
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 31-41.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.118
• Animal Models of Human Diseases • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jianhua ZHENG, Yunzhi FA, Qiaoyan DONG, Yefeng QIU( )(
)( ), Jingqing CHEN(
), Jingqing CHEN( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-08-17
Revised:2023-11-18
Online:2024-02-25
Published:2024-02-25
Contact:
Yefeng QIU, Jingqing CHEN
CLC Number:
Jianhua ZHENG,Yunzhi FA,Qiaoyan DONG,et al. Construction and Evaluation of a Mouse Model with Intestinal Injury by Acute Hypoxic Stress in Plateau[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 31-41. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.118.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.118
基因 Gene | 正向引物 Forward primers(5ʹ→3ʹ) | 反向引物 Reverse primers(5ʹ→3ʹ) |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG | CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT |
| IL-1β | GCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACT | ATCTTTTGGGGTCCGTCAACT |
| TNF-α | CCTGTAGCCCACGTCGTAG | GGGAGTAGACAAGGTACAACCC |
| IL-6 | TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC | TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC |
| MCP-1 | TAAAAACCTGGATCGGAACCAAA | GCATTAGCTTCAGATTTACGGGT |
| IL-10 | AGCCTTATCGGAAATGATCCAGT | GGCCTTGTAGACACCTTGGT |
Table 1 Sequence list of primers used in real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR
基因 Gene | 正向引物 Forward primers(5ʹ→3ʹ) | 反向引物 Reverse primers(5ʹ→3ʹ) |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG | CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT |
| IL-1β | GCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACT | ATCTTTTGGGGTCCGTCAACT |
| TNF-α | CCTGTAGCCCACGTCGTAG | GGGAGTAGACAAGGTACAACCC |
| IL-6 | TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC | TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC |
| MCP-1 | TAAAAACCTGGATCGGAACCAAA | GCATTAGCTTCAGATTTACGGGT |
| IL-10 | AGCCTTATCGGAAATGATCCAGT | GGCCTTGTAGACACCTTGGT |
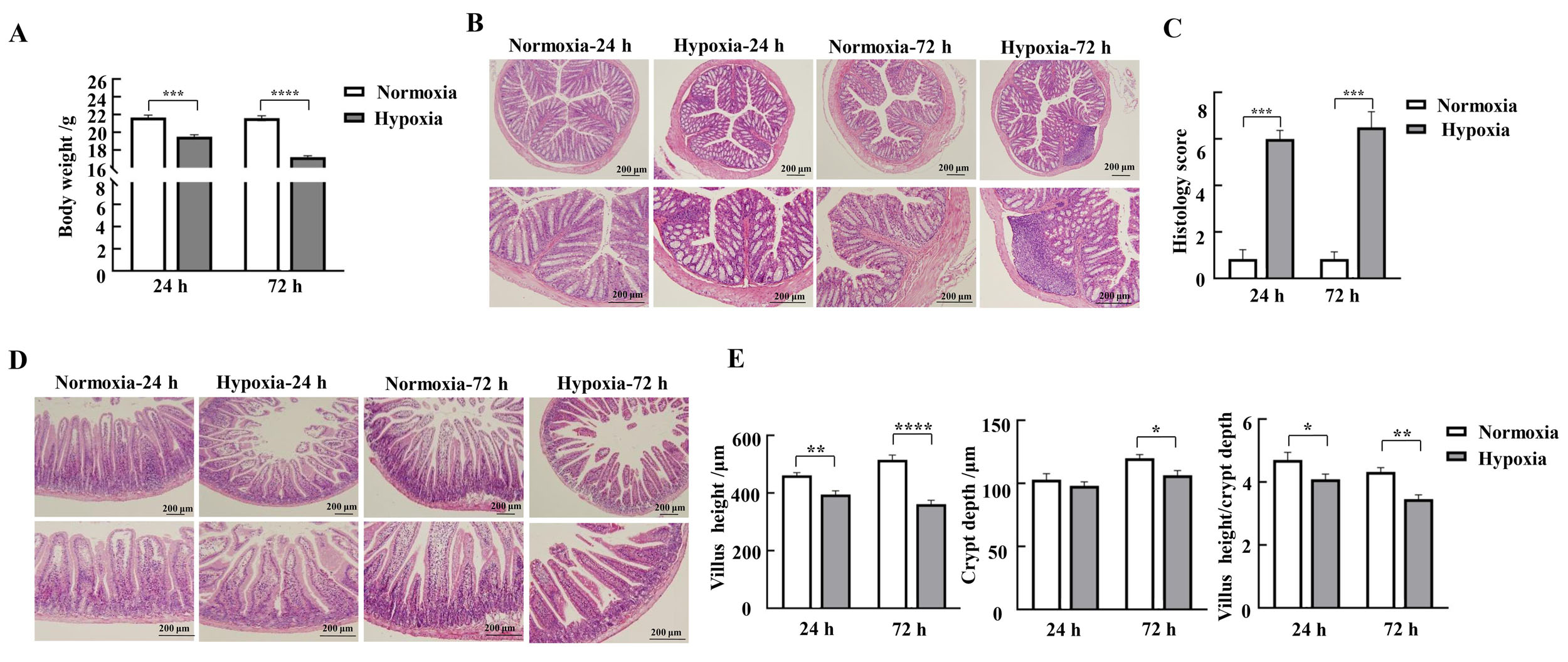
Figure 1 Effects of hypoxic stress on body weight changes and morphology of the mucosa of the colon and duodenum in miceNote:A, Changes in body weight of mice in each group (n=9); B-C, HE staining