
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 112-123.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.167
• Animal Models of Human Diseases • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jingwei MA( ), Gen LI, Yang YANG, Caixia ZANG, Xiuqi BAO, Dan ZHANG(
), Gen LI, Yang YANG, Caixia ZANG, Xiuqi BAO, Dan ZHANG( )(
)( )
)
Received:2022-11-30
Revised:2023-02-11
Online:2023-04-25
Published:2023-04-25
Contact:
Dan ZHANG
CLC Number:
Jingwei MA,Gen LI,Yang YANG,et al. Comparative Study on Different Recovery Periods of the Spermatogenic Dysfunction Mouse Model Induced by Cyclophosphamide[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 112-123. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.167.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2022.167
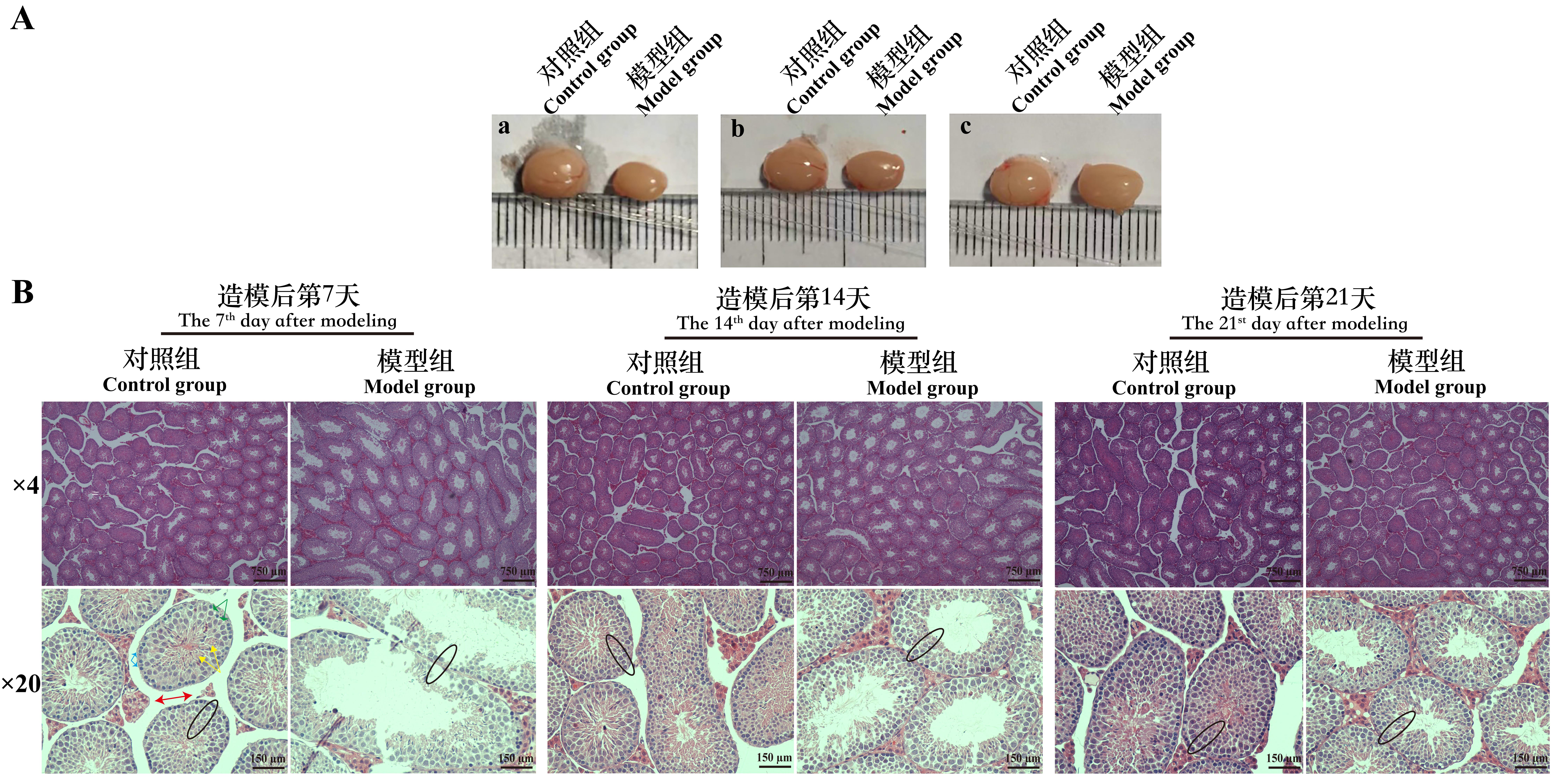
Figure 2 The changes of testicular appearance(A) and testicular histopathology (B) of spermatogenic dysfunction mice on the 7th, 14th and 21st day after cyclophosphamide administration (HE staining)Note: The red arrow indicates interstitial cells; the blue arrow indicates spermatogonium; the green arrow indicates spermatocyte; the yellow arrow indicates spermatid; the coil represents the number of spermatogenic cell layer.
