
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 186-193.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.136
• Animal Models of Human Diseases • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chenghan MEI( ), Beibei CHEN(
), Beibei CHEN( )(
)( )
)
Received:2022-08-30
Revised:2022-12-09
Online:2023-04-25
Published:2023-04-25
Contact:
Beibei CHEN
CLC Number:
Chenghan MEI,Beibei CHEN. Research Progress on Neuroprotective Effects and Mechanisms of Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Analogues in Alzheimer's Disease[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 186-193. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.136.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.136
药物 Drug | 动物 Animal | 给药前月龄或体质量 Age or body mass before dosing | 给药方式及剂量 Dosage and Administration | 给药周期 Dosing intervals | 行为学实验 Behavioural experiments | 结论 Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
利拉鲁肽 Liraglutide[ | APP/PS1小鼠(♂) | 14月龄 | ip,25 nmol/kg体质量 | qd,连续2月 | 新物体识别、水迷宫 | 逆转记忆损害 |
利拉鲁肽 Liraglutide[ | 5xFAD小鼠(♂) | 4月龄 | ih,25 nmol/kg体质量 | qd,连续2月 | 水迷宫 | 改善认知 |
| GLP-1/GIP/Gcg triagonist[ | 3xTg-AD小鼠(♂/♀) | 7月龄 | ip,10 nmol/kg体质量 | qd,连续30 d | 旷场、Y迷宫、水迷宫 | 改善长期空间记忆和工作记忆 |
| GLP-1/GIP dual agonist DA5-CH[ | APP/PS1小鼠(♂/♀) | 9月龄 | ip,10 nmol/kg体质量 | qd,连续28 d | 旷场、Y迷宫、水迷宫 | 改善工作记忆和长期空间记忆 |
利拉鲁肽 Liraglutide[ | Swiss小鼠(脑室内注射Aβ寡聚物,♂) | 3月龄 | ip,25 nmol/kg体质量 | qd,连续7 d | 新物体识别、对象位置记忆模型 | 可逆转Aβ寡聚物引起的记忆障碍 |
艾塞那肽Exendin-4[ | SD大鼠(海马内微量注射Aβ1–42,♂) | 220~260 g | 海马内微量注射, 0.2 nmol(1 µL) | 单次 | 水迷宫 | 显著拮抗Aβ片段引起的空间学习和记忆能力损害 |
