
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine
• XXXX XXXX •
XIAO Linlin1,2, YANG Yixuan1,2, LI Shanshan1,2, RUO Lanshiyu1,2, YIN Siwei1,2, SUN Juming1, SHI Wei1, OUYANG Yiqiang1, LI Xiyi3( )
)
Online:2025-05-16
Contact:
OUYANG Yiqiang, LI Xiyi
CLC Number:
XIAO Linlin,YANG Yixuan,LI Shanshan,et al. A Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease by Introducing Human Triple Mutant APP Gene into Hippocampus using Brain Stereotactic Technology[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.030.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.030
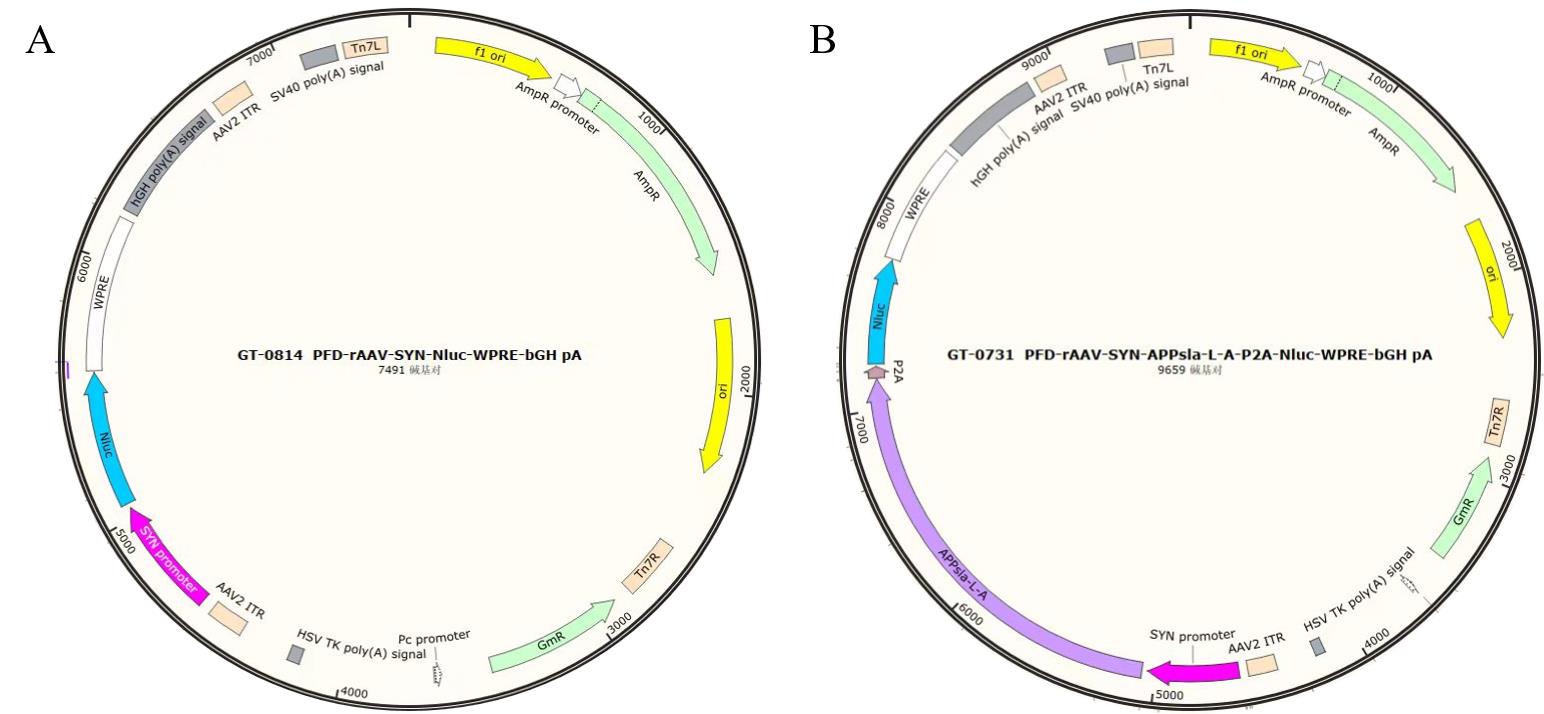
Figure 1 Diagram of adeno-associated viral vectorsNote:A, Structure of the empty viral plasmid; B, Structure of the plasmid carrying the human triple mutant APP gene; APLsla-L-A in the vector diagram represents the human triple mutant APP genes, Nluc represents the NanoLuc luciferase gene, and SYN promoter is the neuron-specific promoter.
