
Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 675-681.DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.049
• Animal Experimental Techniques and Methods • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Haifeng( ), ZHOU Xiaojiang, LI Chenjiang, LI Huaiyin, GAO Ming(
), ZHOU Xiaojiang, LI Chenjiang, LI Huaiyin, GAO Ming( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-03-28
Revised:2024-07-03
Online:2024-12-25
Published:2024-12-25
Contact:
GAO Ming
CLC Number:
WU Haifeng,ZHOU Xiaojiang,LI Chenjiang,et al. Comparison of the Fixation Effects of Six Composite Fixatives on Retinal Tissue of Golden Hamsters[J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 675-681. DOI: 10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.049.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.slarc.org.cn/dwyx/EN/10.12300/j.issn.1674-5817.2024.049
固定液种类 Types of fixative | 视网膜完整度 Integrity of the retina | 视网膜各层结构排列 Uniformity of each layer of the retina | 视网膜结构清晰度 Retinal structural resolution | 视网膜各层染色 Staining of each layer of the retina | 视网膜各层连接 Connection of retinal layers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
4%多聚甲醛 4% paraformaldehyde | 完整无断裂 | 整齐 | 清晰 | 鲜艳 | 紧密 |
Bouin's固定液 Bouin's fixative | 断裂较多 | 较整齐 | 清晰 | 鲜艳 | 紧密 |
Zenker固定液 Zenker fixative | 破碎、脱片 | 各层结构消失 | 不清晰 | 淡染 | 完全脱离 |
Helly固定液 Helly fixative | 较少断裂 | 结构模糊 | 模糊 | 模糊 | 完全脱离 |
Carnoy固定液 Carnoy fixative | 完整无断裂 | 紧密,结构不清 | 不清晰 | 鲜艳 | 紧密 |
Davidson's固定液 Davidson's fixative | 完整无断裂 | 结构整齐 | 清晰 | 鲜艳 | 较多裂隙 |
