
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 663-675.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.147
• Invertebrate Laboratory Animal: Fruit fly • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2025-09-05
Revised:2025-12-03
Online:2025-12-25
Published:2025-12-19
Contact:
WANG Fei
CLC Number:
DENG Xianming,WANG Fei. Research Progress on Drosophila Electron Microscopy Connectome Database and Functional Analysis of Related Neural Circuits[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 663-675. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.147.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2025.147
数据库 Databases | 访问网页 Web accesses | 注释情况 Annotation notes | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|
一龄幼虫中枢神经系统电子显微镜连接组 (L1 CNS) L1 larval central nervous system (CNS) electron microscopy connectome | https://l1em.catmaid.virtualflybrain.org | 人工追踪所有神经元,共3 016个神经元 | [ |
成年雌蝇全脑电子显微镜连接组 (FAFB) Female full adult fly brain electron microscopy connectome | https://fafb.catmaid.virtualflybrain.org | 稀疏注释数据库 | [ |
FAFB的FlyWire完整注释版 FlyWire fully-annotated version of FAFB | https://codex.flywire.ai/ dataset=fafb | 密集注释数据库,共139 255个神经元 | [ |
成年雌蝇半脑电子显微镜连接组 (Hemibrain) Female adult fly hemibrain electron microscopy connectome | https://neuprint.janelia.org | 密集注释数据库,共约25 000个神经元 | [ |
成年雌蝇腹神经索电子显微镜连接组 (FANC) Female adult fly nerve cord electron microscopy connectome | https://fanc.catmaid.virtualflybrain.org | 密集注释数据库,共约14 600个神经元 | [ |
成年雄蝇腹神经索电子显微镜连接组 (MANC) Male adult fly nerve cord electron microscopy connectome | https://neuprint.janelia.org https://codex.flywire.ai/ dataset=manc | 密集注释数据库,共约23 000个神经元 | [ |
成年雌蝇脑及神经索电子显微镜连接组 (BANC) Female adult fly brain and nerve cord electron microscopy connectome | https://codex.flywire.ai/ dataset=banc | 密集注释数据库,共约115 151个神经元 | [ |
成年雄蝇中枢神经系统电子显微镜连接组 (maleCNS) Male adult fly CNS electron microscopy connectome | https://male-cns.janelia.org https://neuprint.janelia.org | 密集注释数据库,共约166 000个神经元 | [ |
Table 1 Resource information of Drosophila melanogaster electron microscopy connectome database
