
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 314-322.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.189
• Animal Experimental Techniques and Methods • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ziyin XIA1( )(
)( ), Yuanyuan CHAI1, Yunxia XU1, Qinwei YU1, Xin HUANG1, Luyong ZHANG1,2(
), Yuanyuan CHAI1, Yunxia XU1, Qinwei YU1, Xin HUANG1, Luyong ZHANG1,2( )(
)( ), Zhenzhou JIANG1(
), Zhenzhou JIANG1( )(
)( )
)
Received:2022-12-14
Revised:2023-04-13
Online:2023-06-25
Published:2023-06-25
Contact:
Luyong ZHANG, Zhenzhou JIANG
CLC Number:
Ziyin XIA,Yuanyuan CHAI,Yunxia XU,et al. Quantification of Uric Acid of Rat Serum by Liquid Chromatography-ultraviolet Detection and Its Comparison Study[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 314-322. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.189.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.189
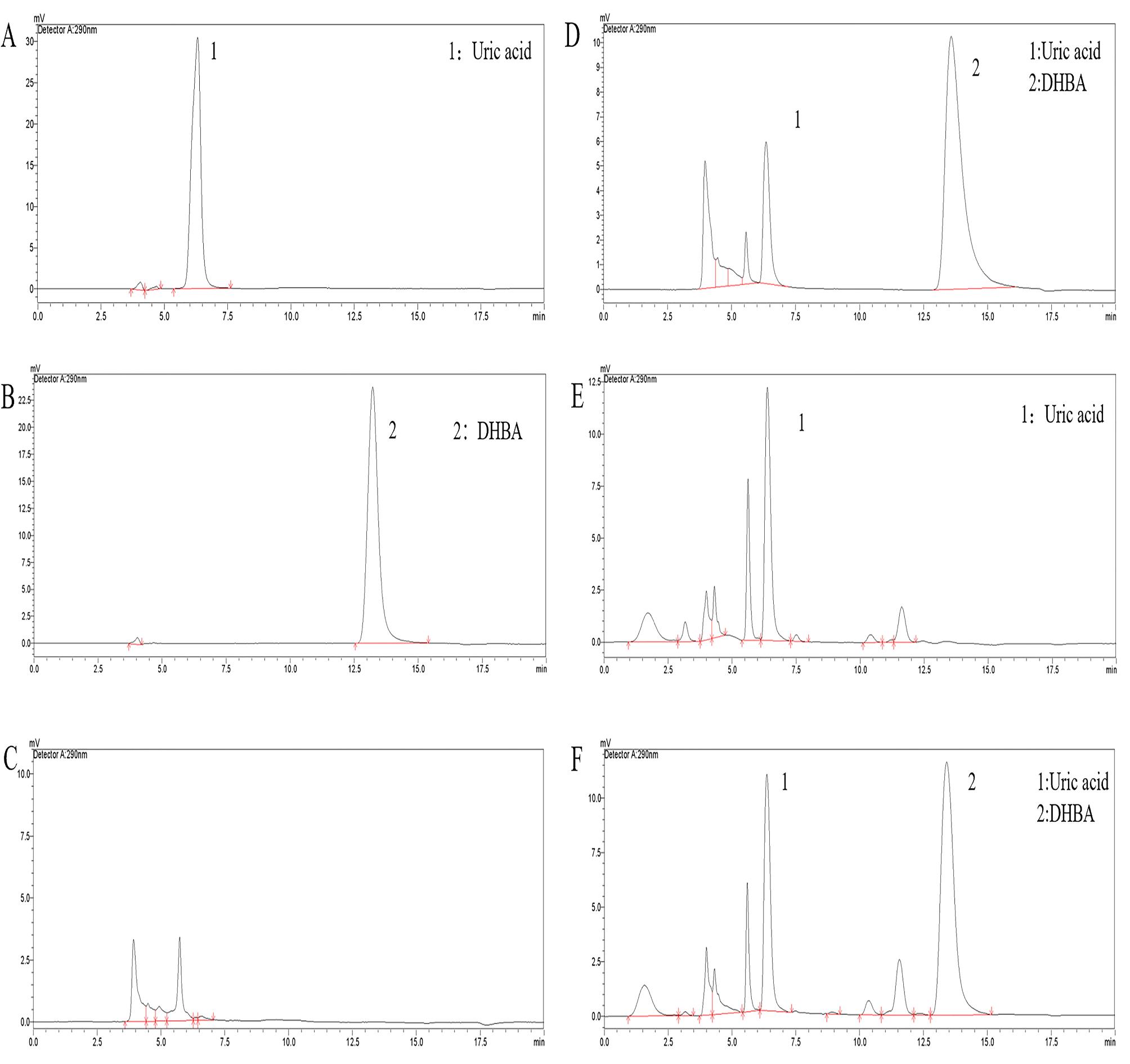
Figure 1 Chromatogram of uric acid specificity verificationNote: A, 10 μg/mL uric acid standard solution; B, 50 μg/mL DHBA (3,4-dihydroxybenzylamine hydrobromide ) standard solution; C, Blank biomatrix; D, Lower limit of quantitation sample; E, Rat serum (without internal standard) in the control group (intraperitoneal injection of an equal amount of 0.5% CMC-Na solution); F, Rat serum in the control group.
