生物3D打印研究及与临床前动物模型的交叉应用展望
Prospects for 3D Bioprinting Research and Transdisciplinary Application to Preclinical Animal Models
生物3D打印研究及与临床前动物模型的交叉应用展望 |
| 胡敏, 董乐轩, 高怡, 奚子芪, 沈子皓, 唐瑞阳, 栾鑫, 汤忞, 张卫东 |
|
Prospects for 3D Bioprinting Research and Transdisciplinary Application to Preclinical Animal Models |
| HU Min, DONG Lexuan, GAO Yi, XI Ziqi, SHEN Zihao, TANG Ruiyang, LUAN Xin, TANG Min, ZHANG Weidong |
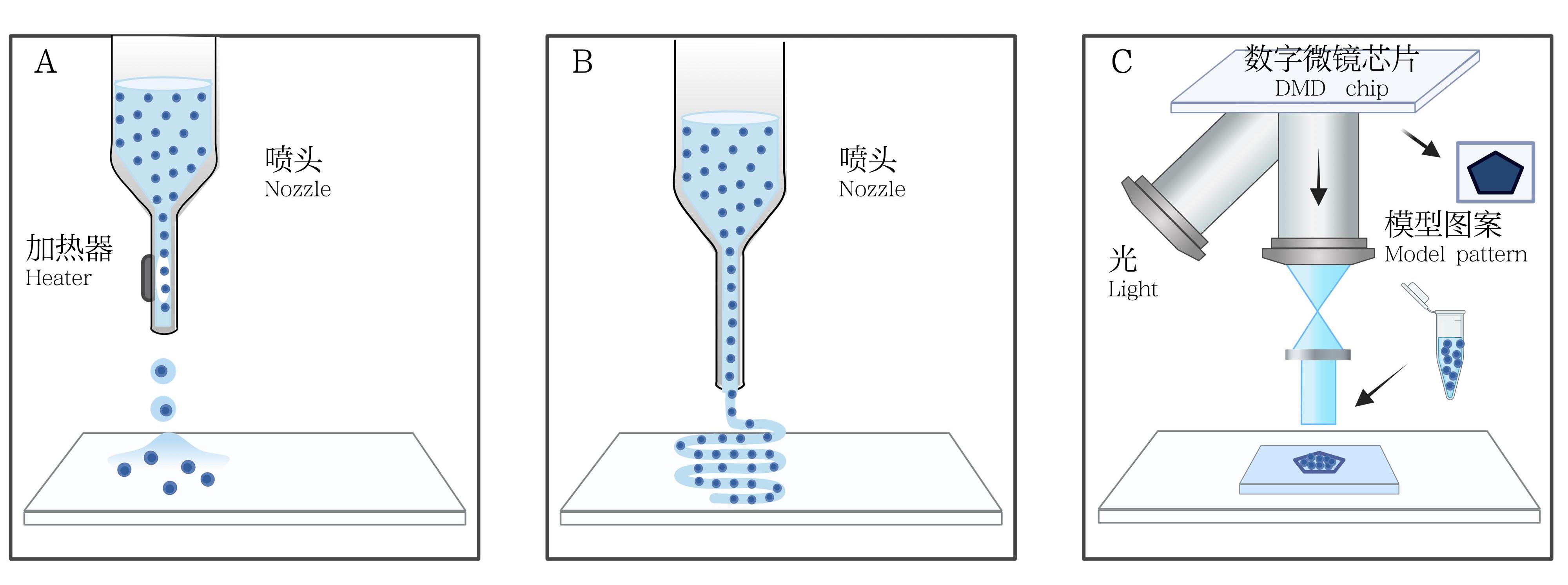
| 图1 3种生物3D打印工艺类型的工作机制示意图 |
| Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the working principles of three types of 3D bioprinting processes |

|