
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 259-268.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.165
• Animal Models of Human Diseases • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Zhiwei, YANG Ran, LIAN Hao, ZHANG Yu, JIN Lilun( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-11-08
Revised:2025-02-07
Online:2025-06-25
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
JIN Lilun
CLC Number:
LIU Zhiwei,YANG Ran,LIAN Hao,et al. Cartilage Protection and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fraxetin on Monosodium Iodoacetate-Induced Rat Model of Osteoarthritis[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 259-268. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.165.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.165
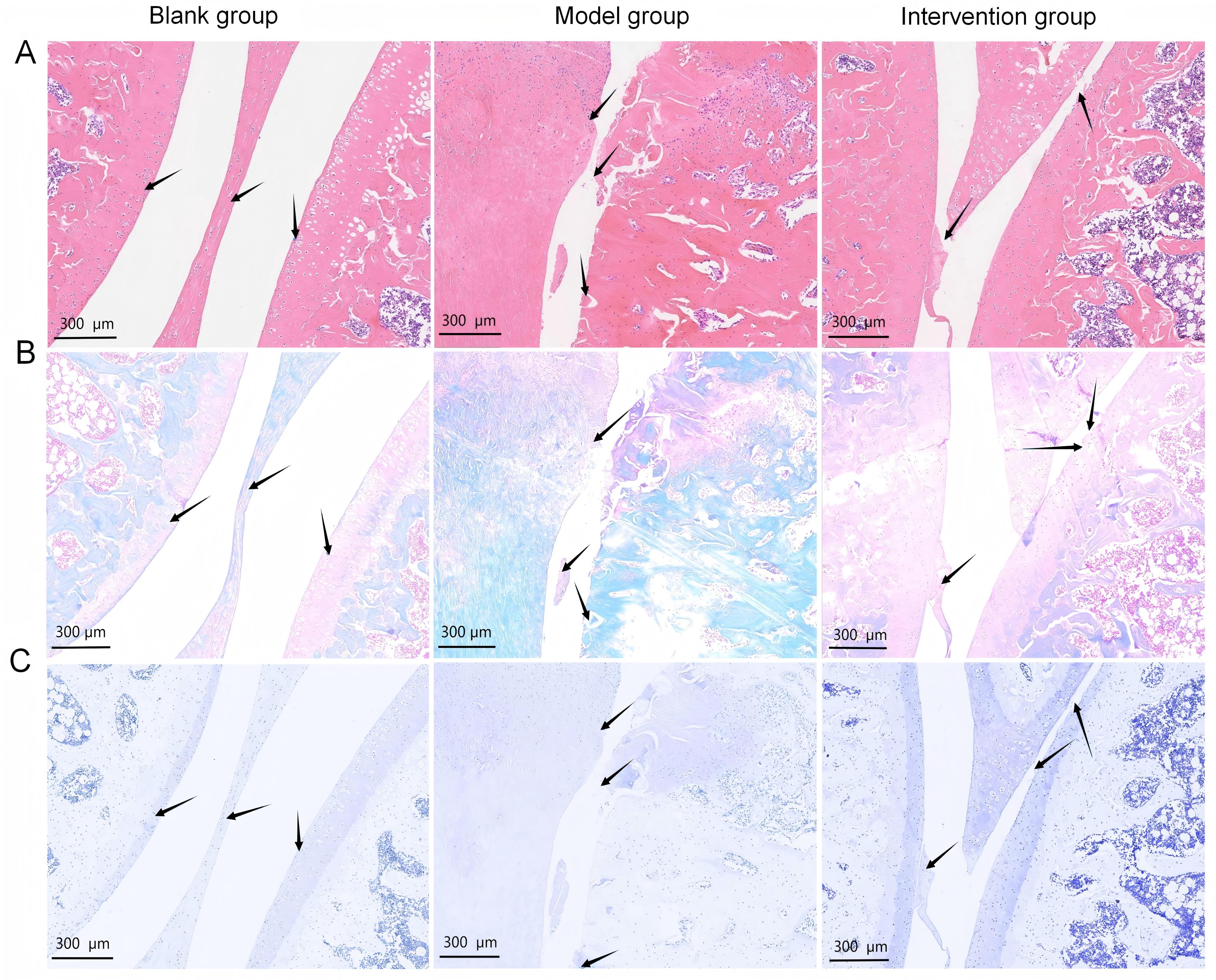
Figure 1 Histopathological changes in rat knee joint cartilage after monosodium iodoacetate injection and fraxetin interventionNote: A, B, and C are the staining results of hematoxylin-eosin, safranin O–fast green, and toluidine blue in the knee cartilage tissue of three groups of rats (scale bar = 300 μm, the black arrow in the picture points to the surface of the knee cartilage). The blank group refers to rats that were first injected with 50 μL of normal saline into the right knee joint cavity, followed by intra-articular injections of 50 μL of normal saline for 7 consecutive days; the model group refers to rats that were injected with one time injection of 50 μL fresh prepared monosodium iodoacetate (60 mg/mL)in the right knee joint cavity to induce osteoarthritis, followed by injections of 50 μL of normal saline for 7 consecutive days; the intervention group refers to rats that were injected with one time injection of 50 μL fresh prepared monosodium iodoacetate (60 mg/mL)in the right knee joint cavity, followed by fraxetin injections (5 mg·kg-1·d-1, dissolved in 50 μL of normal saline) for 7 consecutive days.