尿酸质量浓度 ρ/(μg·mL-1) | 批内准确度和精密度 Intra-A&P/% (n = 5) | 批间准确度和精密度 Inter-A&P/% (n = 15) | 提取回收率 Extraction recovery/% (n =5) | 稳定性 Stability (RE)/% | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RE | RSD | RE | RSD | RSD | 4 °C (n =5) | FTC (n = 5) | RT (n = 3) | -20 °C (n = 3) | -80 °C (n = 3) | ||||
| 10 | -1.99 | 2.42 | -3.67 | 5.07 | |||||||||
| 25 | -2.17 | 1.95 | -3.68 | 4.90 | 89.91±4.55 | 5.06 | -3.12 | -2.19 | -11.47 | -1.09 | -9.51 | ||
| 100 | 0.74 | 1.54 | 1.15 | 3.04 | 84.42±1.61 | 1.90 | -2.48 | -2.23 | -6.85 | -5.01 | -14.51 | ||
| 160 | 2.21 | 0.52 | -0.56 | 3.67 | 83.12±5.63 | 6.77 | -5.46 | -4.57 | -8.41 | -6.74 | -12.76 | ||
Table 1 Intra- and inter-batch accuracy and precision, extraction recovery and stability test of uric acid determination
尿酸质量浓度 ρ/(μg·mL-1) | 批内准确度和精密度 Intra-A&P/% (n = 5) | 批间准确度和精密度 Inter-A&P/% (n = 15) | 提取回收率 Extraction recovery/% (n =5) | 稳定性 Stability (RE)/% | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RE | RSD | RE | RSD | RSD | 4 °C (n =5) | FTC (n = 5) | RT (n = 3) | -20 °C (n = 3) | -80 °C (n = 3) | ||||
| 10 | -1.99 | 2.42 | -3.67 | 5.07 | |||||||||
