













实验动物与比较医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 177-186.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.001
刘佳妮1,2,3( ), 刘剑刚1(
), 刘剑刚1( ), 韦云1(
), 韦云1( )(
)( ), 罗增刚4, 李浩1, 王怡3, 李琨5
), 罗增刚4, 李浩1, 王怡3, 李琨5
收稿日期:2022-01-04
修回日期:2022-03-25
出版日期:2022-06-25
发布日期:2022-06-25
作者简介:刘佳妮(1992—),女,博士研究生,研究方向:老年病的中西医结合临床研究和基础研究。E-mail:liujiani1110@163.com刘剑刚(1963—),男,研究员,研究生导师,研究方向:中药药理学及微循环学,心血管病的中西医结合临床研究和基础研究。E-mail:liujiangang2002@sina.com。ORCID:0000-0002-2313-4592韦云(1981—),女,副主任医师,医学博士,研究生导师,研究方向:中西医结合老年病的临床研究和基础研究。E-mail:weiyun_0913@163.com。ORCID:0000-0001-9270-2701
基金资助:
Jiani LIU1,2,3( ), Jiangang LIU1(
), Jiangang LIU1( ), Yun WEI1(
), Yun WEI1( )(
)( ), Hao LI4, Zenggang LUO1, Yi WANG3, Kun LI5
), Hao LI4, Zenggang LUO1, Yi WANG3, Kun LI5
Received:2022-01-04
Revised:2022-03-25
Published:2022-06-25
Online:2022-06-25
About author:LIU Jiangang E-mail: liujiangang2002@sina.com摘要:
目的 比较和探讨6月龄和12月龄的APP/PS1双转基因模型小鼠嗅球组织病理形态、超微结构特征、空间记忆能力的变化以及美金刚干预的作用。方法 将SPF级3月龄雄性APP/PS1小鼠按随机数字表法分为6月龄、12月龄的模型组(分别为命名为6-APP/PS1组、12-APP/PS1组)和盐酸美金刚(memantine hydrochloride,MEM)干预组(分别命名为6-MEM组、12-MEM组,MEM剂量均为2.60 mg/kg/d),每组10只。另设同龄C57BL/6小鼠作为空白对照组。MEM连续(分别自3月龄和9月龄)灌胃3个月,非MEM处理小鼠接受等容积纯净水灌胃。于6月龄和12月龄时进行Morris水迷宫实验检测,固定取材进行HE染色后光学显微镜下观察嗅球病理组织形态,超薄切片染色后透射电子显微镜下观察嗅球超微结构。 结果 水迷宫结果显示,与同龄的空白对照组比较,6-APP/PS1组和12-APP/PS1组小鼠的穿台次数、穿梭目标象限的时间及路程明显降低(均P<0.05),且12-APP/PS1组比6-APP/PS1组的降低程度更明显(均P<0.05);与同龄的模型组比较,6-MEM组和12-MEM组的穿台次数、目标象限停留时间及路程显著提高(均P<0.05)。组织病理学观察发现,与同龄的空白对照组比较,6-APP/PS1组小鼠嗅球的神经细胞无明显萎缩变形且僧帽细胞数量显著减少(P<0.05),12-APP/PS1组小鼠嗅球的神经细胞萎缩变形且球周细胞、僧帽细胞数量显著减少(均P<0.05);与同龄模型组比较,6-MEM组球周细胞无显著增多但僧帽细胞数量显著增多(P<0.05),12-MEM组球周细胞、僧帽细胞数量有增加趋势但差异无统计学意义(均P>0.05)。超微结构观察显示,与同龄的空白对照组比较,6-APP/PS1组突触结构出现肿胀,突触后致密物厚度及非对称性突触数量减少;12-APP/PS1组突触结构肿胀,非对称性突触及突触后致密物厚度无法观测。与同龄模型组比较,6-MEM组突触肿胀改善明显,突触后致密物厚度及非对称性突触数量增加;12-MEM组突触肿胀改善不明显,突触后致密物及非对称性突触无法观测。结论 随月龄增加,不同时程的APP/PS1小鼠出现了阿尔茨海默病相关的行为学改变,同时伴随嗅球病理及突触特征的显著变化。MEM干预不仅改善空间记忆能力,还可增加6-APP/PS1小鼠嗅球的僧帽细胞数量,减轻突触结构损伤,早期干预的改善效果显著。
中图分类号:
刘佳妮,刘剑刚,韦云,等. 不同时程APP/PS1模型小鼠嗅球病理和突触形态变化及美金刚干预作用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2022, 42(3): 177-186. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.001.
Jiani LIU,Jiangang LIU,Yun WEI,et al. Pathological and Synaptic Morphological Changes of the Olfactory Bulb in APP/PS1 Model Mice at Different Ages and the Intervention Effect of Memantine[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 177-186. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.001.
