
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 705-718.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.106
• Invertebrate Laboratory Animal: Fruit fly • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Hanyue1( ), CHEN Jiawei1, GAO Xiangbin1, LUO Wei1,2(
), CHEN Jiawei1, GAO Xiangbin1, LUO Wei1,2( ), LIU Suning1,2(
), LIU Suning1,2( )
)
Received:2025-07-02
Revised:2025-08-19
Online:2025-12-25
Published:2025-12-19
Contact:
LUO Wei, LIU Suning
CLC Number:
WANG Hanyue,CHEN Jiawei,GAO Xiangbin,et al. Research Overview on Corpora Cardiaca Function of Drosophila melanogaster[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 705-718. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.106.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.106
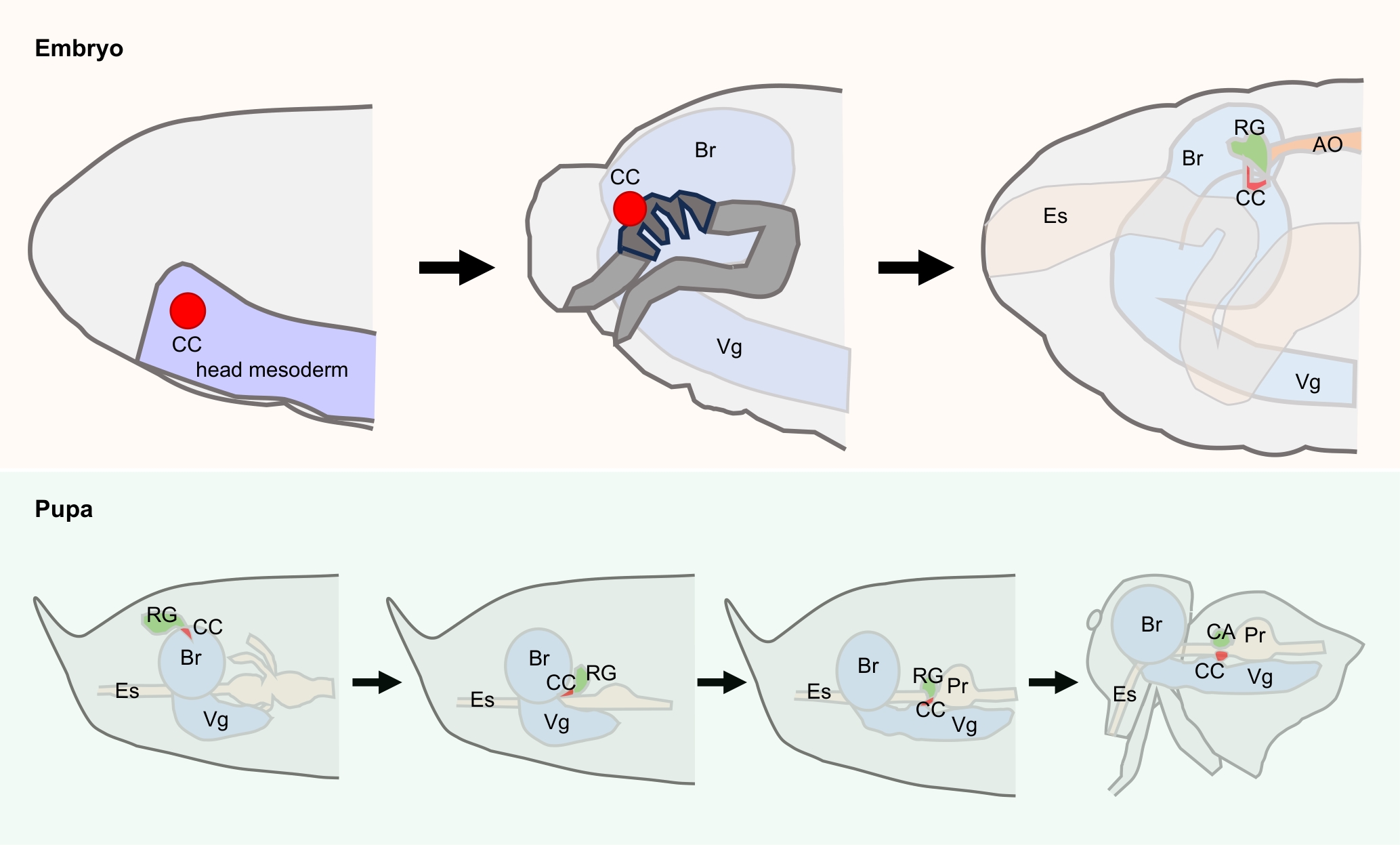
Figure 1 Development process of corpora cardiaca in Drosophila melanogaster during embryonic and pupal stagesNote: CC, corpus cardiacum; CA, corpus allatum; RG, ring gland; AO, aorta; Br, brain; Es, esophagus; Pr, proventriculus; Vg, ventral ganglion.
