
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 613-625.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.168
• Animal Models of Human Diseases • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Siyu1( ), LAI Yuezhao1(
), LAI Yuezhao1( ), GUO Wenting1(
), GUO Wenting1( )(
)( ), CHEN Xuejin2(
), CHEN Xuejin2( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-11-13
Revised:2024-12-04
Online:2024-12-25
Published:2025-01-04
Contact:
GUO Wenting, CHEN Xuejin
CLC Number:
LIU Siyu,LAI Yuezhao,GUO Wenting,et al. Advances in Nucleic Acid Drugs and Gene Therapies based on Animal Models of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 613-625. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.168.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.168
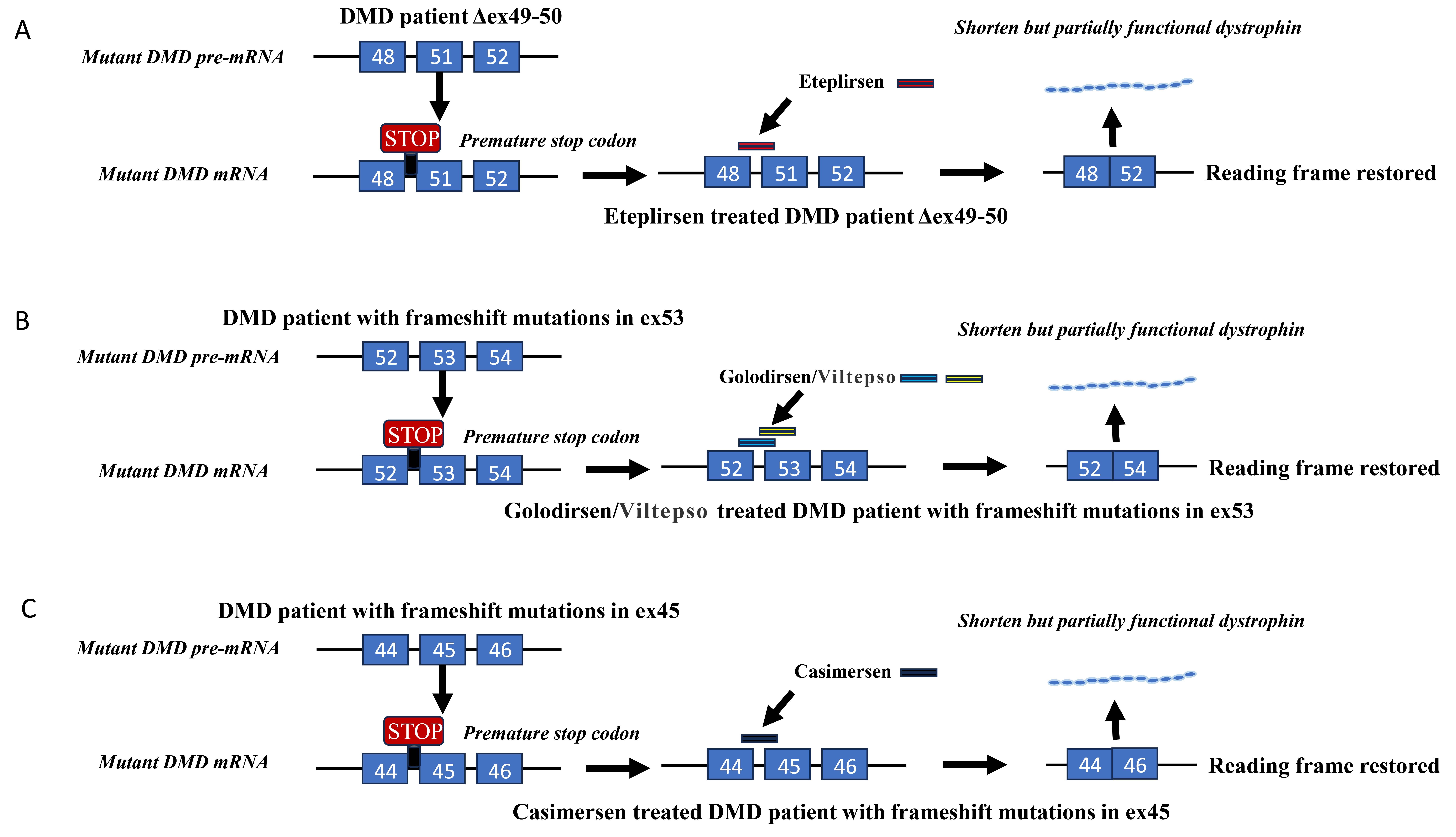
Figure 2 Mechanism of exon skipping therapy for DMD gene in Duchenne muscular dystrophyNote: A, Eteplirsen, for DMD patients with deletion of exons 49 and 50; B, Viltolarsen/Golodirsen, for DMD patients with frameshift mutations affecting exon 53; C, Casimersen, for DMD patients with frameshift mutations affecting exon 45. This figure was adapted from reference [7].