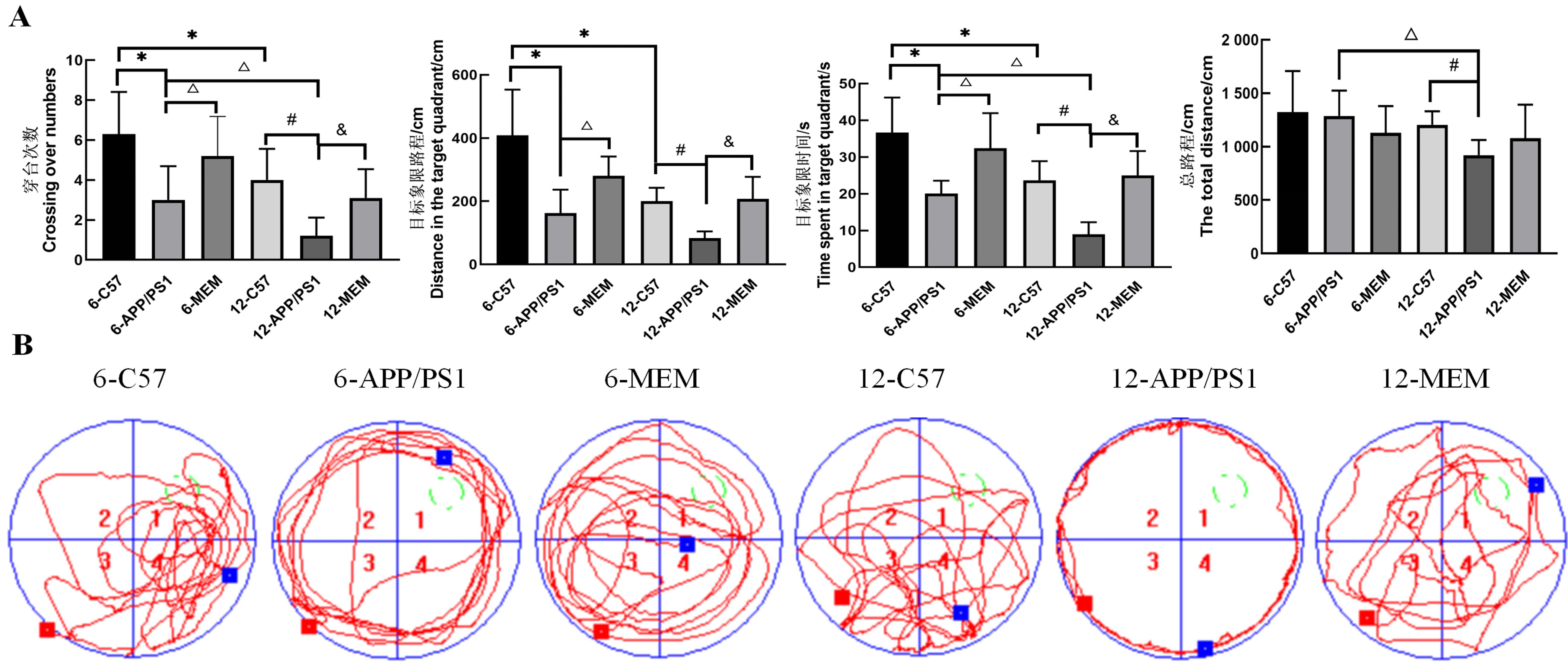
图1 Morris水迷宫实验评估各组小鼠的行为学变化注:A图示不同时程各组小鼠的穿台次数、目标象限路程、目标象限时间和总路程;B图示各组小鼠在水迷宫中游动轨迹(绿色线圈为原逃生平台位置,红色方块为入水点,蓝色方块为90 s截止录制点)。6-C57指6月龄的空白对照组C57BL/6小鼠;6-APP/PS1指6月龄的模型组APP/PS1双转基因小鼠;6-MEM指从3月龄开始用2.6 mg/kg盐酸美金刚干预至6月龄的APP/PS1双转基因小鼠;12-C57指12月龄的空白对照组C57BL/6小鼠;12-APP/PS1指12月龄的模型组APP/PS1双转基因小鼠;12-MEM指从9月龄开始用2.6 mg/kg盐酸美金刚干预至12月龄的APP/PS1双转基因小鼠。每组10只小鼠。与6-C57相比,*P < 0.05;与12-C57相比,#P < 0.05;与6-APP/PS1相比,△P < 0.05;与12-APP/PS1相比,&P < 0.05。
Figure 1 Morris water maze test to evaluate the behavioral changes of mice in each groupNote: Fig. A shows the crossing numbers, distance in the target quadrant, time spent in the target quadrant, and the total distance of mice in each group. Fig. B shows the swimming track of mice in each group in the water maze (the green circle represents the position of the original escape platform, the red dot represents the entry point, and the blue dot represents the 90 s cut-off point). 6-C57 refers to 6-month-old C57BL/6 mice in the blank control group. 6-APP/PS1 refers to 6-month-old APP/PS1 double transgenic mice in the model group; 6-MEM refers to APP/PSI double transgenic mice treated with 2.6 mg/kg memantine hydrochloride from 3- to 6-month-old; 12-C57 refers to 12-month-old C57BL/6 mice; 12-APP/PS1 refers to 12-month-old APP/PS1 double transgenic mice; 12-MEM refers to APP/PS1 double transgenic mice treated with 2.6 mg/kg memantine hydrochloride from 9- to 12-month-old. Each group contained 10 mice. Compared with 6-C57, *P < 0.05; compared with 12-C57, #P < 0.05; compared with 6-APP/PS1, △P < 0.05; compared with 12-APP/PS1, &P < 0.05.