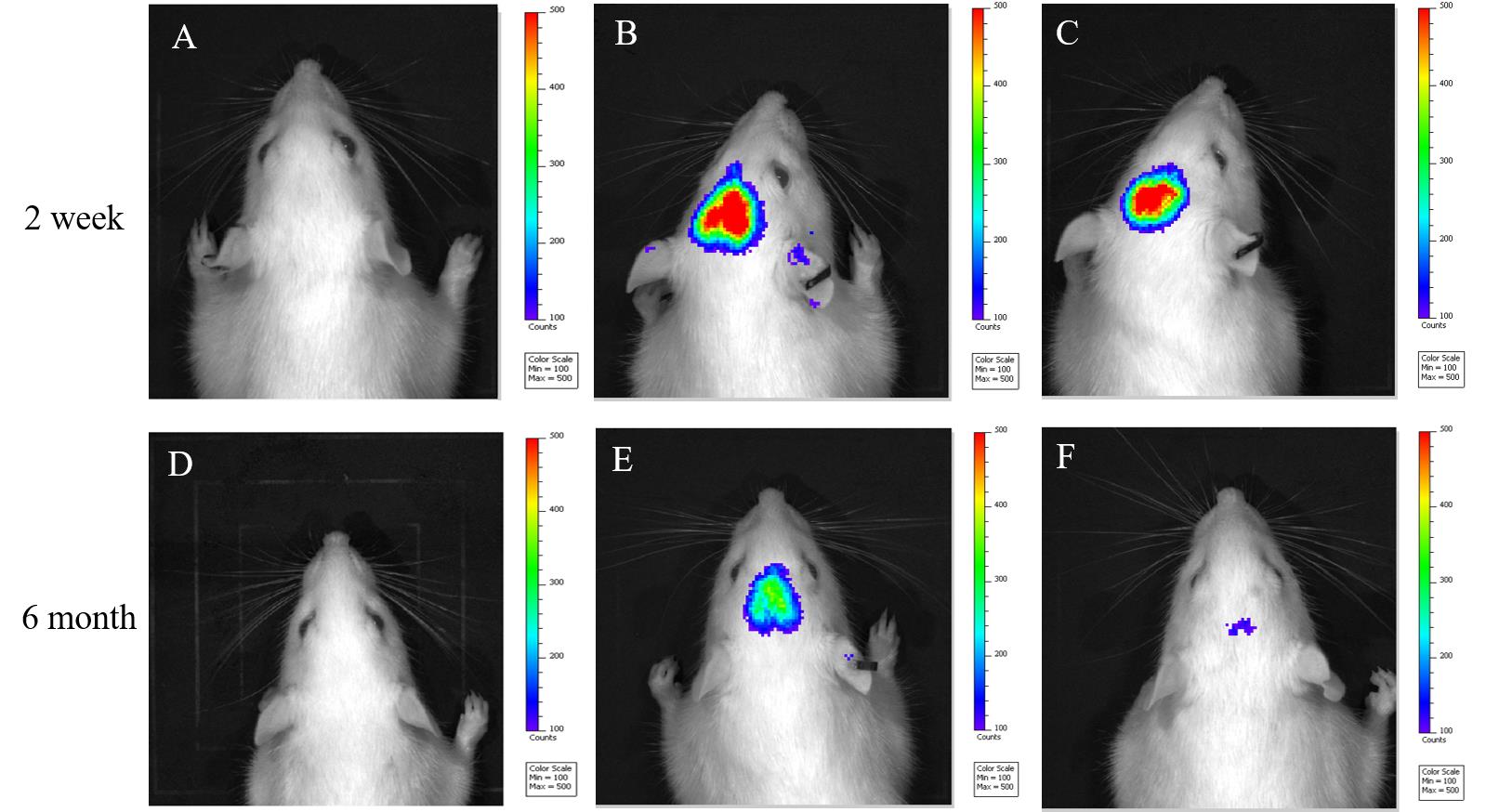
Figure 2 In vivo imaging of rats two weeks and six months after virus injectionNote:Luciferase activity was observed 10 min after intraperitoneal injection of luciferase substrate Furimazine in each group of rats. A,In vivo imaging a rat in the blank control group; B, In vivo imaging a rat two weeks after injection of the empty virus; C,In vivo imaging a rat two weeks after injection of of AAV virus expressing the human triple mutant APP genes in the experimental group; D, In vivo imaging a rat survived for 6 months in the blank control group; E, In vivo imaging a rat six months after injection of the empty virus; F, In vivoimaging a rat six months after injection of the mutant APP genes in the experimental group.