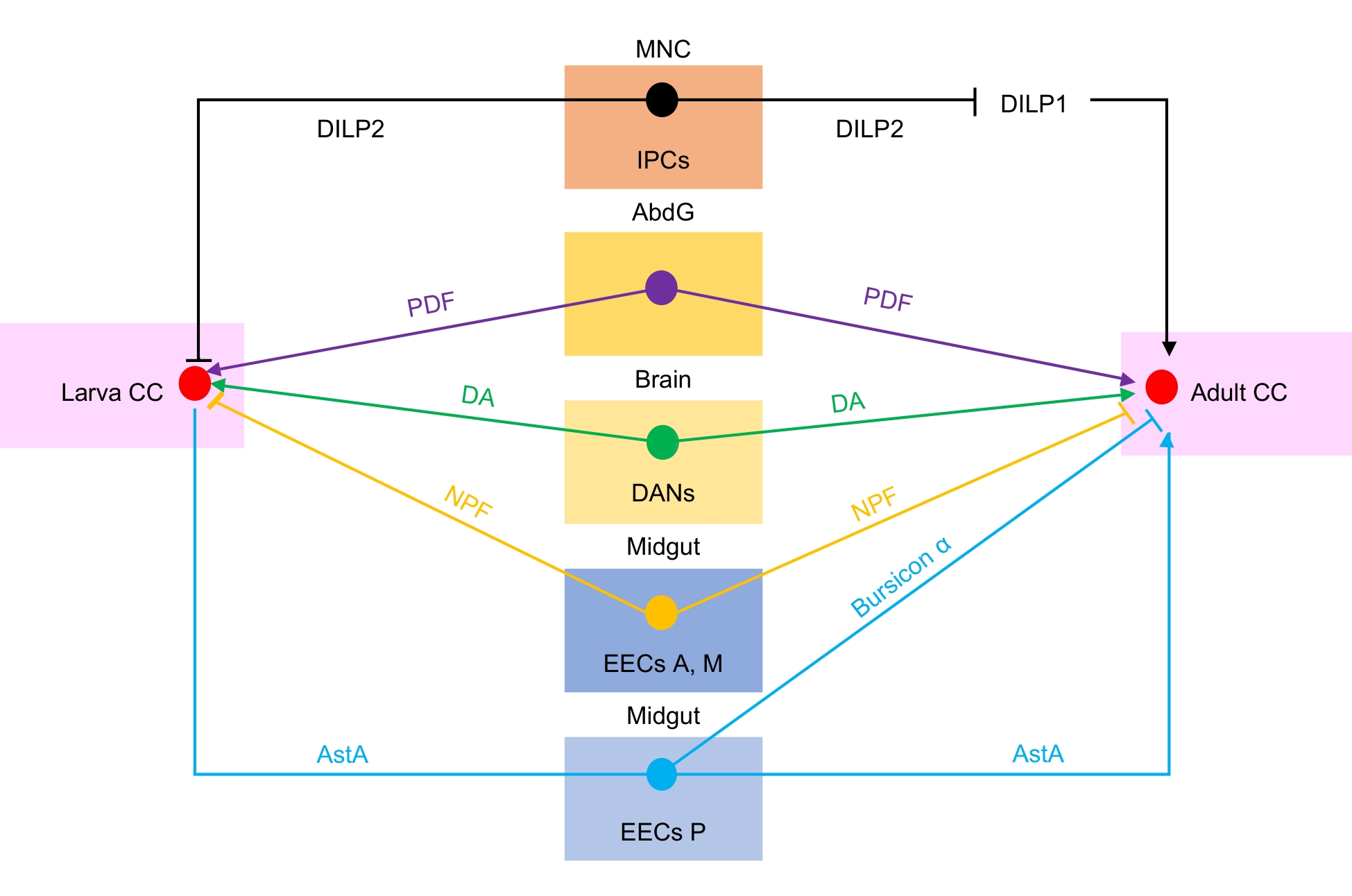
Figure 2 Regulation of corpora cardiaca by other organs in Drosophila melanogaster larvae and adultsNote: Larva CC, larva corpora cardiaca; MNC, median neurosecretory cells; IPCs, insulin-producing cells; AbdG, abdominal ganglia; DANs, dopaminergic neurons; EECs A,M,anterior and middle midgut enteroendocrine cells; EECs P, posterior midgut enteroendocrine cells; Adult CC, adult corpora cardiaca; DILP2, Insulin-like peptide 2; PDF, pigment-dispersing factor; DA, dopamine; NPF, neuropeptide F; AstA, allatostatin A; Bursicon α, Bursicon α. "→", promotion of adipokinetic hormone (AKH) release; "⊥", pointing to the larval and adult corpora cardiaca denotes inhibition of AKH release, whereas the one directed at DILP1 represents negative regulation of DILP1.

Figure 3 Corpora cardiaca regulate physiological processes of target organs via hormone secretionNote: AKHR, adipokinetic hormone receptor; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PKA, protein kinase A; IPCs, insulin-producing cells; LSTR, limostatin receptor; PG, prothoracic gland; InR, insulin receptor; s-LNv, small ventral lateral neurons; AKH,adipokinetic hormone; DILP2, Drosophila insulin-like peptide 2; LST, limostatin; "→", activation of the receptor on the target organ.
