
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 726-737.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.119
• Invertebrate Laboratory Animal: Nematode • Previous Articles Next Articles
SONG Mengjiao( ), SHEN Yidong(
), SHEN Yidong( )(
)( )
)
Received:2025-07-16
Revised:2025-10-17
Online:2025-12-25
Published:2025-12-19
Contact:
SHEN Yidong
CLC Number:
SONG Mengjiao,SHEN Yidong. Approaches and Application Examples for Studying Mitochondrial Morphology and Function in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 726-737. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.119.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.119
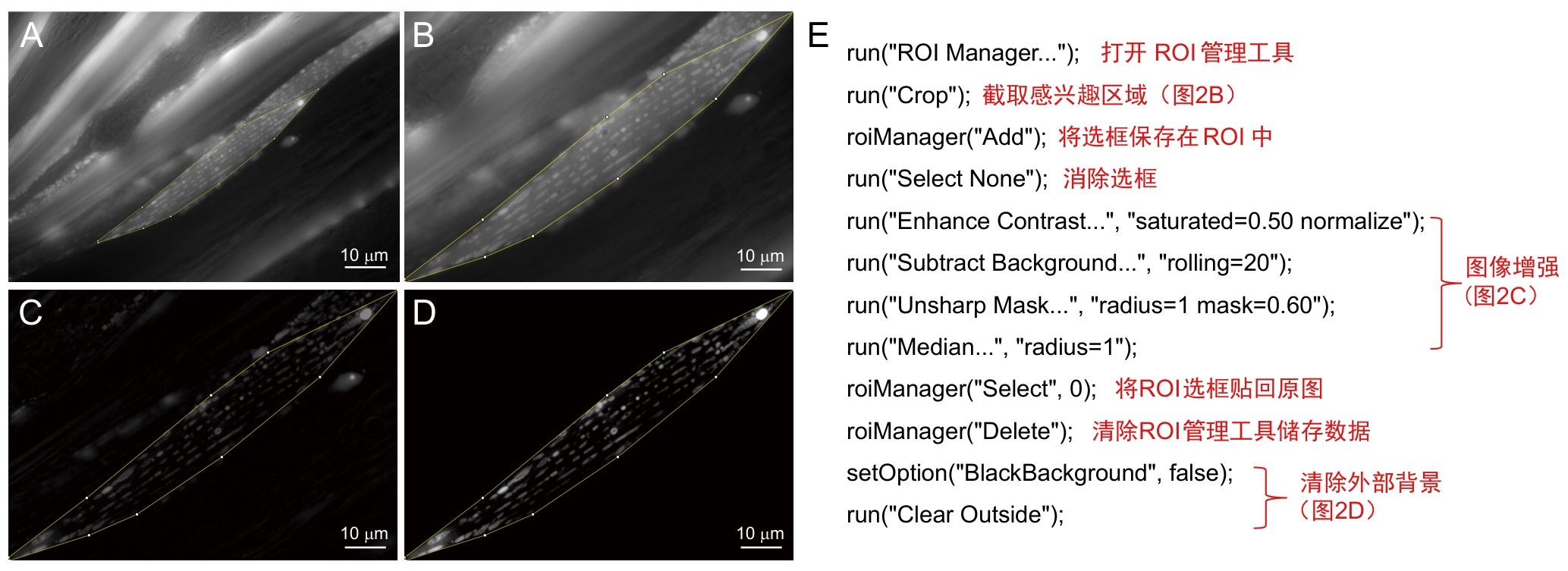
Figure 2 Preprocessing procedures and annotationsNote: A-D, Preprocessing workflow, target region of interest (ROI) is selected from original image (A), cropped (B), subjected to image enhancement (C), and followed by external background removal (D). E, Batch-processing macro for steps A-D, with its annotated script.
