
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 403-410.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.194
• Animal Models of Human Diseases • Previous Articles Next Articles
GONG Leilei1( ), WANG Xiaoxia2, FENG Xuewei1, LI Xinlei1, ZHAO Han1, ZHANG Xueyan1(
), WANG Xiaoxia2, FENG Xuewei1, LI Xinlei1, ZHAO Han1, ZHANG Xueyan1( )(
)( ), FENG Xin1(
), FENG Xin1( )
)
Received:2025-01-02
Revised:2025-04-22
Online:2025-08-25
Published:2025-09-01
Contact:
ZHANG Xueyan, FENG Xin
CLC Number:
GONG Leilei,WANG Xiaoxia,FENG Xuewei,et al. A Mouse Model and Mechanism Study of Premature Ovarian Insufficiency Induced by Different Concentrations of Cyclophosphamide[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 403-410. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.194.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.194
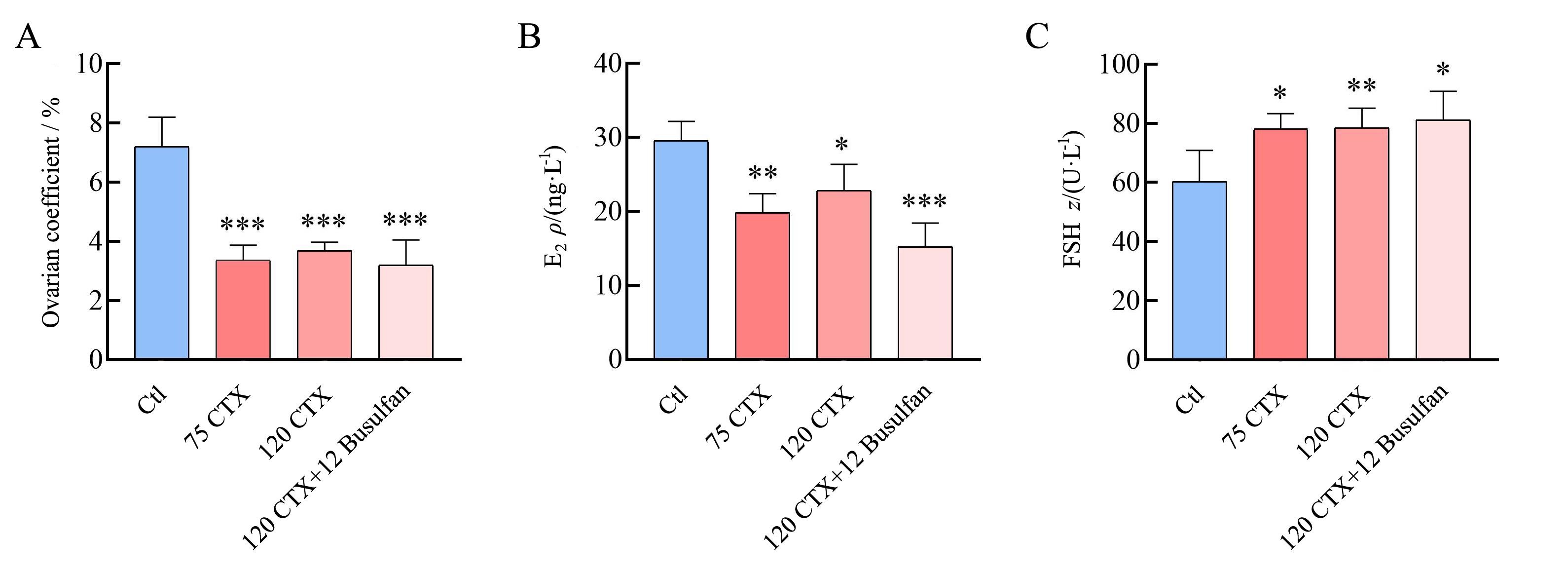
