
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 363-370.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.055
• Excellent Papers at the East China Conference • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaoqian TAN1, Hao YANG2, Huiqing TANG1, Wei QU1, Liang LI1, Zhen QIAN1, Jianzhong GU1, Ping XU1( )(
)( ), Junhua XIAO2(
), Junhua XIAO2( )(
)( )
)
Received:2023-04-28
Revised:2023-06-08
Online:2023-08-25
Published:2023-08-25
Contact:
Ping XU, Junhua XIAO
CLC Number:
Xiaoqian TAN,Hao YANG,Huiqing TANG,et al. Creation and Analysis of Related Genetic Characteristics of BALB/cA.Cg.SHJH hr Mice[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 363-370. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.055.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2023.055
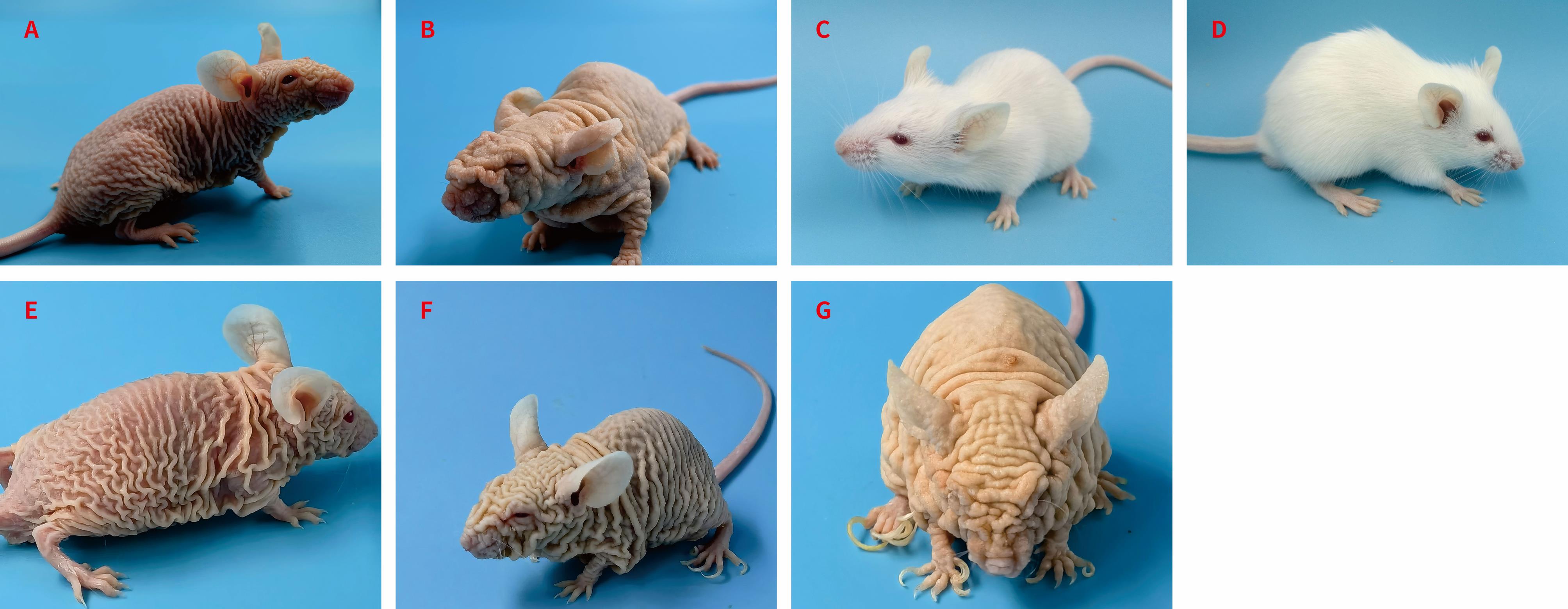
Figure 3 Comparison of phenotype of C.Cg.SHJH hr and SHJH hr,BALB/cAShjh at different agesNote: A, 2-month-old SHJH hr mice; B, 6-month-old SHJH hr mice; C, 2-month-old BALB/cAShjh mice; D, 4-month-old BALB/cAShjh mice; E, 2-month-old C.Cg.SHJH hr mice; F, 6-month-old C.Cg.SHJH hr mice; G, 12-month-old C.Cg.SHJH hr mice.
