基于16S rRNA测序的2型糖尿病db/db小鼠模型口腔菌群差异分析
|
|
潘钱家, 葛峻沂, 胡楠, 华飞, 顾敏
|
Differential Analysis of Oral Microbiota in db/db Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes Utilizing 16S rRNA Sequencing
|
|
PAN Qianjia, GE Junyi, HU Nan, HUA Fei, GU Min
|
|
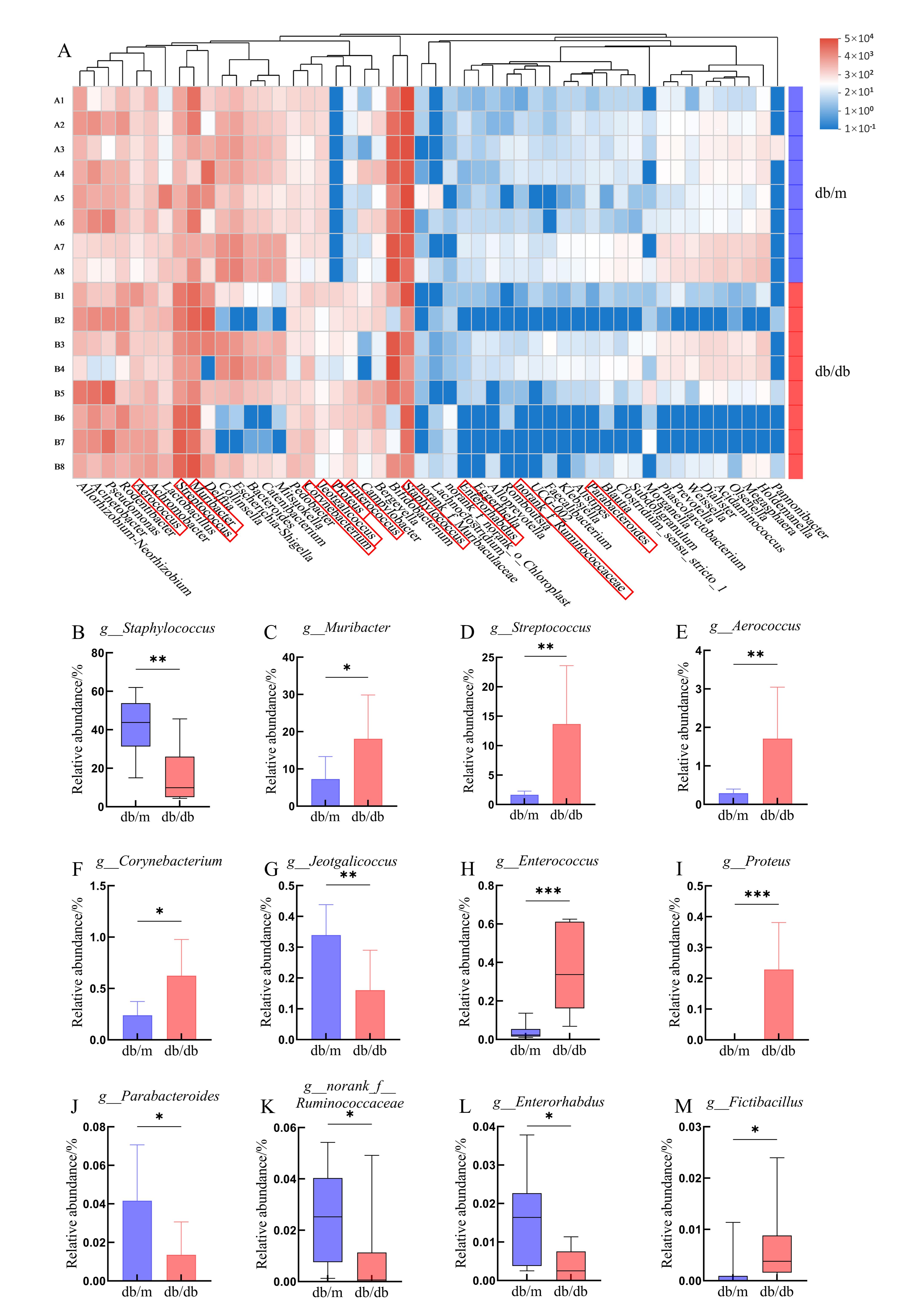
图4 db/db小鼠及db/m小鼠的口腔微生物菌群在属水平上的差异
注:A,db/db和db/m组唾液微生物群中50种优势物种的相对丰度热图;B~M,葡萄球菌属、鼠杆菌属、链球菌属、气球菌属、棒杆菌属、嗜冷咸海鲜球菌属、肠球菌属、变形杆菌属、副拟杆菌属、瘤胃球菌科下未分类属、肠杆菌属、假芽孢杆菌属水平的相对丰度。正态分布的数据由条形图表示,非正态分布的数据用箱线图表示。db/db小鼠为糖尿病实验组;db/m小鼠为正常对照组,每组8只。*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001。
|
Figure 4 Differences in oral microbiota composition between db/db mice and db/m mice at the genus level
Note: A, Heatmap showing the relative abundance of the top 50 dominant species in the saliva microbiota (db/db vs. db/m); B-M, Relative abundance of the following genera: g_Staphylococcus, g_Muribacter, g_Streptococcus, g_Aerococcus, g_Corynebacterium, g_Jeotgalicoccus, g_Enterococcus, g_Proteus, g_Parabacteroides, g_Ruminococcaceae, g_Enterorhabdus, and g_Fictibacillus. Normally distributed data are presented as bar plots, and non-normally distributed data as box plots. Db/db mice served as the diabetic model, while db/m mice were the normal controls, n=8 per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
|
|
|
|
|