Figure 1 Ovarian coefficients and changes of serum hormone levels in mice on day 7 after modeling with CTX or CTX+BusulfanNote: A, Ovarian index of the first batch of mice; B, Serum E2 levels in the first batch of mice; C, Serum FSH levels in the first batch of mice. Ctl represents control group; 75 CTX, 120 CTX, 120 CTX+12 Busulfan represents premature ovarian insufficiency model group established by intraperitoneal injection of 75 mg/kg cyclophosphamide (CTX), 120 mg/kg CTX, 120 mg/kg CTX+12 mg/kg Busulfan respectively; E2 represents estradiol; FSH represents follicle-stimulating hormone. Compared with Ctl (n=8), *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
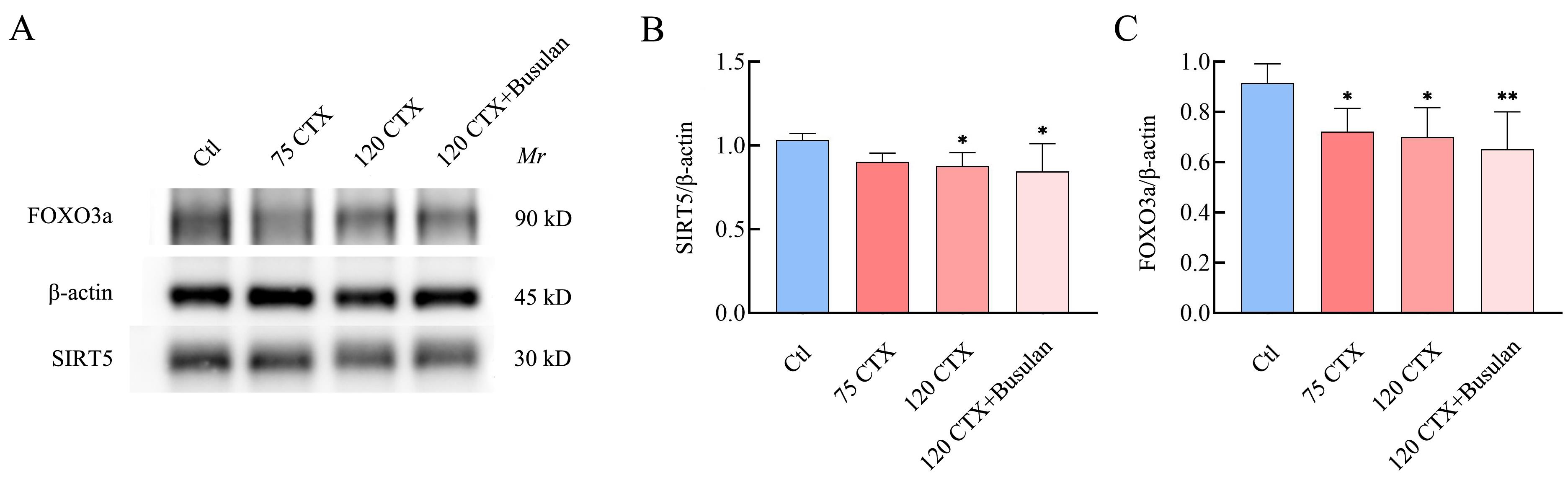
Figure 2 Expressions of SIRT5 and FOXO3a in ovarian tissues on day 7 after modeling with different concentrations of CTX and CTX+BusulfanNote: A, Western blot results of SIRT5 and FOXO3a proteins on day 7 after modeling with different concentrations of CTX and CTX+Busulfan; B, The expression of SIRT5 on day 7 after modeling with different concentrations of CTX and CTX + Busulfan; C, The expression of FOXO3a on day 7 after modeling with different concentrations of CTX and CTX + Busulfan. Compared with Ctl (n=8), *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
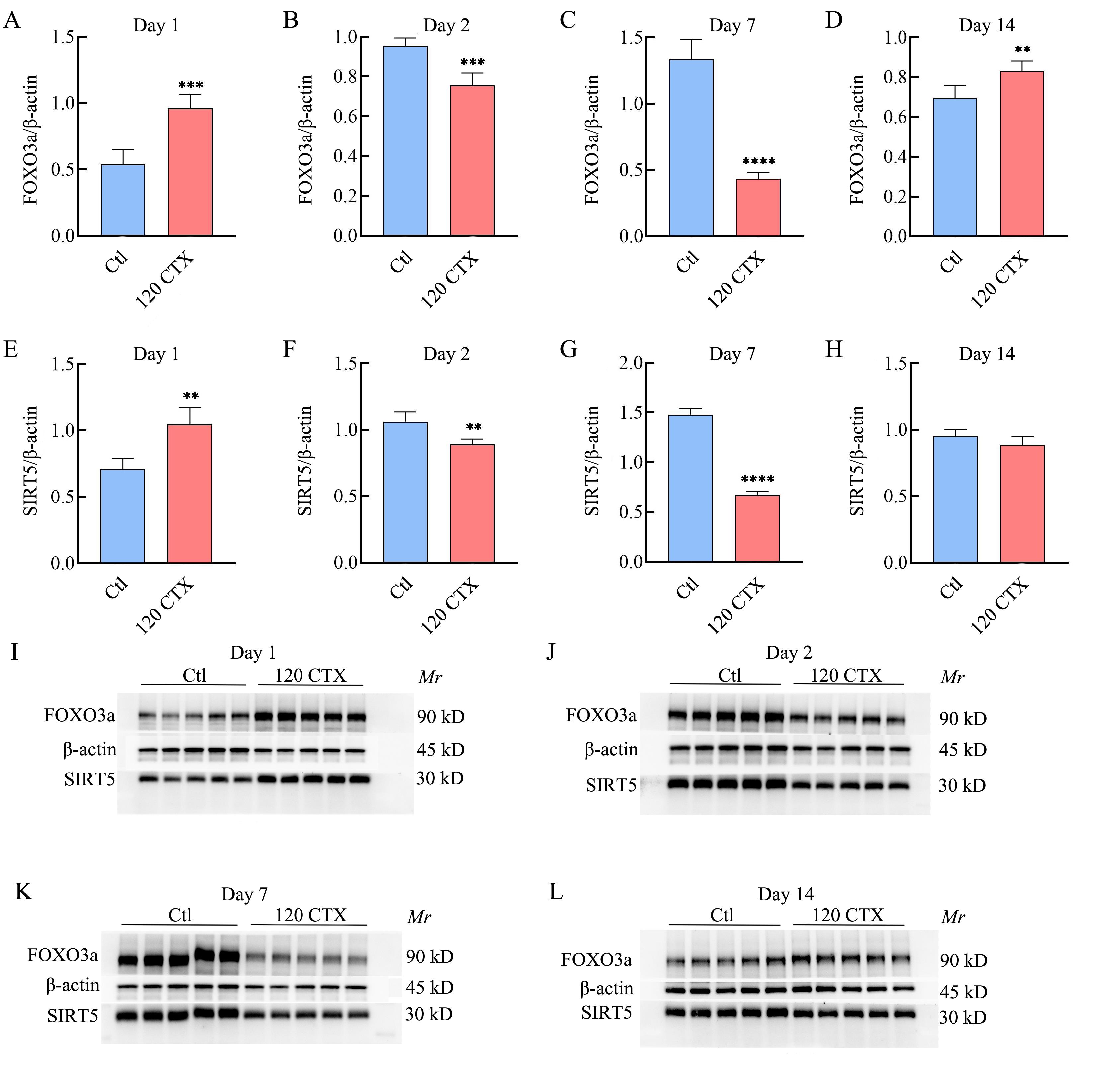
Figure 3 Expression of SIRT5 and FOXO3a in mouse ovarian tissue at different times after 120 mg/kg CTX modelingNote: A and E, The expression of FOXO3a and SIRT5 on day 1 after modeling; B and F, The expression of FOXO3a and SIRT5 on day 2 after modeling; C and G, The expression of FOXO3a and SIRT5 on day 7 after modeling; D and H, The expression of FOXO3a and SIRT5 on day 14 after modeling; I, Western blot results of FOXO3a and SIRT5 on day 1 after modeling; J, Western blot results of FOXO3a and SIRT5 on day 2 after modeling; K, Western blot results of FOXO3a and SIRT5 on day 7 after modeling; L, Western blot results of FOXO3a and SIRT5 on day 14 after modeling. Compared with Ctl (n=5), **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.000 1.