分组 Group | 动物数量 n | Mankin评分 Mankin score | OARSI评分 OARSI sore | 骨体积分数 Tb.BV/TV | 骨表面积密度/(mm2·mm-3) Tb.BS/TV | 骨小梁数量/mm-1 Tb.N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 空白组 Blank group | 6 | 1.17±0.75 | 1.83±0.75 | 0.59±0.01 | 17.44±0.60 | 3.72±0.21 |
| 模型组 Model group | 6 | 10.67±1.86* | 8.00±1.41* | 0.25±0.02* | 13.28±0.86* | 2.47±0.19* |
| 干预组 Intervention group | 6 | 5.67±0.82# | 5.50±1.05# | 0.38±0.02# | 15.59±0.50# | 3.29±0.14# |
Table 1 Comparison of Mankin score, OARSI score, Tb.BV/TV, Tb.BS/TV, and Tb.N of knee cartilage among different groups
分组 Group | 动物数量 n | Mankin评分 Mankin score | OARSI评分 OARSI sore | 骨体积分数 Tb.BV/TV | 骨表面积密度/(mm2·mm-3) Tb.BS/TV | 骨小梁数量/mm-1 Tb.N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 空白组 Blank group | 6 | 1.17±0.75 | 1.83±0.75 | 0.59±0.01 | 17.44±0.60 | 3.72±0.21 |
| 模型组 Model group | 6 | 10.67±1.86* | 8.00±1.41* | 0.25±0.02* | 13.28±0.86* | 2.47±0.19* |
| 干预组 Intervention group | 6 | 5.67±0.82# | 5.50±1.05# | 0.38±0.02# | 15.59±0.50# | 3.29±0.14# |
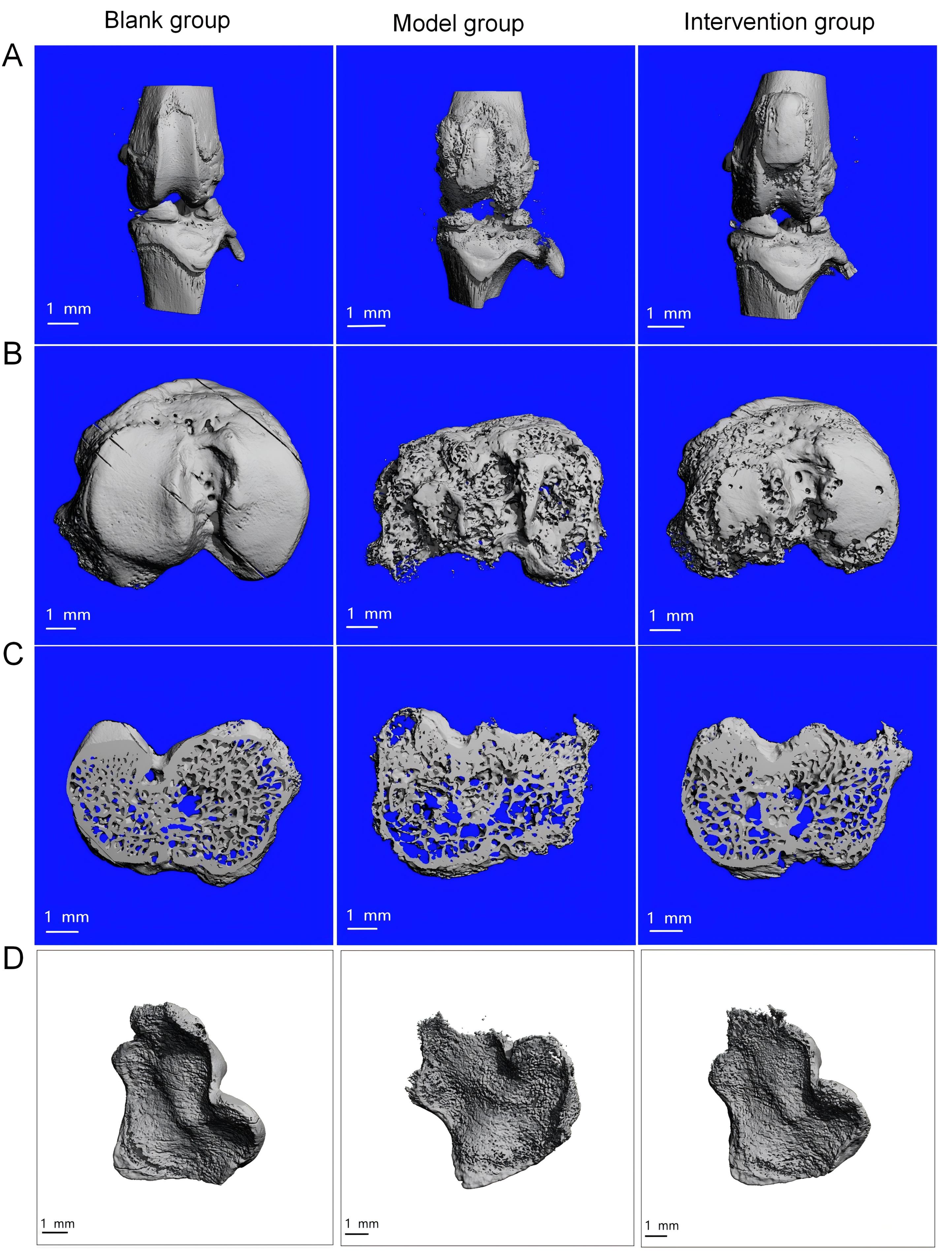
Figure 2 Micro-CT imaging of the rat knee joint after monosodium iodoacetate injection and fraxetin treatmentNote: A, B, C, and D represent micro-CT images of the knee joints of three groups of rats, scanned at the levels of 3D reconstruction, the tibial platform, the subchondral bone, and specific cross-sectional regions, to assess bone structure and evaluate osteoarthritis changes. The blank group refers to rats that were first injected with 50 μL of normal saline into the right knee joint cavity, followed by intra-articular injections of 50 μL of normal saline for 7 consecutive days; the model group refers to rats that were injected with one time injection of 50 μL fresh prepared monosodium iodoacetate (60 mg/mL)in the right knee joint cavity to induce osteoarthritis, followed by injection of 50 μL of normal saline for 7 consecutive days; the intervention group refers to rats that were injected with one time injection of 50 μL fresh prepared monosodium iodoacetate (60 mg/mL)in the right knee joint cavity, followed by intra-articular injections of fraxetin (5 mg·kg-1·d-1, dissolved in 50 μL of normal saline) for 7 consecutive days.