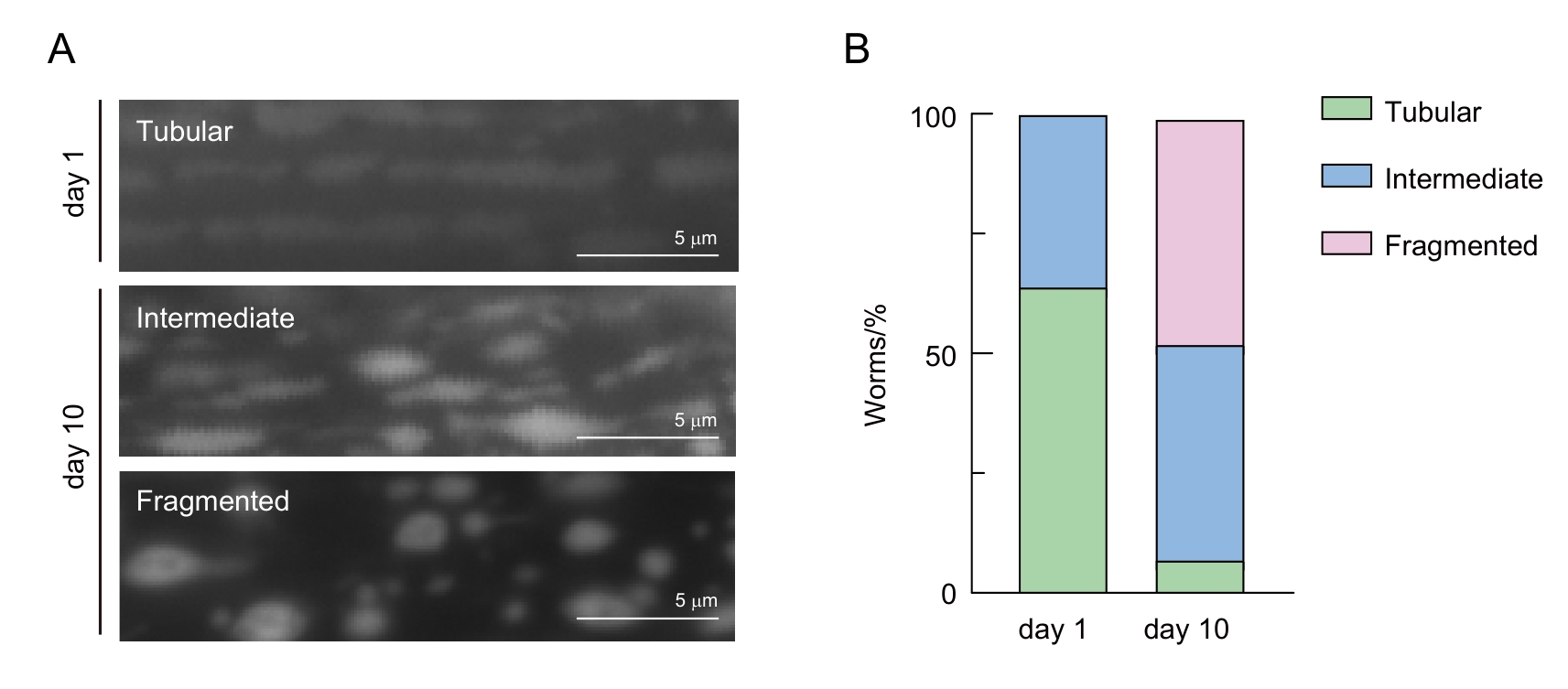
Figure 3 Classification of mitochondrial morphology in C. elegans muscle cellsNote: A, Representative images of different mitochondrial morphologies in young (day 1) and aged (day 10) C. elegans. B, Qualitative analysis of mitochondrial morphology changes with aging. Green, blue, and pink represent the percentages of C. elegans with tubular, intermediate, and fragmented mitochondria, respectively.

Figure 4 Procedures and annotations of Mitochondria Analyzer pluginNote: A-B, Plugin operation interface. C-E, Schematic of software processing workflow, the pre-processed image (C) is converted into a binarized image (D) using defined block sized and C-value parameters. The binarized image (D) is then skeletonized via the Skeletonize (2D) function to obtain the image (E) . From the binarized image (C), parameters such as mitochondrial count, area, perimeter, form factor and aspect ratio can be derived. From the skeleton image (E), data including branch number (Branches), branch lengths and branch junctions can be extracted. F, batch processing macro for steps C–E, accompanied by explanatory notes.