| 位点Loci | C.Cg.SHJH hr | BALB/cA |
|---|---|---|
| Car2 | b | b |
| Ce2 | a | a |
| Es1 | b | b |
| Es3 | a | a |
| Es10 | a | a |
| Gpd1 | b | b |
| Gpi1 | a | a |
| Hbb | d | d |
| Idh1 | a | a |
| Mod1 | a | a |
| Akp1 | b | b |
| Pgm1 | a | a |
| Trf | b | b |
| Pep3 | a | a |
Table 1 Differences in biochemical marker genes between C.Cg.SHJH hr mice and BALB/cAShjh mice
| 位点Loci | C.Cg.SHJH hr | BALB/cA |
|---|---|---|
| Car2 | b | b |
| Ce2 | a | a |
| Es1 | b | b |
| Es3 | a | a |
| Es10 | a | a |
| Gpd1 | b | b |
| Gpi1 | a | a |
| Hbb | d | d |
| Idh1 | a | a |
| Mod1 | a | a |
| Akp1 | b | b |
| Pgm1 | a | a |
| Trf | b | b |
| Pep3 | a | a |
突变位置 Mutation position | 碱基变化 Base alteration | 基因 Gene | 涉及疾病/细胞功能 Related diseases/cell functions | 下游信号通路调控 Signal pathway regulation | PolyPhen-2计算得分 PolyPhen-2 scores |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70559773 | C→T | Hr | 全身性脱毛,伴有丘疹性病变的心房颤动 | 是 | 1.000 |
| 73523427 | A→G | Nudet15 | 造血干细胞和祖细胞急性损失 | 是 | 0.000 |
| 74744708 | T→C | esd | 甲醛分解代谢 | 是 | 0.505 |
| 74811692 | T→C | Lrch1 | 细胞对趋化因子的反应 | 否 | 0.047 |
| 74813612 | T→C | ||||
| 75031916 | G→A | 5031414D18Rik | 自噬体成熟、糖原、脂质代谢过程的调节 | 否 | 0.022 |
| 75032403 | C→A | ||||
| 75036145 | A→G | ||||
| 75125178 | A→G | Lrrc63 | 膜蛋白 | 否 | - |
| 75224148 | C→T | Lcp1 | 肌动蛋白丝束组件 | 否 | 0.166 |
| 78510551 | C→G | Akap11 | 体型缩小,活动能力减退 | 否 | 0.997 |
| 79401743 | G→A | Mtrf1 | 线粒体翻译终止;耳聋,痉挛性共济失调 | 否 | 0.959 |
| 79401763 | G→T | Mtrf1 | |||
| 79406608 | A→G | ||||
