
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 374-383.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.017
• Animal Models of Human Diseases • Previous Articles Next Articles
XIAO Pan1,2, WANG Hongyi1,2, LU Lu1,2, ZHANG Mei1,2, CHEN Keming1,2, SHEN Dongshuai1,2( )(
)( ), NIU Tingxian1,2(
), NIU Tingxian1,2( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-01-30
Revised:2024-05-30
Online:2024-08-25
Published:2024-09-06
Contact:
SHEN Dongshuai, NIU Tingxian
CLC Number:
XIAO Pan,WANG Hongyi,LU Lu,et al. Screening of Hypoxia-Sensitive and Hypoxia-Tolerant Wistar Rats and Preliminary Exploration of Hypoxia Sensitivity in Their G1 Generation[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 374-383. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.017.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.017
遗传代数及低氧敏感性 Genetic algebra and hypoxia sensitivity | 雄性Male | 雌性Female | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 范围Range | n | 范围Range | ||||||
G0代 G0 generation | 100 | 928.18±524.06 | 232~2 965 | 100 | 976.98±738.53 | 151~3 280 | |||
G1代敏感型 G1 hypoxia-sensitive type | 232 | 832.15±486.19 | 165~2 838 | 251 | 1 171.68±399.67acc | 355~1 921 | |||
G1代耐受型 G1 hypoxia-tolerant type | 266 | 1 300.59±712.44aabbcc | 295~3 121 | 283 | 1 748.69±932.60aabbccdd | 384~3 621 | |||
Table 1 Hypoxia tolerance time of G0 and G1 generation rats
遗传代数及低氧敏感性 Genetic algebra and hypoxia sensitivity | 雄性Male | 雌性Female | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 范围Range | n | 范围Range | ||||||
G0代 G0 generation | 100 | 928.18±524.06 | 232~2 965 | 100 | 976.98±738.53 | 151~3 280 | |||
G1代敏感型 G1 hypoxia-sensitive type | 232 | 832.15±486.19 | 165~2 838 | 251 | 1 171.68±399.67acc | 355~1 921 | |||
G1代耐受型 G1 hypoxia-tolerant type | 266 | 1 300.59±712.44aabbcc | 295~3 121 | 283 | 1 748.69±932.60aabbccdd | 384~3 621 | |||