results and pathohistologic scores of mice colon (n=3); D, HE staining results of mice duodenum; E-G, Lengths of mice duodenal villi, depths of crypts, and values of villus length/crypt depth (n=3). Normoxia indicates normoxic control group, and Hypoxia indicates hypoxic stress group. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error; compared with normoxic control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.000 1.
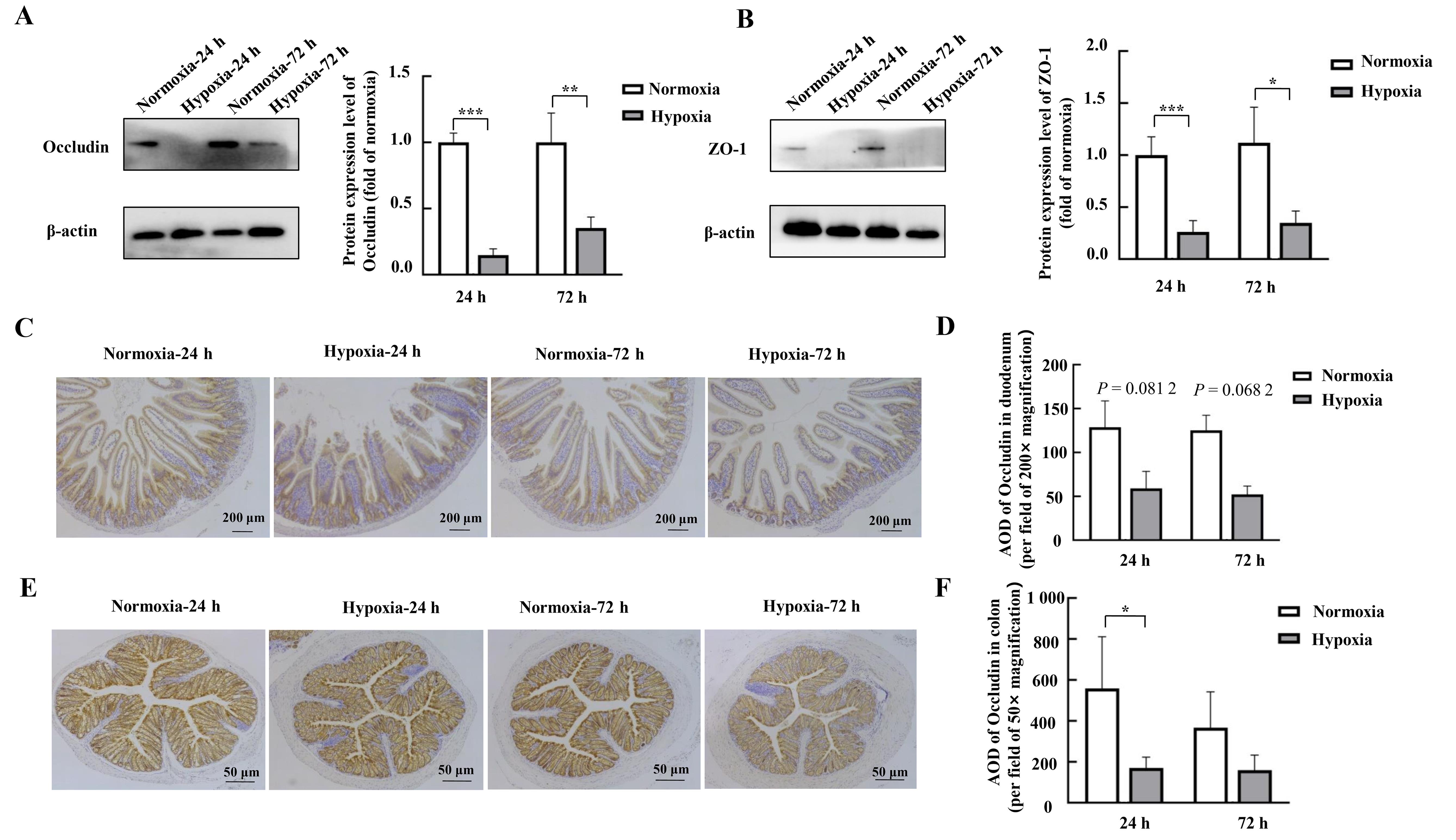
Figure 2 Effects of hypoxic stress on the expression of the tight junction protein in mouse duodenal and colonic tissues as detected by Western blotting and immunohistochemistryNote:A-B, Expression of tight junction proteins Occludin and ZO-1 in mouse duodenal tissues detected by Western blotting and their relative expression level analysis (n=4). C-D, Detection of the tight junction protein Occludin and its average optical densitye (AOD) in mouse duodenal tissues by immunohistochemistry (n=3). E-F, Detection of tight junction protein Occludin and its AOD in mouse colon tissues by immunohistochemistry (n=3). Normoxia indicates control normoxic group, and Hypoxia indicates hypoxic stress group. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error; compared with normoxic control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
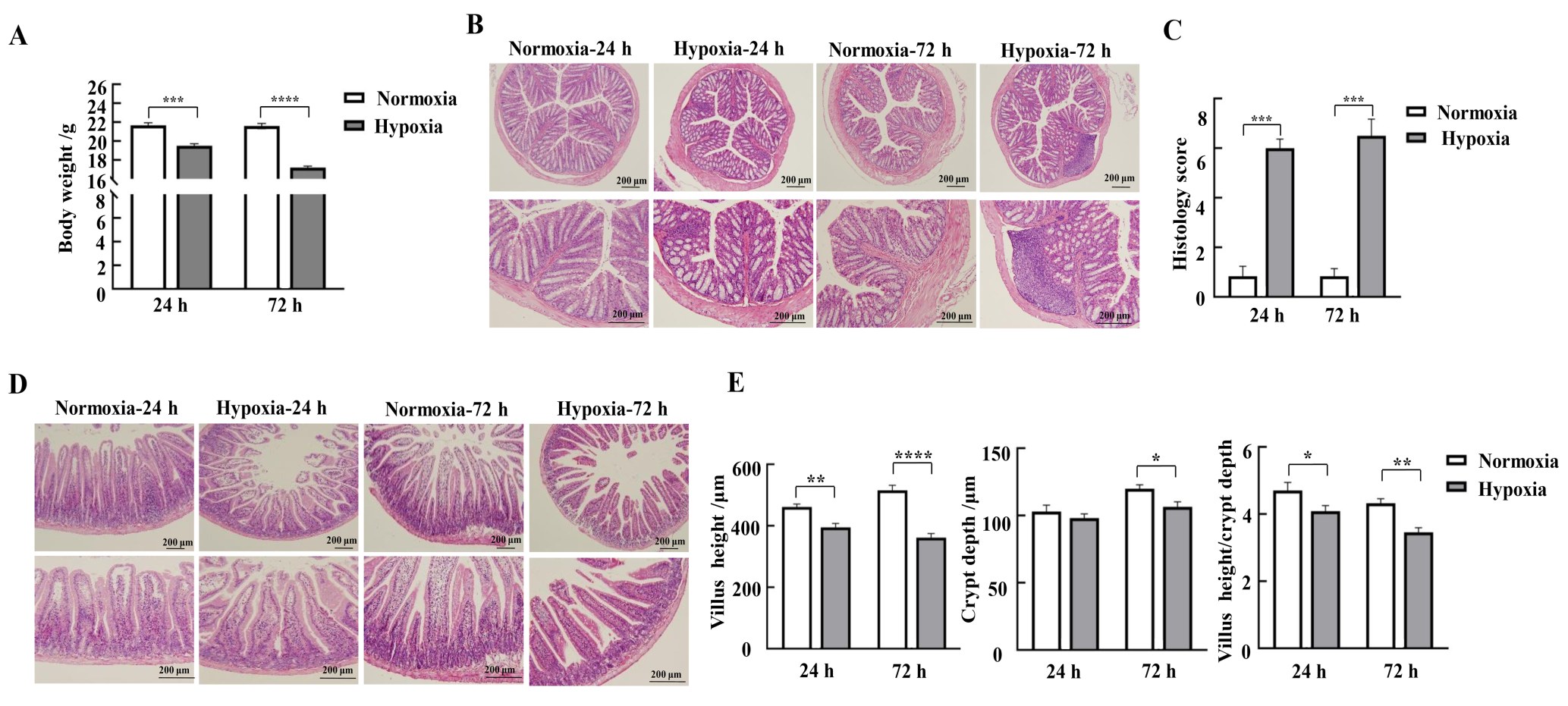
Figure 3 Effects of hypoxic stress on the expression of inflammatory cytokines in mouse duodenal and colonic tissues detected by real-time fluorescence quantitative PCRNote:A-B, Mouse duodenal tissues; C-D, Mouse colon tissues. Normoxia indicates normoxic control group, and Hypoxia indicates hypoxic stress group. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error; n = 6, compared with normoxic control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
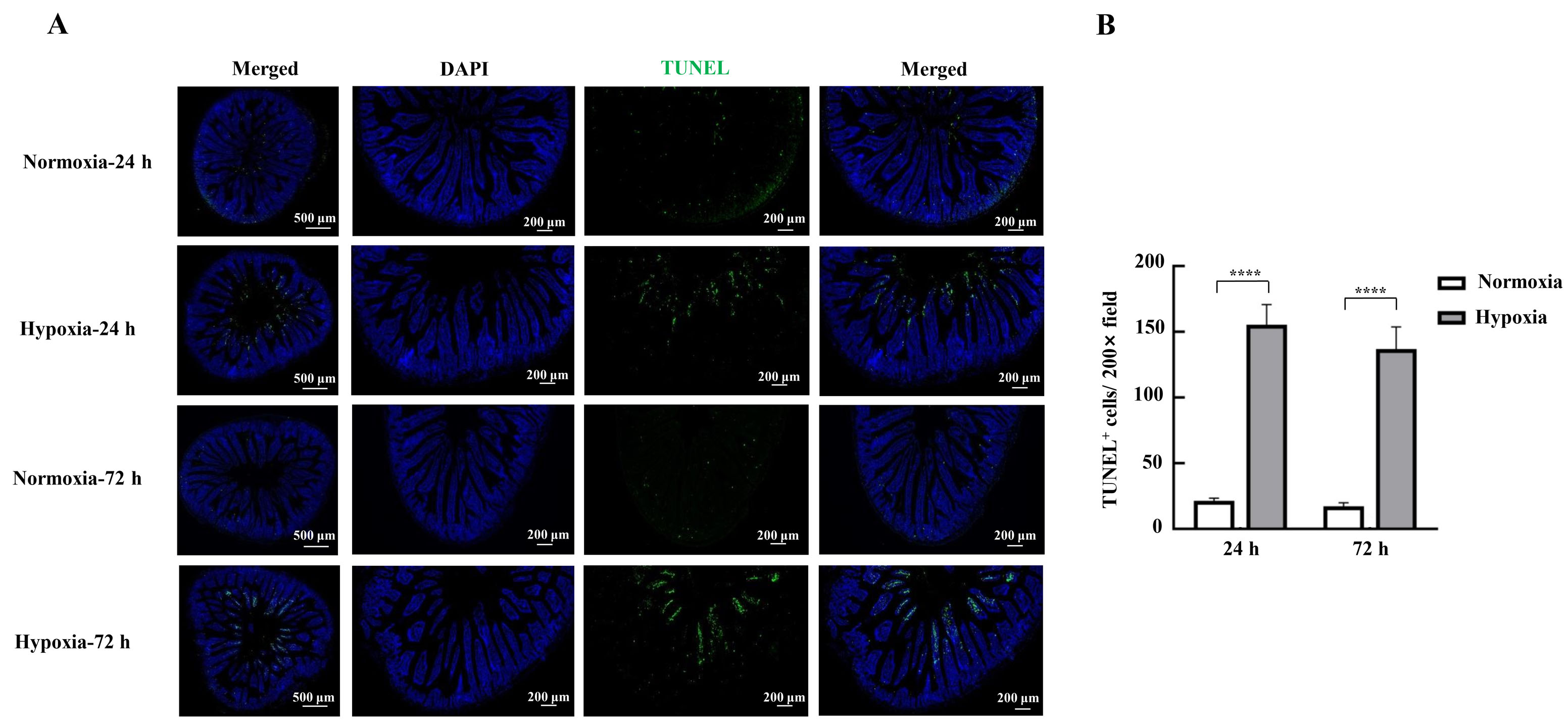
Figure 4 Effects of hypoxic stress on apoptosis of mice intestinal epithelial cells detected by TUNEL staining methodNote:A, Photographs of TUNEL staining of mouse duodenal tissues; B, TUNEL-positive cell count. Normoxia indicates normoxic control group, and Hypoxia indicates hypoxic stress group. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error; n=3, compared with normoxic control group, ****P<0.000 1.