Table 1 Comparison of HE staining effects on retinal tissue of golden hamsters fixed with six fixatives under low magnification
固定液种类 Types of fixative | 视网膜完整度 Integrity of the retina | 视网膜各层结构排列 Uniformity of each layer of the retina | 视网膜结构清晰度 Retinal structural resolution | 视网膜各层染色 Staining of each layer of the retina | 视网膜各层连接 Connection of retinal layers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
4%多聚甲醛 4% paraformaldehyde | 完整无断裂 | 整齐 | 清晰 | 鲜艳 | 紧密 |
Bouin's固定液 Bouin's fixative | 断裂较多 | 较整齐 | 清晰 | 鲜艳 | 紧密 |
Zenker固定液 Zenker fixative | 破碎、脱片 | 各层结构消失 | 不清晰 | 淡染 | 完全脱离 |
Helly固定液 Helly fixative | 较少断裂 | 结构模糊 | 模糊 | 模糊 | 完全脱离 |
Carnoy固定液 Carnoy fixative | 完整无断裂 | 紧密,结构不清 | 不清晰 | 鲜艳 | 紧密 |
Davidson's固定液 Davidson's fixative | 完整无断裂 | 结构整齐 | 清晰 | 鲜艳 | 较多裂隙 |
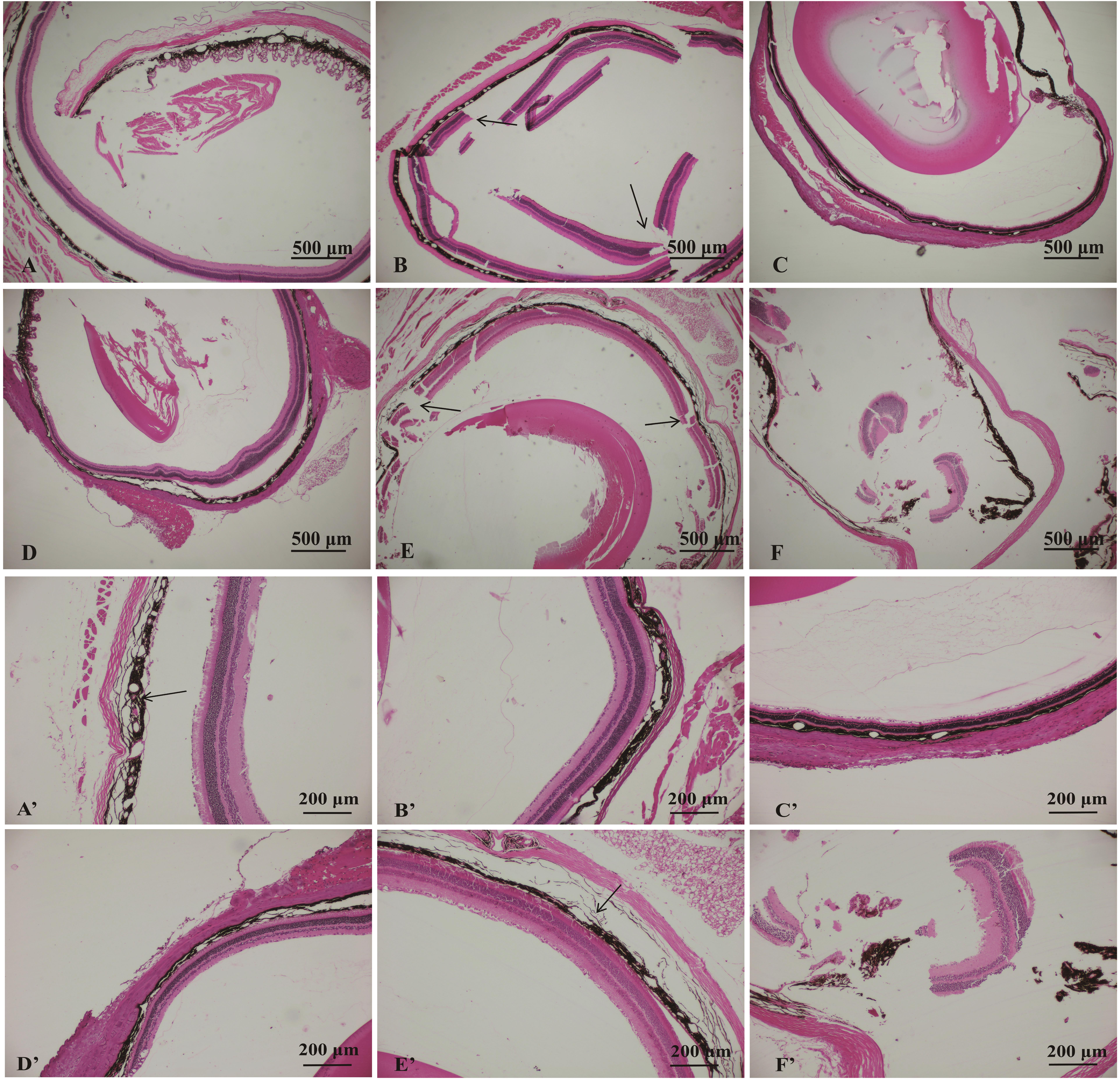
Figure 1 HE staining results of retinal sections of golden hamsters fixed with different fixatives under low magnificationNote: A and A’, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (the arrow in fig A’ shows a large fissure between the retina and the sclera and the uvea); B and B’, fixed with Bouin's fixative (multiple breaks shown by arrows in fig B); C and C’, fixed with Carnoy fixative; D and D’, fixed with Davidson's fixative; E and E’, fixed with Helly fixative (the arrow in fig E shows breaks, while the arrow in the fig E’ shows the separation between the sclera and the uvea ); F and F’, fixed with Zenker fixative. The scale bar=500 μm(A-F) or 200 μm (A’-F’).