组别 Group | 酸碱度 pH | 二氧化碳分压/mmHg PaCO2/mmHg | 氧分压/mmHg PaO2/mmHg | 氧饱和度/% SatO2/% | 标准碳酸氢盐c/(mmol·L-1) SB c/(mmol·L-1) | 实际碳酸氢盐c/(mmol·L-1) AB c/(mmol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
空白对照组 Control group | 7.36±0.05 | 49.65±6.85 | 84.05±6.26 | 92.50±2.07 | 25.80±1.23 | 26.10±2.23 |
模型对照组 Model group | 7.30±0.04a | 45.43±7.04 | 78.29±9.59 | 85.29±2.69aa | 21.29±1.80aa | 21.86±1.77aa |
G1敏感组 G1 sensitive group | 7.30±0.02a | 42.57±1.99a | 76.29±3.15a | 84.00±2.16aa | 20.43±2.30aa | 19.29±2.50aab |
G1耐受组 G1 tolerant group | 7.31±0.03a | 46.86±1.07 | 79.43±1.81 | 88.86±5.34abc | 22.86±2.97ac | 21.58±11.51aac |
Table 2 Measurement results of blood gas indicators in rats
组别 Group | 酸碱度 pH | 二氧化碳分压/mmHg PaCO2/mmHg | 氧分压/mmHg PaO2/mmHg | 氧饱和度/% SatO2/% | 标准碳酸氢盐c/(mmol·L-1) SB c/(mmol·L-1) | 实际碳酸氢盐c/(mmol·L-1) AB c/(mmol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
空白对照组 Control group | 7.36±0.05 | 49.65±6.85 | 84.05±6.26 | 92.50±2.07 | 25.80±1.23 | 26.10±2.23 |
模型对照组 Model group | 7.30±0.04a | 45.43±7.04 | 78.29±9.59 | 85.29±2.69aa | 21.29±1.80aa | 21.86±1.77aa |
G1敏感组 G1 sensitive group | 7.30±0.02a | 42.57±1.99a | 76.29±3.15a | 84.00±2.16aa | 20.43±2.30aa | 19.29±2.50aab |
G1耐受组 G1 tolerant group | 7.31±0.03a | 46.86±1.07 | 79.43±1.81 | 88.86±5.34abc | 22.86±2.97ac | 21.58±11.51aac |
检测指标 Detection index | 空白对照组 Control group | 模型对照组 Model group | G1敏感组 G1 sensitive group | G1耐受组 G1 tolerant group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
白细胞计数, ×109/L WBC, ×109/L | 4.03±1.13 | 4.55±0.47 | 5.58±1.50aab | 4.33±0.46 |
中性粒细胞数, ×109/L NEUT, ×109/L | 0.92±0.24 | 1.09±0.16 | 1.59±0.54aabb | 0.94±0.13cc |
淋巴细胞数, ×109/L LYMPH, ×109/L | 2.95±0.84 | 3.75±1.78 | 3.82±0.87 | 3.47±1.57 |
中性粒细胞百分比/% NEUT% | 22.99±2.20 | 29.81±14.58 | 30.79±7.38 | 27.31±11.20 |
