
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 446-456.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.039
Special Issue: 动物实验设计及统计学方法
• Guidelines for Comparative Medical Research and Reporting • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaoyu LIU1, Xuancheng LU2, Xiaomeng SHI2, Yuzhou ZHANG2, Chao LÜ2, Guoyuan CHEN3, Xiao LU4, Yu BAI5, Jing GAO6, Yao LI7, Yonggang LIU8, Yufeng TAO9( )(
)( ), Wanyong PANG10(
), Wanyong PANG10( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-03-29
Revised:2023-07-21
Online:2023-08-25
Published:2023-08-25
Contact:
Yufeng TAO, Wanyong PANG
CLC Number:
Xiaoyu LIU,Xuancheng LU,Xiaomeng SHI,et al. Explanation and Elaboration for the ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0—Reporting Animal Research and In Vivo Experiments (Ⅲ)[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 446-456. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.039.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.039
| 编号 No. | 实验流程 Procedures | 实验资源 Resources |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 药理研究(包括干预和对照) | 细胞系 |
| ● 药物配方 | ● 鉴别 | |
| ● 剂量 | ● 来源 | |
| ● 体积 | ● 验证和认证 | |
| ● 浓度 | ● RRID[ | |
| ● 给药部位和途径 | ||
| ● 给药频率 | ||
| ● 溶媒或载体溶液的配方和体积 | ||
| ● 任何可以表明所使用的药剂到达靶组织的证据 | ||
| 2 | 外科手术(包括假手术) | 试剂(如抗体、化学品) |
| ● 手术过程描述 | ● 制造商 | |
| ● 使用的麻醉剂(包括上文药理研究部分所列剂量及信息) | ● 供应商 | |
| ● 术前和术后镇痛方案 | ● 目录号 | |
| ● 术前程序(如禁食) | ● 批号(如适用) | |
| ● 无菌术 | ● 药物纯度(如适用) | |
| ● 监测(如评估手术麻醉状况) | ● RRID | |
| ● 流程是否是终末性质的 | ||
| ● 术后程序 | ||
| ● 手术持续时间和麻醉持续时间 | ||
| ● 测量的身体指标 | ||
| 3 | 病原体感染(包括干预和对照) | 设备和软件 |
| ● 传染性病原体 | ● 制造商 | |
| ● 感染最高剂量 | ● 供应商 | |
| ● 溶媒或载体溶液的配方和体积 | ● 型号/版本号 | |
| ● 感染部位和途径 | ● 校准程序(如适用) | |
| ● 感染时间或频率 | ● RRID | |
| 4 | 安乐死 | |
| ● 安乐死方法,包括该方法遵循的人道标准,如AVMA[ | ||
| ● 药剂(如使用)(包括上文药理研究部分所列剂量及信息) | ||
| ● 安乐死前或安乐死期间为减轻疼痛和痛苦而采取的任何措施 | ||