数据库 Databases | 访问网页 Web accesses | 注释情况 Annotation notes | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|
一龄幼虫中枢神经系统电子显微镜连接组 (L1 CNS) L1 larval central nervous system (CNS) electron microscopy connectome | https://l1em.catmaid.virtualflybrain.org | 人工追踪所有神经元,共3 016个神经元 | [ |
成年雌蝇全脑电子显微镜连接组 (FAFB) Female full adult fly brain electron microscopy connectome | https://fafb.catmaid.virtualflybrain.org | 稀疏注释数据库 | [ |
FAFB的FlyWire完整注释版 FlyWire fully-annotated version of FAFB | https://codex.flywire.ai/ dataset=fafb | 密集注释数据库,共139 255个神经元 | [ |
成年雌蝇半脑电子显微镜连接组 (Hemibrain) Female adult fly hemibrain electron microscopy connectome | https://neuprint.janelia.org | 密集注释数据库,共约25 000个神经元 | [ |
成年雌蝇腹神经索电子显微镜连接组 (FANC) Female adult fly nerve cord electron microscopy connectome | https://fanc.catmaid.virtualflybrain.org | 密集注释数据库,共约14 600个神经元 | [ |
成年雄蝇腹神经索电子显微镜连接组 (MANC) Male adult fly nerve cord electron microscopy connectome | https://neuprint.janelia.org https://codex.flywire.ai/ dataset=manc | 密集注释数据库,共约23 000个神经元 | [ |
成年雌蝇脑及神经索电子显微镜连接组 (BANC) Female adult fly brain and nerve cord electron microscopy connectome | https://codex.flywire.ai/ dataset=banc | 密集注释数据库,共约115 151个神经元 | [ |
成年雄蝇中枢神经系统电子显微镜连接组 (maleCNS) Male adult fly CNS electron microscopy connectome | https://male-cns.janelia.org https://neuprint.janelia.org | 密集注释数据库,共约166 000个神经元 | [ |
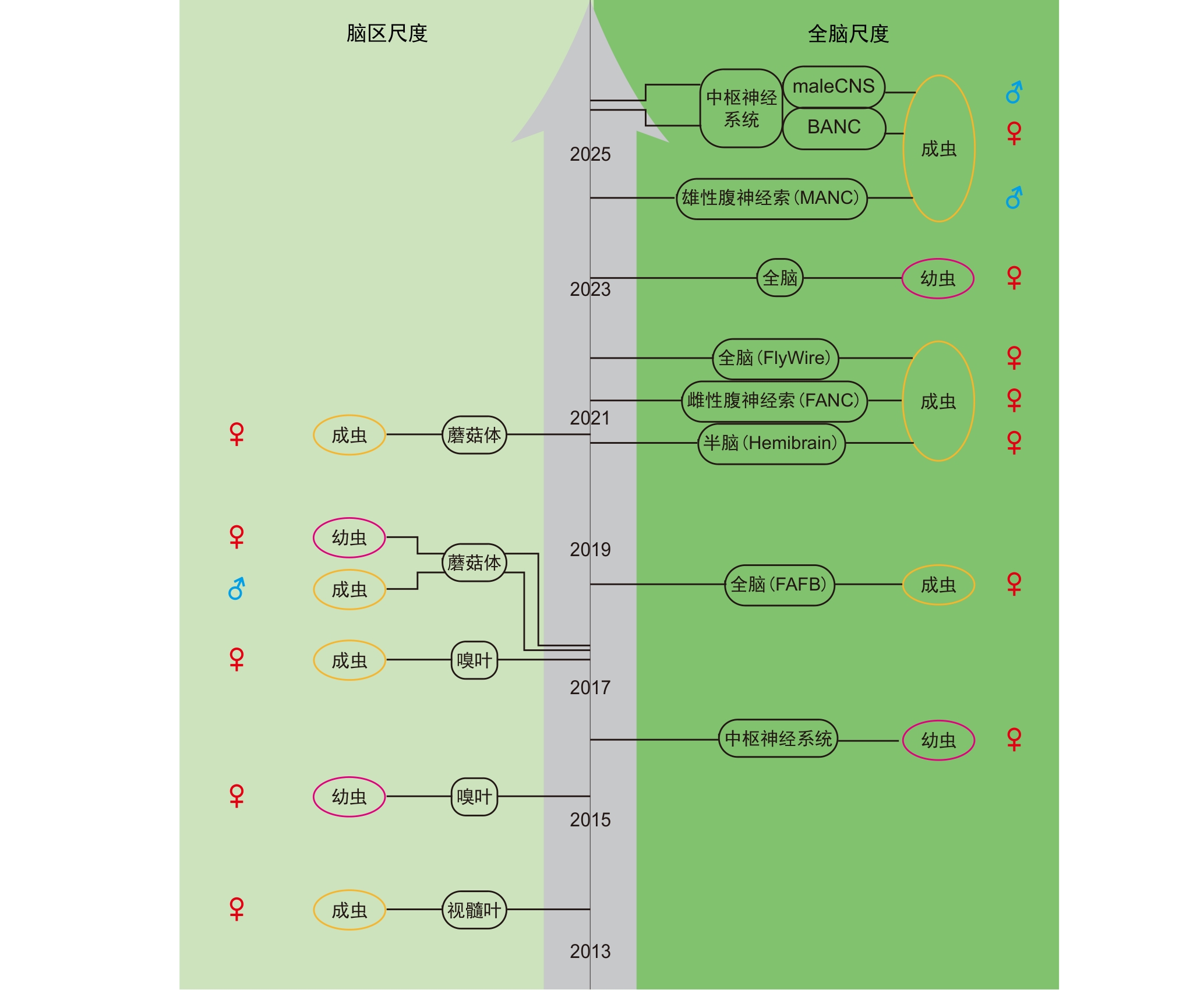
Figure 1 Development history of Drosophila melanogaster electron microscopy connectome databaseNote: Black circular frames indicate various electron microscopy connectome datasets of Drosophila melanogaster at the brain region scale (left) and the whole brain scale (right). FAFB, female full adult fly brain electron microscopy connectome; Hemibrain, female adult fly hemibrain electron microscopy connectome; FANC, female adult fly nerve cord electron microscopy connectome; MANC, male adult fly nerve cord electron microscopy connectome; BANC, female adult fly brain and nerve cord electron microscopy connectome; maleCNS, male adult fly CNS electron microscopy connectome.