红细胞计数, ×1012/L RBC, ×1012/L | 7.77±0.31 | 9.09±0.64aa | 9.49±0.63aa | 8.59±0.26aacc |
血红蛋白 ρ/(g·L-1) HGB ρ/(g·L-1) | 141.86±3.29 | 165.00±9.47aa | 175.71±10.00aabb | 156.00±3.02aabcc |
血细胞比容/% HCT/% | 43.79±1.44 | 47.78±3.09aa | 50.66±3.17aab | 44.96±1.17bcc |
红细胞分布宽度百分比/% RDW/% | 15.10±0.40 | 24.70±0.85aa | 27.29±1.44aabb | 24.70±0.85aacc |
血小板计数, ×109/L PLT, ×109/L | 775.00±77.59 | 1 085.00±82.85aa | 1 183.71±64.17aab | 994.50±75.40aabcc |
血小板分布宽度/% PDW/% | 15.03±0.13 | 14.66±0.15aa | 14.70±0.08aa | 14.66±0.15aa |
Table 3 Measurement results of complete blood count indicators in rats
检测指标 Detection index | 空白对照组 Control group | 模型对照组 Model group | G1敏感组 G1 sensitive group | G1耐受组 G1 tolerant group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
白细胞计数, ×109/L WBC, ×109/L | 4.03±1.13 | 4.55±0.47 | 5.58±1.50aab | 4.33±0.46 |
中性粒细胞数, ×109/L NEUT, ×109/L | 0.92±0.24 | 1.09±0.16 | 1.59±0.54aabb | 0.94±0.13cc |
淋巴细胞数, ×109/L LYMPH, ×109/L | 2.95±0.84 | 3.75±1.78 | 3.82±0.87 | 3.47±1.57 |
中性粒细胞百分比/% NEUT% | 22.99±2.20 | 29.81±14.58 | 30.79±7.38 | 27.31±11.20 |
红细胞计数, ×1012/L RBC, ×1012/L | 7.77±0.31 | 9.09±0.64aa | 9.49±0.63aa | 8.59±0.26aacc |
血红蛋白 ρ/(g·L-1) HGB ρ/(g·L-1) | 141.86±3.29 | 165.00±9.47aa | 175.71±10.00aabb | 156.00±3.02aabcc |
血细胞比容/% HCT/% | 43.79±1.44 | 47.78±3.09aa | 50.66±3.17aab | 44.96±1.17bcc |
红细胞分布宽度百分比/% RDW/% | 15.10±0.40 | 24.70±0.85aa | 27.29±1.44aabb | 24.70±0.85aacc |
血小板计数, ×109/L PLT, ×109/L | 775.00±77.59 | 1 085.00±82.85aa | 1 183.71±64.17aab | 994.50±75.40aabcc |
血小板分布宽度/% PDW/% | 15.03±0.13 | 14.66±0.15aa | 14.70±0.08aa | 14.66±0.15aa |
组别 Group | 肌酐z/(U·L-1) Cr z/(U·L-1) | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 z/(U·L-1) AST z/(U·L-1) | 丙氨酸转氨酶 c/(μmol·L-1) ALT c/(μmol·L-1) | 总胆红素 c/(mmol·L-1) TBIL c/(mmol·L-1) | 肺系数/% Lung coefficient/% | 脑系数/% Brain coefficient/% | 心系数/% Heart coefficient/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