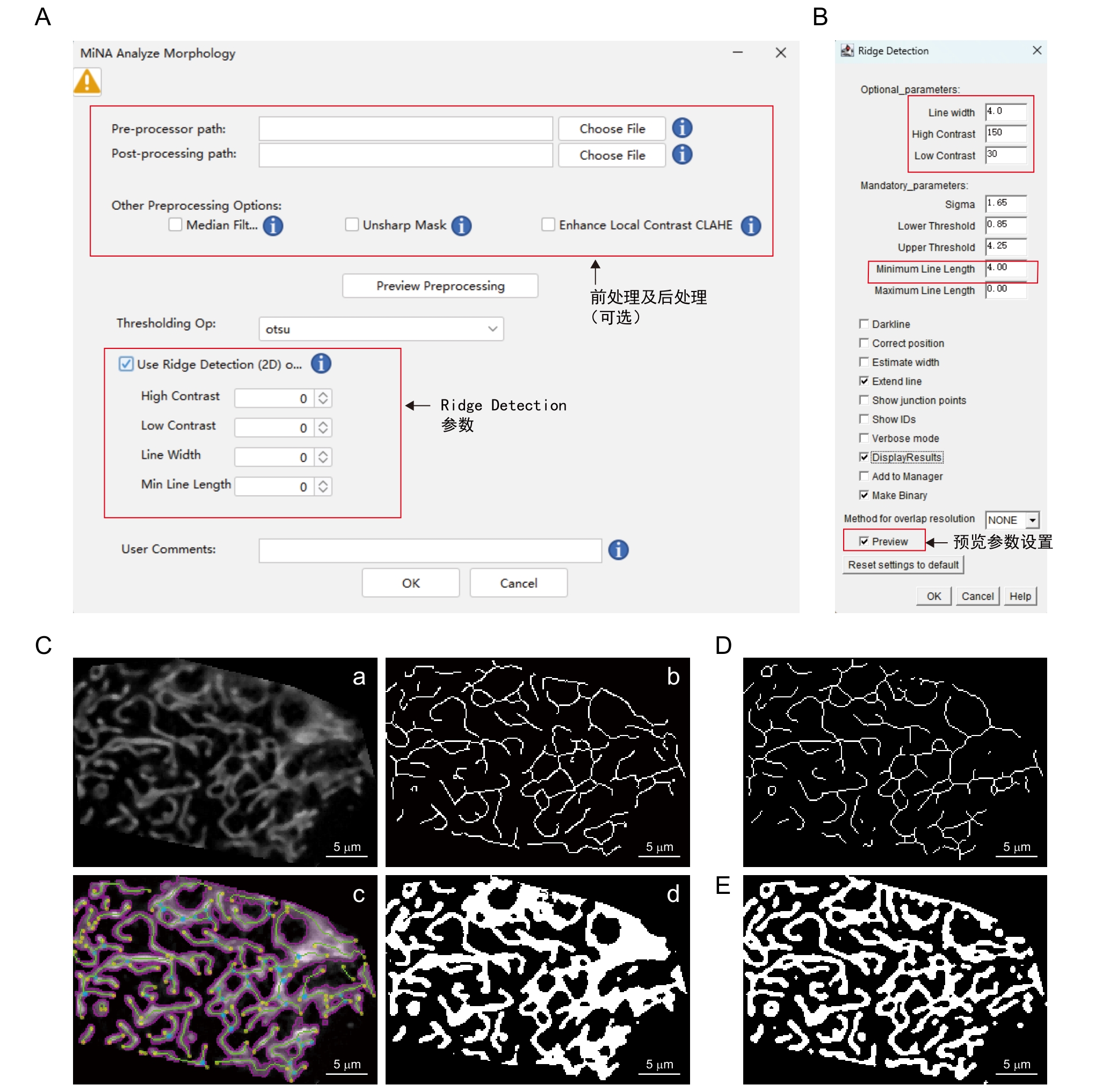
Figure 5 Procedures and annotations of MiNA - Mitochondrial Network Analysis pluginNote: A-B, Plugin operation interface. C, Schematic diagram of the software processing workflow. The pre-processed image (a) undergoes binarization via the auto thresholding method (Auto threshold-Otsu) to extract mitochondrial contours (b). Using the parameters set for Ridge Detection in (B) to obtain the skeleton image (c). Relevant parameters are calculated from both the binarized image and skeleton image, and a contour map (d) is produced. D, Skeletonize algorithm(Skeletonization). E, Mitochondria Analyzer binarization algorithm.
