
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 253-261.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.186
• Experimental Animal and Comparative Pharmacology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Taofeng LU1( ), Hui ZHANG2(
), Hui ZHANG2( ), Jie ZHOU3, Qian LI1, Shuguang WU1, Yanjun WU1(
), Jie ZHOU3, Qian LI1, Shuguang WU1, Yanjun WU1( )(
)( )
)
Received:2022-12-05
Revised:2023-02-09
Online:2023-06-25
Published:2023-06-25
Contact:
Yanjun WU
CLC Number:
Taofeng LU,Hui ZHANG,Jie ZHOU,et al. Effects of Pogostemon cablin on Serum Metabolomiceof Guizhou Miniature Pigs and It's mechanism[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 253-261. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.186.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.186
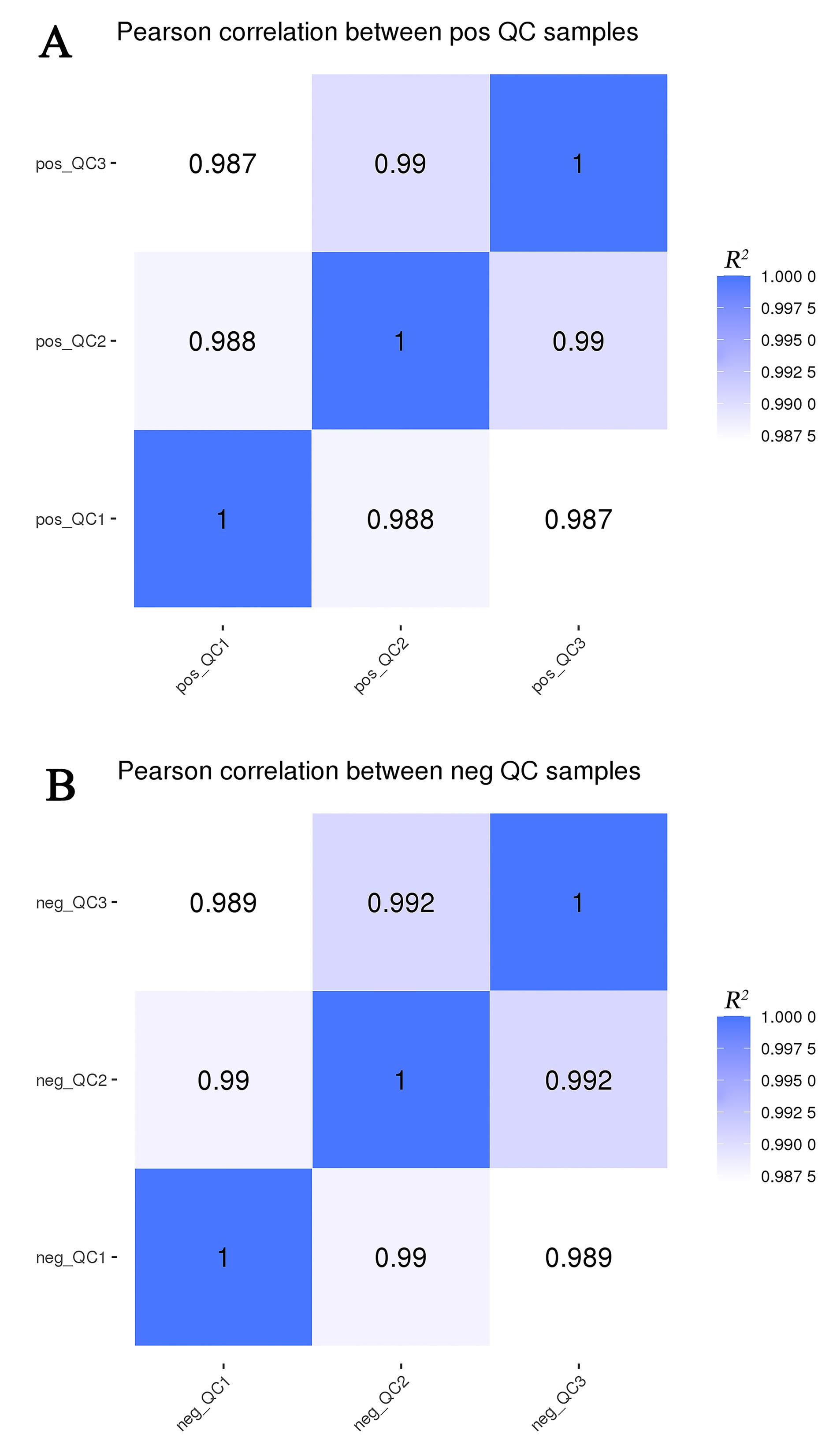
Figure 1 Pairings correlation of QC samples in positive (A) and negative (B) ion modeNote:QC, Quality control sample; pos, Positive ion mode; neg, Negative ion mode.