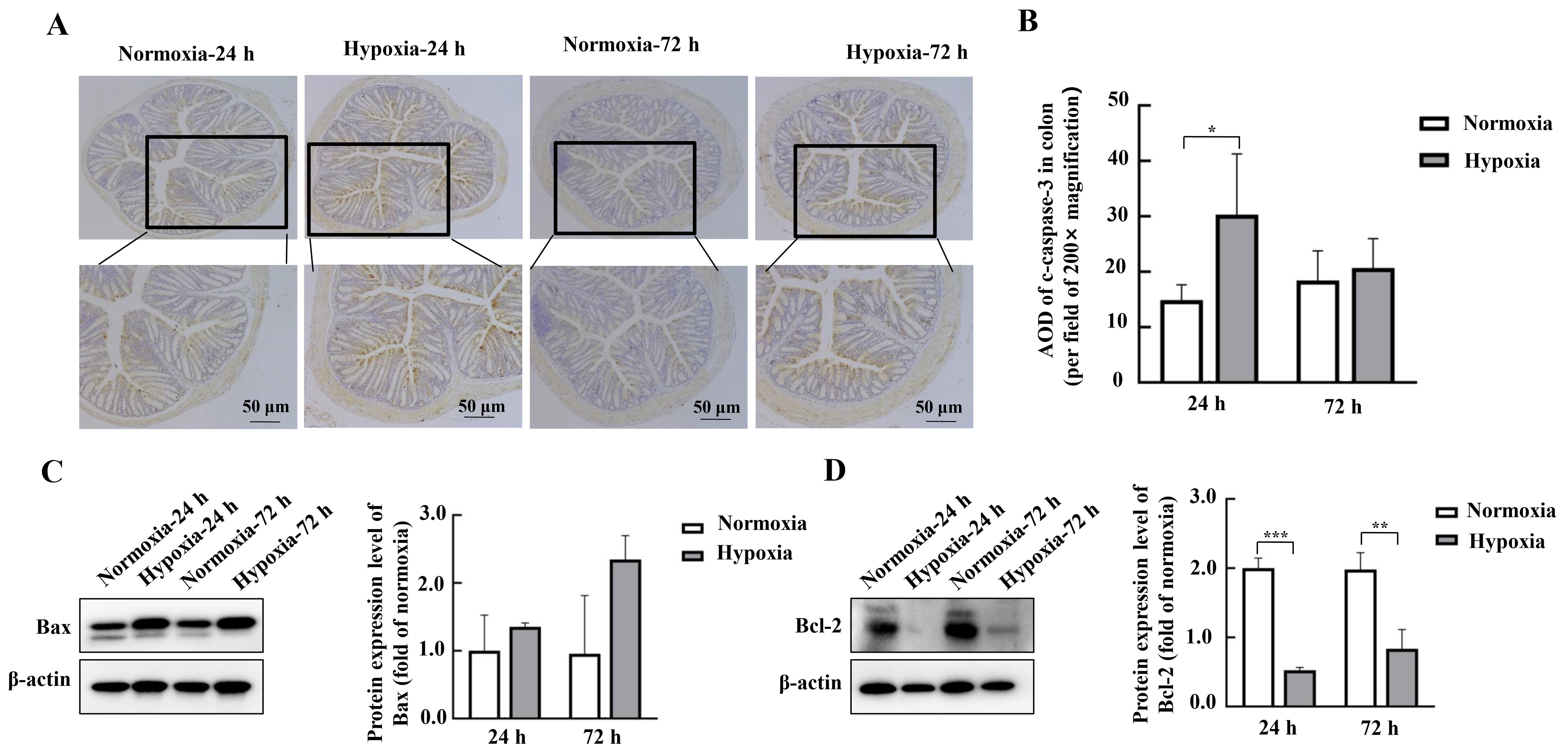
Figure 5 Effects of hypoxic stress on the expression of intestinal apoptosis-related proteins in mouse colon detected by Western blotting and immunohistochemistryNote:A-B, Detection of apoptosis-related protein c-caspase-3 and its average optical density (AOD) in mouse colon tissues by immunohistochemistry (n=3). C-D, Expression of apoptosis-related proteins Bax and Bcl-2 and their relative expression analysis in mouse duodenal tissues detected by Western blotting method (n=6). Normoxia indicates normoxic control group, and Hypoxia indicates hypoxic stress group. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error; n=6, compared with normoxic control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
| 1 | WANG F, ZHANG H, XU T, et al. Acute exposure to simulated high-altitude hypoxia alters gut microbiota in mice[J]. Arch Microbiol, 2022, 204(7):412. DOI: 10.1007/s00203-022-03031-4 . |
| 2 | NUSS R. Medical conditions and high-altitude travel[J]. N Engl J Med, 2022, 386(19):1866-1867. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMc 2203182 . |
| 3 | 王珍, 周亚洲, 王立坤, 等. 持续低氧条件下大鼠肠道微生物变化及其与心肌损伤的关联研究[J]. 微生物学报, 2023, 63(8):3054-3067. DOI: 10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20220862 . |
| WANG Z, ZHOU Y Z, WANG L K, et al. Alterations in gut microbiota and their associations with cardiac injury in rats after exposure to continuous normobaric hypoxia[J]. Acta Microbiol Sin, 2023, 63(8):3054-3067. DOI: 10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20220862 . | |
| 4 | KHANNA K, MISHRA K P, GANJU L, et al. High-Altitude-Induced alterations in Gut-Immune Axis: a review[J]. Int Rev Immunol, 2018, 37(2):119-126. DOI: 10.1080/08830185. 2017. 1407763 . |
| 5 | FRUEHAUF H, VAVRICKA S R, LUTZ T A, et al. Evaluation of acute mountain sickness by unsedated transnasal esophagogastroduodenoscopy at high altitude[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18(10):2218-2225.e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.11.036 . |
| 6 | HAMAD N, TRAVIS S P L. Weight loss at high altitude: pathophysiology and practical implications[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2006, 18(1):5-10. DOI: 10.1097/00042737-200601000-00002 . |
| 7 | LUO H, ZHOU D J, CHEN Z, et al. Establishment and evaluation of an experimental rat model for high-altitude intestinal barrier injury[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2017, 13(2):475-482. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.4012 . |
| 8 | MEIER D, COLLET T H, LOCATELLI I, et al. Does this patient have acute mountain sickness?[J]. JAMA, 2017, 318(18):1810. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2017.16192 . |
| 9 | MCKENNA Z J, GORINI PEREIRA F, GILLUM T L, et al. High-altitude exposures and intestinal barrier dysfunction[J]. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 2022, 322(3): R192-R203. DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00270.2021 . |
| 10 | WU T Y, DING S Q, LIU J L, et al. High-altitude gastrointestinal bleeding: an observation in Qinghai-Tibetan railroad construction workers on Mountain Tanggula[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2007, 13(5):774-780. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i5.774 . |