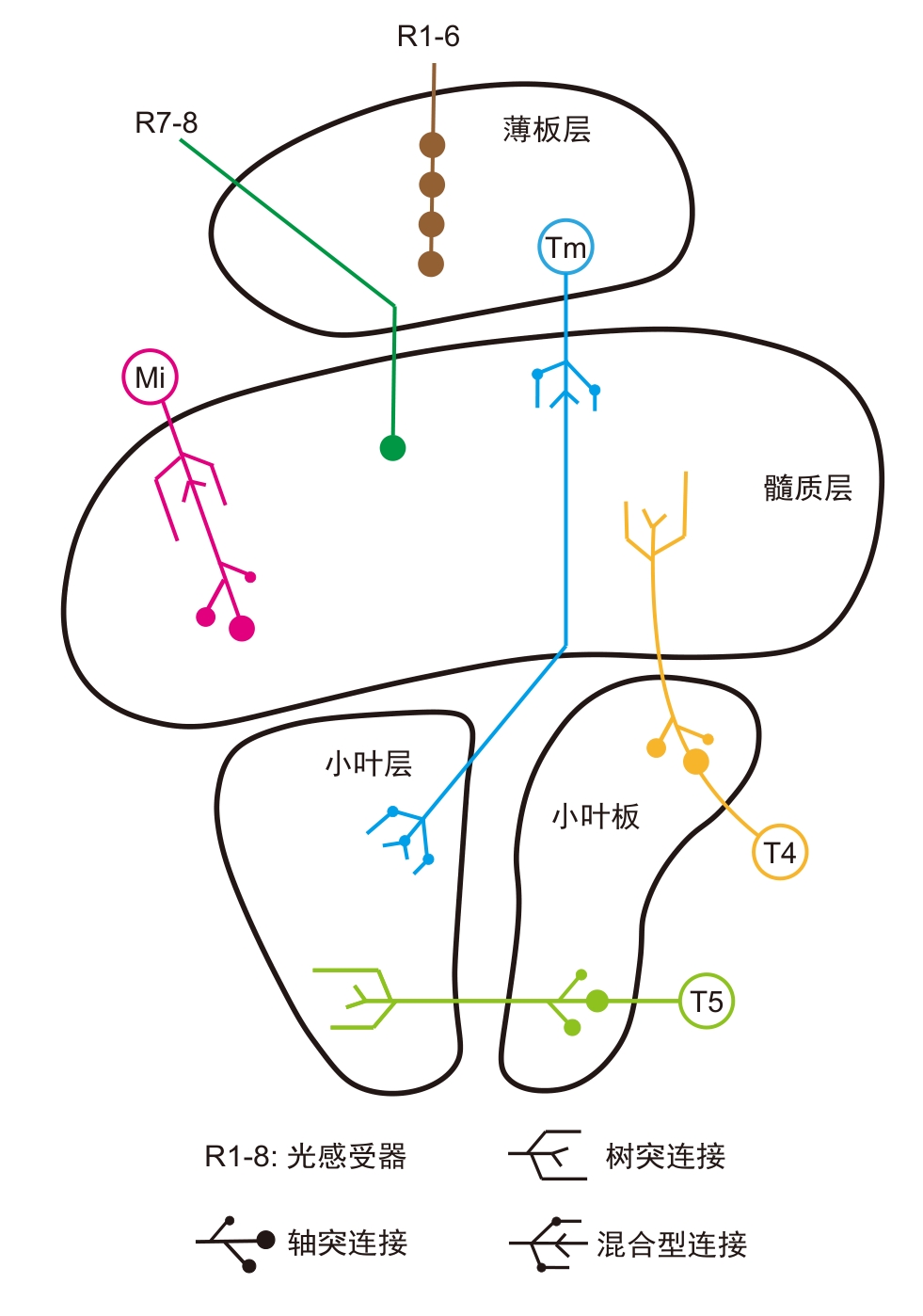
Figure 2 Structure of Drosophila melanogaster optic lobe and types of visual neurons related to motion detection and color perception (adapted from reference [55])
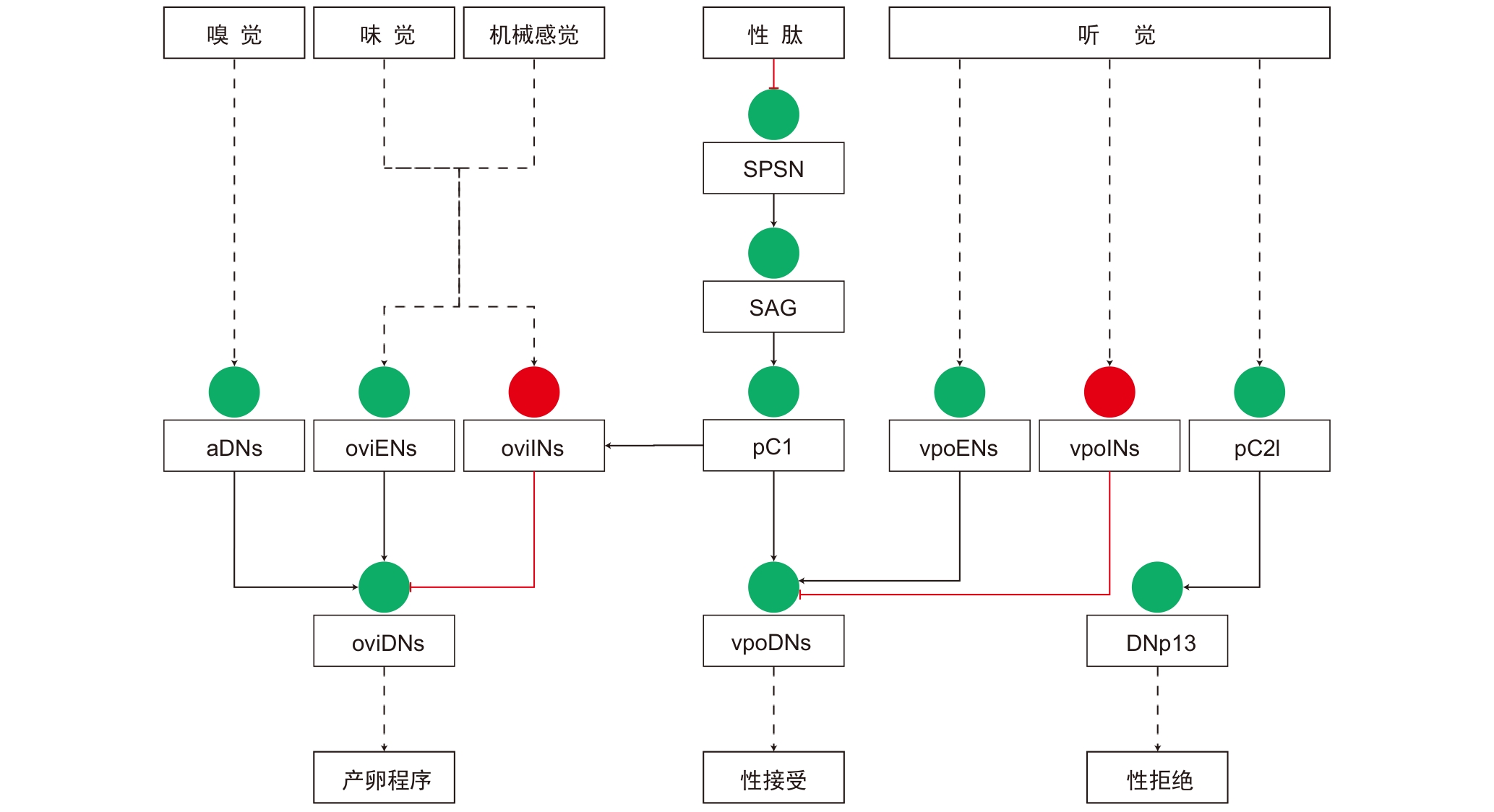
Figure 3 Neural circuits of mating and egg-laying decisions in female DrosophilaNote: Solid lines indicate monosynaptic connections, while dashed lines indicate polysynaptic connections. Red circles and red lines represent inhibitory neurons and connections, respectively. Green circles and black lines represent excitatory neurons and connections, respectively. SPSN, sex peptide sensory neuron; SAG, sex peptide abdominal ganglion neuron; pC1, pC1 interneurons; pC2l, pC2l interneurons; aDNs, anterior dorsal neurons; oviENs, oviposition excitatory neurons; oviINs, oviposition inhibitory neurons; oviDNs, oviposition descending neurons; vpoENs, vaginal plate opening excitatory neurons; vpoINs, vaginal plate opening inhibitory neurons; vpoDNs, vaginal plate opening descending neurons; DNp13, descending neurons 13 on the posterior surface of the brain.
| [1] | SCHLEGEL P, YIN Y J, BATES A S, et al. Whole-brain annotation and multi-connectome cell typing of Drosophila [J]. Nature, 2024, 634(8032):139-152. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07686-5 . |
| [2] | ASINOF S K, CARD G M. Neural control of naturalistic behavior choices[J]. Annu Rev Neurosci, 2024, 47(1): 369-388. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-111020-094019 . |
| [3] | PAREKH R, ASCOLI G A. Neuronal morphology goes digital: a research hub for cellular and system neuroscience[J]. Neuron, 2013, 77(6):1017-1038. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013. 03.008 . |
| [4] | FEINBERG E H, VANHOVEN M K, BENDESKY A, et al. GFP Reconstitution Across Synaptic Partners (GRASP) defines cell contacts and synapses in living nervous systems[J]. Neuron, 2008, 57(3):353-363. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007. 11.030 . |
| [5] | LILLVIS J L, OTSUNA H, DING X Y, et al. Rapid reconstruction of neural circuits using tissue expansion and light sheet microscopy[J]. eLife, 2022, 11: e81248. DOI: 10.7554/eLife. 81248 . |
| [6] | LICHTMAN J W, SANES J R. Ome sweet ome: what can the genome tell us about the connectome?[J]. Curr Opin Neurobiol, 2008, 18(3): 346-353. DOI: 10.1016/j.conb. 2008. 08.010 . |
| [7] | SCHNEIDER-MIZELL C M, GERHARD S, LONGAIR M, et al. Quantitative neuroanatomy for connectomics in Drosophila [J]. eLife, 2016, 5: e12059. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.12059 . |
| [8] | CARDONA A, SAALFELD S, PREIBISCH S, et al. An integrated micro- and macroarchitectural analysis of the Drosophila brain by computer-assisted serial section electron microscopy[J]. PLoS Biol, 2010, 8(10): e1000502. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000502 . |
| [9] | LEE T J, KUMAR A, BALWANI A H, et al. Large-scale neuroanatomy using LASSO: loop-based automated serial sectioning operation[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(10): e0206172. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206172 . |
| [10] | SULOWAY C, PULOKAS J, FELLMANN D, et al. Automated molecular microscopy: the new Leginon system[J]. J Struct Biol, 2005, 151(1):41-60. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsb.2005.03.010 . |
| [11] | LU Z Y, XU C S, HAYWORTH K J, et al. En bloc preparation of Drosophila brains enables high-throughput FIB-SEM connectomics[J]. Front Neural Circuits, 2022, 16:917251. DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2022.917251 . |
| [12] | PLAZA S M, CLEMENTS J, DOLAFI T, et al. neuPrint: an open access tool for EM connectomics[J]. Front Neuroinform, 2022, 16:896292. DOI: 10.3389/fninf.2022.896292 . |