| 79427505 | C→G | Kbtbd | 蛋白酶体介导的泛素依赖蛋白的分解代谢 | 是 | 0.006 |
| 79452831 | G→C | ||||
| 79573278 | A→G | Elf1 | RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录的正调控 | 是 | 0.000 |
| 79595387 | G→A | Sugt1 | 参与动粒功能 | 是 | 0.000 |
| 79637996 | C→G | Lect1 | 内皮细胞增殖负调控 | 否 | 0.005 |
| 79656659 | A→G | ||||
| 79656692 | T→C | ||||
| 86966512 | G→A | Diaph3 | 遗传性听神经病变,先天性造血障碍性贫血 | 是 | 0.958 |
| 96201334 | G→T | Klhl1 | 肌动蛋白结合蛋白 | 否 | 0.001 |
| 88469236 | C→G | Pcdh20 | 细胞黏附 | 否 | 0.000 |
| 99046045 | G→C | Mzt1 | 微管蛋白复合体组成 | 是 | - |
| 99061539 | G→C | Bora | 蛋白激酶活性的激活,细胞周期过程的调控,蛋白质定位的调节 | 是 | 0.995 |
| 99068023 | C→T | Bora | |||
| 99068337 | G→C | ||||
| 99068407 | C→G | ||||
| 99068529 | A→G | ||||
| 99068542 | A→G | ||||
| 99072637 | T→A | ||||
| 99072704 | G→A | ||||
| 99084109 | C→A | Dis3 | CUT分解代谢,RNA加工,rRNA分解代谢 | 是 | 0.000 |
| 99099549 | G→T | ||||
| 99101172 | A→G | Pibf1 | 有丝分裂核分裂,细胞因子产生,蛋白质磷酸化 | 否 | 0.982 |
Table 2 Analysis of genes with missense mutations by exon sequencing in C.Cg.SHJH hr mice
突变位置 Mutation position | 碱基变化 Base alteration | 基因 Gene | 涉及疾病/细胞功能 Related diseases/cell functions | 下游信号通路调控 Signal pathway regulation | PolyPhen-2计算得分 PolyPhen-2 scores |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70559773 | C→T | Hr | 全身性脱毛,伴有丘疹性病变的心房颤动 | 是 | 1.000 |
| 73523427 | A→G | Nudet15 | 造血干细胞和祖细胞急性损失 | 是 | 0.000 |
| 74744708 | T→C | esd | 甲醛分解代谢 | 是 | 0.505 |
| 74811692 | T→C | Lrch1 | 细胞对趋化因子的反应 | 否 | 0.047 |
| 74813612 | T→C | ||||
| 75031916 | G→A | 5031414D18Rik | 自噬体成熟、糖原、脂质代谢过程的调节 | 否 | 0.022 |