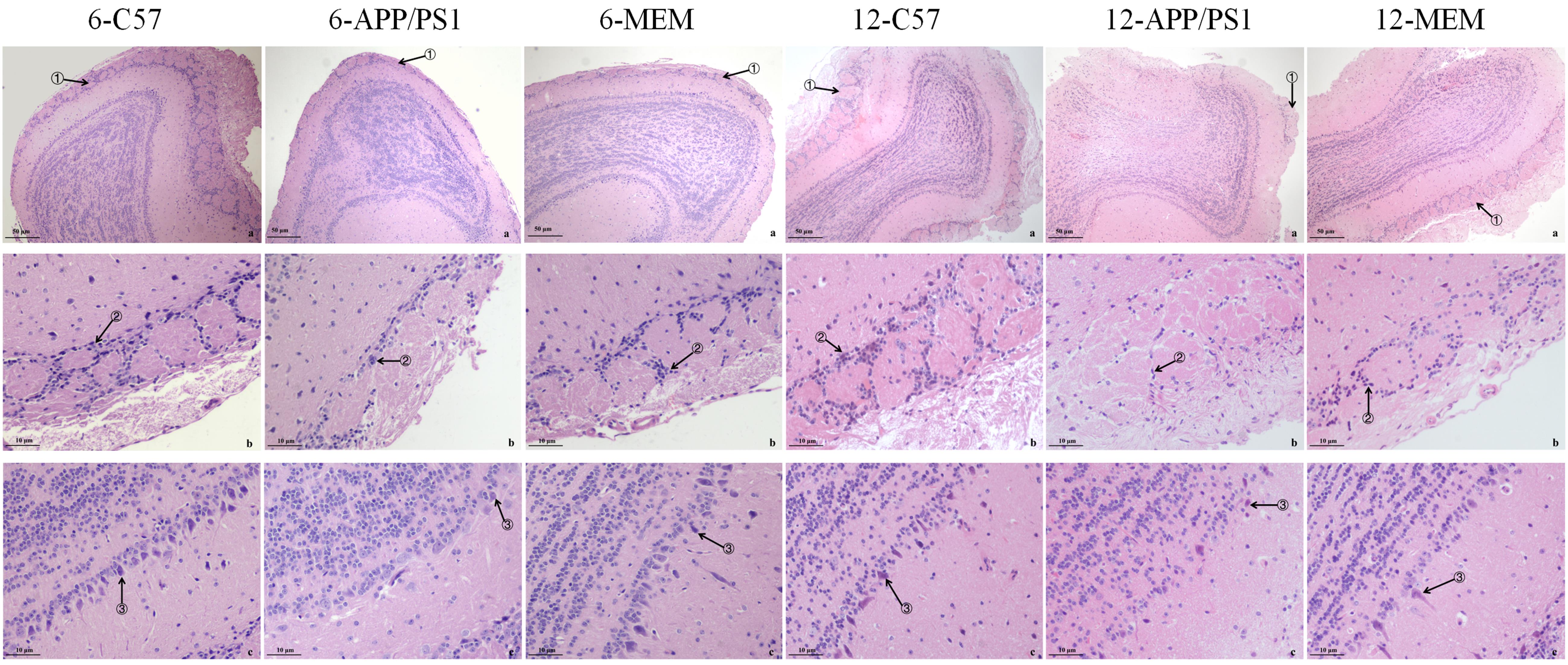
图2 HE染色后光学显微镜观察各组小鼠的嗅球病理变化注:图a示低倍镜下嗅球(×40),图b示高倍镜下小球层(×200),图c示高倍镜下僧帽细胞层(×200)。箭头①为突触小球,箭头②为球周细胞,箭头③为僧帽细胞。6-C57指6月龄的空白对照组C57BL/6小鼠;6-APP/PS1指6月龄的模型组APP/PS1双转基因小鼠;6-MEM指从3月龄开始用2.6 mg/kg盐酸美金刚干预至6月龄的APP/PS1双转基因小鼠;12-C57指12月龄的空白对照组C57BL/6小鼠;12-APP/PS1指12月龄的模型组APP/PS1双转基因小鼠;12-MEM指从9月龄开始用2.6 mg/kg盐酸美金刚干预至12月龄的APP/PS1双转基因小鼠。每组5只小鼠。
Figure 2 Pathological changes of the olfactory bulb in mice in each group observed by optical microscopy after hematoxylin-eosin stainingNote: Fig. a is the olfactory bulb (×40); Fig. b is the glomerular layer (×200); Fig. c is the mitral cell layer (×200). Arrows ①, ②, and ③ show glomeruli, periglomerular, and mitral cells, respectively. 6-C57 refers to 6-month-old C57BL/6 mice in the blank control group; 6-APP/PS1 refers to 6-month-old APP/PS1 double transgenic mice in the model group; 6-MEM refers to APP/PSI double transgenic mice treated with 2.6 mg/kg memantine hydrochloride from 3- to 6-month-old; 12-C57 refers to 12-month-old C57BL/6 mice; 12-APP/PS1 refers to 12-month-old APP/PS1 double transgenic mice; 12-MEM refers to APP/PS1 double transgenic mice treated with 2.6 mg/kg memantine hydrochloride from 9- to 12-month-old. Each group contained five mice.