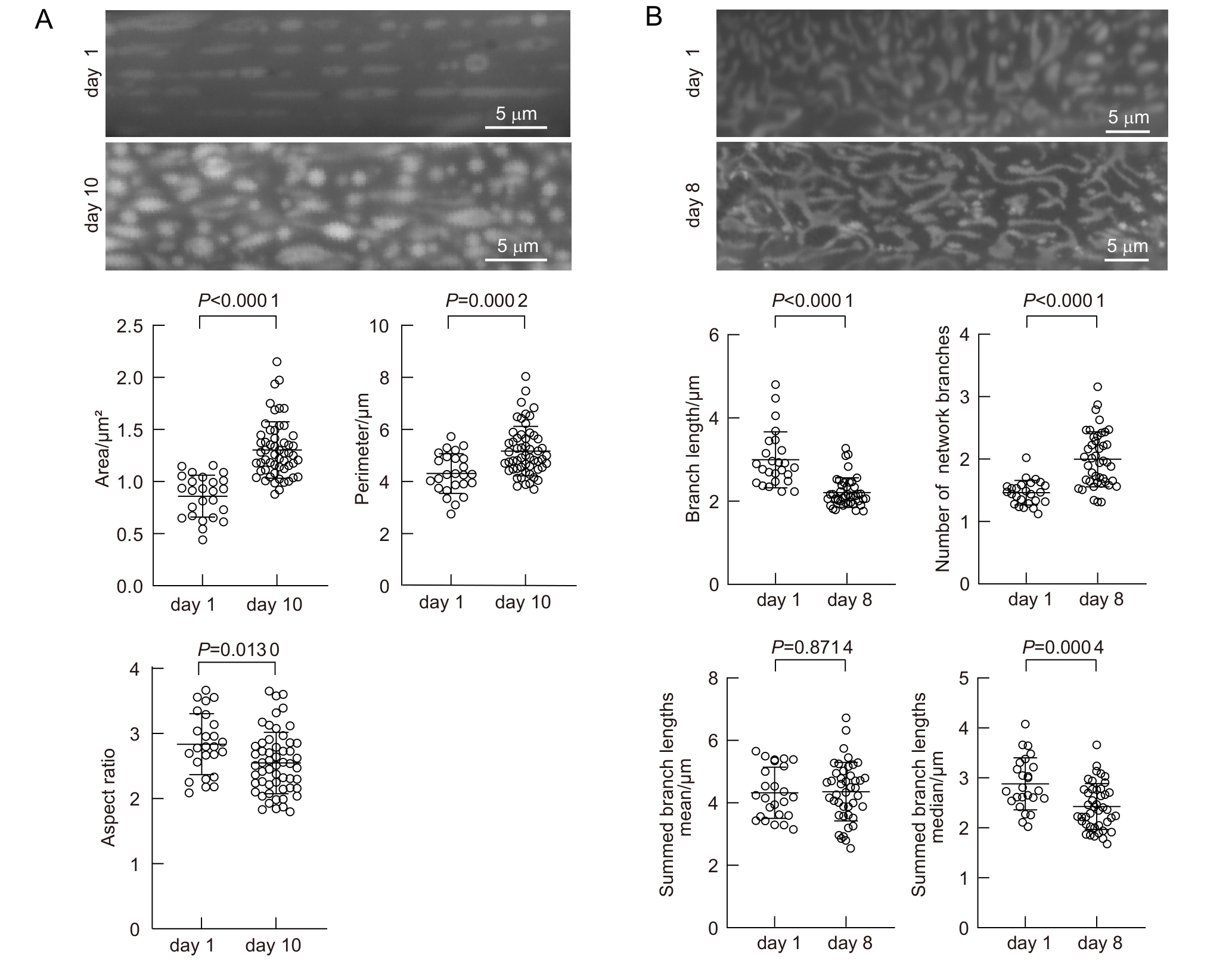
Figure 6 Age-dependent mitochondrial morphology changes in C. elegansNote: A, Average mitochondrial area, perimeter, and aspect ratio in muscle cells of young adults (day 1) and aged adults (day 10). B, Branch length, number of network branches, summed branch lengths mean and summed branch lengths median in hypodermal mitochondria of young (day 1) and aged (day 8) C. elegans. A, n=25 (day 1), n=57 (day 10); B, n=25 (day 1), n=43 (day 8).
