN Zhen-ya,ZHANG Sheng-chao. Establish a High Rebeating Rate Mouse-to-rat Heterotopic Cardiac Transplantation Model [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2008, 28(3): 148-150. |
| [6] | LU Xuan1, XIAO Ming-di2,LI Jing-lai2. Establishment of the Model for Acute Vascular Rejection in Heart Xenotransplantation [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2003, 23(3): 143-145. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||