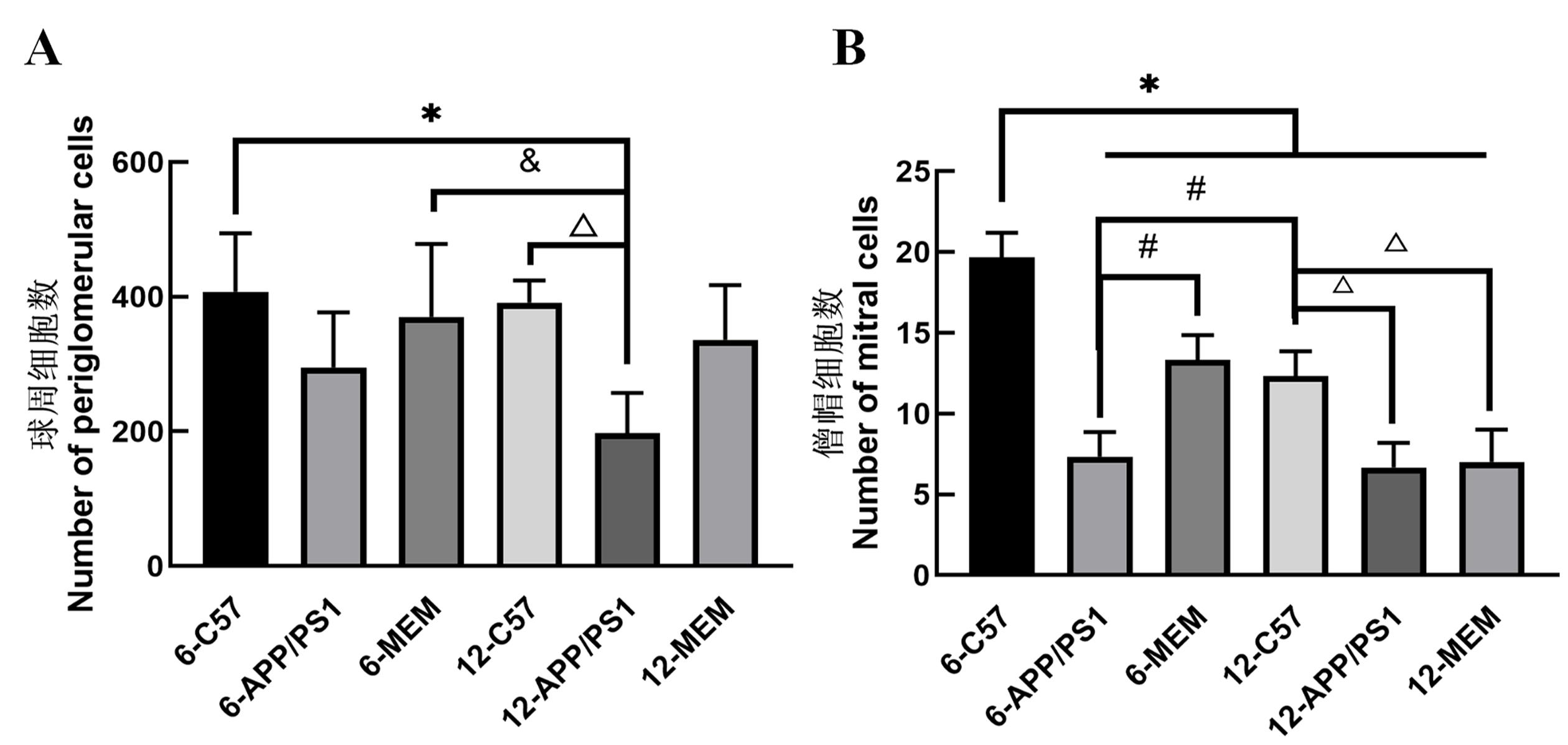
图3 美金刚对球周细胞(A)和僧帽细胞(B)的影响注:6-C57指6月龄的空白对照组C57BL/6小鼠;6-APP/PS1指6月龄的模型组APP/PS1双转基因小鼠;6-MEM指从3月龄开始用2.6 mg/kg盐酸美金刚干预至6月龄的APP/PS1双转基因小鼠;12-C57指12月龄的空白对照组C57BL/6小鼠;12-APP/PS1指12月龄的模型组APP/PS1双转基因小鼠;12-MEM指从9月龄开始用2.6 mg/kg盐酸美金刚干预至12月龄的APP/PS1双转基因小鼠。每组5只小鼠。与6-C57相比,*P < 0.05;与12-C57相比,#P < 0.05;与6-APP/PS1相比,△P <0.05;与12-APP/PS1相比,&P < 0.05。
Figure 3 Effects of memantine on periglomerular cells (A) and mitral cells (B)Note: 6-C57 refers to 6-month-old C57BL/6 mice in the blank control group; 6-APP/PS1 refers to 6-month-old APP/PS1 double transgenic mice in model group; 6-MEM refers to APP/PSI double transgenic mice treated with 2.6 mg/kg memantine hydrochloride from 3- to 6-month-old; 12-C57 refers to 12-month-old C57BL/6 mice; 12-APP/PS1 refers to 12-month-old APP/PS1 double trans-genic mice; 12-MEM refers to APP/PS1 double transgenic mice treated with 2.6 mg/kg memantine hydrochloride from 9- to 12-month-old. Each group contained five mice. Compared with 6-C57, *P < 0.05; compared with 12-C57, #P < 0.05; compared with 6-APP/PS1, △P < 0.05; compared with 12-APP/PS1, &P < 0.05.