| ● 安乐死的时间 | ||
| ● 安乐死后收集的组织及其时间 |
Table 2 Examples of information to include when reporting specific types of experimental procedures and resources
| 编号 No. | 实验流程 Procedures | 实验资源 Resources |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 药理研究(包括干预和对照) | 细胞系 |
| ● 药物配方 | ● 鉴别 | |
| ● 剂量 | ● 来源 | |
| ● 体积 | ● 验证和认证 | |
| ● 浓度 | ● RRID[ | |
| ● 给药部位和途径 | ||
| ● 给药频率 | ||
| ● 溶媒或载体溶液的配方和体积 | ||
| ● 任何可以表明所使用的药剂到达靶组织的证据 | ||
| 2 | 外科手术(包括假手术) | 试剂(如抗体、化学品) |
| ● 手术过程描述 | ● 制造商 | |
| ● 使用的麻醉剂(包括上文药理研究部分所列剂量及信息) | ● 供应商 | |
| ● 术前和术后镇痛方案 | ● 目录号 | |
| ● 术前程序(如禁食) | ● 批号(如适用) | |
| ● 无菌术 | ● 药物纯度(如适用) | |
| ● 监测(如评估手术麻醉状况) | ● RRID | |
| ● 流程是否是终末性质的 | ||
| ● 术后程序 | ||
| ● 手术持续时间和麻醉持续时间 | ||
| ● 测量的身体指标 | ||
| 3 | 病原体感染(包括干预和对照) | 设备和软件 |
| ● 传染性病原体 | ● 制造商 | |
| ● 感染最高剂量 | ● 供应商 | |
| ● 溶媒或载体溶液的配方和体积 | ● 型号/版本号 | |
| ● 感染部位和途径 | ● 校准程序(如适用) | |
| ● 感染时间或频率 | ● RRID | |
| 4 | 安乐死 | |
| ● 安乐死方法,包括该方法遵循的人道标准,如AVMA[ | ||
| ● 药剂(如使用)(包括上文药理研究部分所列剂量及信息) | ||
| ● 安乐死前或安乐死期间为减轻疼痛和痛苦而采取的任何措施 | ||
| ● 安乐死的时间 | ||
| ● 安乐死后收集的组织及其时间 |
新种类 New species | 主频率 Dominant frequency/Hz # | 鸣声时间 Call duration/ms#* | 鸣声间隔 Inter-call interval /ms# | 音节持续时间 Note duration /ms* | 音节间隔Inter-note interval/ms/ | 音节次数Notes per serics | 分析注释Notes analysed* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
最小迷你蛙 Mini mum gen. et sp. nov. | 8 089±140 (7 676~8 306) | 74.8±7.0 (57~87) | 4 299.8±1 604.9 (3 136~10 139) | na | na | n=35 | |
极小迷你蛙 Mini scule gen. et sp. nov. | 6 675±64 (6 549~6 768) | 121.9±8.7 (108~140) | 1 905.1±398.3 (1 589~4 122) | na | na | n=51 | |
比例钻蛙 Rhombophryne proportionalis sp. nov. | 5 460±117 (5 166~5 732) | 1 328.0±284.1 (905~1 765, n = 6) | 62 753±20 613 (38 952~74 744, n = 3) | 45.4±8.2 (27~60) | 63.0±9.0 (45~88) | 13±3 (9~17, n=6) | n=79 |