药物名称 Drug name | 适用DMD基因突变类型 Targeted DMD gene mutation type | 优点 Advantage | 缺点 Drawback |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eteplirsen | 51号外显子缺失 | 首款获批的DMD治疗用反义寡核苷酸药物,安全性良好,肌肉功能改善具有长期稳定性 | 仅适用于51号外显子缺失突变,疗效提升有限[ |
| Golodirsen | 53号外显子缺失 | 有效提高抗肌萎缩蛋白水平,每周静脉注射1次,给药方式方便且易于管理[ | 适用范围有限,仅适用于53号外显子缺失突变,缺乏功能性结果报告[ |
| Viltolarsen | 53号外显子缺失 | 与Golodirsen相比可更高效地提高抗肌萎缩蛋白水平,作用迅速;全球认可度高,获日本和美国批准 | 治疗周期长,与Golodirsen治疗范围重叠,患者覆盖面未扩大[ |
| Casimersen | 45号外显子缺失 | 有效延缓疾病进展,安全性较高,风险低,可为患者提供新选择 | 尚无长期有效的数据,仅适用于45号外显子缺失突变[ |
Table 1 Summary of representative nucleic acid drugs for treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy
药物名称 Drug name | 适用DMD基因突变类型 Targeted DMD gene mutation type | 优点 Advantage | 缺点 Drawback |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eteplirsen | 51号外显子缺失 | 首款获批的DMD治疗用反义寡核苷酸药物,安全性良好,肌肉功能改善具有长期稳定性 | 仅适用于51号外显子缺失突变,疗效提升有限[ |
| Golodirsen | 53号外显子缺失 | 有效提高抗肌萎缩蛋白水平,每周静脉注射1次,给药方式方便且易于管理[ | 适用范围有限,仅适用于53号外显子缺失突变,缺乏功能性结果报告[ |
| Viltolarsen | 53号外显子缺失 | 与Golodirsen相比可更高效地提高抗肌萎缩蛋白水平,作用迅速;全球认可度高,获日本和美国批准 | 治疗周期长,与Golodirsen治疗范围重叠,患者覆盖面未扩大[ |
| Casimersen | 45号外显子缺失 | 有效延缓疾病进展,安全性较高,风险低,可为患者提供新选择 | 尚无长期有效的数据,仅适用于45号外显子缺失突变[ |
| 1 | BOCCANEGRA B, CAPPELLARI O, MANTUANO P, et al. Growth hormone secretagogues modulate inflammation and fibrosis in mdx mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14:1119888. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1119888 . |
| 2 | JAXYBAYEVA A, CHUNKAYEVA D, MYRZALIYEVA B, et al. Duchenne muscular dystrophy in Kazakhstan: a journey from diagnosis to the treatment, the biases and achievements[J]. J Neuromuscul Dis, 2023, 10(2):263-269. DOI: 10.3233/JND-221559 . |
| 3 | RICCI G, BELLO L, TORRI F, et al. Therapeutic opportunities and clinical outcome measures in Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Neurol Sci, 2022, 43():625-633. DOI: 10.1007/s10072-022-06085-w . |
| 4 | FISCHER R, PORTER K, DONOVAN J M, et al. A mixed-method study exploring patient-experienced and caregiver-reported benefits and side effects of corticosteroid use in Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. J Neuromuscul Dis, 2023, 10(4):593-613. DOI: 10.3233/JND-221617 . |
| 5 | DEN HARTOG L, ASAKURA A. Implications of Notch signaling in Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Front Physiol, 2022, 13:984373. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.984373 . |
| 6 | KODIPPILI K, RUDNICKI M A. Satellite cell contribution to disease pathology in Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Front Physiol, 2023, 14:1180980. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1180980 . |
| 7 | SAIFULLAH, MOTOHASHI N, TSUKAHARA T, et al. Development of therapeutic RNA manipulation for muscular dystrophy[J]. Front Genome Ed, 2022, 4:863651. DOI: 10.3389/fgeed.2022.863651 . |
| 8 | MIN Y L, BASSEL-DUBY R, OLSON E N. CRISPR correction of Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Annu Rev Med, 2019, 70:239-255. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-med-081117-010451 . |
| 9 | OLSON E N. Toward the correction of muscular dystrophy by gene editing[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2021, 118(22): e2004840117. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2004840117 . |
| 10 | AARTSMA-RUS A, DE WAELE L, HOUWEN-OPSTAL S, et al. The dilemma of choice for Duchenne patients eligible for exon 51 skipping the European experience[J]. J Neuromuscul Dis, 2023, 10(3):315-325. DOI: 10.3233/JND-221648 . |
| 11 | MAMSA H, STARK R L, SHIN K M, et al. Sarcospan increases laminin-binding capacity of α-dystroglycan to ameliorate DMD independent of Galgt2[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2022, 31(5):718-732. DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddab276 . |