| 11 | BISCHOFF S C, BARBARA G, BUURMAN W, et al. Intestinal permeability: a new target for disease prevention and therapy[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2014, 14:189. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-014-0189-7 . |
| 12 | KÖNIG J, WELLS J, CANI P D, et al. Human intestinal barrier function in health and disease[J]. Clin Transl Gastroenterol, 2016, 7(10): e196. DOI: 10.1038/ctg.2016.54 . |
| 13 | LOSHBAUGH J E, LOEPPKY J A, GREENE E R. Effects of acute hypobaric hypoxia on resting and postprandial superior mesenteric artery blood flow[J]. High Alt Med Biol, 2006, 7(1):47-53. DOI: 10.1089/ham.2006.7.47 . |
| 14 | MUSCH M W, CLARKE L L, MAMAH D, et al. T cell activation causes diarrhea by increasing intestinal permeability and inhibiting epithelial Na+/K+-ATPase[J]. J Clin Invest, 2002, 110(11):1739-1747. DOI: 10.1172/JCI15695 . |
| 15 | DINMORE A J, EDWARDS J S, MENZIES I S, et al. Intestinal carbohydrate absorption and permeability at high altitude (5, 730 m)[J]. J Appl Physiol, 1994, 76(5):1903-1907. DOI: 10.1152/jappl.1994.76.5.1903 . |
| 16 | LI Y Y, WANG Y C, SHI F, et al. Phospholipid metabolites of the gut microbiota promote hypoxia-induced intestinal injury via CD1d-dependent γδ T cells[J]. Gut Microbes, 2022, 14(1):2096994. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2096994 . |
| 17 | BASNYAT B, MURDOCH D R. High-altitude illness[J]. Lancet, 2003, 361(9373):1967-1974. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13591-X . |
| 18 | KARL J P, BERRYMAN C E, YOUNG A J, et al. Associations between the gut microbiota and host responses to high altitude[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2018, 315(6): G1003-G1015. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00253.2018 . |
| 19 | FAN X X, LI S, WU Z L, et al. Glycine supplementation to breast-fed piglets attenuates post-weaning jejunal epithelial apoptosis: a functional role of CHOP signaling[J]. Amino Acids, 2019, 51(3):463-473. DOI: 10.1007/s00726-018-2681-9 . |
| 20 | PATANKAR J V, BUBECK M, ACERA M G, et al. Breaking bad: necroptosis in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal diseases[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14:1203903. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1203903 . |
| 21 | ZHANG W, JIAO L F, LIU R X, et al. The effect of exposure to high altitude and low oxygen on intestinal microbial communities in mice[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(9): e0203701. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203701 . |
| 22 | HUANG X, ZHOU Y Z, ZHAO T, et al. A method for establishing the high-altitude cerebral edema (HACE) model by acute hypobaric hypoxia in adult mice[J]. J Neurosci Methods, 2015, 245:178-181. DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth. 2015.02.004 . |
| 23 | ZHOU Y Z, HUANG X, ZHAO T, et al. Hypoxia augments LPS-induced inflammation and triggers high altitude cerebral edema in mice[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2017, 64:266-275. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.04.013 . |