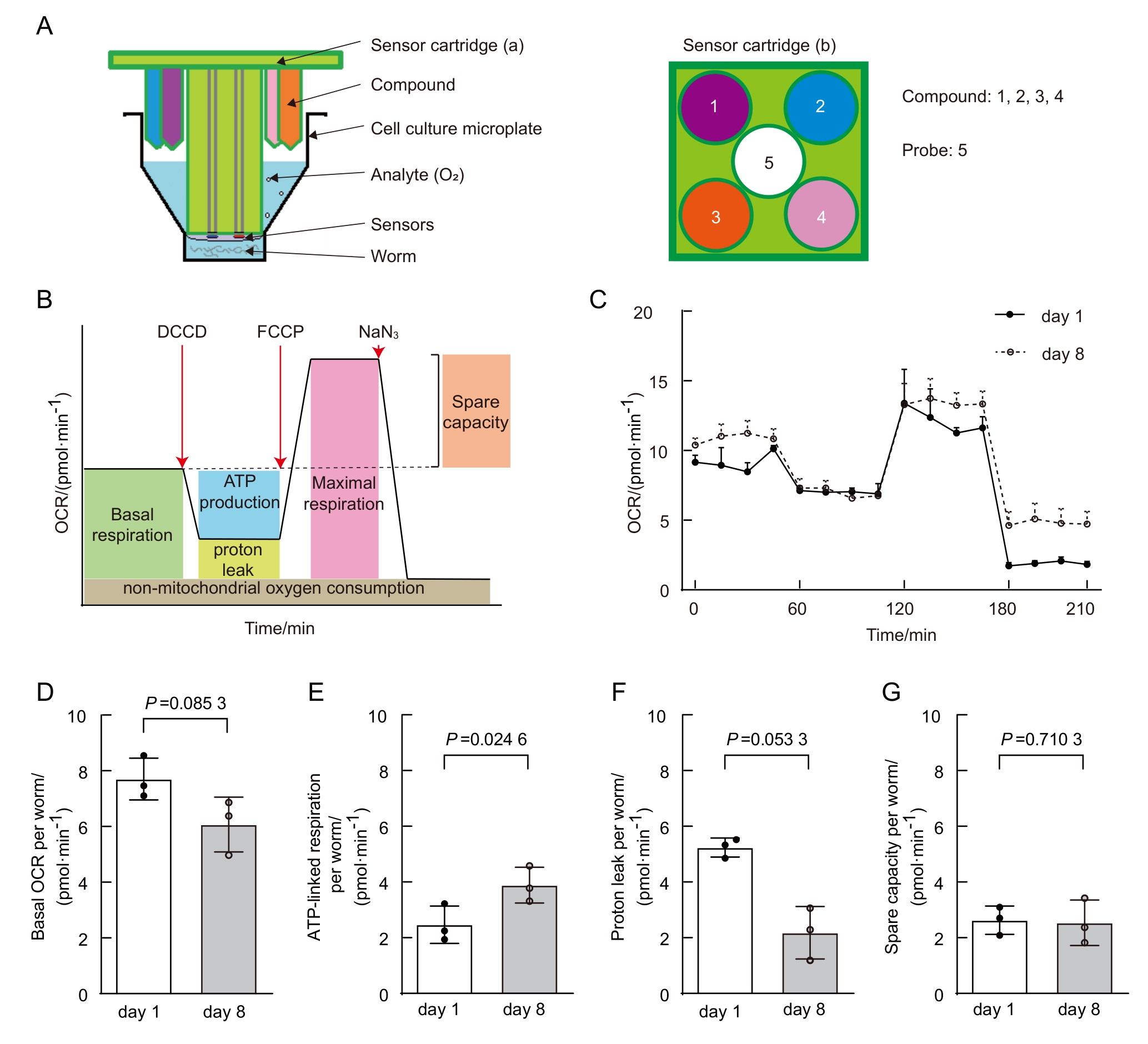
Figure 8 Age-dependent mitochondrial function changes in C.elegans (data from published paper of our lab [20])Note: A, Schematic of Seahorse analyzer plates. The analyzer plates consist of a sensor cartridge and a cell culture microplate. a and b are side-view and top-view of the sensor cartridge, with the sensor at center and the compound injection ports at the periphery of each well. Same injection port (i.e., same color port) is selected for adding same compound. Each probe contains 4 injection ports and two sensors measuring oxygen content and solution pH. B, Typical OCR curve phases. C, Comparison of OCR between young and aged C. elegans. D-G, Comparison of basal respiration (D), ATP-linked respiration (E), proton leak (F), and spare respiratory capacity (G) between young and aged C. elegans.
| [1] | MUKHERJEE I, GHOSH M, MEINECKE M. MICOS and the mitochondrial inner membrane morphology–when things get out of shape[J]. FEBS Lett, 2021, 595(8):1159-1183. DOI:10.1002/1873-3468.14089 . |
| [2] | OKAMOTO K, SHAW J M. Mitochondrial morphology and dynamics in yeast and multicellular eukaryotes[J]. Annu Rev Genet, 2005, 39:503-536. DOI:10.1146/annurev.genet.38. 072902.093019 . |
| [3] | LÓPEZ-OTÍN C, BLASCO M A, PARTRIDGE L, et al. Hallmarks of aging: an expanding universe[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(2):243-278. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2022.11.001 . |
| [4] | YAN C J, DUANMU X Y, ZENG L, et al. Mitochondrial DNA: distribution, mutations, and elimination[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(4):379. DOI:10.3390/cells8040379 . |
| [5] | KLIONSKY D J, ABDELMOHSEN K, ABE A, et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition)[J]. Autophagy, 2016, 12(1):1-222. DOI:10.1080/15548627.2015.1100356 . |
| [6] | MACK H I D, HEIMBUCHER T, MURPHY C T. The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans as a model for aging research[J]. Drug Discov Today Dis Models, 2018, 27:3-13. DOI:10.1016/j.ddmod.2018.11.001 . |
| [7] | JI T, ZHANG X L, XIN Z L, et al. Does perturbation in the mitochondrial protein folding pave the way for neurodegeneration diseases?[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2020, 57:100997. DOI:10.1016/j.arr.2019.100997 . |
| [8] | SOHRABI S, MOR D E, KALETSKY R, et al. High-throughput behavioral screen in C. elegans reveals Parkinson's disease drug candidates[J]. Commun Biol, 2021, 4(1):203. DOI:10.1038/s42003-021-01731-z . |