| [13] | DORKENWALD S, MCKELLAR C E, MACRINA T, et al. FlyWire: online community for whole-brain connectomics[J]. Nat Methods, 2022, 19(1):119-128. DOI: 10.1038/s41592-021-01330-0 . |
| [14] | DORKENWALD S, SCHNEIDER-MIZELL C M, BRITTAIN D, et al. CAVE: connectome annotation versioning engine[J]. Nat Methods, 2025, 22(5):1112-1120. DOI: 10.1038/s41592-024-02426-z . |
| [15] | CARDONA A, SAALFELD S, SCHINDELIN J, et al. TrakEM2 software for neural circuit reconstruction[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(6): e38011. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038011 . |
| [16] | BATES A S, MANTON J D, JAGANNATHAN S R, et al. The natverse, a versatile toolbox for combining and analysing neuroanatomical data[J]. eLife, 2020, 9: e53350. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.53350 . |
| [17] | SAALFELD S, CARDONA A, HARTENSTEIN V, et al. CATMAID: collaborative annotation toolkit for massive amounts of image data[J]. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25(15):1984-1986. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp266 . |
| [18] | ECKSTEIN N, BATES A S, CHAMPION A, et al. Neurotransmitter classification from electron microscopy images at synaptic sites in Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Cell, 2024, 187(10):2574-2594.e23. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.03.016 . |
| [19] | BUHMANN J, SHERIDAN A, MALIN-MAYOR C, et al. Automatic detection of synaptic partners in a whole-brain Drosophila electron microscopy data set[J]. Nat Methods, 2021, 18(7):771-774. DOI: 10.1038/s41592-021-01183-7 . |
| [20] | TAKEMURA S Y, BHARIOKE A, LU Z Y, et al. A visual motion detection circuit suggested by Drosophila connectomics[J]. Nature, 2013, 500(7461):175-181. DOI: 10.1038/nature12450 . |
| [21] | TAKEMURA S Y, XU C S, LU Z Y, et al. Synaptic circuits and their variations within different columns in the visual system of Drosophila [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2015, 112(44):13711-13716. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1509820112 . |
| [22] | OHYAMA T, SCHNEIDER-MIZELL C M, FETTER R D, et al. A multilevel multimodal circuit enhances action selection in Drosophila [J]. Nature, 2015, 520(7549):633-639. DOI: 10.1038/nature14297 . |
| [23] | BERCK M E, KHANDELWAL A, CLAUS L, et al. The wiring diagram of a glomerular olfactory system[J]. eLife, 2016, 5: e14859. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.14859 . |
| [24] | SCHLEGEL P, TEXADA M J, MIROSCHNIKOW A, et al. Synaptic transmission parallels neuromodulation in a central food-intake circuit[J]. eLife, 2016, 5: e16799. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.16799 . |
| [25] | TOBIN W F, WILSON R I, LEE W A. Wiring variations that enable and constrain neural computation in a sensory microcircuit[J]. eLife, 2017, 6: e24838. DOI: 10.7554/eLife. 24838 . |
| [26] | TAKEMURA S Y, ASO Y, HIGE T, et al. A connectome of a learning and memory center in the adult Drosophila brain[J]. eLife, 2017, 6: e26975. DOI: 10.7554/elife.26975 . |
| [27] | EICHLER K, LI F, LITWIN-KUMAR A, et al. The complete connectome of a learning and memory centre in an insect brain[J]. Nature, 2017, 548(7666):175-182. DOI: 10.1038/nature 23455 . |
| [28] | GERHARD S, ANDRADE I, FETTER R D, et al. Conserved neural circuit structure across Drosophila larval development revealed by comparative connectomics[J]. eLife, 2017, 6: e29089. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.29089 . |
| [29] | ZHENG Z H, LAURITZEN J S, PERLMAN E, et al. A complete electron microscopy volume of the brain of adult Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Cell, 2018, 174(3):730-743.e22. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.06.019 . |
| [30] | SCHEFFER L K, XU C S, JANUSZEWSKI M, et al. A connectome and analysis of the adult Drosophila central brain[J]. eLife, 2020, 9: e57443. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.57443 . |