| 25 | -2.17 | 1.95 | -3.68 | 4.90 | 89.91±4.55 | 5.06 | -3.12 | -2.19 | -11.47 | -1.09 | -9.51 | ||
| 100 | 0.74 | 1.54 | 1.15 | 3.04 | 84.42±1.61 | 1.90 | -2.48 | -2.23 | -6.85 | -5.01 | -14.51 | ||
| 160 | 2.21 | 0.52 | -0.56 | 3.67 | 83.12±5.63 | 6.77 | -5.46 | -4.57 | -8.41 | -6.74 | -12.76 | ||
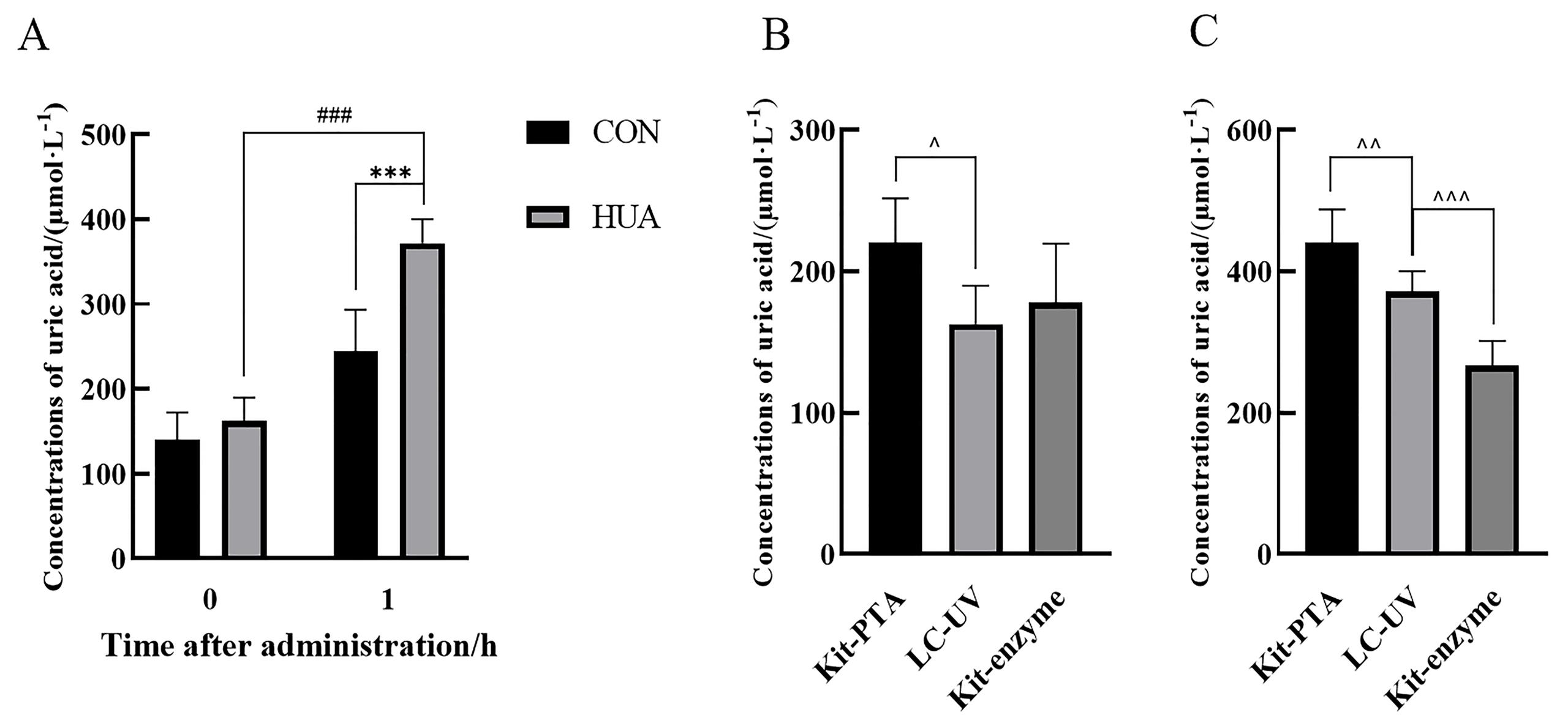
Figure 3 Determination of serum uric acid concentrations in rats before and 1 h after administrationNote:(A) LC-UV method was used to detect the serum uric acid concentration of rats in the two groups before and 1 h after administration (CON, control group administered 0.5% CMC-Na solution; HUA, hyperuricemia group administered 300 mg/kg potassium oxyzate). Compared with the CON group, ???P<0.00 1; Compared to before administration, ###P<0.001. n = 6). (B-C) Serum uric acid concentration was measured using three methods before and 1 h after administration (LC-UV, liquid chromatography-ultraviolet; Kit-PTA, phosphotungstic acid method Kit; Kit-enzyme, uricase method Kit. Compared with LC-UV, ^P<0.05, ^^P<0.01, ^^^P<0.00 1. n = 6).