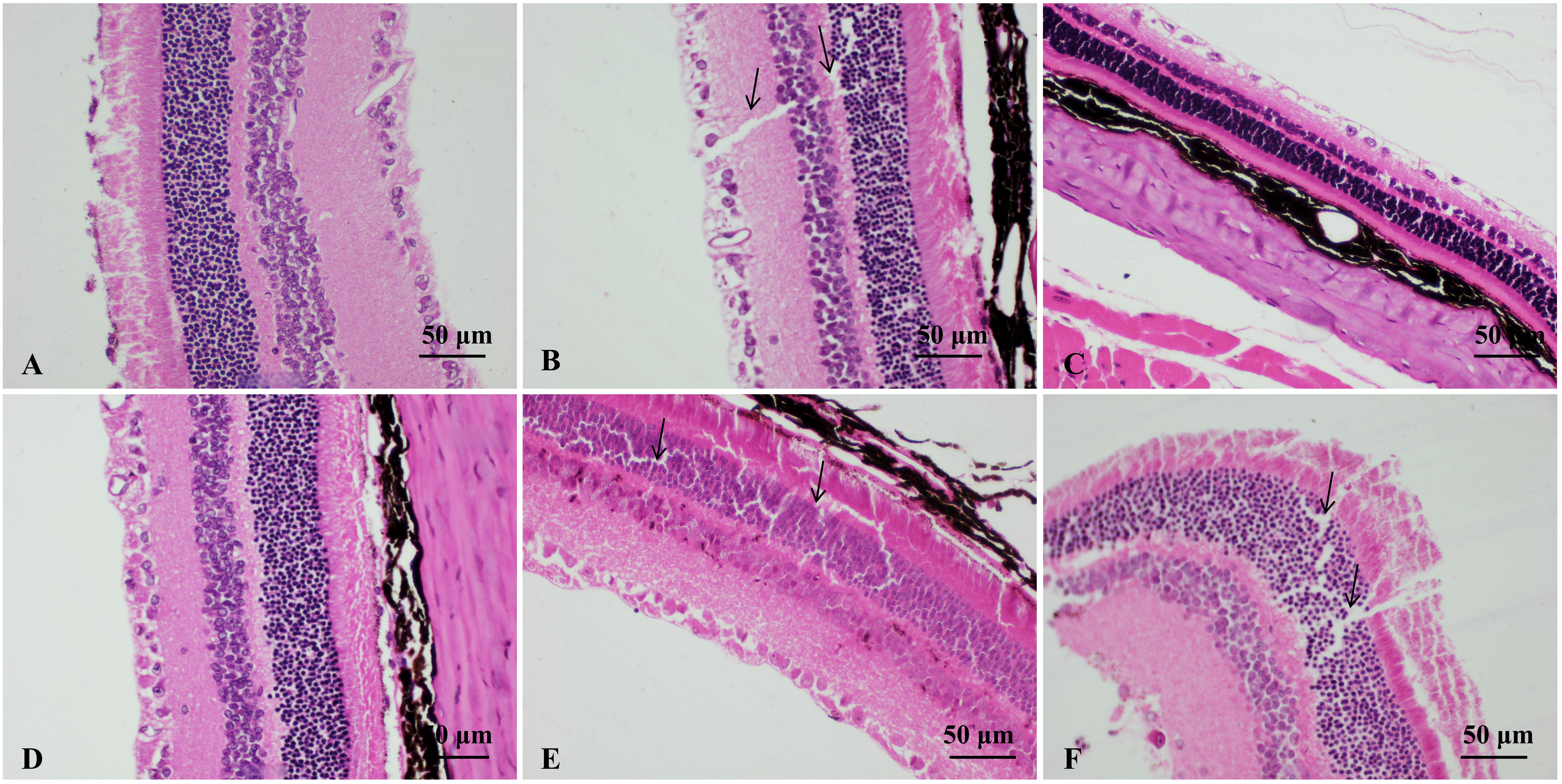
Figure 2 HE staining results of retinal sections of golden hamsters fixed with different fixatives under high magnificationNote:fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde; B, fixed with Bouin's fixative; C, fixed with Carnoy fixative; D, fixed with Davidson's fixative; E, fixed with Helly fixative; F, fixed with Zenker fixative. The fissures are indicated by arrows. The scale bar=50 μm.