| 75032403 | C→A | ||||
| 75036145 | A→G | ||||
| 75125178 | A→G | Lrrc63 | 膜蛋白 | 否 | - |
| 75224148 | C→T | Lcp1 | 肌动蛋白丝束组件 | 否 | 0.166 |
| 78510551 | C→G | Akap11 | 体型缩小,活动能力减退 | 否 | 0.997 |
| 79401743 | G→A | Mtrf1 | 线粒体翻译终止;耳聋,痉挛性共济失调 | 否 | 0.959 |
| 79401763 | G→T | Mtrf1 | |||
| 79406608 | A→G | ||||
| 79427505 | C→G | Kbtbd | 蛋白酶体介导的泛素依赖蛋白的分解代谢 | 是 | 0.006 |
| 79452831 | G→C | ||||
| 79573278 | A→G | Elf1 | RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录的正调控 | 是 | 0.000 |
| 79595387 | G→A | Sugt1 | 参与动粒功能 | 是 | 0.000 |
| 79637996 | C→G | Lect1 | 内皮细胞增殖负调控 | 否 | 0.005 |
| 79656659 | A→G | ||||
| 79656692 | T→C | ||||
| 86966512 | G→A | Diaph3 | 遗传性听神经病变,先天性造血障碍性贫血 | 是 | 0.958 |
| 96201334 | G→T | Klhl1 | 肌动蛋白结合蛋白 | 否 | 0.001 |
| 88469236 | C→G | Pcdh20 | 细胞黏附 | 否 | 0.000 |
| 99046045 | G→C | Mzt1 | 微管蛋白复合体组成 | 是 | - |
| 99061539 | G→C | Bora | 蛋白激酶活性的激活,细胞周期过程的调控,蛋白质定位的调节 | 是 | 0.995 |
| 99068023 | C→T | Bora | |||
| 99068337 | G→C | ||||
| 99068407 | C→G | ||||
| 99068529 | A→G | ||||
| 99068542 | A→G | ||||
| 99072637 | T→A | ||||
| 99072704 | G→A | ||||
| 99084109 | C→A | Dis3 | CUT分解代谢,RNA加工,rRNA分解代谢 | 是 | 0.000 |
| 99099549 | G→T | ||||
| 99101172 | A→G | Pibf1 | 有丝分裂核分裂,细胞因子产生,蛋白质磷酸化 | 否 | 0.982 |
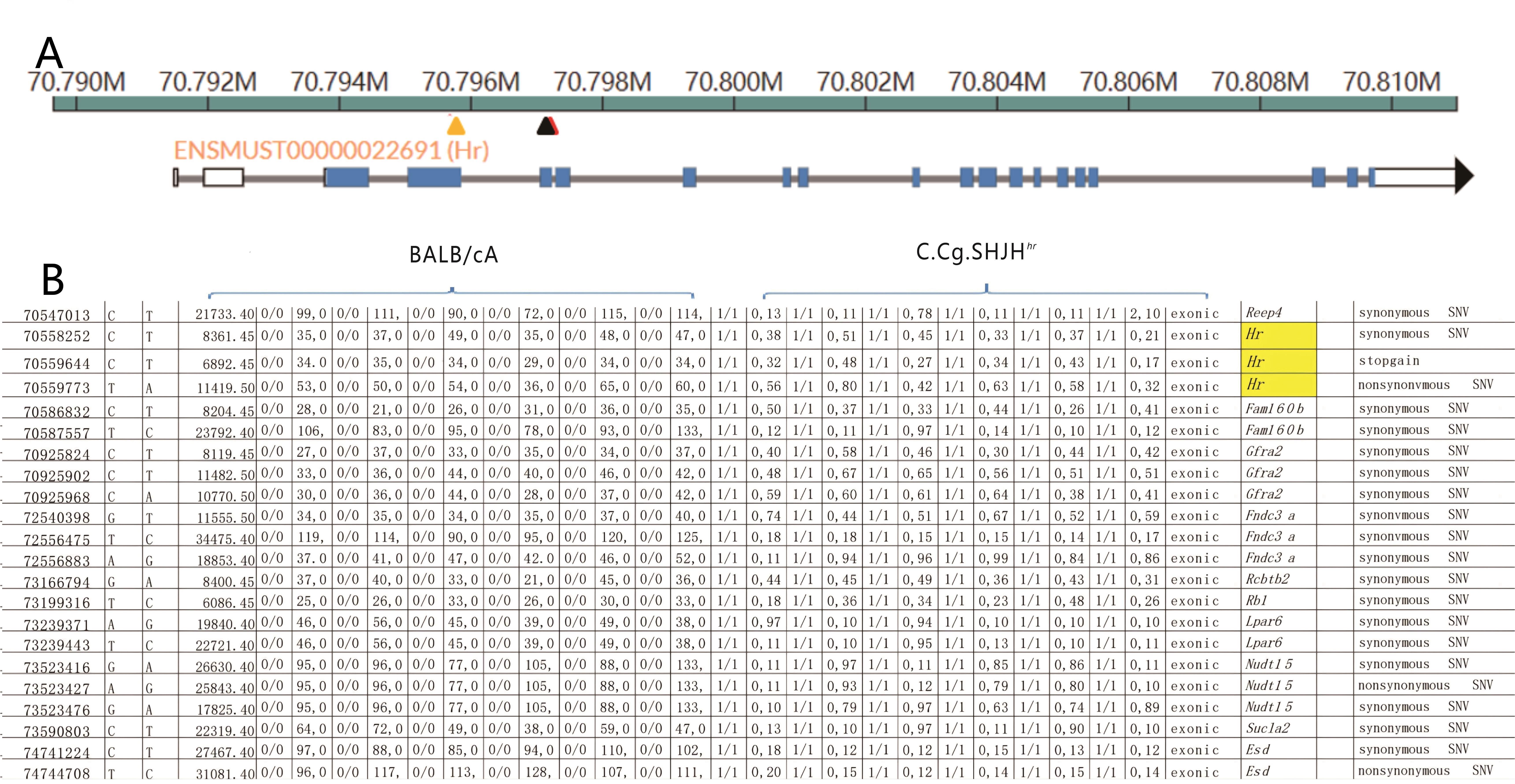
Figure 4 Mutations resulting from genomic exon sequencing between C.Cg.SHJH hr mice and BALB/cAShjh miceNote: A, Three locations obtained from Hr gene sequencing; B, Differentiated locations in exon regions of C.Cg. SHJH hr mice and BALB/cAShjh mice.
