













• •
高一龙( )(
)( ), 贺星亮, 周肖鹏, 李大伟, 包喜军, 李来有
), 贺星亮, 周肖鹏, 李大伟, 包喜军, 李来有
出版日期:2025-12-23
作者简介:高一龙(1982-), 男,硕士,副研究员,研究方向:主要从事警犬遗传育种、繁殖和行为遗传学研究。 E-mail: gaoyilong726@163.com。ORCID:0009-0008-7752-4239基金资助:
GAO Yilong( )(
)( ), HE Xingliang, ZHOU Xiaopeng, LI Dawei, BAO Xijun, LI Laiyou
), HE Xingliang, ZHOU Xiaopeng, LI Dawei, BAO Xijun, LI Laiyou
Published:2025-12-23
Contact:
E-mail: GAO Yilong (ORCID:0009-0008-7752-4239),E-mail: gaoyilong726@163.com。摘要:
目的 本研究旨在挖掘调控史宾格种母犬产仔数的候选基因,解析其繁殖力遗传机制,为该品种高繁殖力基因组选择育种提供参考分子标记。 方法 采用全基因组重测序技术,对高产仔数组与低产仔数组的史宾格母犬群体开展对比分析,通过选择信号分析筛选Fst与Pi高选择区域交集,结合基因注释与功能富集筛选候选基因。 结果 高产组平均窝产仔数(7.41±1.27头)显著高于低产组(3.82±1.20头)(P<0.05),总活仔数差异极显著(高产组7.06±1.10头vs低产组3.67±1.11头,P<0.01)。共检测到3 155 634个SNP,其中63.09%位于基因间区,33.97%位于内含子区,外显子区、非编码区3'端、5'端分别占0.38%、0.57%、0.09%;外显子区SNP中,非同义变异5 256个(43.55%)。经注释筛选得到1 752个差异基因,通过GO与KEGG富集分析,最终确定13个与繁殖性能相关的候选基因:WDR35、SMAD7、RPGR、RERGL、PGRMC2、LOC482182、GIMD1、COX7B2、COX16、BMPR2、BMP6、BICD1、SLC9C1,其功能涉及生殖激素调控、胚胎发育、GTP酶激活及卵细胞凋亡等。 结论 史宾格母犬产仔数性状经历显著人工选择,筛选出的13个候选基因在卵细胞成熟、妊娠初期调控中发挥关键作用,为解析犬繁殖性状遗传机制提供了新依据。
中图分类号:
高一龙,贺星亮,周肖鹏,等.基于全基因组重测序挖掘史宾格母犬产仔数性状候选基因[J]. 实验动物与比较医学.. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.149.
GAO Yilong,HE Xingliang,ZHOU Xiaopeng,et al. Mining Candidate Genes for Litter Size Traits in English Springer Spaniel Bitches Based on Whole Genome Resequencing[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.149.
表 1
Table 1 Comparison of litter size traits in the sequenced sample groups
| JCS-01 | 49 701 009 | 49 495 473 | 99.59% | 3.015 7X | 96.84 | 91.44 | 40.31 |
| JCS-02 | 57 569 978 | 57 424 899 | 99.75% | 3.5008X | 96.94 | 91.66 | 40.50 |
| JCS-06 | 50 170 943 | 50 035 322 | 99.73% | 3.0487X | 96.91 | 91.60 | 40.44 |
| JCS-11 | 56 648 593 | 56 504 709 | 99.75% | 3.4464X | 97.01 | 91.80 | 40.39 |
| JCS-13 | 63 501 199 | 63 282 693 | 99.66% | 3.8588X | 97.04 | 91.79 | 41.18 |
| JCS-15 | 67 124 038 | 66 904 179 | 99.67% | 4.0751X | 96.98 | 91.76 | 40.54 |
| JCS-17 | 60 312 575 | 60 159 920 | 99.75% | 3.6745X | 97.05 | 91.92 | 40.44 |
| JCS-18 | 56 651 718 | 56 505 792 | 99.74% | 3.4491X | 97.10 | 92.02 | 40.49 |
| JCS-20 | 52 034 437 | 51 854 996 | 99.66% | 3.1583X | 96.90 | 91.61 | 41.38 |