GLP-1/GIP dual agonist DA4-JC[ | 3xTg-AD小鼠(♂/♀) | 8月龄 | ip,10 nmol/kg体质量 | qd,连续46 d | 旷场、新物体识别、Y迷宫、水迷宫 | 改善认知 |
Table 1 Applications of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) analogues in Alzheimer's disease (AD) animal model
药物 Drug | 动物 Animal | 给药前月龄或体质量 Age or body mass before dosing | 给药方式及剂量 Dosage and Administration | 给药周期 Dosing intervals | 行为学实验 Behavioural experiments | 结论 Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
利拉鲁肽 Liraglutide[ | APP/PS1小鼠(♂) | 14月龄 | ip,25 nmol/kg体质量 | qd,连续2月 | 新物体识别、水迷宫 | 逆转记忆损害 |
利拉鲁肽 Liraglutide[ | 5xFAD小鼠(♂) | 4月龄 | ih,25 nmol/kg体质量 | qd,连续2月 | 水迷宫 | 改善认知 |
| GLP-1/GIP/Gcg triagonist[ | 3xTg-AD小鼠(♂/♀) | 7月龄 | ip,10 nmol/kg体质量 | qd,连续30 d | 旷场、Y迷宫、水迷宫 | 改善长期空间记忆和工作记忆 |
| GLP-1/GIP dual agonist DA5-CH[ | APP/PS1小鼠(♂/♀) | 9月龄 | ip,10 nmol/kg体质量 | qd,连续28 d | 旷场、Y迷宫、水迷宫 | 改善工作记忆和长期空间记忆 |
利拉鲁肽 Liraglutide[ | Swiss小鼠(脑室内注射Aβ寡聚物,♂) | 3月龄 | ip,25 nmol/kg体质量 | qd,连续7 d | 新物体识别、对象位置记忆模型 | 可逆转Aβ寡聚物引起的记忆障碍 |
艾塞那肽Exendin-4[ | SD大鼠(海马内微量注射Aβ1–42,♂) | 220~260 g | 海马内微量注射, 0.2 nmol(1 µL) | 单次 | 水迷宫 | 显著拮抗Aβ片段引起的空间学习和记忆能力损害 |
GLP-1/GIP dual agonist DA4-JC[ | 3xTg-AD小鼠(♂/♀) | 8月龄 | ip,10 nmol/kg体质量 | qd,连续46 d | 旷场、新物体识别、Y迷宫、水迷宫 | 改善认知 |
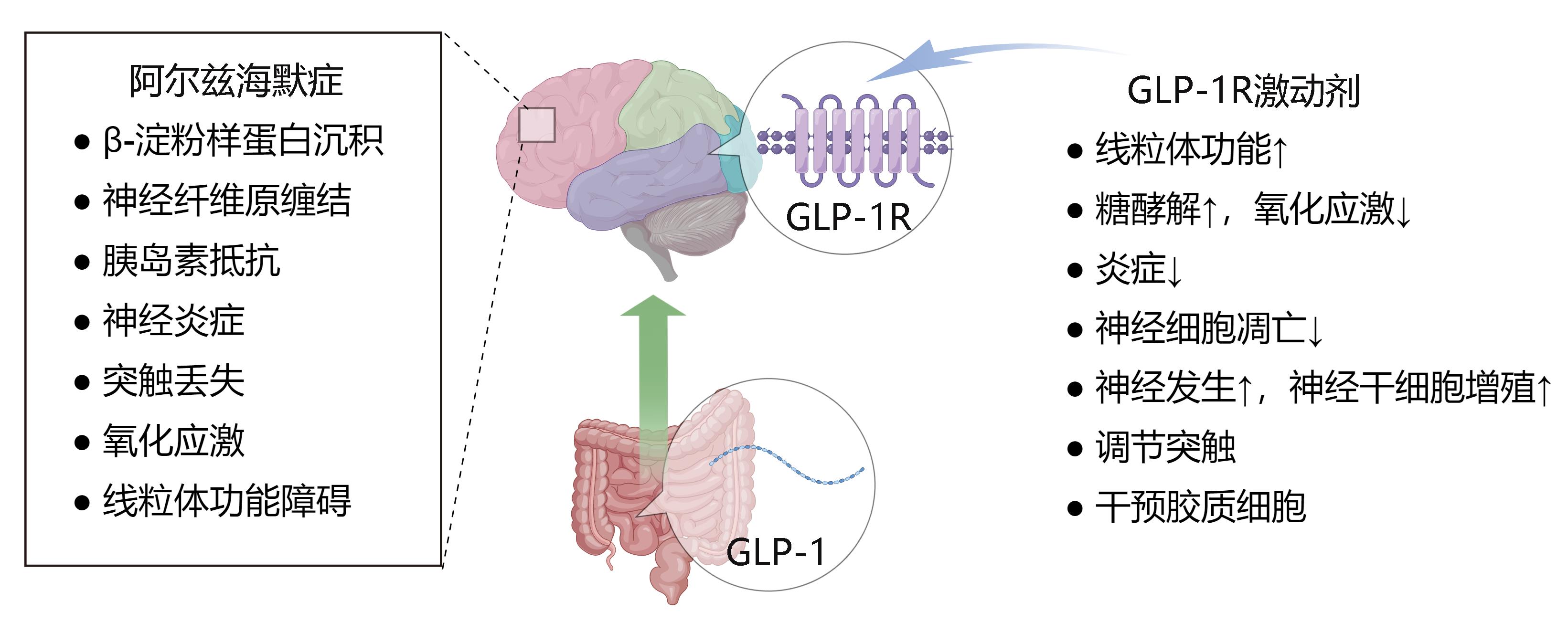
Figure 1 Schematic representation of neuroprotective effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) in Alzheimer's disease (AD)Note:GLP-1,glucagon-like peptide 1; AD, Alzheimer's disease; this figure is drawn by Figdraw soft.