| 12 | REID A L, ALEXANDER M S. The interplay of mitophagy and inflammation in Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Life (Basel), 2021, 11(7):648. DOI: 10.3390/life11070648 . |
| 13 | KAMDAR F, GARRY D J. Dystrophin-deficient cardiomyopathy[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2016, 67(21):2533-2546. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.02.081 . |
| 14 | MANINI A, ABATI E, NUREDINI A, et al. Adeno-associated virus (AAV)-mediated gene therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: the issue of transgene persistence[J]. Front Neurol, 2021, 12:814174. DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.814174 . |
| 15 | NOVAK J S, SPATHIS R, DANG U J, et al. Interrogation of dystrophin and dystroglycan complex protein turnover after exon skipping therapy[J]. J Neuromuscul Dis, 2021, 8(s2): S383-S402. DOI: 10.3233/JND-210696 . |
| 16 | FRANK D E, SCHNELL F J, AKANA C, et al. Increased dystrophin production with golodirsen in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Neurology, 2020, 94(21): e2270-e2282. DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009233 . |
| 17 | SHIRLEY M. Casimersen: first approval[J]. Drugs, 2021, 81(7):875-879. DOI: 10.1007/s40265-021-01512-2 . |
| 18 | WILTON-CLARK H, YOKOTA T. Casimersen for Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Drugs Today, 2021, 57(12):707-717. DOI: 10.1358/dot.2021.57.12.3352740 . |
| 19 | HU G, CHEN C. Promising treatments for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: restoring dystrophin protein expression using nucleic acid therapeutics[J]. Int J Drug Discov Pharmacol, 2023: n.pag. DOI: 10.53941/ijddp.0201002 . |
| 20 | SAZANI P, WELLER D L, SHREWSBURY S B. Safety pharmacology and genotoxicity evaluation of AVI-4658[J]. Int J Toxicol, 2010, 29(2):143-156. DOI: 10.1177/1091581809359206 . |
| 21 | SAZANI P, NESS K P, WELLER D L, et al. Chemical and mechanistic toxicology evaluation of exon skipping phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers in mdx mice[J]. Int J Toxicol, 2011, 30(3):322-333. DOI: 10.1177/1091581811403504 . |
| 22 | HAPPI MBAKAM C, LAMOTHE G, TREMBLAY J P. Therapeutic strategies for dystrophin replacement in Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Front Med, 2022, 9:859930. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.859930 . |
| 23 | STIMPSON G, RAQUQ S, CHESSHYRE M, et al. Growth pattern trajectories in boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2022, 17(1):20. DOI: 10.1186/s13023-021-02158-9 . |
| 24 | MENDELL J R, RODINO-KLAPAC L R, SAHENK Z, et al. Eteplirsen for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Ann Neurol, 2013, 74(5):637-647. DOI: 10.1002/ana.23982 . |
| 25 | ALFANO L N, CHARLESTON J S, CONNOLLY A M, et al. Long-term treatment with eteplirsen in nonambulatory patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Medicine, 2019, 98(26): e15858. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015858 . |
| 26 | TRAYNOR K. Eteplirsen approved for Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Am J Health Syst Pharm, 2016, 73(21):1719. DOI: 10.2146/news160063 . |
| 27 | AARTSMA-RUS A, KRIEG A M. FDA approves eteplirsen for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: the next chapter in the eteplirsen Saga[J]. Nucleic Acid Ther, 2017, 27(1):1-3. DOI: 10.1089/nat.2016.0657 . |
| 28 | MCDONALD C M, SHIEH P B, ABDEL-HAMID H Z, et al. Open-label evaluation of eteplirsen in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy amenable to exon 51 skipping: PROMOVI trial[J]. J Neuromuscul Dis, 2021, 8(6):989-1001. DOI: 10.3233/JND-210643 . |
| 29 | ECHIGOYA Y, LIM K R Q, TRIEU N, et al. Quantitative antisense screening and optimization for exon 51 skipping in Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Mol Ther, 2017, 25(11):2561-2572. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.07.014 . |