| JCS-25 | 46 446 939 | 46 318 986 | 99.72% | 2.8253X | 96.89 | 91.54 | 40.39 |
| JCS-27 | 51 579 104 | 51 417 318 | 99.69% | 3.1311X | 96.98 | 91.77 | 40.37 |
| JCS-30 | 57 620 774 | 57 306 085 | 99.45% | 3.4721X | 98.04 | 94.40 | 40.97 |
| JCS-32 | 56 929 134 | 56 841 636 | 99.85% | 3.4513X | 98.01 | 94.35 | 40.98 |
| JCS-36 | 61 621 912 | 61 516 493 | 99.83% | 3.7334X | 98.06 | 94.47 | 40.86 |
| JCS-38 | 59 543 985 | 59 452 953 | 99.85% | 3.6161X | 97.97 | 94.22 | 40.01 |
| JCS-41 | 55 343 670 | 55 265 057 | 99.86% | 3.3547X | 98.03 | 94.42 | 40.32 |
| JCS-47 | 53 077 925 | 52 998 639 | 99.85% | 3.2192X | 98.03 | 94.39 | 40.13 |
| JCS-49 | 47 499 774 | 47 414 328 | 99.82% | 2.8789X | 98.03 | 94.39 | 40.06 |
| JCS-50 | 50 683 884 | 50 608 669 | 99.85% | 3.0786X | 98.02 | 94.37 | 40.11 |
| JCS-52 | 56 492 470 | 56 374 197 | 99.79% | 3.424X | 98.03 | 94.37 | 40.03 |
表 2 高产仔数组与低产仔数组母犬全基因组重测序数据
Table 2 Resequencing data of whole genome of bitches in high litter size group and low litter size group
| JCS-01 | 49 701 009 | 49 495 473 | 99.59% | 3.015 7X | 96.84 | 91.44 | 40.31 |
| JCS-02 | 57 569 978 | 57 424 899 | 99.75% | 3.5008X | 96.94 | 91.66 | 40.50 |
| JCS-06 | 50 170 943 | 50 035 322 | 99.73% | 3.0487X | 96.91 | 91.60 | 40.44 |
| JCS-11 | 56 648 593 | 56 504 709 | 99.75% | 3.4464X | 97.01 | 91.80 | 40.39 |
| JCS-13 | 63 501 199 | 63 282 693 | 99.66% | 3.8588X | 97.04 | 91.79 | 41.18 |
| JCS-15 | 67 124 038 | 66 904 179 | 99.67% | 4.0751X | 96.98 | 91.76 | 40.54 |
| JCS-17 | 60 312 575 | 60 159 920 | 99.75% | 3.6745X | 97.05 | 91.92 | 40.44 |
| JCS-18 | 56 651 718 | 56 505 792 | 99.74% | 3.4491X | 97.10 | 92.02 | 40.49 |
| JCS-20 | 52 034 437 | 51 854 996 | 99.66% | 3.1583X | 96.90 | 91.61 | 41.38 |
| JCS-25 | 46 446 939 | 46 318 986 | 99.72% | 2.8253X | 96.89 | 91.54 | 40.39 |
| JCS-27 | 51 579 104 | 51 417 318 | 99.69% | 3.1311X | 96.98 | 91.77 | 40.37 |
| JCS-30 | 57 620 774 | 57 306 085 | 99.45% | 3.4721X | 98.04 | 94.40 | 40.97 |
| JCS-32 | 56 929 134 | 56 841 636 | 99.85% | 3.4513X | 98.01 | 94.35 | 40.98 |
| JCS-36 | 61 621 912 | 61 516 493 | 99.83% | 3.7334X | 98.06 | 94.47 | 40.86 |
| JCS-38 | 59 543 985 | 59 452 953 | 99.85% | 3.6161X | 97.97 | 94.22 | 40.01 |
| JCS-41 | 55 343 670 | 55 265 057 | 99.86% | 3.3547X | 98.03 | 94.42 | 40.32 |