| [1] | VAN DYCK H. Book review: insect physiological ecology. mechanisms and patterns[J]. J Insect Conserv, 2005, 9(3):225-226. DOI:10.1007/s10841-005-5474-x . |
| [2] | DROUJININE I A, PERRIMON N. Interorgan communication pathways in physiology: focus on Drosophila [J]. Annu Rev Genet, 2016, 50:539-570. DOI:10.1146/annurev-genet-121415-122024 . |
| [3] | IKEYA T, GALIC M, BELAWAT P, et al. Nutrient-dependent expression of insulin-like peptides from neuroendocrine cells in the CNS contributes to growth regulation in Drosophila [J]. Curr Biol, 2002, 12(15):1293-1300. DOI:10.1016/s0960-9822(02)01043-6 . |
| [4] | KIM S K, RULIFSON E J. Conserved mechanisms of glucose sensing and regulation by Drosophila corpora cardiaca cells[J]. Nature, 2004, 431(7006):316-320. DOI:10.1038/nature02897 . |
| [5] | BROGIOLO W, STOCKER H, IKEYA T, et al. An evolutionarily conserved function of the Drosophila insulin receptor and insulin-like peptides in growth control[J]. Curr Biol, 2001, 11(4):213-221. DOI:10.1016/s0960-9822(01)00068-9 . |
| [6] | CALDERON D, BLECHER-GONEN R, HUANG X F, et al. The continuum of Drosophila embryonic development at single-cell resolution[J]. Science, 2022, 377(6606):eabn5800. DOI:10.1126/science.abn5800 . |
| [7] | LU T C, BRBIĆ M, PARK Y J, et al. Aging Fly Cell Atlas identifies exhaustive aging features at cellular resolution[J]. Science, 2023, 380(6650):eadg0934. DOI:10.1126/science.adg0934 . |
| [8] | WINDING M, PEDIGO B D, BARNES C L, et al. The connectome of an insect brain[J]. Science, 2023, 379(6636):eadd9330. DOI:10.1126/science.add9330 . |
| [9] | ÖZEL M N, GIBBS C S, HOLGUERA I, et al. Coordinated control of neuronal differentiation and wiring by sustained transcription factors[J]. Science, 2022, 378(6626):eadd1884. DOI:10.1126/science.add1884 . |
| [10] | AGI E, REIFENSTEIN E T, WIT C, et al. Axonal self-sorting without target guidance in Drosophila visual map formation[J]. Science, 2024, 383(6687):1084-1092. DOI:10.1126/science.adk3043 . |
| [11] | WEAVER K J, HOLT R A, HENRY E, et al. Effects of hunger on neuronal histone modifications slow aging in Drosophila [J]. Science, 2023, 380(6645):625-632. DOI:10.1126/science.ade1662 . |
| [12] | FURUSAWA K, ISHII K, TSUJI M, et al. Presynaptic Ube3a E3 ligase promotes synapse elimination through down-regulation of BMP signaling[J]. Science, 2023, 381(6663):1197-1205. DOI:10.1126/science.ade8978 . |
| [13] | HANSON M A, GROLLMUS L, LEMAITRE B. Ecology-relevant bacteria drive the evolution of host antimicrobial peptides in Drosophila [J]. Science, 2023, 381(6655):eadg5725. DOI:10.1126/science.adg5725 . |
| [14] | GUTIÉRREZ-GARCÍA K, AUMILLER K, DODGE R, et al. A conserved bacterial genetic basis for commensal-host specificity[J]. Science, 2024, 386(6726):1117-1122. DOI:10.1126/science.adp7748 . |
| [15] | GUO P F, LI B, DONG W, et al. PI4P-mediated solid-like Merlin condensates orchestrate Hippo pathway regulation[J]. Science, 2024, 385(6709):eadf4478. DOI:10.1126/science.adf4478 . |
| [16] | KOWALCZYK W, ROMANELLI L, ATKINS M, et al. Hippo signaling instructs ectopic but not normal organ growth[J]. Science, 2022, 378(6621):eabg3679. DOI:10.1126/science.abg3679 . |
| [17] | JACOBS J, PAGANI M, WENZL C, et al. Widespread regulatory specificities between transcriptional co-repressors and enhancers in Drosophila [J]. Science, 2023, 381(6654):198-204. DOI:10.1126/science.adf6149 . |
| [18] | GANDARA L, JACOBY R, LAURENT F, et al. Pervasive sublethal effects of agrochemicals on insects at environmentally relevant concentrations[J]. Science, 2024, 386(6720):446-453. DOI:10.1126/science.ado0251 . |
| [19] | FINNEGAN D J. Drosophila: A laboratory handbook[J]. Trends Biotechnol, 1990, 8:298. |
| [20] | PARK S, BUSTAMANTE E L, ANTONOVA J, et al. Specification of Drosophila corpora cardiaca neuroendocrine cells from mesoderm is regulated by Notch signaling[J]. PLoS Genet, 2011, 7(8):e1002241. DOI:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002241 . |
| [21] | GARCÍA-FERRÉS M, SÁNCHEZ-HIGUERAS C, ESPINOSA-VÁZQUEZ J M, et al. Specification of the endocrine primordia controlling insect moulting and metamorphosis by the JAK/STAT signalling pathway[J]. PLoS Genet, 2022, 18(10):e1010427. DOI:10.1371/journal.pgen.1010427 . |
| [22] | LEE G, PARK J H. Hemolymph sugar homeostasis and starvation-induced hyperactivity affected by genetic manipulations of the adipokinetic hormone-encoding gene in Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Genetics, 2004, 167(1):311-323. DOI:10.1534/genetics.167.1.311 . |