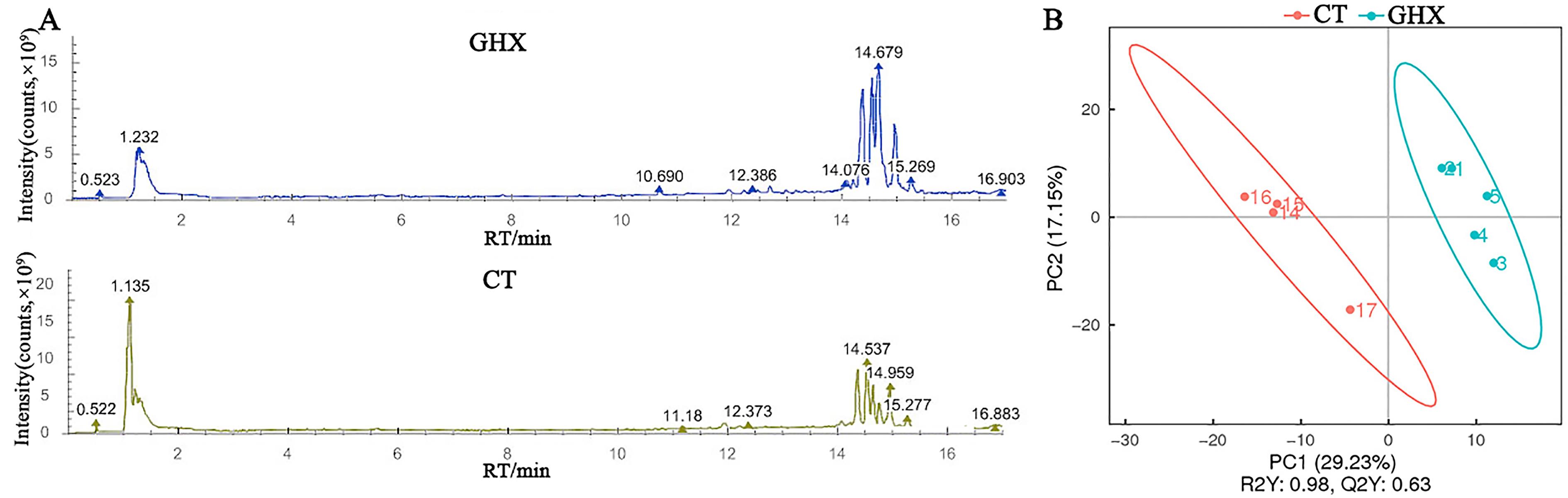
Figure 2 The results of LC-MS/MS negative mode scanning total ion flow diagram (A) and PLS-DA score map (B) of serum metabolites of pigs after administration of Pogostemon cablinNote:A, LC-MS/MS negative mode scanning total ion flow diagram; B, Partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) score map for metabolite data. GHX, Pogostemon cablin drug group given 0.5 g/head of traditional Chinese medicine formula granules per day by mixing materials through oral feeding for consecutive 8 days; CT, The control group given normal feeding without additional treatment; RT, Treatment time.