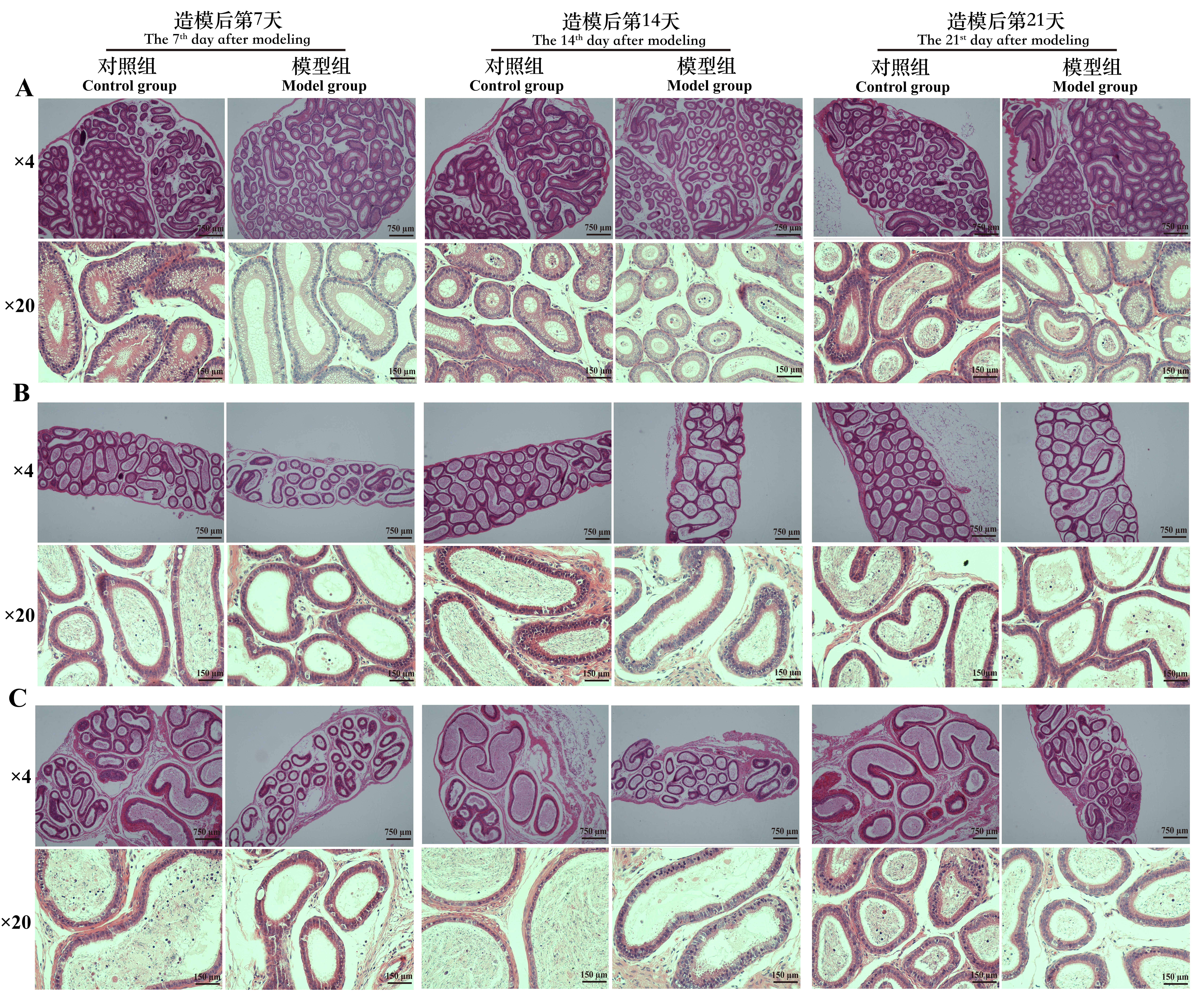
Figure 3 Pathological changes of epididymal head (A), body (B) and tail (C) of spermatogenic dysfunction mice on the 7th, 14th and 21st day after cyclophosphamide administration (HE staining)
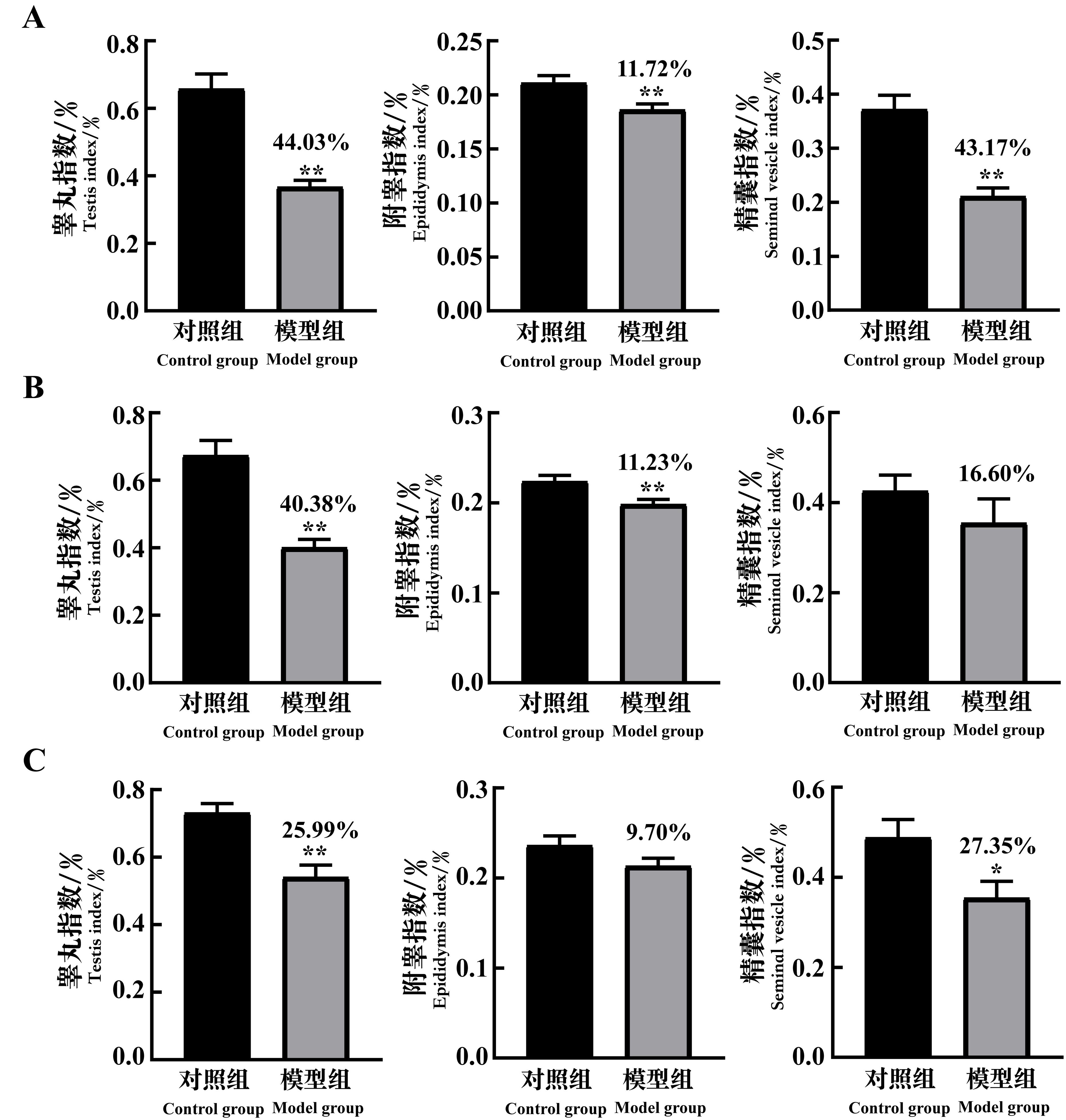
Figure 4 The changes of reproductive organ index of spermatogenic dysfunction mice on the 7th(A), 14th(B)and 21st(C)day after cyclophosphamide administrationNote: In each group, n=8. Compared with the control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. The