| [23] | DAI J D, GILBERT L I. Metamorphosis of the corpus allatum and degeneration of the prothoracic glands during the larval-pupal-adult transformation of Drosophila melanogaster: a cytophysiological analysis of the ring gland[J]. Dev Biol, 1991, 144(2):309-326. DOI:10.1016/0012-1606(91)90424-2 . |
| [24] | BODENSTEIN D. The postembryonic development of Drosophila [J]. Biol. Drosophila, 1950. DOI:http://dx.doi.org/ . |
| [25] | RULIFSON E J, KIM S K, NUSSE R. Ablation of insulin-producing neurons in flies: growth and diabetic phenotypes[J]. Science, 2002, 296(5570):1118-1120. DOI:10.1126/science.1070058 . |
| [26] | CHEYETTE B N, GREEN P J, MARTIN K, et al. The Drosophila sine oculis locus encodes a homeodomain-containing protein required for the development of the entire visual system[J]. Neuron, 1994, 12(5):977-996. DOI:10.1016/0896-6273(94)90308-5 . |
| [27] | CAPOVILLA M, ELDON E D, PIRROTTA V. The giant gene of Drosophila encodes a b-ZIP DNA-binding protein that regulates the expression of other segmentation gap genes[J]. Development, 1992, 114(1):99-112. DOI:10.1242/dev.114.1.99 . |
| [28] | MOHLER J, ELDON E D, PIRROTTA V. A novel spatial transcription pattern associated with the segmentation gene, giant, of Drosophila [J]. EMBO J, 1989, 8(5):1539-1548. DOI:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03538.x . |
| [29] | ALBERGA A, BOULAY J L, KEMPE E, et al. The snail gene required for mesoderm formation in Drosophila is expressed dynamically in derivatives of all three germ layers[J]. Development, 1991, 111(4):983-992. DOI:10.1242/dev.111.4.983 . |
| [30] | BOULAY J L, DENNEFELD C, ALBERGA A. The Drosophila developmental gene snail encodes a protein with nucleic acid binding fingers[J]. Nature, 1987, 330(6146):395-398. DOI:10.1038/330395a0 . |
| [31] | BODMER R. The gene tinman is required for specification of the heart and visceral muscles in Drosophila [J]. Development, 1993, 118(3):719-729. DOI:10.1242/dev.118.3.719 . |
| [32] | DE VELASCO B, SHEN J, GO S, et al. Embryonic development of the Drosophila corpus cardiacum, a neuroendocrine gland with similarity to the vertebrate pituitary, is controlled by sine oculis and glass [J]. Dev Biol, 2004, 274(2):280-294. DOI:10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.07.015 . |
| [33] | WHARTON K A, RAY R P, GELBART W M. An activity gradient of decapentaplegic is necessary for the specification of dorsal pattern elements in the Drosophila embryo[J]. Development, 1993, 117(2):807-822. DOI:10.1242/dev.117.2.807 . |
| [34] | HOLLEY S A, JACKSON P D, SASAI Y, et al. A conserved system for dorsal-ventral patterning in insects and vertebrates involving sog and chordin[J]. Nature, 1995, 376(6537):249-253. DOI:10.1038/376249a0 . |
| [35] | PANKRATZ M J, HOCH M. Control of epithelial morphogenesis by cell signaling and integrin molecules in the Drosophila foregut[J]. Development, 1995, 121(6):1885-1898. DOI:10.1242/dev.121.6.1885 . |
| [36] | BEIMAN M, SHILO B Z, VOLK T. Heartless, a Drosophila FGF receptor homolog, is essential for cell migration and establishment of several mesodermal lineages[J]. Genes Dev, 1996, 10(23):2993-3002. DOI:10.1101/gad.10.23.2993 . |
| [37] | PIGNONI F, BALDARELLI R M, STEINGRÍMSSON E, et al. The Drosophila gene tailless is expressed at the embryonic termini and is a member of the steroid receptor superfamily[J]. Cell, 1990, 62(1):151-163. DOI:10.1016/0092-8674(90)90249-e . |
| [38] | GÁLIKOVÁ M, DIESNER M, KLEPSATEL P, et al. Energy homeostasis control in Drosophila adipokinetic hormone mutants[J]. Genetics, 2015, 201(2):665-683. DOI:10.1534/genetics.115.178897 . |
| [39] | WATERSON M J, CHUNG B Y, HARVANEK Z M, et al. Water sensor ppk28 modulates Drosophila lifespan and physiology through AKH signaling[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2014, 111(22):8137-8142. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1315461111 . |
| [40] | REINHARD N, BERTOLINI E, SAITO A, et al. The lateral posterior clock neurons of Drosophila melanogaster express three neuropeptides and have multiple connections within the circadian clock network and beyond[J]. J Comp Neurol, 2022, 530(9):1507-1529. DOI:10.1002/cne.25294 . |
| [41] | HENTZE J L, CARLSSON M A, KONDO S, et al. The neuropeptide allatostatin a regulates metabolism and feeding decisions in Drosophila [J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5:11680. DOI:10.1038/srep11680 . |
| [42] | SCOPELLITI A, BAUER C, YU Y C, et al. A neuronal relay mediates a nutrient responsive gut/fat body axis regulating energy homeostasis in adult Drosophila [J]. Cell Metab, 2019, 29(2):269-284.e10. DOI:10.1016/j.cmet.2018.09.021 . |