取样时间/h Time/h | 加样质量浓度/(μg·mL-1) ρ/(μg·mL-1) | 加样回收率/% Recovery of spiked samples/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC-UV | 磷钨酸法 Kit-PTA | 尿酸酶法 Kit-enzyme | ||
| 0a | 10 | 99.97±6.86 | 118.83±21.22 | 60.05±11.2 |
| 25 | 95.90±4.54 | 117.90±8.48 | 84.31±4.31 | |
| 1a | 10 | 98.18±3.23 | 125.00±5.34 | 27.37±8.62 |
| 25 | 99.64±0.99 | 112.96±3.85 | 43.55±5.38 | |
Table 2 Comparison of the spiked recovery of LC-UV method and commercially available kits
取样时间/h Time/h | 加样质量浓度/(μg·mL-1) ρ/(μg·mL-1) | 加样回收率/% Recovery of spiked samples/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC-UV | 磷钨酸法 Kit-PTA | 尿酸酶法 Kit-enzyme | ||
| 0a | 10 | 99.97±6.86 | 118.83±21.22 | 60.05±11.2 |
| 25 | 95.90±4.54 | 117.90±8.48 | 84.31±4.31 | |
| 1a | 10 | 98.18±3.23 | 125.00±5.34 | 27.37±8.62 |
| 25 | 99.64±0.99 | 112.96±3.85 | 43.55±5.38 | |
检测方法 Method | 原理 Principle | 特点 Features | 局限性 Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
磷钨酸法 Phosphotungstic acid method | 尿酸在碱性溶液中与磷钨酸反应,生成尿囊素、二氧化碳和钨蓝,钨蓝的生成量与尿酸含量成正比 | 操作简单,检测时间短,成本低,可用于自动化分析 | 特异性差,准确度低,检测结果易受血清中其他还原性物质影响 |
液相色谱-紫外检测法 LC-UV | 溶于流动相中的各组分经过固定相时,由于与固定相发生作用的大小不同,导致其保留时间不同 | 专属性强,准确度高,线性范围广,色谱柱可反复使用 | 成本较高、检测时间较长 |
尿酸酶法 Uricase method | 尿酸在尿酸酶的作用下生成尿囊素、二氧化碳和过氧化氢,过氧化氢与显色剂反应显色 | 操作简单,检测时间短,成本低,可用于自动化分析 | 尿酸酶的活性易被血清中氧嗪酸钾抑制,准确度低 |
Table 3 Comparison of liquid chromatography-ultraviolet (LC-UV) method with phosphotungstic acid method and uricase method for determining serum uric acid
检测方法 Method | 原理 Principle | 特点 Features | 局限性 Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
磷钨酸法 Phosphotungstic acid method | 尿酸在碱性溶液中与磷钨酸反应,生成尿囊素、二氧化碳和钨蓝,钨蓝的生成量与尿酸含量成正比 | 操作简单,检测时间短,成本低,可用于自动化分析 | 特异性差,准确度低,检测结果易受血清中其他还原性物质影响 |
液相色谱-紫外检测法 LC-UV | 溶于流动相中的各组分经过固定相时,由于与固定相发生作用的大小不同,导致其保留时间不同 | 专属性强,准确度高,线性范围广,色谱柱可反复使用 | 成本较高、检测时间较长 |
尿酸酶法 Uricase method | 尿酸在尿酸酶的作用下生成尿囊素、二氧化碳和过氧化氢,过氧化氢与显色剂反应显色 | 操作简单,检测时间短,成本低,可用于自动化分析 | 尿酸酶的活性易被血清中氧嗪酸钾抑制,准确度低 |
| 1 | 孙琳, 王桂侠, 郭蔚莹. 高尿酸血症研究进展[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2017, 37(4):1034-1038. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2017.04.112 . |
| SUN L, WANG G X, GUO W Y. Research progress of hyperuricemia[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2017, 37(4):1034-1038. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2017.04.112 . | |
| 2 | FATHALLAH-SHAYKH S A, CRAMER M T. Uric acid and the kidney[J]. Pediatr Nephrol, 2014, 29(6):999-1008. DOI: 10.1007/s00467-013-2549-x . |
| 3 | XU C F, YU C H, XU L, et al. High serum uric acid increases the risk for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a prospective observational study[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(7): e11578. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011578 . |
| 4 | LIU J, XU C F, YING L M, et al. Relationship of serum uric acid level with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its inflammation progression in non-obese adults[J]. Hepatol Res, 2017, 47(3): E104-E112. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12734 . |
| 5 | PERTICONE M, TRIPEPI G, MAIO R, et al. Risk reclassification ability of uric acid for cardiovascular outcomes in essential hypertension[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2017, 243:473-478. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.05.051 . |
| 6 | PRASAD M, MATTESON E L, HERRMANN J, et al. Uric acid is associated with inflammation, coronary microvascular dysfunction, and adverse outcomes in postmenopausal women[J]. Hypertension, 2017, 69(2):236-242. DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.08436 . |
| 7 | KUBOTA Y, MCADAMS-DEMARCO M, FOLSOM A R. Serum uric acid, gout, and venous thromboembolism: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study[J]. Thromb Res, 2016, 144:144-148. DOI: 10.1016/j.thromres.2016.06.020 . |