data above the model group is the percentage decline compared with the control group.
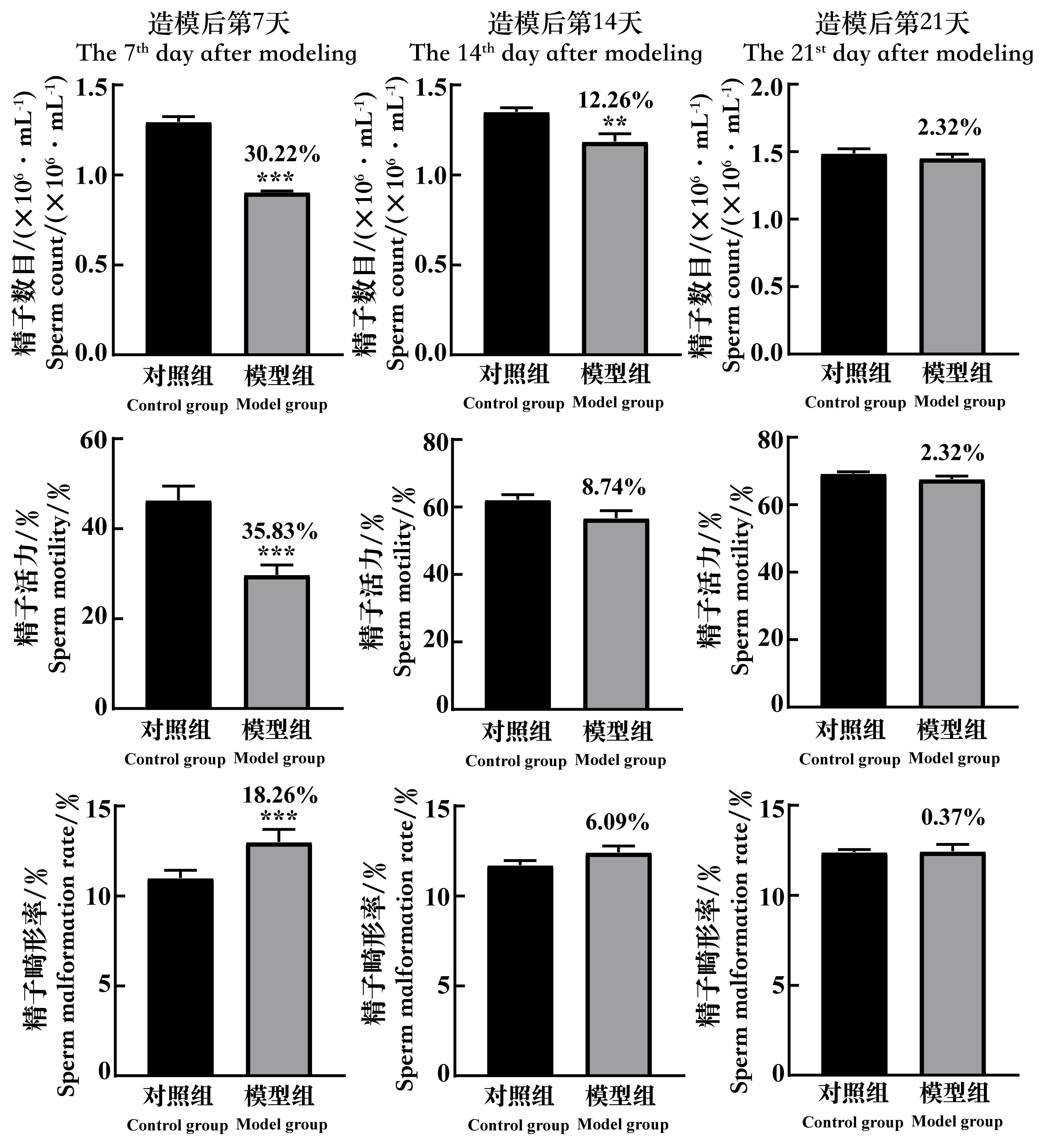
Figure 5 The changes of the sperm count, the sperm motility and the rate of sperm malformation of spermatogenic dysfunction mice on the 7th, 14th and 21st day after cyclophosphamide administrationNote:In each group, n=8. Compared with the control group, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. The data above the model group is the percentage decline compared with the control group.