| [1] | 中华医学会妇产科学分会绝经学组. 早发性卵巢功能不全的临床诊疗专家共识(2023版)[J]. 中华妇产科杂志, 2023, 58(10):721-728. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112141-20230316-00122 . |
| Menopausal Group of Obstetrics and Gynecology Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on clinical diagnosis and treatment of early-onset ovarian insufficiency (2023 edition)[J]. Chin J Obstet Gynecol, 2023, 58(10):721-728. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112141-20230316-00122 . | |
| [2] | PANAY N, ANDERSON R A, BENNIE A, et al. Evidence-based guideline: premature ovarian insufficiency[J]. Hum Reprod Open, 2024, 2024(4): hoae065. DOI:10.1093/hropen/hoae065 . |
| [3] | 冯晓玲, 李力, 曲凡, 等. 早发性卵巢功能不全中西医结合诊疗指南[J]. 中医杂志, 2022, 63(12):1193-1198. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2022.12.017 . |
| FENG X L, LI L, QU F, et al. Guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency with integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2022, 63(12):1193-1198. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2022.12.017 . | |
| [4] | LI M, ZHU Y, WEI J, et al. The global prevalence of premature ovarian insufficiency: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Climacteric, 2023, 26(2):95-102. DOI:10.1080/13697137.2022.2153033 . |
| [5] | 吴洁, 郁琦. 早发性卵巢功能不全的诊断和处理[J]. 中华医学信息导报, 2016(21):21. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6606.2024.01.015 . |
| WU J, YU Q. Diagnosis and treatment of early-onset ovarian insufficiency[J]. China Med News, 2016(21):21. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6606.2024.01.015 . | |
| [6] | RUTH K S, DAY F R, HUSSAIN J, et al. Genetic insights into biological mechanisms governing human ovarian ageing[J]. Nature, 2021, 596(7872):393-397. DOI:10.1038/s41586-021-03779-7 . |
| [7] | 王艳辉, 唐丽, 雷磊. 基于数据挖掘的早发性卵巢功能不全动物模型分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2023, 29(9):225-233. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20230317 . |
| WANG Y H, TANG L, LEI L. Animal model of premature ovarian insufficiency based on data mining[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae, 2023, 29(9):225-233. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20230317 . | |
| [8] | HUANG C Z, ZHAO S M, YANG Y J, et al. TP63 gain-of-function mutations cause premature ovarian insufficiency by inducing oocyte apoptosis[J]. J Clin Invest, 2023, 133(5): e162315. DOI:10.1172/JCI162315 . |
| [9] | FANOURIAKIS A, KOSTOPOULOU M, CHEEMA K, et al. 2019 Update of the Joint European League Against Rheumatism and European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (EULAR/ERA-EDTA) recommendations for the management of lupus nephritis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2020, 79(6):713-723. DOI:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-216924 . |
| [10] | QIN X S, ZHAO Y, ZHANG T Y, et al. TrkB agonist antibody ameliorates fertility deficits in aged and cyclophosphamide-induced premature ovarian failure model mice[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1):914. DOI:10.1038/s41467-022-28611-2 . |
| [11] | DING C Y, ZHU L P, SHEN H, et al. Exosomal miRNA-17-5p derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improves ovarian function in premature ovarian insufficiency by regulating SIRT7[J]. Stem Cells, 2020, 38(9):1137-1148. DOI:10.1002/stem.3204 . |
| [12] | LIU M Y, ZHANG D, ZHOU X W, et al. Cell-free fat extract improves ovarian function and fertility in mice with premature ovarian insufficiency[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2022, 13(1):320. DOI:10.1186/s13287-022-03012-w . |
| [13] | MO J H, HU H, LI P D, et al. Human hair follicle-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve ovarian function in cyclophosphamide-induced POF mice[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2025, 16(1):67. DOI:10.1186/s13287-024-04097-1 . |
| [14] | BHARDWAJ J K, BIKAL P, SACHDEVA S N. Chemotherapeutic drugs induced female reproductive toxicity and treatment strategies[J]. J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2023, 37(7): e23371. DOI:10.1002/jbt.23371 . |