Figure 3 Results of APP expression detection in rat hippocampusNote:A, qPCR results,compared with blank control group, **P<0.01; compared with empty virus group,##P<0.01; B, sequencing comparison results of qPCR products, yellow highlights are mutation sites.
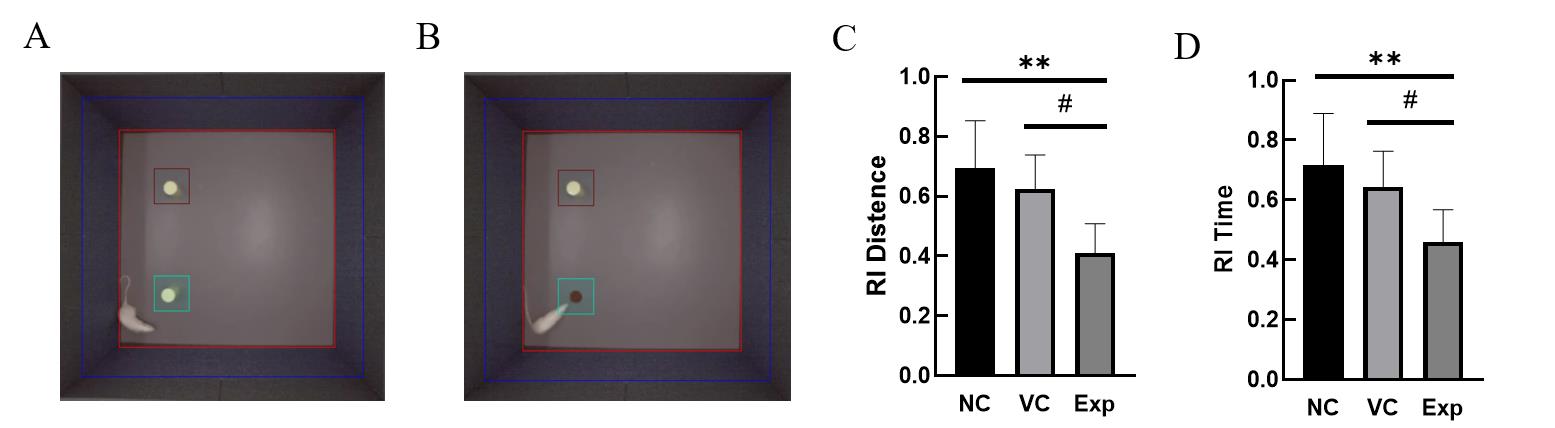
Figure 4 Experimental results of new object recognitionNote:A, Exploratory behavior graphs of rats exploring two identical objects; B, Exploratory behavior graphs of rats exploring new and old objects; C, Results of new object recognition experiments using distance as a statistical index; D, Results of new object recognition experiments using time as a statistical index; NC, VC, and Exp are blank control group, empty virus group, and experimental group, respectively; compared with the blank control group,**P<0.01; compared with the airborne virus group, #P<0.05, n=8 .