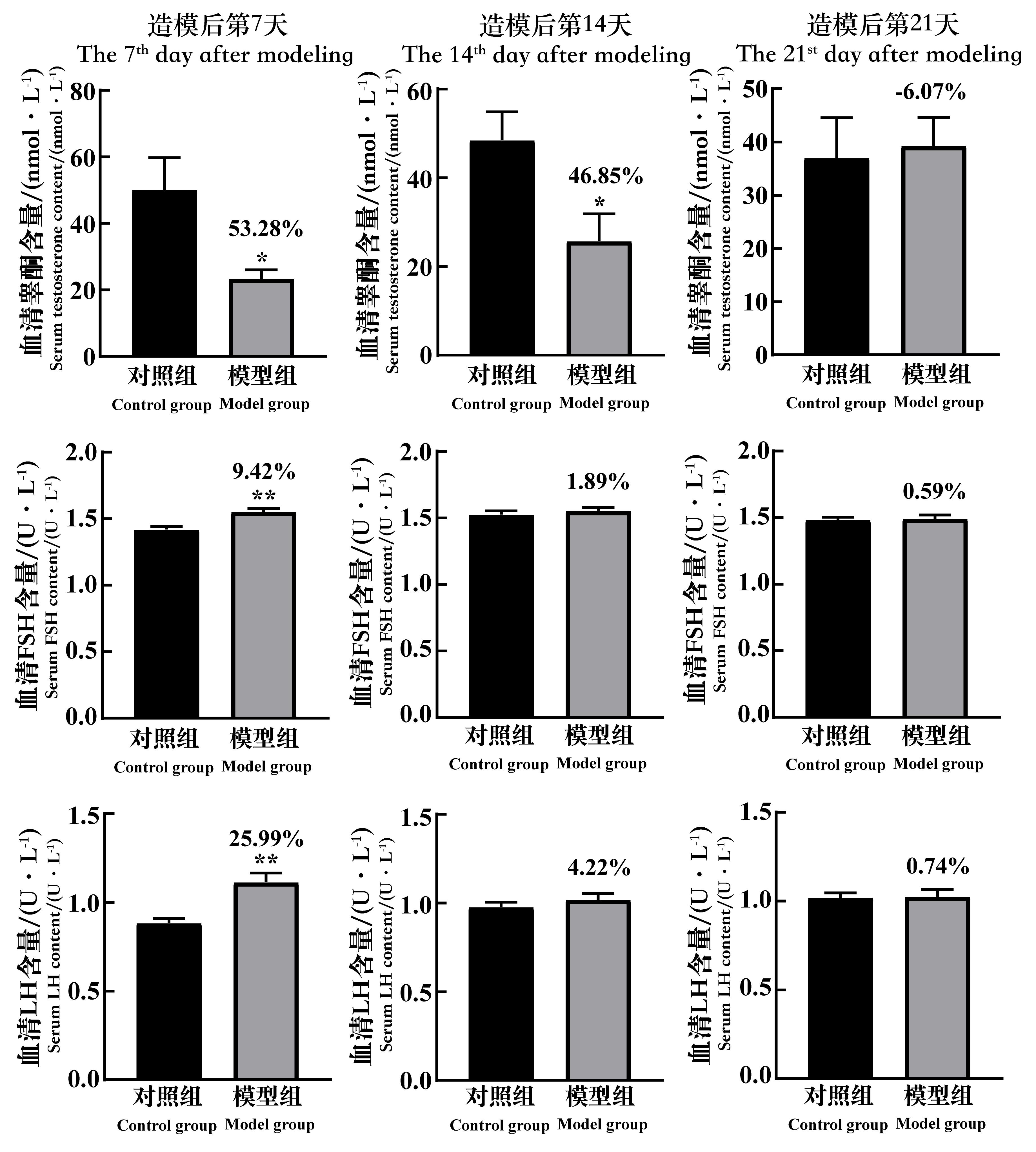
Figure 6 The changes of the serum testosterone content, FSH content and LH content of spermatogenic dysfunction mice on the 7th, 14th and 21st day after cyclophosphamide administrationNote:FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone; LH, luteinizing hormone. In each group, n=8. Compared with the control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01.The data above the model group is the percentage decline compared with the control group.