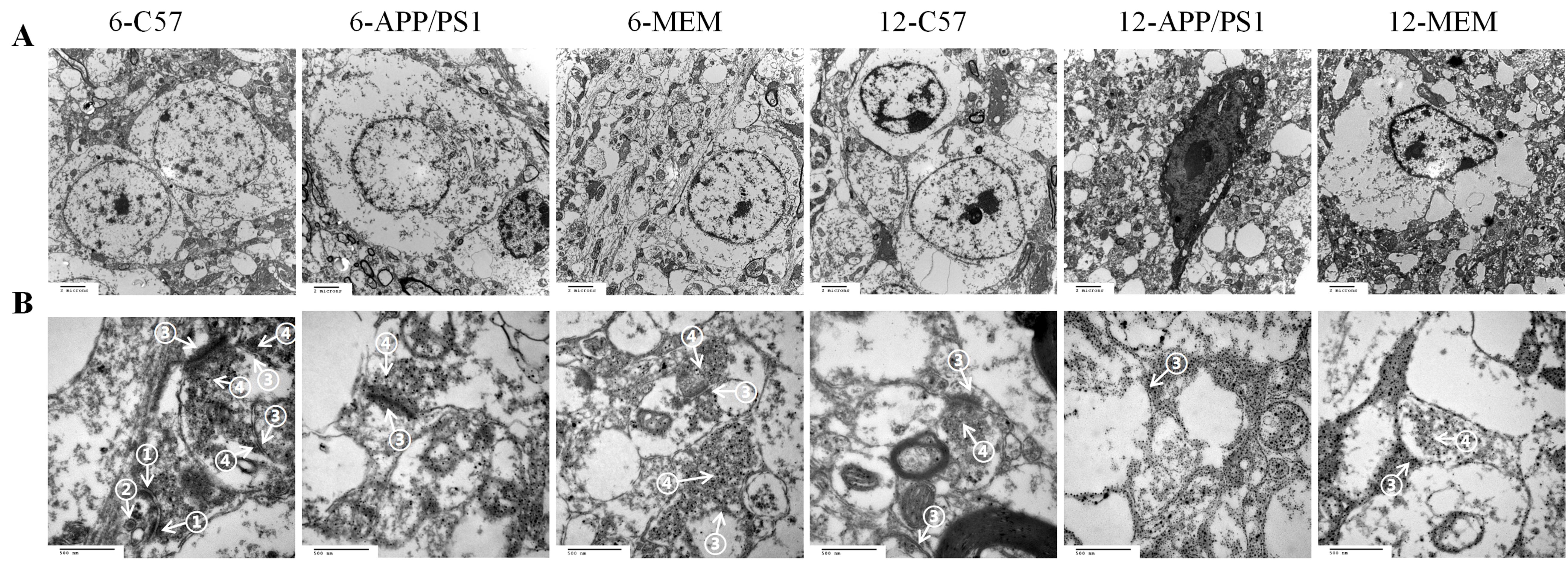
图4 超薄切片染色后透射电子显微镜观察各组小鼠嗅球神经(A,×7 000)和突触(B,×60 000)细胞超微结构注:6-C57指6月龄的空白对照组C57BL/6小鼠;6-APP/PS1指6月龄的模型组APP/PS1双转基因小鼠;6-MEM指从3月龄开始用2.6 mg/kg盐酸美金刚干预至6月龄的APP/PS1双转基因小鼠;12-C57指12月龄的空白对照组C57BL/6小鼠;12-APP/PS1指12月龄的模型组APP/PS1双转基因小鼠;12-MEM指从9月龄开始用2.6 mg/kg盐酸美金刚干预至12月龄的APP/PS1双转基因小鼠。每组5只小鼠。箭头①示对称性突触,箭头②示突触小泡(内含抑制性神经递质),箭头③示非对称性突触,箭头④示突触小泡(内含兴奋性神经递质)。
Figure 4 Ultrastructure of the olfactory bulb nerve cells (A, ×7 000) and synapses (B, ×60 000) in each group observed by transmission electron microscope after ultrathin section stainingNote: 6-C57 refers to 6-month-old C57BL/6 mice in the blank control group; 6-APP/PS1 refers to 6-month-old APP/PS1 double transgenic mice in model group; 6-MEM refers to APP/PSI double transgenic mice treated with 2.6 mg/kg memantine hydrochloride from 3- to 6-month-old; 12-C57 refers to 12-month-old C57BL/6 mice; 12-APP/PS1 refers to 12-month-old APP/PS1 double transgenic mice; 12-MEM refers to APP/PS1 double transgenic mice treated with 2.6 mg/kg memantine hydrochloride from 9- to 12-month-old. Each group contained five mice. Arrows ① show symmetric synapses, arrows ② show synaptic vesicles (containing inhibitory neurotransmitters), arrows ③ show asymmetric synapses, and arrows ④ show synaptic vesicles (containing excitatory neurotransmitters).
