|
肝螺杆菌感染引起VDR-/-小鼠炎性肠病相关肠纤维化模型的建立及机制探讨
|
|
|
|
Establishment of an Intestinal Fibrosis Model Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease in VDR-/- Mice Induced by Helicobacter hepaticus Infection and Mechanism Exploration
|
WU Zhihao 1(  ), CAO Shuyang 2, ZHOU Zhengyu 1(  )(  )
|
|
|
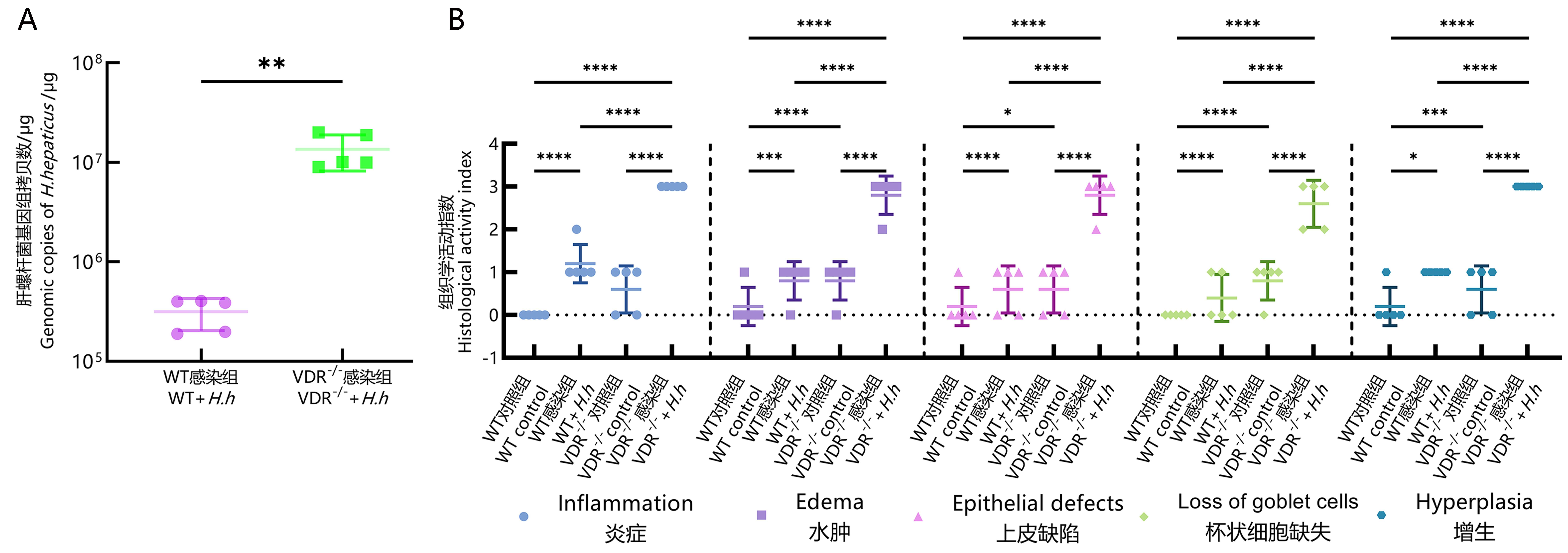
图3. 小鼠感染H.hepaticus后的肠道载菌量(A)和结肠组织HAI评分(B)
注:VDR-/-小鼠感染组的H. hepaticus肠道载菌量显著高于WT小鼠感染组(**P<0.01,n=5)。组织学活动指数评分显示,H.hepaticus感染引起结肠病变,并且VDR缺陷加重了结肠病变(*P<0.05,***P<0.001,****P<0.000 1,n=5)。
|
Figure 3. Colonic bacterial colonization (A) and HAI score of colon tissues (B) in mice infected with H.hepaticus
Note:The intestinal colonization of H.hepaticus was significantly higher in the VDR-/-+H.h group compared to the WT+H.h group(**P<0.01, n=5). Histological activity index showed that the infection with H.hepaticus induced colonic pathology, while VDR deficiency exacerbated the pathological changes in the colon(*P<0.05, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.000 1, n=5).
|
|
 |
|
|