| [43] | YOSHINARI Y, KOSAKAMOTO H, KAMIYAMA T, et al. The sugar-responsive enteroendocrine neuropeptide F regulates lipid metabolism through glucagon-like and insulin-like hormones in Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1):4818. DOI:10.1038/s41467-021-25146-w . |
| [44] | NÄSSEL D R, ZANDAWALA M. Hormonal axes in Drosophila: regulation of hormone release and multiplicity of actions[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2020, 382(2):233-266. DOI:10.1007/s00441-020-03264-z . |
| [45] | BRACO J T, NELSON J M, SAUNDERS C J, et al. Modulation of metabolic hormone signaling via a circadian hormone and biogenic amine in Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(8):4266. DOI:10.3390/ijms23084266 . |
| [46] | JOHNSON E C, SHAFER O T, TRIGG J S, et al. A novel diuretic hormone receptor in Drosophila: evidence for conservation of CGRP signaling[J]. J Exp Biol, 2005, 208(Pt 7):1239-1246. DOI:10.1242/jeb.01529 . |
| [47] | JOHNSON E C, BOHN L M, BARAK L S, et al. Identification of Drosophila neuropeptide receptors by G protein-coupled receptors-β-arrestin2 interactions[J]. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278(52):52172-52178. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M306756200 . |
| [48] | POST S, LIAO S F, YAMAMOTO R, et al. Drosophila insulin-like peptide dilp1 increases lifespan and glucagon-like Akh expression epistatic to dilp2[J]. Aging Cell, 2019, 18(1):e12863. DOI:10.1111/acel.12863 . |
| [49] | AHMAD M, HE L, PERRIMON N. Regulation of insulin and adipokinetic hormone/glucagon production in flies[J]. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol, 2020, 9(2):e360. DOI:10.1002/wdev.360 . |
| [50] | KANNAN K, FRIDELL Y C. Functional implications of Drosophila insulin -like peptides in metabolism, aging, and dietary restriction[J]. Front Physiol, 2013, 4:288. DOI:10.3389/fphys.2013.00288 . |
| [51] | GÄDE G, AUERSWALD L, MARCO H G. Flight fuel and neuropeptidergic control of fuel mobilisation in the twig wilter, Holopterna alata (Hemiptera, Coreidae)[J]. J Insect Physiol, 2006, 52(11-12):1171-1181. DOI:10.1016/j.jinsphys. 2006.08.005 . |
| [52] | STEELE J E. Occurrence of a hyperglycæmic factor in the corpus cardiacum of an insect[J]. Nature, 1961, 192(4803):680-681. DOI:10.1038/192680a0 . |
| [53] | RHEA J M, WEGENER C, BENDER M. The proprotein convertase encoded by amontillado (amon) is required in Drosophila corpora cardiaca endocrine cells producing the glucose regulatory hormone AKH[J]. PLoS Genet, 2010, 6(5):e1000967. DOI:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000967 . |
| [54] | LORENZ M W, GÄDE G. Hormonal regulation of energy metabolism in insects as a driving force for performance[J]. Integr Comp Biol, 2009, 49(4):380-392. DOI:10.1093/icb/icp019 . |
| [55] | TOPRAK U. The role of peptide hormones in insect lipid metabolism[J]. Front Physiol, 2020, 11:434. DOI:10.3389/fphys.2020.00434 . |
| [56] | HEWES R S, TAGHERT P H. Neuropeptides and neuropeptide receptors in the Drosophila melanogaster genome[J]. Genome Res, 2001, 11(6):1126-1142. DOI:10.1101/gr.169901 . |
| [57] | PARK Y, KIM Y J, ADAMS M E. Identification of G protein-coupled receptors for Drosophila PRXamide peptides, CCAP, corazonin, and AKH supports a theory of ligand-receptor coevolution[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2002, 99(17):11423-11428. DOI:10.1073/pnas.162276199 . |
| [58] | STAUBLI F, JORGENSEN T J D, CAZZAMALI G, et al. Molecular identification of the insect adipokinetic hormone receptors[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2002, 99(6):3446-3451. DOI:10.1073/pnas.052556499 . |
| [59] | MARCHAL E, SCHELLENS S, MONJON E, et al. Analysis of peptide ligand specificity of different insect adipokinetic hormone receptors[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(2):542. DOI:10.3390/ijms19020542 . |
| [60] | ORYAN A, WAHEDI A, PALUZZI J V. Functional characterization and quantitative expression analysis of two GnRH-related peptide receptors in the mosquito, Aedes aegypti [J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 497(2):550-557. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.088 . |
| [61] | ZANDAWALA M, HAMOUDI Z, LANGE A B, et al. Adipokinetic hormone signalling system in the Chagas disease vector, Rhodnius prolixus [J]. Insect Mol Biol, 2015, 24(2):264-276. DOI:10.1111/imb.12157 . |
| [62] | ALFA R W, PARK S, SKELLY K R, et al. Suppression of insulin production and secretion by a decretin hormone[J]. Cell Metab, 2015, 21(2):323-334. DOI:10.1016/j.cmet.2015.01.006 . |