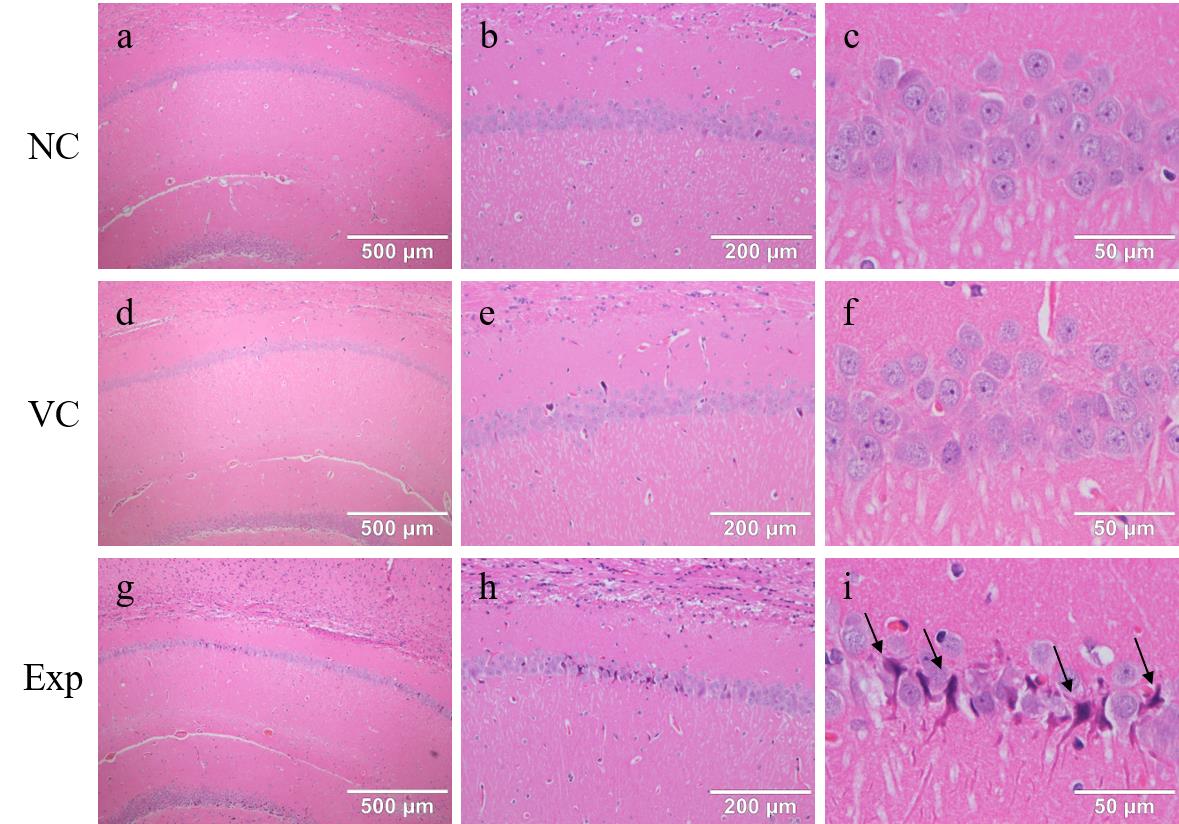
Figure 5 HE staining results of rat hippocampal regionNote:NC, VC, Exp are the HE staining results of the blank control group, the empty virus group, and the experimental group, respectively. Scale bars are shown. The areas indicated by arrows are crumpled necrotic cells.