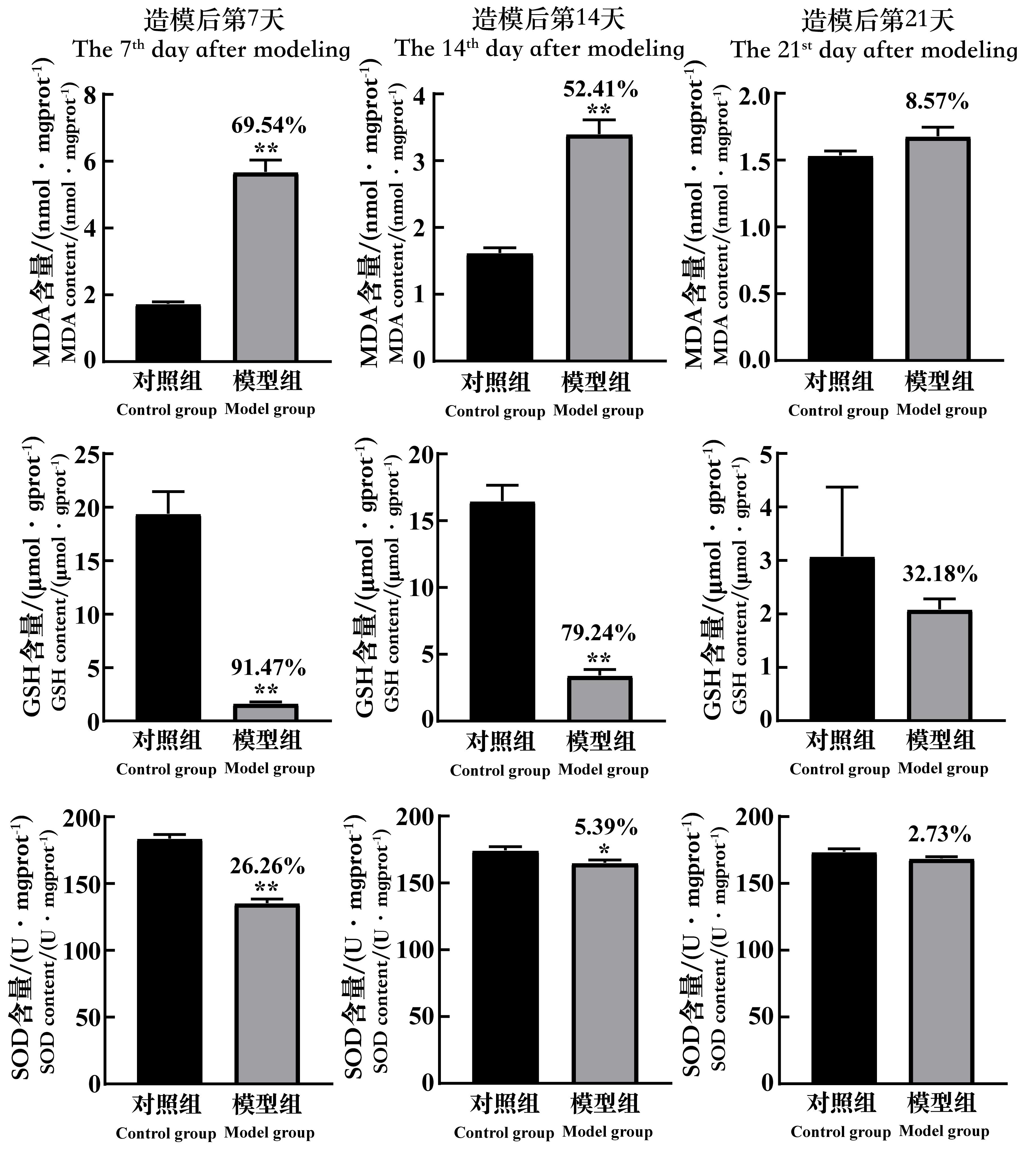
Figure 7 The changes of the MDA, GSH and SOD content in testicular tissue of spermatogenic dysfunction mice on the 7th, 14th and 21st day after cyclophos-phamide administrationNote:MDA,malonaldehyde;GSH,glutathione;SOD, superoxide dismutase; mgprot/gprot, per 1 mg (g) protein. In each group,n=8. Compared with the control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. The data above the model group is the percentage decline compared with the control group.