| 24 | HILL G W, GILLUM T L, LEE B J, et al. Prolonged treadmill running in normobaric hypoxia causes gastrointestinal barrier permeability and elevates circulating levels of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines[J]. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab, 2020, 45(4):376-386. DOI: 10.1139/apnm-2019-0378 . |
| 25 | LI M, HAN T Y, ZHANG W J, et al. Simulated altitude exercise training damages small intestinal mucosa barrier in the rats[J]. J Exerc Rehabil, 2018, 14(3):341-348. DOI: 10.12965/jer. 1835128.064 . |
| 26 | SHIH D Q, TARGAN S R. Insights into IBD pathogenesis[J]. Curr Gastroenterol Rep, 2009, 11(6):473-480. DOI: 10.1007/s11894-009-0072-9 . |
| 27 | LIU L, LIANG L P, YANG C H, et al. Extracellular vesicles of Fusobacterium nucleatum compromise intestinal barrier through targeting RIPK1-mediated cell death pathway[J]. Gut Microbes, 2021, 13(1):1-20. DOI: 10.1080/19490976. 2021. 1902718 . |
| 28 | PATANKAR J V, BECKER C. Cell death in the gut epithelium and implications for chronic inflammation[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 17(9):543-556. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-020-0326-4 . |
| 29 | LIU Y L, XU Q, WANG Y, et al. Necroptosis is active and contributes to intestinal injury in a piglet model with lipopolysaccharide challenge[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(1):62. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-03365-1 . |
| 30 | STRÄTER J, WELLISCH I, RIEDL S, et al. CD95 (APO-1/Fas)-mediated apoptosis in colon epithelial cells: a possible role in ulcerative colitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 1997, 113(1):160-167. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-5085(97)70091-x . |
| 31 | OKUMURA R, TAKEDA K. Roles of intestinal epithelial cells in the maintenance of gut homeostasis[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2017, 49(5): e338. DOI: 10.1038/emm.2017.20 . |
| 32 | CHENG E H, KIRSCH D G, CLEM R J, et al. Conversion of bcl-2 to a bax-like death effector by caspases[J]. Science, 1997, 278(5345):1966-1968. DOI: 10.1126/science.278.5345.1966 . |
| 33 | MCKENNA Z J, BELLOVARY B N, DUCHARME J B, et al. Circulating markers of intestinal barrier injury and inflammation following exertion in hypobaric hypoxia[J]. Eur J Sport Sci, 2023, 23(10):2002-2010. DOI: 10.1080/17461391. 2023. 2203107 . |
| 34 | MCKENNA Z J, FENNEL Z J, BERKEMEIER Q N, et al. Exercise in hypobaric hypoxia increases markers of intestinal injury and symptoms of gastrointestinal distress[J]. Exp Physiol, 2022, 107(4):326-336. DOI: 10.1113/EP090266 . |
| [1] | LIU Yueqin, XUE Weiguo, WANG Shuyou, SHEN Yaohua, JIA Shuyong, WANG Guangjun, SONG Xiaojing. Observation of Digestive Tract Tissue Morphology in Mice Using Probe-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 457-465. |
| [2] | KONG Zhihao, WEI Xiaofeng, YU Lingzhi, FENG Liping, ZHU Qi, SHI Guojun, WANG Chen. Isolation and Identification of Staphylococcus xylosus in Nude Mice with Squamous Skin Scurfs [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 368-375. |