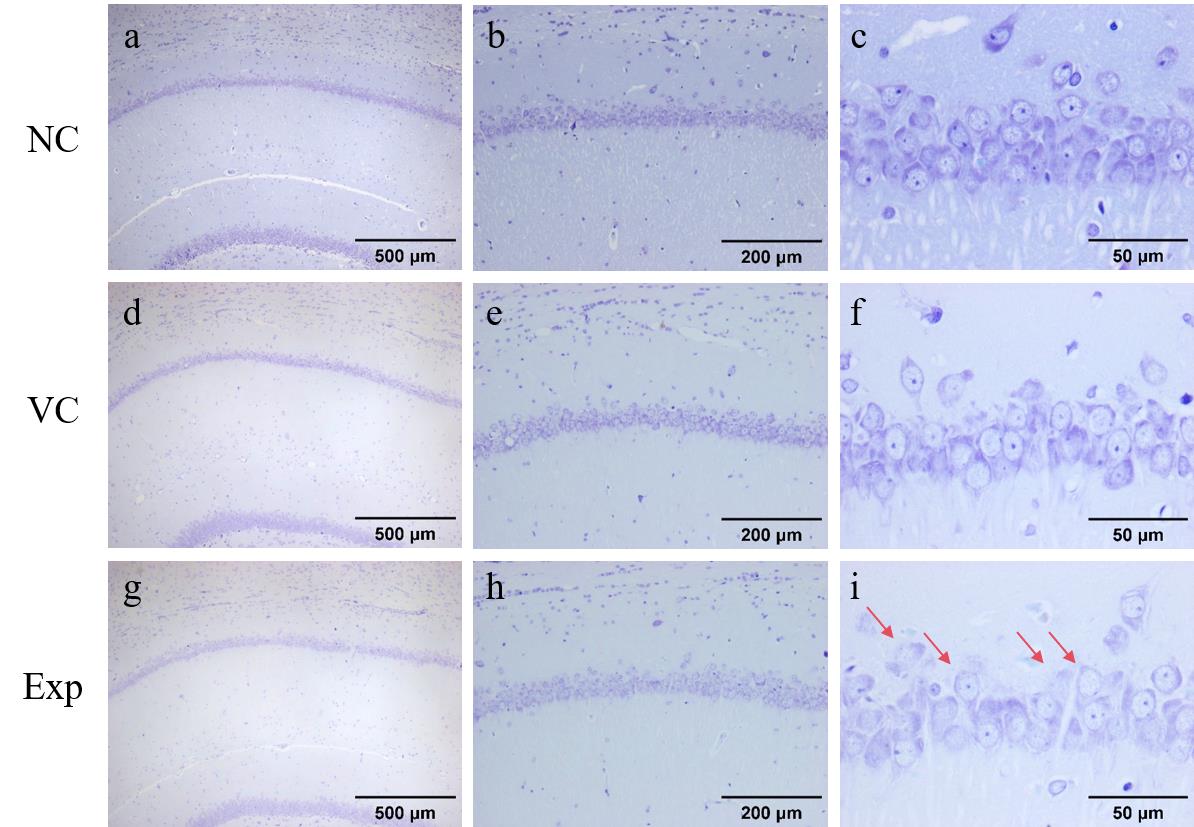
Figure 6 Staining results of Nystrom's body in the hippocampus of the ratNote:NC, VC, Exp are the Nissl staining results of the blank control group, the empty virus group, and the experimental group, respectively. Scale bars are shown. Areas indicated by arrows are cells with sparse nidus and light staining.
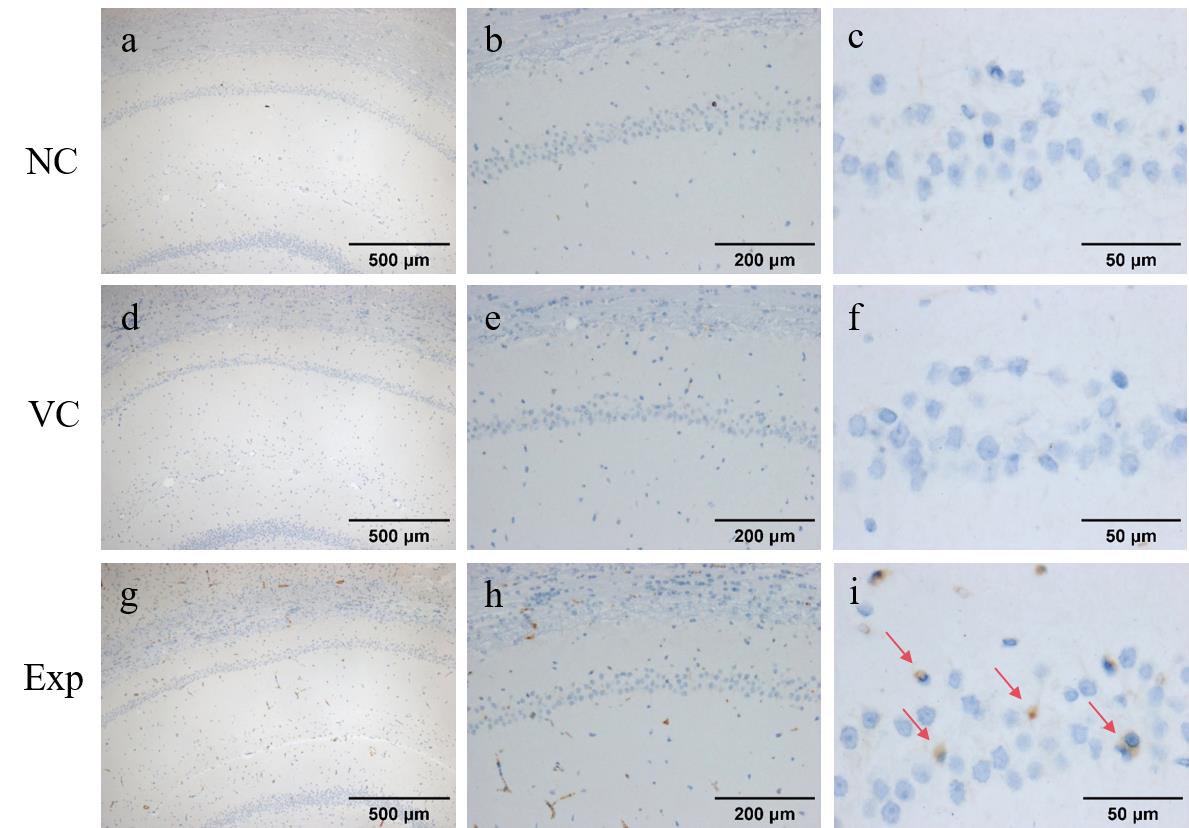
Figure 7 Immunohistochemical results of rat hippocampal regionNote:NC, VC, Exp are the immunization results of blank control group, empty virus group, and experimental group, respectively. Scale bars are shown. The area indicated by the arrow is the area of Aβ protein deposition.
| 1 | 王刚, 齐金蕾, 刘馨雅, 等. 中国阿尔茨海默病报告2024[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2024, 23(3): 219-256. DOI:10.16150/j.1671-2870.2024.03.001 . |
| WANG G, QI J L, LIU X Y, et al. China Alzheimer's Disease Report 2024 [J]. Diagnostics Theory and Practice, 2024, 23(3): 219-256. DOI:10.16150/j.1671-2870.2024.03.001 . | |
| 2 | SCHELTENS P, DE STROOPER B, KIVIPELTO M, et al. Alzheimer's disease[J]. Lancet, 2021, 397(10284): 1577-1590.DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32205-4 . |
| 3 | SCHELTENS P, BLENNOW K, BRETELER M M, et al. Alzheimer's disease[J]. Lancet, 2016, 388(10043): 505-517.DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01124-1 . |
| 4 | BREIJYEH Z, KARAMAN R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer's Disease: Causes and Treatment[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(24).DOI:10.3390/molecules25245789 . |
| 5 | MATHIAS JUCKER L C W. Alzheimer's disease: From immunotherapy to immunoprevention[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(20): 4260-4270.DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2023.08.021 . |
| 6 | ZHOU B, LU J G, SIDDU A, et al. Synaptogenic effect of APP-Swedish mutation in familial Alzheimer's disease[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2022, 14(667): eabn9380.DOI:10.1126/scitranslmed.abn9380 . |
| 7 | KIM M, BEZPROZVANNY I. Analysis of Non-Amyloidogenic Mutations in APP Supports Loss of Function Hypothesis of Alzheimer's Disease [J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(3).DOI:10.3390/ijms24032092 . |
| 8 | ARMBRUST F, BICKENBACH K, MARENGO L, et al. The Swedish dilemma - the almost exclusive use of APPswe-based mouse models impedes adequate evaluation of alternative beta-secretases [J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res, 2022, 1869(3): 119164.DOI:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2021.119164 . |