| JCS-47 | 53 077 925 | 52 998 639 | 99.85% | 3.2192X | 98.03 | 94.39 | 40.13 |
| JCS-49 | 47 499 774 | 47 414 328 | 99.82% | 2.8789X | 98.03 | 94.39 | 40.06 |
| JCS-50 | 50 683 884 | 50 608 669 | 99.85% | 3.0786X | 98.02 | 94.37 | 40.11 |
| JCS-52 | 56 492 470 | 56 374 197 | 99.79% | 3.424X | 98.03 | 94.37 | 40.03 |
表 3 SNP 检测统计信息及注释结果
Table 3 SNP detection statistics and annotation results
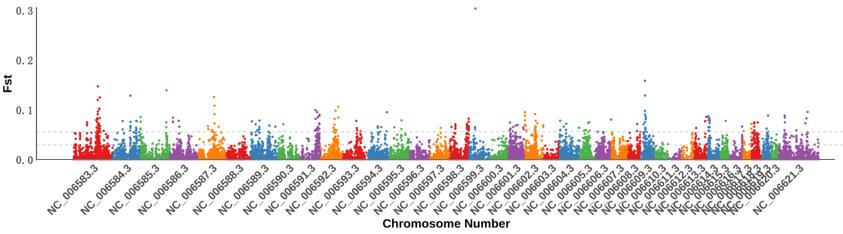
图 1 群体分化 Fst 分布注:2条虚线代表2种选择阈值(Fst Top 1%、5%))
Fig. 1 Population differentiation distribution map of FstNote:Two dashed lines represent the selection threshold (Fst Top 1% and 5%).
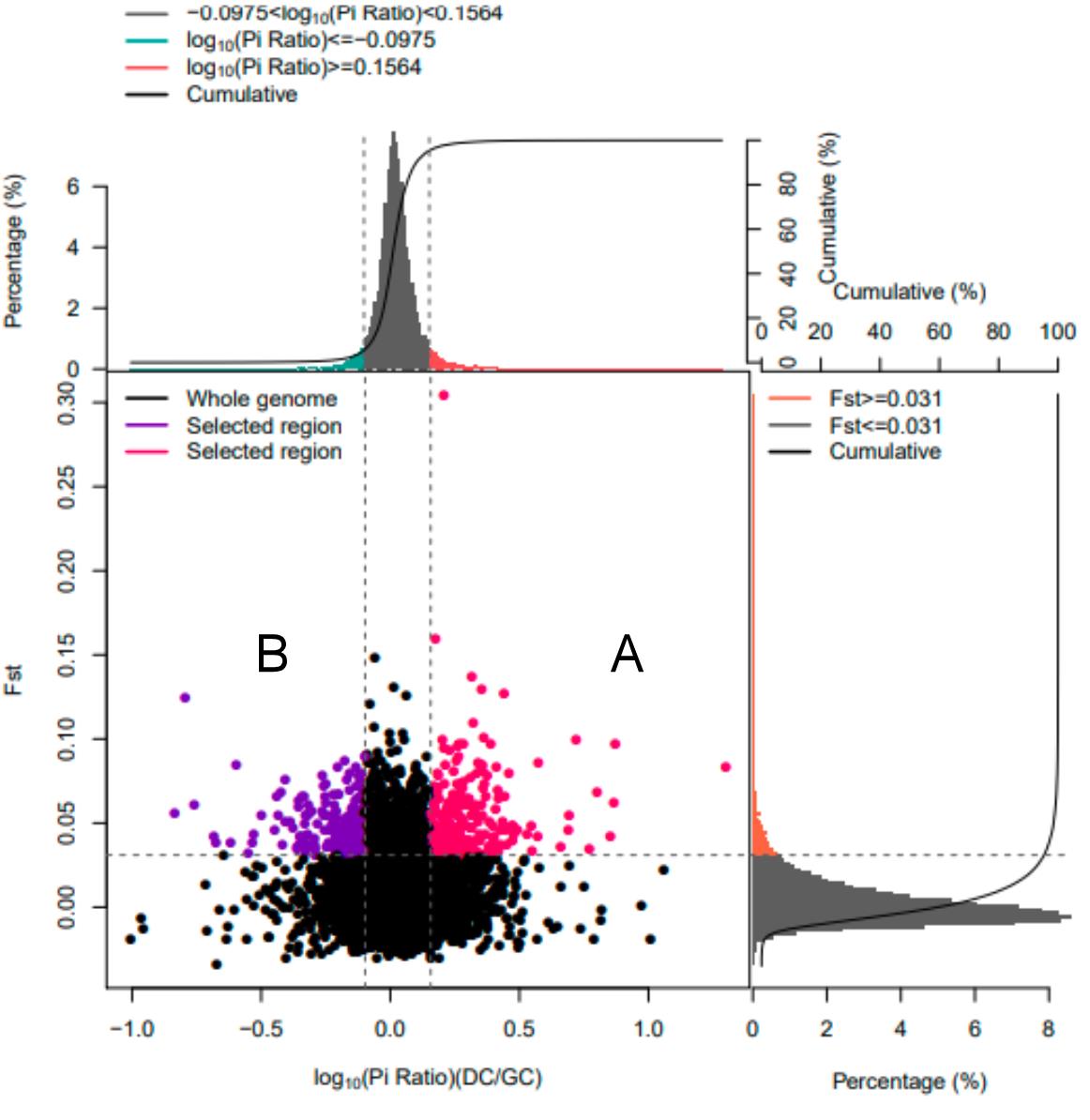
图 3 Fst、Pi 选择消除分析结果注:A:高产仔数母犬群体的信号选择区域;B:低产仔数母犬群体的信号选择区域。横坐标为Pi比率值,纵坐标表示Fst值,分别对应上面的频率分布图和右侧的频率分布图,中部的点图则代表不同窗口内的相应的Fst和Pi比值。其中最上方绿色和红色区域为Pi选择出来的top 5%区域,右侧橘色区域为Fst所选择top 5%区域,中间红色和紫色区域为Fst和Pi的交集,即为候选的位点。
Fig. 3 Selection elimination analysis results of Fst and PiNote: A: Signal selection regions of high litter size bitches population; B: Signal selection regions of low litter size bitches population. The horizontal axis represents Pi ratio values, while the vertical axis shows Fst values corresponding to the frequency distribution charts above and on the right. The dot plot in the middle displays Fst and Pi ratios within different windows. The green and red areas at the top represent the top 5% regions selected by Pi, while the orange area on the right indicates the top 5% regions identified by Fst. The central red and purple areas mark the intersection of Fst and Pi values, identifying candidate sites.
基因 Gene | 染色体 Chromosome | 基因座位(起始-终止)Locus(Start-End ) | SNP变异 SNP variation | 基因功能及注释 Gene function and annotation | 通路名称 Path name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WDR35 | Chr17 | 15 000 306-15 020 189 | Chr17 15 000 306 | 与细胞内的纤毛发生、纤毛维持及相关信号通路调控相关 | 纤毛内运输(Intraflagellar Transport, IFT)通路、Hedgehog 信号通路 |
| SMAD7 | Chr15 | 31 542 000-31 558 721 | Chr15 31,542,000 | 调控卵巢颗粒细胞增殖与凋亡 | MAPK 信号通路 |
| RPGR | ChrX | 33 060 949-33 102 418 | ChrX:33 060 949 | 调控视网膜感光细胞的纤毛功能和蛋白质运输 | 纤毛组装与维持通路、GTPase 信号通路 |
| RERGL | Chr27 | 28 947 686-28 952 314 | Chr27:28 947 686 | 小 GTP 酶编码基因,涉及细胞增殖、分化、信号传导 | Ras 信号通路 |