| 8 | KANBAY M, JENSEN T, SOLAK Y, et al. Uric acid in metabolic syndrome: from an innocent bystander to a central player[J]. Eur J Intern Med, 2016, 29:3-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejim.2015.11.026 . |
| 9 | SHARAF EL DIN U A A, SALEM M M, ABDULAZIM D O. Uric acid in the pathogenesis of metabolic, renal, and cardiovascular diseases: a review[J]. J Adv Res, 2017, 8(5):537-548. DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2016.11.004 . |
| 10 | BORGHI C, AGABITI-ROSEI E, JOHNSON R J, et al. Hyperuricaemia and gout in cardiovascular, metabolic and kidney disease[J]. Eur J Intern Med, 2020, 80:1-11. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejim.2020.07.006 . |
| 11 | 周子正, 徐琳, 高建东. 高尿酸血症动物模型研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2020, 26(8): 1462-1466. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2020.08.002 . |
| ZHOU Z Z, XU L, GAO J D. Research progress of hyperuricemia animal model[J]. Med Recapitul, 2020, 26(8): 1462-1466. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2020.08.002 . | |
| 12 | 王璟. 检测血尿酸的方法比较及进展[J]. 糖尿病临床, 2014, 8(8):362-363. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7851.2014.08.005 . |
| WANG J. Comparison and progress of methods for detecting serum uric acid[J]. Clin J Diabetes World, 2014, 8(8):362-363. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7851.2014.08.005 . | |
| 13 | WANG Q W, WEN X, KONG J M. Recent progress on uric acid detection: a review[J]. Crit Rev Anal Chem, 2020, 50(4):359-375. DOI: 10.1080/10408347.2019.1637711 . |
| 14 | GUMUSTAS M, KURBANOGLU S, USLU B, et al. UPLC versus HPLC on drug analysis: advantageous, applications and their validation parameters[J]. Chromatographia, 2013, 76(21):1365-1427. DOI: 10.1007/s10337-013-2477-8 . |
| 15 | WEN S S, ZHANG Z X, CHEN X P, et al. An improved UPLC method for determining uric acid in rat serum and comparison study with commercial colorimetric kits[J]. Acta Chromatogr, 2019, 31(3):201-205. DOI: 10.1556/1326.2018.00449 . |
| 16 | 江民川, 赵阳, 马芳芳, 等. 尿酸检测方法的研究进展[J]. 化工科技, 2021, 29(3):75-79. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0511.2021.03.014 |
| JIANG M C, ZHAO Y, MA F F, et al. Research progress on uric acid detection methods[J]. Sci Technol Chem Ind, 2021, 29(3):75-79. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0511.2021.03.014 . | |
| 17 | ZHAO J X. A simple, rapid and reliable high performance liquid chromatography method for the simultaneous determination of creatinine and uric acid in plasma and urine[J]. Anal Methods, 2013, 5(23):6781-6787. DOI: 10.1039/C3AY41061G . |
| 18 | BUSZEWSKI B, NOGA S. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC)—a powerful separation technique[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2012, 402(1):231-247. DOI: 10.1007/s00216-011-5308-5 . |
| 19 | 张海晨, 李水军, 孙贺伟, 等. 液相色谱-串联质谱法测定尿酸及与常规检测方法的比较[J]. 检验医学, 2015, 30(5):422-426. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8640.2015.05.004 . |
| ZHANG H C, LI S J, SUN H W, et al. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for uric acid and its comparison with clinical routine determination method[J]. Lab Med, 2015, 30(5):422-426. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8640.2015.05.004 . | |
| 20 | 刘旭圆, 商倩, 李川, 等. HPLC法用于小鼠高尿酸模型中血尿酸测定及相关药物评价[J]. 药物评价研究, 2017, 40(3):319-323. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2017.03.006 . |
| LIU X Y, SHANG Q, LI C, et al. HPLC method for determination of uric acid in plasma of hyperuricemia model mice[J]. Drug Eval Res, 2017, 40(3):319-323. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2017.03.006 . | |
| 21 | MCCALLEY D V. Managing the column equilibration time in hydrophilic interaction chromatography[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2020, 1612:460655. DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460655 . |