卓越无齿蛙 Anodonthyla eximia sp. nov. | 8 406±78 (8 349~8 540) | 59.6±6.5 (53~68) | 3 749.0±1 149.9 (2 654~5 172) | na | na | n=5 | |
米埃尔蓝蛙 Stumpffia miery | 8 057±137 (7 751~8 225) | 73±12 (51~88) | 3 102±456 (2 679~4 247) | na | na | n=10 |
Table 3 Bioacoustic parameters of new species of miniaturised cophyline microhylids (reproduced from reference [149])
新种类 New species | 主频率 Dominant frequency/Hz # | 鸣声时间 Call duration/ms#* | 鸣声间隔 Inter-call interval /ms# | 音节持续时间 Note duration /ms* | 音节间隔Inter-note interval/ms/ | 音节次数Notes per serics | 分析注释Notes analysed* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
最小迷你蛙 Mini mum gen. et sp. nov. | 8 089±140 (7 676~8 306) | 74.8±7.0 (57~87) | 4 299.8±1 604.9 (3 136~10 139) | na | na | n=35 | |
极小迷你蛙 Mini scule gen. et sp. nov. | 6 675±64 (6 549~6 768) | 121.9±8.7 (108~140) | 1 905.1±398.3 (1 589~4 122) | na | na | n=51 | |
比例钻蛙 Rhombophryne proportionalis sp. nov. | 5 460±117 (5 166~5 732) | 1 328.0±284.1 (905~1 765, n = 6) | 62 753±20 613 (38 952~74 744, n = 3) | 45.4±8.2 (27~60) | 63.0±9.0 (45~88) | 13±3 (9~17, n=6) | n=79 |
卓越无齿蛙 Anodonthyla eximia sp. nov. | 8 406±78 (8 349~8 540) | 59.6±6.5 (53~68) | 3 749.0±1 149.9 (2 654~5 172) | na | na | n=5 | |
米埃尔蓝蛙 Stumpffia miery | 8 057±137 (7 751~8 225) | 73±12 (51~88) | 3 102±456 (2 679~4 247) | na | na | n=10 |
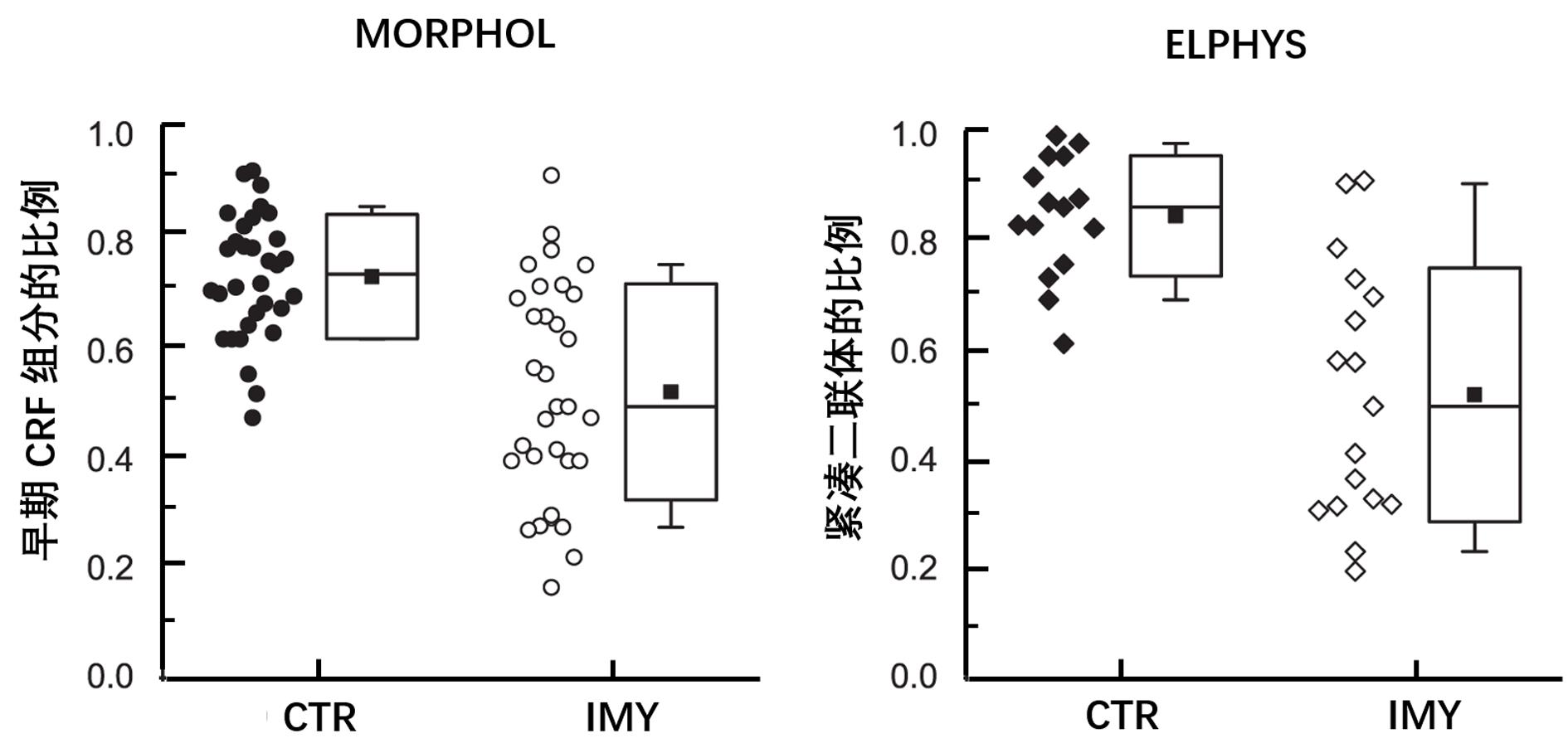
Figure 5 Fractions of the unperturbed elements of calcium release in cardiac myocytes reproduced from reference[150]Note: CRF, calcium release flux. MORPHOL, fractions of compact dyads estimated by morphometry from electron microscopic images. ELPHYS, fractions of the early CRF components estimated by fitting records of integral fluorescence signals. CTR, control myocardium; IMY, injured myocardium. Box plots show the 25%, 50% and 75% percentiles; whiskers show 10% and 90% percentile. Solid squares denote the means.