| 1 | DIBATTISTA M, PIFFERI S, MENINI A, et al. Alzheimer's disease: what can we learn from the peripheral olfactory system?[J]. Front Neurosci, 2020, 14:440. DOI:10.3389/fnins. 2020.00440 . |
| 2 | CHEN M, CHEN Y N, HUO Q W, et al. Enhancing GABAergic signaling ameliorates aberrant gamma oscillations of olfactory bulb in AD mouse models[J]. Mol Neurodegener, 2021, 16(1):14. DOI:10.1186/s13024-021-00434-7 . |
| 3 | XU Z P, YANG S L, ZHAO S, et al. Biomarkers for early diagnostic of mild cognitive impairment in type-2 diabetes patients: a multicentre, retrospective, nested case-control study[J]. EBioMedicine, 2016, 5:105-113. DOI:10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.02.014 . |
| 4 | SAIZ-SANCHEZ D, FLORES-CUADRADO A, UBEDA-BAÑON I, et al. Interneurons in the human olfactory system in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Exp Neurol, 2016, 276:13-21. DOI:10. 1016/j.expneurol.2015.11.009 . |
| 5 | DOTY R L. Olfactory dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases: is there a common pathological substrate?[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2017, 16(6):478-488. DOI:10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30123-0 . |
| 6 | DAMMALLI M, DEY G, MADUGUNDU A K, et al. Proteomic analysis of the human olfactory bulb[J]. OMICS, 2017, 21(8):440-453. DOI:10.1089/omi.2017.0084 . |
| 7 | MURPHY C. Olfactory and other sensory impairments in Alzheimer disease[J]. Nat Rev Neurol, 2019, 15(1):11-24. DOI:10.1038/s41582-018-0097-5 . |
| 8 | ROUBY C, THOMAS-DANGUIN T, VIGOUROUX M, et al. The Lyon clinical olfactory test: validation and measurement of hyposmia and anosmia in healthy and diseased populations[J]. Int J Otolaryngol, 2011, 2011:203805. DOI:10.1155/2011/203805 . |
| 9 | BALLEZA-TAPIA H, HUANOSTA-GUTIÉRREZ A, MÁRQUEZ-RAMOS A, et al. Amyloid β oligomers decrease hippocampal spontaneous network activity in an age-dependent manner[J]. Curr Alzheimer Res, 2010, 7(5):453-462. DOI:10.2174/156720510791383859 . |
| 10 | DANDO S J, MACKAY-SIM A, NORTON R, et al. Pathogens penetrating the central nervous system: infection pathways and the cellular and molecular mechanisms of invasion[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2014, 27(4):691-726. DOI:10.1128/cmr. 00118-13 . |
| 11 | MCSHANE R, WESTBY M J, ROBERTS E, et al. Memantine for dementia[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2019, 3(3): CD003154. DOI:10.1002/14651858.CD003154.pub6 . |
| 12 | QIAO O, ZHANG X Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Cerebralcare Granule® enhances memantine hydrochloride efficacy in APP/PS1 mice by ameliorating amyloid pathology and cognitive functions[J]. Chin Med, 2021, 16(1):47. DOI:10.1186/s13020-021-00456-9 . |
| 13 | LIU M Y, WANG S, YAO W F, et al. Memantine improves spatial learning and memory impairments by regulating NGF signaling in APP/PS1 transgenic mice[J]. Neuroscience, 2014, 273:141-151. DOI:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.05.011 . |
| 14 | 金昊. APP/PS1小鼠不同时期内嗅皮质、海马体积变化特征及对学习记忆能力的影响[D]. 福州: 福建中医药大学, 2018. |
| JIN H. Changes of volume of entorhinal cortex and hippocampus in APP/PS1 mice at different stages and their effects on learning and memory ability[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian University of Chinese Medicine, 2018. | |
| 15 | YUAN Z, ZHOU H Y, ZHOU N, et al. Dynamic evaluation indices in spatial learning and memory of rat vascular dementia in the Morris water maze[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9:7224. DOI:10.1038/s41598-019-43738-x . |
| 16 | ZHANG X M, ZHAO F, WANG C F, et al. AVP(4-8) improves cognitive behaviors and hippocampal synaptic plasticity in the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Neurosci Bull, 2020, 36(3):254-262. DOI:10.1007/s12264-019-00434-0 . |
| 17 | KARUNAKARAN S. Unraveling early signs of navigational impairment in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice using Morris water maze[J]. Front Neurosci, 2020, 14:568200. DOI:10.3389/fnins. 2020. 568200 . |