| [1] | QIN Chao, LI Shuangxing, ZHAO Tingting, JIANG Chenchen, ZHAO Jing, YANG Yanwei, LIN Zhi, WANG Sanlong, WEN Hairuo. Study on the 90-day Feeding Experimental Background Data of SD Rats for Drug Safety Evaluation [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 439-448. |
| [2] | LIU Liyu, JI Bo, LIU Xiaoxuan, FANG Yang, ZHANG Ling, GUO Tingting, QUAN Ye, LI Hewen, LIU Yitian. Exploration of Rat Fetal Lung Tissue Fixation Methods [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 432-438. |
| [3] | LIU Zhiwei, YANG Ran, LIAN Hao, ZHANG Yu, JIN Lilun. Cartilage Protection and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fraxetin on Monosodium Iodoacetate-Induced Rat Model of Osteoarthritis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 259-268. |
| [4] | JIANG Meng, HAO Shulan, TONG Liguo, ZHONG Qiming, GAO Zhenfei, WANG Yonghui, WANG Xixing, JI Haijie. Dynamic Evaluation of Vinorelbine-Induced Phlebitis of Dorsalis Pedis Vein in a Rat Model [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 251-258. |
| [5] | PAN Yicong, JIANG Wenhong, HU Ming, QIN Xiao. Optimization of Surgical Procedure and Efficacy Evaluation of Aortic Calcification Model in Rats with Chronic Kidney Disease [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 279-289. |
| [6] | LIAN Hui, JIANG Yanling, LIU Jia, ZHANG Yuli, XIE Wei, XUE Xiaoou, LI Jian. Construction and Evaluation of a Rat Model of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(2): 130-146. |
| [7] | YIN Yulian, MA Lina, TU Siyuan, CHEN Ling, YE Meina, CHEN Hongfeng. Establishment and Evaluation of a Rat Model of Non-Puerperal Mastitis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 587-596. |
| [8] | YANG Jin, YU Shiya, LIN Nan, FANG Yongchao, ZHAO Hu, QIU Jinwei, LIN Hongming, CHEN Huiyan, WANG Yu, WU Weihang. Effect of Modified Duodenal Exclusion Surgery on Glucose Metabolism in Rats with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 523-530. |
| [9] | QI Longju, CHEN Shiyuan, LIAO Zehua, SHI Yuanhu, SUN Yuyu, WANG Qinghua. Transcriptomic Analysis of Menstrual Blood-Derived Stem Cells Transplantation Combined with Exercise Training in Promoting Spinal Cord Injury Recovery in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 531-542. |
| [10] | ZHANG Naiqun, YUAN Piaopiao, CAO Linrong, YING Na, YANG Taotao. Application of PNR Detection in the Diagnosis and Drug-efficacy Evaluation of Diabetic Kidney Disease in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 543-549. |
| [11] | ZHENG Yiqing, DENG Yasheng, FAN Yanping, LIANG Tianwei, HUANG Hui, LIU Yonghui, NI Zhaobing, LIN Jiang. Application Analysis of Animal Models for Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Based on Data Mining [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 405-418. |
| [12] | XIAO Pan, WANG Hongyi, LU Lu, ZHANG Mei, CHEN Keming, SHEN Dongshuai, NIU Tingxian. Screening of Hypoxia-Sensitive and Hypoxia-Tolerant Wistar Rats and Preliminary Exploration of Hypoxia Sensitivity in Their G1 Generation [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(4): 374-383. |
| [13] | Xiaoyu ZHU, Hantao YUAN, Sibo LI. MicroRNA-887-3p Inhibited MDM4 Expression and Proliferation but Promoted Apoptosis of Intervertebral Disc Annulus Fibrosus Cells in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 270-278. |
| [14] | Fangqi BAO, Haiye TU, Mingsun FANG, Qian ZHANG, Minli CHEN. Advances in Research on Pathological and Molecular Mechanism of Hyperuricemic Nephropathy Based on Animal Models [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 180-191. |
| [15] | Jinhua HU, Jingjie HAN, Min JIN, Bin HU, Yuefen LOU. Effects of Puerarin on Bone Density in Rats and Mice: A Meta-analysis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(2): 149-161. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||