| [9] | YE S W, SONG S D, LIU X J, et al. A small-molecule screen identifies novel aging modulators by targeting 5-HT/DA signaling pathway[J]. Aging Cell, 2025, 24(3): 1-13. DOI:10.1111/acel.14411 . |
| [10] | PANDA M, FAKITSA M, MARKAKI M, et al. Caenorhabditis elegans as an emerging high throughput chronotherapeutic drug screening platform for human neurodegenerative disorders[J]. Adv Drug Deliv Rev, 2025, 224:115655. DOI:10.1016/j.addr.2025.115655 . |
| [11] | YOO I, AHN I, LEE J, et al. Extracellular flux assay (Seahorse assay): Diverse applications in metabolic research across biological disciplines[J]. Mol Cells, 2024, 47(8):100095. DOI:10.1016/j.mocell.2024.100095 . |
| [12] | STIERNAGLE T. Maintenance of C. elegans [J]. WormBook, 2006:1-11. DOI:10.1895/wormbook.1.101.1 . |
| [13] | MALLICK A, RANAWADE A, VAN DEN BERG W, et al. Axin-mediated regulation of lifespan and muscle health in C. elegans requires AMPK-FOXO signaling[J]. iScience, 2020, 23(12):101843. DOI:10.1016/j.isci.2020.101843 . |
| [14] | REGMI S G, ROLLAND S G, CONRADT B. Age-dependent changes in mitochondrial morphology and volume are not predictors of lifespan[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2014, 6(2):118-30. DOI: 10.18632/aging.100639 . |
| [15] | XIA Q, LI P L, CASAS-MARTINEZ J C, et al. Peroxiredoxin 2 regulates DAF-16/FOXO mediated mitochondrial remodelling in response to exercise that is disrupted in ageing[J]. Mol Metab, 2024, 88:102003. DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2024.102003 . |
| [16] | CHAUDHRY A, SHI R, LUCIANI D S. A pipeline for multidimensional confocal analysis of mitochondrial morphology, function, and dynamics in pancreatic β-cells[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2020, 318(2):E87-E101. DOI:10.1152/ajpendo.00457.2019 . |
| [17] | Mitochondria Analyzer[Z/OL]. [2025-07-16]. . |
| [18] | VALENTE A J, MADDALENA L A, ROBB E L, et al. A simple ImageJ macro tool for analyzing mitochondrial network morphology in mammalian cell culture[J]. Acta Histochem, 2017, 119(3):315-326. DOI:10.1016/j.acthis.2017.03.001 . |
| [19] | MiNA - Mitochondrial Network Analysis[Z/OL]. [2025-07-16]. . |
| [20] | NG L F, GRUBER J. Measurement of respiration rate in live Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Bio Protoc, 2019, 9(10):1-12. DOI:10.21769/BioProtoc.3243 . |
| [21] | HAROON S, VERMULST M. Oxygen consumption measurements in Caenorhabditis elegans using the seahorse XF24[J]. Bio Protoc, 2019, 9(13):e3288. DOI:10.21769/BioProtoc.3288 . |