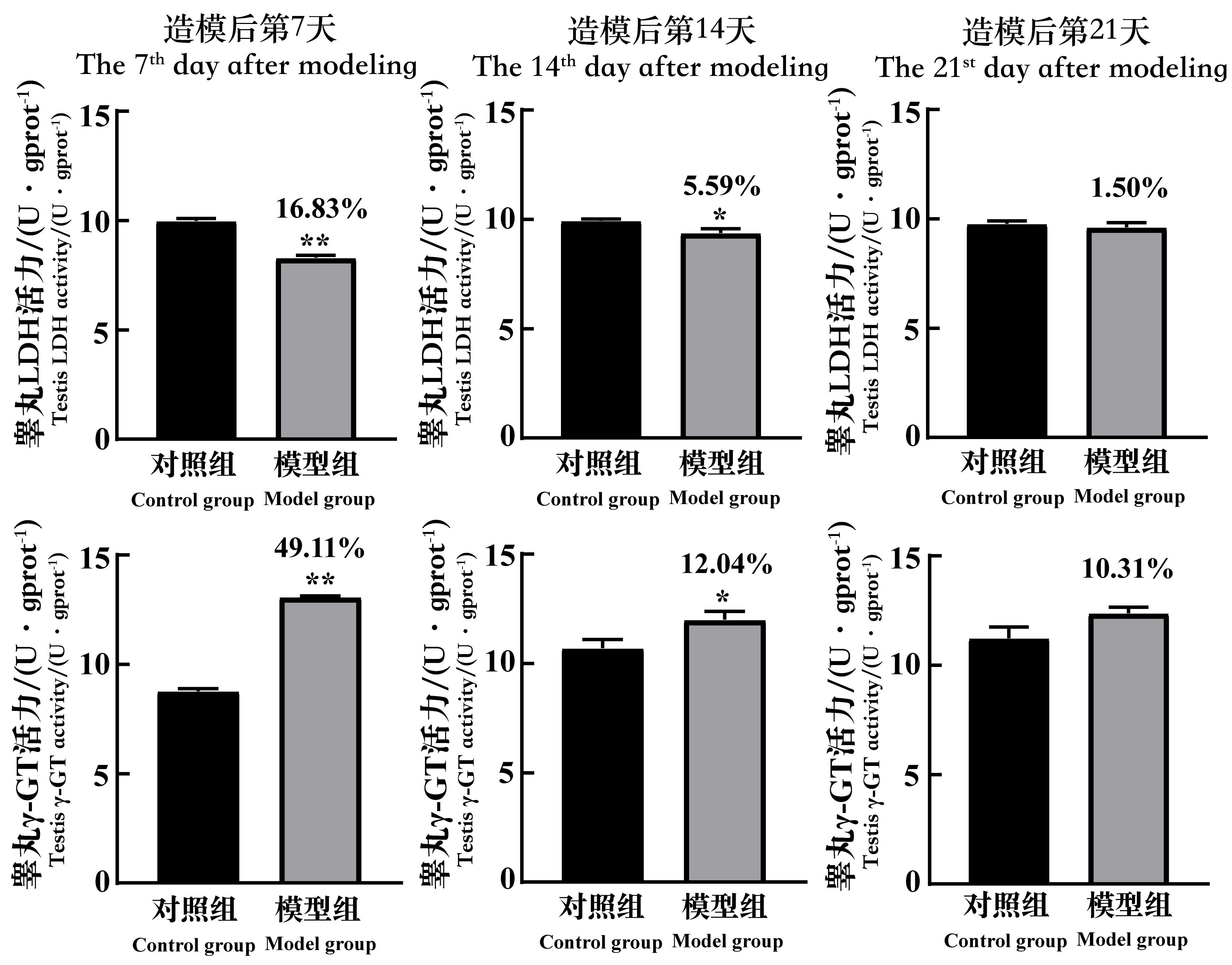
Figure 8 The changes of the LDH and γ-GT activity in testicular tissue of spermatogenic dysfunction mice on the 7th, 14th and 21st day after cyclophosphamide administrationNote:LDH, lactic dehydrogenase; γ-GT, gamma-glutamyl-trans-ferase; mgprot (gprot), per 1 mg(g) protein. In each group, n=8. Compared with the control group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. The data above the model group is the percentage decline compared with the control group.
| 1 | 王梦梦, 克迎迎, 李亚格, 等. 杜仲补天素胶囊改善环磷酰胺诱导的小鼠生精障碍研究[J]. 中草药, 2019, 50(11): 2625-2631. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2019.11.018 . |
| WANG M M, KE Y Y, LI Y G, et al. Effect of Duzhong Butiansu Capsule on improving spermatogenesis obstacle in mice induced by cyclophosphamide[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2019, 50(11): 2625-2631. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2019.11.018 . | |
| 2 | 阚玉璇, 曾梦楠, 张贝贝, 等. 杜仲补天素胶囊对己烯雌酚诱导雄性小鼠生精障碍的实验研究[J]. 中成药, 2020, 42(9):2445-2451. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2020.09.037 . |
| KAN Y X, ZENG M N, ZHANG B B, et al. Experimental study of Eucommia ulmoides Butiansu capsule on spermatogenic disorder induced by diethylstilbestrol in male mice[J]. Chin Tradit Pat Med, 2020, 42(9):2445-2451. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2020.09.037 . | |
| 3 | 李环, 曲振廷, 钱鸿昊, 等. 人参皂苷Rg1联合人参皂苷Rg3对雄性生殖功能损伤模型小鼠生殖功能的改善作用[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2020, 46(4):707-713. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20200407 . |
| LI H, QU Z T, QIAN H H, et al. Improvement effect of ginsenoside Rg1 combined with ginsenoside Rg3 on reproductive function in male model mice with reproductive function injury[J]. J Jilin Univ Med Ed, 2020, 46(4):707-713. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20200407 . | |
| 4 | 陈指龙, 张晓春, 薛立群, 等. 环磷酰胺致小鼠生精障碍作用研究[J]. 动物医学进展, 2017, 38(5):34-38. DOI: 10.16437/j.cnki.1007-5038.2017.05.008 . |
| CHEN Z L, ZHANG X C, XUE L Q, et al. Effect of cyclophosphamide on mouse spermatogenic obstacles[J]. Prog Vet Med, 2017, 38(5):34-38. DOI: 10.16437/j.cnki.1007-5038.2017.05.008 . | |
| 5 | 舒淇琳, 王梅, 曹国琼, 等. 杜仲补天素丸对环磷酰胺诱导的生精障碍保护作用[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2022, 33(9):2119-2121. |
| SHU Q L, WANG M, CAO G Q, et al. Protective effect of Duzhongbutiansuwan on spermatogenesis induced by cyclophosphamide[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2022, 33(9):2119-2121. | |
| 6 | FAN Q G, ZHAO Z Y, MENG Q, et al. Improvement of astragalin on spermatogenesis in oligoasthenozoospermia mouse induced by cyclophosphamide[J]. Reprod Sci, 2022, 29(6):1738-1748. DOI: 10.1007/s43032-021-00808-8 . |
| 7 | DOHLE G R. Male infertility in cancer patients: review of the literature[J]. Int J Urol, 2010, 17(4):327-331. DOI: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2010.02484.x . |
| 8 | ELANGOVAN, CHIOU T J W., TZENG W F, et al.Cyclo-phosphamide treatment causes impairment of sperm and its fertilizing ability in mice[J]. Toxicology, 2006, 222(1-2):60-70. DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2006.01.027 . |
| 9 | SELVAKUMAR E, PRAHALATHAN C, SUDHARSAN P T, et al. Protective effect of lipoic acid on cyclophosphamide-induced testicular toxicity[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2006, 367(1-2):114-119. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2005.11.034 . |
| 10 | FUKUTANI K, ISHIDA H, SHINOHARA M, et al. Suppression of spermatogenesis in patients with Behçet's disease treated with cyclophosphamide and colchicine[J]. Fertil Steril, 1981, 36(1):76-80. DOI: 10.1016/S0015-0282(16)45622-0 . |
| 11 | SAPKOTA Y, WILSON C L, ZAIDI A K, et al. A novel locus predicts spermatogenic recovery among childhood cancer survivors exposed to alkylating agents[J]. Cancer Res, 2020, 80(17):3755-3764. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-0093 . |
| 12 | SIMON, HOWELL, MRCP, et al. Gonadal damage from chemotherapy and radiotherapy[J]. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am, 1998, 27(4):927-943. DOI: 10.1016/S0889-8529(05)70048-7 . |