空白对照组 Control group | 36.00±3.43 | 91.60±12.89 | 38.20±4.98 | 0.04±0.74 | 0.52±0.08 | 0.60±0.05 | 0.32±0.02 |
模型对照组 Model group | 39.71±3.59 | 121.43±25.2 | 39.86±9.48 | 0.34±0.31 | 0.56±0.05 | 0.66±0.03aa | 0.33±0.03 |
G1敏感组 G1 sensitive group | 48.38±8.53aabb | 166.25±87.16aa | 40.87±7.22 | 0.39±0.28 | 0.62±0.05aab | 0.71±0.05aab | 0.34±0.02 |
G1耐受组 G1 tolerant group | 44.75±6.50aa | 132.75±33.94 | 39.75±11.85 | 0.26±0.26 | 0.55±0.04c | 0.64±0.04acc | 0.33±0.03 |
Table 4 Measurement of biochemical indicators and organ coefficients in rats
组别 Group | 肌酐z/(U·L-1) Cr z/(U·L-1) | 天冬氨酸转氨酶 z/(U·L-1) AST z/(U·L-1) | 丙氨酸转氨酶 c/(μmol·L-1) ALT c/(μmol·L-1) | 总胆红素 c/(mmol·L-1) TBIL c/(mmol·L-1) | 肺系数/% Lung coefficient/% | 脑系数/% Brain coefficient/% | 心系数/% Heart coefficient/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
空白对照组 Control group | 36.00±3.43 | 91.60±12.89 | 38.20±4.98 | 0.04±0.74 | 0.52±0.08 | 0.60±0.05 | 0.32±0.02 |
模型对照组 Model group | 39.71±3.59 | 121.43±25.2 | 39.86±9.48 | 0.34±0.31 | 0.56±0.05 | 0.66±0.03aa | 0.33±0.03 |
G1敏感组 G1 sensitive group | 48.38±8.53aabb | 166.25±87.16aa | 40.87±7.22 | 0.39±0.28 | 0.62±0.05aab | 0.71±0.05aab | 0.34±0.02 |
G1耐受组 G1 tolerant group | 44.75±6.50aa | 132.75±33.94 | 39.75±11.85 | 0.26±0.26 | 0.55±0.04c | 0.64±0.04acc | 0.33±0.03 |
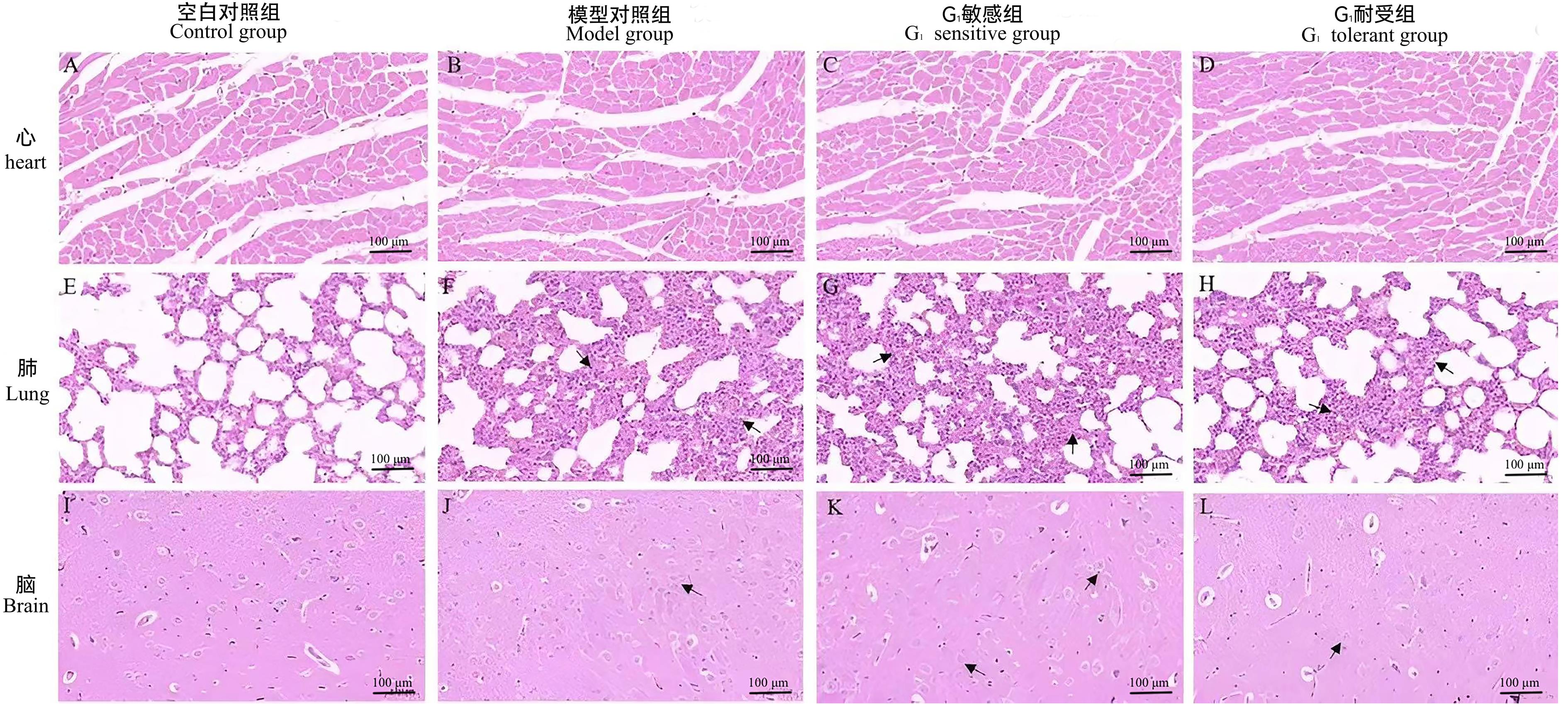
Figure 1 HE staining results of heart, lung, and brain tissue sections in rats (×40)Note: The scale bar in this figure is 0.1 mm. Black arrows in the sections of lung represent significant thickening in alveolar walls or infiltration with inflammatory cells. Black arrows in the sections of brain represent a slight disorder in the arrangement of hippocampal cells or cellular vacuolization.