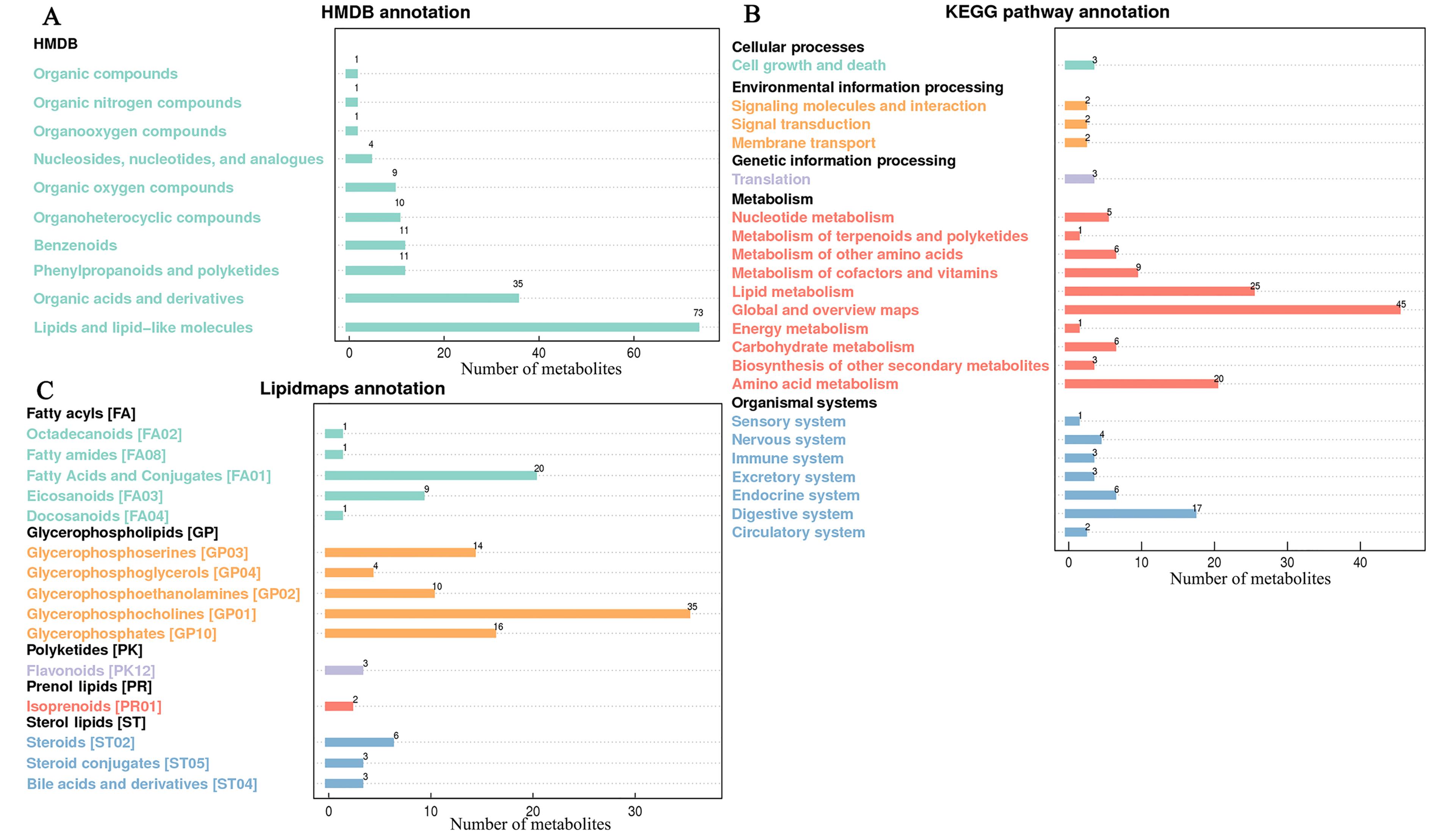
Figure 3 Annotation results of serum metabolites of pigs after administration of Pogostemon cablinNote:A to C are the comparative annotation results of HMDB (Human Metabolome Database) database, KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) database, and LIPID Maps database, respectively.