| 13 | EN L T, BROUGHAM M F H, WALLACE W H B, et al. Impacts of platinum-based chemotherapy on subsequent testicular function and fertility in boys with cancer[J]. Hum Reprod Update, 2020, 26(6):874-885. DOI: 10.1093/humupd/dmaa041 . |
| 14 | SUN Y M, GAO F, XU D, et al. Wenshen Shengjing Decoction improves early embryo development by maintaining low H3K27me3 levels in sperm and pronuclear embryos of spermatogenesis impaired mice[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2021, 2021:8035997. DOI: 10.1155/2021/8035997 . |
| 15 | 刘建国, 赵红乐, 李姣姣, 等. 补肾活血方对环磷酰胺所致小鼠睾丸生精细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中华男科学杂志, 2020, 26(9):826-831. DOI: 10.13263/j.cnki.nja.2020.09.012 . |
| LIU J G, ZHAO H L, LI J J, et al. Bushen Huoxue Recipe reduces cyclophosphamide-induced apoptosis of spermatogenic cells in mice[J]. Natl J Androl, 2020, 26(9):826-831. DOI: 10.13263/j.cnki.nja.2020.09.012 . | |
| 16 | 范红艳, 江素鑫, 李乐乐, 等. CTX对雄性小鼠生殖功能的影响及杨梅素的干预研究[J]. 中药药理与临床, 2019, 35(5):43-46. DOI: 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2019.05.010 . |
| FAN H Y, JIANG S X, LI L L, et al. Influence of cyclophosphamide on reproductive function of male mice and intervention of myricetin[J]. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Med, 2019, 35(5):43-46. DOI: 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2019.05.010 . | |
| 17 | YAN G, TIAN F, LIU P, et al. Sheng Jing Decoction can promote spermatogenesis and increase sperm motility of the oligozoospermia mouse model[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2021, 2021:3686494. DOI: 10.1155/2021/3686494 . |
| 18 | 李勋, 陈建设, 门波, 等. 益肾通络方调控PI3K/Akt通路对环磷酰胺诱导无精/少精症大鼠模型的保护作用研究[J]. 天津医药, 2020, 48(12):1159-1164. DOI: 10.11958/20201749 . |
| LI X, CHEN J S, MEN B, et al. The protective effect of Yishen Tongluo Fang regulating PI3K/Akt pathway on the azoospermia/oligozoospermia model rats induced by cyclophosphamide[J]. Tianjin Med J, 2020, 48(12):1159-1164. DOI: 10.11958/20201749 . | |
| 19 | 伍欢, 李其闯, 贾欣, 等. 环磷酰胺对小鼠精子质量及相关酶的影响[J]. 科教文汇(上旬刊), 2018(9):181-183. DOI: 10.16871/j.cnki.kjwha.2018.09.076 . |
| WU H, LI Q C, JIA X, et al. Effect of cyclophosphamide on sperm quality and related enzymes in mice[J]. Sci Educ Article Collects, 2018(9):181-183. DOI: 10.16871/j.cnki.kjwha.2018.09.076 . | |
| 20 | 王慧慧, 张莉, 徐瑞豪, 等. 杜仲补天素胶囊对白消安诱导的生精障碍小鼠的影响[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2020, 31(2):169-178. DOI: 10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2020.02.008 . |
| WANG H H, ZHANG L, XU R H, et al. Effect of Duzhong Butiansu capsule on busulfan-induced spermatogenic impairment in mice[J]. Tradit Chin Drug Res Clin Pharmacol, 2020, 31(2):169-178. DOI: 10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2020.02.008 . | |
| 21 | 曹兵, 孙亚萍, 司彦坡, 等. 杜仲补天素胶囊对双酚A诱导小鼠生精障碍的保护作用研究[J]. 中国新药杂志, 2020, 29(3):343-351. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3734.2020.03.018 . |
| CAO B, SUN Y P, SI Y P, et al. Protective effect of Duzhong Butiansu capsules on bisphenol A-induced spermatogenic disorder in mice[J]. Chin J New Drugs, 2020, 29(3):343-351. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3734.2020.03.018 . | |
| 22 | 蒋福兴. 血睾屏障体内动态变化细胞生物学机制的研究[D]. 北京: 首都师范大学, 2008. |
| JIANG F X. A study on the cellular biological mechanisms of dynamic changes in the blood testis barrier in vivo [D]. Beijing: Capital Normal University, 2008. | |
| 23 | QIAN L, YU S J. Protective effect of polysaccharides from Lycium barbarum on spermatogenesis of mice with impaired reproduction system induced by cyclophosphamide[J]. Am J Reprod Immunol, 2016, 76(5):383-385. DOI: 10.1111/aji.12558 . |
| 24 | NOOH M M, RIZK S M, SAIED N M, et al. Carnosine remedial effect on fertility of male rats receiving cyclophosphamide, hydroxydaunomycin, oncovin and prednisone (CHOP)[J]. Andrologia, 2021, 53(11): e14233. DOI: 10.1111/and.14233 . |