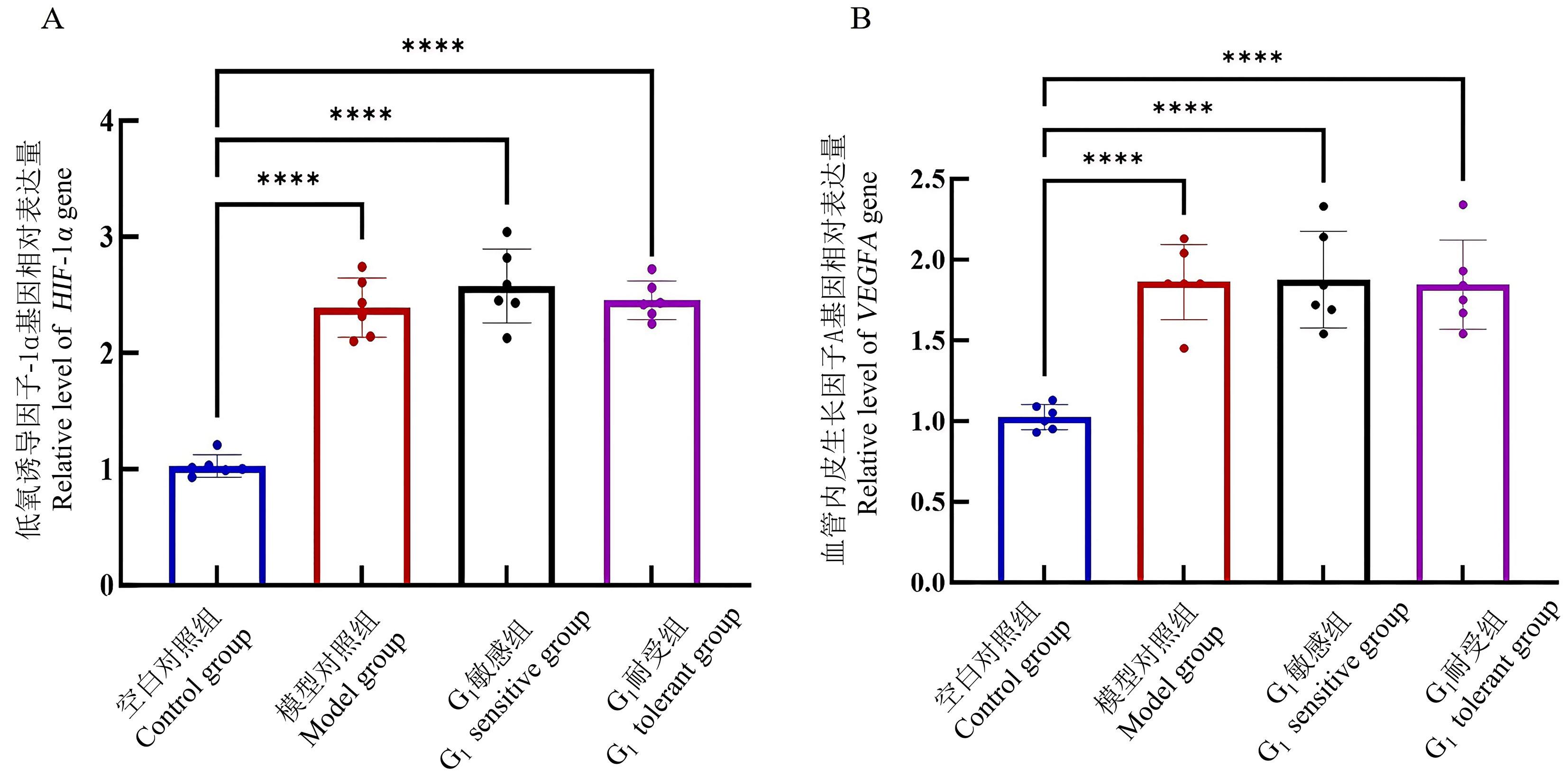
Figure 2 Expression levels of HIF-1 α gene (A) and VEGFA gene (B) in the brain of rats detected by real-time fluorescent quantitative PCRNote:HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; VEGFA, vascular endothelial growth factor A. Compared with control group, ****P<0.000 1.