| 30 | ANWAR S, YOKOTA T. Golodirsen for Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Drugs Today, 2020, 56(8):491-504. DOI: 10.1358/dot.2020.56.8.3159186 . |
| 31 | Anon. Abstracts of the 12th UK neuromuscular translational research conference, 4th and 5th April 20191[J]. J Neuromuscul Dis, 2019, 6(s1): S1-S109. DOI: 10.3233/JND-190000 . |
| 32 | SERVAIS L, MERCURI E, STRAUB V, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy data of golodirsen in ambulatory patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy amenable to exon 53 skipping: a first-in-human, multicenter, two-part, open-label, phase 1/2 trial[J]. Nucleic Acid Ther, 2022, 32(1):29-39. DOI: 10.1089/nat.2021.0043 . |
| 33 | AARTSMA-RUS A, COREY D R. The 10th oligonucleotide therapy approved: golodirsen for Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Nucleic Acid Ther, 2020, 30(2):67-70. DOI: 10.1089/nat.2020.0845 . |
| 34 | ASSEFA M, GEPFERT A, ZAHEER M, et al. Casimersen (AMONDYS 45™): an antisense oligonucleotide for Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Biomedicines, 2024, 12(4):912. DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12040912 . |
| 35 | VASTERLING M E, MAITSKI R J, DAVIS B A, et al. AMONDYS 45 (casimersen), a novel antisense phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer: clinical considerations for treatment in Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Cureus, 2023, 15(12): e51237. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.51237 . |
| 36 | CLEMENS P R, RAO V K, CONNOLLY A M, et al. Long-term functional efficacy and safety of viltolarsen in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. J Neuromuscul Dis, 2022, 9(4):493-501. DOI: 10.3233/JND-220811 . |
| 37 | COHEN S A, BAR-AM O, FUOCO C, et al. In vivo restoration of dystrophin expression in mdx mice using intra-muscular and intra-arterial injections of hydrogel microsphere carriers of exon skipping antisense oligonucleotides[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(9):779. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-05166-0 . |
| 38 | POLITANO L. Read-through approach for stop mutations in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. An update[J]. Acta Myol, 2021, 40(1):43-50. DOI: 10.36185/2532-1900-041 . |
| 39 | 刘延波, 徐乃军, 贾飞勇. Duchenne肌营养不良(DMD)发病机制及治疗研究进展[J]. 生命科学, 2012, 24(4):354-361. |
| LIU Y B, XU N J, JIA F Y. The research progresses of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in it's pathogenesis and therapy[J]. Chin Bull Life Sci, 2012, 24(4):354-361. | |
| 40 | MICHOROWSKA S. Ataluren-promising therapeutic premature termination Codon readthrough frontrunner[J]. Pharmaceuticals, 2021, 14(8):785. DOI: 10.3390/ph14080785 . |
| 41 | CAMPBELL C, BAROHN R J, BERTINI E, et al. Meta-analyses of ataluren randomized controlled trials in nonsense mutation Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. J Comp Eff Res, 2020, 9(14):973-984. DOI: 10.2217/cer-2020-0095 . |
| 42 | MUNTONI F, DESGUERRE I, GUGLIERI M, et al. Ataluren use in patients with nonsense mutation Duchenne muscular dystrophy: patient demographics and characteristics from the STRIDE registry[J]. J Comp Eff Res, 2019, 8(14):1187-1200. DOI: 10.2217/cer-2019-0086 . |
| 43 | MERCURI E, MUNTONI F, OSORIO A N, et al. Safety and effectiveness of ataluren: comparison of results from the STRIDE registry and CINRG DMD natural history study[J]. J Comp Eff Res, 2020, 9(5):341-360. DOI: 10.2217/cer-2019-0171 . |
| 44 | FONTELONGA T M, JORDAN B, NUNES A M, et al. Sunitinib promotes myogenic regeneration and mitigates disease progression in the mdx mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2019, 28(13):2120-2132. DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddz044 . |