| 25 | 龚晓娟, 马盼, 孙敏, 等. DRD1基因敲除影响雄鼠生育的分子机理研究[J]. 实验动物科学, 2021, 38(2):53-56, 60. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6179.2021.02.009 . |
| GONG X J, MA P, SUN M, et al. Study on molecular mechanism of male mice reproduction in DRD1 knockout[J]. Lab Anim Sci, 2021, 38(2):53-56, 60. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6179.2021.02.009 . | |
| 26 | SOLOMON R, ABUMADIGHEM A, KAPELUSHNIK J, et al. Involvement of cytokines and hormones in the development of spermatogenesis in vitro from spermatogonial cells of cyclophosphamide-treated immature mice[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(4):1672. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22041672 . |
| 27 | CAO Y C, WANG X S, LI S Q, et al. The effects of l-carnitine against cyclophosphamide-induced injuries in mouse testis[J]. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol, 2017, 120(2):152-158. DOI: 10.1111/bcpt.12679 . |
| 28 | 乐小炎, 原林, 林少杰, 等. 乌贼墨多糖的制备及对睾丸化疗性损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品工业科技, 2013, 34(17):342-344, 348. DOI: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2013.17.003 . |
| LE X Y, YUAN L, LIN S J, et al. Preparation of squid ink polysaccharides and its protection against chemo-therapeutic injury on testis[J]. Sci Technol Food Ind, 2013, 34(17):342-344, 348. DOI: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2013.17.003 . | |
| 29 | 范红艳, 王艳春, 顾饶胜, 等. 生精障碍动物模型的研究进展[J]. 吉林医药学院学报, 2013, 34(2):120-123. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2995.2013.02.017 . |
| FAN H Y, WANG Y C, GU R S, et al. Research of the animal model of spermatogenic abnormalities[J]. J Jilin Med Coll, 2013, 34(2):120-123. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2995.2013.02.017 . | |
| 30 | 宿文辉, 张天彪, 张丽雁, 等. Rab13 GTPase在大鼠睾丸中的表达及其与生精上皮周期的关系[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2010, 18(5):402-405, 358. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2010.05.09 . |
| SU W H, ZHANG T B, ZHANG L Y, et al. Expression of Rab13 GTPase in rat testis and its relation with seminiferous epithelium cycle[J]. Acta Lab Anim Sci Sin, 2010, 18(5):402-405, 358. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2010.05.09 . |
| [1] | GONG Leilei, WANG Xiaoxia, FENG Xuewei, LI Xinlei, ZHAO Han, ZHANG Xueyan, FENG Xin. A Mouse Model and Mechanism Study of Premature Ovarian Insufficiency Induced by Different Concentrations of Cyclophosphamide [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 403-410. |
| [2] | SONG Ying, GUO Ya-juan, HUANG Ming-qian, LIANG Jin-qiang, HUANG Zhi-ying. Effect of Different Factors on Cyclophosphamide Induced Immunosuppression Mice Model [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2017, 37(1): 36-39. |
| [3] | GU Yun-hao, CAO Chen-jie, HU Bi-yuan, WANG Jun, HAN Dong-dong, XU Ai-hua. Establishment of S180 Tumor Multidrug Resistance Mouse Model by Increasing PFC and Observation on Stability [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2015, 35(5): 367-373. |
| [4] | LI Hao, JI Guo-xia, WANG Ke-zhou, JI Chuan-liang, LI Lan-bo, ZHANG Yan, FENG Mo-zhu, LI Jian-mei, LIU Tao. The Influence of Colla Corii Asini on Growth and Quality of Hair in Mice Treated by Cyclophosphamide [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2015, 35(1): 17-22. |
| [5] | LIU Xiang-mei,ZHANG Yu,MIN Fan-gui,ZHAO Wei-bo,LIU Zhong-hua,ZHANG Li-xin,HUANG Ren. Effects of Cyclophosphamide on Leukocyte of C.parapsilosis Infected Mice [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2007, 27(2): 116-118. |
| [6] | WANG Ren-Li, JIANG Xiu-Rong, ZHANG Yan-Lin, ZHANG Zhong-Shu. The Chromosome Aberration Induced by Mutagen in Mouse Germ Cells and Its Influence on Embryo Development [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 1999, 19(1): 18-21. |
| [7] | ZHAO Xi-Xin-1, YAN Du-Hai-1, WANG He-Ping-2, TIAN Kai-Yu-1, DU Cai-Xia-1. Mouse Leukopenia Model Induced by Intraperitoneal Injection of Cyclophosphamide and Dynamic Analysis [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 1998, 18(1): 12-14. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||