| [22] | SONG M J, DONG S M, ZHANG X F, et al. A moderate static magnetic field promotes C. elegans longevity through cytochrome P450s[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12:16108. DOI:10.1038/s41598-022-20647-0 . |
| [23] | DILLIN A, HSU A L, ARANTES-OLIVEIRA N, et al. Rates of behavior and aging specified by mitochondrial function during development[J]. Science, 2002, 298(5602):2398-2401. DOI: 10.1126/science/1077780 . |
| [24] | AMORIM J A, COPPOTELLI G, ROLO A P, et al. Mitochondrial and metabolic dysfunction in ageing and age-related diseases[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2022, 18(4):243-258. DOI:10.1038/s41574-021-00626-7 . |
| [25] | SUN N, YOULE R J, FINKEL T. The mitochondrial basis of aging[J]. Mol Cell, 2016, 61(5):654-666. DOI:10.1016/j.molcel.2016.01.028 . |
| [26] | BAR-ZIV R, BOLAS T, DILLIN A. Systemic effects of mitochondrial stress[J]. EMBO Rep, 2020, 21(6):e50094. DOI:10.15252/embr.202050094 . |
| [27] | REGMI S G, ROLLAND S G, CONRADT B. Age-dependent changes in mitochondrial morphology and volume are not predictors of lifespan[J]. Aging, 2014, 6(2):118-130. DOI:10.18632/aging.100639 . |
| [28] | SON H G, ALTINTAS O, KIM E J E, et al. Age-dependent changes and biomarkers of aging in Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Aging Cell, 2019, 18(2):e12853. DOI:10.1111/acel.12853 . |
| [29] | MAGLIONI S, MELLO D F, SCHIAVI A, et al. Mitochondrial bioenergetic changes during development as an indicator of C. elegans health-span[J]. Aging, 2019, 11(16):6535-6554. DOI:10.18632/aging.102208 . |
| [30] | MITRA K, WUNDER C, ROYSAM B, et al. A hyperfused mitochondrial state achieved at G1–S regulates cyclin E buildup and entry into S phase[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2009, 106(29):11960-11965. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0904875106 . |
| [31] | DAGDA R K, CHERRA S J, KULICH S M, et al. Loss of PINK1 function promotes mitophagy through effects on oxidative stress and mitochondrial fission[J]. J Biol Chem, 2009, 284(20):13843-13855. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M808515200 . |
| [1] | SUN Han, GUO Peng, YU Xinhe, ZHANG Junqiao, YAO Ying, YANG Wen. Progress in Caenorhabditis elegans as a Degenerative Disease Model for Molecular Pathways Studying [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 738-751. |
| [2] | Hui CHENG, Fei FANG, Jiahao SHI, Hua YANG, Mengjie ZHANG, Ping YANG, Jian FEI. H1 Linker Histone Gene Regulates Lifespan via Dietary Restriction Pathways in Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 271-281. |