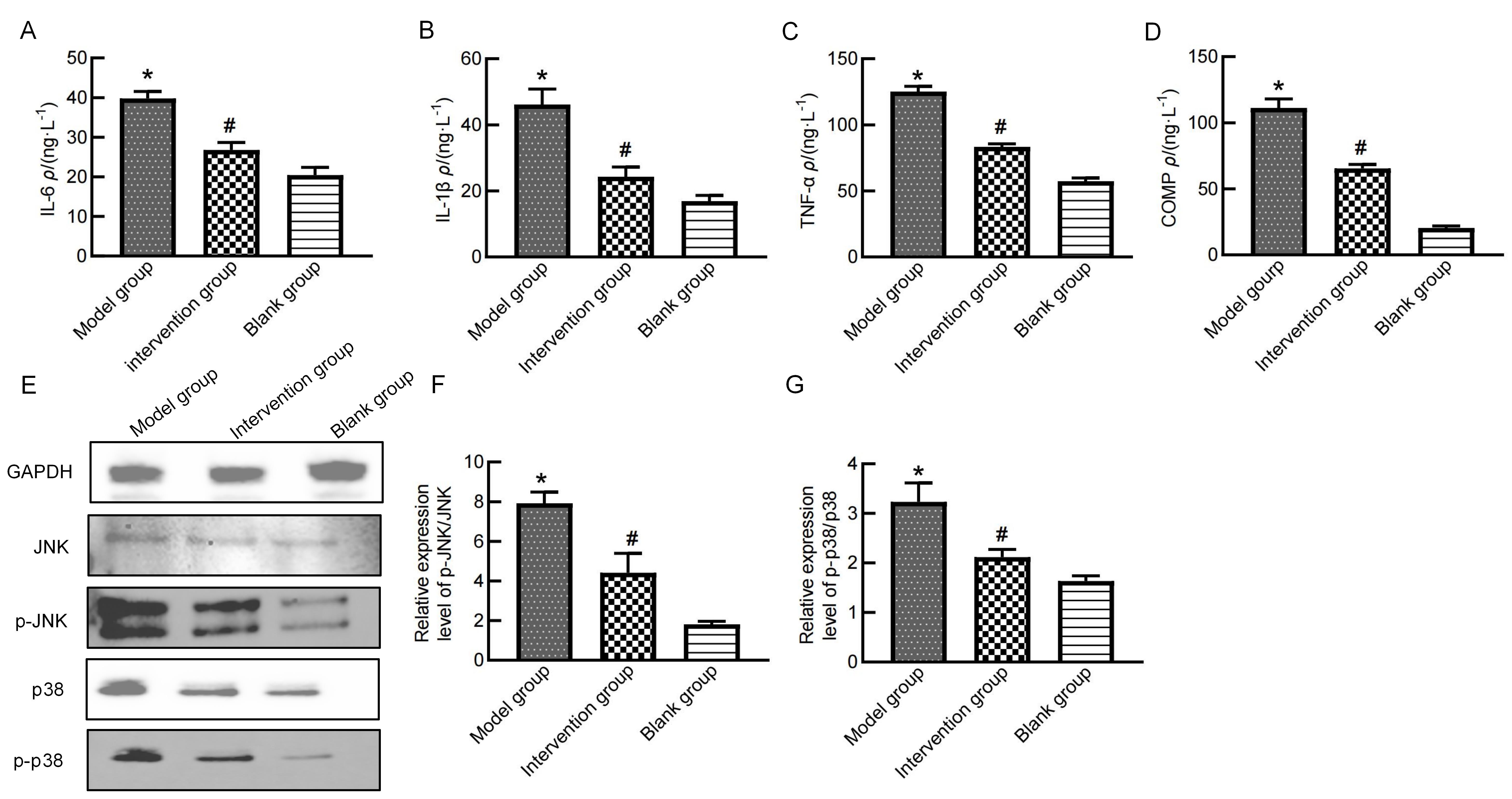
Figure 3 Expression of inflammation-related proteins in rat serum and knee cartilage after fraxetin treatmentNote: A-D, show the serum levels of IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, and COMP detected by ELISA. E shows the expression of p38 MAPK, JNK, p-p38 MAPK, and p-JNK proteins in knee cartilage tissues detected by Western blotting. F and G show the ratios of p-JNK/JNK and p-p38 MAPK/p38 MAPK, reflecting the phosphorylation levels of JNK and p38, which indicate the activation levels of the corresponding pathways. The blank group refers to rats that were first injected with 50 μL of normal saline into the right knee joint cavity, followed by intra-articular injections of 50 μL of normal saline for 7 consecutive days; the model group refers to rats that were injected with one time injection of 50 μL fresh prepared monosodium iodoacetate (60 mg/mL)in the right knee joint cavity to induce osteoarthritis, followed by intra-articular injections of 50 μL of normal saline for 7 consecutive days; the intervention group refers to rats that were injected with one time injection of 50 μL fresh prepared monosodium iodoacetate (60 mg/mL)in the right knee joint cavity, followed by intra-articular injections of fraxetin (5 mg·kg-1·d-1, dissolved in 50 μL of normal saline) for 7 consecutive days. There were 6 rats in each group (n=6). Compared with the blank group, *P<0.05; compared with the model group, #P<0.05.