| 1 | GUDBJARTSSON T, SIGURDSSON E, GOTTFREDSSON M, et al. High altitude illness and related diseases - a review[J]. Laeknabladid, 2019, 105(11):499-507. DOI: 10.17992/lbl.2019.11.257 . |
| 2 | WANG R, SUN Y H, YIN Q, et al. The effects of metronidazole on cytochrome P450 activity and expression in rats after acute exposure to high altitude of 4300m[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2017, 85:296-302. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.024 . |
| 3 | LI X, LI W B, FENG S L, et al. Research progress on mechanism in adaptation of hemoglobin to plateau hypoxia[J]. J Zhejiang Univ Med Sci, 2019, 48(6):674-681. DOI: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2019.12.13 . |
| 4 | WEI D B, WEI L N, LI X, et al. Effect of hypoxia on ldh-c expression in somatic cells of plateau pika[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2016, 13(8):773. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph13080773 . |
| 5 | 王萌. 虎杖苷对高原肺水肿模型大鼠的防治作用及其机制研究[D]. 西安: 第四军医大学, 2011. DOI:10.7666/d.d220369 . |
| WANG M. The protection and therapeutic effects of polydatin on experimental high altitude pulmonary edema model of rats and its mechanism[D]. Xi'an: Fourth Military Medical University, 2011. DOI:10.7666/d.d220369 . | |
| 6 | 霍妍. 槟榔多酚对高原肺水肿的预防作用研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021. |
| HUO Y. Study on the preventive effects of betelnut polyphenols on high altitude pulmonary edema[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2021. | |
| 7 | GRIMMINGER J, RICHTER M, TELLO K, et al. Thin air resulting in high pressure: mountain sickness and hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension[J]. Can Respir J, 2017, 2017:8381653. DOI: 10.1155/2017/8381653 . |
| 8 | DAVIS C, HACKETT P. Advances in the prevention and treatment of high altitude illness[J]. Emerg Med Clin North Am, 2017, 35(2):241-260. DOI: 10.1016/j.emc.2017.01.002 . |
| 9 | 李晨. 阿什旦牦牛 降生高原[J]. 中国农村科技, 2019(7):56-58. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9768.2019.07.019 . |
| LI C. Ashdan Yak: Born on the Plateau[J]. China Rural Sci Technol, 2019(7):56-58. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9768.2019.07.019 . | |
| 10 | 李晏军. 中国杂交水稻技术发展研究(1964~2010)[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2010. DOI:10.7666/d.Y1986663 . |
| LI Y J. A study on the advancement of hybrid rice technology in China (1964-2010)[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2010. DOI:10.7666/d.Y1986663 . | |
| 11 | JIA Z L, ZHAO X J, LIU X S, et al. Impacts of the plateau environment on the gut microbiota and blood clinical indexes in Han and Tibetan individuals[J]. mSystems, 2020, 5(1): e00660-e00619. DOI: 10.1128/mSystems.00660-19 . |
| 12 | LUO B F, WANG R, LI W B, et al. Pharmacokinetic changes of norfloxacin based on expression of MRP2 after acute exposure to high altitude at 4300m[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2017, 89:1078-1085. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha. 2017. 02.092 . |
| 13 | SUN H, YIN C Q, LIU Q, et al. Clinical significance of routine blood test-associated inflammatory index in breast cancer patients[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2017, 23:5090-5095. DOI: 10.12659/msm.906709 . |
| 14 | 常正义, 马迎教, 潘云, 等. 缺氧缺血性脑病患儿血常规结果分析及其临床意义[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2014, 35(4):394-395, 398. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2014.04.005 . |
| CHANG Z Y, MA Y J, PAN Y, et al. Analysis of the blood routine tests results and its clinical implications in patients with hypoxicischemic encephalopathy[J]. Int J Lab Med, 2014, 35(4):394-395, 398. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2014.04.005 . | |
| 15 | 王宁, 马慧萍, 武柠子, 等. 急性缺氧对大鼠部分生理病理变化的影响[J]. 中南药学, 2017, 15(7):883-888. DOI: 10.7539/j.issn.1672-2981.2017.07.005 . |
| WANG N, MA H P, WU N Z, et al. Effect of acute hypoxia on the physiological and pathological changes in rats[J]. Cent South Pharm, 2017, 15(7):883-888. DOI: 10.7539/j.issn.1672-2981.2017.07.005 . | |