| [15] | SWIGONSKA S, NYNCA A, MOLCAN T, et al. The role of lncRNAs in the protective action of tamoxifen on the ovaries of tumor-bearing rats receiving cyclophosphamide[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(23):12538. DOI:10.3390/ijms252312538 . |
| [16] | YAO Y, WANG B, YU K H, et al. Nur77 ameliorates cyclophosphamide-induced ovarian insufficiency in mice by inhibiting oxidative damage and cell senescence[J]. J Ovarian Res, 2024, 17(1):203. DOI:10.1186/s13048-024-01532-y . |
| [17] | LANDE Y, FISCH B, TSUR A, et al. Short-term exposure of human ovarian follicles to cyclophosphamide metabolites seems to promote follicular activation in vitro [J]. Reprod Biomed Online, 2017, 34(1):104-114. DOI:10.1016/j.rbmo.2016. 10.005 . |
| [18] | YUKSEL A, BILDIK G, SENBABAOGLU F, et al. The magnitude of gonadotoxicity of chemotherapy drugs on ovarian follicles and granulosa cells varies depending upon the category of the drugs and the type of granulosa cells[J]. Hum Reprod, 2015, 30(12):2926-2935. DOI:10.1093/humrep/dev256 . |
| [19] | DI EMIDIO G, D'AURORA M, PLACIDI M, et al. Pre-conceptional maternal exposure to cyclophosphamide results in modifications of DNA methylation in F1 and F2 mouse oocytes: evidence for transgenerational effects[J]. Epigenetics, 2019, 14(11):1057-1064. DOI:10.1080/15592294. 2019.1631111 . |
| [20] | PETRILLO S K, DESMEULES P, TRUONG T Q, et al. Detection of DNA damage in oocytes of small ovarian follicles following phosphoramide mustard exposures of cultured rodent ovaries in vitro [J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2011, 253(2):94-102. DOI:10.1016/j.taap.2011.03.012 . |
| [21] | AI G H, MENG M, GUO J, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells promote the repair of chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian failure by inhibiting granulosa cells apoptosis and senescence[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2023, 14(1):75. DOI:10.1186/s13287-023-03297-5 . |
| [22] | LUAN Y, EDMONDS M E, WOODRUFF T K, et al. Inhibitors of apoptosis protect the ovarian reserve from cyclophosphamide[J]. J Endocrinol, 2019, 240(2):243-256. DOI:10.1530/JOE-18-0370 . |
| [23] | NGUYEN Q N, ZERAFA N, LIEW S H, et al. Loss of PUMA protects the ovarian reserve during DNA-damaging chemotherapy and preserves fertility[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(6):618. DOI:10.1038/s41419-018-0633-7 . |
| [24] | JEELANI R, KHAN S N, SHAEIB F, et al. Cyclophosphamide and acrolein induced oxidative stress leading to deterioration of metaphase Ⅱ mouse oocyte quality[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2017, 110:11-18. DOI:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed. 2017.05.006 . |
| [25] | CHEN Y, ZHAO Y, MIAO C Y, et al. Quercetin alleviates cyclophosphamide-induced premature ovarian insufficiency in mice by reducing mitochondrial oxidative stress and pyroptosis in granulosa cells[J]. J Ovarian Res, 2022, 15(1):138. DOI:10.1186/s13048-022-01080-3 . |
| [26] | GONG L L, HOU J L, YANG H J, et al. Kuntai capsule attenuates premature ovarian insufficiency by activating the FOXO3/SIRT5 signaling pathway in mice: A comprehensive study using UHPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap and integrated pharmacology[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 322:117625. DOI:10.1016/j.jep.2023. 117625 . |
| [27] | PACELLA-INCE L, ZANDER-FOX D L, LANE M. Mitochondrial SIRT5 is present in follicular cells and is altered by reduced ovarian reserve and advanced maternal age[J]. Reprod Fertil Dev, 2014, 26(8):1072-1083. DOI:10.1071/RD13178 . |
| [28] | CASTRILLON D H, MIAO L L, KOLLIPARA R, et al. Suppression of ovarian follicle activation in mice by the transcription factor Foxo3a[J]. Science, 2003, 301(5630):215-218. DOI:10.1126/science.1086336 . |