| 103 | 王剑, 卢今, 马政文, 等. 《动物研究:体内实验报告》即ARRIVE 2.0指南的解释和阐述(一)[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(2): 213-224. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.043 . |
| WANG J, LU J, MA Z W, et al. Explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0—reporting animal research and in vivo experiments (Ⅰ)[J]. Lab Anim Comp Med, 2023, 43(2): 213-224. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.043 . | |
| 104 | 陈国元, 卢晓, 白玉, 等. 《动物研究:体内实验报告》即ARRIVE 2.0指南的解释和阐述(二)[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(3): 323-331. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.042 . |
| CHEN G Y, LU X, BAI Y, et al. Explanation and elaboration for the ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0—reporting animal research and in vivo experiments (Ⅱ)[J]. Lab Anim Comp Med, 2023, 43(3): 323-331. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.042 . | |
| 105 | CLAYTON J A, COLLINS F S. Policy: NIH to balance sex in cell and animal studies[J]. Nature, 2014, 509(7500):282-283. DOI: |
| 10 | 1038/509282a. |
| 106 | SHAPIRA S, SAPIR M, WENGIER A, et al. Aging has a complex effect on a rat model of ischemic stroke[J]. Brain Res, 2002, 925(2):148-158. DOI: 10.1016/s0006-8993(01)03270-x . |
| 107 | VITAL M, HARKEMA J R, RIZZO M, et al. Alterations of the murine gut microbiome with age and allergic airway disease [J]. J Immunol Res, 2015, 2015:892568. DOI: 10.1155/2015/ 892568 . |
| 108 | BOUWKNECHT J A, PAYLOR R. Behavioral and physiological mouse assays for anxiety: a survey in nine mouse strains[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2002, 136(2):489-501. DOI: 10.1016/S0166- 4328(02)00200-0 . |
| 109 | SIMON M M, GREENAWAY S, WHITE J K, et al. A comparative phenotypic and genomic analysis of C57BL/6J and C57BL/ 6N mouse strains[J]. Genome Biol, 2013, 14(7): R82. DOI: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-7-r82 . |
| 110 | JACKSON S J, ANDREWS N, BALL D, et al. Does age matter? The impact of rodent age on study outcomes[J]. Lab Anim, 2017, 51(2):160-169. DOI: 10.1177/0023677216653984 . |
| 111 | KHOKHA M K, CHUNG C, BUSTAMANTE E L, et al. Techniques and probes for the study of Xenopus tropicalis development [J]. Dev Dyn, 2002, 225(4):499-510. DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.10184 . |
| 112 | ÕKVA K, NEVALAINEN T, POKK P. The effect of cage shelf on the behaviour of male C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice in the elevated plus maze test[J]. Lab Anim, 2013, 47(3):220-222. DOI: 10.1177/0023677213489280 . |
| 113 | AKKERS R C, VAN HEERINGEN S J, JACOBI U G, et al. A hierarchy of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 acquisition in spatial gene regulation in Xenopus embryos[J]. Dev Cell, 2009, 17(3): 425-434. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.08.005 . |
| 114 | FELASA WORKING GROUP ON REVISION OF GUIDELINES FOR HEALTH MONITORING OF RODENTS AND RABBITS, MÄHLER CONVENOR M, BERARD M, et al. FELASA recommendations for the health monitoring of mouse, rat, hamster, Guinea pig and rabbit colonies in breeding and experimental units[J]. Lab Anim, 2014, 48(3):178-192. DOI: 10.1177/0023677213516312 . |
| 115 | BAKER D G. Natural pathogens of laboratory mice, rats, and rabbits and their effects on research[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 1998, 11(2):231-266. DOI: 10.1128/CMR.11.2.231 . |
| 116 | VELAZQUEZ E M, NGUYEN H, HEASLEY K T, et al. Endogenous Enterobacteriaceae underlie variation in susceptibility to Salmonella infection[J]. Nat Microbiol, 2019, 4(6):1057-1064. DOI: 10.1038/s41564-019-0407-8 . |
| 117 | HOLMDAHL R, MALISSEN B. The need for littermate controls[J]. Eur J Immunol, 2012, 42(1):45-47. DOI: 10.1002/eji. 201142048 . |
| 118 | MALLAPATY S. In the Name of reproducibility[J]. Lab Animal, 2018, 47(7):178-181. DOI: 10.1038/s41684-018-0095-7 . |
| 119 | SUNDBERG J P, SCHOFIELD P N. Commentary: mouse genetic nomenclature[J]. Vet Pathol, 2010, 47(6):1100-1104. DOI: 10.1177/0300985810374837 . |
| 120 | MONTOLIU L, WHITELAW C B. Using standard nomenclature to adequately name transgenes, knockout gene alleles and any mutation associated to a genetically modified mouse strain[J]. Transgenic Res, 2011, 20(2):435-440. DOI: 10.1007/s11248-010-9428-z . |