| 1 | ARNOLD S E, ARVANITAKIS Z, MACAULEY-RAMBACH S L, et al. Brain insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer disease: concepts and conundrums[J]. Nat Rev Neurol, 2018, 14(3):168-181. DOI:10.1038/nrneurol.2017.185 . |
| 2 | BUTTERFIELD D A, HALLIWELL B. Oxidative stress, dysfunctional glucose metabolism and Alzheimer disease[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2019, 20(3):148-160. DOI:10.1038/s41583-019-0132-6 . |
| 3 | MCCLEAN P L, HÖLSCHER C. Liraglutide can reverse memory impairment, synaptic loss and reduce plaque load in aged APP/PS1 mice, a model of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2014, 76(Pt A):57-67. DOI:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.08.005 . |
| 4 | ZHENG J P, XIE Y Z, REN L J, et al. GLP-1 improves the supportive ability of astrocytes to neurons by promoting aerobic glycolysis in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Mol Metab, 2021, 47:101180. DOI:10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101180 . |
| 5 | LI T, JIAO J J, HÖLSCHER C, et al. A novel GLP-1/GIP/Gcg triagonist reduces cognitive deficits and pathology in the 3xTg mouse model of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Hippocampus, 2018, 28(5):358-372. DOI:10.1002/hipo.22837 . |
| 6 | CAO Y, HÖLSCHER C, HU M M, et al. DA5-CH, a novel GLP-1/GIP dual agonist, effectively ameliorates the cognitive impairments and pathology in the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2018, 827:215-226. DOI:10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.03.024 . |
| 7 | BATISTA A F, FORNY-GERMANO L, CLARKE J R, et al. The diabetes drug liraglutide reverses cognitive impairment in mice and attenuates insulin receptor and synaptic pathology in a non-human primate model of Alzheimer's disease[J]. J Pathol, 2018, 245(1):85-100. DOI:10.1002/path.5056 . |
| 8 | WANG X H, WANG L, JIANG R R, et al. Exendin-4 antagonizes Aβ1-42-induced attenuation of spatial learning and memory ability[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2016, 12(5):2885-2892. DOI:10.3892/etm.2016.3742 . |
| 9 | CAI H Y, YANG D, QIAO J, et al. A GLP-1/GIP dual receptor agonist DA4-JC effectively attenuates cognitive impairment and pathology in the APP/PS1/tau model of Alzheimer's disease[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2021, 83(2):799-818. DOI:10.3233/JAD-210256 . |
| 10 | HÖLSCHER C. Potential role of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in neuroprotection[J]. CNS Drugs, 2012, 26(10):871-882. DOI:10.2165/11635890-000000000-00000 . |
| 11 | GRIECO M, GIORGI A, GENTILE M C, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1: a focus on neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Front Neurosci, 2019, 13:1112. DOI:10.3389/fnins.2019.01112 . |
| 12 | HOLST J J. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1[J]. Physiol Rev, 2007, 87(4):1409-1439. DOI:10.1152/physrev. 00034.2006 . |
| 13 | ANDERSEN A, LUND A, KNOP F K, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 in health and disease[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2018, 14(7):390-403. DOI:10.1038/s41574-018-0016-2 . |
| 14 | DOYLE M E, EGAN J M. Mechanisms of action of glucagon-like peptide 1 in the pancreas[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2007, 113(3):546-593. DOI:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2006.11.007 . |
| 15 | CALSOLARO V, EDISON P. Novel GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) analogues and insulin in the treatment for Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases[J]. CNS Drugs, 2015, 29(12):1023-1039. DOI:10.1007/s40263-015-0301-8 . |
| 16 | YILDIRIM SIMSIR I, SOYALTIN U E, CETINKALP S. Glucagon like peptide-1 (GLP-1) likes Alzheimer's disease[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr, 2018, 12(3):469-475. DOI:10.1016/j.dsx.2018. 03.002 . |
| 17 | MÜLLER T D, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1)[J]. Mol Metab, 2019, 30:72-130. DOI:10.1016/j.molmet.2019.09.010 . |
| 18 | ATHAUDA D, FOLTYNIE T. The glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP) receptor as a therapeutic target in Parkinson's disease: mechanisms of action[J]. Drug Discov Today, 2016, 21(5):802-818. DOI:10.1016/j.drudis.2016.01.013 . |
| 19 | BULGART H R, NECZYPOR E W, WOLD L E, et al. Microbial involvement in Alzheimer disease development and progression[J]. Mol Neurodegener, 2020, 15(1):42. DOI:10.1186/s13024-020-00378-4 . |
| 20 | MINTUN M A, LO A C, DUGGAN EVANS C, et al. Donanemab in early Alzheimer's disease[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 384(18):1691-1704. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa2100708 . |