| 18 | COLES M, WATT G, KREILAUS F, et al. Medium-dose chronic cannabidiol treatment reverses object recognition memory deficits of APP Swe /PS1ΔE9 transgenic female mice[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11:587604. DOI:10.3389/fphar.2020.587604 . |
| 19 | GIMÉNEZ-LLORT L, MARIN-PARDO D, MARAZUELA P, et al. Survival bias and crosstalk between chronological and behavioral age: age- and genotype-sensitivity tests define behavioral signatures in middle-aged, old, and long-lived mice with normal and AD-associated aging[J]. Biomedicines, 2021, 9(6):636. DOI:10.3390/biomedicines9060636 . |
| 20 | LI M Q, SU S X, CAI W H, et al. Differentially expressed genes in the brain of aging mice with cognitive alteration and depression- and anxiety-like behaviors[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8:814. DOI:10.3389/fcell.2020.00814 . |
| 21 | LI P, XU J, GU H H, et al. Memantine ameliorates cognitive deficit in AD mice via enhancement of entorhinal-CA1 projection[J]. BMC Neurosci, 2021, 22(1):41. DOI:10.1186/s12868-021-00647-y . |
| 22 | DOTY R L. Olfactory dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases: is there a common pathological substrate? [J]. Lancet Neurol, 2017, 16(6):478-488. DOI:10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30123-0 . |
| 23 | UBEDA-BAÑON I, SAIZ-SANCHEZ D, FLORES-CUADRADO A, et al. The human olfactory system in two proteinopathies: Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases[J]. Transl Neurodegener, 2020, 9(1):22. DOI:10.1186/s40035-020-00200-7 . |
| 24 | MORIGUCHI S, INAGAKI R, FUKUNAGA K. Memantine improves cognitive deficits via KATP channel inhibition in olfactory bulbectomized mice[J]. Mol Cell Neurosci, 2021, 117:103680. DOI:10.1016/j.mcn.2021.103680 . |
| 25 | LI W Y, LI S S, SHEN L H, et al. Impairment of dendrodendritic inhibition in the olfactory bulb of APP/PS1 mice[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2019, 11:2. DOI:10.3389/fnagi.2019.00002 . |
| 26 | ZOU Y M, LU D, LIU L P, et al. Olfactory dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat, 2016, 12:869-875. DOI:10.2147/NDT.S104886 . |
| 27 | DONG H W, ENNIS M. Activation of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors suppresses excitability of mouse main olfactory bulb external tufted and mitral cells[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2018, 11:436. DOI:10.3389/fncel.2017.00436 . |
| 28 | RIBAK C E, VAUGHN J E, SAITO K, et al. Glutamate decarboxylase localization in neurons of the olfactory bulb[J]. Brain Res, 1977, 126(1):1-18. DOI:10.1016/0006-8993(77)90211-6 . |
| 29 | WANG R, REDDY P H. Role of glutamate and NMDA receptors in Alzheimer's disease[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2017, 57(4):1041-1048. DOI:10.3233/JAD-160763 . |
| 30 | PARSONS C G, STÖFFLER A, DANYSZ W. Memantine: a NMDA receptor antagonist that improves memory by restoration of homeostasis in the glutamatergic system - too little activation is bad, too much is even worse[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2007, 53(6):699-723. DOI:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.07.013 . |
| 31 | ALBERDI E, SÁNCHEZ-GÓMEZ M V, CAVALIERE F, et al. Amyloid β oligomers induce Ca2+ dysregulation and neuronal death through activation of ionotropic glutamate receptors[J]. Cell Calcium, 2010, 47(3):264-272. DOI:10.1016/j.ceca. 2009.12.010 . |
| 32 | TERAVSKIS P J, ASHE K H, LIAO D Z. The accumulation of tau in postsynaptic structures: a common feature in multiple neurodegenerative diseases? [J]. Neuroscientist, 2020, 26(5-6):503-520. DOI:10.1177/1073858420916696 . |
| 33 | LIMA CALDEIRA G, PEÇA J, CARVALHO A L. New insights on synaptic dysfunction in neuropsychiatric disorders[J]. Curr Opin Neurobiol, 2019, 57:62-70. DOI:10.1016/j.conb.2019.01.004 . |
| 34 | GARAD M, EDELMANN E, LEßMANN V. Impairment of spike-timing-dependent plasticity at schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses in adult APP/PS1 mice depends on proximity of aβ plaques[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(3):1378. DOI:10.3390/ijms22031378 . |