固定液种类 Types of fixative | 视网膜完整度 Integrity of retina | 视网膜各层结构排列 Uniformity of each layer of the retina | 细胞核形态 Nuclear morphology | 细胞间紧密程度 Degree of intercellular tightness | 细胞质染色强度 Cytoplasmic staining intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
4%多聚甲醛 4% paraformaldehyde | 完整无脱落 | 松散 | 良好 | 整齐无裂隙 | 清晰 |
Bouin's固定液 Bouin's fixative | 完整无脱落 | 紧密 | 较好 | 松散 | 清晰 |
Zenker固定液 Zenker fixative | 脱落松散 | 松散 | 基本正常 | 裂隙较多 | 较淡 |
Helly固定液 Helly fixative | 很多裂隙 | 消失 | 模糊 | 裂隙较多 | 模糊 |
Carnoy固定液 Carnoy fixative | 较完整 | 消失 | 固缩,不清 | 松散 | 模糊 |
Davidson's固定液 Davidson's fixative | 完整 | 紧密 | 良好 | 整齐无裂隙 | 清晰 |
Table 2 Comparison of HE staining effects on retinal tissue of golden hamsters fixed with six fixatives under high magnification
固定液种类 Types of fixative | 视网膜完整度 Integrity of retina | 视网膜各层结构排列 Uniformity of each layer of the retina | 细胞核形态 Nuclear morphology | 细胞间紧密程度 Degree of intercellular tightness | 细胞质染色强度 Cytoplasmic staining intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
4%多聚甲醛 4% paraformaldehyde | 完整无脱落 | 松散 | 良好 | 整齐无裂隙 | 清晰 |
Bouin's固定液 Bouin's fixative | 完整无脱落 | 紧密 | 较好 | 松散 | 清晰 |
Zenker固定液 Zenker fixative | 脱落松散 | 松散 | 基本正常 | 裂隙较多 | 较淡 |
Helly固定液 Helly fixative | 很多裂隙 | 消失 | 模糊 | 裂隙较多 | 模糊 |
Carnoy固定液 Carnoy fixative | 较完整 | 消失 | 固缩,不清 | 松散 | 模糊 |
Davidson's固定液 Davidson's fixative | 完整 | 紧密 | 良好 | 整齐无裂隙 | 清晰 |
| 1 | 李娟娟, 陈晨, 张利伟, 等. 缺血-再灌注损伤鼠模型中视网膜微循环的结构损伤[J]. 中华实验眼科杂志, 2019, 37(1):5-9. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-0160.2019.01.002 . |
| LI J J, CHEN C, ZHANG L W, et al. Structural changes of retinal microcirculation in mouse model of ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Chin J Exp Ophthalmol, 2019, 37(1):5-9. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-0160.2019.01.002 . | |
| 2 | SANO H, NAMEKATA K, KIMURA A, et al. Differential effects of N-acetylcysteine on retinal degeneration in two mouse models of normal tension glaucoma[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10(2):75. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-1365-z . |
| 3 | STORM T, BURGOYNE T, DUNAIEF J L, et al. Selective ablation of megalin in the retinal pigment epithelium results in megaophthalmos, macromelanosome formation and severe retina degeneration[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2019, 60(1):322-330. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.18-25667 . |
| 4 | 陈肖君, 林鑫, 于瑶瑶, 等. HUC-MSCs对视网膜挫伤大鼠的治疗作用[J]. 潍坊医学院学报, 2020, 42(5):356-359. DOI: 10.16846/j.issn.1004-3101.2020.05.011 . |
| CHEN X J, LIN X, YU Y Y, et al. Therapeutic effect of HUC-MSCs in rat retinal contusion[J]. Acta Acad Med Weifang, 2020, 42(5):356-359. DOI: 10.16846/j.issn.1004-3101.2020.05.011 . | |
| 5 | 袁晨, 张梅, 谢学军. 血-视网膜内屏障体外模型构建研究进展[J]. 国际眼科杂志, 2021, 21(6):991-995. DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.1672-5123.2021.6.10 . |
| YUAN C, ZHANG M, XIE X J. Progress in the construction of inner blood retinal barrier model in vitro [J]. Int Eye Sci, 2021, 21(6):991-995. DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.1672-5123.2021.6.10 . | |
| 6 | 张懿, 孙兴怀, 王中峰. 生长抑素对视网膜的生理调控及神经保护作用[J]. 中华实验眼科杂志, 2021, 39(10):915-918. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115989-20191112-00492 . |
| ZHANG Y, SUN X H, WANG Z F. Physiological role and neuroprotective effects of somatostatin in retina[J]. Chin J Exp Ophthalmol, 2021, 39(10):915-918. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115989-20191112-00492 . | |