| [31] | MAISAK M S, HAAG J, AMMER G, et al. A directional tuning map of Drosophila elementary motion detectors[J]. Nature, 2013, 500(7461):212-216. DOI: 10.1038/nature12320 . |
| [32] | WINDING M, PEDIGO B D, BARNES C L, et al. The connectome of an insect brain[J]. Science, 2023, 379(6636): eadd9330. DOI: 10.1126/science.add9330 . |
| [33] | LIN A, YANG R Z, DORKENWALD S, et al. Network statistics of the whole-brain connectome of Drosophila [J]. Nature, 2024, 634(8032):153-165. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07968-y . |
| [34] | SEUNG H S. Predicting visual function by interpreting a neuronal wiring diagram[J]. Nature, 2024, 634(8032):113-123. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07953-5 . |
| [35] | SHIU P K, STERNE G R, SPILLER N, et al. A Drosophila computational brain model reveals sensorimotor processing[J]. Nature, 2024, 634(8032):210-219. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07763-9 . |
| [36] | BATES A S, PHELPS J S, KIM M, et al. Distributed control circuits across a brain-and-cord connectome[J]. bioRxiv, 2025. DOI: 10.1101/2025.07.31.667571. DOI: 10.1101/2025.07. 31.667571 . |
| [37] | TASTEKIN I, DE HAAN VICENTE I, BERESFORD R J, et al. From sensory detection to motor action: the comprehensive Drosophila taste-feeding connectome[J]. bioRxiv, 2025. DOI: 10.1101/2025.08.25.671814 . |
| [38] | BERG S, BECKETT I R, COSTA M, et al. Sexual dimorphism in the complete connectome of the Drosophila male central nervous system[J]. bioRxiv, 2025. DOI: 10.1101/2025.10.09. 680999 . |
| [39] | TAKEMURA S Y, HAYWORTH K J, HUANG G B, et al. A connectome of the male Drosophila ventral nerve cord[J]. bioRxiv, 2023. DOI: 10.1101/2023.06.05.543757 . |
| [40] | AZEVEDO A, LESSER E, PHELPS J S, et al. Connectomic reconstruction of a female Drosophila ventral nerve cord[J]. Nature, 2024, 631(8020):360-368. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07389-x . |
| [41] | NERN A, LOESCHE F, TAKEMURA S Y, et al. Connectome-driven neural inventory of a complete visual system[J]. Nature, 2025, 641(8065):1225-1237. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-08746-0 . |
| [42] | FISCHBACH K F, DITTRICH A P M. The optic lobe of Drosophila melanogaster. I. A Golgi analysis of wild-type structure[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 1989, 258(3): 441-475. DOI: 10.1007/BF00218858 . |
| [43] | KIM S, CASSIDY J J, YANG B Y, et al. Hexagonal patterning of the insect compound eye: facet area variation, defects, and disorder[J]. Biophys J, 2016, 111(12):2735-2746. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.11.004 . |
| [44] | SHARKEY C R, BLANCO J, LEIBOWITZ M M, et al. The spectral sensitivity of Drosophila photoreceptors[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 18242. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-74742-1 . |
| [45] | CURRIER T A, PANG M M, CLANDININ T R. Visual processing in the fly, from photoreceptors to behavior[J]. Genetics, 2023, 224(2): iyad064. DOI: 10.1093/genetics/iyad064 . |
| [46] | TAKEMURA S Y, NERN A, CHKLOVSKII D B, et al. The comprehensive connectome of a neural substrate for 'ON' motion detection in Drosophila [J]. eLife, 2017, 6: e24394. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.24394 . |
| [47] | SHINOMIYA K, HUANG G, LU Z Y, et al. Comparisons between the ON- and OFF-edge motion pathways in the Drosophila brain[J]. eLife, 2019, 8: e40025. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.40025 . |
| [48] | SHINOMIYA K, NERN A, MEINERTZHAGEN I A, et al. Neuronal circuits integrating visual motion information in Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Curr Biol, 2022, 32(16):3529-3544.e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.06.061 . |