| PGRMC2 | Chr19 | 12 726 628-12 735 981 | Chr19:12 726 628 | 参与激素代谢、细胞应激响应的多功能基因 | 类固醇激素生物合成通路 |
| LOC482182 | Chr13 | 59 333 984-59 340 152 | Chr13:59 333 984 | 未表征基因,可能与神经系统发育及细胞增殖调控有关 | 细胞表面信号传递 |
| GIMD1 | Chr32 | 27 203 619-27 218 453 | Chr32:27 203 619 | GIMD1编码的蛋白质可能具有 GTP 结合活性和核苷酸结合活性;DKK2参与调控 WNT 信号通路,在胚胎发育、组织稳态 | 免疫细胞活化与存活调控 |
| COX7B2 | Chr13 | 42 746 234-42 748 911 | Chr13:42 746 234 | 线粒体呼吸链复合体 Ⅳ(细胞色素 c 氧化酶,COX)的一个亚基,参与细胞能量代谢关键过程 | 氧化磷酸化通路 |
| COX16 | Chr8 | 44 007 617-44 010 352 | Chr8:44 007 617 | 线粒体 COX 复合体组装的关键辅助因子,通过调控 COX 正确形成维持线粒体呼吸功能 | 细胞色素c氧化酶 复合物组装通路 |
| BMPR2 | Chr37 | 11 386 691-11 420 837 | Chr37:11 386 691 | 骨形态发生蛋白(BMP)受体家族的重要成员,属于丝氨酸 / 苏氨酸激酶受体,在细胞信号传导、胚胎发育、组织稳态及疾病发生中发挥关键作用。 | BMP 信号通路 |
| BMP6 | Chr35 | 7 810 492-7 825 638 | Chr35:7 810 492 | BMP6 可抑制颗粒细胞凋亡,促进雌激素合成,维持卵泡正常生长 | 生殖系统调控通路 |
| BICD1 | Chr27 | 16 534 098-16 548 213 | Chr27:16 534 098 | BICD1 作为细胞内物质运输辅助因子,参与调控卵细胞成熟、受精和早期胚胎形成 | 参与囊泡介导的运输和高尔基体到内质网的逆向运输等通路 |
| SLC9C1 | Chr33 | 16 824 626-16 838 942 | Chr33:16 824 626 | 溶质载体基因、与精子的运动和 生育能力相关 | 离子跨膜运输通路 |
表 4 候选基因的 染色体座位、SNP变异注释及 GO、KEGG富集分析
Table 4 SNP variation annotation and locus of of candidate genes and enrichment analysis of GO and KEGG
基因 Gene | 染色体 Chromosome | 基因座位(起始-终止)Locus(Start-End ) | SNP变异 SNP variation | 基因功能及注释 Gene function and annotation | 通路名称 Path name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WDR35 | Chr17 | 15 000 306-15 020 189 | Chr17 15 000 306 | 与细胞内的纤毛发生、纤毛维持及相关信号通路调控相关 | 纤毛内运输(Intraflagellar Transport, IFT)通路、Hedgehog 信号通路 |
| SMAD7 | Chr15 | 31 542 000-31 558 721 | Chr15 31,542,000 | 调控卵巢颗粒细胞增殖与凋亡 | MAPK 信号通路 |
| RPGR | ChrX | 33 060 949-33 102 418 | ChrX:33 060 949 | 调控视网膜感光细胞的纤毛功能和蛋白质运输 | 纤毛组装与维持通路、GTPase 信号通路 |
| RERGL | Chr27 | 28 947 686-28 952 314 | Chr27:28 947 686 | 小 GTP 酶编码基因,涉及细胞增殖、分化、信号传导 | Ras 信号通路 |
| PGRMC2 | Chr19 | 12 726 628-12 735 981 | Chr19:12 726 628 | 参与激素代谢、细胞应激响应的多功能基因 | 类固醇激素生物合成通路 |
| LOC482182 | Chr13 | 59 333 984-59 340 152 | Chr13:59 333 984 | 未表征基因,可能与神经系统发育及细胞增殖调控有关 | 细胞表面信号传递 |
| GIMD1 | Chr32 | 27 203 619-27 218 453 | Chr32:27 203 619 | GIMD1编码的蛋白质可能具有 GTP 结合活性和核苷酸结合活性;DKK2参与调控 WNT 信号通路,在胚胎发育、组织稳态 | 免疫细胞活化与存活调控 |
| COX7B2 | Chr13 | 42 746 234-42 748 911 | Chr13:42 746 234 | 线粒体呼吸链复合体 Ⅳ(细胞色素 c 氧化酶,COX)的一个亚基,参与细胞能量代谢关键过程 | 氧化磷酸化通路 |