| 9 | SCHILLING S, PRADHAN A, HEESCH A, et al. Differential effects of familial Alzheimer's disease-causing mutations on amyloid precursor protein (APP) trafficking, proteolytic conversion, and synaptogenic activity [J]. Acta Neuropathol Commun, 2023, 11(1): 87.DOI:10.1186/s40478-023-01577-y . |
| 10 | JAWORSKI T, DEWACHTER I, LECHAT B, et al. AAV-tau mediates pyramidal neurodegeneration by cell-cycle re-entry without neurofibrillary tangle formation in wild-type mice [J]. PLoS One, 2009, 4(10): e7280.DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0007280 . |
| 11 | XIA D, LIANOGLOU S, SANDMANN T, et al. Novel App knock-in mouse model shows key features of amyloid pathology and reveals profound metabolic dysregulation of microglia [J]. Mol Neurodegener, 2022, 17(1): 41.DOI:10.1186/s13024-022-00547-7 . |
| 12 | CLAYTON K, DELPECH J C, HERRON S, et al. Plaque associated microglia hyper-secrete extracellular vesicles and accelerate tau propagation in a humanized APP mouse model [J]. Mol Neurodegener, 2021, 16(1): 18.DOI:10.1186/s13024-021-00440-9 . |
| 13 | TESSON L, COZZI J, MENORET S, et al. Transgenic modifications of the rat genome [J]. Transgenic Res, 2005, 14(5): 531-546.DOI:10.1007/s11248-005-5077-z . |
| 14 | PANG K, JIANG R, ZHANG W, et al. An App knock-in rat model for Alzheimer's disease exhibiting Abeta and tau pathologies, neuronal death and cognitive impairments [J]. Cell Res, 2022, 32(2): 157-175.DOI:10.1038/s41422-021-00582-x . |
| 15 | PUPO A, FERNANDEZ A, LOW S H, et al. AAV vectors: The Rubik's cube of human gene therapy [J]. Mol Ther, 2022, 30(12): 3515-3541.DOI:10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.09.015 . |
| 16 | ASCHAUER D F, KREUZ S, RUMPEL S. Analysis of transduction efficiency, tropism and axonal transport of AAV serotypes 1, 2, 5, 6, 8 and 9 in the mouse brain [J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(9): e76310.DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0076310 . |
| 17 | ROSTAGNO A A. Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease [J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 24(1).DOI:10.3390/ijms24010107 . |
| 18 | KAYED R, LASAGNA-REEVES C A. Molecular mechanisms of amyloid oligomers toxicity [J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2013, 33 : S67-78.DOI:10.3233/JAD-2012-129001 . |
| 19 | FOLKESSON R M K, KLOSKOWSKA E, et al. A transgenic rat expressing human APP with the Swedish Alzheimer's disease mutation. [J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2007, 358(3): 777-782. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.04.195 |