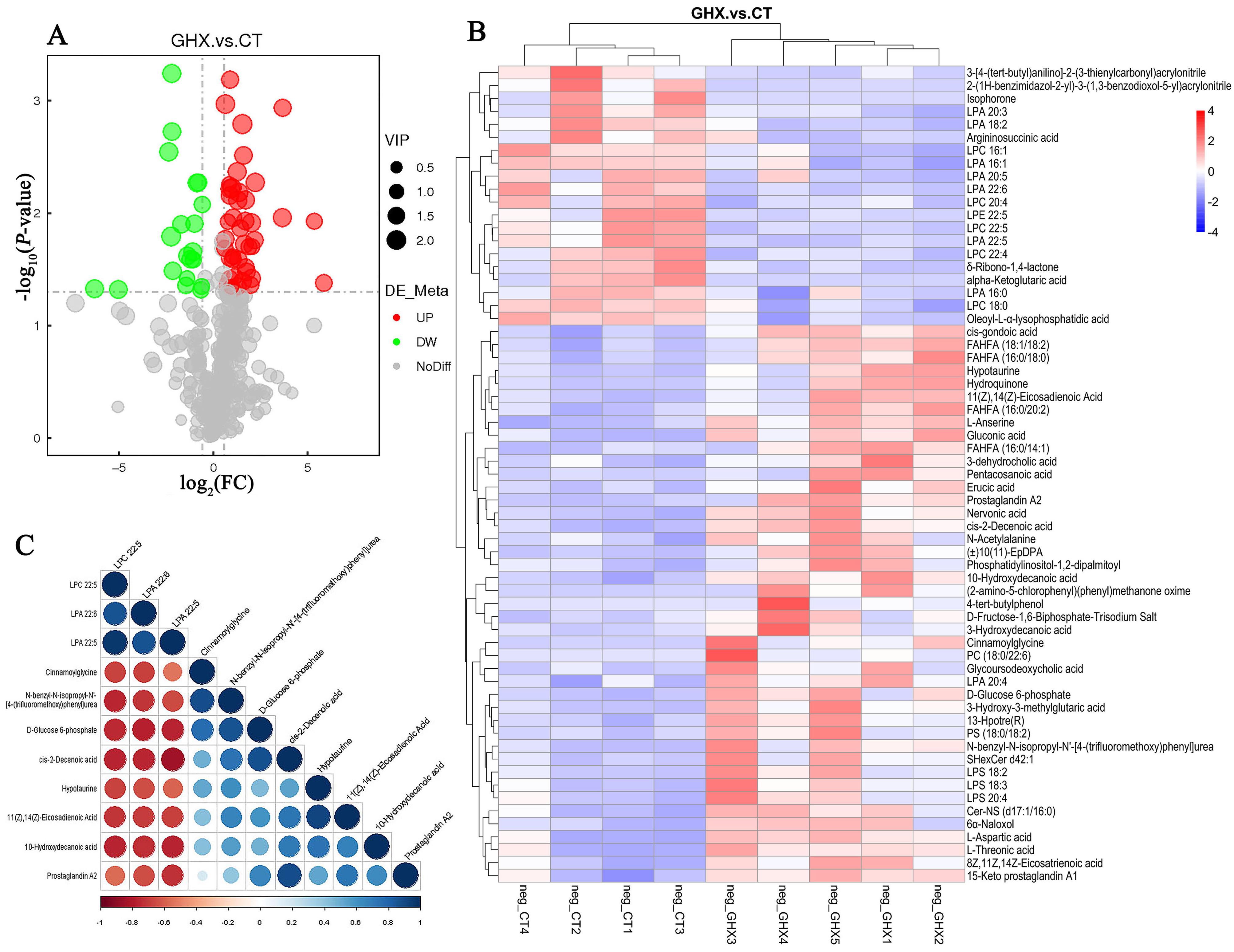
Figure 4 Volcanic map (A), clustering heat map (B) and correlation analysis diagram (C) of differential serum metabolites of pigs after administration of Pogostemon cablinNote:GHX, Pogostemon cablin drug group given 0.5 g/head of traditional Chinese medicine formula granules per day by mixing materials through oral feeding for consecutive 8 days; CT, The control group given normal feeding without additional treatment; FC, Fold change.