| [63] | SLOTH ANDERSEN A, HERTZ HANSEN P, SCHAFFER L, et al. A new secreted insect protein belonging to the immuno globulin superfamily binds insulin and related peptides and inhibits their activities[J]. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275(22):16948-16953. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M001578200 . |
| [64] | YAMANAKA Y, WILSON E M, ROSENFELD R G, et al. Inhibition of insulin receptor activation by insulin-like growth factor binding proteins[J]. J Biol Chem, 1997, 272(49):30729-30734. DOI:10.1074/jbc.272.49.30729 . |
| [65] | GARBE J C, YANG E, FRISTROM J W. IMP-L2: an essential secreted immunoglobulin family member implicated in neural and ectodermal development in Drosophila [J]. Development, 1993, 119(4):1237-1250. DOI:10.1242/dev.119. 4.1237 . |
| [66] | HONEGGER B, GALIC M, KÖHLER K, et al. Imp-L2, a putative homolog of vertebrate IGF-binding protein 7, counteracts insulin signaling in Drosophila and is essential for starvation resistance[J]. J Biol, 2008, 7(3):10. DOI:10.1186/jbiol72 . |
| [67] | ALIC N, HODDINOTT M P, VINTI G, et al. Lifespan extension by increased expression of the Drosophila homologue of the IGFBP7 tumour suppressor[J]. Aging Cell, 2011, 10(1):137-147. DOI:10.1111/j.1474-9726.2010.00653.x . |
| [68] | LAYALLE S, ARQUIER N, LÉOPOLD P. The TOR pathway couples nutrition and developmental timing in Drosophila [J]. Dev Cell, 2008, 15(4):568-577. DOI:10.1016/j.devcel.2008.08.003 . |
| [69] | COLOMBANI J, BIANCHINI L, LAYALLE S, et al. Antagonistic actions of ecdysone and insulins determine final size in Drosophila [J]. Science, 2005, 310(5748):667-670. DOI:10.1126/science.1119432 . |
| [70] | SARRAF-ZADEH L, CHRISTEN S, SAUER U, et al. Local requirement of the Drosophila insulin binding protein imp-L2 in coordinating developmental progression with nutritional conditions[J]. Dev Biol, 2013, 381(1):97-106. DOI:10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.06.008 . |
| [71] | CALDWELL P E, WALKIEWICZ M, STERN M. Ras activity in the Drosophila prothoracic gland regulates body size and developmental rate via ecdysone release[J]. Curr Biol, 2005, 15(20):1785-1795. DOI:10.1016/j.cub.2005.09.011 . |
| [72] | MIRTH C, TRUMAN J W, RIDDIFORD L M. The role of the prothoracic gland in determining critical weight for metamorphosis in Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Curr Biol, 2005, 15(20):1796-1807. DOI:10.1016/j.cub.2005.09.017 . |
| [73] | NOYES B E, KATZ F N, SCHAFFER M H. Identification and expression of the Drosophila adipokinetic hormone gene[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 1995, 109(2):133-141. DOI:10.1016/0303-7207(95)03492-p . |
| [74] | KIM J, NEUFELD T P. Dietary sugar promotes systemic TOR activation in Drosophila through AKH-dependent selective secretion of Dilp3[J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6:6846. DOI:10.1038/ncomms7846 . |
| [75] | YAMANAKA N, REWITZ K F, O'CONNOR M B. Ecdysone control of developmental transitions: lessons from Drosophila research[J]. Annu Rev Entomol, 2013, 58:497-516. DOI:10.1146/annurev-ento-120811-153608 . |
| [76] | KIM S K, TSAO D D, SUH G S B, et al. Discovering signaling mechanisms governing metabolism and metabolic diseases with Drosophila [J]. Cell Metab, 2021, 33(7):1279-1292. DOI:10.1016/j.cmet.2021.05.018 . |
| [77] | GRÖNKE S, MÜLLER G, HIRSCH J, et al. Dual lipolytic control of body fat storage and mobilization in Drosophila [J]. PLoS Biol, 2007, 5(6):e137. DOI:10.1371/journal.pbio.0050137 . |
| [78] | ARRESE E L, ROJAS-RIVAS B I, WELLS M A. The use of decapitated insects to study lipid mobilization in adult Manduca sexta: effects of adipokinetic hormone and trehalose on fat body lipase activity[J]. Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 1996, 26(8-9):775-782. DOI:10.1016/s0965-1748(96)00024-0 . |
| [79] | GÄDE G. Activation of fat body glycogen phosphorylase in Locusta migratoria by corpus cardiacum extract and synthetic adipokinetic hormone[J]. J Insect Physiol, 1981, 27(3):155-161. DOI:10.1016/0022-1910(81)90122-0 . |
| [80] | AUERSWALD L, GÄDE G. Endocrine control of TAG lipase in the fat body of the migratory locust, Locusta migratoria [J]. Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 2006, 36(10):759-768. DOI:10.1016/j.ibmb.2006.07.004 . |
| [81] | TOMCALA A, BÁRTŮ I, SIMEK P, et al. Locust adipokinetic hormones mobilize diacylglycerols selectively[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol, 2010, 156(1):26-32. DOI:10.1016/j.cbpb.2010.01.015 . |
| [82] | AUERSWALD L, GÄDE G. The role of Ins(1, 4, 5)P(3) in signal transduction of the metabolic neuropeptide Mem-CC in the cetoniid beetle, Pachnoda sinuata [J]. Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 2002, 32(12):1793-1803. DOI:10.1016/s0965-1748(02)00138-8 . |