| 16 | 次仁曲珍. 血生化指标检测对高原移居者出现高原病症状诊断的意义[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2016, 16(5):109-110.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-3141.2016.05.083 . |
| Cirenquzhen. Significance of blood biochemical index detection in the diagnosis of symptoms of altitude sickness in plateau migrants[J]. World Latest Med Inf, 2016, 16(5):109-110.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3141.2016.05.083 . | |
| 17 | WU D, YI Y, SUN F, et al. Effects of age and sex on the hematology and blood chemistry of Tibetan macaques (Macaca thibetana)[J]. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci, 2014, 53(1):12-17. |
| 18 | TANG B Z, QU Y, MU D Z. Research progress of hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha in hypoxic-ischemic injury[J]. Chin J Reparative Reconstr Surg, 2009, 23(6):755-758. |
| 19 | KE Q D, COSTA M. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1)[J]. Mol Pharmacol, 2006, 70(5):1469-1480. DOI: 10.1124/mol. 106. 027029 . |
| 20 | ROWLAND K J, YAO J J, WANG L D, et al. Up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha and hemodynamic responses following massive small bowel resection[J]. J Pediatr Surg, 2013, 48(6):1330-1339. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg. 2013.03.031 . |
| 21 | WANG Z W, CHEN L, HAO X R, et al. Elevated levels of interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-α and vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with knee articular cartilage injury[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2019, 7(11):1262-1269. DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i11.1262 . |
| [1] | YIN Yulian, MA Lina, TU Siyuan, CHEN Ling, YE Meina, CHEN Hongfeng. Establishment and Evaluation of a Rat Model of Non-Puerperal Mastitis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 587-596. |
| [2] | Bingxin XU, Kaijian FAN, Tingyu WANG, Huijin CHEN. Effect of Dexamethasone on Cartilage Degeneration in Rats with Collagen-induced Arthritis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2022, 42(5): 416-422. |
| [3] | WEI Jie, ZUO Qin, WANG Hong, LI Huan, ZHOU Jiaqi, GUANG Jiaona, FAN Tao, LIU Zuomin, FU Rui, YUE Bingfei. Population Genetic Quality Analysis of Microsatellite DNA in Wistar Rats Based on T/CALAS 21—2017 [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 528-534. |
| [4] | ZHANG Shuting, YAO Qingqing, LI Yishan, SHI Yiwei. Changes and Significance of Arterial Blood Gas Analysis Indexes in Rats with Chronic Hypoxic Pulmonary Hypertension [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2021, 41(1): 27-32. |
| [5] | LV Xiaojun, WU Sen, ZHANG Ju, XU Xiaoling, PAN Wangping, LI Hougang, WANG Pinghui, HE Kaiyong. Experimental Study on Establishment of Obesity Model in Rats Induced by High-Calorie Diet [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2020, 40(5): 374-. |
| [6] | DING Guang-yu, PAN Mian-li, HU Han, LIU Yi, SHEN Long-hai. Comparative Study on Iron Deficiency Anemia Rats Model by Three Different Formula Feeds [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2016, 36(6): 433-436. |
| [7] | XIAO Cheng-rong, TAN Hong-ling, MA Zeng-chun, WANG Yu-guang, WANG De-wen, SUN Jing-xiang, GAO Yue. Spontaneous Tumorigenesis, Hematological and Serum Biochemical Parameters of Senile Wistar Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2014, 34(4): 324-329. |
| [8] | XIA Chun-mei, DING Shuang-shuang,ZHANG Zhou. Establishment of Diabetic Nephropathy Model in Rat [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2002, 22(2): 78-82. |
| [9] | ZHOU Guang-Xing-1, YANG You-Ming-1, LI Xiao-Tian-2, SHI Hao-1, 吕Mei-Ming-1 , ZHAO Wei-Zhi-1, ZHU Ping-Shu-1. Experimental Studies on the Animal Model of Fetal Distress in Ewe [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 1998, 18(1): 1-5. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||