| 7 | 赵福新, 汪琪, 王莉, 等. Vipr2敲除对小鼠视网膜功能的影响[J]. 中华眼视光学与视觉科学杂志, 2022, 24(7):485-493. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115909-20210826-00342 . |
| ZHAO F X, WANG Q, WANG L, et al. The effect of Vipr2 knockout on retinal function in mice[J]. Chin J Optom Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2022, 24(7):485-493. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115909-20210826-00342 . | |
| 8 | 罗灿峤, 莫木琼, 聂钊铭, 等. 比较5种混合固定液对小鼠眼球标本制片质量和染色效果的影响[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2015, 25(13):2065-2067. |
| LUO C Q, MO M Q, NIE Z M, et al. Effect of 5 mixed stationary liquids on the mouse eyeball specimen sectioning and the staining quality[J]. Chin J Health Lab Technol, 2015, 25(13):2065-2067. | |
| 9 | 张云龙. 无醛混合固定液与甲醛固定液对大鼠器官组织检材形态学保存效果的比较研究[J]. 基层医学论坛, 2020, 24(16):2223-2225. DOI: 10.19435/j.1672-1721.2020.016.002 . |
| ZHANG Y L. A comparative study on the morphological preservation effect of formaldehyde-free fixative and formaldehyde on tissue samples of rat organs[J]. Med Forum, 2020, 24(16):2223-2225. DOI: 10.19435/j.1672-1721.2020.016.002 . | |
| 10 | 高延娥, 杜秀娟, 董卫红, 等. 心脏灌流固定在大鼠视网膜石蜡切片中的应用[J]. 中国实用眼科杂志, 2016, 34(10):1109-1111. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-4443.2016.10.019 . |
| GAO Y E, DU X J, DONG W H, et al. Application of cardiac perfusion fixation in rat retinal parafin section[J]. Chin J Pract Ophthalmol, 2016, 34(10):1109-1111. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-4443.2016.10.019 . | |
| 11 | 高洪彬, 林英, 宋向荣, 等. 四种固定液对小鼠视网膜固定效果的比较[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志, 2016, 32(3):352-353. DOI: 10.13315/j.cnki.cjcep.2016.03.032 . |
| GAO H B, LIN Y, SONG X R, et al. Comparison of the effects of four fixatives on retinal fixation in mice[J]. Chin J Clin Exp Pathol, 2016, 32(3):352-353. DOI: 10.13315/j.cnki.cjcep.2016.03.032 . | |
| 12 | STRADLEIGH T W, ISHIDA A T. Fixation strategies for retinal immunohistochemistry[J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2015, 48:181-202. DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2015.04.001 . |
| 13 | LIU Y, EDWARD D P. Assessment of PAXgene fixation on preservation of morphology and nucleic acids in microdissected retina tissue[J]. Curr Eye Res, 2017, 42(1):104-110. DOI: 10.3109/02713683.2016.1146777 . |
| 14 | BACZEWSKA M, EDER K, KETELHUT S, et al. Refractive index changes of cells and cellular compartments upon paraformaldehyde fixation acquired by tomographic phase microscopy[J]. Cytometry A, 2021, 99(4):388-398. DOI: 10.1002/cyto.a.24229 . |
| 15 | MIKI M, OHISHI N, NAKAMURA E, et al. Improved fixation of the whole bodies of fish by a double-fixation method with formalin solution and Bouin's fluid or Davidson's fluid[J]. J Toxicol Pathol, 2018, 31(3):201-206. DOI: 10.1293/tox.2018-0001 . |
| 16 | 孙自强, 王军, 陈明亮, 等. 小鼠眼球标本石蜡切片制作方法的改进[J]. 河南大学学报(医学版), 2015, 34(1):36-39. |
| SUN Z Q, WANG J, CHEN M L, et al. Improved method for paraffin sections of mouse eyeball[J]. J Henan Univ Med Sci, 2015, 34(1):36-39. | |
| 17 | 宋惠欣, 蒋文君, 毕宏生. 三种不同固定液对豚鼠眼球的固定效果比较[J]. 国际眼科杂志, 2018, 18(6):1010-1013. DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.1672-5123.2018.6.07 . |
| SONG H X, JIANG W J, BI H S. A comparative study on the effect of fixation for guinea pigs eyeballs among three different fixation solution[J]. Int Eye Sci, 2018, 18(6):1010-1013. DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.1672-5123.2018.6.07 . | |