| [83] | GÄDE G, AUERSWALD L. Mode of action of neuropeptides from the adipokinetic hormone family[J]. Gen Comp Endocrinol, 2003, 132(1):10-20. DOI:10.1016/s0016-6480(03)00159-x . |
| [84] | VAN MARREWIJK W J A, VAN DEN BROEK A T M, BEENAKKERS A M TH. Adipokinetic hormone is dependent on extracellular Ca2+ for its stimulatory action on the glycogenolytic pathway in locust fat body in vitro [J]. Insect Biochem, 1991, 21(4):375-380. DOI:10.1016/0020-1790(91)90003-W . |
| [85] | VROEMEN S F, VAN DER HORST D J, VAN MARREWIJK W J. New insights into adipokinetic hormone signaling[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 1998, 141(1-2):7-12. DOI:10.1016/s0303-7207(98)00079-3 . |
| [86] | YU Y, HUANG R, YE J, et al. Regulation of starvation-induced hyperactivity by insulin and glucagon signaling in adult Drosophila [J]. eLife, 2016, 5:e15693. DOI:10.7554/eLife.15693 . |
| [87] | MOCHANOVÁ M, TOMČALA A, SVOBODOVÁ Z, et al. Role of adipokinetic hormone during starvation in Drosophila [J]. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol, 2018, 226:26-35. DOI:10.1016/j.cbpb.2018.08.004 . |
| [88] | HUANG R, SONG T T, SU H F, et al. High-fat diet enhances starvation-induced hyperactivity via sensitizing hunger-sensing neurons in Drosophila [J]. eLife, 2020, 9:e53103. DOI:10.7554/eLife.53103 . |
| [89] | REWITZ K F, YAMANAKA N, GILBERT L I, et al. The insect neuropeptide PTTH activates receptor tyrosine kinase torso to initiate metamorphosis[J]. Science, 2009, 326(5958):1403-1405. DOI:10.1126/science.1176450 . |
| [90] | KANG P, LIU P D, HU Y H, et al. NF-κB-mediated developmental delay extends lifespan in Drosophila [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2025, 122(19):e2420811122. DOI:10.1073/pnas.2420811122 . |
| [91] | JOURJINE N, MULLANEY B C, MANN K, et al. Coupled sensing of hunger and thirst signals balances sugar and water consumption[J]. Cell, 2016, 166(4):855-866. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2016.06.046 . |
| [92] | GHOSH S, LENG W H, WILSCH-BRÄUNINGER M, et al. A local insulin reservoir in Drosophila alpha cell homologs ensures developmental progression under nutrient shortage[J]. Curr Biol, 2022, 32(8):1788-1797.e5. DOI:10.1016/j.cub.2022.02.068 . |
| [93] | STOFFOLANO J G, CROKE K, CHAMBERS J, et al. Role of Phote-HrTH (Phormia terraenovae hypertrehalosemic hormone) in modulating the supercontractile muscles of the crop of adult Phormia regina Meigen[J]. J Insect Physiol, 2014, 71:147-155. DOI:10.1016/j.jinsphys.2014.10.014 . |
| [94] | BHARUCHA K N, TARR P, ZIPURSKY S L. A glucagon-like endocrine pathway in Drosophila modulates both lipid and carbohydrate homeostasis[J]. J Exp Biol, 2008, 211(Pt 19):3103-3110. DOI:10.1242/jeb.016451 . |
| [95] | LEBRETON S, MANSOURIAN S, BIGARREAU J, et al. The adipokinetic hormone receptor modulates sexual behavior, pheromone perception and pheromone production in a sex-specific and starvation-dependent manner in Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Front Ecol Evol, 2016, 3:151. DOI:10.3389/fevo.2015.00151 . |
| [96] | KO K I, ROOT C M, LINDSAY S A, et al. Starvation promotes concerted modulation of appetitive olfactory behavior via parallel neuromodulatory circuits[J]. eLife, 2015, 4:e08298. DOI:10.7554/eLife.08298 . |
| [97] | ISABEL G, MARTIN J R, CHIDAMI S, et al. AKH-producing neuroendocrine cell ablation decreases trehalose and induces behavioral changes in Drosophila [J]. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 2005, 288(2): R531-R538. DOI:10.1152/ajpregu.00158.2004 . |
| [98] | HOU Q L, CHEN E H, JIANG H B, et al. Adipokinetic hormone receptor gene identification and its role in triacylglycerol mobilization and sexual behavior in the oriental fruit fly (Bactrocera dorsalis)[J]. Insect Biochem Mol Biol, 2017, 90:1-13. DOI:10.1016/j.ibmb.2017.09.006 . |
| [99] | LU K, ZHANG X Y, CHEN X, et al. Adipokinetic hormone receptor mediates lipid mobilization to regulate starvation resistance in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens [J]. Front Physiol, 2018, 9:1730. DOI:10.3389/fphys.2018.01730 . |
| [100] | ZEMANOVÁ M, STAŠKOVÁ T, KODRÍK D. Role of adipokinetic hormone and adenosine in the anti-stress response in Drosophila melanogaster [J]. J Insect Physiol, 2016, 91-92:39-47. DOI:10.1016/j.jinsphys.2016.06.010 . |
| [101] | HE Q K, DU J, WEI L Y, et al. AKH-FOXO pathway regulates starvation-induced sleep loss through remodeling of the small ventral lateral neuron dorsal projections[J]. PLoS Genet, 2020, 16(10):e1009181. DOI:10.1371/journal.pgen.1009181 . |