| 35 | LI W Y, LI S S, SHEN L H, et al. Impairment of dendrodendritic inhibition in the olfactory bulb of APP/PS1 mice[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2019, 11:2. DOI:10.3389/fnagi.2019.00002 . |
| 36 | PALOP J J, MUCKE L. Amyloid-β-induced neuronal dys-function in Alzheimer's disease: from synapses toward neural networks[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2010, 13(7):812-818. DOI:10.1038/nn.2583 . |
| 37 | WESSON D W, BORKOWSKI A H, LANDRETH G E, et al. Sensory network dysfunction, behavioral impairments, and their reversibility in an Alzheimer's β-amyloidosis mouse model[J]. J Neurosci, 2011, 31(44):15962-15971. DOI:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2085-11.2011 . |
| 38 | BOYLE P A, YANG J Y, YU L, et al. Varied effects of age-related neuropathologies on the trajectory of late life cognitive decline[J]. Brain, 2017, 140(3):804-812. DOI:10.1093/brain/aww341 . |
| 39 | SCHUBERT C R, FISCHER M E, PINTO A A, et al. Sensory impairments and risk of mortality in older adults[J]. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2016, 72(5):710-715. DOI:10.1093/gerona/glw036 . |
| 40 | EKSTRÖM I, SJÖLUND S, NORDIN S, et al. Smell loss predicts mortality risk regardless of dementia conversion[J]. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2017, 65(6):1238-1243. DOI:10.1111/jgs.14770 . |
| 41 | FRIESEN M, ZIEGLER-WALDKIRCH S, EGENOLF M, et al. Distinct Aβ pathology in the olfactory bulb and olfactory deficits in a mouse model of Aβ and α-syn co-pathology[J]. Brain Pathol, 2022, 32(3): e13032. DOI:10.1111/bpa.13032 . |
| 42 | WESSON D W, BORKOWSKI A H, LANDRETH G E, et al. Sensory network dysfunction, behavioral impairments, and their reversibility in an Alzheimer's β-amyloidosis mouse model[J]. J Neurosci, 2011, 31(44):15962-15971. DOI:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2085-11.2011 . |
| [1] | 肖林林, 杨逸萱, 黎珊杉, 罗兰诗雨, 尹思威, 孙俊铭, 施维, 欧阳轶强, 李习艺. 利用脑立体定位技术将人源三突变APP基因导入海马区构建阿尔茨海默病大鼠模型[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2025, 45(3): 269-278. |
| [2] | 林晴晴, 戴锦龙, 陈志森, 郭健敏, 杨威. 一例新西兰白兔系统性淀粉样变性病理学诊断[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2024, 44(6): 695-699. |
| [3] | 魏枫, 程维维, 尹雅芙. 阿尔茨海默病转基因小鼠模型特点和应用进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2022, 42(5): 432-439. |
| [4] | 盛哲津, 李利妹. 阿尔茨海默病动物模型的研究进展[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2022, 42(4): 342-350. |
| [5] | 邱波, 王艳, 胡建廷. 一例SD大鼠自发性心脏海绵状血管瘤的病理学观察[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2019, 39(5): 402-404. |
| [6] | 邱波, 王艳, 胡建廷. 1例SD大鼠自发性肾母细胞瘤肾脏的病理形态学观察[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2018, 38(4): 314-317. |
| [7] | 邱波, 王艳, 英永, 屈卉锦, 王凤乾, 张海静, 张鑫, 胡建廷. 1例自发性肝硬化新西兰兔肝脏病理形态学观察[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2017, 37(6): 485-487. |
| [8] | 马登磊, 张兰. P301S突变tau转基因动物模型及其应用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2017, 37(6): 491-496. |
| [9] | 顾组曦, 汤家铭, 米金霞, 吴文斌, 赵源, 樊海艇, 张超超. 10月龄淀粉样前体蛋白和早老素双转基因(APP/PS-Tg)小鼠相关指标检测[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2015, 35(2): 170-174. |
| [10] | 尹秀华, 姜珍, 刘天云, 潘平, 秦婷, 夏春林, 孙茂民. 复合型AD大鼠模型脑组织、血清及牙周组织中部分炎症因子的表达[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2013, 33(6): 439-443. |
| [11] | 李娜, 王维, 黎陈静, 张颖妍, 张晟, 章海燕, 张周. APPswe/PS1dE9转基因小鼠繁殖性能及生长发育观察[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2012, 32(3): 222-227. |
| [12] | 骆庆和, 赵文娟, 殷明. 阿尔茨海默病动物模型研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2012, 32(1): 80-88. |
| [13] | 郭晓冲1,3,何冠英2,吴旭1,张维东2,李如波1,王昌亮1,于天水1,张国华1. 大鼠死后肾上腺突触素含量变化与死亡时间关系的研究[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2008, 28(6): 387-389. |
| [14] | 夏春梅,龚琦,傅燕,张周. 阿尔茨海默病双表达转基因小鼠(hAPP/hACHE)模型的初步建立[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2007, 27(2): 127-129. |
| [15] | 秦川1,常洋1,张文明1,朱华1,张均田2,屈志炜2,冯征2. APP转基因小鼠脑内单胺类递质的变化[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2001, 21(2): 79-81. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||