| 20 | KLOSKOWSKA E P T, NILSSON T, et al. Cognitive impairment in the Tg6590 transgenicrat model of Alzheimer's disease [J]. Cell Mol Med, 2010, 14(6B): 1816-1823. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00809 |
| 21 | FENG W, ZHANG Y, WANG Z, et al. Microglia prevent beta-amyloid plaque formation in the early stage of an Alzheimer's disease mouse model with suppression of glymphatic clearance [J]. Alzheimers Res Ther, 2020, 12(1): 125.DOI:10.1186/s13195-020-00688-1 . |
| 22 | LI Z, ZHANG Y, MENG X, et al. A novel DPP-4 inhibitor Gramcyclin A attenuates cognitive deficits in APP/PS1/tau triple transgenic mice via enhancing brain GLP-1-dependent glucose uptake [J]. Phytother Res, 2022, 36(3): 1297-1309.DOI:10.1002/ptr.7387 . |
| 23 | HAMPTON D W, WEBBER D J, BILICAN B, et al. Cell-mediated neuroprotection in a mouse model of human tauopathy [J]. J Neurosci, 2010, 30(30): 9973-9983.DOI:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0834-10.2010 . |
| 24 | KIM H Y, LEE D K, CHUNG B R, et al. Intracerebroventricular Injection of Amyloid-beta Peptides in Normal Mice to Acutely Induce Alzheimer-like Cognitive Deficits [J]. J Vis Exp, 2016, (109).DOI:10.3791/53308 . |
| 25 | SU Y, WALKER J R, PARK Y, et al. Novel NanoLuc substrates enable bright two-population bioluminescence imaging in animals [J]. Nat Methods, 2020, 17(8): 852-860.DOI:10.1038/s41592-020-0889-6 . |
| 26 | TIAN X, ZHANG Y, LI X, et al. A luciferase prosubstrate and a red bioluminescent calcium indicator for imaging neuronal activity in mice [J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1).DOI:10.1038/s41467-022-31673-x . |
| [1] | Liya YANG, Tao SONG, Jialin HE, Yiming GUO, Mingkang QI, Hanbi WANG, Huiping WANG. Establishment of a Vaginal Atrophy Rat Model and its Application in Pharmacodynamic Evaluation [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 531-540. |
| [2] | Xinpeng LU, Rong LIU, Wenbo Huang, Jin ZHAO, Hongtao LI. A Comparative Study of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Rat Models Established by Different Methods [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 201-206. |
| [3] | AN Xin, LIU Lanjing, BU Jianping. Changes of Retinal Morphology and Expressions of RhoA and ROCK-2 in Ocular Ischemic Syndrome Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2020, 40(5): 397-. |
| [4] | XIAO Kunlin, ZHANG Rui, Sun Hong, XIAO Kuntai, MA Jianbing. Evaluation of Monoiodoacetic Acid-induced Knee Osteoarthritis SD Rats with Diseasse Progression at Different Time Points [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2020, 40(1): 47-52. |