| 21 | LONG J M, HOLTZMAN D M. Alzheimer disease: an update on pathobiology and treatment strategies[J]. Cell, 2019, 179(2):312-339. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2019.09.001 . |
| 22 | CASADESUS G, PUIG E R, WEBBER K M, et al. Targeting gonadotropins: an alternative option for Alzheimer disease treatment[J]. J Biomed Biotechnol, 2006, 2006(3):39508. DOI:10.1155/JBB/2006/39508 . |
| 23 | HAASS C, KAETHER C, THINAKARAN G, et al. Trafficking and proteolytic processing of APP[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 2012, 2(5): a006270. DOI:10.1101/cshperspect.a006270 . |
| 24 | PERRY T A, GREIG N H. A new Alzheimer's disease interventive strategy: GLP-1[J]. Curr Drug Targets, 2004, 5(6):565-571. DOI:10.2174/1389450043345245 . |
| 25 | CRARY J F, TROJANOWSKI J Q, SCHNEIDER J A, et al. Primary age-related tauopathy (PART): a common pathology associated with human aging[J]. Acta Neuropathol, 2014, 128(6):755-766. DOI:10.1007/s00401-014-1349-0 . |
| 26 | SHI Y, HOLTZMAN D M. Interplay between innate immunity and Alzheimer disease: APOE and TREM2 in the spotlight[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2018, 18(12):759-772. DOI:10.1038/s41577-018-0051-1 . |
| 27 | GALE S C, GAO L, MIKACENIC C, et al. APOε4 is associated with enhanced in vivo innate immune responses in human subjects[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2014, 134(1): 127-34. DOI:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.01.032 . |
| 28 | MITTAL K, KATARE D P. Shared links between type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer's disease: a review[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev, 2016, 10(2): S144-S149. DOI:10.1016/j.dsx.2016.01.021 . |
| 29 | BARBAGALLO M, DOMINGUEZ L J. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer's disease[J]. World J Diabetes, 2014,5(6):889-893. DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i6.889 . |
| 30 | KELLAR D, CRAFT S. Brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer's disease and related disorders: mechanisms and therapeutic approaches[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2020, 19(9):758-766. DOI:10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30231-3 . |
| 31 | ARNOLD S E, ARVANITAKIS Z, MACAULEY-RAMBACH S L, et al. Brain insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer disease: concepts and conundrums[J]. Nat Rev Neurol, 2018, 14(3):168-181. DOI:10.1038/nrneurol.2017.185 . |
| 32 | LAWS S M, GASKIN S, WOODFIELD A, et al. Insulin resistance is associated with reductions in specific cognitive domains and increases in CSF tau in cognitively normal adults[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1):9766. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-09577-4 . |
| 33 | BIUNDO F, DEL PRETE D, ZHANG H, et al. A role for tau in learning, memory and synaptic plasticity[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1):3184. DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-21596-3 . |
| 34 | FORNER S, BAGLIETTO-VARGAS D, MARTINI A C, et al. Synaptic impairment in Alzheimer's disease: a dysregulated symphony[J]. Trends Neurosci, 2017, 40(6):347-357. DOI:10.1016/j.tins.2017.04.002 . |
| 35 | MUSTAPIC M, TRAN J, CRAFT S, et al. Extracellular vesicle biomarkers track cognitive changes following intranasal insulin in Alzheimer's disease[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2019, 69(2):489-498. DOI:10.3233/JAD-180578 . |
| 36 | TALBOT K. Brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer's disease and its potential treatment with GLP-1 analogs[J]. Neurodegener Dis Manag, 2014, 4(1): 31-40. DOI:10.2217/nmt. 13.73 . |
| 37 | MCCLEAN P L, PARTHSARATHY V, FAIVRE E, et al. The diabetes drug liraglutide prevents degenerative processes in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease[J]. J Neurosci, 2011, 31(17):6587-6594. DOI:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0529-11.2011 . |
| 38 | XIE Y Z, ZHENG J P, LI S Q, et al. GLP-1 improves the neuronal supportive ability of astrocytes in Alzheimer's disease by regulating mitochondrial dysfunction via the cAMP/PKA pathway[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2021, 188:114578. DOI:10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114578 . |
| 39 | HÖLSCHER C. Insulin signaling impairment in the brain as a risk factor in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2019, 11:88. DOI:10.3389/fnagi.2019.00088 . |