| [1] | GIORGINO R, ALBANO D, FUSCO S, et al. Knee osteoarthritis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and mesenchy- mal stem cells: what else is new? an update[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(7):6405. DOI:10.3390/ijms24076405 . |
| [2] | ZHAO J L, YANG W Y, LIANG G H, et al. The efficacy and safety of Jinwu Gutong capsule in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 293:115247. DOI:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115247 . |
| [3] | 王庆, 冯文昌, 庄迪, 等. 消瘀散贴膏联合针刀治疗膝骨关节炎的疗效及对炎症因子的影响[J]. 辽宁中医杂志, 2020, 47(10):155-159. DOI: 10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2020.10.048 . |
| WANG Q, FENG W C, ZHUANG D, et al. Clinical effect of Xiaoyusan plaster combined with acupotomy on knee osteoarthritis and its effect on inflammatory factors[J]. Liaoning J Tradit Chin Med, 2020, 47(10):155-159. DOI: 10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2020.10.048 . | |
| [4] | 崔若琳, 王庆, 杨玲, 等. 消瘀散新组方修复膝骨关节炎模型兔的软骨损伤及MMP-13表达[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(1):30-38. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.099 . |
| CUI R L, WANG Q, YANG L, et al. Repair effects of Xiaoyusan new formula on cartilage injury and MMP-13 expression in knee osteoarthritis model rabbits[J]. Lab Anim Comp Med, 2023, 43(1):30-38. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.099 . | |
| [5] | 曹桂云, 宁波, 秦金淼, 等. 基于标准汤剂的秦皮(白蜡树)配方颗粒质量标准分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2023, 29(13):122-129. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20230148 . |
| CAO G Y, NING B, QIN J M, et al. Analysis on quality standard of fraxini cortex (Fraxinus chinensis) dispensing granules based on standard decoction[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae, 2023, 29(13):122-129. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20230148 . | |
| [6] | 杨凌, 庄迪, 金立伦. 转录组测序筛选大鼠滑膜炎差异表达基因及秦皮素治疗靶点的体外验证[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2023, 43(1):11-20. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.100 . |
| YANG L, ZHUANG D, JIN L L. Screening of differentially expressed genes in rat synovitis by transcriptome sequencing and in vitro verification of therapeutic target of fraxetin[J]. Lab Anim Comp Med, 2023, 43(1):11-20. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.100 . | |
| [7] | WANG Q, ZHUANG D, FENG W C, et al. Fraxetin inhibits interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis, inflammation, and matrix degradation in chondrocytes and protects rat cartilage in vivo [J]. Saudi Pharm J, 2020, 28(12):1499-1506. DOI:10.1016/j.jsps.2020.09.016 . |
| [8] | WU Q, YAO X B, SHAN N, et al. Platelet-rich plasma ameliorates cartilage degradation in rat models of osteoarthritis via the OPG/RANKL/RANK system[J]. Folia Histochem Cytobiol, 2024, 62(3):154-164. DOI:10.5603/fhc. 100179 . |
| [9] | 李培金, 韩倩, 王威, 等. 姜黄素治疗骨关节炎过程中潜在的铁死亡关键基因的分析与验证[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2024, 26(9):2455-2465. DOI:10.11842/wst.20230705004 . |
| LI P J, HAN Q, WANG W, et al. Analysis and verification of potential ferroptosis key genes in curcumin treatment of osteoarthritis[J]. World Sci Technol-Mod Tradit Chin Med Mater Med, 2024, 26(9):2455-2465. DOI:10.11842/wst. 20230705004 . | |
| [10] | XU Z X, KE T, ZHANG Y F, et al. Danshensu inhibits the IL-1β- induced inflammatory response in chondrocytes and osteoarthritis possibly via suppressing NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Mol Med, 2021, 27(1):80. DOI:10.1186/s10020-021-00329-9 . |
| [11] | KOVÁCS B, VAJDA E, NAGY E E. Regulatory effects and interactions of the Wnt and OPG-RANKL-RANK signaling at the bone-cartilage interface in osteoarthritis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(18):4653. DOI:10.3390/ijms20184653 . |
| [12] | ROSAS S, KWOK A, MOORE J, et al. Osteoarthritis as a systemic disease promoted prostate cancer in vivo and in vitro [J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(11):6014. DOI:10.3390/ijms25116014 . |