| [5] | LI Min, CHANG Xue-hui, ZHANG Liang-zhi, LEI Zhen, LUO Shen. Comparative Analysis on Rat Models of Parkinson's Disease Established by Injecting 6- hydroxy Dopamine with Different Sites [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2018, 38(4): 261-266. |
| [6] | GAO Feng, ZHANG Shi-geng, ZHANG Nan, ZHANG Bu-yi, DAI Yu-liang, LI Shao-jiang. Establishment of Over Active Bladder Model Associated with Chronic Cystitis in Rat [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2016, 36(5): 340-344. |
| [7] | FENG Jia, XIANG Yang, XIA Yan, CHEN An-ping, YANG Nian-an, GONG Shu-shi, YUAN Lin. Comparative Study on Three Kinds of Osteoporosis Model in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2015, 35(1): 52-55. |
| [8] | QIAO ming, LIU Lan-ying, WANG He-sheng. Establishment and Evaluation of Chronic Allergic Asthma Models in Rat [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2014, 34(1): 79-82. |
| [9] | SHI Zhi-chong, YANG Jun, TAN Yan-bin, SUN Yu-li, YU Xiao-qi, PAN Jie, XIAO Pin. Effect of a Kind of Strong-bone Capsule on Increasing Bone Mineral Density in Castrated Female Rat [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2011, 31(2): 111-114. |
| [10] | ZHOU Wen-jiang1,2,TAO Lin-lin3. Advances in Application of Animal Model Infected with Cryptococcus neoformans [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2010, 30(3): 220-224. |
| [11] | LI Dong-mei1,2,HU Wen-juan1,2,LIU Xiang-yun1,2,ZHANG Xiao-fang2,YAN Han2,XIE Shu-wu2,WU Jian-hui2,SUN Zu-yue2. Study on Experimental Autoimmune Prostatitis in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2008, 28(3): 151-154. |
| [12] | LIU Na-xin1,GUAN Min-qiang2,CHEN Tong-ke2,ZHAO Hui-ling2,CHEN Xi-wen2. Modification and Comparison of Two Methods for Creating Rats Models of Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2008, 28(2): 110-113. |
| [13] | ZHANG Da-wei1,YANG Yong-mei1 JIN Xing2,ZHANG Jing-yong2,MENG Hong3. Establishment of Thromboangitis Obliterans Model in Rat [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2003, 23(4): 203-206. |
| [14] | RONG Zhao-hui, QU Jie-ming, HE Li-xian, LI Xi-ying. Study on Inflammatory Reaction and Lung Injury in Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2001, 21(4): 198-204. |
| [15] | HE Li-qun, NIE Yong-hong, ZHOU Shi-Ling. A New Rat Model of Uric Acid Nephropathy [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2001, 21(1): 22-25. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||