| 40 | CHEN S, YIN L, XU Z, et al. Inhibiting receptor for advanced glycation end product (AGE) and oxidative stress involved in the protective effect mediated by glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor on AGE induced neuronal apoptosis[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2016, 612:193-198. DOI:10.1016/j.neulet.2015.12.007 . |
| 41 | DAY S M, YANG W Z, WANG X, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 cleavage product improves cognitive function in a mouse model of down syndrome[J]. eNeuro, 2019, 6(2): ENEURO. 0031-ENEURO.0019.2019. DOI:10.1523/ENEURO.0031-19.2019 . |
| 42 | OZBEN T, OZBEN S. Neuro-inflammation and anti-inflammatory treatment options for Alzheimer's disease[J]. Clin Biochem, 2019, 72:87-89. DOI:10.1016/j.clinbiochem. 2019. 04.001 . |
| 43 | LIU X Y, ZHANG N, ZHANG S X, et al. Potential new therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease: Glucagon-like peptide-1[J]. Eur J Neurosci, 2021, 54(10):7749-7769. DOI:10.1111/ejn.15502 . |
| 44 | ROWLANDS J, HENG J L, NEWSHOLME P, et al. Pleiotropic effects of GLP-1 and analogs on cell signaling, metabolism, and function[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2018, 9:672. DOI:10.3389/fendo.2018.00672 . |
| [1] | LIU Liyu, JI Bo, LIU Xiaoxuan, FANG Yang, ZHANG Ling, GUO Tingting, QUAN Ye, LI Hewen, LIU Yitian. Exploration of Rat Fetal Lung Tissue Fixation Methods [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 432-438. |
| [2] | LIU Ziqi, LI Yunying, LI Qin, LI Yuanhan, HE Fangyan, WEN Weibo. Research Progress on Animal Models of Gastric Ulcer of Spleen-Stomach Deficiency Cold Type [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, (): 1-12. |
| [3] | TAN Dengxu, MA Yifan, LIU Ke, ZHANG Yanying, SHI Changhong. Reshaping Intercellular Interactions: Empowering the Exploration of Disease Mechanisms and Therapies Using Organoid Co-Culture Models [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 309-317. |
| [4] | TONG Xiyang, QUE Changtian, ZHANG Feng, ZHAO Lu, WANG Hongping. Analysis of Common Causes of Out-of-Specification Results in the Test for Depressor Substances [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 331-339. |
| [5] | LUO Lianlian, YUAN Yanchun, WANG Junling, SHI Guangsen. Advances in Mouse Models of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 290-299. |
| [6] | XIAO Linlin, YANG Yixuan, LI Shanshan, LUO Lanshiyu, YIN Siwei, SUN Juming, SHI Wei, OUYANG Yiqiang, LI Xiyi. Establishment of a Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease by Introducing Human Triple Mutant APP Gene into Hippocampus via Brain Stereotactic Technology [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 269-278. |
| [7] | SHEN Huangyi, HUANG Yufei, YANG Yunpeng. Research Progress on Characteristics Analysis of Gut Microbiota and Its Sex Differences in Laboratory Animals [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 349-359. |
| [8] | CHEN Yuhan, CHEN Jinling, LI Xin, OU Yanhua, WANG Si, CHEN Jingyi, WANG Xingyi, YUAN Jiali, DUAN Yuanyuan, YANG Zhongshan, NIU Haitao. Analysis of Animal Models of Myasthenia Gravis Based on Its Clinical Characteristics in Chinese and Western Medicine [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 176-186. |
| [9] | LUO Shixiong, ZHANG Sai, CHEN Hui. Research Progress in Establishment and Evaluation of Common Asthma Animal Models [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 167-175. |
| [10] | WANG Biying, LU Jiashuo, ZAN Guiying, CHEN Ruosong, CHAI Jingrui, LIU Jinggen, WANG Yujun. Establishment Methods and Application Progress of Rodent Models for Drug Addiction [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 158-166. |
| [11] | XIAO Wenxian, LÜ Longbao. Research Progress on Human Ovarian Aging Using Non-Human Primates as Laboratory Animals [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 47-54. |
| [12] | LIU Rongle, CHENG Hao, SHANG Fusheng, CHANG Shufu, XU Ping. Study on Cardiac Aging Phenotypes of SHJH hr Mice [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 13-20. |
| [13] | LIU Yishu, CAI Liping. Advances and Challenges of Using Experimental Pigs in Da Vinci Surgical Robot Training [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 667-674. |
| [14] | YANG Jiahao, DING Chunlei, QIAN Fenghua, SUN Qi, JIANG Xusheng, CHEN Wen, SHEN Mengwen. Research Progress on Animal Models of Sepsis-Related Organ Injury [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 636-644. |
| [15] | ZHAO Xiaona, WANG Peng, YE Maoqing, QU Xinkai. Establishment of a New Hyperglycemic Obesity Cardiac Dysfunction Mouse Model with Triacsin C [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 605-612. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||