| 1 | AHMAD W, FAIYAZ UL HAQUE M, BRANCOLINI V, et al. Alopecia universalis associated with a mutation in the human hairless gene[J]. Science, 1998, 279(5351):720-724. DOI: 10.1126/science.279.5351.720 . |
| 2 | AHMAD W, RATTERREE M S, PANTELEYEV A A, et al. Atrichia with papular lesions resulting from mutations in the rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta) hairless gene[J]. Lab Anim, 2002, 36(1):61-67. DOI: 10.1258/0023677021911777 . |
| 3 | BALE S J. Of hairless mice and men: the genetic basis of congenital alopecia universalis/congenital atrichia[J]. J Cutan Med Surg, 1999, 3(6):309-311. DOI: 10.1177/120347549900300607 . |
| 4 | BERGMAN R, SCHEIN-GOLDSHMID R, HOCHBERG Z, et al. The alopecias associated with vitamin D-dependent rickets type IIA and with hairless gene mutations: a comparative clinical, histologic, and immunohistochemical study[J]. Arch Dermatol, 2005, 141(3):343-351. DOI: 10.1001/archderm.141.3.343 . |
| 5 | PANTELEYEV A A, PAUS R, AHMAD W, et al. Molecular and functional aspects of the hairless (hr) gene in laboratory rodents and humans[J]. Exp Dermatol, 1998, 7(5):249-267. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1998.tb00295.x-i1 . |
| 6 | SUNDBERG J P, PRICE V H, KING L E Jr. The hairless gene in mouse and man[J]. Arch Dermatol, 1999, 135(6):718-720. DOI: 10.1001/archderm.135.6.718 . |
| 7 | ZLOTOGORSKI A, HOCHBERG Z, MIRMIRANI P, et al. Clinical and pathologic correlations in genetically distinct forms of atrichia[J]. Arch Dermatol, 2003, 139(12):1591-1596. DOI: 10.1001/archderm.139.12.1591 . |
| 8 | LIU Y, SUNDBERG J P, DAS S, et al. Molecular basis for hair loss in mice carrying a novel nonsense mutation (Hrrh-R) in the hairless gene (Hr)[J]. Vet Pathol, 2010, 47(1):167-176. DOI: 10.1177/0300985809352970 . |
| 9 | 唐慧青, 常书福, 于志锋, 等. SHJH hr 小鼠部分生物学特性及衰老表型的测定与分析[J]. 实验动物与比较医学,2023, 43(1):44-52. DOI:10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.069 . |
| TANG H Q, CHANG S F, YU Z F, et al. Investigation on biological characteristics and aging phenotype of SHJH hr mice[J]. Lab Anim Comp Med, 2023, 43(1): 44-52. DOI:10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.069 . | |
| 10 | GAO J F, LI Y C, GUAN Y L, et al. The accelerated aging skin in rhino-like SHJHhr mice[J]. Exp Dermatol, 2022, 31(10):1597-1606. DOI: 10.1111/exd.14632 . |
| 11 | FOSTER H L, DAVID SMALL J, FOX J G. The Mouse in biomedical research[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1981. |
| 12 | 钱强, 徐园, 王亚恒, 等. 基于多重PCR靶向二代测序的近交系小鼠遗传质量监测方法建立[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2019, 39(2): 111-117. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5817.2019.02.008 . |
| QIAN Q, XU Y, WANG Y H, et al. Mouse genetic quality monitoring method establishment based on next-generation sequencing through multiplex PCR[J]. Lab Anim Comp Med, 2019, 39(2): 111-117. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5817.2019.02.008 . | |
| 13 | SNELL G D. Congenic resistant strains of mice[M]//Origins of inbred mice. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1978:119-156. DOI: 10.1016/b978-0-12-507850-4.50016-0 . |
| 14 | POSEY J E, O'DONNELL-LURIA A H, CHONG J X, et al. Insights into genetics, human biology and disease gleaned from family based genomic studies[J]. Genet Med, 2019, 21(4):798-812. DOI: 10.1038/s41436-018-0408-7 . |
| 15 | LUPSKI J R. Clinical genomics: from a truly personal genome viewpoint[J]. Hum Genet, 2016, 135(6):591-601. DOI: 10.1007/s00439-016-1682-6 . |