| 121 | HUANG W, FENG Y L, LIANG J L, et al. Loss of microRNA-128 promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and heart regeneration [J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1):700. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018- 03019-z . |
| 122 | RANSON A, CHEETHAM C E J, FOX K, et al. Homeostatic plasticity mechanisms are required for juvenile, but not adult, ocular dominance plasticity[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2012, 109(4):1311-1316. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1112204109 . |
| 123 | CLARKSON J M, DWYER D M, FLECKNELL P A, et al. Handling method alters the hedonic value of reward in laboratory mice [J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1):2448. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-20716-3 . |
| 124 | HURST J L, WEST R S. Taming anxiety in laboratory mice[J]. Nat Methods, 2010, 7(10):825-826. DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.1500 . |
| 125 | HEWITT J A, BROWN L L, MURPHY S J, et al. Accelerating biomedical discoveries through rigor and transparency[J]. ILAR J, 2017, 58(1):115-128. DOI: 10.1093/ilar/ilx011 . |
| 126 | ALMEIDA J L, COLE K D, PLANT A L. Standards for cell line authentication and beyond[J]. PLoS Biol, 2016, 14(6): e1002476. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002476 . |
| 127 | LEARY S, UNDERWOOD W, ANTHONY R, et al. J K. AVMA guidelines for the euthanasia of animals[J]. Anim Welf, 2013, 22(3):412. DOI: 10.1017/ s0962728600005492 . |
| 128 | BANDROWSKI A E, MARTONE M E. RRIDs: a simple step toward improving reproducibility through rigor and transparency of experimental methods[J]. Neuron, 2016, 90(3):434-436. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.04.030 . |
| 129 | BANDROWSKI A, BRUSH M, GRETHE J S, et al. The resource identification initiative: a cultural shift in publishing[J]. Neuroinform, 2016, 14(2):169-182. DOI: 10.1007/s12021-015- 9284-3 . |
| 130 | TEYTELMAN L, STOLIARTCHOUK A. Protocols.io: Reducing the knowledge that perishes because we do not publish it[J]. Inf Serv Use, 2015, 35(1-2):109-115. DOI: 10.3233/isu-150769 . |
| 131 | REYNOLDS P S, FISHER B J, MCCARTER J, et al. Interventional vitamin C: a strategy for attenuation of coagulopathy and inflammation in a swine multiple injuries model[J]. J Trauma Acute Care Surg, 2018, 85(1S ): S57-S67. DOI: 10.1097/ TA.0000000000001844 . |
| 132 | BAUTERS D, BEDOSSA P, LIJNEN H R, et al. Functional role of ADAMTS5 in adiposity and metabolic health[J]. PLoS One, 2018,13(1): e0190595. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0190595 . |
| 133 | LIAN X Y, WU X Y, LI Z X, et al. The combination of metformin and 2-deoxyglucose significantly inhibits cyst formation in miniature pigs with polycystic kidney disease[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2019, 176(5):711-724. DOI: 10.1111/bph.14558 . |
| 134 | BARTLANG M S, NEUMANN I D, SLATTERY D A, et al. Time matters: pathological effects of repeated psychosocial stress during the active, but not inactive, phase of male mice[J]. J Endocrinol, 2012, 215(3):425-437. DOI: 10.1530/JOE-12-0267 . |
| 135 | PAUL A K, GUEVEN N, DIETIS N. Morphine dosing strategy plays a key role in the generation and duration of the produced antinociceptive tolerance[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2017, 121:158-166. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.04.034 . |
| 136 | HAWKINS P, MORTON D B, BURMAN O, et al. A guide to defining and implementing protocols for the welfare assessment of laboratory animals: eleventh report of the BVAAWF/FRAME/RSPCA/UFAW Joint Working Group on Refinement[J]. Lab Anim, 2011, 45(1):1-13. DOI: 10.1258/ la.2010.010031 . |
| 137 | HAGEMO J S, JØRGENSEN J J, OSTROWSKI S R, et al. Changes in fibrinogen availability and utilization in an animal model of traumatic coagulopathy[J]. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med, 2013, 21:56. DOI: 10.1186/1757-7241-21-56 . |