| [49] | CHRISTENSON M P, SANZ DIEZ A, HEATH S L, et al. Hue selectivity from recurrent circuitry in Drosophila [J]. Nat Neurosci, 2024, 27(6):1137-1147. DOI: 10.1038/s41593-024-01640-4 . |
| [50] | SCHLEGEL P, BATES A S, STÜRNER T, et al. Information flow, cell types and stereotypy in a full olfactory connectome[J]. eLife, 2021, 10: e66018. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.66018 . |
| [51] | ZHENG Z H, LI F, FISHER C, et al. Structured sampling of olfactory input by the fly mushroom body[J]. Curr Biol, 2022, 32(15):3334-3349.e6. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.06.031 . |
| [52] | KIM H, HORIGOME M, ISHIKAWA Y, et al. Wiring patterns from auditory sensory neurons to the escape and song-relay pathways in fruit flies[J]. J Comp Neurol, 2020, 528(12):2068-2098. DOI: 10.1002/cne.24877 . |
| [53] | BAKER C A, MCKELLAR C, PANG R, et al. Neural network organization for courtship-song feature detection in Drosophila [J]. Curr Biol, 2022, 32(15):3317-3333.e7. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.06.019 . |
| [54] | DEUTSCH D, CLEMENS J, THIBERGE S Y, et al. Shared song detector neurons in Drosophila male and female brains drive sex-specific behaviors[J]. Curr Biol, 2019, 29(19):3200-3215.e5. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.08.008 . |
| [55] | MATSLIAH A, YU S C, KRUK K, et al. Neuronal parts list and wiring diagram for a visual system[J]. Nature, 2024, 634(8032):166-180. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07981-1 . |
| [56] | ARANHA M M, VASCONCELOS M L. Deciphering Drosophila female innate behaviors[J]. Curr Opin Neurobiol, 2018, 52:139-148. DOI: 10.1016/j.conb.2018.06.005 . |
| [57] | BUSSELL J J, YAPICI N, ZHANG S X, et al. Abdominal-B neurons control Drosophila virgin female receptivity[J]. Curr Biol, 2014, 24(14): 1584-1595. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.06.011 . |
| [58] | VON PHILIPSBORN A C. Neuroscience: the female art of saying no. Curr Biol, 2020, 30(19): R1080-R1083. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.08.023 . |
| [59] | WANG K Y, WANG F, FORKNALL N, et al. Neural circuit mechanisms of sexual receptivity in Drosophila females[J]. Nature, 2021, 589(7843): 577-581. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2972-7 . |
| [60] | WANG F, WANG K Y, FORKNALL N, et al. Circuit and behavioral mechanisms of sexual rejection by Drosophila females[J]. Curr Biol, 2020, 30(19): 3749-3760.e3. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.07.083 . |
| [61] | STÜRNER T, BROOKS P, SERRATOSA CAPDEVILA L, et al. Comparative connectomics of Drosophila descending and ascending neurons[J]. Nature, 2025, 643(8070): 158-172. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-08925-z . |
| [62] | ZHOU C, PAN Y F, ROBINETT C C, et al. Central brain neurons expressing doublesex regulate female receptivity in Drosophila [J]. Neuron, 2014, 83(1): 149-163. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.05.038 . |
| [63] | KUBLI E. Sex-peptides: seminal peptides of the Drosophila male[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS, 2003, 60(8): 1689-1704. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-003-3052 . |
| [64] | LIU H F, KUBLI E. Sex-peptide is the molecular basis of the sperm effect inDrosophila melanogaster [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2003, 100(17): 9929-9933. DOI: 10.1073/pnas. 1631700100 . |
| [65] | YANG C H, RUMPF S, XIANG Y, et al. Control of the postmating behavioral switch in Drosophila females by internal sensory neurons[J]. Neuron, 2009, 61(4): 519-526. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.12.021 . |
| [66] | YAPICI N, KIM Y J, RIBEIRO C, et al. A receptor that mediates the post-mating switch in Drosophila reproductive behaviour[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7174): 33-37. DOI: 10.1038/nature06483 . |