| 16 | KURAMOTO T, KUWAMURA M, TAGAMI F, et al. Kyoto rhino rats derived by ENU mutagenesis undergo congenital hair loss and exhibit focal glomerulosclerosis[J]. Exp Anim, 2011, 60(1):57-63. DOI: 10.1538/expanim.60.57 . |
| 17 | CICHON S, ANKER M, VOGT I R, et al. Cloning, genomic organization, alternative transcripts and mutational analysis of the gene responsible for autosomal recessive universal congenital alopecia[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 1998, 7(11):1671-1679. DOI: 10.1093/hmg/7.11.1671 . |
| 18 | ZLOTOGORSKI A, AHMAD W, CHRISTIANO A M. Congenital atrichia in five Arab Palestinian families resulting from a deletion mutation in the human hairless gene[J]. Hum Genet, 1998, 103(4):400-404. DOI: 10.1007/s004390050840 . |
| 19 | HSIEH J C, SISK J M, JURUTKA P W, et al. Physical and functional interaction between the vitamin D receptor and hairless corepressor, two proteins required for hair cycling[J]. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278(40):38665-38674. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M304886200 . |
| 20 | PANTELEYEV A A, CHRISTIANO A M. The Charles River hairless rat mutation is distinct from the hairless mouse alleles[J]. Comp Med, 2001, 51(1):49-55. |
| 21 | POTTER G B, BEAUDOIN G M, DERENZO C L, et al. The hairless gene mutated in congenital hair loss disorders encodes a novel nuclear receptor corepressor[J]. Genes Dev, 2001, 15(20):2687-2701. DOI: 10.1101/gad.916701 . |
| 22 | THOMPSON C C, BOTTCHER M C. The product of a thyroid hormone-responsive gene interacts with thyroid hormone receptors[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1997, 94(16):8527-8532. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.16.8527 . |
| 23 | SUNDBERG J P, DUNSTAN R W, COMPTON J G. Hairless mouse, HRS/Jhr/hr [M]//Integument and mammary glands. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1989:192-197. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-83749-4_32 . |
| 24 | LI Y C, GAO J F, GUAN Y L, et al. Novel rhino-like SHJH hr mice with thyroid dysfunction[J]. Zool Res, 2021, 42(6):734-738. DOI: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2021.211 . |
| [1] | LUO Lianlian, YUAN Yanchun, WANG Junling, SHI Guangsen. Advances in Mouse Models of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 290-299. |
| [2] | SHEN Yan, XU Wang-yang, ZHU Hou-bao. Research Progress on Pathogenesis of Hereditary Diseases Caused by Mutations of Oxidoreductase DHTKD1 and Related Mouse Models [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2018, 38(6): 468-472. |
| [3] | MA Deng-lei, ZHANG Lan. P301S Mutant Tau Transgenic Mouse and Their Applications [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2017, 37(6): 491-496. |
| [4] | YANG Jin-lian, LU Yan-min, YANG Fan, ZHENG Hong, QU Cheng-kui, WANG Si-ying. The Effects of Leukemia Related Gain-of-function Mutant SHP-2 on Murine Angiogenesis in vivo [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2012, 32(4): 259-264. |
| [5] | CHEN Zhen-yue1,2,XU Xiao-lei2,WU Li-qun1,LU Guo-ping1. Premature Aging in Zebrafish Heterozygous breakdance Mutant [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2010, 30(6): 410-414. |
| [6] | LIU Yue-huan1,WU Jiu-sheng2, SA Xiao-ying1, SHI Zhang-kui1. The Coat Color Mutants of Mongolian Gerbil and Its Genetics [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2002, 22(3): 168-171. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||