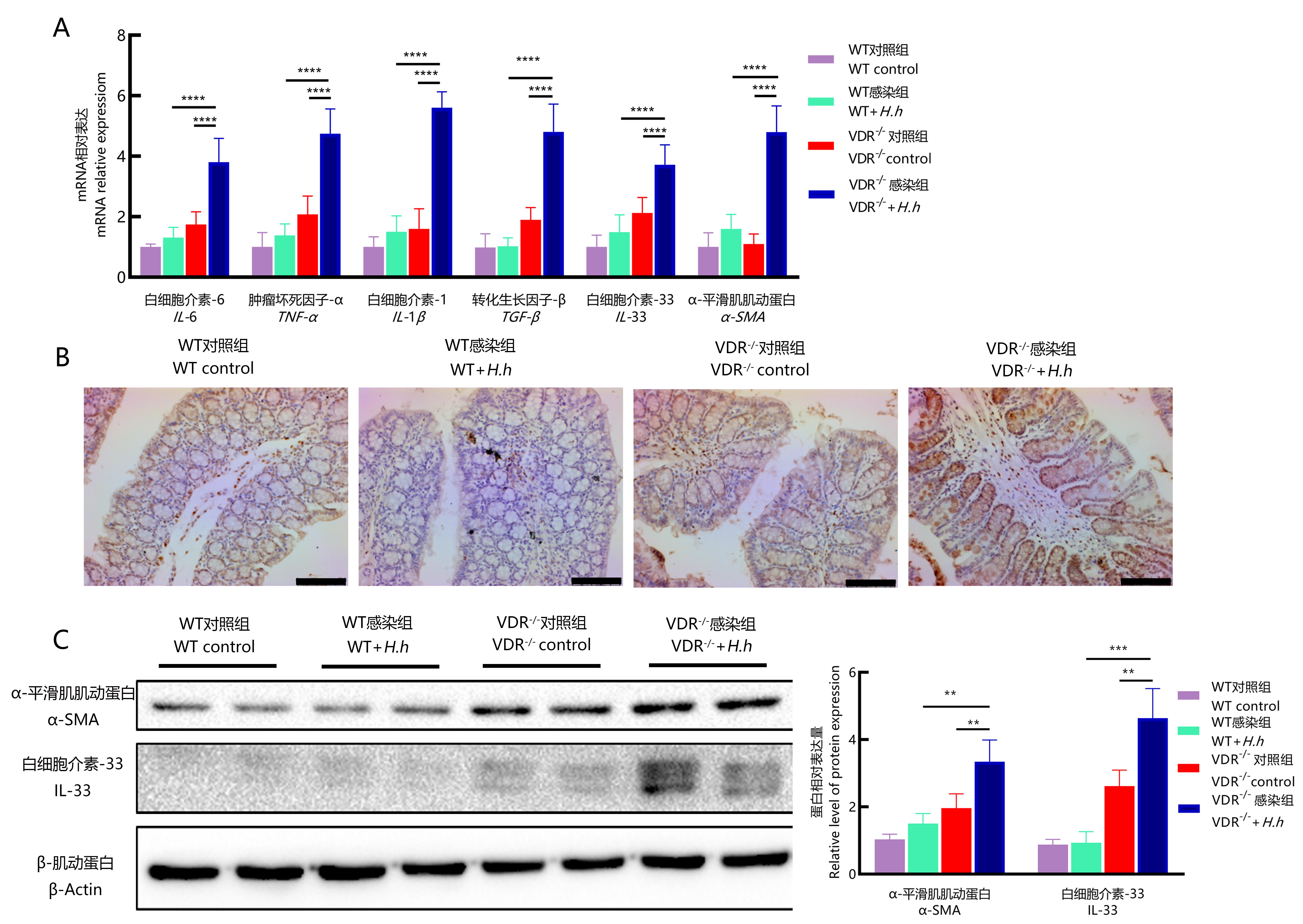
图5. H.hepaticus感染小鼠16周后结肠组织mRNA表达水平检测(A)、IL-33免疫组织化学染色(B)和蛋白质印迹(C)
Figure 5. Detection of mRNA expression levels in colon tissue of mice infected with H. hepaticus after 16 weeks (A), IL-33 immunohistochemical staining (B), and Western blotting (C)
|
肝螺杆菌感染引起VDR-/-小鼠炎性肠病相关肠纤维化模型的建立及机制探讨
|
|
Establishment of an Intestinal Fibrosis Model Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease in VDR-/- Mice Induced by Helicobacter hepaticus Infection and Mechanism Exploration
|
|
图5. H.hepaticus感染小鼠16周后结肠组织mRNA表达水平检测(A)、IL-33免疫组织化学染色(B)和蛋白质印迹(C) |
Figure 5. Detection of mRNA expression levels in colon tissue of mice infected with H. hepaticus after 16 weeks (A), IL-33 immunohistochemical staining (B), and Western blotting (C) |
 |