| [3] | XU Qiuyu, YAN Guofeng, FU Li, FAN Wenhua, ZHOU Jing, ZHU Lian, QIU Shuwen, ZHANG Jie, WU Ling. A Mouse Model of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Established Through Subcutaneous Administration of Letrozole Sustained-Release Pellets and Hepatic Transcriptome Analysis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 119-129. |
| [4] | LIU Rongle, CHENG Hao, SHANG Fusheng, CHANG Shufu, XU Ping. Study on Cardiac Aging Phenotypes of SHJH hr Mice [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 13-20. |
| [5] | WU Zhihao, CAO Shuyang, ZHOU Zhengyu. Establishment of an Intestinal Fibrosis Model Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease in VDR-/- Mice Induced by Helicobacter hepaticus Infection and Mechanism Exploration [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 37-46. |
| [6] | ZHANG Nan, LI Huaiyin, LIAN Xiaodi, WEI Juanpeng, GAO Ming. Effects of Different Durations of Light Exposure on Body Weight and Learning and Memory Abilities of NIH Mice [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 73-78. |
| [7] | ZHAO Xiaona, WANG Peng, YE Maoqing, QU Xinkai. Establishment of a New Hyperglycemic Obesity Cardiac Dysfunction Mouse Model with Triacsin C [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 605-612. |
| [8] | TAN He, YANG Xiaohui, ZHANG Daxiu, WANG Guicheng. Optimal Adaptation Period for Metabolic Cage Experiments in Mice at Different Developmental Stages [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 502-510. |
| [9] | MENG Yu, LIANG Dongli, ZHENG Linlin, ZHOU Yuanyuan, WANG Zhaoxia. Optimization and Evaluation of Conditions for Orthotopic Nude Mouse Models of Human Liver Tumor Cells [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 511-522. |
| [10] | Jing QIN, Yong ZHAO, Caiqin ZHANG, Bing BAI, Changhong SHI. Construction and Evaluation of Theranostic Near-infrared Fluorescent Probe for Targeting Inflammatory Brain Edema [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 243-250. |
| [11] | Xiaoyu ZHU, Hantao YUAN, Sibo LI. MicroRNA-887-3p Inhibited MDM4 Expression and Proliferation but Promoted Apoptosis of Intervertebral Disc Annulus Fibrosus Cells in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 270-278. |
| [12] | Yisu ZHANG, Xinru LIU, Ruojie WU, Rui LIU, Hong OUYANG, Xiaohong LI. Establishment and Evaluation of Mouse Model of Pregnancy Pain-depression Comorbidity Induced by Chronic Unpredictable Stress, Complete Freund's Adjuvant and Formalin [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 259-269. |
| [13] | Dong WU, Rui SHI, Peishan LUO, Ling'en LI, Xijing SHENG, Mengyang WANG, Lu NI, Sujuan WANG, Huixin YANG, Jing ZHAO. Effects of Different Pellet Feed Hardness on Growth and Reproduction, Feed Utilization Rate, and Environmental Dust in Laboratory Mice [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 313-320. |
| [14] | Yun LIU, Tingting FENG, Wei TONG, Zhi GUO, Xia LI, Qi KONG, Zhiguang XIANG. Glycyrrhizic Acid Showed Therapeutic Effects on Severe Pulmonary Damages in Mice Induced by Pneumonia Virus of Mice Infection [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 251-258. |
| [15] | Jinhua HU, Jingjie HAN, Min JIN, Bin HU, Yuefen LOU. Effects of Puerarin on Bone Density in Rats and Mice: A Meta-analysis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 149-161. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||