| 138 | EMERY M, NANCHEN N, PREITNER F, et al. Biological characterization of gene response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia in mouse retina[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(2): e0150266. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150266 . |
| 139 | HOLMES A M, EMMANS C J, COLEMAN R, et al. Effects of transportation, transport medium and re-housing on Xenopus laevis (Daudin)[J]. Gen Comp Endocrinol, 2018, 266: 21-28. DOI: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2018.03.015 . |
| 140 | CONOUR L A, MURRAY K A, BROWN M J. Preparation of animals for research: issues to consider for rodents and rabbits[J]. ILAR J, 2006, 47(4):283-293. DOI: 10.1093/ilar.47.4.283 . |
| 141 | OBERNIER J A, BALDWIN R L. Establishing an appropriate period of acclimatization following transportation of laboratory animals[J]. ILAR J, 2006, 47(4):364-369. DOI: 10.1093/ilar.47.4.364 . |
| 142 | KRAHN D D, GOSNELL B A, MAJCHRZAK M J. The anorectic effects of CRH and restraint stress decrease with repeated exposures[J]. Biol Psychiatry, 1990, 27(10):1094-1102. DOI: 10.1016/0006-3223(90)90046-5 . |
| 143 | PITMAN D L, OTTENWELLER J E, NATELSON B H. Plasma corticosterone levels during repeated presentation of two intensities of restraint stress: chronic stress and habituation [J]. Physiol Behav, 1988, 43(1):47-55. DOI: 10.1016/0031-9384 (88)90097-2 . |
| 144 | BROCK A J, GOODY S G, MEAD A N, et al. Assessing the value of the zebrafish conditioned place preference model for predicting human abuse potential[J]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2017, 363(1):66-79. DOI: 10.1124/jpet.117.242628 . |
| 145 | TURNER P V, BRABB T, PEKOW C, et al. Administration of substances to laboratory animals: routes of administration and factors to consider[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2011, 50 (5):600-613. |
| 146 | FUEGER B J, CZERNIN J, HILDEBRANDT I, et al. Impact of animal handling on the results of 18F-FDG PET studies in mice[J]. J Nucl Med, 2006, 47(6):999-1006. |
| 147 | ASLAN Y, TADJUIDJE E, ZORN A M, et al. High efficiency non- mosaic CRISPR mediated knock-in and mutations in F0 Xenopus[J]. Development, 2017: 144(15): 2852-2858. DOI: 10.1242/dev.152967 . |
| 148 | MICHEL M C, MURPHY T J, MOTULSKY H J. New author guidelines for displaying data and reporting data analysis and statistical methods in experimental biology[J]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2020, 372(1):136-147. DOI: 10.1124/jpet.119.264143 . |
| 149 | SCHERZ M D, HUTTER C R, RAKOTOARISON A, et al. Morphological and ecological convergence at the lower size limit for vertebrates highlighted by five new miniaturised microhylid frog species from three different Madagascan Genera[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(3): e0213314. DOI: 10.1371/ journal.pone.0213314 . |
| 150 | NOVOTOVÁ M, ZAHRADNÍKOVÁ A Jr, NICHTOVÁ Z, et al. Structural variability of dyads relates to calcium release in rat ventricular myocytes[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1):8076. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-64840-5 . |
| 151 | WASSERSTEIN R L, SCHIRM A L, LAZAR N A. Moving to a world beyond “p<0.05”[J]. Am Stat, 2019, 73(sup1):1-19. DOI: 10.1080/00031305.2019.1583913 . |
| 152 | ALTMAN DSC D G. Why we need confidence intervals[J]. World J Surg, 2005, 29(5):554-556. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-005- 7911-0 . |
| 153 | MOHER D, HOPEWELL S, SCHULZ K F, et al. CONSORT 2010 explanation and elaboration: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials[J]. Int J Surg, 2012, 10(1):28-55. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2011.10.001 . |
| 154 | NAKAGAWA S, CUTHILL I C. Effect size, confidence interval and statistical significance: a practical guide for biologists[J]. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc, 2007, 82(4):591-605. DOI: 10.1111/ j.1469-185X.2007.00027.x . |
| [1] | ZHENG Qingyong, YANG Donghua, MA Zhichao, ZHOU Ziyu, LU Yang, WANG Jingyu, XING Lina, KANG Yingying, DU Li, ZHAO Chunxiang, DI Baoshan, TIAN Jinhui. Recommendations for Standardized Reporting of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis of Animal Experiments [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 496-507. |