代谢物 Metabolites | 代谢物中文名称 Metabolites in Chinese | 保留时间/min Retention time/min | log2(FC) | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cinnamoylglycine | 肉桂酰甘氨酸 | 8.378 | 3.670 | 0.001 |
| N-benzyl-N-isopropyl-N'-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl] urea | N-苄基-N-异丙基-N'-(4-三氟甲基)苯尿素 | 4.541 | 2.217 | 0.005 |
| Hypotaurine | 亚牛磺酸 | 14.485 | 1.703 | 0.008 |
| D-Glucose 6-phosphate | D-葡萄糖-6-磷酸 | 1.158 | 1.595 | 0.003 |
| cis-2-Decenoic acid | 顺-2-癸烯酸 | 12.057 | 1.536 | 0.002 |
| 11(Z),14(Z)-Eicosadienoic acid | 二十碳二烯酸(顺-11,14) | 14.820 | 1.349 | 0.007 |
| Prostaglandin A2 | 前列腺素A2 | 12.727 | 1.289 | 0.008 |
| 10-Hydroxydecanoic acid | 10-羟基癸烯酸 | 11.707 | 1.261 | 0.004 |
| Lysophosphatidyl choline 22:5 | 溶血磷脂酰胆碱22:5 | 14.673 | -2.190 | 0.002 |
| Lysophosphatidyl acid 22:6 | 溶血磷脂酸22:6 | 14.010 | -2.201 | <0.001 |
| Lysophosphatidyl acid 22:5 | 溶血磷脂酸22:5 | 14.139 | -2.361 | 0.003 |
Table 1 The basic information of the main differential metabolites of pigs after administration of Pogostemon cablin
代谢物 Metabolites | 代谢物中文名称 Metabolites in Chinese | 保留时间/min Retention time/min | log2(FC) | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cinnamoylglycine | 肉桂酰甘氨酸 | 8.378 | 3.670 | 0.001 |
| N-benzyl-N-isopropyl-N'-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl] urea | N-苄基-N-异丙基-N'-(4-三氟甲基)苯尿素 | 4.541 | 2.217 | 0.005 |
| Hypotaurine | 亚牛磺酸 | 14.485 | 1.703 | 0.008 |
| D-Glucose 6-phosphate | D-葡萄糖-6-磷酸 | 1.158 | 1.595 | 0.003 |
| cis-2-Decenoic acid | 顺-2-癸烯酸 | 12.057 | 1.536 | 0.002 |
| 11(Z),14(Z)-Eicosadienoic acid | 二十碳二烯酸(顺-11,14) | 14.820 | 1.349 | 0.007 |
| Prostaglandin A2 | 前列腺素A2 | 12.727 | 1.289 | 0.008 |
| 10-Hydroxydecanoic acid | 10-羟基癸烯酸 | 11.707 | 1.261 | 0.004 |
| Lysophosphatidyl choline 22:5 | 溶血磷脂酰胆碱22:5 | 14.673 | -2.190 | 0.002 |
| Lysophosphatidyl acid 22:6 | 溶血磷脂酸22:6 | 14.010 | -2.201 | <0.001 |
| Lysophosphatidyl acid 22:5 | 溶血磷脂酸22:5 | 14.139 | -2.361 | 0.003 |
| 1 | 罗晶, 殷宁, 黄小英, 等. 芳香中药防治新型冠状病毒肺炎作用机制探究[J]. 江西中医药大学学报, 2020, 32(3): 66-73. |
| LUO J, YIN N, HUANG X Y, et al. Study on the mechanism of aromatic traditional Chinese medicine compound on prevention and treatment of new coronavirus pneumonia[J]. J Jiangxi Univ Tradit Chin Med, 2020, 32(3): 66-73. | |
| 2 | 梁嘉丽. 环氧广藿香烯抗炎及抗胃溃疡的药效及机制研究[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学, 2018. |
| LIANG J L. Evaluation of patchoulene epoxide on the activity of anti-inflammation and gastroprotection[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2018. | |
| 3 | 陈春宇, 董汉玉, 纪瑞锋, 等. 基于中医药理论的芳香类中药防治新型冠状病毒肺炎(COVID-19)的作用探讨[J]. 中草药, 2020, 51(11): 3051-3061. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.11.025 . |
| CHEN C Y, DONG H Y, JI R F, et al. Discussion on role of aromatic Chinese herbs in prevention and treatment of COVID-19 based on theory of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2020, 51(11): 3051-3061. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.11.025 . | |
| 4 | 徐雯, 吴艳清, 丁浩然, 等. 广藿香的药理作用及机制研究进展[J]. 上海中医药杂志, 2017, 51(10):103-106. DOI: 10.16305/j.1007-1334.2017.10.028 . |
| XU W, WU Y Q, DING H R, et al. Research progress on pharmacological effects and mechanism of Herba Pogostemonis[J]. Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med, 2017, 51(10):103-106. DOI: 10.16305/j.1007-1334.2017.10.028 . | |
| 5 | 齐乐辉, 王知斌, 孟永海, 等. 中药广藿香有效成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 化学工程师, 2018, 32(2):49-50, 56. DOI: 10.16247/j.cnki.23-1171/tq.20180249 . |
| QI L H, WANG Z B, MENG Y H, et al. Research progress of the active ingredient and pharmacological action of Chinese medicine patchouli[J]. Chem Eng, 2018, 32(2):49-50, 56. DOI: 10.16247/j.cnki.23-1171/tq.20180249 . | |
