慢性肾脏病大鼠主动脉钙化模型的术式优化及效果评价
|
|
潘颐聪, 蒋汶洪, 胡明, 覃晓
|
Optimization of Surgical Procedure and Efficacy Evaluation of Aortic Calcification Model in Rats with Chronic Kidney Disease
|
|
PAN Yicong, JIANG Wenhong, HU Ming, QIN Xiao
|
|
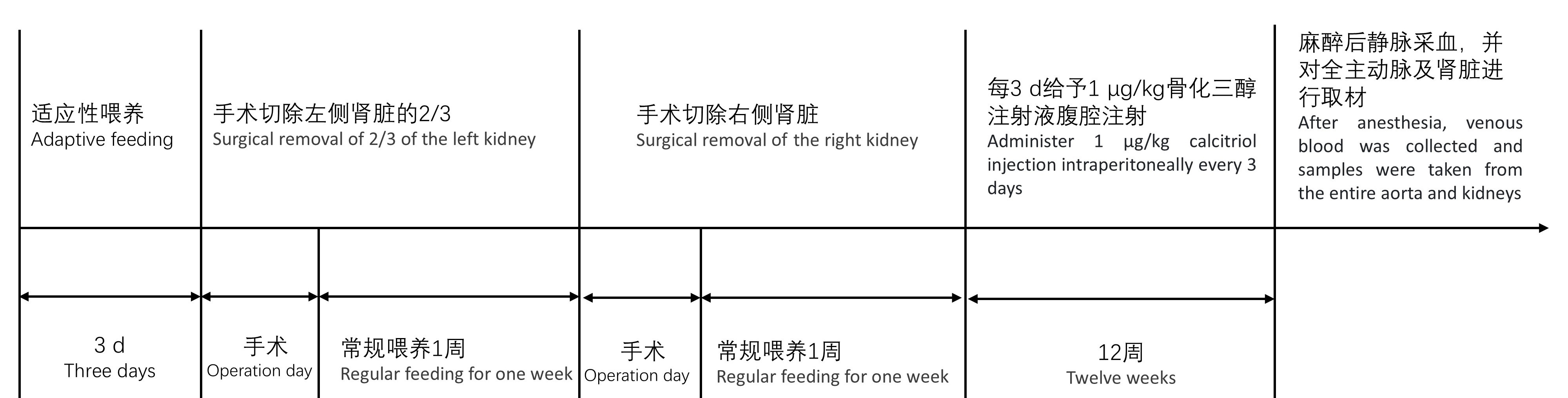
图1 SD大鼠慢性肾脏病主动脉钙化建模及评价实验流程图
注:8周龄SD大鼠饲养于SPF级动物屏障设施,常规饮食适应3 d后进行左肾2/3切除术,术后常规饲养,1周后进行右肾切除术。1周后每3 d给予1 μg/kg骨化三醇注射液。注射12周后进行静脉采血,并对全主动脉及肾脏进行取材,血清用于血生化检测,肾脏行冠状面石蜡切片后进行HE染色,主动脉一部分制成石蜡切片进行茜素红S染色、von Kossa染色,一部分进行冻存用于实时荧光定量PCR检测。
|
Figure1 Flowchart of the experimental process for modeling and evaluating aortic calcification in SD rats with chronic kidney disease
Note:Eight-week-old SD rats were housed in SPF-grade animal barrier facilities and underwent left kidney two-thirds nephrectomy after three days of regular dietary adaptation. After surgery, they were routinely housed and underwent right kidney nephrectomy one week later. After one week, administer 1 μg/kg calcitriol injection every three days. After 12 weeks of injection, venous blood collection was performed, and samples were taken from the entire aorta and kidneys. Serum was used for blood biochemistry testing, and paraffin-embedded kidneys were sectioned in coronal side for HE staining. A portion of the aorta was sectioned in paraffin for Alizarin Red S staining and von Kossa staining, and a portion was frozen for real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection.
|
|
|
|
|