| COX16 | Chr8 | 44 007 617-44 010 352 | Chr8:44 007 617 | 线粒体 COX 复合体组装的关键辅助因子,通过调控 COX 正确形成维持线粒体呼吸功能 | 细胞色素c氧化酶 复合物组装通路 |
| BMPR2 | Chr37 | 11 386 691-11 420 837 | Chr37:11 386 691 | 骨形态发生蛋白(BMP)受体家族的重要成员,属于丝氨酸 / 苏氨酸激酶受体,在细胞信号传导、胚胎发育、组织稳态及疾病发生中发挥关键作用。 | BMP 信号通路 |
| BMP6 | Chr35 | 7 810 492-7 825 638 | Chr35:7 810 492 | BMP6 可抑制颗粒细胞凋亡,促进雌激素合成,维持卵泡正常生长 | 生殖系统调控通路 |
| BICD1 | Chr27 | 16 534 098-16 548 213 | Chr27:16 534 098 | BICD1 作为细胞内物质运输辅助因子,参与调控卵细胞成熟、受精和早期胚胎形成 | 参与囊泡介导的运输和高尔基体到内质网的逆向运输等通路 |
| SLC9C1 | Chr33 | 16 824 626-16 838 942 | Chr33:16 824 626 | 溶质载体基因、与精子的运动和 生育能力相关 | 离子跨膜运输通路 |
| [1] | LI H, DURBIN R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform[J]. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(14):1754-1760. DOI:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324 . |
| [2] | LI H, HANDSAKER B, WYSOKER A, et al. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools[J]. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(16):2078-2079. DOI:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352 . |
| [3] | WANG K, LI M Y, HAKONARSON H. ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2010, 38(16): 1-7. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkq603 . |
| [4] | DE LOS REYES M, SONGSASEN N. New insights in canine reproduction[J]. Animals, 2021, 11(7):2021. DOI:10.3390/ani11072021 . |
| [5] | TORRECILHA R B P, MILANESI M, WADE C M, et al. Association of missense variants in GDF9 with litter size in Entlebucher Mountain dogs[J]. Anim Genet, 2020, 51(1):78-86. DOI:10.1111/age.12882 . |
| [6] | GARCIA P, ASPEE K, RAMIREZ G, et al. Influence of growth differentiation factor 9 and bone morphogenetic protein 15 on in vitro maturation of canine oocytes[J]. Reprod Domest Anim, 2019, 54(2):373-380. DOI:10.1111/rda.13371 . |
| [7] | 刘成武. 犬繁殖性状相关候选基因: 雌激素受体基因研究进展[J]. 中国工作犬业, 2014(4):12-13. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-0135.2014.04.003 . |
| LIU C W. Research progress of estrogen receptor gene, a candidate gene related to reproductive traits in dogs[J]. China Working Dog, 2014(4):12-13. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-0135.2014.04.003 . | |