| 6 | 黎玉翠. 广藿香酮及广藿香醇的抗炎、抗真菌活性及药物代谢研究[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学, 2013. |
| LI Y C. Metabolism, anti-inflammatory and anti-fungal activities of pogostone and patchouli alcohol[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2013. | |
| 7 | 王磊, 李跟旺. 广藿香抗菌消炎调节免疫作用的最新研究[J]. 西部中医药, 2018, 31(2): 138-140. |
| WANG L, LI G W. The latest research of antibacterial action, anti-inflammatory action and regulating immunity of patchouli[J]. West J Tradit Chin Med, 2018, 31(2): 138-140. | |
| 8 | 魏晓露. 广藿香油抗病毒的物质基础研究[D]. 成都: 成都中医药大学, 2013. |
| WEI X L. Research on material basis of antiviral of patchouli oil[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Chinese Medicine, 2013. | |
| 9 | 仝小林, 李修洋, 赵林华, 等. 从"寒湿疫"角度探讨新型冠状病毒肺炎的中医药防治策略[J]. 中医杂志, 2020. 61(6): 465-470, 553. |
| TONG X L, LI X Y, ZHAO L H, et al. Discussion on traditional Chinese medicine prevention and treatment strategies of coronavirus disease 2019 ( COVID-19) from the perspective of "cold-dampness pestilence"[J]. J Trad Chinese Med,2020.61(6):465-470, 553. | |
| 10 | 邵仲柏, 朱月霞, 刘书豪, 等. 临床使用治疗新型冠状病毒肺炎中药复方中高频数中药抗病毒研究概述[J]. 中草药, 2020, 51(5): 1153-1158. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.05.009 . |
| SHAO Z B, ZHU Y X, LIU S H, et al. A review on clinical application of high frequency traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of coronavirus pneumonia 2019[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2020, 51(5): 1153-1158. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.05.009 . | |
| 11 | 邓燕君, 刘博文, 贺桢翔, 等. 基于网络药理学和分子对接法探索藿香正气口服液预防新型冠状病毒肺炎(COVID-19)活性化合物研究[J]. 中草药, 2020, 51(5): 1113-1122. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.05.004 . |
| DENG Y J, LIU B W, HE Z X, et al. Study on active compounds from Huoxiang Zhengqi Oral Liquid for prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) based on network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2020, 51(5): 1113-1122. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.05.004 . | |
| 12 | 魏聪聪, 朱明丹, 冯利民, 等. 代谢组学技术在中医证候学和药效物质基础研究中的应用[J]. 江苏中医药, 2012, 44(1): 1-3. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-397X.2012.01.001 . |
| WEI C C, ZHU M D, FENG L M, et al. Application of metabonomics technology in the study of TCM syndromes and pharmacological material basis[J]. Jiangsu J Tradit Chin Med, 2012, 44(1): 1-3. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-397X.2012.01.001 . | |
| 13 | 马素娜, 关亚奇, 张淼, 等. 代谢组学技术在中医证候学研究中的应用优势[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2019, 30(7):1714-1716. |
| MA S N, GUAN Y Q, ZHANG M, et al. The advantage of metabolomics in the study of TCM syndrome[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2019, 30(7):1714-1716. | |
| 14 | 杨艳, 韦炎龙, 方峰. 代谢组学阐明中医药治疗代谢性疾病的机制研究[J]. 中医药临床杂志, 2020, 32(9):1601-1605. DOI: 10.16448/j.cjtcm.2020.0901 . |
| YANG Y, WEI Y L, FANG F. Research progress of mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of metabolic diseases from metabolomics[J]. Clin J Tradit Chin Med, 2020, 32(9):1601-1605. DOI: 10.16448/j.cjtcm.2020.0901 . | |
| 15 | 李小海, 刘新峰, 伍瑶斌, 等. 多排螺旋CT重建技术测量贵州成年小型猪支气管[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2019, 42(1): 40-43. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1633.2019.01.010 . |
| LI X H, LIU X F, WU Y B, et al. Bronchial data of adult Guizhou miniature pig measured by multiplice spiral computed tomography and its reconstruction technique in vivo[J]. Chin J Anat, 2019, 42(1): 40-43. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1633.2019.01.010 . | |
| 16 | 王郭琦, 吴曙光, 陈明飞, 等. 贵州小型猪肾阳虚动物模型的建立[J]. 贵州科学, 2019, 37(5): 48-51. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6563.2019.05.009 . |