| [13] | YAO Q, WU X H, TAO C, et al. Osteoarthritis: pathogenic signaling pathways and therapeutic targets[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1):56. DOI:10.1038/s41392-023-01330-w . |
| [14] | ULIVI V, GIANNONI P, GENTILI C, et al. p38/NF-kB-dependent expression of COX-2 during differentiation and inflammatory response of chondrocytes[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2008, 104(4):1393-1406. DOI:10.1002/jcb.21717 . |
| [15] | LU J S, ZHANG H B, PAN J Y, et al. Fargesin ameliorates osteoarthritis via macrophage reprogramming by downregulating MAPK and NF-κB pathways[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2021, 23(1):142. DOI:10.1186/s13075-021-02512-z . |
| [16] | DING D, YAN J B, FENG G N, et al. Dihydroartemisinin attenuates osteoclast formation and bone resorption via inhibiting the NF-κB, MAPK and NFATc1 signaling pathways and alleviates osteoarthritis[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2022, 49(1):4. DOI:10.3892/ijmm.2021.5059 . |
| [17] | LIAO J C, WEI Z X, ZHAO C, et al. Inhibition of osteoclastogenesis for periprosthetic osteolysis therapy through the suppression of p38 signaling by fraxetin[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2018, 42(3):1257-1264. DOI:10.3892/ijmm.2018.3698 . |
| [18] | 蔡宛儒, 余芳. 髋膝联合电针治疗早期膝骨关节炎的临床研究[J]. 湖北中医药大学学报, 2024, 26(5):88-90. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-987x.2024.05.24 . |
| CAI W R, YU F. Clinical research on hip-knee coherent electro-acupuncture in treating early knee osteoarthritis[J]. J Hubei Univ Chin Med, 2024, 26(5):88-90. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-987x.2024.05.24 . | |
| [19] | 任国飞, 李同林, 卞恒杰. 抗骨增生胶囊联合洛索洛芬钠治疗早期膝骨关节炎的临床研究[J]. 现代药物与临床, 2024, 39(10):2651-2655. DOI:10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2024.10.034 . |
| REN G F, LI T L, BIAN H J. Clinical study on Kanggu Zengsheng Capsules combined with loxoprofen sodium in treatment of early knee osteoarthritis[J]. Drugs Clin, 2024, 39(10):2651-2655. DOI:10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2024.10.034 . | |
| [20] | 韩杰, 柴源, 章晓云, 等. 中药复方治疗不同分期膝骨关节炎的研究进展[J]. 中医正骨, 2022, 34(11): 57-61. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6015.2022.11.011 . |
| HAN J, CHAI Y, ZHANG X Y, et al. Advancement of research on the treatment of different stages of knee osteoarthritis with compounds[J]. J Tradit Chin Orthop Trauma, 2022, 34(11):57-61. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6015.2022.11.011 . | |
| [21] | WU B, WANG R, LI S N, et al. Antifibrotic effects of Fraxetin on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis by targeting NF-κB/IκBα, MAPKs and Bcl-2/Bax pathways[J]. Pharmacol Rep, 2019, 71(3):409-416. DOI:10.1016/j.pharep.2019.01.008 . |
| [22] | WITAICENIS A, SEITO L N, SILVEIRA CHAGAS A DA, et al. Antioxidant and intestinal anti-inflammatory effects of plant-derived coumarin derivatives[J]. Phytomedicine, 2014, 21(3):240-246. DOI:10.1016/j.phymed.2013.09.001 . |
| [23] | DE SOUSA VALENTE J. The pharmacology of pain associated with the monoiodoacetate model of osteoarthritis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 974. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00974 . |
| [24] | MA T W, ZHANG Z H, SONG X P, et al. Combined detection of COMP and CS846 biomarkers in experimental rat osteoarthritis: a potential approach for assessment and diagnosis of osteoarthritis[J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2018, 13(1): 230. DOI: 10.1186/s13018-018-0938-3 . |
| [25] | CHEN J Y, ZHANG L, ZHANG H, et al. Triggering of p38 MAPK and JNK signaling is important for oleanolic acid-induced apoptosis via the mitochondrial death pathway in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts[J]. Phytother Res, 2014, 28(10): 1468-1478. DOI: 10.1002/ptr.5150 . |