| [8] | LEE S H, OH H J, KIM M J, et al. Oocyte maturation-related gene expression in the canine oviduct, cumulus cells, and oocytes and effect of co-culture with oviduct cells on in vitro maturation of oocytes[J]. J Assist Reprod Genet, 2017, 34(7):929-938. DOI:10.1007/s10815-017-0910-x . |
| [9] | MCKENNA A, HANNA M, BANKS E, et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data[J]. Genome Res, 2010, 20(9):1297-1303. DOI:10.1101/gr.107524.110 . |
| [10] | DANECEK P, AUTON A, ABECASIS G, et al. The variant call format and VCFtools[J]. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27(15):2156-2158. DOI:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr330 . |
| [11] | 贺生中, 狄和双, 郑筱峰, 等. 贵宾犬FSHβ基因多态性与产仔数的相关性分析[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2013, 41(6):24-26. DOI:10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2013.06.141 . |
| HE S Z, DI H S, ZHENG X F, et al. Correlation analysis between FSHβ gene polymorphism and litter size in poodles[J]. Jiangsu Agric Sci, 2013, 41(6):24-26. DOI:10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2013.06.141 . | |
| [12] | 刘成武, 杨敏. 德国牧羊犬FSHR基因第1外显子SNP T89C与产仔数关系研究[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2014(17):66-68, 230. DOI:10.13881/j.cnki.hljxmsy.2014.1038 . |
| LIU C W, YANG M. Study on the relationship between the SNP T89C in exon 1 of the FSHR gene and litter size in German shepherd dog[J]. Heilongjiang Anim Sci Vet Med, 2014(17):66-68, 230. DOI:10.13881/j.cnki.hljxmsy.2014.1038 . | |
| [13] | 王丽华, 狄和双, 陈爱凤, 等. 贵宾犬ESRα基因多态性及其与繁殖性能的关系[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2013, 41(5):28-30. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-1302.2013.05.009 . |
| WANG L H, DI H S, CHEN A F, et al. Polymorphism of ESRα gene in poodle and its relationship with reproductive performance[J]. Jiangsu Agric Sci, 2013, 41(5):28-30. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-1302.2013.05.009 . | |
| [14] | 狄和双. 犬FSH和ESR基因多态性与产仔数的相关性研究[C/OL]//第16次全国犬业科技学术研讨会论文集. 2015[2025-09-10]. . |
| DI H S.Correlation between canine FSH and ESR gene polymorphisms and litter size[C/OL]//Proceedings of the 16th National Conference on Canine Science and Technology. 2015[2025-09-10]. . | |