| [2] | MIN Fangui, FU Hongkun, LIU Yonggang, LIU Xiangmei, LIU Zhonghua, LI Yao, TAO Yufeng. Special Welfare and Ethical Requirements for Infectious Animal Experiments [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 239-246. |
| [3] | LI Tengfei, ZHENG Qingyong, XU Jianguo, LI Yiyi, ZHOU Yongjia, XU Caihua, ZHANG Mingyue, TIAN Jiexiang, WANG Gang, TIAN Jinhui. Improving the Certainty of Evidence in Animal Experiment Systematic Review/Meta-Analysis: An Empirical Study of the GRADE Method [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 101-111. |
| [4] | ZHENG Qingyong, LI Tengfei, XU Jianguo, ZHOU Yongjia, MA Zhichao, WANG Na, LI Molan, YANG Wenjing, WU Peirun, WANG Haidong, TIAN Jinhui. Advances and Challenges in the Research of Integration Methods of Animal Experimental Evidence [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 567-576. |
| [5] | Editorial Board of Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine . Guideline Checklist for Publishing Research Papers on Animal Experimentation and Comparative Medicine in China (2024 Edition) [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 577-582. |
| [6] | Zhengwen MA, Xiaying LI, Xiaoyu LIU, Yao LI, Jian WANG, Jin LU, Guoyuan CHEN, Xiao LU, Yu BAI, Xuancheng LU, Yonggang LIU, Wanyong PANG, Yufeng TAO. Interpretation and Elaboration for the ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0—Animal Research: Reporting In Vivo Experiments (V) [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 105-114. |
| [7] | Jinhuan MIAO, Xia XU, Lu ZHOU, Haiyan CHENG, Yan HE. Visual Analysis of Animal Experiments on Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Nursing Technology Based on VOSviewer [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 626-635. |
| [8] | Xiaying LI, Yonglu TIAN, Xiaoyu LIU, Xuancheng LU, Guoyuan CHEN, Xiao LU, Yu BAI, Jing GAO, Yao LI, Yusheng WEI, Wanyong PANG, Yufeng TAO. Explanation and Elaboration for the ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0—Reporting Animal Research and In Vivo Experiments (Ⅳ) [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 659-668. |
| [9] | Shuo WANG, Yunhui LÜ, Xiaokang WANG, Zhenhao ZHANG, Yongchun CUI. Construction and Verification of Quality Evaluation Indicator System for Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Animal Experimental Platform [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 604-611. |
| [10] | Guoyuan CHEN, Xiao LU, Yu BAI, Lingzhi YU, Ying QIAO, Jian WANG, Jin LU, Xiaoyu LIU, Xuancheng LU, Jing GAO, Yao LI, Wanyong PANG. Explanation and Elaboration of the ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0—Reporting Animal Research and In Vivo Experiments (Ⅱ) [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 323-331. |
| [11] | Jian WANG, Jin LU, Zhengwen MA, Guoyuan CHEN, Xiao LU, Yu BAI, Xiaoyu LIU, Xuancheng LU, Jing GAO, Yao LI, Wanyong Pang. Explanation and Elaboration for the ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0—Reporting Animal Research and In Vivo Experiments (Ⅰ) [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 213-224. |
| [12] | Xiangrong DING, Shurui HUO, Jiejie DAI. Research Progress on Influenza A Virus and Nervous System Disease of Human and Experimental Animals [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 180-185. |
| [13] | Junyan ZHANG, Xiaoyu LIU, Yao LI, Guoyuan CHEN, Xiao LU, Yu BAI, Xuancheng LU, Wanyong PANG, Baojin WU. Introduction to the International Guide for Animal Research Reporting ARRIVE 2.0, and Its Implementation Plan in the Journal [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 86-94. |
| [14] | Xiangmei LIU, Zhongchun MA, Hongkun FU, Feng GAO, Yufeng TAO. Discussion on Expression of Laboratory Accreditation Scope in the Field of Toxicology Testing [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 526-530. |
| [15] | Xiaokang WANG, Ruojin ZHAO, Yunhui LÜ, Guangxin YUE, Shangyu LIU, Ting HE, Peng PENG, Liang MENG, Jubo LI, Baojie ZHANG, Chen SHEN, Yongchun CUI, Xin WANG. A Novel Model for in-vivo Training of Postgraduates on Cardiac Electrical Conduction System Mapping Skills [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 466-471. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||