| WANG G Q, WU S G, CHEN M F, et al. Construction of kidney Yang deficiency animal model with Guizhou miniature pigs[J]. Guizhou Sci, 2019, 37(5): 48-51. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6563.2019.05.009 . | |
| 17 | 张慧, 吴延军, 姚瑾, 等. 五苓散对高脂血症模型贵州小型猪的治疗作用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学, 2021, 41(2): 138-142. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2020.188 . |
| ZHANG H, WU Y J, YAO J, et al. Therapeutic effect of Wuling Powder on Guizhou mini-pigs of hyperlipidemia model[J]. Lab Anim Comp Med, 2021, 41(2): 138-142. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2020.188 . | |
| 18 | 于兰, 金鑫, 南红梅. 代谢组学技术在中医"整体观念、辨证论治"理论研究中的应用[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2015, 7(20): 191-192. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9308.2015.20.140 . |
| YU L, JIN X, NAN H M. The application of the theory of the "holistic concept, the syndrome differentiation and treatment" of the traditional Chinese medicine[J]. China Continuing Med Educ, 2015, 7(20): 191-192. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9308.2015.20.140 . | |
| 19 | Xiaoyong C, Shuaiwei W, Peiling G, et al. Comprehensive analysis of lipid metabolism in influenza virus infection[J]. Microbial Pathogenesis,2023,175. |
| 20 | MARTÍN-ACEBES M A, VÁZQUEZ-CALVO Á, SAIZ J C. Lipids and flaviviruses, present and future perspectives for the control of dengue, Zika, and West Nile viruses[J]. Prog Lipid Res, 2016, 64: S0163-S7827(16)30015>-7. DOI: 10.1016/j.plipres.2016.09.005 . |
| 21 | SONG J W, LAM S M, FAN X, et al. Omics-driven systems interrogation of metabolic dysregulation in COVID-19 pathogenesis[J]. Cell Metab, 2020, 32(2): S1550-S4131(20)30317-X. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.06.016 . |
| 22 | HE S S, WANG Y L, XIE J H, et al. 1H NMR-based metabolomic study of the effects of flavonoids on citrinin production by Monascus[J]. Food Res Int, 2020, 137: S0963-S9969(20)30557-3. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109532 . |
| 23 | ZHANG Z L, WANG T, LIV F, et al. The proteomic characteristics of airway mucus from critical ill COVID-19 patients[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 269:119046. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs. 2021.119046 . |
| 24 | JIANG M, KUANG S F, LAI S S, et al. Na+-NQR confers aminoglycoside resistance via the regulation of l-alanine metabolism[J]. mBio, 2020, 11(6): e02086-e02020. DOI: 10.1128/mBio.02086-20 . |
| 25 | 胡恺. 神经胶质细胞与胶质瘤细胞亚牛磺酸代谢特征的差异研究[D]. 大连: 大连医科大学, 2018. |
| HU K. Study on the difference of metabolic characteristics of glutamate in glial cells and glioma cells[D]. Dalian: Dalian Medical University, 2018. | |
| 26 | ZHOU J, YAO N, WANG S X, et al. Fructus Gardeniae-induced gastrointestinal injury was associated with the inflammatory response mediated by the disturbance of vitamin B6, phenylalanine, arachidonic acid, taurine and hypotaurine metabolism[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2019, 235:47-55. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.01.041 . |
| [1] | CHEN Ming-fei, YAO Gang, ZHAO Hai, QIAN Ning, WU Shu-guang. Primiparous Reproductive Performance of Outbred Guizhou Miniature Pigs and its Correlation and Path Analysis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2017, 37(4): 324-327. |
| [2] | FENG Ji-Feng-1, GAN Shi-Xiang-1, DONG Fei-Luo-1, LING Gui-Lan-1, ZHU Wen-Shi-2. Determination of Superoxide Dismutase and Peroxidase Isozymes in Guizhou Miniature Pig [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 1995, 15(1): 20-22. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||