| 45 | SIRBU C A, IVAN R, AUTHIER F J, et al. Orphan drugs in neurology-a narrative review[J]. J Pers Med, 2023, 13(3):420. DOI: 10.3390/jpm13030420 . |
| 46 | SHEIKH O, YOKOTA T. Advances in genetic characterization and genotype-phenotype correlation of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy in the personalized medicine era[J]. J Pers Med, 2020, 10(3):111. DOI: 10.3390/jpm10030111 . |
| 47 | COLLOTTA D, BERTOCCHI I, CHIAPELLO E, et al. Antisense oligonucleotides: a novel Frontier in pharmacological strategy[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14:1304342. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1304342 . |
| 48 | BIRCH S M, LAWLOR M W, CONLON T J, et al. Assessment of systemic AAV-microdystrophin gene therapy in the GRMD model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2023, 15(677): eabo1815. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abo1815 . |
| 49 | ALBINI S, PALMIERI L, DUBOIS A, et al. Assessment of therapeutic potential of a dual AAV approach for Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(14):11421. DOI: 10.3390/ijms241411421 . |
| 50 | LONG C Z, AMOASII L, MIREAULT A A, et al. Postnatal genome editing partially restores dystrophin expression in a mouse model of muscular dystrophy[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6271):400-403. DOI: 10.1126/science.aad5725 . |
| 51 | TABEBORDBAR M, ZHU K X, CHENG J K W, et al. In vivo gene editing in dystrophic mouse muscle and muscle stem cells[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6271):407-411. DOI: 10.1126/science.aad5177 . |
| 52 | NELSON C E, HAKIM C H, OUSTEROUT D G, et al. In vivo genome editing improves muscle function in a mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Science, 2016, 351(6271):403-407. DOI: 10.1126/science.aad5143 . |
| 53 | KUPATT C, WINDISCH A, MORETTI A, et al. Genome editing for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a glimpse of the future?[J]. Gene Ther, 2021, 28(9):542-548. DOI: 10.1038/s41434-021-00222-4 . |
| 54 | AMOASII L, HILDYARD JCW, LI H, et al. Gene editing restores dystrophin expression in a canine model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Science, 2018, 362(6410): 86-91.DOI:10.1126/science.aau1549 . |
| 55 | MORETTI A, FONTEYNE L, GIESERT F, et al. Somatic gene editing ameliorates skeletal and cardiac muscle failure in pig and human models of Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Nat Med, 2020,26(2): 207-214. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-019-0738-2 . |
| 56 | LEK A, WONG B, KEELER A, et al. Unexpected death of a Duchenne muscular dystrophy patient in an N-of-1 trial of rAAV9-delivered CRISPR-transactivator[R/OL]. medRxiv (Preprint), 2023.(2023-05-30)[2024-12-01]. . DOI: 10.1101/2023.05.16.23289881 . |
| 57 | REN S W, FU X, GUO W T, et al. Profound cellular defects attribute to muscular pathogenesis in the Rhesus monkey model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy[J]. Cell, 2024, 187(23):6669-6686.e16. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.08.041 . |
| [1] | Min LIANG, Yang GUO, Jinjin WANG, Mengyan ZHU, Jun CHI, Yanjuan CHEN, Chengji WANG, Zhilan YU, Ruling SHEN. Construction of Dmd Gene Mutant Mice and Phenotype Verification in Muscle and Immune Systems [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 42-51. |
| [2] | YANG Zhi-cong,YAO Jing,FANG Zhan-qiang. Acute Toxicity and Safety Assessment of DDTs to White Cloud Mountain Minnow Tanichthys albonubes larval stages [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2007, 27(2): 123-126. |
| [3] | MIN Yang, LU Qin, LIU Quan-hai. Carotid Artery Stenosis Model Induced by FeCl3 in Rat [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2001, 21(4): 215-216. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||