| [26] | LI X H, ZHANG Z L, LIANG W N, et al. Tougu Xiaotong capsules may inhibit p38 MAPK pathway-mediated inflammation: In vivo and in vitro verification[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2020, 249: 112390. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep. 2019. 112390 . |
| [1] | QIN Chao, LI Shuangxing, ZHAO Tingting, JIANG Chenchen, ZHAO Jing, YANG Yanwei, LIN Zhi, WANG Sanlong, WEN Hairuo. Study on the 90-day Feeding Experimental Background Data of SD Rats for Drug Safety Evaluation [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 439-448. |
| [2] | LIU Liyu, JI Bo, LIU Xiaoxuan, FANG Yang, ZHANG Ling, GUO Tingting, QUAN Ye, LI Hewen, LIU Yitian. Exploration of Rat Fetal Lung Tissue Fixation Methods [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 432-438. |
| [3] | JIANG Meng, HAO Shulan, TONG Liguo, ZHONG Qiming, GAO Zhenfei, WANG Yonghui, WANG Xixing, JI Haijie. Dynamic Evaluation of Vinorelbine-Induced Phlebitis of Dorsalis Pedis Vein in a Rat Model [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 251-258. |
| [4] | PAN Yicong, JIANG Wenhong, HU Ming, QIN Xiao. Optimization of Surgical Procedure and Efficacy Evaluation of Aortic Calcification Model in Rats with Chronic Kidney Disease [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 279-289. |
| [5] | LIAN Hui, JIANG Yanling, LIU Jia, ZHANG Yuli, XIE Wei, XUE Xiaoou, LI Jian. Construction and Evaluation of a Rat Model of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 130-146. |
| [6] | SUN Xiaorong, SU Dan, GUI Wenjuan, CHEN Yue. Establishment and Evaluation of a Moderate-to-Severe Knee Osteoarthritis Model in Rats Induced by Surgery [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 597-604. |
| [7] | YIN Yulian, MA Lina, TU Siyuan, CHEN Ling, YE Meina, CHEN Hongfeng. Establishment and Evaluation of a Rat Model of Non-Puerperal Mastitis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 587-596. |
| [8] | YANG Jin, YU Shiya, LIN Nan, FANG Yongchao, ZHAO Hu, QIU Jinwei, LIN Hongming, CHEN Huiyan, WANG Yu, WU Weihang. Effect of Modified Duodenal Exclusion Surgery on Glucose Metabolism in Rats with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 523-530. |
| [9] | QI Longju, CHEN Shiyuan, LIAO Zehua, SHI Yuanhu, SUN Yuyu, WANG Qinghua. Transcriptomic Analysis of Menstrual Blood-Derived Stem Cells Transplantation Combined with Exercise Training in Promoting Spinal Cord Injury Recovery in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 531-542. |
| [10] | ZHANG Naiqun, YUAN Piaopiao, CAO Linrong, YING Na, YANG Taotao. Application of PNR Detection in the Diagnosis and Drug-efficacy Evaluation of Diabetic Kidney Disease in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 543-549. |
| [11] | ZHENG Yiqing, DENG Yasheng, FAN Yanping, LIANG Tianwei, HUANG Hui, LIU Yonghui, NI Zhaobing, LIN Jiang. Application Analysis of Animal Models for Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Based on Data Mining [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 405-418. |
| [12] | XIAO Pan, WANG Hongyi, LU Lu, ZHANG Mei, CHEN Keming, SHEN Dongshuai, NIU Tingxian. Screening of Hypoxia-Sensitive and Hypoxia-Tolerant Wistar Rats and Preliminary Exploration of Hypoxia Sensitivity in Their G1 Generation [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 374-383. |
| [13] | Xiaoyu ZHU, Hantao YUAN, Sibo LI. MicroRNA-887-3p Inhibited MDM4 Expression and Proliferation but Promoted Apoptosis of Intervertebral Disc Annulus Fibrosus Cells in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 270-278. |
| [14] | Jinhua HU, Jingjie HAN, Min JIN, Bin HU, Yuefen LOU. Effects of Puerarin on Bone Density in Rats and Mice: A Meta-analysis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 149-161. |
| [15] | Liya ZHAO, Liju NI, Caiqin ZHANG, Jianping TANG, Yangzheng YAO, Yanyan NIE, Xiaoxue GU, Ying ZHAO. Establishing a Genetic Detection Protocol of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Panels in Inbred Rats Based on Multiplex PCR-LDR [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 548-558. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||