| [3] | Han LI, Xiaorui ZHANG, Chengfang ZHANG. Mechanism of Intermittent Fasting in Improving Olanzapine-induced Metabolic Disorders in Mice [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 3-10. |
| [4] | Li Ying-niang, Dai Wei, Sheng Jian. Analysis of Goiter in Zebrafish [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2019, 39(6): 462-466. |
| [5] | PU Xiang-qiang, WANG Xiang, QIANG Guang-hui, MA Jin, DING Yue-yue, LV Hai-tao. The Dynamic Changes of Mitochondria in Endothelial Cells of Immunological Coronaritis in Mice [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2018, 38(3): 169-175. |
| [6] | CHANG Kai, WANG Yu, PANG Wen-biao, GAO Ji-ping, CHEN Zhao-yang, SONG Guo-hua. Antagonistic Effect of Selenium on Change of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential of NRK-52E Cells Induced by Sodium Fluoride [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2017, 37(3): 179-184. |
| [7] | LI Yuan, ZHANG Mei-ying. Research Progress on Autophagy with Parkinson Disease and Related Models [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2015, 35(4): 335-340. |
| [8] | SHEN Xing-jiao, YUE Bing-fei, MA Li-ying. Analysis of the Polymorphism of Mitochondrial DNA Control Region in Three Closed Colonies of Rabbits [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2014, 34(1): 29-34. |
| [9] | GAO Jun, NI Li-ju, SUN Feng-ping, WANG Jin-xiang, HU Jian-hua, GAO Cheng, LI Kai, XIAO Jun-hua, ZHOU Yu-xun. Sequence Analysis on Complete Mitochondrial Genome and Phylogeny of Microtus fortis fortis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2013, 33(3): 167-173. |
| [10] | ZHANG Ping-hu, TAO Yuan-qing, JIANG Zhen-zhou, WANG Zhong-dong, FAN Wei, ZHANG Lu-yong. Feasibility Analysis of Himalayana Marmot as an Alternative Model of Drug Mitochondrial Toxicity Evaluation [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2012, 32(5): 436-440. |
| [11] | GUAN Min-qiang1,CAO Qiong-jie2,CHEN Zhong-yi2,RUAN Dong-fen2,Lou Zhe-feng2,JIN Long-jin2. Analysis of Genetic Stability of on Closed Colony Mice by mtDNA Sequence [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2009, 29(2): 113-116. |
| [12] | Xie Jian-yun1’2,Feng Jie1,Bai Xiong3, Hu Jian-hua1,Gao Cheng1 . Study on Sequence Variation of Mitochondrial D-loop Gene and Polymorphism among four populations of Reed Vole (Microtus fords) [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2008, 28(5): 299-303. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||