| [15] | 屈子啸, 杨帅朋, 朱向星, 等. 基于全基因组重测序挖掘大白-长白二元母猪产仔数性状候选基因[J]. 广东农业科学, 2023, 50(3):120-128. DOI:10.16768/j.issn.1004-874X.2023.03.014 . |
| QU Z X, YANG S P, ZHU X X, et al. Mining candidate genes for litter size traits in large white-Landrace crossbred sows based on whole genome resequencing[J]. Guangdong Agric Sci, 2023, 50(3):120-128. DOI:10.16768/j.issn.1004-874X.2023.03.014 . | |
| [16] | 吕玲燕, 林昌华, 张胜斌, 等. 基于重测序数据的猪繁殖性状全基因组关联分析[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2025, 61(1):235-241. DOI:10.19556/j.0258-7033.20231205-05 . |
| LÜ L Y, LIN C H, ZHANG S B, et al. Genome-wide association study of pig reproductive traits based on resequencing data[J]. Chin J Anim Sci, 2025, 61(1):235-241. DOI:10.19556/j.0258-7033.20231205-05 . | |
| [17] | 李梦营, 依明·苏来曼, 李梦妮, 等. 基于全基因组重测序筛选皮山红羊和哈萨克羊繁殖性状候选基因的研究[J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 43(1):74-80. DOI:10.13880/j.cnki.65-1174/n.2025.22.006 . |
| LI M Y, SULAIMAN Yiming, LI M N, et al. Screening of candidate genes for reproductive traits in Pishan Red and Kazakh sheep based on whole genome resequencing[J]. J Shihezi Univ Nat Sci, 2025, 43(1):74-80. DOI:10.13880/j.cnki.65-1174/n.2025.22.006 . | |
| [18] | 徐高骁. 基于卵巢全转录组学和代谢组学筛选影响猪产仔数性状的候选基因、非编码RNA及miR-183-circTCP1轴的功能验证[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2019. DOI:10.27409/d.cnki.gxbnu.2019.000054 . |
| XU G X. Based on ovarian transcriptome and metabolome,screened MRNA and non-coding RNA influence litter size of sow and verify the functions of MIR-183-CIRCTCP1 pathway[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2019. DOI:10.27409/d.cnki.gxbnu.2019.000054 . | |
| [19] | CAGNONE G L M, TSAI T S, MAKANJI Y, et al. Restoration of normal embryogenesis by mitochondrial supplementation in pig oocytes exhibiting mitochondrial DNA deficiency[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6:1-15. DOI:10.1038/srep23229 . |
| [20] | KIRILLOVA A, SMITZ J E J, SUKHIKH G T, et al. The role of mitochondria in oocyte maturation[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(9):1-17. DOI:10.3390/cells10092484 . |
| [1] | 何永平, 谢美贤, 庞智慧, 李庆秀, 何华红, 张讷敏, 李薇. 实验用猫的驯化及繁殖方法初步研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(1): 67-72. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||