| [67] | HÄSEMEYER M, YAPICI N, HEBERLEIN U, et al. Sensory neurons in the Drosophila genital tract regulate female reproductive behavior[J]. Neuron, 2009, 61(4): 511-518. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.01.009 . |
| [68] | KUBLI E, BOPP D. Sexual behavior: how sex peptide flips the postmating switch of female flies. Curr Biol, 2012, 22(13): R520-R522. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.04.058 . |
| [69] | CHAPMAN T, BANGHAM J, VINTI G, et al. The sex peptide of Drosophila melanogaster: female post-mating responses analyzed by using RNA interference[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2003, 100(17): 9923-9928. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1631635100 . |
| [70] | FENG K, PALFREYMAN M T, HÄSEMEYER M, et al. Ascending SAG neurons control sexual receptivity of Drosophila females[J]. Neuron, 2014, 83(1): 135-148. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014. 05.017 . |
| [71] | CHIU H, ROBIE A A, BRANSON K, et al. Cell type-specific contributions to a persistent aggressive internal state in female Drosophila [J]. eLife, 2025, 12: RP88598. DOI: 10.7554/elife.88598 . |
| [72] | SCHRETTER C E, ASO Y, ROBIE A A, et al. Cell types and neuronal circuitry underlying female aggression in Drosophila [J]. eLife, 2020, 9: e58942. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.58942 . |
| [73] | DEUTSCH D, PACHECO D, ENCARNACION-RIVERA L, et al. The neural basis for a persistent internal state in Drosophila females[J]. eLife, 2020, 9: e59502. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.59502 . |
| [74] | WANG F, WANG K Y, FORKNALL N, et al. Neural circuitry linking mating and egg laying in Drosophila females[J]. Nature, 2020, 579(7797): 101-105. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2055-9 . |
| [75] | VIJAYAN V, WANG Z, CHANDRA V, et al. An internal expectation guides Drosophila egg-laying decisions[J]. Sci Adv, 2022, 8(43): 19. DOI:10.1126/sciadv.abn3852 . |
| [76] | YANG C H, BELAWAT P, HAFEN E, et al. Drosophila egg-laying site selection as a system to study simple decision-making processes[J]. Science, 2008, 319(5870): 1679-1683. DOI: 10.1126/science.1151842 . |
| [77] | VIJAYAN V, WANG F, WANG K Y, et al. A rise-to-threshold process for a relative-value decision[J]. Nature, 2023, 619(7970): 563-571. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06271-6 . |
| [78] | LOUIS M, DE POLAVIEJA G. Collective behavior: social digging in Drosophila larvae[J]. Curr Biol, 2017, 27(18): R1010-R1012. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.08.023 . |
| [79] | LIN C C, PROKOP-PRIGGE K A, PRETI G, et al. Food odors trigger Drosophila males to deposit a pheromone that guides aggregation and female oviposition decisions[J]. eLife, 2015, 4: e08688. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.08688 . |
| [80] | DUMÉNIL C, WOUD D, PINTO F, et al. Pheromonal cues deposited by mated females convey social information about egg-laying sites in Drosophila melanogaster [J]. J Chem Ecol, 2016, 42(3): 259-269. DOI: 10.1007/s10886-016-0681-3 . |
| [81] | NOJIMA T, RINGS A, ALLEN A M, et al. A sex-specific switch between visual and olfactory inputs underlies adaptive sex differences in behavior[J]. Curr Biol, 2021, 31(6): 1175-1191.e6. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.12.047 . |
| [82] | VON SCHILCHER F. The role of auditory stimuli in the courtship of Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Anim Behav, 1976, 24(1): 18-26. DOI: 10.1016/s0003-3472(76)80095-4 . |
| [83] | VON SCHILCHER F. The function of pulse song and sine song in the courtship of Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Anim Behav, 1976, 24(3): 622-625. DOI: 10.1016/s0003-3472(76)80076-0 . |