| [102] | HONG S H, LEE K S, KWAK S J, et al. Minibrain/Dyrk1a regulates food intake through the Sir2-FOXO-sNPF/NPY pathway in Drosophila and mammals[J]. PLoS Genet, 2012, 8(8):e1002857. DOI:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002857 . |
| [103] | GUNTUR A R, GU P Y, TAKLE K, et al. Drosophila TRPA1 isoforms detect UV light via photochemical production of H2O2 [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2015, 112(42):E5753-E5761. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1514862112 . |
| [104] | INAGAKI H K, PANSE K M, ANDERSON D J. Independent, reciprocal neuromodulatory control of sweet and bitter taste sensitivity during starvation in Drosophila [J]. Neuron, 2014, 84(4):806-820. DOI:10.1016/j.neuron.2014.09.032 . |
| [105] | ARRESE E L, SOULAGES J L. Insect fat body: energy, metabolism, and regulation[J]. Annu Rev Entomol, 2010, 55:207-225. DOI:10.1146/annurev-ento-112408-085356 . |
| [106] | CHOI S, LIM D S, CHUNG J. Feeding and fasting signals converge on the LKB1-SIK3 pathway to regulate lipid metabolism in Drosophila [J]. PLoS Genet, 2015, 11(5):e1005263. DOI:10.1371/journal.pgen.1005263 . |
| [1] | WANG Mingzhu, GAO Yinghao, TAN Shuangshuang, WU Wei. Construction and Characterization of UAS-Irk3-EGFP Transgenic Drosophila Lines [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 656-662. |
| [2] | ZHOU Guanyu, ZHU Shiming, LIU Fangfang. Research Advances on Periplaneta americana as an Experimental Animal Model [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 794-802. |
| [3] | CHEN Haotian, LIU Jingnan. Applications and Advances of Drosophila in Research of Obesity and Its Related Metabolic Diseases [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 688-704. |
| [4] | WANG Ye, WANG Lu. Drosophila melanogaster Transposons: Characterization, Regulation, and Their Role in Genome Evolution [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 676-687. |
| [5] | DENG Xianming, WANG Fei. Research Progress on Drosophila Electron Microscopy Connectome Database and Functional Analysis of Related Neural Circuits [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 663-675. |
| [6] | SHAO Qiming, BIAN Yong, SHI Aimin. Key Points for Establishing Occupational Health and Safety Management System in Laboratory Animal Institutions [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 188-196. |
| [7] | Longmei XU, Ruling SHEN, Chun FAN, Wei WU. Generation of 12 Drosophila Transgenic Negative Control Lines Based on Site-specific ΦC31 Integrase and pUASTattB Vector [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 541-547. |
| [8] | Ling YANG, Di ZHUANG, Lilun JIN. Screening of Differentially Expressed Genes in Rat Synovitis by Transcriptome Sequencing and in Vitro Verification of Therapeutic Target of Fraxetin [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 11-20. |
| [9] | LI Zifa, ZHANG Hao, REN Meng, XU Kaiyong, HU Minghui, ZHOU Miaomiao, WANG Kezhou. Protective Effect of Quercetin on Lipid Metabolism Disorder in Mice Livers Caused by Cadmium [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2021, 41(4): 305-312. |
| [10] | WU Li-hong, LI Hong-tao, Guan Hong-bing, GU Wei-wang, Huang Li-wen. Immunization with Leptin Promotes Fat Accumulation and Up-regulates mRNA Expression of PPARγand SREBP-1 [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2019, 39(4): 287-293. |
| [11] | SUN Min, SHA Hai-bo, TU Xin, ZOU Jiang-huan, LAI Bei-bei, GAO Xiang, QI Xin. hnRNP U Haploinsufficiency Leads to Growth Retardation, Decreased Activities and Abnormal Glucose Metabolism in Mice [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2015, 35(3): 175-181. |
| [12] | XU Yun-peng, HAO Min, CHANG Xiao-tong. Effect of Induced Obesity on Metabolism of Lipid and Glucose in Young SD Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2015, 35(2): 97-101. |
| [13] | ZHANG Quan, ZHU Hui-xia, LI Ling-yu, TAN Hai-ming, XUE Zheng-feng. Research Progress on Sendai Virus against Tumors [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2014, 34(6): 515-518. |
| [14] | GUAN Yu, YAN Xiao-li, WANG Guo-hua, ZHANG Xiao-feng. Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Rat Liver Iron Metabolism [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2014, 34(3): 205-209. |
| [15] | XI Sai-fei, SI Xu-wei, ZHU Ke-yan, CHEN Xiao-zhen, YANG Tao-tao, CHEN Min-li. The Characteristics of Glucolipid Metabolism and Insulin Resistance in ZDF(fa/fa) Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2014, 34(2): 102-106. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||