| [29] | KUMAR S, LOMBARD D B. Functions of the sirtuin deacylase SIRT5 in normal physiology and pathobiology[J]. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol, 2018, 53(3):311-334. DOI:10.1080/10409238. 2018.1458071 . |
| [30] | WANG Y F, ZHU Y B, XING S G, et al. SIRT5 prevents cigarette smoke extract-induced apoptosis in lung epithelial cells via deacetylation of FOXO3[J]. Cell Stress Chaperones, 2015, 20(5):805-810. DOI:10.1007/s12192-015-0599-7 . |
| [1] | JIANG Juan, SONG Ning, LIAN Wenbo, SHAO Congcong, GU Wenwen, SHI Yan. Comparison of Histopathological and Molecular Pathological Phenotypes in Mouse Models of Intrauterine Adhesions Induced by Two Concentrations of Ethanol Perfusion [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 393-402. |
| [2] | LUO Lianlian, YUAN Yanchun, WANG Junling, SHI Guangsen. Advances in Mouse Models of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 290-299. |
| [3] | Jingwei MA, Gen LI, Yang YANG, Caixia ZANG, Xiuqi BAO, Dan ZHANG. Comparative Study on Different Recovery Periods of the Spermatogenic Dysfunction Mouse Model Induced by Cyclophosphamide [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 112-123. |
| [4] | Shiyan YU. Advances in the Application of Mouse Models to Study Digestive Mucosal Immunity and Infectious Diseases [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 3-10. |
| [5] | YAO Ding, ZHOU Jing, YAN Guofeng, WANG Huiyang, WANG Yadi, MA Zhengwen. Establishment of Salt-sensitive Hypertension Model in C57BL/6J Mice [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2020, 40(4): 314-. |
| [6] | CHAI Wenjun, SUN Lei, LIU Xiaoli, PAN Hongyu, GUO Tianan, XU Ye, YAN Mingxia. Establishment of Bone Metastasis Mouse Models through Injecting Human Lung Cancer Cells into Left Ventricle#br# under Ultrasound Guidance#br# [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2020, 40(3): 183-. |
| [7] | JIANG Hongli, MA Hongye, XUE Jinhong, SUN Lingshuang, CHEN Lei. The Role of Villin-1 in Model of Habu Nephritis Mice with Unilateral Nephrectomy [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2020, 40(1): 1-8. |
| [8] | HE Yi-min, GU Ming-min. Preliminary Phenotypic Analysis of Myh13 Knockout Mouse [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2019, 39(3): 193-200. |
| [9] | SHEN Yan, XU Wang-yang, ZHU Hou-bao. Research Progress on Pathogenesis of Hereditary Diseases Caused by Mutations of Oxidoreductase DHTKD1 and Related Mouse Models [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2018, 38(6): 468-472. |
| [10] | JI Lian, MA Tie, DI Zheng-hong, Liu Dong-yan. Establishment of Atopic Dermatitis Mouse Model [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2018, 38(4): 267-271. |
| [11] | GU Xiao-wen, SUN Rei-lin, FEI Jian. Construction of Afp-cre-lacZ Transgenic Mouse Model [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2017, 37(2): 89-93. |
| [12] | SONG Ying, GUO Ya-juan, HUANG Ming-qian, LIANG Jin-qiang, HUANG Zhi-ying. Effect of Different Factors on Cyclophosphamide Induced Immunosuppression Mice Model [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2017, 37(1): 36-39. |
| [13] | GU Yun-hao, CAO Chen-jie, HU Bi-yuan, WANG Jun, HAN Dong-dong, XU Ai-hua. Establishment of S180 Tumor Multidrug Resistance Mouse Model by Increasing PFC and Observation on Stability [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2015, 35(5): 367-373. |
| [14] | PENG Xiu-hua, CHEN Li-xiang, REN Xiao-nan, SHI Bi-sheng, XU Chun-hua, ZHOU Wen-jiang, ZHOU Xiao-hui. Establishment and Preliminary Evaluation of Hepatitis B Virus Transfection Mouse Model by Using Hydrodynamic Injection [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2015, 35(1): 1-5. |
| [15] | LI Hao, JI Guo-xia, WANG Ke-zhou, JI Chuan-liang, LI Lan-bo, ZHANG Yan, FENG Mo-zhu, LI Jian-mei, LIU Tao. The Influence of Colla Corii Asini on Growth and Quality of Hair in Mice Treated by Cyclophosphamide [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2015, 35(1): 17-22. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||