| 18 | SOUSA S, ROCHA M J, ROCHA E. Characterization and spatial relationships of the hepatic vascular-biliary tracts, and their associated pancreocytes and macrophages, in the model fish guppy (Poecilia reticulata): a study of serial sections by light microscopy[J]. Tissue Cell, 2018, 50:104-113. DOI: 10.1016/j.tice.2017.12.009 . |
| 19 | WANG H, YANG L L, JI Y L, et al. Different fixative methods influence histological morphology and TUNEL staining in mouse testes[J]. Reprod Toxicol, 2016, 60:53-61. DOI: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2016.01.006 . |
| 20 | LATENDRESSE J R, WARBRITTION A R, JONASSEN H, et al. Fixation of testes and eyes using a modified Davidson's fluid: comparison with bouin's fluid and conventional Davidson's fluid[J]. Toxicol Pathol, 2002, 30(4):524-533. DOI: 10.1080/01926230290105721 . |
| [1] | Ying TAN, Wenping LIAO, Qilong GAO, Yong LI, Xinhui SHI, Jingkun WANG. Physiological Indexes and Histopathology Analysis of Sodium Iodate-Induced Retinitis Pigmentosa in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 124-135. |
| [2] | ZHAO Yupeng, ZHOU Pinghui, GUAN Jianzhong. Comparison of Different Slicing and Staining Methods of Caudal Intervertebral Discs in Rats [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2021, 41(2): 100-107. |
| [3] | FAN Fangling, XIA Shuang, GAN Lu, XIA Fang. Analysis of Nutritional Components and Amino Acid Composition of SPF Golden Hamster Milk [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2020, 40(2): 144-148. |
| [4] | ZHANG Hua-qiong, XIA Shuang, WU Yan-ru, HE Fan. Establishment and Quality Control of SPF Golden Hamster Colonies [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2019, 39(1): 56-60. |
| [5] | CUI Xiao-xia, SHANG Shi-chen, MA Lan-zhi, HUANG Bin, SHANG Yu-pu, WANG Dong-ping, CHEN Zhen-wen, WANG Quan-xin. Detection of Blood Physiological Parameters in Albino Mutant Golden Hamster [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2017, 37(6): 478-481. |
| [6] | YANG Dong-mei, ZHU Qin, LI Na, GUO Li-yun, ZHANG Xiao-fan, ZHANG Jie-ying, HU Min, DAI Jie-jie. Preliminary Establishment and Research on Form Deprivation Myopia Model in Tree Shrew [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2017, 37(3): 171-178. |
| [7] | DONG Wan-wei, ZHANG A-nuo, GUO Xiao-chong, WEI Zheng-li, YANG Wei, ZHAO Wen, SHEN Wei, ZHENG Zhi-hong. Construction of Golden Hamster Apoa5 Gene Expression Vector and Its Expression in Different Organs [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2015, 35(4): 283-287. |
| [8] | XIA Fang, ZHANG Hua-Qiong, HUANG Lin, ZHANG Shui-Tian, LUO Su-Lan, HE Fan. Establishment of SPF Golden Hamsters Breeding Colony by Cesarean [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2005, 25(3): 165-167. |
| [9] | YING Xian-Ping, QIAN Qin, QU Ya-Qin, JIANG Wen-Qin, PAN Zhen-Ye. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Detection of Virus Antibody in Golden Hamster [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 2000, 20(1): 34-36. |
| [10] | DUAN Kai-Wen, CHEN Qian-Ming, ZHOU Min, ZENG Guang-Ming. Study on Buccal Pouch Blood Flow and Hemorrheology in Golden Harmster [J]. Laboratory Animal and Comparative Medicine, 1997, 17(3): 146-147. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||