| [84] | HINDMARSH STEN T, LI R F, HOLLUNDER F, et al. Male-male interactions shape mate selection in Drosophila [J]. Cell, 2025, 188(6): 1486-1503.e25. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.01.008 . |
| [85] | ROEMSCHIED F A, PACHECO D A, ARAGON M J, et al. Flexible circuit mechanisms for context-dependent song sequencing[J]. Nature, 2023, 622(7984): 794-801. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06632-1 . |
| [86] | VON PHILIPSBORN A C, LIU T X, YU J Y, et al. Neuronal control of Drosophila courtship song[J]. Neuron, 2011, 69(3): 509-522. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.01.011 . |
| [87] | KOHATSU S, KOGANEZAWA M, YAMAMOTO D. Female contact activates male-specific interneurons that trigger stereotypic courtship behavior in Drosophila [J]. Neuron, 2011, 69(3): 498-508. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.12.017 . |
| [88] | CLOWNEY E J, IGUCHI S, BUSSELL J J, et al. Multimodal chemosensory circuits controlling male courtship in Drosophila [J]. Neuron, 2015, 87(5): 1036-1049. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.07.025 . |
| [89] | SHIRANGI T R, STERN D L, TRUMAN J W. Motor control of Drosophila courtship song[J]. Cell Rep, 2013, 5(3): 678-686. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.09.039 . |
| [90] | SHIRANGI T R, WONG A M, TRUMAN J W, et al. Doublesex regulates the connectivity of a neural circuit controlling Drosophila male courtship song[J]. Dev Cell, 2016, 37(6): 533-544. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.05.012 . |
| [91] | O'SULLIVAN A, LINDSAY T, PRUDNIKOVA A, et al. Multifunctional wing motor control of song and flight[J]. Curr Biol, 2018, 28(17): 2705-2717.e4. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.06.038 . |
| [92] | LILLVIS J L, WANG K Y, SHIOZAKI H M, et al. Nested neural circuits generate distinct acoustic signals during Drosophila courtship[J]. Curr Biol, 2024, 34(4): 808-824.e6. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.01.015 . |
| [93] | SHIOZAKI H M, WANG K Y, LILLVIS J L, et al. Activity of nested neural circuits drives different courtship songs in Drosophila [J]. Nat Neurosci, 2024, 27(10): 1954-1965. DOI: 10.1038/s41593-024-01738-9 . |
| [1] | WANG Hanyue, CHEN Jiawei, GAO Xiangbin, LUO Wei, LIU Suning. Research Overview on Corpora Cardiaca Function of Drosophila melanogaster [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 705-718. |
| [2] | WANG Mingzhu, GAO Yinghao, TAN Shuangshuang, WU Wei. Construction and Characterization of UAS-Irk3-EGFP Transgenic Drosophila Lines [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 656-662. |
| [3] | CHEN Haotian, LIU Jingnan. Applications and Advances of Drosophila in Research of Obesity and Its Related Metabolic Diseases [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 688-704. |
| [4] | WANG Ye, WANG Lu. Drosophila melanogaster Transposons: Characterization, Regulation, and Their Role in Genome Evolution [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 676-687. |
| [5] | LI Huiping, GAO Hongbin, WEN Jinyin, YANG Jinchun. Construction and Preliminary Application of Animal Disease Model Digital Atlas Database Platform [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(3): 300-308. |
| [6] | Longmei XU, Ruling SHEN, Chun FAN, Wei WU. Generation of 12 Drosophila Transgenic Negative Control Lines Based on Site-specific ΦC31 Integrase and pUASTattB Vector [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 541-547. |
| [7] | CHEN Ying, PAN Hua, ZHOU Guang-xing. Preliminary Establishment of Shared Database about Comparative Histology in 6 Species of Laboratory Animals [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2014, 34(6): 463-466. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

